Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
21 746~7
Arrangement for a sprung wheel mounting on
the frame of a bicycle
Description
The invention concerns an arrangement as set forth in the
classifying portion of claim 1.
Sprung wheel mountings of that kind on the frame of a bicycle
are known in particular in relation to mountain bikes (EP 0 377 220 Al)
and serve to enhance the degree of travel comfort, in part;clllAr on an
uneven hi gkk~y. They ;nCl~ a t~l~scopic fork which is variable in
respect of its length and on which the front wheel is l~LaLa~ly
mounted, and a pivot in the form of a rotary pivot in which the frame
is pivotably supported on the telescopic fork.
DE 37 08 579 Al discloses a front wheel mounting for
motorcycles, in which provided on a fork bridge which connects the two
tllhlll~r sliders is a ball joint connected to a pivoting arm which is
pivotable about an axis which is perpendicular to the plane of the
frame. In addition an upwardly cranked portion which connects the upper
lS fork bridge which interconnects the two st~n~h;on tubes to the
(oLoL~-ycle steering is connected to the l,~oLoL~ycle frame by way of a
ball joint. A spring element is supported between the ,~Lol~y-cle frame
and the pivoting arm. That front wheel suspension however has not
proven successful in the case of motorcycles because of the lack of
fine sensitivity and easy movement of the steering.
In addition, DE 36 23 567 Al discloses a front wheel sllcp~n~;on
for l~Lw ~ycles, in which a telescopic fork ccmprising tubular sliders
and stAnrh;on tubes is connected to the motorcycle frame by way of a
control head. The control head is connected to the st~n~h;on tube in
such a way as to be ~p~hl~ of providing for axial motion c~ L~n~tion.
A pivoting lever which is pivotable on the frame is connected to the
telescopic fork by way of a rotary- joint at a fork bridge which
connects the two tubular sliders. A spring is disposed ~between the
pivoting lever and the motorcycle frame.
The object of the present invention is to provide an aLL~ny~l~nL
of the kind set forth in the opening part of this specification, which
with simple means provides a further improvement in the level of travel
cullfolL of the bicycle.
- AMENDED PA OE
21~4657
In accordance with the invention that object is attained by the
characterising features of claim 1.
That provides for rP~ ntly absorbing and damping shocks which
act on the front wheel. Additional springs in the telescopic forks are
no longer required but may also be provided.
The journal 'Motorrad' 1984, issue 25, pages 67 to 70, discloses
various mechanical anti-dive systems for motorcycles, which are
intended to support braking forces by way of a lever system at the
lower fork bridge. That is intended effectively to prevent fork dive.
However those systems have not proven successful in a practical
context. One of those known anti-dive systems has a pivoting arm which
is arranged between the frame and the t~l~scop;c fork and which is
mounted pivotably on the frame about an axis ~el~en~;~]lAr to the plane
of the frame and which is supported on the telescopic fork. An
expensive lever system in the form of a tr;An~llAr link is required for
resiliently supporting the pivoting arm on the frame. In comparison
therewith the invention provides for a substantially s;mrl~r operable
structure.
The telescop;c fork has two tllh~ Ar sliders, at the lower ends
of which the front wheel is rotatably mounted. In addition,
telescopically guided in the two tubular sl;~rs are two associated
stAnch;on tubes or bars which are pivotably connected to the frame by
way of the first pivot. The two tubular sl;~rs are pivotably connected
to the pivoting arm jointly by way of the second pivot. In order for
the two stAn~h;on tubes or bars and the two tllhlllAr sliders to be
fiX~ly connected together,; two fork bridges are provided. The two
pivots which are in the form of ball joints are also arranged on the
two fork bridges.
The springing for the telescopic fork is provided by resilient
support of the pivoting arm on the frame, more specifically between the
pivoting arm axis which extends pependicularly to the plane of the
frame, and the first pivot. The spring element may be a pneumatic or
hydraulic spring, a coil spring, or an ela~u,~l block with res;l;~nt
AMENDED PA OE
21746~7
properties, a so-called rubber spring. The spring element preferably
also performs a damping function. A damping function however may also
be provided by damping elements, for example oil dampers, between the
t-lhlllAr sliders and the stanchion tubes.
The steering axis can be formed by the two pivots and can extend
between the two telescopic fork portions which are formed by the two
tlhll~r sliders and the two stAn~h;on tubes or bars which are guided
therein.
The steering axis may also extend inclinedly relative to the
plane fonmed by the telescopic fork portions, the upper pivot being
behind that plane, as viewed in the direction of forward travel. In
addition the two upper fixing locations of the two telescopic fork
portions on the upper fork bridge which can be of a rectili~eAr or
slightly curved or triangular configuration can be in the form of
r~s;l;~nt joints. However a rigid connection between the t~le~cop;c
fork portions and the upper fork bridge is preferred. That upper pivot
which is in the form of a ball joint, and the two fixing locations of
the telescopic fork portions may form a triangle with each other or may
be disposed a~p~O~Lmately on one line.
The invention will be described in greater detail hereinafter by
means of ~mho~;ments illustrated in the drawings in which:
Figure 1 is a diayl~,..~Lic p~rspective view of a first
~mbo~;m~nt~
Figure 2 shows a second embodiment,
Figure 3 shows a detail view of the e~ho~im~nt ill~sLl~Led in
Figure 2,
Figure 4 shows an ~nho~;mP~t relating to the Lol.,~Lion of a ball
joint,
Figure 5 shows a perspective view of a further ~mho~;m~nt with a
rear wheel mounting, and
Figure 6 is a perspective detail view of the rear wheel mounting
of the ~nhc~;m~nt shown in Figure 4.
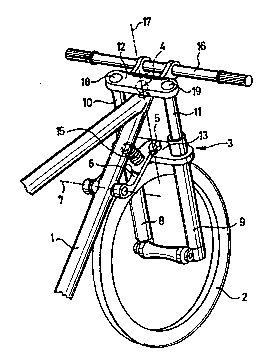
In the illustrated embodiments a front wheel 2 of a bi~ycle of
which a frame 1 is illustrated is mounted on the frame 1 by way of a
t~ copic fork 3. The telescopic
AMENDED PAGE
` _ 3a 2174657
'I''ll~ ~lilly ~ci::, Illdy d~ f;~ lfflly l~ldtiV~ Lo t~le
plane formed by the telescopic fork portions, the upper pivot being
behind that plane, as viewed in the direction of forward trav,el. In
addition the two upper fixing locations of the two telesc~?pic fork
S portions on the upper fork bridge which can be of a re ~;1; n~r or
slightly curved or triangular configuration can be i~ the form of
res;l;~nt joints. However a rigid connection be ~ the t~l~scop;c
fork portions and the upper fork bridge is ~ e~l ~ . That upper pivot
which can be in the form of a pivot with a fix ~ axis or in the form
of a ball joint, and the two fixing locatio ~ of the t~ scop;c fork
portions may fo~m a triangle with each / ther or may be disposed
a~Loximately on one line.
The invention will be described ~ n greater detail hereinafter by
means of embcdiments illustrated in~ he drawings in which:
Figure 1 is a diay~ ic perspective view of a first
~hc~;m~nt,
Figure 2 shows a seco ~ embcdiment,
Figure 3 shows a ~ tail view of the embcdiment illustrated in
Figure 2,
Figure 4 s ~ an ~c~impnt relating to the formation of a ball
joint,
Figure /shows a perspective view of a further ~ho~;m~nt with a
rear wheel ~unting, and
Fi ~ e 6 is a perspective detail view of the rear wheel mounting
of the ~ hc~;ment shcwn in Figure 4.
/ In the illus~La~ed ~nhc~;m~nts a front wheel 2 of a bicycle of
~ich a frame 1 is illustrated is mounted on the frane 1 by way of a
~tel~sccp;c fork 3. The telescopic¦fork 3 has two tllhlllAr sl;~rs 8 and
9. The ~ront wheel 2 is rotatably mounted at the lower ends of the two
t~lhlllAr sliders 8 and 9 in known m~nn~r. m e two tl~hl~lAr sl;~ers 8 and
9 are fixedly connected together by way of a fork bridge 13. The two
~hlllAr sliders 8 and 9 are held at a given spacing from each other by
the fork bridge 13.
2174~57
Telescopically guided in the two tubular sliders 8 and 9 are two
associated stanchion tubes 10 and 11 which can also be in the form of
bars. The two stanchion tubes 10 and 11 are fixedly connected together
by way of a fork bridge 12. The fork bridge 12 is rigidly connected to
the two stanchion tubes 10 and 11 in the region of the upper ends
thereof. Ha~lebArs 16 of the bicycle can also be fixed to the fork
bridge 12. In the illusLL~ed ~mbo~ nts the stanchion tubes 10 and 11
are pivotably connected to the frame 1 by way of the fork bridge 12.
For that purpose the pivot 4 is disposed on the fork bridge 12.
Of the pivots 4 and 5 the lower pivot 5 is preferably in the form
of a ball joint. In Figure 1 both pivots 4 and 5 are in the form of
ball joints. In the illustrated ~nhc~iments a pivoting arm 6 is mounted
on the frame 1 pivotably about an axis 7. The axis 7 extends
~e~ lArly to the plane of the frame or parallel to the axis of
the front wheel 2 when the front wheel 2 is in the position for
travelling straight ahead. The pivoting arm 6 is supported on the two
tuhlllAr sliders 8 and 9 by way of the pivot 5 and the fork bridge 13.
The pivot 5 which in the illustrated ~hc~ ntS is in the form of a
ball joint and which is provided on the fork bridge 13 has a ball
socket in the pivoting arm 6 and a pivot ball which is provided on the
fork bridge 13 and which is guided in the ball socket. The pivoting arm
6 is fitted with its ball socket on the pivot ball.
In the illustrated ~Thc~;m~nts a spring 15 is provided between
the frame 1 and the pivoting arm 6. The spring 15 can be so ~eSi~n~
that it ensures the resilient telescopicability of the telescopic fork
3. The stanchion tubes 10, 11 can project more deeply into the tl-hlllAr
sliders in order to enhance the degree of ~e~hAn;cAl strength. However
telescopic springs may addit;~nAlly also be provided. The spring 15 may
be an elasLu,~L block, a pneumatic/hydraulic spring or a m~hAn;~Al
coil cu"~Lession spring. The spring 15 preferably also has damping
L Lies.
In the ~ho~;mPnt shown in Figure 1, for the upper bal1 joint,
the pivot ball is provided on the frame 1 and the ball socket of the
pivot 4 is provided on the fork bridge 12.
217~657
In the illustrated embodiments the action of the spring 15 is put
to use in such a way that the ball socket and the pivot ball of the
pivots 4 and 5 are held finmly one within the other. The biasing force
of the spring 15 is operative between the two pivots 4 and 5.
In the embodiments shown in Figures 1 and 5, 6, the upper and
lower fork bridges 12 and 13 extend in a recti1;ne~r configuration
between the two fork portions of the telescopic fork 3. In that
aLLang~~ t a steering axis 17 is fonmed by the two pivots 4 and 5. The
steering axis 17 extends parallel to the two telescopic fork portions
and centrally therebetween. Fixing locations 18, 19 of the two
telescopic fork portions (in Figures 1 and 5, 6, the st~nchion tubes 10
and 11) are disposed at the two ends of the fork bridge 12 which is of
a straight configuration.
In the embodiment shown in Figure 2 the upper fork bridge 12 is
of a tri~n~ r confi~lration. The two fixing locations 18 and 19 of
the telescopic fork portions (the stanchion tubes or bars 10 and 11)
are disposed at two corners of the triangle. The pivot 4 is disposed at
the other corner of the triangle. In this ~hQ~ent, as can be seen
fram Figure 3, the pivot 4 occurs as the point of intersection of a
fixed axis 25 with a central plane 26 in which lie the pivot axes or
points which are formed by elastic joints in the fixing locations 18,
19. A mounting pin 24 is fixed to the fork bridge 12 and projects
=rdly, to form the fixed axis 25. The mounting pin 24 is L~LaLably
guided on the frame 1 in an upper rolling bearing 20 and a lower
rolling bearing 21 and forms the axis 2S. The steering axis 17 extends
;ncl;n~ly relative to the plane formed by the telescopic forks and is
~ef;nFd by the pivot 4 and the pivot 5.
The fixing locations 18 and 19 of the telescopic forks on the
upper fork bridge 12 are in the form of elastic joints. As Figure 3
30 -shows, for that purpose a joint or pivot pin 23 provided on the
respective st~n~h;on tube 10, 11 is mounted in an elastic bush 22 of
metal or rubber. The respective elastic joint is formed thereby in the
fork bridge 12 at the fixing locations 18 and 19. The described elastic
2174657
joints may also be provided at the fixing locations 18, 19 of the
~ko~imPnts shown in Figures 1 and 5. In that case the pivot 4 is
between the fixing locations 18, 19.
In the illustrated embodiments of the front wheel suspension
arrangement however the fixing locations 18 and 19 of the telescopic
fork on the upper fork bridge 10 may also be rigid. In that way the
st~n~h;on tubes 10 and 11 are then rigidly connected to the fork bridge
12. The pivot 4 can be in the form of a ball joint comprising a ball
and a socket. It may also be of the ~es;gn configuration as shcwn in
Figure 4. In this case also the arrangement has a pivot 4 which acts
like a ball joint and whose pivot point is formed by the fixed axis 25
the mounting pin 24 which is mounted in the rolling bearings 20, 21,
and a central plane 26 of the elastic bush 22, as shcwn in Figure 4.
The two rolling bearings 20, 21 may also be arranged between the
elastic bush 22 and the mounting pin 24 which is then fixedly connected
to the frame 1.
Figures 5 and 6 show the mounting of a rear wheel 28. The
mounting of the front wheel can be designed as described with reference
to Figures 1 through 4.
The wheel suspension for the rear wheel comprises a pivoting arm
27 which is mounted on the frame 1 pivotably at a pivot 31 about an
axis 33 which extends perpendicularly to the plane of the frame. A
wheel fork 26 is rigidly fixed to the pivoting arm 27. The wheel
pivoting arm 27 extends inclinedly upwardly relative to the horizontal
at an acute angle of about 45. The fork 26 is fixed somewhat above the
middle of the pivoting arm 27 to the pivoting arm at a connecting
location 36. The upper end of the pivoting arm 27 is connected by way
of reinforcing bars 14 to the rearward half of the fork 26. The fork 26,
the upper part of the pivoting arm 27 and the reinforcing bars 14 fonm
a triangle. That triangle guarantees a high level of strength for the
rear wheel suspension. The pivot 31 for the pivotable mounting of the
rear wheel suspension is mounted pivotably on the frame 1 above the
bottom bearing assembly 34.
2174657
-
In addition to the pivotable mounting the rear wheel suspension
is addit;on~lly supported on the frame by means of a spring element 30
which also has damping ~lo~elLies. The additional support point of the
wheel s l~p~n.~;~n iS disposed at the connecting location 36 of the fork
26 to the pivoting arm 27.
m e spring element 30 may be in the form of an elastomer block,
pneumatic spring, hydraulic spring or ~e~h~n;c~l spring. m e spring
element 30 also has a damping function.
In the illustrated e~bcdiment the spring element is supported at
a location 35 in the vicinity of the bottom bearing ~s~hly 34 on the
frame 1 and is connected by way of a pull element 29 which is in the
form of a plll1 r¢d to the wheel sll~p~n~;~n at the connecting location
36 which is in the region of the rigid fixing of the fork 26 to the
pivoting arm 27. The pull element 29 also engages a plate-like
~g~m~nt location 32 on the spring element 30. When the frame 1 is
loaded, the spring element 30 is c~"~l~ssed by way of the pull element
29. In that situation the forces are ~pl;~ to the frame 1 by way of
the support location 35.
me pull element 29 can be replace~hle and when using different
lengths can be adapted to different conditions, bicycle size or bcdy
weight.
m e holding element 29 can also be adjustable in terms of its
effective length, for example it can be provided with a screwthread and
a nut which is supported against the spring element 33 at the
~n~a~m~t location 32.
Tensile forces which take effect in a springing situation are
transmitted to the frame 1 by way of the pull element 29, the
spring/damping element 30 and by way of the support 35 in the vicinity
of the bottam bearing assembly 34. The forces which are operative at
the rear wheel suspension arrangement and which take effect in the
pivot 33 and the support 35 are carried in the same region of the
frame.
2174657
-
It is also possible to use a spring element 30 which supports the
reinforced rear wheel suspension and the frame 1 relative to each
other, similarly as is the case with the solution according to the
invention at the front wheel suspension arrangement. The spring element
S is then preferably supported between the connecting location 36 between
the fork 26 and the pivoting arm 27, and the frame member 37 which
carries the saddle of the bicycle.