Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
21~~I~1
SPECIFICATTON
TITLE OF THE INVENTION
Method of Manufacturing the Cycloheptimidazole
Derivatives.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
This invention relates to a new method of synthesiz-
ing cycloheptimidazole derivatives which are active angiotensin
II receptor antagonists and are useful for treating hyper-
tension and congestive heart failure.
2. Description of the Prior Art
We have synthesized a number of cycloheptimidazole
derivatives in order to develop novel agents possessing potent
antihypertensive activities. Recently we proposed a new
class of cycloheptimidazole derivative compounds of the
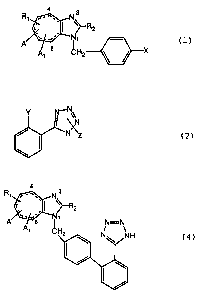
following general formula:
(wherein Rl is hydrogen or isopropyl; R2 represents
a lower alkyl; R3 represents a carboxyl or tetrazoyl; A and Al
are individually a substituent at the 4- or 8-position, Al is
a hydrogen or hydroxy when A is a hydrogen or A and A1 may form
an oxo group or =CHCOOR3 (R3 represents a lower alkyl); the
- 1 -
71142-45
4
2~~sm~
dotted line is two double bonds or saturated single bonds);
and a method of their synthesis and their use as potent anti-
hypertensive, anticongestive heart failure agents and
intraocular pressure lowering agents (Japanese Unexamined
Patent Publication No. 5-320139 (1993) and Japanese Patent
Application No. 5-190153 (1993)).
In preparation of the above cycloheptimidazole
derivatives, cycloheptimidazole compounds are reacted with
halomethylbiphenyl compounds under the basic condition to
give the cycloheptimidazole derivatives, and nitrile group
(R4=CN) is then converted into carboxy group or tetrazol
group (as shown below).
4
R,~~_~,
>-Rz + XCf'~z --
~~ ~Ni
8 H
4
N3
Ri ~.-,.
C/. , I \/ R2 R
A' z
(wherein R4 is nitrite, X represents halogen atom),
However, in the method we previously reported we
must take two step synthetic reactions and further must use
an expensive and hard to handle reagent such as SnN3 (Tin
azide) and there are some difficulties in the process.
3. Object of the Invention
A primary object of the present invention is to find
an alternative process for the preparation of the cyclohept-
- 2 -
71142-45
21 i5~~~
imidazole derivatives, which method is simple, does not use
toxic or expensive reagents and gives a good yield of the
cycloheptimidazole derivatives.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The inventors have conducted intensive studies, and
found a new simple and good yield synthetic method involving
a palladium catalyzed cross-coupling reaction.
In accordance with the present invention, a compound
of general formula ( 1 )
4 3
R~~~_.,~ N
Cc . I ~~R2
A/~~.,'~ N~ (1)
X
(wherein Rl is hydrogen or isopropyl; R2 represents
a lower alkyl; A and Al are each a substituent at the 4- or
8-position, and Al is hydrogen or hydroxy when A is hydrogen
or A and A1 together form an oxo group or =CHCOOR3 (R3
represents a lower alkyl); the dotted line represents two
double bonds or saturated single bonds; X is halogen atom or
trifluoromethanesulfonate) is reacted with a compound of the
following general formula (2):
Y N~N~ ;
J \,N
/ N~Z (2)
- 3 -
71142-45
21:a 6121
(wherein Y is -B(OH)2 or -Sn(R5)3 (R5 represents a
lower alkyl group; and Z is a protecting group for the
tetraolyl group) to give the compound of following general
formula ( 3 )
F
(3)
(wherein the symbols are as defined above), then the
compound (3) is deprotected to give the compound of general
formula (4):
4 3
N
C, , I ~~-R2
I,
A' C H
(4)
(wherein the symbols are as defined above).
Preferably Z represents tert-butyl, trityl (-C(Ph)3),
methoxymethyl, benzylmethyl, p-nitrophenyl group and R2
represents a Cl-C4 alkyl group.
The compounds of the general formulae (1) and (2)
are also novel and are aspects of the present invention as
well as their production processes.
- 4 -
71142-45
4
21~6I21
DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION
(A) A method for preparing a compound of general
formula (1).
(I) A compound of general formula (1) (wherein A
and Al are each a substituent at the 4- or 8-position, and
A1 is hydrogen or hydroxy when A is hydrogen or A and Ai may
form an oxo group) may be prepared by the following reaction:
4
4 3
R~ ~.,, Ns Rt~~..~,, N
I ~?-R2 + XCHz ~ ~ X ----~ ~, I ~~""R2
/ ' Nt
H
Nt At ~H
At 2
X
(5) (6) (1)
(wherein Rl, A, Al, R2, X are the same as mentioned
above).
The reaction of cycloheptimidazole (5) and halogeno-
benzylhalogene compound (6) can be generally carried out in
the presence of a base. A base is used in this reaction such
as sodium hydride, sodium hydroxide and potassium carbonate.
As a solvent used in this reaction, dimethyl formamide (DMF),
dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), tetrahydrofuran (THF), acetone and
dioxane may be employed. Furthermore a phase transfer
catalyst such as tetra - n - butylammonium hydrogensulfate is
applicable in this reaction and H2G and benzene are used as a
solvent. Cycloheptimidazole (5) (the above described) may be
prepared by a method described in Japanese Unexamined Patent
Publication No. 5-320139 (1993).
- 5 -
71142-45
CA 02156121 2005-03-11
71142-45
(i) The cycloheptimidazole (5) in which A and Al
together form an oxo group and the dotted line represents two
double bonds, i.e., compounds of general formula (9), are
prepared by the following reaction:
Ry O + HN R dil NaOH _ R1 ~ ~ N~ 2
R
/ OTs H2N- 2 ~ N
H
c~
(
(wherein Rl is hydrogen or isopropyl; R2 represents
a lower alkyl). Tosyl tropolone (7) is reacted with amidine
(8) in the presence of a base to yield oxoimidazole (9)
(C. A. 74,53785u, Japanese Examined Patent Publication JP-B-45-31,171).
(ii) The cycloheptimidazole (5) in which A and Al
are each hydrogen and the dotted line represents single bonds,
i.e., compounds of the general formula (12), are prepared by
the following reaction:
O (8) EtONa R1~ ~R
+ / N z
/ OCH3
(10) (11)
N
(H)
N
H
(12)
- 6 -
z~~s~2~
(wherein Rl, R2 are the same as mentioned above).
Methyl tropolone (10) is reacted with amidine (8) in
the presence of EtONa to give cycloheptimidazole (11), and (11)
is hydrogenated over Pt02 etc, to 1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8-hexahydro-
cycloheptimidazole (12).
(iii) The cycloheptimidazoles (5) in which A and Al
together form an oxo group and the dotted line represents
single bonds, i.e., compoundsof the general formula (13), are
prepared by the following reaction:
N (H) N
'~2
'N N
O H O H
(9) (13)
(wherein Rl, R2 are the same as mentioned above).
The oxocycloheptimidazole compound (9) is hydrogenated
over Pd/c or Pt02 etc. to give the compound (13).
(iv) The cycloheptimidazole compound (5) in which A
is hydrogen and Al is hydroxyl is obtained from the compound
(13) by using a reducing agent such as sodium borohydride and
lithium aluminum hydride.
(II) The compounds of general formula (1) (Wherein A
or Al =CHCOOR3 and R3 represents a lower alkyl) are prepared
by the following reactions:
_ 7 _
71142-45
2~5~1~~
N x_CH2 / \ X R
R y ( \/ R2
N
O H
(13)
LiCH2COOR3
(C2H50)2P(O)COOR3
SOCIZ/pyridine
(wherein R1, R2, R3, X are the same as mentioned
above).
The compound (13) is reacted with p-halogenobenzyl-
halogen compound (6) in the presence of a base and a phase
transfer catalyst such as tetra - n - butylammonium hydrogen-
sulfate to give the compound (14). The obtained compound (14)
is reacted witr~ LiCH2COOR3 to give the compound (15), and then
followed by the dehydration with SOC12/pyridine to give the
compound (16). Also the reaction of the compound (14) with
(C2H5O)2P(O)CH2COOR3 in the presence of base gives the
compound (16 ) .
(B) A method for preparing a compound of general
formula (2) .
(I) Boronic acids of general formula (2) are
_ g -
71142-45
CA 02156121 2005-03-11
71142-45
prepared by the following reaction:
N~N~ HO~ OOH
I N B N-N
\ N\Z 1) n-BuLi or Mg \ r ~N
N\Z
/ 2) B(OCH3)3 /
3) HZS04
(17) (2a)
(wherein X is halogen atom, Z represents protecting
group).
The compound of (17) is reacted with n-BuLi or Mg
and then added B(OCH3)3 followed by hydrolysis with dilute
H2S04 to give the boronic acid (2a). ~(Jikken Kagakukouza
(Experimental Chemistry) 24, Yuukigousei (Organic Synthesis)
VI, Maruzen (KK), Japan, 1992, P. 61-90.)
(II) Tin compounds of general formula (2) are
prepared by the following reaction:
Sn(R5)s N
N'
\ N~Z ~ ~ ~N
1 ) n-BuLi
/ N Z
2) Sn(R5)3Ci
(17) (2b)
(wherein X is halogen atom, Z represents protecting
group, R5 represents a lower alkyl group).
The compound (17) is reacted with n-BuLi and then
Sn(R5)3C1 to give the tin compound (2b).
- 9 -
21~612~.
(C) A method for preparing a compound of general
formula (3).
In accordance with the present invention, the
compound of general formula (1) is reacted with the compound
of general formula (2) to give the compound of general
formula (3).
(I) In the case of Y is -B(OH)2 in the compound of
general formula (2), the compound of the general formula (1)
is reacted with the compound of the general formula (2) in the
presence of a base and a catalyst to give the compound of the
general formula (3). (Suzuki; Synthetic Communication, 11(7),
513 (1981).) The catalyst used in this reaction may be a
palladium catalyst, such as Pd(PPh3)4, PdCl2 and Pd/C. The
base used in this reaction is for example sodium carbonate,
potassium carbonate, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide.
A solvent may be used in this reaction such as water, ethanol,
methanol, benzene and toluene. The reaction is conducted
preferably at room temperature or at a temperature at which
the solvent refluxes.
(II) In the case of Y is -Sn(R5)3 (wherein R5 is a
lower alkyl group) in the compound of general formula (2),
the compound of the general formula (1) is reacted with the
compound of the general formula (2) in the presence of a
catalyst to give the compound of the general formula (3).
(Shille; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl, 25, 508-524 (1988).)
The catalyst used in this reaction may be a palladium, copper
or lithium catalyst such as Pd(PPh3)4, PdCl2, Pd/C, CuI and
LiCl. A solvent may be used in this reaction such as tetra-
- 10 -
71142-45
2.~~6I~~
hydrofuran (THF), dimethoxyethane (DME) and dimethyl formamide
(DMF). The reaction is conducted preferably at room temperature
or at a temperature at which the solvent refluxes.
(D) Deprotection.
The compound of the general formula (3) is deprotected
with a strong acid such as HC1 and CH3S03H in benzene or
toluene at reflux to give the object compound (4).
For better understanding the present invention, the
following working examples are presented. By no means,
however, the present invention should not be considered to be
restricted to these working examples.
Example 1:
5-[2-4-(2-Propyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1(4H)-
cycloheptimidazolyl)methylbiphenylyl)]tetrazole.
(a) 1-(4-Iodobenzyl)-2-propyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazole.
2-Propyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-cycloheptimidazole
(S.Og) was dissolved in toluene (150m1) and 30~ NaOH aqueous
solution (60m1) was added. The mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 30 min. 4-Iodobenzylbromide (9.2g) and tetra-
n-butylammonium hydrogensulfate (2.Og) were then added and
the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 8hrs.
The solution was filtered, and the filtrate was extracted with
ethyl acetate (50m1x2), and the organic layer was washed with
water and brine and dried (Na2S04), filtered, and concentrated
under vacuum. The resulting product was purified by silica gel
column chromatography (Si02 120g). Elution was carried out with
n-hexane/ethyl acetate (1/1). The object compound was obtained
- 11 -
71142-45
216121
as a yellow color crystal (8.69g): mp (°C) 64-65; Mass (m/e):
M+=408, 217 (BP): IR (cm 1): 2926, 1632, 1464, 1428. 1H-NMR
(CDC13): 0.95 (3H, t, -CH2CH2CH3), 1.70 (2H, m, -CH2CH2CH3),
1.87 (2H, m, Cyclo), 1.92 (2H, m, Cyclo), 2.58 (2H, m, Cyclo),
2.65 (2H, m, Cyclo), 2.96 (2H, t, -CH2CH2CH3), 5.47 (2H, s,
-CH2-C6H5), 6.71 (2H, d, aromatic), 7.62 (2H, d, aromatic).
(b) 2-tertrButyl-5-[2-(4-(2-propyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazolyl)methylbiphenyl)]tetrazole.
A solution of the compound (150mg) which was obtained
by the method as described above (a) in toluene (lOml) and
ethanol (lml) was added to [2-(2-tert-butyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-
phenyl] boronic acid (96mg) (example 3), Pd(PPh3)4 (35mg) and
2M Na2C03 (0.7m1). The mixture was stirred at reflux for 3 hrs.
The solution was concentrated under vacuum. The resulting
product was purified by silica gel column chromatography.
Elution was carried out with ethyl acetate/n-hexane (10:1).
The object compound was obtained as a yellow color oil. IR
(cm 1): 2926, 1632, 1464, 1428. Mass (m/e) . M+=482, 426,178
(BP). 1H-NMR (CDC13): 0.96 (3H, t, -CH2CH2CH3), 1.55 (9H, s,
-(CH3)3), 1.75 (2H, m, -CH2CH2CH3), 1.802.00 (4H, m, Cyclo),
2.59 (2H, t, Cyclo), 2.68 (2H, m, Cyclo), 3.01 (2H, q,
-CH2CH2CH3), 5.57 (2H, s, -CH2C6H5), 6.90 (2H, d, aromatic),
7.09 (2H, d, aromatic), 7.35-~-7.60 (3H, m, aromatic), 7.89
(2H, d, aromatic).
(c) 5-[2-(4-(2-Propyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
1(4H)-cycloheptimidazolyl)methylbiphenylyl)Jtetrazole.
A solution of the compound (100mg) which was obtained
by the method as described above (b) in toluene lOml and
- 12 -
71142-45
2156121
methanesulfonic acid (200mg) was refluxed for 3hrs. The
solution was concentrated under vacuum, and poured into ice
water. The aqueous solution was adjusted pH8 with 10~ NaOH.
The resulting precipitate was collected by filtration, and
was recrystallized with ethanol. The product was obtained
as white crystal (77.4mg): mp (°C) 214-216; Mass (m/e):
M+=426, 383, 355, 178 (BP), 152. 1H-NMR (CDC13): 0.90 (3H, t,
-CH2CH2CH3), 1.58 (2H, m, -CH2CH2CH3), 1.68~(2H, m, Cyclo),
1.75 (2H, m, Cyclo), 2.30 (2H, m, Cyclo), 2.47 (2H, m, Cyclo),
2.53 (2H, t, -CH2CH2CH3), 5.45 (2H, s, -CH2C6H5), 6.75 (2H, d,
aromatic), 7.00 (2H, d, aromatic), 7.42 (2H, d, aromatic),
7.52 (2H, d, aromatic), 7.60 (2H, d, aromatic), 7.85 (2H, d,
aromatic).
Example 2:
5-[2-(4-(2-Propyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1(4H)-
cycloheptimidazolyl)methylbiphenylyl)]tetrazole.
To a solution of 1-(4-iodobenzyl)-2-propyl-8-oxo-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazole (100mg) which was
prepared in a similar manner as described in step (a) of
Example land 2-(2-tert.-butyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]tri-n-
butylstanano (120mg) (Example 4) in THF 8m1, added were
lithium chloride (31.15mg) and Pd(PPh3)4 l.4mg. The reaction
mixture was refluxed for 48hrs. The reaction mixture was
filtered, and filtrate was concentrated under vacuum. After
the addition of ethyl acetate, the mixture was washed with
brine, dried (Na2S04), filtered, and organic solvent was
evaporated under vacuum. The resulting oil was purified by
silica gel column chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate/n-
- 13 -
71142-45
2~ i6l~I
hexane (1/1), 2-tert.-butyl-5-[2-(4-(2-propyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazolyl)methylbiphenylyl)]tetrazole
was obtained as a yellow oil (45mg): Mass (m/e): M+=482, 426,
369, 178 (BP). IR (cm 1): 2926, 1632, 1464, 1428, 1389.
1H-NMR (CDC13): 0.96 (3H, t, -CH2CH2CH3), 1.55 (9H, s, -(CH3)3)'
1.74 (2H, m, -CH2CH2CH3), 1.802.00 (4H, m, Cyclo), 2.59 (2H,
t, Cyclo), 2.68 (2H, m, Cyclo), 3.01 (2H, q' -CH2CH2CH3), 5.57
(2H, s, -CH2C6H5), 6.90 (2H, d, aromatic), 7.09 (2H, d,
aromatic), 7.35-..7.60 (3H, m, aromatic), 7.89 (2H, d, aromatic).
According to the procedure described in Example 1,
tert.-butyl group of 2-tert.-butyl-5-[2-(4-(2-propyl-8-oxo-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazolyl]methylbiphenylyl)]-
tetrazole was deprotected to give the target compound of 5-[2-
(4-(2-propyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazolyl)-
methylbiprenylyl)]tetrazole.
Example 3:
[2-(2-tert.-Butyl-2H-tetrazole-5-yl)phenyl] boronic
acid.
To a cooled (-78°C) solution of 5-(2-brornophenyl)-
2-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-2H-tetrazole (3.3g) in THF (20m1) was
added 1.6M n-BuLi in hexane (7.80m1) and triisopropyl borate
(2.30g) was added. The cooling bath was removed, and the
mixture was stirred at room temperature for lh. HC1 (0.5N)
was added, and the mixture was stirred vigorously for 30min.
The layers were separated, and the aqueous phase was extracted
with ether. The combined organic phases were extracted with
1N KOH (3x10m1). The aqueous extracts were acidified (pHl)
with 2N HC1 (20m1), and the precipitate was collected by
- 14 -
71142-45
21~612~
filtration to give 1.878 of the boronic acid as a white solid:
mp=117-~~~122°C. 1H-NMR (CDC13): 1.72 (9H, s, -C(CH3)3), 7.46
(2H, m, aromatic), 7.90 (2H, m, aromatic).
Example 4:
[2-(2-tert.-Butyl-2H-tetrazole-5-yl)phenyl] tri-n-
butylstanane.
To a cooled (-78°C) solution of 5-(2-bromophenyl)-2-
(1,1-dimethylethyl)-2H-tetrazole (1.23g) in THF 8m1 was added
to 1.6M n-BuLi in hexane (3.27m1). After lh., tri-n-butyltin
chloride (1.71g) was added, and stirring was continued for 3hr
at -78°C. The mixture was warmed to room temperature and
stirred for 18h. Water was added, and the mixture was
extracted with ether (30m1x2). The combined extracts were
washed with water and brine, dried, and concentrated. The
resulting oil was purified by silica gel column chromatography
eluting with n-hexane, the butylstanane was obtained as a yellow
oil (l.Og). 1H-NMR (CDC13): 0.78 (9H, t, -(CH3)3), 0.93 (6H,
t, - (CH2-) 3 ) , 1. 21 (6H, m, - (CH2-) 3) , 1. 43 (6H, m, - (CH2-) 3) '
1.80 (9H, s, (CH3)3), 7.43 (1H, d, aromatic), 7.45 (1H, d,
aromatic), 7.60 (1H, m, aromatic), 8.00 (1H, m, aromatic).
Example 5:
2-Ethyl-8-ethoxycarbonylmethylidene-1-[(2'-1H-
tetrazole-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
cycloheptimidazole.
(a) 1-(4-Bromobenzyl)-2-ethyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazole.
2-Ethyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-cycloheptimidazole
(2.5g) was dissolved in toluene (50m1) and 30~ NaOH aqueous
- 15 -
71142-45
solution (30m1) was added. The mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 30min. 4-Bromobenzylbromide (3.6g) and tetra-
n-butylammonium hydrogensulfate (0.5g) were then added and
the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 8hrs.
The solution was filtered, and filtrate was extracted with
ethyl acetate (20m1x2), and the organic layer was washed with
water and brine and dried (Na2S04), filtered, and concentrated
under vacuum. The resulting product was purified by silica
gel column chromatography (Si02 100g). Elution was carried out
witr. n-hexane/ethyl acetate (1/1). The object compound was
obtained as a yellow color oil (4.Og). Mass (m/e): M+=347,
319, 169 (BP). IR (cm 1): 2950, 1640, 1480, 1400, 1330.
1H-NMR (CDC13): 1.27 (3H, t, -CH2CH3), 1.85 1.87 (2H, m,
Cyclo), 1.91~1.94 (2H, m, Cyclo), 2.602.65 (4H, m, Cyclo),
3.01 (2H, q, CH2CH3), 5.48 (2H, s, -CH2C6H4), 6.86 (2H, d,
aromatic), 7.41 (2H, d, aromatic).
(b) 1-(4-Bromobenzyl)-2-ethyl-8-ethoxycarbonylmethyl-
8-hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazole.
To a solution of (Me3Si)2NLi (2.88m1) in THF (5m1)
was added dry ethyl acetate (0.25m1) at -78°C, and the mixture
was stirred for l5min. Then compound (0.5g) which was prepared
by Example 5 (a) in dry THF was dropwised. The reaction
mixture was stirred at -78°C for lh, and treated with 6N HC1
to adjust the pH5Ø The reaction mixture was extracted with
ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate layer was washed with water
and then brine and dried (Na2S04), filtered, and concentrated
under vacuum. The resulting product was purified by silica gel
column chromatography. Elution was carried out with chloroform/-
- 16 -
71142-45
~~~s12~
methanol (20/1). The object compound was obtained as a yellow
oil (388mg). Mass (m/e): M+=435, 348, 169 (BP), 90. IR (cm 1):
3300, 2900, 1720, 1170, 1000. 1H-NMR (CDC13): 1.28 (3H, t,
-CH2CH3), 1.33 (3H, t, -CH2CH3), 1.80 ~2.20 (6H, m, Cyclo),
2.71 (2H, m, -CH2COOEt), 2.78 (2H, q, -CH2CH3), 2.97 (2H, m,
Cyclo), 4.57 (2H, q, -CH2CH3), 5.81 (2H, s, -CH2C6H5), 7.20 "~
7.40 (4H, m, aromatic).
(c) 1-(4-Bromobenzyl)-2-ethyl-8-ethoxycarbonyl-
methylidene-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazole.
(1) 1-(4-Bromobenzyl)-2-ethyl-8-ethoxycarbonyl-
methyl-8-hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazole
(0.38g) which was prepared in step (b) of Example 5 was
dissolved in pyridine (2m1), and SOC12 (0.32g) was added
thereto, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for
lh. The reaction mixture was poured into 10~ HC1 (20m1) at
0°C, and extracted with ethyl acetate, and ethyl acetate layer
was washed with brine and dried (Na2S04 ) , filtered, and concentrated
under vacuum. The resulting product was purified by silica gel
column chromatography. Elution was carried out with chloroform/-
methanol (20/1). The object compound was obtained as a yellow
oil (280mg).
(2) KH (0.08g) was dissolved in THF 5m1, and then
diethyl phosphonoacetate (0.37g) was added at 5°C. After the
mixture was stirred at 10°C for lOmin, 1-(4-bromobenzyl)-2-
ethyl-8-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazole (0.5g)
in THF lml which was prepared in step (a) of Example 5 was
added. The mixture was stirred at 40°C for 5hrs. The
reaction mixture was poured into ice water (20m1), and extracted
- 17 -
71142-45
~~~s~
with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water
and then brine and dried (Na2S04), filtered, and concentrated
under vacuum. The resulting product was purified by silica
gel column chromatography. Elution was carried out with
chloroform/methanol (20/1). The object compound was obtained
as a yellow color oil (60mg). Mass (m/e): M++1=418, 371, 343,
171 (BP), 90. IR (cm 1): 2900, 1710, 1230, 1170, 1000.
1H-NMR (CDC13): 1.26 (3H, t, -CH2CH3), 1.26 (3H, t, -CH2CH3),
1.85 (2H, m, Cyclo), 1.90 (2H, m, Cyclo), 2.91 (2H, q,
CH2CH3), 2.92 (2H, q, CH2CH3), 4.054.20 (4H, m, Cyclo),
5.28 (2H, s, -CH2C6H5), 5.68 (1H, s, =CHCOOC2H5), 6.80 (2H, d,
aromatic), 7.55 (2H, d, aromatic).
(d) 2-tert.-Butyl-5-[2-(4-(2-ethyl-8-ethoxycarbonyl-
methylidene-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1(4H)-cycloheptimidazolyl)methyl-
biphenylyl)]tetrazole.
To a solution of the compound (280mg) which was
prepared by Example 5 (c) in toluene (5m1) and ethanol (O.lml),
added were [2-(2-tert.-butyl-2H-tetrazole-5-yl)phenyl] boronic
acid (175.5mg), Pd(PPh3)4 (26.8mg) and 2M Na2C03 (1.6m1). The
mixture was stirred at reflux for 4.5hrs. The reaction mixture
was poured into water (30m1), and extracted with toluene
(20m1x3) , and toluene layer was washed with brine and dried (Na2S04)'
filtered, and concentrated under vacuum. The resulting product
was purified with silica gel column chromatography. Elution
was carried out with ethyl acetate/n-hexane (1/1). The object
compound was obtained as a yellow oil (230mg). Mass (m/e):
M++1=539, 451, 253, 178 (BP). IR (cm 1): 3420, 3000, 1230,
2950, 1720. 1H-NMR (CDC13): 1.25 (3H, s, t-Bu), 1.82 (2H, m,
- 18 -
71142-45
~~~6121
Cyclo), 1.89 (2H, m, Cyclo), 2.55 (2H, q,'-CH2CH3), 2.80-2.83
(2H, m, Cyclo), 3.04~~3.07 (2H, m, Cyclo), 4.12 (2H, q,
-CH2CH3), 5.17 (2H, s, -CH2C6H5), 5.56 (1H, s, =CHCOOC2H5),
6.82 (2H, d, aromatic), 7.14 (2H, d, aromatic), 7.39-~-7.88
(4H, m, aromatic).
(e) 2-Ethyl-8-carboxymethylidene-1-[(2'-(1H-
tetrazole-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
cycloheptimidazole.
A solution of the compound (200mg) which was
obtained by the Example 5 (d) as described above in toluene
20m1 and methanesulfonic acid (400mg) was refluxed for 3hrs.
The solution was concentrated under vacuum, and poured into
ice water. The aqueous solution was adjusted pH4 with 10$
NaOH. The resulting precipitate was collected by filtration,
and was recrystallized with methanol (2m1). The product was
obtained as white crystal (120mg). mp: 191~193°C. Mass
(m/e): M+=408 (M+-COOH), 367, 192 (BP), 134. IR (cm 1):
2914, 1692, 1611, 1452, 1362, 1197. 1H-NMR (CD30D): 1.30
(3H, t, -CH2CH3), 1.94 (4H, bs, Cyclo), 2.65-3.03 (6H, m,
-CH2CH3+Cyclo), 5.43 (2H, s, -CH2C6H5), 5.92 (1H, s, =CHCOOH),
6.80~J7.70 (8H, m, aromatic), 7.96 (1H, s, -NH).
- 19 -
71142-45