Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2 ~ 7 ~ 8
Building panel of metal
This invention relates to a building panel of metal as a support element for
wall boards, facade panels and the like.
Wall boards, facade panels and the like generally consist of a supporting
elçm~nt which is provided on one or both sides with a c~ in~ layer. A elad-lin~
layer may be a plaster coating for PY~mple, which is mostly applied on an
interme li~te layer. The c~ ing layer can however be a natural stone or a ceramic
rl ~ lin~. An in.c~ ting board can be placed on the other side of the building panel
and serves for heat and/or sound in.~ tion. These in~ tin~ boards can also, if
desired, serve as ~U~JpOlki for a further plaster layer. Such a building panel serving
as a support Pl~mPnt should be as stiff as possible, of low weight and inP~n~j~/e to
make. Moreover, they should f~ilit~te simple and reliable a~lcl~o-ing of the
cl~d-lin~ or in~ ting layers. Tf the building panels are used for m~kin~ facade
panels, they must also be ;~en~ ve to moisture. Mol~vel incombustibility is
often a requirement.
The invention is based on the object of providing a building panel of metal
which is light, stable, incolllbl-slible, ;~ n~;l;ve to moisture and inexpensive to
make, and on which rl-1~1ines can be fitted durably by adhesive and/or screws orrivets in a simple way.
The building panel of metal is cl~ cd accor~ g to the invention by
two parallel and ml~ ly spaced, flat face plates of sheet metal, each having a
plurality of holes, and an intervening stiffening elem~nt in the form of an PYr~nrled
metal mesh bent into zig-zag form and which is welded to the respective face plates
bearing thereon along its bending edges.
In order to manufacture the building panel accordhlg to the invention, face
plates of relatively thin sheet metal can be used, since these are given high stiffness
overall by the stiffening elçm~nt in the form of an eYr2nded metal mesh bent into
zig-zag form and the welding to this Pyr~n~le l metal mesh. The holes provided in
the face plates and also the perforations provided in the eYr~n~l~ metal mesh of the
stiffening elemPn~ reduce the overall weight of the building panel. Since the whole
building panel consists of metal, it is incombustible and also not sensitive to
moisture, with suitable protection against corrosion. They can also be made
21 75398
. _
--2--
in.~ ;vely, since perforated sheet metal and eYp~n~ed metal mesh are made in
large ql~ntitie-s for other purposes. The bending in zig-zag form of the exr~n-led
metal mesh and the welding of its bending edges to the respective face plates
bearing thereon are simple work processes, which also conlribules to cost-effective
5 manufacture of the building panel. The holes provided in the face plates have a
further illl~)o~ function, in addition to the reduction in weight. Thus, they
f~cilit~te simple and durable fixing of rl~d~lings on the outer sides of the face plates
by bonding and/or sclewing. When bonding, the strength of adhesion is ~ i.cted in
that adhesive squeezes through the holes to the inside of the face plates and there
10 spreads out somewhat. The a&esi~e thus gets a form like a nail or rivet head on
the inside of the face plates, which conllibules to reliable, interlocking keying of the
adhesive. If self-tapping screws are used instead of or in addition to the adhesive,
the holes provided in the face plates f~çilit~te simple screwing in of these self-
tapping screws.
The face plates preferably consist of e~pan~led metal mesh rolled flat. The
manufacture of such sheets of ?xr~n~led metal rolled flat is very economical,
because the desired holes are thereby created and at the same time the area of the
face plates is increased without creating any waste.
Purther advantageous a,l~lge"~e"~ of the invention are chdl~-;le,i2ed in the
20 other depen-lent claims.
The invention is explained in more detail in the following, with reference to
the embo~lim~nt~ shown in the drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a cross-section of the novel building panel,
Figures 2 and 3 are cross-sections of the building panel with various
25 cl~rlrlin~ layers applied thereto.
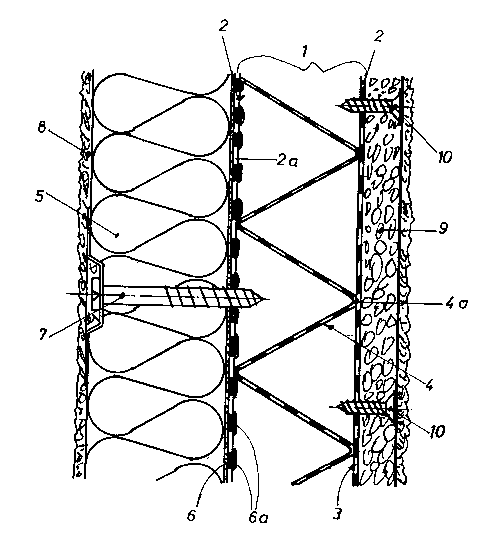
The building panel 1 of metal con.c;~ firstly of two flat, parallel face plates
2 ar~anged at a large ~ t~nce from one another. Each of the face plates Z is
provided with a plurality of holes 3. Flat rolled oyp~n~ed metal meshes are
preferably used as the face plates. In making the ~xp~nded metal mesh for the face
30 plates 2, the slits in the sheet metal are so selected that, after rolling the expanded
metal mesh flat, the holes 3 which remain are approximately round. The round
shape is preferred, since self-tapping screws can then be screwed into the holes 3.
217539~
--3--
In between the two face plates 2 there is a stiffening element 4. This
stiffening element co~-c;cl~; of an eYp~n~e~l metal mesh of zig-zag form. The
eYp~n~led metal mesh 4 is welded to the respective face plates 2 bearing thereonalong its b~n-lin~ edges 4a. The welding can be effected by means of a laser, seam
welding or other weld;ng te~hni-l1)e. The .G~p~n~ed metal mesh 4 is advantageously
so bent in zig-zag form that each two adjoining sections 4b include an angle c~ of
about 60. The holes 3 in the face plates 2 should have a tli~rneter which
cO~ ollds to the ~ meter of the screws to be used for fixing cl~ ling layers. A
neter of about 4 - 6 mm is advantageous.
0 If desired perforated sheet metal can be used for the face plates 2 in place of
flat rolled eYp~ldetl metal mesh, but such pc,lolaled sheet metal has the
disadvantage that waste is created in making the holes.
The b~ ing panel 1 can consist of various suitable materials, such as steel,
st~inlP-~c steel, alu.. i~.. or other metal for ~Y~nnrle. If the face plates 2 and the
stiffening ~lem~nt 4 consist of steel, they should preferably be given a corrosion-
resistant coating, which is advantag~ousl~ applied electrolytically.
It will now be explained with reference to Figures 2 and 3 how different
cln~l-1ing sheets can be applied durably to the novel building panel 1 in a simple
manner. In the embodiment shown in Figure 2, an inc~ ting sheet 5 of mineral
20 material is stuck on to one (the left) face plate 2 by means of an adhesive,
preferably a mineral adhesive 6. As can be seen in the drawing, the adhesive 6 has
squeezed through the holes 3 of the face plate 2 and forms enlargements 6a on the
inside 2a of the face plate, like a rivet head or a nail head. These enlargements 6a
provide an interlocking key in addition to the adhesive effect of the adhesive. The
25 in~ ting material board can additionally be secured by self-tapping screws 7 which
are screwed into some of the holes 3. A plaster coating 8 is applied to the outside of
the in~ ting layer 5. A substrate board 9 is attached to the other (right) face plate
2 by means of self-tapping screws 10, which are screwed into corresponding holes3. The sul)~ e board 9 can for example con~ ; of a blown glass granulate bound
30 with a foamed organic binder. A method of making such sul,~ te boards is
described in EP 290 881 A2. Finally, a plaster layer 11 is applied to the substrate
board 9. If desired, the plaster layer 11 can be applied directly to the face plate 2,
217~398
--4--
whereby some of the plaster layer penetrates the holes 3 and keys well there. Such
a sandwich co~ ;lion, which concictc of the aforementioned building materials isincombustible as a whole.
The same applies also to the emboAim~nt shown in Figure 3. Here a
5 cl~ lAing 12 of natural stone or ceramic is bonded by means of a mineral adhesive 6
to one of the face plates 2. If desired the cl~d~ 12 can be secured additionally by
means of metal bolts 13, so-called self-~ choli,lg bolts, which are anchored at one
end 13a in the cl^dAing 12 and extend through the building panel 1. A nut 14 is
su.ewed on to the other end of the bolt 13.
R~ic~lly ~l^1Ain~ sheets of the most varied kind can be at~ached in a simple
way to the bniltlin~ panel in the ways described above by bonding and/or sc.t:wi-~g
as well as by rivets if desired, the holes 3 in the face plates 2 serving to key the
adlle~ive or anchor the screws or rivets. The rladAings are aA~pted to the current
requir~..,c:,l~. Given a suitable thi~l~n~-cc, the building panels can also serve æ
support ~lem~ntc for prefabricated facade elements of large area, which can be
finished at the factory in a sandwich ~l~uulu~e, decorated, incul~te(l and provided
with pre-æsembled wil~dow units. The facade panels thus manufactured and which
can have a size of 2.5 x 6 - 10 m then only need to be l ~o.led from the factoryto the buil~ site and can there be mounteA on a suitable support structure of the
20 building with small ~ ce in the molmting, to form a fully functional outer wall.
The relatively small weight of and the insepal~le nature of the b~ ling panel
according to the invention play an important role in this.