Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
WO 95/07840 PCT/US94/10555
1
METHOD OF FORMING A STACKED ARTICLE GROUP
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention.
This invention relates to packaging methods and apparatus. Particularly, this
invention relates to a method of forming stacked or multiple layer article
groups
outside packaging media, which utilizes a divider panel between top and bottom
members of each group. The packaging method of the present invention is usable
to
package different types, styles and sizes of articles, in a wide range of
stacked group
patterns, and into a variety of packaging media, in a fast and reliable
manner.
2. Background of the Invention.
In the past, various apparatus and processes have been proposed and utilized
to package selected article groups. Prior art apparatus and processes have
limited
adjustability, limited output capability, and have been difficult to construct
and
utilize. And, no process or apparatus, insofar as is known, provides reliable
high
2o speed packaging of stacked or layered product groups.
Prior art packaging assemblies include U.S. Patent 4,802,324 to applicants'
assignee for a Vertical Cartoning Assembly and Method which discloses the
placement and assembly of cartons over pre-selected article groups being moved
on a
conveyor. U.S. Patent 5,036,644, also to applicants' assignee, discloses a
Packaging
Sleever Assembly which transfers flat packaging sleeves directly onto pre-
selected
article groups and subsequently wraps and closes the cartons. Various end
loading
packaging machines have also been proposed in the art. For example, U.S.
Patent
3,778,959 to Langen et al. discloses an end loader which utilizes a plurality
of
transversely extending spaced apart fences or flights mounted on a conveyor to
rake
. 30 or capture a predetermined number of containers from infeed container
slips. U.S.
Patent 4,237,673 to Calvert et al. discloses a machine also for loading
container
sleeves through their open ends. U.S. Patent 4,936,077 to Langen et al.
discloses a
WO 95/07840 ~ ~ PCT/ITS94/10555
2
carton loading machine which utilizes pusher mechanisms with spring loaded
pusher
heads to stagger adjacent product group rows during transfer into the carton.
In view of the limitations and shortcomings of prior art processes and
apparatus, it is an object of this invention to provide a method of reliably
forming
s stacked product groups at high speed. Another object of this invention is to
provide .
a packaging method which is usable with a variety of package types, articles
and
stacked group configurations and sizes. A particular object of the invention
is to
provide a method of forming stacked or multiple layer article groups outside
of a
packaging member, via a base member disposed between a lower article sub-group
io and an upper article sub-group.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
is
The present invention provides a method forming stacked article groups,
comprising the steps of: supplying at least two streams of articles; forming
first
article groups having at least one article; placing a support base on a top
surface of
each first article group; forming a second article group, having at least one
article,
20 on top of the support base on each first article group, whereby stacked
article groups
are formed. Various embodiments of the basic method are disclosed, including
continuous and intermittent methods, methods of group formation in a linear
stream
with article input from one or two sides, in aligned and staggered
orientations, in-line
methods, bi-level and single level input methods and side loading methods. The
2s important aspect of each of the various embodiments of the basic method is
that the
stacked article group is formed outside of a packaging unit, and a divider or
base
support sheet is utilized.
In a preferred embodiment, the support base is constructed of paperboard
and has a thin, substantially flat, rectilinear configuration with a surface
area
3o substantially coextensive with that of the top surface of the first article
group. The
completed stacked article groups are subsequently placed in a packaging unit
such as
WO 95107840 ~ ~ PCT/US94/10555
3
a paperboard carrier. The method is ideally suited for beverage can packaging
purposes.
The benefits of this invention will become clear from the following
description by reference to the drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG. 1 is a top plan view of one embodiment of the packaging assembly
to and method provided by the present invention;
FIG. 2 is a side view of the packaging assembly shown in FIG. 1;
FIG. 3 is a crossectional view of the packaging assembly shown in FIG. 1;
FIG. 4 is a top view of an alternative embodiment of the packaging assembly
and method;
FIG. 5 is a side view of the packaging assembly shown in FIG. 4;
FIG. 6 is a top view of an alternative embodiment of the packaging assembly
and method;
FIG. 7 is a side view of the packaging assembly shown in FIG. 6;
FIG. 8 is a top view of an alternative embodiment of the packaging assembly
2o and method;
FIG. 9 is a side view of the packaging assembly shown in FIG. 8;
FIG. 10 is a top view of an alternative embodiment of the packaging
assembly and method;
FIG. 11 is a side view of the packaging assembly shown in FIG. 10;
FIG. 12 is a top view of an alternative embodiment of the packaging
assembly and method;
FIG. 13 is a side view, partially in crossection, of the pusher face of the
assembly shown in FIG. 12;
FIG. 14 is a side view of the packaging assembly shown in FIG. 12;
FIG. 15 is a top view of an alternative embodiment of the packaging
assembly and method;
FIG. 16 is a side view of the packaging assembly shown in FIG. 15;
WO 95/07840 ~ PCT/US94/10555
4
FIG. 17 is a perspective view of an exemplary stacked-type carton as
constructed by the apparatus and method of the present invention;
FIG. 18 is a crossectional view of the carton and stacked article group shown
in FIG. 17;
FIG. 19 is a top view of an alternative embodiment of a cross loading or side
loading mechanism used with the packaging assembly;
FIG. 20 is a side view of the mechanism shown in FIG. 19;
FIG. 21 is a top view of an alternative embodiment of the cross loading
mechanism; 'and
l0 FIG. 22 is a side view of the mechanism shown in FIG. 21.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
2o The processes and apparatus of the present invention are for forming
stacked
article groups in a high speed packaging operation. As shown in the drawings,
the
method of this invention is implemented via a high-speed packaging apparatus .
The
apparatus is adjustable to provide reliable, continuous and high speed
packaging of
articles or products of varying types, sizes and quantities into packages of
varying
types and sizes. For example, the apparatus is usable to load standard twelve
ounce
beverage cans into 24(12/12), 30(15/15) and 36(18/18) pack stacked
combinations.
Moreover, the process of loading beverage containers into paperboard cartons,
for
example, is accomplished quickly and reliably, under typical industry
tolerances for
both container and carton construction. The resultant filled cartons output by
the
3o apparatus are of high quality and consistency, having maximized squareness
and
tautness for improved storage qualities and transportability. Although the
embodiments disclosed load stacked can groups into paperboard cartons, its
within
the purview of this invention to process the stacked article groups in a
variety of
WO 95/07840 ~ PCTlUS94/10555
ways subsequent their formation, including side loading, shrink wrapping,
banding
or having paperboard or other material formed around them.
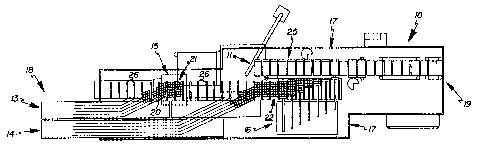
Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, a first embodiment of the packaging assembly 10
generally comprises a carton supply and transport mechanism or stream 11, an
5 article group selection and transport mechanism or stream 12, a pair of
article supply
mechanisms or streams 13 and 14, a divider placement mechanism 15, and an
article
group transfer or cross loading mechanism 16. These mechanisms are shown to be
supported by a unitary frame structure 17, although if aligned properly,
separate
support structures may be utilized consistent with the teachings of this
invention.
1o The carton supply mechanism 11 is shown to be disposed proximate an input
end 18 of the assembly 10. Carton sleeves or blanks 25 are subsequently
transported
in a linear fashion to an output end 21 of the apparatus 10. The article
supply
mechanisms 13 and 14 are also shown to be disposed at the input end 20 of the
apparatus 10. A first portion of each article supply mechanism 13 and 14 is
disposed
spatially parallel to the article group selection and transport mechanism 12,
and a
second portion merges, at a predetermined angle, with the article group
selection
transport mechanism 12 to supply streams of product or articles 20 to two
separate
positions along the article group selection and transport mechanism 12. These
merging mechanisms 12-14 are further constructed and arranged to meter
individual
2o articles 20, via a fixed flight bar arrangement, into predetermined stacked
article
groups 21 and 22 on the mechanism 12.
The stacking function of the device 10 is accomplished by forming a first
group 21 at a low level, placing a separator or divider sheet 24 on the lower
group 21
via the divider sheet placement mechanism 15, and then simultaneously forming
a
second group 22 downstream at a higher level and allowing the upper group 22
to
slide across the divider sheet 24 by the action of the flight bars 26 of the
article group
selecting mechanism 12. In an alternative embodiment, the second group may be
formed on an upper dead plate and dropped or otherwise deposited onto the
divider
sheet.
WO 95/07840 PCT/US94/10555
6
The article group selection and transport mechanism 12 is disposed adjacent
and parallel to the carton supply and transport mechanism 11 and extends
downstream, in a linear orientation. Merged or combined article groups 23 are
transported downstream thereon in a spaced and metered fashion, each group 23
being aligned with a carton 25 traveling on the carton supply and transport
mechanism 11.
The cross loading or side loading mechanism 16 is disposed adjacent to and
parallel with the second portion of the article group selection and transport
mechanism 12, extending and traveling longitudinally with respect to the
apparatus
10. The cross loading mechanism 16 has a plurality of loading arms which
extend
transversely or perpendicularly with respect to the transport mechanisms 11,
13 and
14, to move product groups 23 on the article group selection transport
mechanism 12
into aligned cartons 25 traveling on the carton transport mechanism 11,
thereby
loading the cartons 25 with product groups 23.
Preferably, each of the aforementioned mechanisms 11-14 and 16 has a
conveyor type structure with an endless chain or belt configured about
rotatable drive
and idler end means and moving longitudinally with respect to the input
(upstream)
and output (downstream) ends 18 and 19 of the apparatus 10. The movement of
each
mechanism is further synchronized with one another, for example by a common
drive
2o and/or gearing means.
FIGS. 4 and 5 show a second, alternative, embodiment of the method and
assembly for forming a stacked article group. Basically, the assembly 35
inputs
articles from the same side of the article group selection and transport
stream or line
and in an aligned orientation. In contrast, the previous embodiment showed
article
infeed from the same side of the selection and transport line, but in a
staggered
orientation.
The assembly 35 generally comprises a carton supply and transport
mechanism or stream (not shown), an article group selection and transport
mechanism or stream 36, a pair of article supply mechanisms or streams 38 and
39,
3o and a divider placement mechanism 40. An article group transfer mechanism
or
WO 95/07840 PCT/US94/10555
7
some other form of carton loading or forming mechanism (not shown) is utilized
to
form carriers or some other form of packaging based on the stacked article
groups
formed by this mechanism 35. These elements are also preferably supported by a
unitary frame structure (not shown), although if aligned properly, separate
support
structures may be utilized consistent with the teachings of this invention.
Each of the
aforementioned element also preferably has a conveyor type structure with an
endless
chain or belt configured about rotatable drive and idler end means and moving
longitudinally with respect to the input (upstream) and output (downstream)
ends of
the apparatus 35. The movement of each mechanism is further preferably
io synchronized with one another, for example by a common drive and/or gearing
means.
The article supply mechanisms 38 and 39 are shown to be disposed at the
input end of the apparatus 35. A first portion of each article supply
mechanism 38
and 39 is disposed spatially parallel to the article group selection and
transport
mechanism 36, and a second portion merges, at a predetermined angle, with the
article group selection transport mechanism 36 to supply streams of product or
articles at a single, aligned position, overhead with respect to each other,
along the
article group selection and transport mechanism 36. Alternatively, the lines
38 and
39 could angle directly into the selection and transport line 36. These
merging
2o mechanisms 36, 38 and 39 are further constructed and arranged to meter
individual
articles, via a fixed flight bar arrangement 37, into predetermined stacked
article
groups 42 and 43 on the mechanism 36.
The stacking function of the device 35 is accomplished by forming a first
group 43 at a low level, placing a separator or divider sheet 44 on the lower
group 43
. 25 via the divider sheet placement mechanism 40, and then simultaneously
forming a
second group 42 at a higher level and allowing the upper group 42 to slide
across the
divider sheet 44 by the action of the flight bars 37 of the article group
selecting
mechanism 36. In an alternative embodiment, the second group may be formed on
an
upper dead plate and dropped or otherwise deposited onto the divider sheet 44.
WO 95/07840 PCT/US94/10555
8
FIGS. 6 and 7 show a third embodiment of the method and assembly for
forming a stacked article group. Basically, the assembly 52 inputs articles
from
opposing sides of the article group selection and transport stream and in a
staggered
orientation. In contrast, the two preceding embodiments showed article input
from
the same side of the group selection and transport mechanism.
The assembly 52 generally comprises a carton supply and transport
mechanism or stream (not shown), an article group selection and transport
mechanism or stream 53, a pair of article supply mechanisms or streams 55 and
56,
and a divider placement mechanism 57. An article group transfer mechanism or
to some other form of carton loading or forming mechanism (not shown) is
utilized to
form carriers or some other form of packaging based on the stacked article
groups
formed by this mechanism 52. These elements are also preferably supported by a
unitary frame structure (not shown), although if aligned properly, separate
support
structures may be utilized consistent with the teachings of this invention.
Each of the
aforementioned element also preferably has a conveyor type structure with an
endless
chain or belt configured about rotatable drive and idler end means and moving
longitudinally with respect to the input (upstream) and output (downstream)
ends of
the apparatus 52. The movement of each mechanism is further preferably
synchronized with one another, for example by a common drive and/or gearing
means.
The article supply mechanisms 55 and 56 are preferably disposed at the input
end of the apparatus 52, and on opposing sides of the selection and transport
line 53.
A first portion of each article supply mechanism 55 and 56 is disposed
spatially
parallel to the article group selection and transport mechanism 36, and a
second
portion merges, at a predetermined angle, with the article group selection
transport
mechanism 53 to supply streams of product or articles at two distinct,
staggered
positions along the article group selection and transport mechanism 53. These
merging mechanisms S5, 56 and 53 are further constructed and arranged to meter
individual articles, via a fixed flight bar arrangement 54, into predetermined
stacked
3o article groups 59 and 58 on the mechanism 52.
WO 95/07840
PCT/US94/10555
9
The stacking function of the device 52 is accomplished by forming a first
group 59 at a low level, placing a separator or divider sheet 60 on the lower
group 59
via the divider sheet placement mechanism 57, and then forming a second group
58 at
a higher level downstream and allowing the upper group 58 to slide across the
divider
sheet 60 by the action of the flight bars 54 of the article group selecting
mechanism
53.
Referring to FIGS. 8 and 9, a portion of a fourth embodiment of the stacked
article cartoning apparatus 66 is shown wherein upper article sub-groups 67
are
deposited on the top surface of divider sheet 68 on lower article sub-group 69
to form
a stacked article group 70. In this embodiment, an upper stream 71 of article
sub-
groups 67 is disposed above and in longitudinal alignment with a lower stream
72 of
article sub-groups 69. The upper stream 71 is shown to include a dead plate 73
across which the upper article sub-groups 67 are moved by the action of upper
pusher
bars 74. The lower stream 72 includes a conveyor 75 and flight bars 76. As
shown,
the upper article sub-groups 67 are dropped directly, vertically on top of the
divider
sheet 68 as they move over the terminal edge 77 of the dead plate.
Longitudinal
movement of the upper and lower article sub-groups 67 and 69 is synchronized.
FIGS. 10 and 11 show a fifth embodiment of the method and
assembly for forming a stacked article group. Basically, the assembly 83
inputs
2o articles from the same side of the article group selection and transport
stream, in a
staggered orientation. Importantly, the article input lines are disposed at
the same
vertical level or plane, while the article group selection and transport line
level is
vertically indexed to perform the stacking function. In contrast, the
preceding
embodiments showed article input at two different vertical levels onto a
single and
constant level selection and transport line.
The assembly 83 generally comprises a carton supply and transport
mechanism or stream (not shown), an article group selection and transport
mechanism or stream 84, a pair of article supply mechanisms or streams 88 and
89,
and a divider placement mechanism 92. An article group transfer mechanism or
so some other form of carton loading or forming mechanism (not shown) is
utilized to
WO 95/07840 PCT/US94110555
form carriers or some other form of packaging based on the stacked article
groups
formed by this mechanism 83. These elements are also preferably supported by a
unitary frame structure (not shown). Each of the aforementioned elements also
preferably has a synchronized conveyor type structure with an endless chain or
belt
5 configured about rotatable drive and idler end means and moving
longitudinally with ,
respect to the input (upstream) and output (downstream) ends of the apparatus
83.
The article supply mechanisms 88 and 89 are shown to be disposed on the
same side of the selection and transport line 84, although they may be located
on
opposing sides as discussed above. Additionally, input is shown in a staggered
10 orientation at distinct points along the longitudinal stream of the
selection and
transport line 84, although input may be made in an aligned fashion, also as
discussed
above. These merging mechanisms 84, 88 and 89 are constructed and arranged to
meter individual articles, via a fixed flight bar arrangement 87 having upper
and
lower bars which are shown to be coupled to a separate conveyor 86, into
predetermined stacked article groups 90 and 91 on the mechanism 83.
The stacking function of the device 83 is accomplished by forming the first
group 90, placing a separator or divider sheet 93 on group 90 via the divider
sheet
placement mechanism 92, lowering the position of the group 90 as it moves
downstream, and then forming a second group 91 at the same vertical level as
that at
2o which the first group 90 was formed, downstream, and allowing the second
group 91
to slide across the divider sheet 93 by the action of the flight bars 87 of
the article
group selecting mechanism 84. Importantly, the article group selection and
transport
mechanism 84 is a lowerator-type mechanism which varies the vertical level of
each
base platform 85 as it moves downstream, and thus the position of its
corresponding
transported article group 90. The flight bars 87 are shown to move at a
constant
level, in synchronization with the lowerator platforms 85. In this
orientation, the
lower bar functions to select and meter articles, while the upper bar
primarily
functions to stabilize the formed stacked group.
FIGS. 12-14 show a sixth embodiment of the method and assembly for
3o forming a stacked article group. The assembly 99 is an intermittent system,
in
WO 95/07840 PCTIUS9=1/10555
11
contrast to the continuous systems discussed above, which loads cartons with
stacked
article groups formed outside of the package into cartons from the side. The
assembly 99 generally comprises a carton set-up line 100, a carton placer 101,
a low
infeed line 104, a high infeed line 107 a divider placer 110 and a pusher
mechanism
s 111..
Cartons 103 are placed from the carton placer101, preferably a rotary-type
placer, onto the carton set-up conveyor 100, each between conveyor lugs 102,
for
longitudinal downstream transport. The low infeed line 104 is disposed
adjacent the
carton set-up line 100 and comprises a conveyor 105 with spaced flight bars
106,
1o between which the low article groups 114 are disposed. The low infeed line
104 is
disposed at the same level or plane as that of the carton set-up line 100. The
high
infeed line 107 is disposed adjacent the low infeed line 104 and comprises a
conveyor
108 with spaced flight bars 109 between which high groups 115 are disposed.
The
high infeed line 107 is disposed at a higher level than that of the low infeed
line 104
15 and carton set-up line 100. The low and high groups 114 and 115 may be
placed
between the flight bars 106 and 109 respectively, by an upstream selection
action as
described above, or by other means known in the art.
The flight bars 106 and 109 are shown to be aligned with the lugs 102 of the
carton set-up line 100, and the respective conveyors of the carton set-up line
100,
20 low infeed line 104 and high infeed line 107 are synchronized with each
other so that
the pusher mechanism 111 can laterally move across each line 107 and 104
pushing
the article groups 114 and 115 thereon into cartons 103. As the pusher
mechanism
111 contacts the high group 115, the divider placer 110 deposits a divider 117
onto
the top of the low group 114. The pusher mechanism 111 then moves the high
group
25 115 off of conveyor 108 and across the top surface of the divider sheet 117
to form a
stacked article group 116, which is then side loaded into the carton 103 by
continued
action of the pusher mechanism 111. The reciprocating pusher mechanism 111
comprises a slotted or bifurcated loading face 112 and a loading arm 113 that
can
pass across the two lines 107 and 104.
WO 95/07840 PCT/US94/10555
12
FIGS. 15 and 16 show a seventh embodiment of the method and assembly for
forming a stacked article group. The assembly 123 is also an intermittent
system
which loads cartons with stacked article groups formed outside of the package
into
cartons from the side. The assembly 123 generally comprises a carton set-up
line
124, a carton placer 125, a low infeed line 128, a high infeed line 131 a
divider
placer 134 and a pair of pusher mechanisms 135 and 136.
Cartons 127 are placed from the carton placer 125, preferably a rotary-type
placer, onto the carton set-up conveyor 124, each between conveyor lugs 126,
for
longitudinal downstream transport. The low infeed line 128 is disposed
adjacent the
to carton set-up line 124 and comprises a conveyor 129 with spaced flight bars
130,
between which the low article groups 137 are disposed. The low infeed line 128
is
disposed at the same level or plane as that of the carton set-up line 124. The
high
infeed line 131 is disposed adjacent the low infeed line 128 and comprises a
conveyor
132 with spaced flight bars 133 between which high groups 138 are disposed.
The
high infeed line 131 is disposed at a higher level than that of the low infeed
line 128
and carton set-up line 124. The low and high groups 137 and 138 may be placed
between the flight bars 130 and 132 respectively, by an upstream selection
action as
described above, or by other means known in the art.
The flight bars 130 and 132 are shown to be aligned with the lugs 126 of the
carton set-up line 124, and the respective conveyors of the carton set-up line
124,
low infeed line 128 and high infeed line 131 are synchronized with each other
so that
the first pusher mechanism 135 can move across each line 131 and 128 pushing
the
article groups 138 and 137 thereon into cartons 127. As the first pusher
mechanism
135 contacts the high group 138, the divider placer 134 deposits a divider 140
onto
the top of the low group 137. The pusher mechanism 135 then moves the high
group
138 off of conveyor 132 and across the top surface of the divider sheet 140 to
form a
stacked article group 139, which is then moved downstream on conveyor 129 and
aligned with the second pusher mechanism 136. The stacked group 139 is then
side
loaded into the carton 127 by the lateral action of the second pusher
mechanism 136.
WO 95/07840 PCTlUS94/10555
13
Both reciprocating pusher mechanisms 135 and 136 comprise a substantially
flat,
unitary loading face connected to an elongated loading arm.
Referring to FIGS. 17 and 18, the method of this invention is usable to
construct carriers or cartons 146 containing articles 147 which are layered on
top of
one another or stacked, as shown by way of example. The paperboard carrier
blank
or sleeve 146 is comprised of leading and trailing side panels 148 foldably
connected
to top panel 150 and to a bottom panel 151. End panels 152 connect the top,
bottom
and side panels 150, 151 and 148. Various alternative end panel structures may
be
processed by the method and assembly of this invention. As shown, the carrier
146
to contains a bottom layer or sub-group 153 of articles, shown for purpose of
illustration as beverage cans 147, and an upper layer or sub-group 154 of cans
in
stacked relationship. The lower ends of the upper cans 154 are supported on a
thin,
paperboard divider sheet 155 (also referred to as a base or support sheet)
with the
bottom cans 153 resting on the bottom panel 151. The top panel 150 is disposed
closely adjacent, and preferably is in contact with, the top chimes of the
upper level
154 of cans to provide for a tight fit between the cans 147 and the carrier
146.
FIGS. 19 and 20 show an alternative embodiment of a cross loading or side
loading mechanism 161 which is usable with the assemblies discussed above. The
cross loading mechanism 161 is shown in use with a carton transport line 162
and an
2o article group transport line 163, transporting cartons 165 and stacked
article groups
166, respectively. The side loading mechanism 161 generally comprises three
pully/shaft assemblies 167a,b,c, at least one drive chain or belt 168
connected to the
assemblies 167, and a plurality of loader heads 169 connected to the chain
168. The
mechanism 161 is shown to have a sloping face wherein the loader heads 169
approach the article group transport mechanism 163 at an angle. The loader
heads
169 are further aligned with the article groups 166 and the cartons 165 such
that as
the heads 169 angle inwardly, they continuously contact the article groups 166
and
move them across the line 163 and into the aligned and synchronized cartons
165.
Importantly, the loader heads 169 have a predetermined height such that they
contact
3o and support the tall side face of the stacked article group 166.
WO 95/07840 PCTlUS94/10555
14
FIGS. 21 and 22 show an alternative embodiment of a cross loading or side
loading mechanism 175 which is usable with the assemblies discussed above. The
cross loading mechanism 175 is shown in use with a carton transport line 176
and an
article group transport line 177, transporting cartons 180 and stacked article
groups
181, respectively. The side loading mechanism 175 generally comprises a lower
,
member 178 and an upper member 179. The lower member 178 includes a conveyor
182 which is disposed adjacent the article group transport line 177 and a
plurality of
flight bars 183 connected to the conveyor 182 which contact a lower portion of
each
stacked article group 181. The upper member 179 is disposed directly over head
to relative to the lower member 178 and includes a conveyor 185 and a
plurality of
flight bars 186 which contact an upper portion of each stacked article group
181.
The mechanism 175 further comprises a pair of guide rails 184 which have a
predetermined configuration and are disposed at a vertical level which is
between the
flights 183 and 186. Further, the guide rails 184 are disposed a predetermined
distance apart to accommodate the dimensions of an article group 181, and
angle
towards the carton transport line 176. The conveyors 182 and 185 are
synchronized
and the flights 183 and 186 are aligned so that the top and bottom portions of
the
stacked article group 181 are stabilized and moved along an identical travel
path for
side loading into the cartons 180.
2o Although the apparatus shown in the drawings are utilized in a beverage can
cartoning operation with paperboard carrier sleeves, modifications consistent
with the
teachings of this invention may be made to package various other stacked
containers
or articles, in various carrier configurations, or to package the article
groups via
shrink wrapping, banding or the like. As many changes are possible to the
embodiments of this invention utilizing the teachings thereof, the
descriptions above,
and the accompanying drawings should be interpreted in the illustrative and
not the
limited sense.