Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
21~6~ 4
Fluorinated pyrimidines as herbicides
The applications EP 223406, EP 249707, EP 249708; EP 287072, EP
315889, EP 321846, EP 402751 and WO 94-13065 describe pyrimidine
derivatives having strong herbicidal action. Their action and
their selectivity, however, are not always adequate.
It is an object of the present invention to find compounds which
10 overcome this disadvantage.
We have found that this object is achieved by fluorinated pyrimi-
dines of the formula I
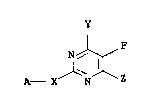
N
where A is one of the following radicals:
(R2)n~ (R2)n~ (R2)n ~ (R2)n~
W~ Rl W~ Rl _ W~--R
W~ Rl ~ (R2~n~ ~ W/~R
(R2)n~ (R2)n
W~ ~ Rl W~ ~ Rl
The symbols have the following meanings:
~66 ~'~ 4
W is =0~ =N-R3~ =N-o-R3, =N-NR4Rs;
X is -0-, -S- or -NR6-;
Y and Z are halogen, Cl-C6-alkyl, C1-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy,
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-alkylamino and/or
di-Cl-C4-alkylamino;
10 Rl is hydrogen;
Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C6-alkylcarbonyl, Cl-C6-alkoxycarbonyl;
a succinyliminooxy group;
a 5-membered heteroaromatic comprising one to three
nitrogen atoms which can carry one to four halogen atoms
and/or one or two of the following radicals: Cl-C6-alkyl,
Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy and/or
Cl-C4-alkylthio;
a radical oR7;
a radical
()m - N
R9
where R3 and R9 can be identical or different;
or a radical
NH -- - Rl o
o
R2 is hydrogen;
halogen;
7~
,
amino;
Cl-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkynyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy,
Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-alkylsulfonyl, Cl-C4-alkylamino,
di-Cl-C4-alkylamino, which can carry one of the following
substituents, which in the case of dialkylamino can be
identical or different: C1-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio,
di-Cl-C4-alkylamino, thienyl, furyl, a five-membered
aromatic heterocycle having one to four nitrogen atoms or
one to three nitrogen atoms and additionally a sulfur or
oxygen atom in the ring, it being possible for the
five - hered ring heterocycles to carry one to three
halogen atoms and/or one to three of the following
radicalss nitro, cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy,
Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl; or phenyl which is
unsubstituted or substituted by one to three halogen atoms
and/or one to three methyl groups; or phenoxy which i9
unsubstituted or ~ubstituted by one to three halogen atoms
and/or one to three methyl groups, or a six-membered
aromatic heterocycle having one to three nitrogen atoms in
the ring, which can carry one to three halogen atoms and/or
one to three of the following radicals: nitro, cyano,
Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl;
phenyl, substituted phenyl;
phenoxy, substituted phenoxy;
phenylthio, substituted phenylthio, phenylsulfonyl,
substituted phenylsulfonyl;
a five-membered heteroaromatic having one to four nitrogen
atoms or one to three nitrogen atoms and additionally a
sulfur or oxygen atom in the ring, which can carry one to
three halogen atoms and/or one to three of the following
radicals: nitro, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C4-alkoxy,
C1-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or
phenyl, which is unsubstituted or substituted by one to
three halogen atoms and/or one to three methyl groups;
a benzo-fused 5-membered heteroaromatic, which can comprise
one to three nitrogen atoms or a nitrogen atom and
additionally an oxygen or sulfur atom and can carry one of
the following radicals: halogen, nitro, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl,
Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl,
C1-C4-haloalkoxy or phenyl, which is unsubstituted or
21~7S~
substituted by one to three halogen atoms and/or one to
three methyl groups;
a thienyl or furyl radical which can carry one to three
halogen atoms and/or one to three of the following
radicals: nitro, cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy,
Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or
phenyl, which is unsubstituted or substituted by one to
three halogen atoms and/or one to three methyl groups;
a benzothienyl or benzofuryl radical, which can carry one
to five halogen atoms and/or one to three of the following
radicals: nitro, cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy,
Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or
phenyl, which is unsubstituted or substituted by one to
three halogen atoms and/or one to three methyl groups
a 6-membered heteroaromatic having one to four nitrogen
atoms in the ring, which can carry one to three halogen
atoms and/or one to three of the following radicals: nitro,
cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio,
Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or phenyl, which is
unsubstituted or substituted by one to three halogen atoms
and/or one to three methyl groups;
a naphthyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl or quinazolinyl
radical which in each case can carry up to three halogen
atoms and/or up to three of the following radicals: nitro,
cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio,
Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or phenyl, which is
unsubstituted or substituted by one to three halogen atoms
and/or one to three methyl groups;
a 5-membered heteroaromatic bonded via an oxygen atom and
having one to four nitrogen atoms or one to three nitrogen
atoms and additionally a sulfur or oxygen atom in the ring,
which can carry one to three halogen atoms and/or one to
three of the following radicals: nitro, cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl,
Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl,
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or phenyl, which is unsubstituted or
substituted by one to three halogen atoms and/or one to
three methyl groups;
a benzo-fused 5-membered heteroaromatic bonded via an
oxygen atom, which can contain one to three nitrogen atoms
or a nitrogen atom and additionally an oxygen or sulfur
atom and can carry one of the following radicals: halogen,
`~ ~lfi~751
nitro, cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl, C1-C4-alkoxy, C1-C4-alkylthio,
Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or phenyl, which is
unsubstituted or substituted by one to three halogen atoms
and/or one to three methyl groups;
a thienyl or furyl radical bonded via an oxygen atom, which
can carry one to three halogen atoms and/or one to three of
the following radicals: nitro, cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl,
Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl,
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or phenyl, which is unsubstituted or
substituted by one to three halogen atoms and/or one to
three methyl groups;
a benzothienyl or benzofuryl radical bonded via an oxygen
atom, which can carry one to five halogen atoms and/or one
to three of the following radicals: nitro, cyano,
Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl,
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or phenyl, which is unsubstituted or
substituted by one to three halogen atoms and/or one to
three methyl groups;
a 6-membered heteroaromatic bonded via an oxygen atom and
having one to four nitrogen atoms in the ring, which can
carry one to three halogen atoms and/or one to three of the
following radicals: nitro, cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl,
Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl,
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or phenyl, which is unsubstituted or
substituted by one to three halogen atoms and/or one to
three methyl groups;
a naphthyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl or quinazolinyl
radical bonded via an oxygen atom, which in each case can
carry one to three halogen atoms and/or up to three of the
following radicals: nitro, cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl,
Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, Cl-C4-haloalkyl,
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy or phenyl, which is unsubstituted or
sub~tituted by one to three halogen atoms andtor one to
three methyl groups;
a radical
21~7S4
N~F
~`~
~ 0~ N ~ Z
where Z', Xl', X2 and X3' have the meanings indicated above
for Z, Xl, x2 and X3 can be identical to or different from
them;
a group
where W' and Rl' have the same meanings as ~ and Rl, and
can be identical to or different from these units;
R3 is hydrogen, phenyl, substituted phenyl or Cl-C6-alkyl,
C3-C6-alkenyl or C3-C6-alkynyl, which can carry one to three
of the following substituents: halogen, Cl-C6-alkyl,
Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C6-alkylcarbonyl, Cl-C6-alkoxycarbonyl,
carboxyl, Cl-C4-alkylthio, phenyl, substituted phenyl;
R4 is hydrogen, Cl-C6-alkyl or phenyl;
R5 is hydrogen, phenyl, substituted phenyl or Cl-C6-alkyl which
can carry one to three of the following substituents:
halogen, Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C6-alkylcarbonyl,
Cl-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, carboxyl, Cl-C4-alkylthio, phenyl,
substituted phenyl;
R6 is hydrogen, Cl-C6-alkyl, formyl, carbamoyl or
Cl-C6-alkoxycarbonyl;
40 R7 is hydrogen, an alkali metal cation, the equivalent of an
alkaline earth metal cation or an organic ammonium ion;
a C3-Cl2-cycloalkyl group which can carry one to three
Cl-C4-alkyl radicals;
- 2~;6754
a C1-C4-alkyl group which can carry one to five halogen
atoms and/or one or two of the following radicals:
Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, cyano, Cl-C6-alkylcarbonyl,
Cl-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, C3-Cl2-cycloalkyl, a radical
-0-N=CRllRl2, where Rll and Rl2 can be identical or
different, phenyl, phenoxy or phenylcarbonyl, it being
possible for the aromatic radicals in turn to carry one to
five halogen atoms and/or one to three of the following
radicals: Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy,
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy and/or Cl-C4-alkylthio;
a Cl-C6-alkyl group which can carry one to five halogen
atoms and carries one of the following radicals: a
5-membered heteroaromatic cont~ining one to three nitrogen
atoms, which can carry one to four halogen atoms and/or one
or two of the following radicals: Cl-C6-alkyl,
Cl-C4-haloalkyl, Cl-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy and/or
Cl-C4-alkylthio;
an alkyl group which in the 2-position carries one of the
following radicals: Cl-Cl2-alkoxyimino,
C3-Cl2-alkenyloxyimino, C3-C6-haloalkenyloxyimino or
benzyloxyimino;
a C3-C6-alkenyl or a C3-C6-alkynyl group, it being possible
for these groups in turn to carry one to five halogen
atoms;
phenyl which is unsubstituted or mono- to trisubstituted by
nitro, Cl-C6-alkyl or Cl-C6-alkoxy or mono- to
pentasubstituted by halogen;
a radical -N=CRl3Rl4, where Rl3 and Rl4 can be identical or
different;
a 5-membered aromatic heterocycle bonded via a nitrogen
atom and having one to four nitrogen atoms in the ring or a
benzo-fused 5-membered aromatic heterocycle bonded via a
nitrogen atom and having one to three nitrogen atoms in the
ring, which can be substituted by halogen, Cl-C6-alkyl or
Cl-C4-haloalkyl;
R3 and R9 are hydrogen;
Cl-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl or C3-C6-alkynyl, it being
possible for these radicals in each case to carry one to
five halogen atom~ and/or one or two of the following
2 1 6~75~
groups: C1-C4-alkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio, cyano,
Cl-C6-alkylcarbonyl, Cl-C6-alkoxycarbonyl,
di-Cl-C4-alkylamino, cyclo-C3-C12-alkyl;
cyclo-C3-Cl2-alkyl, which can carry one to three Cl-C4-alkyl
substituents;
phenyl or substituted phenyl;
together are a C3-Cl2-alkylene chain closed to give ring or
together are a C3-C12-alkylene chain closed to give a ring
with a heteroatom, which can be oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen,
and which in each case can carry one to three Cl-C4-alkyl
substituents;
or a group
fH~/
o R16
Rl is Cl-C6-alkyl or phenyl, which can carry one to four of the
following substituents: halogen, nitro, cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl;
Rll and Rl2 are alkyl, which can carry a Cl-C4-alkoxy or
Cl-C4-alkylthio group, or together are a C3-Cl2-alkylene
chain;
Rl3 and Rl4 are Cl-C6-alkyl which can carry a phenyl radical, or a
Cl-C4-alkoxy and/or a Cl-C4-alkylthio group,
C3-Cl2-cycloalkyl, phenyl, or together are a C3-Cl2-alkylene
chain which can carry one to five Cl-C6-alkyl groups and
can be bridged by an alkylene chain;
Rl5 is hydrogen or C1-C6-alkyl which can be substituted by
hydroxyl, amino, hydrogen sulfide, C1-C4-alkylthio,
carboxyl, carbamoyl, guanidinyl, phenyl, hydroxyphenyl,
imidazolyl or indolyl radicals or together with R9 is
bonded via a C3-Cl2-alkylene chain to give a ring;
R16 i8 Cl-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl or C3-C6-alkynyl;
m is 0 or 1;
21 667~ ~
n is 0, 1, 2 or 3;
substituted phenyl, substituted phenoxy, substituted phenylthio
or substituted phenylsulfonyl in each case means that the phenyl
ring can carry one to five halogen atoms and/or one to three of
the following radicals: nitro, cyano, Cl-C6-alkyl, Cl-C4-halo-
alkyl, Cl-C6-alkoxy, Cl-C4-haloalkoxy, Cl-C4-alkylthio,
Cl-C4-alkylamino, di-Cl-C4-alkylamino, Cl-C6-alkylcarbonyl,
Cl-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, phenyl, phenyl substituted by one to three
10 halogen atoms or one to three methyl groups, phenoxy, phenoxy
substituted by one to three halogen atoms or one to three methyl
groups or, on two adjacent atoms, a unit -O-(CH2)o~0~, it being
possible for o to assume the values 1 or 2.
Fluorinated pyrimidines of the formula I are preferred where A is
one of the following radicals:
( R2 ) n~ ( R2 ) n~ ~ ( R2 ) n~
W~ Rl W~ Rl W~ R
(R2)n~(R2)n~J~ (R2)n
W~ Rl W~ Rl W~ R
and where the symbols indicated have the following meanings:
W is =0;
X is -O- or -S-;
Y and Z are alkyl, haloalkyl, alkoxy, haloalkoxy, alkylthio or
dialkylamino;
40 Rl is hydrogen;
a 5-membered heteroaromatic containing one to three
- nitrogen atoms;
a radical oR7;
2 1 ~ 6 7~
a radical
~R8
()m--N
R9
where R8 and R9 can be identical or different;
R2 is hydrogen;
halogen;
alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, alkoxy, alkylamino,
dialkylamino, each of which can carry one of the
following substituents, which can be identical or
different in the case of dialkylamino: alkoxy, alkylthio,
dialkylamino, thienyl, furyl, a fivc -mhered aromatic
heterocycle having one to four nitrogen atom~ or one to
three nitrogen atoms and additionally a sulfur or oxygen
atom in the ring, it being possible for the fivc - hered
ring heterocycles to carry one to three of the following
radicals: nitro, cyano, alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio,
haloalkyl;
phenyl, substituted phenyl
phenoxy, substituted phenoxy;
phenylthio, substituted phenylthio, phenylsulfonyl,
substituted phenylsulfonyl;
a 5-membered heteroaromatic from the group consisting of
pyrrole,-pyrazole, imidazole, 1,2,3-triazole,
1,2,4-triazole, tetrazole, oxazole, isoxazole, thiazole,
isothiazole, 1,3,4-oxadiazole, furazan, 1,3,4-thiadiazole
and 1,2,3-thiadiazole, which can carry one to three
halogen atoms and/or one to three of the following
radicals: alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio, haloalkyl,
haloalkoxy;
a thienyl or furyl radical which can carry one to three
halogen atoms and/or one to three of the following
radicals: alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio, haloalkyl,
haloalkoxy;
-- 216~7~4
a benzothienyl or benzofuryl radical which can carry one
to three of the following radicals: alkyl, alkoxy,
alkylthio, haloalkyl, haloalkoxy;
a 6-membered heteroaromatic from the group consisting of
pyridine, pyridazine, pyrimidine, pyrazine,
1,2,3-triazine, 1,2,4-triazine and 1,3,5-triazine, which
can carry one to three halogen atoms and/or one to three
of the following radicals: alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio,
haloalkyl, haloalkoxy;
a naphthyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl or quinazolinyl
radical which in each case can carry up to three halogen
atoms and/or up to three of the following radicals:
alkyl, alkoxy, haloalkyl, haloalkoxy;
a thienyl or furyl radical bonded via an oxygen atom,
which can carry one to three halogen atoms and/or one to
three of the following radicals: alkyl, alkoxy,
alkylthio, haloalkyl, haloalkoxy;
a benzothienyl or benzofuryl radical bonded via an oxygen
atom, which can carry one to three of the following
radicals: alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio, haloalkyl,
haloalkoxy;
a 6-membered heteroaromatic bonded via an oxygen atom and
from the group consisting of pyrimidine and
1,3,5-triazine, which can carry one to three halogen
atom~ and/or one to three of the following radicals:
alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio, haloalkyl, haloalkoxy;
a naphthyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl or quinazolinyl
radical bonded via an oxygen atom which can carry one to
three of- the following radicals: alkyl, alkoxy,
haloalkyl, haloalkoxy;
a radical
Y'
~ 0~ Z ~
21 66 75 ~
where Y' and Z' have the meanings indicated above for X
and Z and can be identical to or different from them;
a group
where W' and Rl' have the same meanings as W or R1, and
can be identical to or different from these units;
R7 is hydrogen, an alkali metal cation, or the equivalent of
an alkaline earth metal cation;
an alkyl group which can carry one to five halogen atom~
and/or one or two of the following radicals: alkoxy,
alkylthio, cyano, alkylcarbonyl, alkoxycarbonyl,
cycloalkyl;
an alkyl group which can carry one to five halogen atoms
and carries one of the following radicals: a 5-membered
heteroaromatic containing one to three nitrogen atoms;
an alkyl group which, in the 2-position, carries one of
the following radicals: alkoxyimino or alkenyloxyimino;
an alkenyl or an alkynyl group, it being possible for
these groups in turn to carry one to five halogen atoms;
phenyl which is unsubstituted or mono- to trisubstituted
by nitro or alkyl or mono- to pentasubstituted by
halogen;-
a radical -N=CRl3Rl4, where Rl3 and Rl4 can be identical
or different;
0 R~ and R9 are hydrogen;
alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl;
cycloalkyl;
phenyl or substituted phenyl;
-- 21~67~ 1
together an alkylene chain closed to give a ring or
together an alkylene chain closed to give a ring and
containing a heteroatom which can be oxygen, sulfur or
nitrogen;
Rl3 and Rl4 are alkyl which can carry a phenyl radical,
cycloalkyl, phenyl or together an alkylene chain;
m is 0 or 1;
n is 0, 1, 2 or 3;
where substituted phenyl, substituted phenoxy,
substituted phenylthio, substituted phenylsulfonyl means
that the phenyl ring can carry one to five halogen atoms
and/or one to three of the following radicals: nitro,
cyano, alkyl, haloalkyl, alkoxy, haloalkoxy, alkylthio,
dialkylamino, alkylcarbonyl or, on two adjacent atoms, a
unit -0-(CH2)o~O~, it being possible for o to assume the
values 1 or 2.
(R2)n~J~ (R2)n~ (R2)n~
W~ Rl W~ Rl W~ R
and where the symbols indicated have the following meanings:
30 W is =0;
X is -0- or -S-;
Y and Z are alkoxy;
R1 is a radical oR7;
R2 is hydrogen;
gO halogen;
alkyl, alkoxy, dialkylamino;
phenyl, substituted phenyl;
21667S~
14
a 5-membered heteroaromatic from the group consisting of
pyrazole and thiazole, which can carry one of the
following radicals: halogen, alkoxy
a thienyl radical which can carry a halogen atom and/or
the following radical: alkoxy;
a 6-membered heteroaromatic from the group consisting of
pyridine, pyrimidine and 1,3,5-triazine, which can carry
one of the following radicals: halogen, alkoxy;
a thienyl or furyl radical bonded via an oxygen atom,
which can carry a halogen atom and/or the following
radical: alkoxy;
a 6-membered heteroaromatic bonded via an oxygen atom and
from the group consisting of pyrimidine and
1,3,5-triazine, which can carry one of the following
radicals: halogen, alkoxy;0
a radical
Y'
N ~ F
~ O/~N~Z
where Y~ and Z~ have the meanings indicated above for X
and Z and can be identical to or different from them;
a group
W
~/
Rl '
where W' is an alkoxyimino group and Rl' is hydrogen or
an alkyl group;
-
R7 is hydrogen or an alkali metal cation;
216~754
.
an alkyl group which can carry one or two of the
following radicals: alkoxy, alkylthio;
an alkenyl or an alkynyl group;
phenyl which is unsubstituted or monosubstituted by nitro
or monosubstituted by halogen;
a radical -N=CRl3Rl4, where Rl3 and Rl4 can be identical
or different;
n is l;
where substituted phenyl, substituted phenoxy,
substituted phenylthio or substituted phenylsulfonyl
means that the phenyl ring can carry one or two of the
following radicals: alkoxy, alkylthio, a unit
-0-(CH2)o~0~ on two adjacent atoms, it being possible for
o to assume the values 1 or 2.
The substituents mentioned in the description preferably have the
following meanings:
Cl-C6-alkyl: methyl, ethyl, l-propyl, 2-propyl, l-butyl, 2-butyl,
2-methylpropyl, l,l-dimethylethyl, l-pentyl, 2-pentyl, 3-pentyl,
2-methylbutyl, 3-methylbutyl, 2-methyl-2-butyl, 3-methyl-2-butyl,
l,l-dimethylpropyl, 1,2-dimethylpropyl, 2,2-dimethylpropyl,
l-hexyl, 2-hexyl, 3-hexyl, 2-methylpentyl, 3-methylpentyl,
4-methylpentyl, 2-methyl-2-pentyl, 3-methyl-2-pentyl,
30 4-methyl-2-pentyl, 2-methyl-3-pentyl, 3-methyl-3-pentyl,
2,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,3-dimethylbutyl, 3,3-dimethylbutyl,
3,3-dimethyl-2-butyl, 2-ethylbutyl, 1,1,2-trimethylpropyl,
1,2,2-trimethylpropyl, in particular methyl, ethyl, propyl,
2-propyl, butyl, 2-butyl, l,l-dimethylethyl, pentyl,
2,2-dimethylpropyl, hexyl;
Cl-C4-haloalkyl: chloromethyl, difluoromethyl, dichloromethyl,
trifluoromethyl, trichloromethyl, chlorodifluoromethyl,
l-fluoroethyl, 2-fluoroethyl, 2,2-difluoroethyl,
40 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl, 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl,
2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl and pentafluoroethyl,
decafluorobutyl, l,l-bis-trifluoromethyl-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl,
preferably difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, trichloromethyl and
chlorodifluoromethyl;
., 2166~sia~ .
C3-C6-alkenyl: propenyl, l-butenyl, 2-butenyl, 2-methylpropenyl,
pentenyl, 2-pentenyl, 2-methylbutenyl, 3-methylbutenyl,
2-methyl-2-butenyl, hexenyl, 2-hexenyl, 3-hexenyl,
2-methylpentenyl, 3-methylpentenyl, 4-methylpentenyl,
2-methyl-2-pentenyl, 3-methyl-2-pentenyl, 4-methyl-2-pentenyl,
2,3-dimethylbutenyl, 2-ethylbutenyl, 3,3-dimethylbutenyl,
2,3-dimethyl-2-butenyl;
C3-C6-alkynyl: propynyl, butynyl, 2-butynyl, pentynyl, 2-pentynyl,
10 3-methylbutynyl, hexynyl, 2-hexynyl,3-hexynyl, 3-methylpentynyl,
4-methylpentynyl, 4-methyl-2-pentynyl;
C3-Cl2-cycloalkyl: cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl,
cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl, cyclooctyl, cyclononyl, cyclodecyl,
cycloundecyl and cyclododecyl, particularly preferably
cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl;
Cl-C4-alkoxy: methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy, l-methylethoxy, butoxy,
2-butoxy, l-methylpropoxy, 2-methylpropoxy, l,l-dimethylethoxy,
20 in particular methoxy, ethoxy, l-methylethoxy;
Cl-C6-alkoxy: Cl-C4-alkoxy and also pentoxy, 2-pentoxy, 3-pentoxy,
l-methylbutoxy, 2-methylbutoxy, 3-methylbutoxy,
2-methyl-2-butoxy, 3-methyl-2-butoxy, l,l-dimethylpropoxy,
1,2-dimethylpropoxy, 2,2-dimethylpropoxy, l-hexoxy, 2-hexoxy,
3-hexoxy, 2-methylpentoxy, 3-methylpentoxy, 4-methylpentoxy,
2-methyl-2-pentoxy, 3-methyl-2-pentoxy, 4-methyl-2-pentoxy,
2-methyl-3-pentoxy, 3-methyl-3-pentoxy, 2,2-dimethylbutoxy,
2,3-dimethylbutoxy, 3,3-dimethylbutoxy, 2,3-dimethyl-2-butoxy,
30 3,3-dimethyl-2-butoxy, in particular methoxy, ethoxy,
l-methylethoxy;
Cl-C4-haloalkoxy: difluoromethoxy, trifluoromethoxy,
chlorodifluoromethoxy, l-fluoroethoxy, 2-fluoroethoxy,
2,2-difluoroethoxy, 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethoxy,
2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy, 2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethoxy and
pentafluoroethoxy, 1,1,2,3,3,3-hexafluoropropoxy,
heptafluoropropoxy, decafluorobutoxy,
1,1-bis-trifluoromethyl-2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy, preferably
40 difluoromethoxy, trifluoromethoxy and chlorodifluoromethoxy;
Cl-C4-alkylthio: methylthio, ethylthio, propylthio,
l-methylethylthio, butylthio, 2-butoxy, l-methylpropylthio,
2-methylpropylthio, l,l-dimethylethylthio, in particular
methylthio, ethylthio, l-methylethylthio;
21~i~75~
Cl-C4-alkylamino: methylamino, ethylamino, propylamino,
l-methylethylamino, butylamino, 2-butylamino,
1-methylpropylamino, 2-methylpropylamino, l,l-dimethylethylamino,
in particular methylamino, ethylamino, l-methylethylamino;
di-C1-C4-alkylamino: dimethylamino, n-methyl-n-ethylamino,
diethylamino, n-methyl-n-propylamino, n-ethyl-n-propylamino,
dipropylamino, diisopropylamino, n-isopropyl-n-methylamino,
n-ethyl-n-isopropylamino, n-isopropyl-n-propylamino,
10 dibutylamino, di-2-methylpropylamino, di-l-methylpropylamino,
n-butyl-n-methylamino and also isomers, n-butyl-n-ethylamino and
also isomers, n-butyl-n-propylamino and also isomer~;
Cl-C6-alkylcarbonyl: acetyl, propionyl, l-propylcarbonyl,
2-propylcarbonyl, 1-butylcarbonyl, 2-butylcarbonyl,
2-methylpropylcarbonyl, 1,1-dimethylethylcarbonyl,
l-pentylcarbonyl, 2-pentylcarbonyl, 3-pentylcarbonyl,
2-methylbutylcarbonyl, 3-methylbutylcarbonyl,
2-methyl-2-butylcarbonyl, 3-methyl-2-butylcarbonyl,
20 1,1-dimethylpropylcarbonyl, 1,2-dimethylpropylcarbonyl,
2,2-dimethylpropylcarbonyl, 1-hexylcarbonyl, 2-hexylcarbonyl,
3-hexylcarbonyl, 2-methylpentylcarbonyl, 3-methyl-pentylcarbonyl,
4-methylpentylcarbonyl, 2-methyl-2-pentylcarbonyl,
3-methyl-2-pentylcarbonyl, 4-methyl-2-pentylcarbonyl,
2-methyl-3-pentylcarbonyl, 3-methyl-3-pentylcarbonyl,
2,2-dimethylbutylcarbonyl, 2,3-dimethylbutylcarbonyl,
3,3-dimethylbutylcarbonyl, 3,3-dimethyl-2-butylcarbonyl,
2-ethylbutylcarbonyl, 1,1,2-trimethylpropylcarbonyl,
1,2,2-trimethylpropylcarbonyl, in particular acetyl, propionyl,
30 propylcarbonyl, 2-propylcarbonyl, butylcarbonyl, 2-butylcarbonyl,
1,1-dimethylpropionyl, pentylcarbonyl,
2,2-dimethylpropylcarbonyl, hexylcarbonyl;
Cl-C6-alkoxycarbonyl: acetoxycarbonyl, propoxycarbonyl,
1-propoxycarbonyl, 2-propoxycarbonyl, 1-butoxycarbonyl,
2-butoxycarbonyl, 2-methylpropoxycarbonyl,
1,1-dimethylethoxycarbonyl, 1-pentoxycarbonyl, 2-pentoxycarbonyl,
3-pentoxycarbonyl, 2-methylbutoxycarbonyl,
3-methylbutoxycarbonyl, 2-methyl-2-butoxycarbonyl,
40 3-methyl-2-butoxycarbonyl, 1,1-dimethylpropoxycarbonyl,
1,2-dimethylpropoxycarbonyl, 2,2-dimethylpropoxycarbonyl,
l-hexoxycarbonyl, 2-hexoxycarbonyl, 3-hexoxycarbonyl,
2-methylpentoxycarbonyl, 3-methylpentoxycarbonyl,
4-methylpentoxycarbonyl, 2-methyl-2-pentoxycarbonyl,
3-methyl-2-pentoxycarbonyl, 4-methyl-2-pentoxycarbonyl,
2-methyl-3-pentoxycarbonyl, 3-methyl-3-pentoxycarbonyl,
2,2-dimethylbutoxycarbonyl, 2,3-dimethylbutoxycarbonyl,
21~67~4
3,3-dimethylbutoxycarbonyl, 3,3-dimethyl-2-butoxycarbonyl,
2-ethylbutoxycarbonyl, 1,1,2-trimethylpropoxycarbonyl,
1,2,2-Trimethylpropoxycarbonyl, in particular acetoxycarbonyl,
propoxycarbononyl, 2-propoxycarbonyl, butoxycarbonyl,
2-butoxycarbonyl, l,1-dimethylpropionyl, pentoxycarbonyl,
2,2-dimethylpropoxycarbonyl, hexoxycarbonyl;
Cl-C12-alkoxyimino: methoxyimino, ethoxyimino, propoxyimino,
2-propoxyimino, butoxyimino, l,l-dimethylethoxyimino,
10 pentoxyimino, hexoxyimino, heptyloxyimino, octyloxyimino,
nonyloxyimino, decyloxyimino, undecyloxyimino, dodecyloxyimino,
in particular methoxyimino and ethoxyimino;
C3-Cl2-alkenyloxyimino: propenyloxyimino, 2-propenyloxyimino,
butenyloxyimino, pentenyloxyimino, hexenyloxyimino,
heptenyloxyimino, octenyloxyiminoj nonenyloxyimino,
decenyloxyimino, undecenyloxyimino, dodecenyloxyimino, in
particular 2-propenyloxyimino;
20 C3-C6-haloalkenyloxyimino: 2,3,3-trifluoro-2-propenyloxyimino,
2,3,3-trichloro-2-propenyl- oxyimino, pentafluoro-2-propenyloxyi-
mino, pentachloro-2- propenyloxyimino;
C3-Cl2-alkylene chain: propylene, butylene, pentylene, hexylene,
heptylene, octylene, nonylene, decylene, undecylene, dodecylene,
in particular butylene, pentylene;
5-membered heteroaromatics which may be mentioned are especially
the following heterocycles: 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-furyl,
30 3-furyl, l-pyrrolyl, 2-pyrrolyl, 3-pyrrolyl, l-pyrazolyl,
3-pyrazolyl, 4-pyrazolyl, 5-pyrazolyl, l-imidazolyl,
2-imidazolyl, 4-imidazolyl, 5-imidazolyl, 2-oxazolyl, 4-oxazolyl,
5-oxazolyl, 2-thiazolyl, 4-thiazolyl, 5-thiazolyl, 3-isoxazolyl,
4-isoxazolyl, 5-isoxazolyl, 3-isothiazolyl, 4-isothiazolyl,
5-isothiazolyl, 1,2,3-triazol-1-yl, 1,2,3-triazol-4-yl,
1,2,3-triazol-5-yl, (lh)1,2,4-triazol-1-yl,
(lh)1,2,4-triazol-3-yl, (lh)1,2,4-triazol-5-yl,
(4h)1,2,4-triazol-2(5)-yl, (4h)1,2,4-triazol-4-yl, l-tetrazolyl,
5-tetrazolyl, 2-oxazolyl, 4-oxazolyl, 5-oxazolyl, 3-isoxazolyl,
40 4-isoxazolyl, 5-isoxazolyl, 2-thiazolyl, 4-thiazolyl,
5-thiazolyl, 3-isothiazolyl, 4-isothiazolyl, 5-isothiazolyl,
1,2,3-oxadiazol-4-yl, 1,2,3-oxadiazol-5-yl, 1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl,
1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl, 3(4)-furazanyl, 1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(5)-yl,
1,2,3-thiadiazol-4-yl, 1,2,3-thiadiazol-5-yl,
1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl, 1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl,
1,2,4-thiadiazol-3-yl, 1,2,4-thiadiazol-5-yl.
- 216675~
6-membered heteroaromatics which may be mentioned are especially
the following heterocycles: 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl,
2-pyrimidinyl, 4(6)-pyrimidinyl, 5-pyrimidinyl, 3(6)-pyrazinyl,
4(5)-pyrazinylt 1,3,5-triazin-2-yl, 1,2,4-triazin-3-yl,
1,2,4-triazin-5-yl, 1,2,4-triazin-6-yl, 1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3(6)-yl.
Benzo-fused 5- or 6-membered ring aromatics are especially:
benzofuranyl, benzothienyl, indolyl, benzoxazolyl,
benzisoxazolyl, benzthiazolyl, benzisothiazolyl, benzpyrazolyl,
10 indazolyl, 1,2,3-benzothiadiazolyl, 2,1,3-benzothiadiazolyl,
benzotriazolyl, benzofuroxanyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl,
cinnolinyl, quinazolinyl, quinoxalinyl, phthalazinyl or
benzoxazinyl.
The compounds of the formula I according to the invention are
obtained by reacting a derivative of the formula
A-XH
20 where the symbols A and X have the meaning indicated above, in
the presence of a base with a pyrimidine of the formula II
Rl7' ~ X z (II)
30 where the symbols Y and Z have the meanings indicated above and
where Rl7 is a nucleofugic leaving group such as halogen, prefer-
ably chlorine or bromine, alkylsulfonyl, preferably methylsulfo-
nyl, phenylsulfonyl or substituted phenylsulfonyl, preferably
4-methylphenylsulfonyl, or another equivalent leaving group.
Bases which can be used are alkali metal or alkaline earth metal
hydrides such as NaH or CaH2, alkali metal hydroxides such as NaOH
or KOH, alkali metal alkoxides such as potassium tert-butoxide,
alkali metal carbonates such as sodium carbonate or potassium
carbonate, alkali metal amides such as sodium amide, lithium
40 diisopropylamide or lithium tetramethylpiperidide or tertiary
amines. When using an inorganic base, a phase-transfer catalyst
can be added if this promotes the conversion. The solvents used
are especially protic or aprotic polar solvents such as, for ex-
ample, lower alcohols, tetraalkyl-substituted cyclic or acyclic
ureas, dimethylformamide or dimethyl sulfoxide.
216~7~4
Compounds of the formula I can also be prepared by starting from
the corresponding carboxylic acids, i.e. compounds of the formula
I where W is oxygen and Rl is hydroxyl, and first converting these
in a customary manner to an activated form such as a halide or
imidazolide and then reacting this with an appropriate nucleo-
phile. These two steps can also be simplified, for example, by
allowing the carboxylic acid to act on the nucleophile in the
presence of a dehydrating agent, such as carbodiimide.
10 Compounds of the formula II can be prepared starting from 2-fluo-
romalonic acid esters, 2-fluorocyanoacetic esters, 2-fluoromalo-
nonitrile or 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds of the formulae III and IV
F F
(III) ~ OR (IV)
O o O O
20 by methods known from the literature (eg. A.R. Katritzky and
C.W. Rees, Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry, Pergamon Press
1984; EP 582288).
The compounds I and their agriculturally utilizable salts are
suitable, both as isomer mixtures and in the form of the pure
isomers, as herbicides. The herbicidal compositions containing I
control vegetation on noncultivated areas very well, particularly
at high application rates. In crops such as wheat, rice, corn,
soybeans and cotton, they act against broad-leaved weeds and
30 grass weeds without noticeably damaging the crop plants. This ef-
fect occurs especially at lower application rates.
Taking into account the versatility of the application method,
the compounds I or compositions containing them can additionally
be employed in a further number of crop plants for the elimin-
ation of undesired plants. The following crops, for example, are
suitables
Allium cepa, Ananas comosus, Arachis hypogaea, Asparagus
officinalis, Beta vulgaris spp. altissima, Beta vulgaris spp.
40 rapa, Brassica napus var. napus, Brassica napus var.
napobrassica, Brassica rapa var. silvestris, Camellia sinensis,
Carthamus tinctorius, Carya illinoinensis, Citr-us limon, Citrus
sinensis, Coffea arabica (Coffea canephora, Coffea liberica),
Cucumis sativus, Cynodon dactylon, Daucus carota, Elaeis
guineensis, Fragaria vesca, Glycine max, Gossypium hirsutum
(Gossypium arboreum, Gossypium herbaceum, Gossypium vitifolium),
Helianthus annuus, Hevea brasiliensis, Hordeum vulgare, Humulus
`- 21 6~75ll
21
lupulus, Ipomoea batatas, Juglans regia, Lens culinaris, Linum
usitatissimum, Lycopersicon lycopersicum, Malus spp., Manihot
esculenta, Medicago sativa, Musa spp., Nicotiana tabacum (N.
rustica), Olea europaea, Oryza sativa, Phaseolus lunatus,
Phaseolus vulgaris, Picea abies, Pinus spp., Pisum sativum,
Prunus avium, Prunus persica, Pyrus communis, Ribes sylvestre,
Ricinus communis, Saccharum officinarum, Secale cereale, Solanum
tuberosum, Sorghum bicolor (S. vulgare)~ Theobroma cacao,
Trifolium pratense, Triticum aestivum, Triticum durum, Vicia
10 faba, Vitis vinifera, Zea mays.
Moreover, the compounds I can also be used in crops which are
tolerant to the action of herbicides as a result of breeding,
including genetic engineering methods.
The herbicidal compositions or the active compounds can be
applied pre-emergence or post-emergence. If the active compounds
are less tolerable for certain crop plants, application
techniques can be used in which the herbicidal compositions are
20 sprayed with the aid of the spray equipment such that the leaves
of the sensitive crop plants are not affected if possible, while
the active compounds reach the leaves of undesired plants growing
underneath or the uncovered soil surface tpost-directed, lay-by).
The compounds I or the herbicidal compositions containing them
can be applied by spraying, atomizing, dusting, broadcasting or
watering, for example in the form of directly sprayable aqueous
solutions, powders, suspensions, even high-percentage aqueous,
oily or other suspensions, or dispersions, emulsions, oil
30 dispersions, pastes, dusting compositions, broadcasting
compositions or granules. The application forms depend on the
intended uses; in each case they should if possible guarantee the
finest dispersion of the active compounds according to the
invention.
Suitable inert additives are mineral oil fractions of medium to
high boiling point~, such as kerosene or diesel oil, further coal
tar oils and also oils of vegetable or ~ni~l origin, aliphatic,
cyclic and aromatic hydrocarbons, eg. paraffin,
40 tetrahydronaphthalene, alkylated naphthalenes or their
derivatives, alkylated benzenes or their derivatives, methanol,
ethanol, propanol, butanol, cyclohexanol, cyclohexanone or
strongly polar solvents, such as N-methylpyrrolidone or water.
Aqueous application forms can be prepared from emulsion
concentrates, suspensions, pastes, wettable powders or
water-dispersible granules by addition of water. To prepare
- ~166754
22
emulsions, pastes or oil dispersions, the substrates can be
homogenized in water as such, or dissolved in an oil or solvent,
by means of wetting agents, adherents, dispersants or
emulsifiers. However, concentrates consisting of active
substance, wetting agent, adherent, dispersant or emulsifier and,
possibly, solvent or oil can also be prepared, which are suitable
for dilution with water.
Suitable surface-active substances (adjuvants) are the alkali
10 metal, alkaline earth metal and ammonium salts of aromatic
sulfonic acids, eg. ligno-, phenol-, napthalene- and
dibutylnaphthalenesulfonic acid, as well as of fatty acids,
alkyl- and alkylaryl-sulfonates, alkyl, lauryl ether and fatty
alcohol sulfates, and also salts of sulfated hexa-, hepta- and
octadecanols as well a~ of fatty alcohol glycol ethers,
condensation products of sulfonated naphthalene and its
derivatives with formaldehyde, condensation products of
naphthalene or of naphthalenesulfonic acids with phenol and
formaldehyde, polyoxyethylene octylphenyl ethers, ethoxylated
20 isooctyl-, octyl- or nonylphenol, alkylphenyl or tributylphenyl
polyglycol ethers, alkylaryl polyether alcohols, isotridecyl
alcohol, fatty alcohol-ethylene oxide condensates, ethoxylated
castor oil, polyoxyethylene alkyl ethers or polyoxypropylene
alkyl ethers, lauryl alcohol polyglycol ether acetate, sorbitol
esters, lignin-sulfite waste liquors or methylcellulose.
Powdered, broadcasting and dusting compositions can be prepared
by mixing or joint grinding of the active substances with a solid
carrier.
Granules, eg. coated, impregnated and homogeneous granules, can
be prepared by binding of the active compounds to solid carriers.
Solid carriers are mineral earths such as silicic acids, silica
gels, silicates, talc, kaolin, limestone, lime, chalk, bole,
loess, clay, dolomite, diatomaceous earth, calcium sulfate and
magnesium sulfate, magnesium oxide, ground synthetic substances,
fertilizers, such as ammonium sulfate, ammonium phosphate,
ammonium nitrate, ureas and vegetable products such as grain
flower, tree bark, wood and nut shell meal, cellulose powder or
40 other solid carriers.
The concentrations of the active compounds I in the
ready-to-apply preparations can be varied within wide ranges. The
formulations in general contain from 0.001 to 98% by weight,
preferably from 0.01 to 95% by weight, of active compound. The
- 2i~67~
active compounds are in this case employed in a purity of from
90% to 100%, preferably 95% to 100% (according to NMR spectrum).
The compounds I according to the invention can be formulated, for
example, as follows:
I 20 parts by weight of the compound No.I.001 are dissolved
in a mixture which consists of 80 parts by weight of
alkylated benzene, 10 parts by weight of the addition
product of 8 to 10 mol of ethylene oxide to 1 mol of
oleic acid N-monoethanolamide, 5 parts by weight of cal-
cium salt of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid and 5 parts by
weight of the addition product of 40 mol of ethylene
oxide to 1 mol of castor oil. ~y pouring out the solution
and finely dispersing it in 100,000 parts by weight of
water, an aqueous dispersion is obtained which contains
0.02% by weight of the active compound.
II 20 parts by weight of the compound No.I.124 are dissolved
in a mixture which consists of 40 parts by weight of
cyclohexanone, 30 parts by weight of isobutanol, 20 parts
by weight of the addition product of 40 mol of isooctyl-
phenol and 10 parts by weight of the addition product of
40 mol of ethylene oxide to 1 mol of castor oil. By pour-
ing the ~olution into and finely dispersing it in
100,000 parts by weight of water, an aqueous dispersion
is obtained which contains 0.02% by weight of the active
compound.
30 III 20 parts by weight of the active compound No. I.059 are
dissolved in a mixture which consists of 25 parts by
weight of cyclohexanone, 65 parts by weight of a mineral
oil fraction of boiling point 210 to 280 C and 10 parts
by weight of the addition product of 40 mol of ethylene
oxide to 1 mol of castor oil. By pouring the solution
into and finely dispersing it in 100,000 parts by weight
of water, an aqueous dispersion is obtained which con-
tains 0.02 % by weight of the active compound.
40 IV 20 parts by weight of the active compound No. I.001 are
well mixed with 3 parts by weight of the sodium salt of
diisobutylnaphthalenesulfonic acid, 17 parts by weight of
- the sodium salt of a lignosulfonic acid from a sulfite
waste liquor and 60 parts by weight of powdered silica
gel and ground in a hammer mill. By finely dispersing the
mixture in 20,000 parts by weight of water, a spray
2~ 667~4
24
mixture is obtained which contains 0.1 % by weight of the
active compound.
V 3 parts by weight of the active compound No. I.124 are
mixed with 97 parts by weight of finely divided kaolin.
In this way a dusting composition is obtained which con-
tains 3% by weight of the active compound.
VI 20 parts by weight of the active compound No. I.059 are
intimately mixed with 2 parts by weight of calcium salt
of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, 8 parts by weight of
fatty alcohol polyglycol ether, 2 parts by weight of
sodium salt of a phenol-urea-formaldehyde condensate and
68 parts by weight of a paraffinic mineral oil. A stable
oily dispersion is obtained.
VII 1 part by weight of the compound I.001 is dissolved in a
mixture which consists of 70 parts by weight of cyclo-
hexanone, 20 parts by weight of ethoxylated isooctylphe-
nol and 10 parts by weight of ethoxylated ca~tor oil. A
stable emulsion concentrate is obtained.
VIII 1 part by weight of the compound I.124 is dissolved in a
mixture which consists of 80 parts by weight of cyclo-
hexanone and 20 parts by weight of Emulphor EL. A stable
emulsion concentrate is obtained.
To broaden the spectrum of action and to obtain synergistic
effects, the fluorinated pyrimidines I can be mixed with numerous
30 representatives of other herbicidal or growth-regulating active
compound groups and applied jointly. For example, suitable
mixture components are diazines, 4H-3,1-benzoxazine derivatives,
benzothiadiazinones, 2,6-dinitroanilines, N-phenylcarbamates,
thiocarbamates, halocarboxylic acids, triazines, amide~, ureas,
diphenyl ethers,-triazinones, uracils, benzofuran derivatives,
cyclohexane-1,3-dione derivatives which, for example, carry a
carboxyl or carbimino group in the 2-position, quinolinecar-
boxylic acid derivatives, imidazolinones, sulfonamides,
sulfonylureas, aryloxy- or heteroaryloxyphenoxypropionic acids
40 and their salts, esters and amides and others.
Additionally, it can be of use to apply the compounds I on their
own or jointly, in combination with other herbicides,
additionally mixed with further crop protection compositions, for
example with compositions for controlling pests or
phytopathogenic fungi or bacteria. Further of interest is the
miscibility of mineral salt solutions which are employed for the
2 1 ~
elimination of nutritional and trace element deficiencies.
Nonphytotoxic oils and oil concentrates can also be added.
The compounds of the formula I can furthermore affect the various
stages of development of a plant and are therefore empIoyed as
growth regulators. The diversity of action of the plant growth
regulators is especially dependent
a) on the plant species and variety,
b) on the time of application, based on the stage of development
of the plant, and on the time of year,
c) on the type and method of application (eg. seed dressing,
soil treatment, foliar application or stem injection in the
case of trees),
d) on climatic factors (eg. temperature, amount of precipita-
tion, and additionally also length of day and light inten-
sity),e) on the soil condition (including fertilization),
f) on the formulation or application form of the active compound
and
g) on the concentrations of the active substance applied.
A few of the number of various application possibilities of the
30 plant growth regulators of the formula I according to the
invention in plant cultivation, in agriculture and in
horticulture are mentioned below:
A. The vegetative growth of the plants can be severely inhibited
by the compounds which can be used according to the inven-
tion, which is manifested, in particular, in a reduction of
the longitudinal growth. The treated plants accordingly ex-
hibit compact growth; additionally a darker leaf coloration
is to be observed.
A decreased intensity of the growth of grasses on roadsides,
hedgerows, canal banks and on plots of gras-s such as parks,
sp~rts grounds and orchards, ornamental lawns and airfields
proves to be advantageous in practice, so that labor- and
cost-intensive mowing can be reduced.
- 216~7~4
The increase in the resistance of crops susceptible to lodg-
ing, such as cereals, corn, sunflowers and soybeans, is also
of economic interest. The culm shortening and culm
strengthening caused in this case decrease or eliminate the
danger of lodging (of being bent over) of plants under unfa-
vorable weather conditions before harvesting.
The application of growth regulators for inhibiting the lon-
gitudinal growth and for temporally altering the course of
ripening in cotton i8 also important. Completely mechanized
harvesting of this important crop plant is thus made pos-
sible.
In the case of fruit and other trees, pruning costs can be
saved using the growth regulators. In addition, the alterna-
tion of fruit trees can be broken by means of growth regula-
tors.
The lateral branching of the plants can also be increased or
inhibited by application of growth regulators. There is
interest in this if, eg. in the case of tobacco plants, the
formation of side shoots (suckers) is to be inhibited in
favor of leaf growth.
In the case of winter rape, for example, the frost resistance
can also be considerably increased using growth regulators.
In this case, on the one hand, the longitudinal growth and
the development of an excessively luxuriant (and thereby par-
ticularly frost-susceptible) herbage or biomass are inhib-
ited. On the other hand, after sowing and before the winterfrosts set in the young rape plants are held back in the
vegetative development stage despite favorable growth condi-
tions. As a re~ult, the frost danger to those plants which
are prone to premature degeneration of the inhibition of
flowering and to transition into the generative phase is also
eliminated. Even in other crops, eg. winter cereals, it is
advantageous if the populations are indeed well tillered by
treatment with compounds according to the invention in the
fall, but are not too luxuriant when going into the winter.
As a result, the increased frost sensitivity and, because of
the relatively low herbage or biomass, attack by various dis-
eases (eg. fungal disease) can be prevented. The inhibition
of the vegetative growth additionally makes possible a more
compact planting of the soil with many crop plants, so that
an additional yield can be achieved, based on the soil area.
-- 21667a~i
27
B. Additional yields both of parts of plants and of plant con-
stituents can be achieved using the growth regulators. Thus
it is possible, for example, to induce the growth of greater
amounts of buds, flowers, leaves, fruit, seeds, roots and tu-
bers, to increase the content of sugar in sugar beet, sugar
cane and citrus fruits, to raise the protein content in cere-
als or soybeans or to stimulate rubber trees to an increased
flow of latex.
In this case, the compounds of the formula I can cause
increases in yield by intervention in the plant metabolism or
by promotion or inhibition of vegetative and/or of generative
growth.
C. Finally, both reduction or prolongation of the development
stages and acceleration or retardation of the ripening of the
harvested parts of plants before or after harvesting can be
achieved using plant growth regulators.
Of economic interest, for example, is the facilitation of
harvesting, which is made possible by the temporally concen-
trated fall or decrease in the adhesiveness to the tree in
the case of citrus fruits, olives or in the case of other
species and varieties of pomes, drupes and indehiscent fruit.
The same mechanism, that is the promotion of the formation of
abscission tissue between the fruit or leaf and shoot part of
the plant, is also essential for a well-controllable defoli-
ation of productive plants such as, for example, cotton.
30 D. The consumption of water by plants can furthermore be reduced
using growth regulators. This is particularly important for
usable agricultural areas which have to be artificially
watered with a high outlay in terms of cost, eg. in arid or
semiarid areas. By the use of the substances according to the
invention, t-he intensity of watering can be reduced and thus
a more cost-effective management can be carried out. Under
the influence of growth regulators, a better utilization of
the water present occurs because, inter alia,
- the opening width of the stomata is reduced,
- - a thicker epidermis and cuticle are formed,
- the root penetration of the soil is improved and
- - the microclimate in the plant population is favorably
influenced by a more compact growth.
2166~5~
28
The compounds I are particularly suitable for culm shortening
of crop plants such as barley, rape and wheat.
The growth regulators of the formula I to be used according
to the invention can be supplied to the crop plants~both from
seeds (as seed-dressing agents) and via the soil, ie. by the
roots and, particularly preferably, by spraying over the
leaf. The compositions are prepared here in a similar manner
to the herbicides (see above).
A~ a result of the high plant compatibility, the application
rate of active compound is not critical. The optimum applica-
tion rate varies depending on the control target, time of
year, target plants and stages of growth.
Depending on the control target, time of year, target plants and
stage of growth, the application rates of active compound are
from 0.001 to 3.0, preferably from 0.01 to 2.0, kg/ha of active
substance (a.s.)
Use examples
The herbicidal and growth-regulatory action of the fluorinated
pyrimidines of the formula I was shown by greenhouse tests:
The cultivation containers used were plastic flowerpots
containing loamy sand with approximately 3.0% of humus as a
substrate. The seeds of the test plants were sown separately
according to species.
In the case of pre-emergence treatment, the active compounds
suspended or emulsified in water were applied directly after
sowing by means of finely dispersing nozzles. The containers were
lightly watered in order to promote germination and growth, and
then covered with transparent plastic hoods until the plants had
taken root. This covering causes a uniform germination of the
test plants if this has not been adversely affected by the active
compoundq.
40 For the purpose of post-emergence treatment, the test plants are
first grown, depending on growth form, to a height of growth of
from 3 to 15 cm and treated only then with the active compounds
suspended or emulsified in water. For this purpose, the test
plants are either sown directly and raised in the same containers
or they are first grown separately as seedlings and transplanted
into the test containers a few days before treatment. The
-- 2166754
29
application rate for post-emergence treatment is 0.0625 or 0.0313
kg/ha of a.s.
The plants were kept in a speeies-specific manner at 10-25 C or
20-35 C. The test period extended over 2 to 4 weeks. During this
time, the plants were tended, and their reaction to the
individual treatments was assessed.
Assessment was carried out on a scale from 0 to 100. In this
10 case, 100 means no emergence of the plants or complete
destruction at least of the above-ground parts and 0 means no
damage or normal course of growth.
The plants used in the greenhouse tests were made up of the
following species:
Botanical name Common name
Alopecurus blackgrass
20 myosuroides
Sinapis alba white mustard
Solanum nigrum black nightshade
Table 1 - Herbicidal activity on post-emergence application in
the greenhouse
~ ~ N
\ O ~ \ ~ F
OH
/o
Ex. No. 1.001
Application rate 0.0625 ¦ 0.0313
(kg/ha of a.s.)
40 Damage in % test plants
ALOHY 90 85
SINAL 95 95
SOLNI - 95 95
21667~1
c
3 ~ o o o o o o ~o o o
OOOOOOOOOOO
~ X U
~, o U~ Z Z - o o o o o o o
~. ~
.' ~Z~ Om o~
~' /,2 ZZ
~/
C >~
Ul ~ _~
_ --\
( ~U ~r
+ ~ Z
~, , p ~ _
- ooooooooooo
ooooooooo,~_I
.a zOOOOOOOOOOO
`- 21667~
31
-
O O O O O O O O O O O O 0 0~ 0~ 0 0
OOOOOOoO OOO Oo~Oo O
x
oooooooo ooo ooou~o o
oooooooo ooo ooooo o
Z = ~ ~ ~ '~ N ~ J
u; m m u m ~ u ll ll 0, ll
~o~ o o O O O b o o o o o o O
O o ooooooo oOo OOOO O O
Z
21~i~754
C;
o o o o 3 o o o o ~ ~o o o o 3 o o ~o o
o o o o ~ o o 3 3 3 3 3 3 o 3 3 3 o o
ooooo oooooooooooooo
~ ~a ~ o o
ooooo ooooooooo ZZZZ
,~ C
., ,
,~ c,
. , ,~~ t~
n
r~ C r
~' n ,o L .C~
~ O O
Z o ~ O
Iz ~ ~ IZ ~ m ~: ~
oo~oo ~ ZZZ~
OoOooo oOooOooooOOo O O
Z
No. Rl . W XY Z (R2)n Rn
1.048 H N-OEt O OMeOMe
1.049 H, N-OtBu O OMeOMe - -
1.050 H N-OCH=CH2 O OMe OMe
1.051 H N- O OMeOMe
OcH2cH=cH2
1.052 H ,N-OPh O OMeOMe
1.053 H N-NH2 O OMeOMe
1.054 H N-NHMe O OMeOMe
1.055 H N mlC2 0OMeOMe - - C5
1.056 H N-NHPh O OMeOMe - - C5
1.057 OH O O OMeOMe - 2-Cl w
1.058 OH o o OMeOMe - 3-Cl w
1.059 OH O O OMeOMe - 4-Cl
1.060 OH O S OMeOMe - 4-Cl
1.061 OH O NH OMeOMe - 4-Cl
1.062 OH O N-CN OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.063 OH N-OH O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.064 OH N-OMe O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.065 OH O . O OMe OMe 5-Me 4-Cl
1.066 O~Na+ O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.067 O-K+ O O OHe OMe - 4-Cl
No . R~ W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Rn1.068 O~ 1/2Ca2+ O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.069 O,-(NH4)+ O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.070 O~(NMe4)+ O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.071 OMe O O OMe OHe - 4-Cl
1.072 OEt O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.073 O-CH2-OMe O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.074 O-CH2-SMe O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.075 OCH2CH=CH2 OHe OMe - 4-Cl
1.076 OCH2C_CH O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.077 / O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
o--11 lP ~` ~
1.078 O-Cyclopropyl O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.079 OCH2-CO2Me O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.080 1 O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
~,0
1.081 OPh O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.082 O-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.083 ON-CMe2 - O O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.084 ON=CMe2 O S OMe OMe - 4-Cl
`- 21667~
U C~ U U ~ U U U U U U ~ U C~
c
N
,1
r.~ 0 a~ 0 0 ~ 0 a~
o o o o 3 o 3 ~ o o o o 3 o 3 i~ o o
o oooooo oooo~o~ooooo
o oooooo ooooooooooo
~ m
o oooooo oooooooooZZ
~1 1
r, ,~ c
~ J ~ ~1 ~r ~r
~; : c ~ ~ ~ c .~
--I t` 1- a~ .c d
l J ~ ~ P~ ~ I I .~ r t I ~ N ~,)
. 5 1 ~ ~ ~ oN
~ I Z -- -- Z , ~ ~-1 H ~
Z I I I I I I ' :~ :C X
~ o o o o o ~z z z ~ ~: m ::
n ~o r.~ o ~ ~ ~ ~ o _l ~
o o o
Oo oooooo oooooooo~
z
No . Rl W XY Z ( R2 ) n Rn
1.103 H NPh O OMeOMe - 4-Cl
1.104 H, N-OH O OMeOMe - 4-Cl
1.105 H N-OMe O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.106 H N-OEt O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.107 H N-OtBu O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.108 H N-OCH=CH2 O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.109 H N- O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
OcH2cH=cH2
1.110 H N-OPh O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.111 H N-NH2 O OMe OMe - 4-Cl CS~
1.112 H N-NHMe O OMe OMe - 4-Cl ~ r~
O~
1.113 H N-NMe2 O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.114 H N-NHPh O OMe OMe - 4-Cl
1.115 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,3-Cl2
1.116 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,4-Cl2
1.117 OH O O OHe OMe - 2,5-Cl2
1.118 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,6-Cl2
1.119 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,4-Cl2
1.120 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,5-Cl2
1.121 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,4,6-Cl3
1.122 OH O O OHe OMe - 2-Br
` - 21667~
37
m m m I I I m m m m m m I I I m m
I
~n I I I I I I I
000 ~ 0 ~ 00 ~ 0 ~ 00 ~ 000 ~ 0
o o 3 o o o o o o o O O O O o ~ o o o o
0 ~ ~ 000000 ~ 0 ~ 0000000
~OOOOOOOOOOOOOOO~
~c u
ootnzzooooooooooooooo
T 1
oooooZZooooooooooooo
-- + N \/
U + +~r O ~ U U ~ I
+ ~ m ~ u ~ ~ o
-' Z Z 0 J~ U U ~ m
m 5~ X ~ I I u u
oo-ooooooooooooooooo
z
~16 ~ 7 ~ ~
38
m m m m m m m m m m m m m m m m
N
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
O O O O 0 ~000 000000 0 ~0
ooo ooo~no oooooo oo
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
,_ ~ ~ ~ o
~) ~ I Z Z 0~ Z I -- _ Z
O ;)- O O O O O O O O O
z ~ .. ..... ...... .
No. Rl W XY Z ~R2)n Rn
1.160 1-Imidazolyl O O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.161 1,,2,4-Triazol-1-yl O O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.162 NH-SO2Me O O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.163 NH-SO2Ph O O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.164 NHSO2C6H4-4-Me O O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.165 H O O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.166 Me O O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.167 H NMe O OMe OMe - 4-Br ~-~
1.168 H NtBu O OMe OMe - 4-Br C~
1.169 H NPh O OMe OMe - 4-Br -~
1.170 H N-OH O OMe OMe - 4-Br ~ ~Ca
1.171 H N-OMe O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.172 H N-OEt O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.173 H N-OtBu O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.174 H N-OCH=CH2 O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.175 H N- O OMe OMe - 4-Br
OCH2CH=CH2
1.176 H N-OPh O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.177 H N-NH2 O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.178 H N-NHMe O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.179 H N-NMe2 O OMe OMe - 4-Br
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Rn
1.180 H N-NHPh O OMe OMe - 4-Br
1.181 O,H O O OMe OMe - 2-F
1.182 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-F
1.183 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-F
1.184 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,3,4,5,6-Fs
1.185 OH 'O O OMe OMe - 2-Me
1.186 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-He
1.187 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Me
1.188 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Et
1.189 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Et
1.190 OH o o OMe OMe - 4-Et O C~
1.191 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-CMe2
1.192 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-CMe2
1.193 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-CMe2
1.194 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,3-Me2
1.195 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,4-Me2
1.196 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,5-Me2
1.197 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,6-Me2
1.198 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,4-Me2
1.199 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,5-Me2
1.200 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,4,6-Me3
~16675l~
, ~ , , , 4, , , ~ , ,
~, u ~, 3 ~o o~ ~o ~ o ~ o o o o ~ o ~ ~ ~ o ~
o o ~o ~o ~o o o~ o ~o o o o ~o o o ~ ~o ~o o o o~
c~
ooooooU~ooooooU~ZZooooo
Om ~
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o z z o o o
~ +
m m m m m m :c m m m m m m m m m m :: m æ X
ooooooooooooooooooooo
ooOoooooo~
Z.....................
- 216675~
~OOOO1)000~ ~OO ~OO~
L
N
o ~ ~ ~ o o o o o o o
~ _ o X ~ ~o o o o
OOOOOOOOOO OOO OOOU~
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
~S; N + O ~ ~J Z .-4 o~ \ Z I N N
~ d a~ I m 11 ~
:~ ~ `' U C, ~-- I ~
--~ Z X ~ ~ N N / '~ N ~ C,~ O
,C C~ U 11
~ I Z Z
OO-OOOOOOO OO OOOO
N ~ D 1` Ct~ 0~ O _I ~ 1`~ ~ U l ~ I`
Z
- 21667~4
43
J _~ J ~ ) J .) ~
O ~ ~ O ~ ~ ~ ~ O ~ ~ O ~ O O O O
a:
o 0 0 0 0 ~0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
O OOOOOO OOOOOOOOOZZ
_l C
c ~ ~1 C
~: : a -~ ~ ~ o,
a~ r O O u
~1 ~ ~ ~ Z O ~ O
11 Z -- -- z , ~ ~ ~ ~ I I u~
O z I ~ a~
-ooooo ~ ,~zzz~
0 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ N
Z ...... ...... ...
No. Rl W XY Z (R2)n Rn
1.257 H NPh O OMe OMe - 4-OCMe2
1.258 H N-OH O OHe OMe - 4-OCMe2
1.259 H N-OMe OOMe OMe - 4-OCMe2
1.260 H N-OEt OOMe OMe - 4-OCHe2
1.261 H N-OtBu OOMe OMe - 4-OCMe2
1.262 H N-OCH=CH2 OOMe OMe - 4-OCMe2
1.263 H N- OOMe OMe - 4-OCMe2
OcH2cH=cH2
1.264 H N-OPh OOMe OMe - 4-OCMe
1.265 H N-NH2 OOHe OMe - 4-OCMe
1.266 H N-NHMe OOMe OMe - 4-OCMe2
1.267 H N-NHe2 OOMe OHe - 4-oCHe2
1.268 H N-NHPh OOMe OMe - 4-OCHe2
1.269 OH O OOMe OMe - 2-OCHF2
1.270 OH O OOHe OMe - 3-OCHF2
1.271 OH O OOHe OMe - 4-OCHF2
1.272 OH O O OHe OMe - 2,3-OMe
1.273 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,4-OMe
1.274 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,5-OMe
1.275 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,6-OMe
1.276 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,4-OCMe2
No. Rl W X Y Z (R2)n Rn
1.277 OH O O OMe OHe - 3,5-OMe2
1.278 aH O O OMe OMe - 2,4,6-OMe3
1.279 OH O O OMe OMe
~\
1.280 OH O O OMe OMe - ~ o
o/
1.281 OH O O OMe OMe ~ l
~3~ 0 ) ~
1.282 OH O O OMe OMe -
1.283 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-NHMe
1.284 OH O O OHe OMe - 3-NHMe
1.285 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-NHMe
1.286 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-NMe2
1.287 OH ' O O OMe OMe - 3-NMe2
1.288 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-NMe2
1.289 OH O S OMe OMe - 4-NMe2
1.290 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-SMe
~6675~
g6
N N N N N N N N N ~ _ N
: O O O O O O O O O Z Z Z O O O :J C/ J O
UUUUUUuUUUuUOOOZ
N
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
X
O ~ O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
o o o o o o o o o o
Z
~16~75 1
47
Z Z
-
,
o o
o o
o o
o o
m
o ~ ~
Z
21~67a4
g8
, .. .. . . . .. .. . .. .
,....................... .
4 ~4 ~4 ~ ~4 ~ ~4 1,14 4 '14
C
Ul ~ ~
g _IIIIIIU)IIII
OOOOOO
OOOOOOOOOOO
X t.
.U ~ C~
\ /
~\ Z 3:
r \\ //
~O Z ~ o
r
ZZOOOOo
\\3
Lq ~
5, +
~ + _1 5Z
Z ~C --
O O O O O O O O O O O
_~ N t`~ ~ IJ~ ~O 1` CO O~ O ~
al ~ o o o o o o o o o ~1 ~t
.4 Z O O O O O
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.012 O~(NMe4)+ O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
2.013 ,OHe O O OMe OMe - 1-Pyrrolyl
2.014 OEt O O OMe OMe - 1-Pyrrolyl
2.015 O-CH2-OMe O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
2.016 O-CH2-SMe O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
2.017 OCH2CH=CH2 . OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
2.018 OCH2C_CH O O OMe OHe - l-Pyrrolyl
2.019 ~ ~ O O OMe OMe - 1-Pyrrolyl
O N a:,
2.020 O-Cyclopropyl O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
2.021 OCH2-C02Me O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
2.022 1 O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
0 ~0
2.023 OPh O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
2.024 O-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
2.025 ON=CMe2 O O OMe OMe - 1-Pyrrolyl
2.026 ON=CMe2 O S OMe OHe - l-Pyrrolyl
2.027 O O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
~0
2.028 ON=CMe-SMe O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrrolyl
~l~U j J~t
, 1 5SL
so
m
L4 ~4 4 ~ i~l 1~4 L4 ~4 '4 U4 4 4 ~4 ~4 4 4 C4 4 1 4
-
N
X
O ~0 o Oæ ~ o æO o 0~ o O o o~ Oæ Oæ 0~ 0 Oæ
a~ a~ a~ ~ a~ a~ ~ a~ ~ a~ ~ ~ a~ a~ a~ ~ ~ a~
~ O æ o~ Oæ 0~ ~0 Oæ O O 0 0 o Oæ Oæ Oæ Oæ O 0~
x
ooooooooooooooooooo
:: æ
m ~ o o o
oooooooooooooZZZZZZ
~î
_I C
_ ~ C
r
r: a ~ _I c
r ~ 4 ~o
~ 04
a~ I ~ 2 ~o 1
æ _~ ~ V h ~ ~ O
Z -- -- ¦ ~ ~ H ~ ¦ ¦ U~ -
o b o ~ z z z ~ m m m m m m
01 0 _~ ~ ~ ~ Ul ~ ~ CD O~ O O X ~
~ooO o OOO o Ooooooooooo
~ .... .............. .
:- 216fi7~
51
O
J ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 3 3
14 L4 ~1 ~4 4 ~ 4 14
U~ I
O O O O O O O O O ~ O O O O O 0~ ~0 0 0~ 0 0~
~7 U C~ C7 0 C~ O O ~ O ~ C~ ~ O O O O
mlZ
ooooooooooooooozzoooo
mm
3~l1N ~ ~ ~
mmm ~ L4
U U L4 mm~m mx
1o 1o 1o 1o lZ lz lz lz 1o 1o
zzzzzzzzooooooooozzoo
mmmmmmmmmmmmlZ
mmmmmmmmooooooooooooo
~ ~ 0 ~ o ~ o _1 ~ ~ ~ n ~o
ooooooooooooooooooooo
Z
No. Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.077 O-K+ O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.078 O~ l/2Ca2+O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.079 O-(NH4)+ O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.080 O~(NMe4)+ O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.081 OMe O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.082 OEt 'O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.083 O-CH2-OMe O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.084 0-CH2-SMe O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.085 OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yle~
2.086 OCH2C_CH- O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl_~
2.087 ~ ~ O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl~ ~n
O N
2.088 O-Cyclopropyl O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.089 OCH2-CO2He O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.090 1 O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
N
2.091 OPh O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.092 o-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.093 ON=CMe2 O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.094 ON=CMe2 O S OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
No . Rl . W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.095 O O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
N=O
2.096 ONzCMe-SMe O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.097 O-NMe2 O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.098 O-(l-Piperidyl) O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.099 0-(4-Morpholinyl) O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.100 o\\ O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
-- N
~ CS;~
2.101 1-Pyrrolyl O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl ~ C~
2.102 l-Pyrazolyl O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl ~n
2.103 l-Imidazolyl O O OMe OMe - l-Hethylpyrrol-3-yl
2.104 1,2,4-Tria2Ol-l-yl O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.105 NH-SO2Me O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.106 NH-SO2Ph O O OHe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.107 NHSO2C6H4-4-Me O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.109 H O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.110 Me O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.111 H NMe O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.112 H NtBu O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.113 H NPh O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
No. Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het2.114 H N-OH O OHe OMe - 1-Hethylpyrrol-3-yl
2.115 H N-OMe O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.116 H N-OEt O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.117 H N-Ot~u O OMe OHe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.118 H N-OCH=CH2 O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.119 H N-OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.120 H N-OPh O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.121 H N-NH2 O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.122 H N-NHMe O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.123 H N-NMe2 O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.124 H N-NHPh O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrrol-3-yl ~ _~
2.125 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.126 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.127 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.128 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,5-Dimethylpyrrol-1-yl
2.129 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,4-Dimethylpyrrol-3-yl
2.130 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,5-Dimethylpyrrol-3-yl
2.131 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,3-Dimethylpyrrol-4-yl
2.132 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,5-Dimethylpyrrol-3-yl
2.133 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,4-Dimethylpyrrol-5-yl
2.134 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,3-Dimethylpyrrol-5-yl
~1667~
l~ 4 ; 4 4 ; 1. ~1 ~ ~ '- ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ I ; ;
O ~ O ~ ~ ~ O
L L L L L L L Ll .-1 LlLl S ` L V S
-
OOOC~OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
OOoOoOOOOOOOO0000o~OOoOO
X
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
m m m m m m m m m m m m m :1: m m m m m m m
oo,ooooooooooooooooooo
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het2.156 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methyl-5-phenylpyrrol-1-yl
2.157 pH O O OMe OMe - 3,5-Bistrifluoromethylpyrrol-l-yl
2.lS8 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Nitropyrrol-1-yl
2.159 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Phenylpyrrol-3-yl
2.160 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,3,5-Trimethylpyrrol-4-yl
2.161 OH O O OMe OMe - 1-Phenylpyrrol-2-yl
2.162 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Phenylpyrrol-3-yl
2.163 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methyl-1-phenylpyrrol-3-yl
2.164 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methyl-1-phenylpyrrol-4-yl
2.165 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methyl-1-phenylpyrrol-2-yl
2.166 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,5-Dimethyl-1-phenylpyrrol-4-yl
2.167 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methyl-1-phenylpyrrol-5-yl
2.168 OH O O OMe OMe - 1-Metho~y~ ol-2-yl
2.169 OH O O OMe OMe - 1-Metho~y~yLrol-3-yl
2.170 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methoxypyrrol-1-yl
2.171 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methoxy-l-methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.172 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Hethoxy-1-methylpyrrol-4-yl
2.173 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methoxy-1-methylpyrrol-5-yl
2.174 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Metho~y~y~ol-l-yl
2.175 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methoxy-1-methylpyrrol-2-yl
2.176 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methoxy-1-methylpyrrol-4-yl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.177 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methoxy-1-methylpyrrol-5-yl
2.178 ,OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Difluorometho~y~yLLol-l-yl
2.179 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Difluoromethoxy-1-methylpyrrol-3-yl
2.180 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Difluoromethoxy-1-methylpyrrol-4-yl
2.181 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Difluoromethoxy-1-methylpyrrol-5-yl
2.182 OH ' O O OMe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxypyrrol-1-yl
2.183 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxy-1-methylpyrrol-2-yl ~
2.184 OH O O OHe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxy-1-methylpyrrol-4-yl ~'
2.185 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxy-1-methylpyrrol-5-yl C~
2.186 OH O O OMe OMe - 1-Indolyl ~~
2.187 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methylindol-2-yl
2.188 OH O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylindol-3-yl
2.189 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methylindol-1-yl
2.190 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.191 H O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.192 OH O NH OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.193 OH O N-CN OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.194 OH N-OH O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.195 OH N-OMe O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.196 OH O O OMe OMe 5-Me 2-Thienyl
2.197 O~Na+ O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
No. Rl . W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.198 O-K+ O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.199 p~ 1/2Ca2+ O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.200 O-~NH4)+ O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.201 O~~ We4)+ O O OMe OHe - 2-Thienyl
2.202 OMe O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.203 OEt O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.204 O-CH2-OMe O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.205 O-CH2-SMe O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.206 0CH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl e~
2.207 OCH2C_CH O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl C~
2.208 ~ ~ o o OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl ~ cn
O N
2.209 O-Cyclopropyl O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.210 OCH2-CO2Me O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.211 1 O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
0 ~,0
2.212 OPh O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.213 o-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.214 ON=CMe2 O O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.215 ON=CMe2 O S OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
216 ~ 7 ~ 4
-
59
c c c c c c c c c c c c c r c c c c
a a a, a, a a a a a, a a a a a a a a a
r .~ .r r ~ ~ r r r r r r r r r r ~
L S ~ S. S. S. S S S r S S S. ~ S S. S
~;
~ ~
O O o O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
~ ~ a\ ~ ~ 0 ~
O o o o o o o ~ o 3~ o 3 o o ~ o o o
o ooooo oooooooooooo
a~ m
o ooooo ooooooooo~Z~
r~l
r~ I
r~C I ~-
c
., r r~ ~ ~
_~ C) L, r l ~ ~ n 'r
a, ~ r1 C ~
O r~ r E~ m
1) 1 0~ 2 o ~ .~ .r
o~ I Z ~ _ I ~ I I UO~
z I I I I ~ m :~: m a)
O O O O ~ r~ r-~ _I Z Z Z m :~ m m m
~D 1~ a~ ~ o r~ N ~ O r~
O ~ r l r~
No . Rl W X Y Z ~ R2 ) n Het
2.234 H N-OH O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.235 H N-OMe O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.236 H N-OEt O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.237 H N-OtBu O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.238 H N-OCH=CH2 O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.239 H N-OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.240 H N-OPh O OHe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.241 H N-NH2 O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.242 H N-NHMe O OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.243 H N-NMe2 0 OMe OMe - 2-Thienyl
2.244 H N-NHPh O OMe OMe - 2-Tkienyl o C~
2.245 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.246 H O O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.247 OH O NH OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.248 OH O N-CN OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.249 OH N-OH O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.250 OH N-OMe O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.251 OH O O OMe OMe 5-Me 3-Thienyl
2.252 O~Na+ O O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.253 O-K+ O O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.254 O~ 1/2Ca2+ O O OHe OMe - 3-Thienyl
` ` 21667~1
.
61
c c c c c c c c r c c c c c c c c
a a a ~ a a a, a a a, a a a a a a a
L ,C C C r L L L L L L ,C C r
-
W ~
O~OOOOOOO oXoo 50Coooo
OOOOOOOOO OOO OOOOO
X
OOOOOOOOO OOO OOOU~o
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
Z S ~Z
~ t) C) :c :~ b t :r L U I I
¢ ~ I I C.) U C~ p~ I Z Z O
O Q O O O O O O O O O O O O
Z ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ N t~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ t~ ~
2166754
62
CCCCC CCCC CCCCCCCC
a a a a, a a a a a a a a a a a a a
,C S 1- L S
-
N
O O O O ~
ooooo oooooooooooooo
x
ooooooooooooooooooo
a~
a~ ~ s o o
ooooooooooooooZZZZZ
I
~ C
., c ~ ~ r
r E~
o ~\ O '~ -I , er O O N
8 ' U~ U~ O
Il Z -- _ I p,
z ~ m ~ a~
O ~ O O ~ Z Z Z ~ m rl 3:
z ~ ~ ~ ~J ~ ~ ~ N ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ N ~1 ~1 ~
. . . ...... .
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.291 H N-OEt O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.292 H N-OtBu O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.293 H N-OCH=CH2 O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.294 H N-OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.295 H N-OPh O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.296 H N-NH2 O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.297 H N-NHMe O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.298 H N-NMe2 0 OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl CS~
2.299 H N-NHPh O OMe OMe - 3-Thienyl
2.300 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methyl-2-thienylw ~.
2.301 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methyl-2-thienyl
2.302 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methyl-2-thienyl
2.303 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methyl-3-thienyl
2.304 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methyl-3-thienyl
2.305 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methyl-3-thienyl
2.306 OH O O OMe OMe - 4,5-Dimethyl-3-thienyl
2.307 OH O O OMe OMe - 4,5-Dimethyl-2-thienyl
2.308 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Chloro-5-thienyl
2.309 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Chloro-5-thienyl
2.310 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Chloro-5-thienyl
~1667~4
64
C~ C~
~SL~CCCCCC~
c c c ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ I I :~ a a a a a a c c c
a, a, a c c c c c c I c , , , , , , a a a
, , , a a a a a a, ~ ~ a LL~LL-
~
SLL-~-~-~-~-~-~ I-~II~IILLL
IIILLLLLL~OL
~ LL
,,, o ~ ~ o o o a a J . ~ L.
LLL~
m ~ ~ m a~ m ~ u~ z
a
-
N
111 ~IIIIIIII
a) ~ a) a) a) a) a) a) a) ~ a) a) ~ ~ a) ~ a\ a~ ~ a) a)
c~ ~ c~ c~ c~ ~ c~ o~ o~ c~
a) a) a) a) a) a) a) ~ a) a) a) ~ a) a) a) a) ~ a) a) ~ ~
~oooooo~oo~oooooo~ooooooo
xooooooooooooooooooooo
3 o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
_ 5: m m m m !r m :c ~ :~ m m m m m m m m m m :~:
~;oOoOooooooooooooooooo
~ N N N N N N N N N N ~ ~1
o
Z N ~ ~ N ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ N ~ ~ N
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.332 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Ethoxy-4-thienyl
2.333 ,OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Ethoxy-4-thienyl
2.334 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Ethoxy-4-thienyl
2.335 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Difluoromethoxy-5-thienyl
2.336 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxy-5-thienyl
2.337 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Difluoromethoxy-5-thienyl
2.338 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Difluoromethoxy-4-thienyl
2.339 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxy-4-thienyl
2.340 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Difluoromethoxy-4-thienyl
2.341 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methylthio-5-thienyl
2.342 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methylthio-5-thienyl
2.343 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methylthio-5-thienyl
2.344 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methylthio-4-thienyl
2.345 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methylthio-4-thienyl
2.346 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methylthio-4-thienyl
2.347 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Dimethylamino-5-thienyl
2.348 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Dimethylamino-5-thienyl
2.349 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Dimethylamino-5-thienyl
2.350 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Dimethylamino-4-thienyl
2.351 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Dimethylamino-4-thienyl
2.352 OH o O OMe OMe - 2-Dimethylamino-4-thienyl
2:~6754
,. ..
c c c c ~ ~ f~ ~q ~ ~ r .C Ln L~ Ln ~ el~
a a a a
~ , ~ ~I ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ k k - ` -
J ~ ~ a a, _,,,
h ~ J~ f .~ f
. ~r ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ : Ln Ln
a) . ,. I I ~ ~ I I I I
5~ L ~ CQ ~ ) ~Ln ~I ~r Ln ~ ~ ')
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
~OOOOOOOOOO00~00~0000000
~ ;o~ o o o o ~o o o o o o 3 o o o~ o o ~o o o o
xoo~ou~ooooooooooooooooo
3 o o o o o o O o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
m m ~: m m m m m m m m m m m m m m m m
: O ~ O O O m o m o o o O O O O O O O O O O
~ ~ Ln u~ o ~ ~ ~ ~ Ln ~ o ~1
Ln Ln Ln Ln Ln Ln Ln ~ ~O ~ ~O ~D ~D ~ ~O ~ ~ r~ 1` 1`
o
No ~ Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.374 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Chloro-4-furyl
2.375 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Bromo-5-furyl
2.376 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Bromo-5-furyl
2.377 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Bromo-5-furyl
2.378 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Bromo-4-furyl
2.379 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Bromo-4-furyl
2.380 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Bromo-4-furyl
2.381 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,3-Dichloro-4-furyl
2.382 OH O O OMe OMe - 2,5-Dichloro-3-furyl
2.383 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Nitro-5-furyl
2.384 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methoxy-5-furyl ~ C~2.385 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methoxy-5-furyl e
2.386 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methoxy-5-furyl
2.387 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methoxy-4-furyl
2.388 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methoxy-4-furyl
2.389 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methoxy-4-furyl
2.390 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Ethoxy-5-furyl
2.391 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Ethoxy-5-furyl
2.392 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Ethoxy-5-furyl
2.393 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Ethoxy-4-furyl
2.394 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Ethoxy-4-furyl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.395 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Ethoxy-4-furyl
2.396 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Difluoromethoxy-S-furyl
2.397 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxy-5-furyl
2.398 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Dif}uoromethoxy-5-furyl
2.399 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Difluoromethoxy-4-furyl
2.400 OH ~O O OMe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxy-4-furyl
2.401 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Difluoromethoxy-4-furyl
2.402 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methylthio-5-furyl
2.403 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methylthio-5-furyl ~'
2.404 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methylthio-5-furyl
2.405 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methylthio-4-furyl ~ G
2.406 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methylthio-4-furyl
2.407 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methylthio-4-furyl
2.408 OH O o OMe OMe - 4-Dimethylamino-5-furyl
2.409 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Dimethylamino-5-furyl
2.410 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Dimethylamino-5-furyl
2.411 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Dimethylamino-4-furyl
2.412 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Dimethylamino-4-furyl
2.413 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Dimethylamino-4-furyl
2.414 OH O O OMe OMe - Benzofur-2-yl
2.415 OH O S OMe OMe - Benzofur-2-yl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.416 OH O O OMe OMe - Benzofur-3-yl
2.417 ,H O O OMe OMe - Benzofur-3-yl
2.418 OH O S OMe OMe - Benzofur-3-yl
2.419 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrazolyl
2.420 H O O OMe OMe - l-Pyrazolyl
2.421 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-3-yl
2.422 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-3-yl
2.423 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.424 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.425 OH O NH OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl C5
2.426 OH O N-CN OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl ~ c~
2.427 OH N-OH O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.428 OH N-OMe O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.429 OH O O OMe OMe 5-Me l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.430 O~Na+ O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.431 O-K+ O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.432 O~ l/2Ca2+ O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.433 O-(NH4)+ O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.434 O~(NMe4)+ O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.435 OMe O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.436 OEt O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.437 O-CH2-OMe O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.438 ~-CH2-SMe O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.439 OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.440 OCH2C-CH O O OMe OMe - l-Hethylpyrazol-4-yl
2.441 ~ ~ O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
O N
2.442 O-Cyclopropyl O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.443 OCH2-CO2Me o o OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.444 1 0 0 OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
o~,o
N
2.445 OPh O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.446 O-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.447 ON=CMe2 0 0 OMe OMe - l-Hethylpyrazol-4-yl
2.448 ON=CMe2 0 S OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.449 0 0 0 OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
N=O
2.450 ON=CMe-SMe O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.451 O-NMe2 0 0 OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.452 O-(l-Piperidyl) O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.453 0-(4-Morpholinyl) O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
No Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.454 ~ O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
, -- N~
//
2.455 1-Pyrrolyl O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.456 1-Pyrazolyl O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.457 1-Imidazolyl O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.458 1,2,4-Triazol-l-yl O O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.459 NH-S02Me O O OMe OMe - 1-Hethylpyrazol-4-yl
2.460 NH-SO2Ph O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl C~
2.461 NHSO2C6H4-4-Me O O OHe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl C~
2.462 H O O OMe OHe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.463 Me O O OHe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.464 H NMe O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.465 H NtBu O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.466 H NPh O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.467 H N-OH O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.468 H N-OMe O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.469 H N-OEt O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.470 H N-OtBu O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.471 H N-OCH=CH2 O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.472 H N-OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.473 H N-OPh O OHe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.474 ,H N-NH2 O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.475 H N-NHMe O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.476 H N-NMe2 O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.477 H N-NHPh O OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-4-yl
2.478 OH O O OMe OMe - 1-Methylpyrazol-5-yl
2.479 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methylpyrazol-5-yl
2.480 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methylpyrazol-l-yl
2.481 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methylpyrazol-l-yl
2.482 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methylpyrazol-l-yl
2.483 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,4-Dimethylpyrazol-3-yl
2.484 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,S-Dimethylpyrazol-3-yl
2.485 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,3-Dimethylpyrazol-4-yl
2.486 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,S-Dimethylpyrazol-4-yl
2.487 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,3-Dimethylpyrazol-S-yl
2.488 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,4-Dimethylpyrazol-S-yl
2.489 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,4,5-Trimethylpyrazol-l-yl
2.490 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,4,5-Trimethylpyrazol-3-yl
2.491 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,3,5-Trimethylpyrazol-4-yl
2.492 OH O o OMe OMe - 1,3,4-Trimethylpyrazol-5-yl
2.493 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methoxypyrazol-3-yl
No. Rl W . X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.494 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.495 ,OH O O OMe OMe - 1-Methoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.496 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.497 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.498 OH O S OMe OMe - 1-Methoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.499 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-4-methoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.500 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-4-methoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.501 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-4-methoxypyrazol-5-yl ~a
2.502 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-4-methoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.503 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-3-methoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.504 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-3-methoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.505 OH O O OMe OMe - 1-Methyl-3-methoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.506 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-3-methoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.507 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Hethyl-5-methoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.508 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-5-methoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.509 OH O O OMe OMe - 1-Methyl-5-methoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.510 OH O S OMe OMe - 1-Methyl-5-methoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.511 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Ethoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.512 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Ethoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.513 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Ethoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.514 OH o S OMe OMe - l-Ethoxypyrazol-4-yl
No. Rl W X y Z (R2 )n Het
2.515 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Ethoxypyrazol-S-yl
2.516 ,OH O S OMe OMe - 1-Ethoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.517 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Isopropoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.518 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Isopropoxy~y~azol-3-yl
2.519 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Isopropoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.520 OH 'O S OMe OMe - l-Isopropoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.521 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Isopropoxypyrazol-S-yl
2.522 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Isopropoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.523 OH O O OHe OMe - l-Methyl-4-difluoromethoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.524 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-4-difluoromethoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.525 OH O O OHe OMe - l-Methyl-4-difluoromethoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.526 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-4-difluoromethoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.527 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-3-difluoromethoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.528 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-3-difluoromethoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.529 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-3-difluoromethoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.530 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-3-difluoromethoxypyrazol-5-yl
2.531 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-5-difluoromethoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.532 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-5-difluoromethoxypyrazol-3-yl
2.533 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-5-difluoromethoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.534 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-5-difluoromethoxypyrazol-4-yl
2.535 OH o O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-4-methylthiopyrazol-3-yl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.536 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-4-methylthiopyrazol-3-yl
2.537 ~H O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-4-methylthiopyrazol-5-yl
2.538 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-4-methylthiopyrazol-5-yl
2.539 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Hethyl-3-methylthiopyrazol-4-yl
2.540 OH O S OMe OMe - 1-Methyl-3-methylthiopyrazol-4-yl
2.541 OH 'O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-3-methylthiopyrazol-5-yl
2.542 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-3-methylthiopyrazol-5-yl
2.543 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-5-methylthiopyrazol-3-yl
2.544 OH O S OMe OMe - l-Methyl-5-methylthiopyrazol-3-yl
2.545 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methyl-5-methylthiopyrazol-4-yl
2.546 OH O S OMe OMe - 1-Methyl-5-methylthiopyrazol-4-yl ~ _~
2.547 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,5-Dimethylpyrazol-l-yl
2.548 OH O O OMe OHe - 4-Chloropyrazol-l-yl
2.549 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Bromopyrazol-l-yl
2.550 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Phenylpyrazol-1-yl
2.551 OH O O OHe OMe - 3,4,5-Trimethylpyrazol-1-yl
2.552 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Chloro-3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl
2.553 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Isopropylpyrazol-l-yl
2.554 OH O O OMe OMe - 3(5)-Phenylpyrazol-l-yl
2.555 OH O O OMe OMe - 3(5)-Methyl-5(3)-phenylpyrazol-1-yl
2.556 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,5-Bistrifluoromethylpyrazol-l-yl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.557 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Nitropyrazol-l-yl
2.558 pH O O OHe OMe - l-Phenylpyrazol-4-yl
2.559 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,3,5-Trimethylpyrazol-4-yl
2.560 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Phenylpyrazol-5-yl
2.561 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Phenylpyrazol-3-yl
2.562 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,4-Dimethylpyrazol-3-yl
2.563 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methyl-l-phenylpyrazol-3-yl
2.564 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,5-Dimethylpyrazol-3-yl
2.565 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,3-Dimethylpyrazol-4-yl
2.566 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,5-Dimethylpyrazol-4-yl
2.567 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methyl-l-phenylpyrazol-4-yl
2.568 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methyl-l-phenylpyrazol-4-yl
2.569 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,5-Dimethyl-l-phenylpyrazol-4-yl
2.570 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methyl-l-phenylpyrazol-5-yl
2.571 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,4-Dimethylpyrazol-5-yl
2.572 OH O O OMe OMe - 1,3-Dimethylpyrazol-5-yl
2.573 OH O O OMe OMe - ~enzopyrazol-l-yl
2.574 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Methylbenzopyrazol-3-yl
2.575 OH O O OMe OMe - l-Imidazolyl
2.576 H O O OMe OMe - l-Imidazolyl
2.577 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methylimidazol-l-yl
21~675!-1
77
_~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 11~1 U) r-l~1 ~I r l ~
C O O O ~- C C ~
n ~ r r I ~ ~ I I I I I I
~r r ~r r I r ~ _,
'~ ' 't ~ (` C C C C ~`
C O C O C O C C ~ , , ,, , , I r t~
X X X
O ~ O
N
3~ O O O O O o o O O O ~ O O O i~ i~ O O O O
æ ~ ~ ~ æ ~ æ ~ æ ~ æ X ~o o o ~o o o
x o o o u~ o u~ o v~ o o o o o o o o u~ o u~ o u~
:~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
~mmmmm~mmmmmmmmmmmmmmm
~;ooooooooooooooooooooo
~ a~ O ~1 ~ ~ ~ Ul ~ r` a~ ~ O _I N t~ O r a~
o
Z ~ N ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ N ~ t`~
` - 216675~i
78
In ~ ~ ~ ~ C C` C~ C C` C C C
r r t~ r
_,,,,,,,, ~,, n t ~ n
C ~ O C C O O C O O C C~
r t~ ~ r tl r ~ ~ ~ r r ,, " , , , , , ,
r ~ ~r r tr ~ 3 E ~ ~ ~
C C C c c, o C o
XXX XXXXXXX~r~ Ir~
O O O O O O O O O O
k ~ e ~
r~_~,~,~,~,~,r~,~,r~,r~r~_I~,~,~,~,r~
c
-
I
o o ~ o o o ~ o o O O O O o 20 0 0 0
g ~O O o o o O O O O O O o o O
x
otnov~ou~ou~o~no~nou~Ou~ou,ov~
oooooooooooooooooooo
:~ m ;c x :c m :1: ~ m 3~ r~
Q O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
a~ o ~ o ~ m
'O~OOOOOOOOOO~
` ~ ~16ii7~4
79
N ~
~ G
,,,, , I ~ ,~
C C C C r~ C ~ r
n r r I r
E~ I ~ E3 ~ r~ r~ C ~ I I Ln
O C C C ,~ O - S. I n ,~ I C C C
O , , , , ~,, r h ~ r~ r
S r L I C1~ C ~ I C n ~ n
r ,, E~ r ~3 Ln r ,~ ,~ ,~
n E~ ~ I C rl I rl ~1 ~ ~ L ~ ~-
r n s. C o , o , ~ C I , ,~
U rl C I IL') ~ rl r I ~
k ~ O ~ n LnE~ C C O ~ ~ ~
~ ~ s ~ ~ ~ rl I r C
Ln Ln Ln Ln ~ C ~O Ln ~ ~ n n n ,~
rl ~ ~ 1 1 rl r .~ , , ~ I I I
rl r~ rl r~l rl ~ r1 rl ~ ~ rl rl '~ ~ ~ L L rl rl ~1
Ln J - ~ I I ~ 0 rl J~ ) 3 3
-- -- 0 ~ N 0 ` ` ` 0
Ln ~: Ln Ln ~ P~
0 1 ` ` I
--~ ~ r ~ r ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~4 r l ~r~ ~ r~ rl r ~ r ~ ~
-
000 ~10000 al 00000000000
OOOC)O'OOOOOOOOO~O~OO~O
O ~ o ~ ~0 ~ 0 0 ~0 0 ~0 20 ~0 0~ ~0 ~0 0 0~
o cn O u~ O O o o o o o o o o o o o ~n o u~ o
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
0~
m m m m m m m ~ m m m m m m 5: m :~: m m m
O Q O O O O O O O O O O O O O O m O O O O
O~ O r ~ ~ ~ ~ Ltl ~ CO ~ O r~ r Ln
.
- 2166754
~1 ~1
,~ ,1 ~ In
~ ~ I I ,1 ~1
er U~ C C
r
,, a n
C C,, ,1 , .~ .
L L ~1 r l C--I ~1 C
a n ~
.~ .r I Ir1 ¦ n I rl n
r1 L L ~ ~ I ~ r-l ~1 ~~1~--1r l ~1 ~1 1 ~
~1 N C r I I ~ I I I I ~ C
r l _I n r I I ~ ~ I I I I r n
I I ~ a ,, ~ I r- ~ ~ ~ n
C ~~ O O L ~ C C ~1 r~ C G C C~r L~
r~l ~r 1 rl I L t~ t` ~ I
n II . .C I ~ ~r n r~ ~ n n r n I I ,
.~ ~1 ~ JJ ~ ~ I ~ ~ ¦ C r l r~l _I ~ r ~ ~ I ~r I
L XX r l r l ~ ~ L L rl ~ 1 L L L I
OO ~ I I ~ n
~ e ~ c c c ~
r ~Ln ~ Ln ~ ~ ~ r ~ ~ a a a r~ r~ r
~I r l _I r-l ~1 ~D Cl ~1 ~I r-l ` L L L r~l r l r l r l
J J C~ I a\ a) G ~ ~r ~r J J I C~ 3
Ln Ln ~ ~ N t~ ~n Ln
r l r~ r ~ L~ r1 _~ ~ r ~ r
_IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O C) ~ C)
O 00~ 000000000000000 ~000
~C
u~ O o O o o O O O o o O O u~ O u~ O u~ O O O
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
-
m m m m m m m m :c m m m 3: m m m m m m m
o o o o o o o o o o o o m o o o o o o o o
O ~ ~ ~) ~ Ln ~D 1` CO a~ o r~l ~ ~ d' Ln ~O 1` CO O~ O
O ~ ~ ~ r ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Ln Ln Ln Ln Ln Ln Ln Ln u~ Ln
~1667~4
81
_I _I
--I ~1 ~ In
I I
In C C
r~ r
~T ~r
C C - -
r L L
~r T
., ., I I
L L ~ ~
I I
` ` O O ~1 ~1
X X ~1 ~I I I~ ~ ~ ~ u~ u
O O ~ :~~1 ~ ~rI I I I I I
r ,~ ~ ,CO I -- ' -- ' -- --
~ ~ -- ', C(' r r o
a) 0 a~ ~ ~ r~ G
ES E~ T r ~T
~ ~ T
O C
~ T ~T >1 ~ G ~ O ~ G O ~ ~ ~ ~
~ J ~ r r ~ r I n _ . _
C C C C~ C~
-
~IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
OOOO0~0000~000000~00~0000
OOO00~000000~OOOO~OOO
~C
o o o o o u~ o u~ o u~ O ~n o tn o o o o o o o
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
:: m ~ m ~ x 5~ m :r:
o o- o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
w r~ o ~ ~ o _
Z
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.682 OH O O OMe OMe - Benzoxazol-2-yl
2.683 ,OH O O OMe OMe - Isoxazol-3-yl
2.684 OH O S OMe OMe - Isoxazol-3-yl
2.685 OH O O OMe OMe - Isoxazol-4-yl
2.686 OH O S OMe OMe - Isoxazol-4-yl
2.687 OH ' O O OMe OMe - Isoxazol-5-yl
2.688 OH O S OMe OMe - Isoxazol-5-yl
2.689 OH O O OMe OMe - Benzisoxazol-3-yl
2.690 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methylisoxazol-5-yl
2.691 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Isopropylisoxazol-5-yl
2.692 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Phenylisoxazol-5-yl m C~
2.693 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methyl-4-chloroisoxazol-5-yl
2.694 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methylisoxazol-4-yl
2.695 OH O O OMe OMe - 3,5-Dimethylisoxazol-4-yl
2.696 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methoxyisoxazol-3-yl
2.697 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methoxyisoxazol-3-yl
2.698 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methoxyisoxazol-4-yl
2.699 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methoxyisoxazol-4-yl
2.700 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methoxyisoxazol-5-yl
2.701 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methoxyisoxazol-5-yl
2.702 OH O o OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
67~
c
~ , .
C C C C C C o C C C C C C C` C C C C C o
r ~ r t~ r t~ ~ r ~ ~ ~ r ~ ~ r
~ a n n n n n a n IT a n ~ n n ~I n n n ~r
.. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. . .. .. . .. .
r ~ S ~ S L ~ r r
u~IIIIIIIIIIII I
o o O ~ ~ C) O C) O ~ O ~ ~ O o o o o o
ooo~oo~oooo~oooooo~ooo o
otnzzooooooooooooooo o
O ~
ooooZZooooooooooooo o
~ ~ ~ O t~
+~ + ~ z ~ )N C'N
m m m m m m,,,,, ~
m o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
c; O O O O O O O ~
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.723 OCH2-CO2Me O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.724 , I O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
N
2.725 OPh O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.726 o-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.727 ON=CMe2 O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.728 ON=CMe2 O S OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.729 O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.730 ON=CHe-SMe O O OHe OHe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.731 0-NMe2 0 0 OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl ~ ~-
2.732 O-(l-Piperidyl) O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.733 0-(4-Morpholinyl) O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.734 ~ O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
-- N/~ .
0~
2.735 1-Pyrrolyl O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.736 1-Pyrazolyl O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.737 1-Imidazolyl O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
2.738 1,2,4-Triazol-l-yl O O OMe OMe - 2-Thiazolyl
~- 21667~ll
-
m
OCCiOOCCCOCCCCCCOCCCCC
rr~ r~
anaaaaaaaaaaaananaaaa
~ r ,c r S r r .~ r L ,rr .ç r
-
P~
5~ C) C~ 3~ C~ C~ ~ ~ C~ 3~ C~ C~ ~ C~ C~
o ~ ~o ~ c~ ~ o 3 3 ~o o ~ o o~ ~o ~ 3 3 ~ o 3
~c
ooooooooooooooooooooo
æ m ~ O O P~ z ~
o o o o o z z z z z z z z æ z z z z z o o
C)
s m
~ ~ U
o o
u~ tn o
U~
Z Z mZ m ~ m 5: m m m m m m m m m m m mO Om
` `- 2166754
86
Ir
C
r--l --1 r~J r- r--l r~~ r~ r--I r--I r~
r ~ ~ I I Ir ~r u~ u~
r-t er er er r-l ~ 01 t~ un I
r-- ~ e , r~ ~ r- ~ O C C C C O t~l
~Ic c c a~ c co c o c r
~ S r r ~ r ~r n r n n a
n r n 0~ n nn r n n , , , , , ,
~SSS~S ~SSs___I__, ,
,, n I I I I I I I ~ ~ ~ C C
C C ~ _~ ~1 ~1 0 ~1 ~ C C X C t~ t,
L~ ~ ~ O ~ n n
n n - _ C: C~ S S ., S S ... , ,
-- ~ ~ - S S
S S~ ~s~ J ~ S
U
~, ~ ~ ~ ~ er u~ er er ~ ~ ~r u~
c
~;
)
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
x
o u~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o u~
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
mmmmmmmmm~mmmmmmmmmmm
ooooooooooooooooooooo
O ~ ) er In ~D 1~ a~ 0~ O r~ er U') ~0 1'~ ~ ~ O
` - 21667~4
87
r l r-l r ~ _I r1 ~ C C
n n
m , _,,,, ,~ I I I I I I I I , ,
C C C ~ C C~ r ~
r ~ ~ r r t~ I I I I I I I I I L L
~r n r a r n ~-~,,,,,,,, I I
C`CCCCC~CC
r L L S S L ~ r r
o o o o
u ~ ~ u u
C C C C, ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ s , , , , , , , , I
t~ r ~ r ~ X X X X I s L L S L S L L ~I r
n r ~r r : O O O O O ~
, , , , . _ s. s' S S u I I I I I I I I J c:
L L L L -- J J J J ~ rl r~) ~ ~') el' ~ ~ ~r J al
C~ O O c
U U
G I r1 ~ ~ ~ r~ r I _I r~l ~ Ul
-
O;
~IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
o o o o o o o o o ~o o o o o~ ~ o o o o o o
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
x
o u~ o u~ o o o o o o o o u~ o u~ o u~ o u~ o o
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
~;
ooooooooooooooo.oooooo
_I ~ ~ ~ u~ ~O ~ ~ ~ O ~ o 1` CD ~ O r~
.
21~6~54
.
88
,
" U) U~
~ ~ ~ ~ P ~ ~ ~ C C`
u~ u~ ~ ~ u~ In ~ r
. .
C C C C C C C C L L
t~ r ~ r
a n n ~ n ~r ~ 0
._ ., ., ., . ., ., , ,1 ~
? X ? X ? X ? X
C O C O C O C O ~
r 4 ~ 4
C
a
I
u~ I I I
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO~OO
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOC~OOOOC~
X C~
:~ I
o v~ o u~ o v~ o u~ o u~ o o u~ æ z o o o o o o
o ~
oooooooooooooooZZoooo
o
+
~ +
m m ~ m ~ ~: m m ~ ,Z ~4,
ooooooooooo:Cooooooooo
~ o ~ 7 ~r 11 ) ~ t~ c~ o~ o _I N
O O O O O O O O ~1 ~1 ~1 ~
- 211~67S4
89
4 L~4 r~ ~ 4 ~4 ~'4 4 ~4 1 4 4 4 ~4 r~ 1~4
C
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
x
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o u~ o
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
+ + ~, -- U ~ ¦ ~ Ur' /~( I ~ N p
3: 3: b O : C) 11 U _~
I U t.) I ) ~4 I Z Z
OO-OOOOOO OO OOOO
.
- ~16675~
I
L ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ L4 4 4 ~ L~4 ~4 4 ~4 ~ 4 ~ ~ 4 ~ L4
N
5~ ~ Z ~ ~ ~o
~: ~ ~ : ~: a:
OOOOO OOOOOOOOOOOOOo
x
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
a)
o ~o
OOOOO OOOOOOOOOZZZZZ
, ,
~ C
_ ~ L, ~~ ~ r ~r
~ . ~10 t~ L n~
J ~ ~ Z~o ~ o "
Il Z ~ ~ ~ H t'~
oZ o o o ~ ~ I ~ z z; 3z 5: :~ m ~
.
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.859 H N-OEt O OMe OMe - 2-Pyridyl
2.860 ,H N-OtBu O OMe OHe - 2-Pyridyl
2.861 H N-OCH=CH2 O OMe OMe - 2-Pyridyl
2.862 H N-OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe - 2-Pyridyl
2.863 H N-OPh O OMe OMe - 2-Pyridyl
2.864 H 'N-NH2 O OMe OMe - 2-Pyridyl
2.865 H N-NHMe O OMe OMe - 2-Pyridyl
2.866 H N I.lc2 O OMe OMe - 2-Pyridyl
2.867 H N-NHPh O OMe OMe - 2-Pyridyl
2.868 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.869 H O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl ~ CJ~
2.870 OH O S OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.871 OH O NH OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.872 OH O N-CN OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.873 OH N-OH O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.874 OH N-OMe O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.875 OH O O OMe OMe 5-Me 3-Pyridyl
2.876 O~Na+ O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.877 O-K+ O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.878 O~ l/2Ca2+ O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.879 O-(NH4)+ O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
No . Rl W . X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.880 O~(NMe4)~ O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.881 OMe O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.882 OEt O O OMe OHe - 3-Pyridyl
2.883 O-CH2-OMe O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.884 O-CH2-SMe O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.885 OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.886 OCH2C-CH O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.887 ~ ~ O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
O N
2.888 O-Cyclopropyl O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl C~2.889 OCH2-CO2Me O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl ~ _~
2.890 1 0 0 OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
0 ~0
2.891 OPh O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.892 O-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.893 ON=CMe2 O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.894 ON=CMe2 O S OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.895 O O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
~0
2.896 ON=CMe-SMe O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.897 O-NMe2 O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.898 O-(l-Piperidyl) O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.899 0-(4-Morpholinyl) O O OMe OHe - 3-Pyridyl
2.900 ~\ O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
-- N~
O
2.901 l-Pyrrolyl O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.902 1-Pyrazolyl O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.903 1-Imidazolyl O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl ~
2.904 1,2,4-Triazol-1-yl O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl w ~ .
2.905 NH-S02Me O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.906 NH-SO2Ph O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.907 NHSOzC6H4-4-Me O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.908 H O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.909 Me O O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.910 H NMe O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.911 H NtBu O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.912 H NPh O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.913 H N-OH O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.914 H N-OMe O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
No . Rl W X Y Z t R2 ) n Het
2.915 H N-OEt O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.916 ,H N-OtBu O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.917 H N-OCH=CH2 O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.918 H N-ocH2cH=cH2 OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.919 H N-OPh O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.920 H N-NH2 O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.921 H N-NHMe O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.922 H N-NMe2 0 OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl r~
2.923 H N-NHPh O OMe OMe - 3-Pyridyl
2.924 OH - O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.925 H O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.926 OH O S OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.927 OH O NH OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.928 OH O N-CN OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.929 OH N-OH O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.930 OH N-OMe O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.931 OH O O OMe OMe 5-Me 4-Pyridyl
2.932 O~Na+ O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.933 O-K+ O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.934 O~ l/2Ca2+ O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.935 O-(NH4)+ O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.936 O~(NMe4)+ O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.937 OMe O O OMe OHe - 4-Pyridyl
2.938 OEt O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.939 O-CH2-OMe O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.940 O-CH2-SMe O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.941 OCH2CHzCH2 OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.942 OCH2C_CH O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.943 ~ ~ O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
O N
2.944 O-Cyclopropyl O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.945 OCH2-CO2Me O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.946 1 0 0 OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
0 ~,0
2.947 OPh O O OHe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.948 o-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.949 ON=CMe2 O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.950 ON=CMe2 O S OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.951 O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
~0
2.952 ON=CMe-SMe O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.953 O-NMe2 O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.954 ,O-(l-Piperidyl) O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.955 0-~4-Morpholinyl) O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.956 O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.956 ~\ O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
-- N~J
O
2.957 1-Pyrrolyl O O OHe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.958 l-Pyrazolyl O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl ~
2.559 l-Imidazolyl O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl ~Z
2.660 1,2,4-Triazol-l-yl O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.961 NH-SO2Me O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.962 NH-SO2Ph O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.963 NHSO2C6H4-4-Me O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.964 H O O OMe OHe - 4-Pyridyl
2.965 Me O O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.966 H NMe O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.967 H NtBu O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.969 H NPh O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.970 H N-OH O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
2.971 H N-OMe O OMe OMe - 4-Pyridyl
~1667~ 1
97
4 4 '4 4 4 4 ~4 ~4 4 4 4
1.~4 ~4 4 ~4 ~4 L14 4 ~4 ~
~U I I
-
~;
~OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO~O
~OOOOooOOOOOOoOOOOOOOO
XOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
U
~ 11
U
N ~1) ~ .C
~ ~ U U O 1 ~ 4
3~ Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z 2 0 0 o O O O O O O o o O
m 3~ o O O O O O O o O O O O
r a~ o~ o, ~ ~ ~r Ln u~ o _~ ~
- 2 1 667~
98
'- ~ ~ '~ ~ '. '. 44 4 4 4 1~ ~ ~ 4 4 '. ~ '.
4 11 4 ~ 11 4 4 4 ~ 11 4
L ~~ 1L -
~o ~o Ln L~ L') Ln ~ ~ " ` ~
o ~ o ~ c c c e c ~ c c ~ c ~
L, ,C L, .C ~) .C ~ C C
L L
L L L L L L L L ~ J
~_ t, C, C~ L t ~ C, ~ , IY 1
~, ~1 N U~ Ln ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ u~ ~r ~ N ~ ~ Ln er
- l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l
~ ~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o 3 o o o o o
o O 0 0 ~0 ~0 o o o ~o ~o o o ~0 o o
~cooooooooooooooooooooo
3 o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
xOOOOOOoOOOOoOOoOOoOoo
o ~ n ~ r~ o ~1 ~ ~
~Ln~ oooooooooo~
~ oooooooooooooo
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.1014 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Ethoxy-6-pyridyl
2.1015 pH O O OMe OMe - 6-Ethoxy-S-pyridyl
2.1016 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Ethoxy-5-pyridyl
2.1017 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Ethoxy-5-pyridyl
2.1018 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Ethoxy-S-pyridyl
2.1019 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Ethoxy-4-pyridyl
2.1020 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Ethoxy-4-pyridyl
2.1021 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Isopropoxy-6-pyridyl
2.1022 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Isopropoxy-6-pyridyl ~3
2.1023 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Isopropoxy-6-pyridyl
2.1024 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Isopropoxy-6-pyridyl
2.1025 OH O O OMe OMe - 6-Isopropoxy-5-pyridyl
2.1026 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Isopropoxy-5-pyridyl
2.1027 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Isopropoxy-5-pyridyl
2.1028 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Isopropoxy-5-pyridyl
2.1029 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Isopropoxy-4-pyridyl
2.1030 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Isopropoxy-4-pyridyl
2.1031 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Difluoromethoxy-6-pyridyl
2.1032 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Difluoromethoxy-6-pyridyl
2.1033 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxy-6-pyridyl
2.1034 OH o O OMe OMe - 2-Difluoromethoxy-6-pyridyl
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n Het
2.1035 OH O O OMe OMe - 6-Difluoromethoxy-5-pyridyl
2.1036 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Difluoromethoxy-S-pyridyl
2.1037 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxy-5-pyridyl
2.1038 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Difluoromethoxy-5-pyridyl
2.1039 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Difluoromethoxy-4-pyridyl
2.1040 OH ' O O OMe OMe - 3-Difluoromethoxy-4-pyridyl
2.1041 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Methylthio-6-pyridyl
2.1042 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methylthio-6-pyridyl
2.1043 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methylthio-6-pyridyl
2.1044 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methylthio-6-pyridyl
2.1045 OH O O OMe OMe - 6-Methylthio-5-pyridyl 0 C~
2.1046 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Methylthio-5-pyridyl C~
2.1047 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Methylthio-5-pyridyl
2.1048 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methylthio-5-pyridyl
2.1049 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Methylthio-4-pyridyl
2.1050 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Hethylthio-4-pyridyl
2.1051 OH O O OMe OMe - 5-Dimethylamino-6-pyridyl
2.1052 OH O O OMe OMe - 4-Dimethylamino-6-pyridyl
2.1053 OH O O OMe OMe - 3-Dimethylamino-6-pyridyl
2.1054 OH O O OMe OMe - 2-Dimethylamino-6-pyridyl
2.1055 OH O O OMe OMe - 6-Dimethylamino-5-pyridyl
- 21~6754
101
,.........
Ln Ln u~
~ ~ ~ ~ a ~ L4 1 4 L4 1-4 1-4 14 ~4 '4 4 1 ~
a~ I I I I
3: ~r ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ er ~ ~ 1 Lll Ln ~ L~ ~ L~
-
~OOOOOOOOOO~OOOOOOOOOO
0 ~0 0 ~0 0 ~0 0 ~0 0 ~0 0 0 0 i~ O O 0 0~ 0~ O O
X O O O O O O O U~ O o Ul O o Ul o o o o o o o
~OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
~ooooOO~:OmOmoo:~oooooooo
n cn o ,~ r Ln ~D 1` CO O~ O ~ ~ ~ ~ Ln ~D
Ln Ln Ln Ln ~ 0 W ~
ooooooooooooooooooooo
o
216~7~
102
k k k e e k
k k k e e k ~
e ~ e k k e k ~4; 4 4 .~4 '4 ~4
4 4 4 ; 4 4 4 .-1.,1.,~ .-1._1.~1 ._1
~ er ~ ~ L~ Ln
N ~ ~~ ~L ~ Ln ~ ~~
4~4 4 4 4 4 4 ;~. :~ ~ ~1 ' ~ '
~, ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~r ~ ~ L~ Ln O O ~
k k k k k 8 k .~ k k e k k k k
a c~ a a a ~ a ~ - a a a a a a a
~ Ln ~o Ln ~ , . Ln ~o Ln ~
S: ~ ~ N ~ ~ ~ er ~r Ln ~ Ln ~ ~ er ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~r
N
D~
~ o o ~o o~ 3 o~
~OOOOO~OOOOOOOOgOOOOOO
xooooooooooooooooooooo
~ooooooooooooooooooooo
-
_, m m 5: m :: m m m m ~ m m m m m m m m :c m m
~: o a o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
o ~1 ~ ~ ~ Ln ~ l~ O ~1 ~ ~ ~ Ln ~ r
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
o ....... ~ ............ .
- 216675 ~
03
Ln L~
,1 _I ~ ~ ,1 ~1 C C C :~ ~ C C C C
CC. CCCC~1~1~1~ 'O~
a ~T ~T .C a ~T IT a IT
~' N t` ~ ' C C C. C C C
r ~ r r r r ~ L L L ~ ~ L L L L
h' h' N
- r r ~d r T r I I I ~,1 1 1 1 1 1
Ln Ln Ln C~ ~ ~ er ~ ~r
~ ~ L4 L4 1.14 11.1 i~4 1~ 1 p4 ~4 4 '~4 ~ ~ ~) ~O ~ r~
r.
-
r.~ ~o ~o o ~o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o~ o o o o o o o o o o o o 3 o o o o o o o o
x o o rn o o rn o o v) o o rn o o u~ o o o u~ o o
3 0 0 0 o o O o o o o o O o o o o o o O o o
m m m m m m m m m m m m m m
o m o o m o o m o o m o o m o o o m o O m
co a~ o ~ r Ln ~o r~ o ~ r Ln ~o r~ a~
O~ ~ O O O O o O o o o o
O
Z ~ ~ r~ r~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ r, ~I ~ r~ ~ ~ ~ r~l
- 21~6~4
104
C, C, C~ r~
c c c c a 0 d C C C C C C C
~r ~r n n ~ C C c C C c C ~ r ~~ ~ r
L ~ ~ r- ~ ~ r ~ ~ ~ ~ -- ~ ~ .~ .~ ~
~r ~ ~ , , , , ,, , , O C O O O O O
,J r -- Ul ~ Ul 61 U U U~
01 Ct Ol 01 01 01 01 H ~ H H I-- 1-- H
c
~OOOOOOOOOOOOO~O~OO~O
~OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOo~OOO~
x u~ o o c~ O o u~
:~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
m :~ m m m m m ~ 5: m m m m m ~ m :~
~; o o m o o m o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
r~ r~ r ~ r~ _~
2166~4
105
C t. t- t. t- C
.. .. .. .. .. ..
C C C C O C
r
r r r r r r
C t C t t t
.~ .~ .r .~ .~ .~
~ 01 & 01 01 01 &
~IIIIII
c
I
~OOOOOO
S~ X :~:
~OOOOOO
X U~
gOOOOOO
m o:
~oooooo
O -1 N ~1 ~ Il')
O . . .
Z ~ ~ ~ r~J
67~4
106
UUUUUUUUUUUU
UUUUUUUUUUUU
UUUUUUUUUUUU
ZZZZZZZZZZZZ
O O O O O O O O O O O O
P~XXX~XXXX~
~U
O ~q Z Z O O O O O O O O
~ ~\ hZ
In Z ~
OOZZOOOOOO
+
U _ ~
Z ~ Z Z
- OOOOOOOOOOOO
,~ o O O O O O O O O O ~1 ~
,~ ZOOOOOOOOOOOO
No . Rl W XY Z Al A2 A3 A4 ( R2) n
3.013 OMe O O OMeOMe N CH CH CH -
3.014 OEt O O OMeOMe N CH CH CH
3.015 O-CH2-OMe O O OMeOMe N CH CH CH
3.016 O-CH2-SMe O O OMeOMe N CH CH CH
3.017 OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.018 OCH2C_CH O, O OMeOMe N CH CH CH
3.019 ~ O O OMeOMe N CH CH CH
O N ~_~
3. 020 O-Cyclopropyl O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH - C5
3 .021 OCH2-CO2Me O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH - -~
3.023 1 0 0 OMe OMe N CH CH CH - ~ c~n
0 ~,0
3.024 OPh O OOMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.025 o-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.026 ON=CMe2 0 0OMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.027 ON=CMe2 O SOMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.028 o O OOMe OMe N CH CH CH
~0
3.029 ON=CMe-SMe O OOMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.030 O-NMe2 O OOMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.031 O-(l-Piperidyl) O o OMe OMe N CH CH CH
`- ~1667~1
108
UU UUUU UUUUUUUUUUUUU
UU UUUU UUUUUUUUUUUUU
x ~ m m ~
UU UUUU ~UUUUUUUUUUUU
ZZ ZZZZ ZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
00 0000 00000000 0000
o o o o o o 3 o o ~o o o o o ~o o o o 3
~ 00 0000 00., .,00 ~ 0 ~ 0000
o o o 3 3 o 3 o o o o o o o 3 3 o 3 o
oo oooo ooooooooooooo
~ ~ m ~
ooooZZ~ZZ1ZZZ
u
z O.~ r I O O
> >~ o
o I I U~
I ' N D: tll 11)
o ~ z z z ~
Z O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
No. Rl W XY Z Al A2 A3 A4 (R2) n3.051 H N-OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.052 H N-OPh O OMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.053 H N-NH2 O OMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.054 H N-NHMe O OMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.055 H N-NMe2 O OMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.056 H N-NHPh O OMe OMe N CH CH CH
3.057 OH O O OMe OMe CH N CH CH
3.0S8 OH O O OMe OMe CH CH N CH
3.059 OH O O OMe OMe CH CH CH N
3.060 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH - ~__3.061 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-NMe2 cr
3.062 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-Cl o -~
3.063 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-OMe C~
3.064 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-SMe
3.065 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-Ph
3.066 OH o o OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-(4-Chlorophenyl)
3.067 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-(4 B~ Pnyl)
3.068 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-(4-Methoxy-2-pyridyl)
3.069 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-(3-Methoxy-2-pyridyl)
3.070 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-(4-Methoxy-3-pyridyl)
3.071 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-(3-Methoxy-4-pyridyl)
3.072 OH O O OMe OMe N CH CH CH 5-(2-Thienyl)
-- 21667~4
110
... .... ... ... ............ , ~
, _ , .. _
~. C
c: r~
~ a a
~7 N ~ ~ 'r N
UUUZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
UUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUU
UUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUU
,4
ZZZUUUUUUUUUUUUUUU
0~ ~ O ~ O ~ O ~ ~ O ~ 0 ~0 ~0 0
o ~ ~ ~ 0~ ~ a O ~ 3~ 0 0 0 50 0~ 0 0 ~0
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
X
Oo-mOooooOooooooogoo
Z O O O O O o o
Table 4 - Salicylic acid derivatives
(R2)n I F
~Z
W~ R
No. Rl W X Y Z (R2)n C~
4.001 OH O O OMe OMe -
4.002 OH O S OMe OMe - ~ C~
4.003 OH O NH OMe OMe
4.004 OH O N-CN OMe OHe
4.005 OH N-OH O OMe OMe
4.006 OH N-OMe O OMe OMe
4.007 OH O O OMe OMe
4.008 O~Na+ O O OMe OMe
4.009 O-K+ O O OMe OMe
4.010 O~ l/2Ca2+ O O OMe OMe
4.011 O-(NH4)+ OMe OMe
No- Rl W XY Z (R2)n
4.012 O~(NMe4)+ O O OMe OMe
4.013 OMe O O OHe OMe
4.014 OEt O O OMe OMe
4.015 O-CH2-OMe O O OMe OMe
4.016 O-CH2-SMe O O OMe OMe
4.017 OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe
4.018 OCH2C_CH O O OMe OMe
4.019 ~ ~ O O OMe OMe -
O N ~5~
4.020 O-Cyclopropyl O O OHe OMe -
4.021 OCH2-C02Me O O OMe OMe - C
4.023 1 O O OMe OMe
N
4.024 OPh O O OMe OMe
4.025 O-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe
4.026 ON=CMe2 O O OMe OMe
4.027 ON=CMe2 O S OMe OMe
4.028 O O O OMe OMe
\,~=o
4.029 ON=CMe-SMe O O OMe OMe
-- 2~6~S4
.
113
OOOO OOOOOOOOOOOOOoO
OO~O OOOooOOooo~OOOOO
x
oooo ooooooOoooOOooo
~ o lY
OOOO OOOOOOOOOZZZZZZ
,~ I
,~ C
~: r~ r~l f~
., f r~ ;~ t`
r l ~
r~ O ~-
'~ ' ' I '~ '` ~ ,C x
N ~1 ~ 1~ ~ ,~ .~ I ~ ~ U
alI I ,~ z ~ -, ~, , ~ o o r~
O ~ O
Z _ _ I ~
I I I I I ~ m ~
O O O r1 r~ I Z Z Z ~ ~ C
O r1 ~ 0~ O _I ~ 1~1 ~r U~ ~ r~ 0
Ooooo ooooooooooooooo
:~; .... .............. .
` 21667~
114
O O O O O O O O O O O o o o o o o o O o~ O
0 ~ ~ ~ 0 ~
o o ~ o o c~ o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
z
x c~
m I
ooooooooooozzoooooooo
N
m
N 11
m m
3 ~ 1l N ~ N .C
ooooZ~i~Z oo
z z æ z z Z z z o o o o o Z z o o o o o O
m m m m 5: m m :~: Z t4 ~ ~ ~
m m :1: m m o O O O o O O o o o o O O
O~ O ~ D r~ 0 O~ O ~ I") ~ Ul ~ I` 0 a~
Oooooooooooooooooooooo
Z
No. Rl W XY Z (R2)n
4.070 OHe O O OHe OHe 6-Cl
4.072 O,Et O O OHeOHe 6-Cl
4.073 O-CH2-OHe O O OHeOMe 6-Cl
4.074 O-CH2-SHe O O OHeOMe 6-Cl
4.075 OCH2CH=CH2 O OHe OMe 6-Cl
4.076 OCH2C_CH O O OHeOHe 6-Cl
4.077 ~ ~ o O OHeOMe 6-Cl
O N
4.078 O-Cyclopropyl O O OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.079 OCH2-CO2Me O OOHe OMe 6-Cl ~_~
4.080 1 0 0 OMeOMe 6-Cl ~ cJ~
~0 Ul C~
4.081 OPh O OOHe OMe 6-Cl
4.082 o-C6H4-4-NO2 OHe OHe 6-Cl
4.083 ON=CMe2 O OOHe OHe 6-Cl
4.084 O O OOHe OHe 6-Cl
~0
4.085 ON=CMe-SHe O OOHe OMe 6-Cl
4.086 O-NMe2 O OOMe OMe 6-Cl
4.087 O-(1-Piperidyl) O O OMe OHe 6-Cl
- ~16675il
116
-
yy yyyyyyyyyyuyyyyyy
o o~0 0 æO Oæ æO ~0 ~0 æO O OX O 0 ~0 Oæ ~ g
æO æOOæ æO Oæ æO æO o Oæ 0 æO æO Oæ 3 0 æO ~ æ
ooooooooooooooooooo
11
m ~ m u
m ~ o o o o o
:~P.IIIII
oooooooooooZZZZZZZZ
I
., ~ .
C
C, ~
~) I I ~I C ~ L ,~
O Z 'J ~ ~ O O ~
~, o ~ O
O ~ I Z Z Z
a~ o. o,1 ~ ~ ~ u~ w r~ a~ o o ~
~ o o o o o o o
O o o o o o o o o o o o o
Z
- 216675~
117
N
-
YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOoooo
O O O O O O O ~ O O O O O O O O O O O O O
ooooooou~
N
u
ll
æ
m ~ ~ ~ P a)
O O z mz z mz mO o
ZZZZZZoozzooooooooooo
~ + ~
o ~ 11
m
m m m m m m o o Om Om Om O O O O O O ~0 0 1
~ o o o ,~
z
- 21~67~
118
-
~U UUU UUUU UUUUU U
O O O O O O O O O 0 0~ 0 0 0 0
O O O O O O O O ~ ~0 0 0 0 0 0
Oo ooO OOOO OOOOO o
-
,1 ~ ~
U ~~ o
N ~ O U ~ ~r
U \b ~) ~ o/ pl U 11 ~ ~~ z
O - O O O O O O O O O -~
~ O~ O _I ~ ~) ~ ~1 ~ 1~ CO O~ O
Z
No . Rl W X Y Z ( R2 ) n
4.143 1-Pyrazolyl O S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.144 l-Imidazolyl O S OHe OMe 6-Cl
4.145 1,2,4-Triazol-1-yl O S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.146 NH-SO2Me O S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.147 NH-SO2Ph O S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.148 NHSO2C6H4-4-Me 'O . S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.149 H O S OMe OHe 6-Cl
4.150 Me O S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.151 H NMe S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.152 H NtBu S OMe OMe 6-Cl 2
4.153 H NPh S OMe OMe 6-Cl CJ~
4.154 H N-OH S OMe OMe 6-Cl _~
4.155 H N-OMe S OMe OMe 6-Cl CJ~
4.156 H N-OEt S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.157 H N-OtBu S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.158 H N-OCH=CH2S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.159 H N-OCH2CH=CH2 SOMe OMe 6-Cl
4.160 H N-OPh S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.161 H N-NH2 S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.162 H N-NHMe S OMe OMe 6-Cl
4.163 H N-NMe2 S OMe OMe 6-Cl
2 1 ~ 4
120
N
-
~ S 2 ~ X ~ ~
~ N --I ~ U l O l O
s m 2 U U I 11 .~ ~S O
~ , u u u 1l u U m I I z 1I z
u u ml ~ IIY u lu lu lu u U lu lu u u u lu u lu
O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O
ooooooooooooooooooooo
U~oooooooooooooooooooo
g ps,
z
Zoooooooooooooooooooo
m m m m m m m m m m m m m m m m m m m m
m o- o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
z
No. Rl W X Y Z (R2)n
4.185 OH O O OMe OMe 6-CH=N-O-Ph
4-186 O,H O O OMe OHe 6-~MC-~7 O-Ph
4.187 OH O O OMe OMe 6-OMe
4.188 OH O O OMe OMe 6-OCHF2
4.189 OH O O OMe OMe 6-OEt
4.l90 OH O O OMe OMe
(~la~)
4.191 OH O O OHe OMe 6- ~ ~ C1 E
~n
4.192 OH O O OMe OMe 6-OCFzCHF
4.193 OH O O OMe OMe 6-OCH2CH=CH2
4.194 OH O O OHe OMe 6-0-Ph
4.l95 OH O O OMe OMe 6-0-(4-Chlorophenyl)
4.l96 OH O O OMe OMe 6-0-(4-Bromophenyl)
4.197 OH O O OMe OMe 6-0-(4-Isopropoxyphenyl)
4.l98 OH O O OMe OMe 6-0-(2-Hethylphenyl)
4.l99 OH O O OMe OMe 6-0-(3-Methoxyphenyl)
4.200 OH O O OMe OMe 6-0-(2-Pyridyl)
4.20l OH O O OMe OMe 6-0-(3-Pyridyl)
No. Rl W X Y Z (R2)n
4.202 OH O O OMe OMe 6-O-(4-Pyridyl)4.203 OH O O OMe OMe 6-0-(6-Hethoxy-2-pyridyl)
4.204 OH O O OMe OMe 6-O-(2-Pyrimidyl)
4.205 OH O O OHe OMe 6-O-(3-Pyrimidyl)
4.206 OH O O OHe OMe 6-o-(4-pyrimidyl)
4.207 OH O O OMe OMe 6-0-(1,3,5-Triazinyl)
4.208 OH O OMe OMe 6-O-(1-Pyrazolyl)
4.209 OH O O OMe OMe 6-O-(1-Methylpyrazol-4-yl)
4.210 OH O O OMe OMe 6-SMe
4.211 OH O O OMe OMe 6-SPh ~'
4.212 OH O O OMe OMe 6-SO2Me
4.213 OH O O OMe OMe 6-SO2Ph ~ ~~
4.214 OH O OMe OMe 6-S02-C6H4-4-Me
4.215 OH O O OMe OMe 6-
4.215 OH O O OMe OMe
6- ~ /F
~ ~ N
4.216 OH O o OMe OMe
4.217 OH O O OMe OMe 6-NMe2
4.218 OH O O OMe OMe 6-O-(2-Naphthyl)
`- 216~7~
123
N a~
P:
In
a~ a~ a~ ~ a~
oUooo~ooo~oo
a~ a) a~ ~ a~
ooooooooo
O o ~n z o o o o o o o
a~ ~\ Z
:~ Z~ o ol
ooooZZooooo
3 ~3~
/=, 3
N
O
Z Z ~ Z
-o mO o o o o o o o b o
U~
a . O O O O O O O o o _1 1
~ o O O O O o O O o o o o
r z
No. R1 W XY Z (R2)n
5.012 O~(NMe4)+ O O OMe OMe
5.013 O,Me O O OMe OMe
5.014 OEt O O OMe OMe
5.015 O-CH2-OMe O O OMe OMe
5.016 O-CH2-SMe O O OMe OMe
5.017 OCH2CH=CH2 OMe OMe
5.018 OCH2C_CH O O OMe OMe
5.019 ~ ~ O O OMe OMe
O N
5.020 O-Cyclopropyl O O OMe OMe
5.021 OCH2-C02Me O O OMe OMe
5.022 1 0 0 OMe OMe
0 ~,0
5.023 OPh O O OMe OMe - -
5.024 o-C6H4-4-NO2 OMe OMe
5.025 ON=CMe2 O O OMe OMe
5.026 ON=CMe2 O S OMe OMe
5.027 O . O O OMe OMe
~0
5.028 ON=CMe-SMe O O OMe OMe
No. Rl W X Y Z
5.029 O-NMe2 O O OMe OMe
5.030 O~ Piperidyl) O O OMe OMe
5.031 0-(4-Morpholinyl) O O OMe OMe
5.032 O-NEt2 O O OMe OMe
~ O OMe OMe
5.034 1-Pyrrolyl O O OMe OMe
5.035 1-Pyrazolyl O O OMe OMe
5.036 l-Imidazolyl O O OMe OMe
5.037 1,2,4-Triazol-l-yl O O OMe OMe
5.038 NH-S02Me O O OMe OMe
5.039 NH-S02Ph O O OMe OMe
5.040 NHSO2C6H4-4-Me O O OMe OMe
5.041 H - O O OMe OMe
5.042 Me O O OMe OMe
5.043 H NMe O OHe OMe
5.044 H NtBu O OMe OMe
5.045 H NPh O OMe OMe
5.046 H N-OH O OMe OMe
5.047 H N-OMe O OMe OMe
No. Rl W XY Z (R2)n
5.048 H N-OEt O OMe OMe
5.049 H N-OtBu O OMe OMe
5.050 H N-OCH=CH2 O OMe OMe
5.051 H N-OCH2CH=CHz O OMe OMe
5.052 H N-OPh O OMe OMe
5.053 H 'N-NH2 O OMe OMe
5.054 H N-NHMe O OMe OMe
5.055 H N-NMe2 O OHe OMe
5.056 H N-NHPh O OMe OMe
2`5
216 6 ~ 5 i~
127
Preparation examples
5-Fluoro-4,6-dihydroxy-2-methylsulfonylpyrimidine
44 g (0.293 mol) of dimethyl 2-fluoromalonate were dissolved in
450 ml of methanol and treated with 106.5 g (0.59 mol) of 30
NaOMe solution. 41.6 g (0.15 mol) of bis(S-methylisothiourea)
sulfate were then added and the mixture was stirred at RT for
lO three days. It was then concentrated, and the residue was dis-
solved in water and brought to pH 1 using hydrochloric acid. The
solid which was deposited was filtered off with ~uction and re-
crystallized from 1200 ml of water. 18 g of a colorless solid,
m.p. 230-238 C, were obtained. The mother liquor was concentrated
to 100 ml, a further 4.6 g of product (m.p. 230 C) being de-
posited. Total yield: 22.6 g (44~).
4,6-Dichloro-5-fluoro-2-methylsulfonylpyrimidine
20 19.7 g (0.112 mol) of 5-fluoro-4,6-dihydroxy-2-methyl~ulfonyl-
pyrimidine were dissolved in 103 g (0.67 mol) of phosphorus
oxychloride and treated with 8.2 g (0.068 mol) of N,N-dimethyl-
aniline. The mixture was heated under reflux until starting
material was no longer present (about 4 h). The mixture was al-
lowed to cool and was concentrated, 100 ml of water were added,
the mixture was stirred and the precipitate which deposited was
filtered off with suction. It was washed with ice water and dried
at 40 C under reduced pressure. 19.9 g (83~) of a colorless solid,
m.p. 54-56 C, remained.
5-Fluoro-4,6-dimethoxy-2-methylsulfonylpyrimidine
9 g (42 mmol) of 4,6-dichloro-5-fluoro-2-methylsulfonylpyrimidine
were dissolved in 32 ml of methanol and treated with 22.7 g
(126 mmol) of sodium methoxide solution (30~). The mixture was
additionally heated at 50 C for 4 h, a solid being deposited.
After cooling to room temperature, it was adjusted to pH 7 using
glacial acetic acid and stirred into 100 ml of ice water. The
precipitate formed was filtered off with suction, washed with ice
40 water and dried at room temperature on an oil pump. 8.1 g (94~)
of a colorless powder, m.p. 78-79 C, were obtained.
5-Fluoro-4,6-dimethoxy-2-methylsulfonylpyrimidine
11.6 g (57 mmol) of 5-fluoro-4,6-dimethoxy-2-methylsulfonyl-
pyrimidine were initially introduced into 80 ml of glacial acetic
acid, 0.86 g of disodium tungstate was added and the mixture was
-- 2166754
128
warmed to 30 C. 17.1 ml (171 mmol) of hydrogen peroxide solution
(30%) were then added and the mixture was stirred overnight at
room temperature. It was poured into 400 ml of ice water, the
mixture was stirred for 30 min and the precipitate was then fil-
tered off with suction and washed with ice water. After drying in
a vacuum drying oven at 50 C, 12.1 g (90%) of a colorless solid,
m.p. 130-133 C, remained.
2-(5-Fluoro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yloxy)-6-phenylbenzoic acid
lO (Comp. 1.001)
1.8 g (8.5 mmol) of 6-phenylsalicylic acid were dissolved in
30 ml of dried dimethyl sulfoxide and treated in portions with
1.9 g (17 mmol) of potassium tert-butoxide, the temperature of
the reaction mixture rising to approximately 30 C. The mixture was
cooled to room temperature, 2.0 g (8.5 mmol) of 5-fluoro-
4,6-dimethoxy-2-methylsulfonylpyrimidine were added and it was
stirred at 60 C for approximately 4 h. The reaction mixture was
poured into a mixture of 100 ml of cold water and 2 ml of ortho-
20 phosphoric acid and extracted with methyl tert-butyl ether. The
organic phase was washed with a little water, dried over sodium
sulfate and concentrated. The residual oil was purified by chro-
matography on silica gel using hexane/acetone. 2.4 g of a color-
less powder, m.p. 178-182 C, were obtained.
The following compounds were prepared in a similar manner to the
process described above:
1.004 6-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-(5-fluoro-4,6-dimethoxy-
pyrimidin-2-yloxy)benzoic acid, m.p. 160-165 C
1.007 6-(4-Bromophenyl)-2-(5-fluoro-4,6-dimethoxy-
pyrimidin-2-yloxy)benzoic acid, m.p. 160-168
2.1008 6-(2-Methoxy-6-pyridyl)-2-(5-fluoro-4,6-dimethoxy-
pyrimidin-2-yloxy)benzoic acid, m.p. 178 C
2.1014 6-(2-Ethoxy-6-pyridyl)-2-(5-fluoro-4,6-dimethoxy-
pyrimidin-2-yloxy)benzoic acid, m.p. 178-179 C.