Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2171076 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | METHOD FOR PREVENTING FRAUD IN AN INBAND SIGNALLING TELEPHONY SYSTEM AND TRUNK MODULE REALIZING SUCH A METHOD |
| (54) French Title: | METHODE POUR EMPECHER LES FRAUDES DANS LES SYSTEMES TELEPHONIQUES A SIGNALISATION INTRABANDE ET MODULE DE LIAISON UTILISANT CETTE METHODE |
| Status: | Deemed Abandoned and Beyond the Period of Reinstatement - Pending Response to Notice of Disregarded Communication |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | ROBIC AGENCE PI S.E.C./ROBIC IP AGENCY LP |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (22) Filed Date: | 1996-03-05 |
| (41) Open to Public Inspection: | 1996-09-28 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | No |
|---|
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
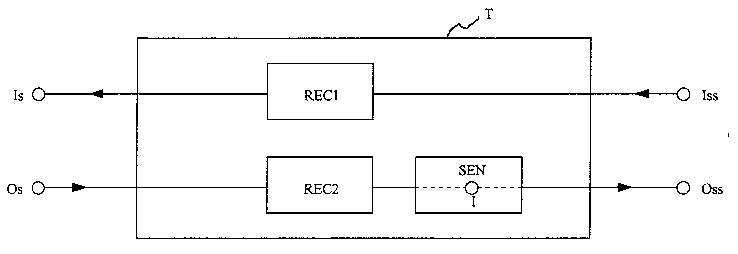
The disclosed method prevents fraud in an inband
signalling telephony system, such as a No. 5 signalling
system. It includes a first step of detecting a fraudulent
inband signal at a predetermined location of an outgoing
signal path between an input terminal Os and an output
terminal Oss of a trunk module T included in the inband
signalling telephony system. The predetermined location is
situated between the input terminal Os and an injection
terminal I of the outgoing signal path where an inband
signal can be injected. In a second step, the fraudulent
inband signal is removed from the outgoing signal path by
interrupting this path during a time interval at least
equal to the duration of the inband signal.
The trunk module realizing this method includes a
receiver similar to the receivers used in the inband
signalling path of the trunk module to detect incomming
inband signals and to filter these out before transmitting
the signal to a user station connected to the trunk module.
This receiver is coupled betwwen the above mentioned input
terminal Os and the injection terminal I.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Time Limit for Reversal Expired | 1999-03-05 |
| Application Not Reinstated by Deadline | 1999-03-05 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 1998-03-05 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 1996-09-28 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 1998-03-05 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| ALCATEL N.V. |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| MARCEL DEVOS |