Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 "PUMP/SEPARATOR APPARATUS FOR VISCOUS LIQUIDS"
2
3 This invention relates to a pump/separator apparatus for handling
4 viscous liquids, such as heavy oil bitumen which is being extracted from an
underground oil-bearing stratum.
6 The extractian of heavy oil bitumen from an underground
7 "reservoir" presents significant handling problems, by reason of the high
viscosity
8 of bitumen, and the presence of other liquids, gases and even solid
particles in
9 admixture with the bitumen. The pumping/separation action is presently
carried
out using bladed impellers or vane-type pumps, which pump the mixture to
11 surface installations at which separation of the mixture into its
constituent parts
12 can take place.
13 In view of the high viscosity of bitumen, conventional pumps and
14 separators require steam invention to lower the viscosity of the bitumen
and
therefore make it easier to handle, and to be pumped. Then, with the aid of
the
16 lifting surfaces on the blades, the bituminaus mixture can be lifted to the
surface,
17 and after evacuation to a secondary location, required separation processes
can
18 take place.
19 These conventional pumps are subject to blade impingement of
solids when abrasive materials are present in the pumped fluid mixture, which
is
21 often the case. The resulting erosion of the impeller blades causes the
blade
22 pump to be subject to increasing inefficiencies, due to worn impellers and
23 significant down time for r~;pairs and replacements, resulting in high
operating
-2
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 and maintenance costs, and incipient pump failures. There is also an
additional
2 cost by reason of double-handling of the bituminous mixture, namely first
the
3 pumping action to raise the mixture to the surface, and secondly a
subsequent
4 separation into the component parts, namely solids, liquids and gases.
One of the most difficult problems facing conventionally bladed
6 pumps is cavitation. This phenomenon occurs when the suction pressure on the
7 pump inlet drops below the vapour pressure at the inlet temperature of the
fluid
8 being pumped. Given the temperature and density of a typical heavy oil
bitumen,
9 this can be a common occurrence. The resulting vapour bubbles or pockets in
the heavy oil bitumen are impacted by the lifting surfaces of the impeller
blades,
11 and these pockets collapse;, with the result that the fluid bitumen slurry
flows
12 slowly into the void left by the collapsed pocket. The resulting implosion
wears
13 away at the surface of the impeller blade, causing rapid erosion of the
impeller
14 and significant deterioration in the pump performance. It also causes
severe
discharge fluctuations, which may damage sensitive downstream equipment.
16 Unchecked, continual cavitation can cause the pump to lose its "prime", or
to trip
17 safety sensors which shut-off the pumping action completely.
18 The present invention seeks to provide an improved
19 pump/separator apparatus for handling viscous liquids, such as heavy-oil
bituminous fluid mixtures, and which overcomes the limitations of conventional
21 pumps having lifting surfaces and requirement for secondary handling to
22 separate the constituent components.
-3-
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 According to the invention there is provided a pump/ separator
2 apparatus for pumping a viscous fluid mixture upwardly from an underground
3 location and for carrying out at least partial separation of the mixture
into
4 separate component parts. or phases during the pumping operation, said
apparatus comprising:
6 a substantially cylindrical housing having an intake at or near its
7 lower end to receive the viscous fluid mixture, and an upper discharge end;
and
8 an inner impeller rotatably mounted in the housing, said impeller
9 rotatably mounted in the housing, said impeller having a radial extent which
is
less than the radial extent of the internal chamber defined by the housing,
and
11 said impeller being rotatablf: around the axis of the housing in order to
generate
12 a spirally upwardly moving column of fluid which thereby induces inward
flow of
13 the fluid mixture through the intake;
14 and a stack of disks arranged in the housing in a separation zone
located above an intake chamber defined in the housing adjacent to the intake,
16 said disks being spaced apart from each other with respect to the axis of
the
17 housing, and serving to guide the flow of fluid upwardly through the
housing and
18 to assist in separation of the fluid into at least some of its separate
component
19 parts or phases.
Preferably, thc: intake comprises a circumferential inlet formed in
21 the wall of the housing, and a stack of inlet vanes is preferably mounted
in the
22 intake chamber in the housing.
-4-
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 The inlet vanes may comprise a Set of generally planar and parallel
2 vanes which are spaced apart from each other with respect to the axis of the
3 housing.
4 The pump/separator apparatus according to the invention may
comprise a multi-component assembly, including more than one pump, each
6 having its own respective electric drive motor coupled therewith.
7 Preferably, a diffuser is arranged in the housing to separate the
8 intake chamber from the separation zone. Also, the separation zone may be
sub-
9 divided by a further diffuser', and with a respective stack of rotary disks
in each
sub-divided portion.
11 Preferred emk~odiment of pump/separator apparatus according to
12 the invention will now be described in detail by way of example only, with
13 reference to the accompanying drawings, in which:
14 Figure 1 a is a diagrammatic illustration of a combined disk
pump/separator apparatus according to the invention, the apparatus being shown
16 enlarged in Figure 1 b;
17 Figure 2 illusi:rates schematically a multi-pump and drive motor
18 assembly according to a furi:her embodiment of the invention;
19 Figure 3 is an enlarged and schematic illustration of the internal
components of a pump of the apparatus;
21 Figure 4 is an enlarged view, similar and expanded from Figure 3,
22 and illustrating the path of flow of a viscous fluid mixture through the
pump stage
23 of the apparatus;
_5_
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 Figure 5a, b and c show respectively a perspective view viewed
2 from the fluid intake, plan view and elevational view of a further
embodiment of
3 pump for use in the apparatus; and
4 Figures 6a and b are schematic illustrations of the path of flow of
bituminous heavy oil through a disk diffuser of a pump of the apparatus in
6 exploded view and assembled respectively.
7 Referring now to the drawings, there will be described
8 embodiments of pump/separator apparatus according to the invention for
9 pumping a viscous fluid mixture upwardly from an underground location and
for
carrying out at least partial separation of the mixture into separate
component
11 parts or phases during the pumping operation. In general terms, the
apparatus
12 comprises a cylindrical housing 2.15 having an intake 12 at or near its
lower end
13 to receive the viscous fluid mixture, and an upper discharge end to which
the
14 fluid can be pumped. There is an inner impeller rotatably mounted in the
housing
and which is operable to generate a spirally upwardly moving column of fluid
16 which rotates around the axis of the housing, and thereby induces inward
flow of
17 the mixture through the intake. A stack of rotary disks 2.9 is arranged in
the
18 housing in a separation zone 13 which is located above an intake chamber
19 defined by the housing adjacent to the intake, and in which the disks are
spaced
apart from each other with respect to the axis of the housing, and which serve
to
21 guide the flow of fluid upwardly through the housing to the discharge end,
and
22 also to assist in separation of the fluid into at least some of its
separate
23 component parts or phases.
-6-
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 Referring first to Figure 1, an apparatus according to the invention
2 is designated generally by reference 10, and is intended to pump heavy oil
3 bitumen upwardly from an underground stratum 2. The assembly 10 is shown in
4 Figure 1 b in enlarged view, and also located within a well casing pipe
extending
downwardly from a surface location and throughout the underground stratum 2.
6 At the surface, there is provided electronic control equipment 1, connected
by
7 electric cable 7 to the apparatus 10. The apparatus 10 includes a
8 separator/pump connected by bolts to the bottom of the tubing flange at the
9 discharge head of the pump. The tubing flange is attached to tubing which
extends down the well casing pipe, and with the tubing always being of smaller
11 diameter than the casing.
12 Figure 1 b illustrates a single pump 4 in the assembly 10, for ease of
13 illustration, but in practical applications, more than one pump will be
mounted in
14 series below the highest pump at the bottom of the tubing.
A pump intake 5 allows the bituminous heavy oil fluid mixture to be
16 admitted to the apparatus 10, and then to be pumped upwardly via a pump and
17 housing assembly 4. Reference numerals 8 and 9 designate electric motors to
18 operate the apparatus.
19 The intake 5 its mounted below the lowest pump 4 and allows for
the entry of fluid into the pump stack (in practice, the location of the pump
intake
21 is decided by geo-technic<~I strata being drilled), and the pumps are
located
22 above the intake 5. Mounted below the intake 5 is a protective seal 6 which
is
23 intended to protect the one or more motors 8,9 mounted below, while still
_7_
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 allowing for fluctuations in motor oil volume and also to accept the pump
thrust,
2 thereby isolating the motors 8,9 from this force. As indicated, the motors)
8,9
3 are located below the protector 6. The motors are generally 60 Hz 3 phase
4 squirrel cage motors running at 2500 to 3500 rpm. The bottom of the motors
8,9
may or may not have a basE; or sensing device, as required.
6 Above the pump or pumps 4 is the tubing which extends to the
7 surface or well head. This tubing may incorporate various drains and valves
8 situated to perform obvious functions relating to fluid transfer. The well
head
9 itself is intended to seal the top of the well from gas or fluid leaks,
while allowing
various lines to penetrate it.
11 Electrical energy is applied to the motors through a flat cable 7
12 which is attached to the motor and runs along the side of the protector,
the pump
13 and other downhole equipment, and in between the tubing and the well
casing.
14 The cable runs through the well head and into a junction box intended to
safely
vent stray gases in the motor cable shell. Power is connected to the junction
box
16 from a switching or motor control cabinet 1 and originates at a transformer
that
17 converts utility company voltage to that of the electrical system of the
motor.
18 Control and monitoring of motor speed and other characteristics are
undertaken
19 from the surface. Some monitoring of the pump performance also may be
performed.
21 Figure 2 illustrates a dual pump stage and drive motor arrangement
22 which may form a practical and preferred embodiment of the invention.
_g_
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
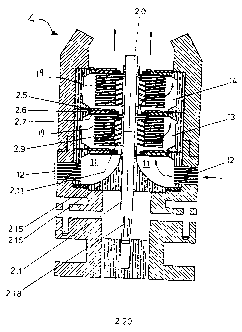
1 Figure 3 shows in detail one example of a turbo-disk
2 pump/separator for use in an apparatus according to the invention, and which
3 shows the internal pumping flow path for the high viscosity fluid through
the
4 interior of the housing of pump unit 4 shaven schematically in Figure 1.
Referring to f=igure 3, the pump/separator unit comprises three
6 major separate components. First of all, the intake 12 comprises a
7 circumferential slot formed in the wall of pump housing 2.15, and which
8 communicates with an intake chamber 11 defined at a lower end of the casing
9 2.15, and which receives tf~e incoming flow of viscous fluid mixture. A
stack of
five planar guide disks 12 is arranged in the intake, and which are vertically
11 spaced apart to define flow passages therebetween. The disks 12 have no
12 motion and are positioned about the general vertical axis of the housing of
the
13 apparatus, which is defined by motor drive shaft 2.0, driven via its lower
end 2.18
14 by a motor spline connector 2.20, such as to permit fluid to flow into the
intake
2.12 and to screen out particles larger than can be accommodated by the pump.
16 The disks 12 measure 90 mm in diameter and are 2.5 mm in thickness, spaced
17 vertically at 2 mm intervals.
18 Having reference also to Figure 5a - 5c, a second major
19 component of the pump/separator unit 4 comprises a central induction core
2.11,
30 which is formed by seven spiral slots 31 which can be set at a variety of
21 angles from the vertical, arranged about a hollow 20 mm drive core 32
machined
22 to match the motor output shaft 2Ø This is shown by reference 2.11 in
Figure 3,
23 and which effectively forms an inner impeller rotatably mounted in the
housing
_g..
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 and which is operable to generate a spirally upwardly moving column of fluid
2 which rotates around the axis of the housing, and thereby induces inward
flow of
3 the fluid mixture through the intake 12.
4 A keyway 2.1 is provided to lock the drive core 2.16 onto the power
input shaft 2.0 of the eleci:ric motor. The induction core is situated about
the
6 hollow drive core and forms the central section, to which the five disks 12
of the
7 intake are attached, for rotation therewith.
8 The spiral slots 2.11 cut into the central induction core are angled in
9 such a way that, the greater the viscosity of the fluid to be pumped, the
flatter will
be the angle which is formed. Thus, compression separators can be constructed
11 to incorporate a variety of spiral slots. By way of example only, in tests
with a
12 bitumen heavy oil of viscosity two hundred thousand times that of water,
slot
13 angles of about 60 degrees measured against the vertical were found to be
14 suitable.
In one or more separation zones 13, 14 within the pump housing
16 2.15, and above the intake ~;hamber 11, there are arranged stacks of rotary
disks
17 2.9 about the spiral slots 2'.11 forming a rotor 19, and a diffuser
arrangement
18 comprising diffuser hub 2.5, diffuser vane 2.6 and diffuser plate 2.7
separate the
19 zones 13 and 14, and similar a diffuser arrangement separates zone 13 from
the
intake chamber 11. The diffuser arrangement 2.5,2.6,2.7 is shown in greater
21 detail in Figures 6a and 6b.
22 By way of explanation, the head loss at an abrupt enlargement or at
23 the exit of a pipe can be considerably reduced by the substitution of a
gradual,
-10-
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 tapered enlargement, usually called a diffuser or a cooperator, the function
of
2 which is to gradually reducE; the velocity of the fluid and thus eliminate,
as far as
3 is practicable, the eddies responsible for energy dissipation. According to
4 Bernouilli's equation, in a pf:rfect diffuser there would be an increase in
pressure
in the direction of flow if steady flow and uniform conditions over the inlet
and
6 outlet cross-sections are assumed. The actual pressure rise is less than the
7 perfect model assumed because of head loss, and the loss of head which does
8 occur in the diffuser is dependent an inlet conditions, the angle of
divergence,
9 degree of pipe friction present and the eddies formed in the flow.
As can be seen more clearly in Figure 4, the bottom horizontal disk
11 2.9 of the rotor 19 is only open in the centre thereof, in the vicinity of
the rotor
12 spiral 2.11. This is the only inlet into the rotor 19 from the intake ar
diffuser
13 immediately below the stagf: of the pump, and enables fluid to be brought
up the
14 central rotor spiral 2.11 to the top horizontal disk 2.9 and to fill the
spiral core.
There is no outlet at the top horizontal disk 2.9 in the vicinity of the rotor
spiral
16 2.11, as a result of which fluid is forced to exit radially outwardly
through the
17 spaces between the disks 2.9 as shown in greater detail in Figure 4 and 5c
and
18 out the diffuser, although the diffuser arrangement shown in Figures 6a,6b
is
19 upside down relative to that shown in Figures 3 and 4. Each diffuser
arrangement
comprises a diffuser hub 2.5 and diffuser vane 2.6, the function of which is
to
21 cause fluid leaving the rotor 19 with radial and circumferential movement
only to
22 be directed upwards and back into the centre of the rotor spiral 2.11 of
the pump
23 stage immediately above as smoothly as possible, to enable each stage to
act
-11
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 cumulatively. The diffuser hub 2.5 allows fluid to enter from the outside of
the
2 diffuser, and then the spiral arms of diffuser vane 2.6 turn the flow
direction so as
3 to spiral inwards more than upwards.
4 To operate the; pump, power is fed to the motor to cause rotation of
motor shaft 2.0, to build up speed quickly to rotation at approximately 3500
rpm.
6 The rotating motor shaft is common to the pump/separator shaft which is
7 mounted above the motor, the intake and the protector. Therefore, rotation
of the
8 motor is transferred to the pump/shaft and causes the separator/pump to
rotate
9 as well.
The separator~/pump uses the principles exhibited by a common
11 meteorological tornado to develop a spirally upwardly moving force which
draws
12 the heavy oil bituminous fluid upwardly, and this is a more efficient means
of fluid
13 transfer, rather than relying upon impact between the fluid components and
a
14 lifting surface (as in conventional lifting impeller pump arrangements) to
impart
upward movement. The lessening of particle impacts, gives greater control over
16 the substance heating and friction and factors, which reduces motor
horsepower
17 requirements.
18 The separator/pumping incorporates flat or concave disks attached
19 to the rotary shaft as described above. The heavy oil bitumen is introduced
through the intake mounted directly below the lowest pump at the centre of the
21 rotating rotary where the baundary layer drag/viscosity drag an either side
of the
22 disk imparts energy to the pumped material and the fluid moves outward in a
-12-
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 helical path to a suitable configured discharge opening and into a diffuser
where
2 the kinetic energy of the fluid is exchanged for static pressure.
3 The size, number, spacing and speed of the disks will vary
4 according to the characteristics of the heavy bitumen being pumped and the
desired performance. Since there is little relative motion between the fluid
lift
6 vortex boundary layer and the surface of the disk, there is little erosion
or
7 abrasion of the impeller disk, even when pumping the most abrasive of
slurries.
8 Further, with substantially no cavitation, the pump separator can
effectively be
9 used to pump and separatE: gases, liquids or solids, or any combination of
the
two or three phases.
11 This versatility allows the separator/pump to move fluid and
12 separate materials or combinations of materials not normally associated
with
13 pumping and later separating.
14 The viscous fluid mixture which is to be handled undergoes a
separation process, while the pumping operation is being carried out. The
16 particles of the fluid have different specific gravities, depending on
whether they
17 tend towards solid, liquid or gaseous states. As the separator/pump is
rotated at
18 high speeds, the frictional drag forces that are part of the pumping
process also
19 convey energy in the form of heat to the heavy oil bitumens. This heat
improves
the viscosity of the bitumen to a point where it will readily flow and be
capable of
21 being pumped. The centrifugal and centripedal forces imparted to the
bitumen
22 during the fluid inter phase with the separator/pump causes heavier
particles to
23 move towards the outside of the pump housing faster than those particles of
-13
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 lesser specific gravity, such as liquids and gases. This process eventually
2 separates the fluids into distinct cross-sectians, with heavier particles
furthest
3 away from the centre and lighter fluids closer to the centre, as in a
conventional
4 centrifuge.
Accordingly, the pumping surfaces of the apparatus impart energy
6 by the principle of "boundary layer drag", and separation occurs by mass
mixing
7 and subsequent centrifugal separation as an integral part of the lifting
process.
8 Figure 4 is an illustration, similar to Figure 3, and showing the
9 spirally upwardly moving flow of fluid through the interior of the
apparatus.
When the rotor 19 is spinning, the forces originating from the drag
11 an the fluid at the boundary layer of the spinning horizontal disks 2.9
impart radial
12 and circumferential fluid movement, which in turn begins to evacuate fluid
from
13 the rotor spiral again. This motion is continuous if the angle of the
individual
14 spirals of the rotor spiral 2.11 is not too steep in relation to the
viscosity of the
fluid, and it therefore follows that a shallower angle of the spirals in the
rotor
16 spiral 2.11 is necessary to accommodate thicker fluids, as discussed above.
17 Since the fluid leaves the rotor with radial and circumferential
18 movement only, this fluid motion must be directed upwards and back into the
19 centre of the rotor spiral 2.11 of the pump stage immediately above. In
order for
the successive pump stages to act cumulatively, this must be carried out as
21 smoothly as possible, and this is the function of the diffuser arrangements
22 installed between each stage, as discussed above. In particular, as the
fluid flow
23 is to be directed back into the centre of the pump stage immediately above,
the
-14-
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 diffuser hub 2.5 allows fluid to enter from the outside of the diffuser, and
then the
2 spiral arms of the diffuser vane 2.6 turn the flow direction inwards. The
fluid
3 already has a spiral flow tendency imparted by the rotor horizontal disks
2.9 of
4 the pump stage below, anti this spiral flow tendency is increased as the
fluid
enters through the diffuser vanes and into the next pump stage above.
6 During operation of the pump/separator unit, the bottom stages of
7 the pump are immersed in fluid, and fluid flow towards the first stage is
initiated
8 by the net positive suction head of the fluid around the outside of the pump
and
9 the intake 12. The amount of fluid pressure required above the intake 12 on
the
outside of the pump is a function of viscosity and net flow, and the spiral
nature
11 of the fluid flow is not necessary at the intake 12 as the rotor of the
first pump
12 stage will initiate it.
13 Although a diffuser arrangement is shown between the intake 12
14 and the first pump stage, such a diffuser is not necessary, since, as in a
vortex,
the fluid takes an progressively more of a spiral nature as it approaches the
first
16 rotor spiral 2.11, but the fluid flow some distance away may be linear and
not yet
17 spiral.
18 The rotor spiral 2.11 distributes fluid to the spaces between
19 horizontal disks 2.9, and by varying the angle of the spiral 2.11, a
variety of
viscosities of fluids can be handled. Furthermore, the spiral 2.11 distributes
the
21 thicker fluids more evenly towards horizontal disk spaces with the result
that all
22 horizontal disks 2.9 add movement to the fluid and help initiate spiral
fluid
23 movement. Since centrifug<~I forces act: on heavier particles more than
lighter
-15-
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 particles, heavier particles such as sand will move to the outside of the
body
2 more quickly and remain there, whereas light oils and water will not be
thrown
3 outwards so quickly, and gas bubbles should stay fairly central to the flow.
4 Assuming laminar flow through the diffusers and impellers, little or not re-
mixing
will occur, and a fluid column will stay separated as it passes through the
6 pump/separator unit.
7 Although two pump stages are shown in the arrangement of
8 Figures 3 and 4, a single pump stage could be used as a common centrifuge to
9 separate fluids. Alternatively, several stages could be used, the top stages
being
left without diffusers to avoid any re-mixing which may occur after each pass
11 through the diffuser and into the next rotor..
12 Figure 5 illustrates an alternative arrangement of components of a
13 pump/separator unit for use in an apparatus according to the invention, and
14 Figure 6 is a schematic illustration of the induced flow paths of the high
viscosity
fluid as it undergoes pumping and separation treatment by the apparatus
16 according to the invention.
17
18
-16-
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 Improvements Over Existincl Technology - Advantages over existing technolow
2
3 Separation of the Heavy Oil Bitumen
4 Heavy oil bitumen can contain varying degrees of gases, liquids
and solids. All of these constituent parts react differently to the pumping
process
6 due to the varying centrifugal force acting an them, as they have a tendency
to
7 migrate to different radial parts of the flow cross-section. As this can be
8 performed as part of the pumping process (in apparatus according to the
9 invention) without the usual degradation of impeller performance, the
process of
pumping and separating carp be performed concurrently.
11 The impeller of a traditional pump is keylocked onto the shaft that
12 runs from the motor through the centre of the pump, but is free-floating up
and
13 down on that shaft. If the traditional pump should experience a bubble of
gas
14 running through it, the impeller will go into a condition known as
"upthrust".
Upthrust refers to a condition when the motor rpm increases dramatically due
to
16 the large and sudden reduction in the density (and thus resistance) of the
fluid
17 being pumped. When the pump goes into this condition, the impellers push up
18 against the seals at the top of the pump causing premature wear and
resistance.
19 In addition, if the gas bubbles are large enough to cause the pump to
cavitate
(e.g. an air lock stops the flow of fluid) the motor is in danger of damage as
well
21 because the rpm may increase briefly beyond safe limits, as well as the
motor
22 may be deprived of the cooling offered by the regular flow of fluid.
-17-
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 This potential danger predicates most traditional installation to also
2 install an additional piece of equipment referred to as a "gas separator"
which
3 forces the gas to be pumpE;d to the surface in the gap between the well
casing
4 and the pressurized well tubing. However, a gas separator is not necessary
as
additional equipment on thE; heavy oil bitumen separator/pump according to the
6 invention.
7
8 Abrasives
9 Most heavy oil bitumen deposits are located in sandstones and
other porous ground strata which "shed" into the oil as it is being gathered.
Such
11 abrasives can represent up to 50 percent of the total volume being pumped.
12 Since a typical known impeller type pump uses the lifting surface an the
impeller
13 to push the pumped materials up the tubing, the contact between the
abrasive
14 and the impeller face results in premature wear of the impeller face and
seals
and the associated reduced performance. The additional strain an both the
16 pump and the 'motor to maintain flows can reduce their lives to as little
as there
17 months or less in extreme cases making the more abrasive fluid uneconomical
to
18 recover.
19 The separator/pump according to the Invention uses the principles
exhibited by a common mei:eorological tornado to develop a force which causes
21 a vacuum-type pressure to pull the heavy oil bitumen fluid rather than grab
and
22 push it. The result is a more efficient pump that does not rely on the
impact
23 between fluid particles and a lifting surface to impart movement. The
lessening of
-18
CA 02185176 2002-O1-28
1 the particle impacts gives greater control over the substance heating and
friction
2 which reduces motor horsepower requirements.
3 Finally, while there has been described use of a pump~separator
4 apparatus according to the invention to pump high viscosity fluids such as
heavy
oil bitumen mixtures, it should be understood that the apparatus may be used
to
6 handle and to lift other fluid/liquid/solid dispersion mixtures, in which
the liquid
7 content may be oil, water or slurry. The apparatus may be used, for example,
to
8 pump silt from estuaries, in harbours, or in a pumping installation for
pumping
9 raw sewage.
-19-