Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
217~08
VXo~
FTR~RGr~ S PREPORM COMPRESSION PROC~SS
BAC~GROUND OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates generally to the molding of
plastic parts. More particularly, the invention
relates to fiberglass reinforced parts, and still more
particularly, to molding of preforms therefor, i . e ., to
forming of the reinforcement to be used in the molding
of the final product.
Attention is directed to the following U. S.
patents:
2,751,626 - Issued June 26, 1956
2,949,054 - Issued August 16, 1960
3,621,092 - Issued November 16, 1971
4,407,772 - Issued October 4, 1983
4,463,959 - Issued August 7, 1984
5,213,821 - Issued May 25, 1993
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The invention provides a method for forming a
fiber preform for use in a resin transfer molding
process, the method comprising the steps of providing a
hollow form having a closed first end and an opposite
second open end, placing in the form a predet~rm;n~,l
amount of fibrous material and binder, compressing the
fibrous material and binder by inserting a ram into the
second end of the form and moving the ram through a
predet~rmi nPr~ distance, and curing the binder to
produce the preform.
The invention also provides tooling for forming a
part having an outer endless p~r; ~h~ry with a
predet~rmin~fi length, a first end surface extending
from along the entire length of the outer periphery,
and a second end surface extending from along the
entire length of the outer perlphery in spaced relation
to the first end surface, the tooling comprising a
tubular form including opposite ends and an endless
inner periphery defining the outer periphery of a part
2l 72ta~
--2-- 2~5Q ,o
to be formed, an end cap closing one of the opposite
ends of the tubular form and including an end face
which is located in the one end, which extends from
along the entirety of the inner periphery, and which
defines the first end surface of the part to be formed,
and a ram enterable into the other of the opposite ends
of the tubular form, and including an end face
extending from along the entirety of the inner
periphery in spaced relation to the end face of the end
cap, and defining the second end surface of the part to
be f ormed .
The invention also provides a process for forming
a part having an outer endless periphery, a f irst end
surface extending from along the entirety of the outer
periphery, and a second end surface extending from
along the entirety of the outer periphery in spaced
relation to the first end surface, the process
comprising the steps of providing a tubular form having
first and second opposite ends and including an inner
periphery defining the outer periphery of the part to
be formed, placing in the tubular form a predet~ n~
amount of fibrous material and binder, closing the
first end of the tubular form with an end cap including
an end face which extends into the first end and from
along the entire length of the inner periphery, and
which defines the first end surface of the part to be
formed, compressing the fibrous material and binder by
inserting into the second end of the tubular form and
through a predetermined distance a ram having an end
face extending from along the entirety of the inner
periphery and defining the second end surface of the
part to be formed, and curing the binder to produce the
f ormed part .
A principal feature of the invention is the
provision of a method for manufacturing fiber preforms
with structural features such as bosses and ribs.
2l ?~ a~
--3--
Other features and advantages of the invention
will become apparent to those skilled in the art upon
review of the following detalled description, claims
and drawings.
DBSCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is a perspective view of an outboard
motor cover~ portion constructed in accordance with the
method or process of the invention.
Figure 2 is a sectional view of apparatus
embodying the invention and at one stage in the
process .
Figure 3 is a sectional view similar to Figure 2
at another stage in the process.
Figure 4 is a perspective view of a preform formed
by the process shown in Figs. 2 and 3.
Figure 5 is a sectional view of a mold containing
the pre f orm .
Before one embodiment of the inventLon is
explained in detail, it is to be understood that the
invention is not limited Ln its application to the
details of the construction and the arrangements of
components set forth in the following description or
illustrated in the drawings. The invention is capable
of other embodiments and of being practiced or being
carried out in various ways. Also, it is understood
that the phraseology and terminology used herein is f or
the purpose of description and should not be regarded
as limiting.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
Shown in Fig. 1 is a fiber-reinforced polymer or
fiberglass ob~ect 10 to be formed in a resin transfer
molding process. The illustrated ob~ect 10 is a lower,
half engine cover for an outboard motor (not shown).
However, it should be understood that the method or
process of the invention is applicable to a wide
variety of fiber-reinforced plastic end parts or
2t72ita~
--4-- 2,6000
products which have a compound shape. The cover 10
includes a pair of bosses 11 used ln a known manner to
mount the cover 10 on an outboard motor.
Shown in Fig. 4 i5 a fiber preform 12 to be used
in manufacturing the engine cover 10. More
particularly, and as described below, the preform 12 is
used in the resin trans~er molding process to form one
of the bosses 11. The preform 12 has an endless or
generally cylindrical outer periphery 13, a first or
outer face surface 15 which extends continuously from
the outer periphery 13, and a second or Lnner face
surface 17 which also extends from the outer periphery
13 .
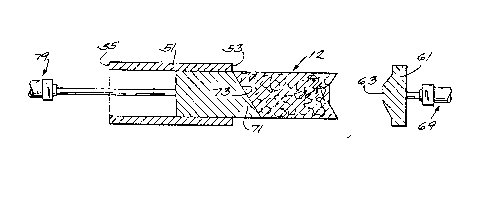
Shown in Figures 2 and 3 of the drawings is
tooling or apparatus 41 for compressing and molding the
fiberglass preform 12 shown in Figure 4. The tooling
or apparatus 41 includes a hollow or tubular form or
member 51 having a longitudinal axis 52 and a hollow
interior with opposite first and second ends 53 and 55.
The form 51 also has an inner, endless peripheral wall
or surface 57 which has an axially constant shape and
preferably extends recti 1 inf~Arly between the ends 53
and 55 and corresponds to the shape of the outer
periphery 13 of the preform 12 to be compressed and
2 5 mo lded .
The tooling or apparatus 41 also includes an end
cap or member 61 which is movable between a first
position (shown in Figure 2) closing the first end 53
of the tubular form 51 and a second position (shown in
Figure 3 ) remote from or spaced from the first end 53
of the tubular form 51. The end cap 61 includes an end
face 63 which, when the end cap 61 is in the closing
position, extends into the first end 53 of the tubular
form 51 and continuously from the inne~ peripheral
surface 57 of the tubular form 51. The end face 63 can
have any desired compound or non-planar shape,
including being convex as shown, to form or define one
~ 2~72108
of the surfaces 15 and 17 of the preform 12 to be
c ompre s s ed a nd mo lded .
Means 69 (shown schematically in the form of a
pneumatic or hydraulic ram) is also provided for
displacLng the end cap 61 between the closing position
and the remote position. Any suitable means can be
employed .
The tooling or apparatus 41 also includes a ram or
member 71 which is insertable into the second end 55 of
the tubular form 51 and which includes an end face 73
which, when the ram 71 is inserted into the tubular
form 51, extends continuously from the inner peripheral
wall or surface 57 of the tubular form 51. The end
face 73 can have any compound shape to form or define
the other of the surfaces 15 and 17 of the preform 12
to be compressed and molded. In the illustrated
construction, the end face 73 is angled or extends in
non-perpendicular relationship to the axis 52.
~eans 79 (shown schematically in the form of a
pneumatic or hydraulic ram) is also provided for
displacing the ram 71 along the axis 52 and into and
from the second end 55 of the tubular form 51. The
means 79 moves the ram 71 between a first position (not
shown) spaced to the left in the drawings from the
second end 55 of the tubular form 51, a second position
shown in Figure 2 and located in the tubular form 51 at
a first distance from the second end 55, and a third
position shown in Figure 3 and located in the tubular
form 51 at a second distance greater than the first
distance from the second end 55 such that the preform
12 is removed from the tubular part or member 51. Any
suitable means can be employed.
The prQcess or method of the invention comprises:
(a) providing a hollow or tubular form (such as
the form 51) having first and second opposite ends and
including an inner periphery defining the outer
periphery of the preform to be formed;
~ 2t721Q~
--6--
(b) closing the first end of the tubular form by
moving a member (such as the end cap 61) to a position
which closes the first end of the tubular fDrm Sl, the
member including an end face (such as the end face 63)
which extends into the first end and from along the
entLre length of the Lnner perLphery, and whLch defines
the first end surface of the piece or part to be
molded;
(c) placLng in the tubular form, preferably
through the second end thereof and while the ram 71 is
in the remote or spaced first position, a predet.orm;n-~
amount of fibrous material (or fiberglass) and binder;
(d) compressing the fiberglass and binder by
inserting a member ( such as the ram 71 ) into the second
end 55 of the tubular form and moving the ram through a
first distance, the ram having an end face 73 extending
from along the entire length of the inner periphery and
spaced from the end face of the end cap to define both
the second end surface of the preform and the distance
between the end surfaces of the preform;
(e) curing the binder to produce the molded or
f o~med pref orm;
( f ) removing the end cap 61 from the first end of
the tubular form 51 to the remote or spaced position;
and
(g) displacing the preform from the tubular form
by further inserting the ram 71 into the tubular form
51 to the third position so as to effect removal of the
preform from the tubular form 51. The process can then
be recycled.
It should be noted that any suitable fibrous
material, any suitable binder, and any suitable amounts
thereof can be employed. Also, the fibrous material
can be placed in the form 51 either before or after the
end of the form 51 is closed by the end cap 61,
although it is preferred to place the fibrous material
in the form 51 after the end of the form 51 is closed
by the end cap 61.
2t721~8
.
--7-- z,~oo
Fiqure 5 shows how the preform 12 is used in the
resin transfer molding process. A mold cavity lO0 is
formed by mold halves 104 and 108. The cavity 104 has
the shape of the cover 10 to be formed. ~he mold half
104 has therein a recess 112 corresponding to one of
the })osses 11 on the cover 10. The preform 12 is
placed in the recess 112, and additional fibrous
material ( such as continuous strand mat or chopped
fiber) 116 is placed in the l~ ;n~ r of the cavity.
Resin i6 then in~ected or otherwise introduced into the
cavity, and the resin is cured to provide the fiber-
reinforced polymer cover 10 comprised of the preform
12, any other preforms required (such as for the other
boss 12), and the cured resin.
various of the features of the invention are set
forth in the following claims.