Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
X193699
1
The invention concerns a structure arrangement comprising a
plurality of portions having a relief structure which has an optical-
diffraction effect, in particular for visually identifiable, optical
security elements for value-bearing documents, for example banknotes,
credit cards, passes or cheque documents, or other items to be
_ safeguarded.
In the simplest case a structure arrangement of that kind is
afforded by a rectilinear wave or corrugation structure which is
disposed on the surface of a carrier element and at which incident
ambient light is reflected with diffraction and/or refraction. In the
form of the reflected light, a viewer can receive a visually perceptible
item of information which corresponds to the relief structures of the
portions, which structures have an optical-diffraction effect, the
information being dependent inter alia on the viewing angle.
Diffraction of incident ambient light at the relief structures
of the portions and thus the information which is emitted therefrom in
the form of an optical diffraction image are determined by the number of
wave or grating lines per unit of length of a portion, the so-called
spatial frequency, and by the cross-sectional shape of the relief
structure which is defined inter alia by the differences in respect of
height in the relief structure, more specifically both by the
differences in respect of height between the individual raised portions
relative to each other, and also between raised portions and troughs of
the relief structure. The relief structures of the portions can be of
such a configuration and the portions can be so arranged that a given
item of information can be emitted in a given viewing angle range and
thus perceived by a viewer, while in another viewing angle range no
information or another item of information can be perceived.
By virtue of the use of per se known security elements with a
structure arrangement having an optical-diffraction effect, in regard to
the articles to be safeguarded, as were referred to in the opening part
2193699
2
of this specification, it is possible for items of authenticity
information in respect of the safeguarded article to be rendered visible
even to the unpractised lay person, and at the same time for forgery,
for example in the form of duplication, having regard to known forgery
procedures, in particular optical duplication procedures, to be rendered
impossible or made sufficiently difficult.
The endeavour is so to design a structure arrangement that a
visually perceptible item of information produced therefrom satisfies
aesthetic aspects so that a viewer has for example a particularly
brilliant or highly homogenous, uniform image impression which in
particular can include a symbol or character which provides an item of
information. However the endeavour can also be to arouse, on the part
of the viewer, the impression of a particularly brilliant colour
representation or the impression of highly homogenous uniform colouring
(including within larger surface portions). It is frequently also
desirable to produce with the utmost sharpness and precision a change in
the information, as can be caused for example by varying the viewing
angle, for example by pivoting the carrier element which carries the
structure arrangement, about an axis which is in the plane of the
carrier element, or by rotating it about a notional axis perpendicular
to that plane. In the past, the attempt was made to achieve that by
using structure arrangements with portions as the smallest carrier unit
of a given item of optical information, so-called pixels, the dimensions
of which were of the order of magnitude of 60 x 60 ,um, which therefore
can no longer be resolved with the naked eye. It was therefore
possible, on a given macroscopically perceptible area, to provide a
plurality of portions which give mutually different items of optical
information and which can be "activated" simultaneously or singly in
dependence on the above-mentioned viewing parameters. In order further
to enhance the impression of h~nogenous uniform image perception, it has
already been proposed that the size of the portions is to be further
,
2193699
3
reduced. Due to the accordingly required larger number of
correspondingly smaller portions however that procedure suffers from the
disadvantage that the influence of the edges of the portions on the
diffraction image produced increases, insofar as there are undesirable
additional diffraction phenomena which are caused by the transition from
one relief structure within a portion to a further relief structure in
adjoining portions. Furthermore, that measure reduces the effective
degree of utilisation of the surface area in the structure arrangement
as the number and therewith the total area of the regions which do not
c ontribute ~ affording information are drastically increased, for example
the corner regions of a square portion with in particular arcuately
curved relief lines whose length decreases towards the corners.
The object of the present invention is to improve a structure
arrangement of the kind set forth in the opening part of this
specification, in such a way that it is superior to conventional
structure arrangements in regard to the brilliance and the homogeneity
of the image impressions afforded and also in regard to the exactitude
of changes, which can be achieved by means of the structure arrangement,
between different image impressions, while the structure arrangement can
be produced in a simple and economical manner.
In accordance with the invention, in a structure arrangement of
the kind set forth in the opening part of this specification, that
object is attained in that a predominant number of the portions is of a
strip or band configuration and has a transverse extent which can no
longer be resolved with the naked eye and is below 0.3 mn.
In this context the term strip or band configuration means that
the longitudinal extent of the portions is a multiple of their
transverse extent. Thus, with such a structure arrangement, the number
and the total area of the regions which do not contribute to providing
optical information, within the structure arrangement, can be reduced.
The invention further provides that the undesired influence of the
n ~
~~.~~6~ 9
4
transitional regions between relief structures of mutually adjoining
portions on the desired diffraction image which affords a given item of
information is reduced by drastically reducing the edge length of the
portions. The fact that the portions of strip or band configuration
' 5 have a transverse extent which can no longer be resolved with the naked
eye and is below 0.3 nm means that a viewer also has the impression of a
uniform homogenous colour sensation. Preferably the transverse extent
is selected to be very much smaller, but is more than 3 zun, preferably
more than 5 ,um. In addition it has been found particularly advantageous
for the longitudinal extent of the portions to be more than 0.3 Iran;
preferably portions with a longitudinal extent of more than 0.4 nm and
in particular more than 0.5 mm are selected for the formation of the
structure arrangement according to the invention.
It is further proposed that the portions of strip or band
configuration are to be of such a design that their longitudinal extent
is at least ten times their transverse extent.
It will be appreciated that a structure arrangement according to
the invention can be formed, at least in a region-wise manner, from
portions of a single relief structure which has an optical-diffraction
effect. Structure arrangements according to the invention which
comprise a first group of portions with a first structure having an
optical-diffraction effect and at least one further group of portions
with a structure which has an optical-diffraction effect and which is
different from the first structure are found to be particularly
advantageous when for example there is a wish to "store", in an in
particular limited surface region of the structure arrange~nt, which
can be perceived-- by a viewer, a plurality of items of optical
information which are intended to give the viewer, in dependence on the
above-mentioned parameters (incidence of light, viewing angle),
different optical impressions which originate fr~n the detected surface
region. Particularly for the situation where a sharp, exact change in
2193699
information, for example a change in colour or a change from one symbol
to another, is desired, if for example the carrier element of the
structure arrangement is pivoted about an axis which is disposed in the
plane of the carrier element, a structure arrangement is proposed in
5 which the portions of strip or band configuration are arranged to extend
substantially at an equal spacing from each other and in particular in
parallel relationship. To provide for effective utilisation of the area
involved, it is further recqtanended that the strips or bands are of such
a dimension that their longitudinal extent is determined by the extent
of the structure arrangement or a part thereof, in the direction in
question.
A development of the invention, of quite considerable
significance, is considered to lie in solving the problem of
ccxrmunicating a given individual item of information in a brilliant and
uniform manner over a very large viewing angle. In the past, it was
possible for this to be achieved only in an unsatisfactory manner, with
one and the same relief structure having an optical-diffraction effect.
As mentioned above, a structure arrangement according to the invention,
which effectively affords a remedy here, has groups of portions with a
structure having an optical-diffraction effect, which structure differs
in accordance with the allocation to respective groups, wherein the
structure of portions, which are preferably located on the same surface
region of the structure arrangement, of the first and at least one
further group, is of such a configuration that, when the structure
arrangement is illuminated, visually perceptible items of information
which originate from the portions involving different group allocations
are identical, as seen from different sub-ranges of said viewing angle
range. In other words, for the communication of a given individual item
of information in a viewing angle range, a respective group of portions
is responsible for each of the various sub-ranges of that viewing angle
range.
2193699
6
With such a structure arrangement, it is possible for example to
break up a large viewing angle range into a plurality of smaller sub-
ranges and to associate with each sub-range strip-like or band-like
portions of a given group, in which the desired individual item of
information for that sub-range is "stored" and is emitted in the form of
a diffraction image into that sub-range when the structure arrangement
is illuminated. In accordance with the invention, by virtue of a
suitable configuration for the structure of the portions involving
different group allocations and by virtue of suitable arrangements of
the portions, it is possible to provide that the above-mentioned sub-
ranges adjoin each other and thus, in a larger viewing angle range
formed by the sub-ranges, it is possible to perceive the same item of
optical information, but from portions involving different group
allocations. It is recommended that the strip-like or band-like
portions involving different group allocations are arranged alternately,
that is to say A1/A2/A1/A2 or in accordance with a sequence
A1/Al/A2/A1/A1/A2 or Al/A2/A3/Al/A2/A3.
In accordance with a further proposal, provided on an in
particular limited surface region of the structure arrangement are both
groups of portions Al, A2 etc. far'~.ng a given item of information
A in sub-ranges a l, Ot2, etc. of a viewing angle range oc and also groups
of portions Bl, B2 etc. for communicating a given other item of
information B in sub-ranges /31, f_~ 2 etc. of another viewing angle range
When the viewing angle ranges adjoin each other, the image
impression seen by a viewer changes when he alters his direction of
viewing from the viewing angle range a into the viewing angle range /3 .
Another object of the present invention is to provide a transfer
foil, in particular a hot stamping foil, as well as an optical security
element as referred to in the opening part of this specification, for
value-bearing documents or other items to be safeguarded, in which the
disadvantages and difficulties which occur in connection with known
2193699
structure arrangements do not arise. That object is attained by a
transfer foil and by an optical security element with a structure
arrangement according to the invention, which is of the configuration as
described above. A further subject of the invention is a value document
carrier which, instead of a security element with a structure
arrangement having an optical-diffraction effect, has a security region
to which a structure arrangement according to the invention was applied
by a suitable transfer process, in particular by a hot stamping process.
Further features, details and advantages of the invention are
apparent frcan the accompanying drawings and frcxn the following
description of particularly advantageous embodiments of the structure
arrangement according to the invention.
In the drawings:
Figure 1 is a diagrammatic view of an article to be safeguarded,
with a security element,
Figure 2 shows a part of a structure arrangement in accordance
with the state of the art,
Figure 3 shows a portion of a structure arrangement according to
the invention,
Figure 4 shows a diagrammatic view of a further structure
arrangement,
Figure 5 shows a diagrammatic view of the optical information of
the diffraction image in the case of a structure arrangement as shown in
Figure 5a or 5b,
Figures 5a and 5b show a structure arrangement with portions
arranged in a line-wise manner,
Figure 6 shows a transfer foil with a structure arrangement
according to the invention, and
Figure 7 shows a value document carrier with a structure
arrangement having an optical-diffraction effect, which is stamped
thereon.
CA 02193699 2005-04-13
z193s99
8
Figure 1 shows an article 1 to be safeguarded, for example a
cheque card canprising plastic material, or the like. A security
element which is generally identified by reference numeral 4 is shown on
a surface 2 of the article 1 to be safeguarded. The security element 4
includes a substrate region 6, a thin metal layer 8 and a transparent
cover layer 10. On its side which is towards the article 1 to be
protected, the corer layer 10 has a relief-like surface stmct~e 12 which
ca~rises wave or grating lines - hereinafter referred to as a structure
arrangement -, to which the metal layer 8 was applied, in particular by
a vapour deposition procedure.
Figure 2 is a diagrammatic plan view of a structure arrangement
constituting the state of the art, with portions 16 which have a relief
structure 18 and 20 respectively which has an optical-diffraction effect
and which corresponds to a given it~n of information. Reference numeral
22 denotes the edges of the portions 16, that is to say the transitional
regions fran a relief structure having an optical-diffraction effect, to
a further relief structure. Those edges 22 cause undesired additional
diffraction phenomena which falsify the ~tically perceptible items of
information which are to be communicated by the relief structures 18 and
20. The circles identified by reference numeral 24 illustrate the
regions which do not contribute to producing the desired diffraction
image or which at least make a lesser contribution thereto.
Figure 3 in contrast shows a portion 26 of a structure
arrangement according to the invention. As can be seen from Figure 3
the portion 26 is of a strip or band c~figuration, that is to say its
longitudinal extent L is a multiple of its transverse extent B.* Figure
3 also diagrammatically indicates a relief structure 28 which is
hanogenous over the portion 26. In this structure arrangement according
to the invention, there are only two zones 30 in which the contribution
to the diffraction image produced when the arrangement is illuminated is
smaller in canp~arison with the rest of the surface of the portion 26.
* Translator's note: At this point the German text has a passage at
page 11, line 1 to page 11, line 29 which constitutes a literal
repetition of page 10, line 6 to page 10, line 34 and which has been
omitted fxnm this translation as being a clearly apparent clerical
error.
219699
9
Figure 4 shows a larger region of a structure arrangement
according to the invention, in which strip-like or band-like regions 32
are arranged to extend straight and in the form of lines whereas other
strip-like portions 34 are in an arcuately curved configuration and
arrangement. Further portions 36 are in the form of concentric rings, a
configuration which presents itself in particular when the aim is to
produce a rotationally symmetrical diffraction image, that is to say if
the same item of information is to be communicated to a viewer,
independently of the orientation of the structure arrangement, upon
rotation thereof about a notional axis when extends perpendicularly to
the plane of the drawing through a point 38.
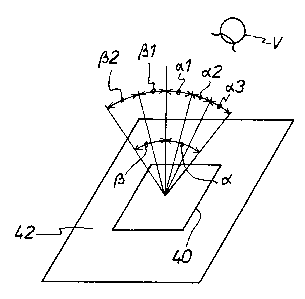
Figure 5 is a diagrammatic view of optical information
distribution, which is cca~ununicated in the form of a diffraction image,
within a viewing angle range oc . Such information distribution is to be
obtained in particular with a structure arrangement as is shown in
Figure 5a. In that respect, Figure 5a is a diagrammatic view on an
enlarged scale of a part of a surface region 40, as viewed by a viewer
V, of a structure arrangement 42 as shown in Figure 5.
In order to provide a uniform impression, which is as homogenous
as possible, of a given item of information, for example the colour
impression red, over the entire viewing angle range d , that range has
been broken up into three sub-ranges oc l, ~ 2 and Oc3 which are related
to portions 43 and 44 and 45 respectively of the surface region 40 of
the structure arrangement 42. The portions 43, 44, 45 have relief
structures A1, A2 and A3 respectively which are of such a configuration
that, over the entire viewing angle range a , a viewer v can receive the
identical item of-.information which however within the sub-ranges o~ l,
Oc 2, Oc' 3 originates from a respective other group of portions 43, 44
and 45 respectively. The portions 43, 44, 45 are arranged for that
purpose in a line-wise manner and in the sequence A1/A2/A3.
If, as shown in Figure 5b, additional groups of portions 46, 47
2193699
1~
with structures Bl, B2 which afford another item of information, for
example a representation of a character, are provided in the surface
region 40, then that item of information - the representation of a
character - can be perceived by virtue of suitable configuration and
- 5 orientation of the portions in a viewing angle range h or in sub-ranges
/31 and (32, as indicated in broken lines in Figure 5.
Figure 6~ shows a simple design in principle of a transfer foil
50 according to the invention with an upper carrier foil 52 which is to
be removed after the structure arrangement has been applied to an
article to be safeguarded. A transparent layer 54 with a structure
arrangement 56 according to the invention adjoins the side of the
carrier foil, which is towards the article to be safeguarded; the
structure arrangement 56 is provided, by vapour deposition, with a thin
metal layer 58. Finally the transfer foil has an adhesive layer 60, by
means of which the assembly can be joined to an article to be
safeguarded.
Figure 7 shows a value document carrier, in particular a region
of a flat web 62 of a plastic material, which, instead of a security
element applied to its surface, has a security region 64 with a
structure arrangement 66 according to the invention which is applied by
a stamping operation.