Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent: | (11) CA 2202852 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | INCLINE WEDGE VARIABLE TARGET SIZE SAWGUIDES FOR CIRCULAR GANG SAWS |
| (54) French Title: | GUIDE-LAME A TAILLES VARIABLES A COINS INCLINES POUR SCIES ALTERNATIVES CIRCULAIRES A LAMES MULTIPLES |
| Status: | Expired and beyond the Period of Reversal |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | ANTONY C. EDWARDSEDWARDS, ANTONY C. |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | 2000-07-18 |
| (22) Filed Date: | 1997-04-16 |
| (41) Open to Public Inspection: | 1997-10-18 |
| Examination requested: | 1999-04-14 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | No |
|---|
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
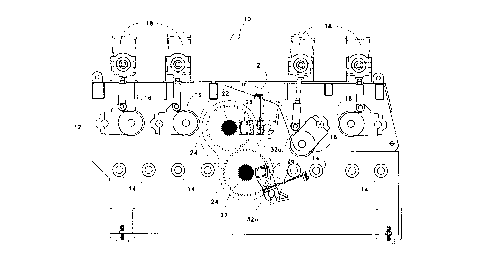
The device for selectively actuable positioning of sawguides for circular gang saws
mounted on a saw arbor shaft comprises a first shaft such as a guide bar extending along a first
axis generally parallel to the saw arbor shaft, first and second sawguides slidably mounted on the
first shaft for longitudinal sliding thereon on opposed sides of first and second wedges mounted
in threaded engagement, in left and right hand threaded engagement respectively, on a selectively
rotatable second shaft extending between the first and second sawguides along a second axis
generally perpendicular to the first axis, threadably journalled in the first and second wedges and
rotatably centered and anchored between the first and second sawguides, the first and second
wedges threadably mounted on the second shaft in opposed facing relation with the vertices of the
first and second wedges closest to a center position centered along the second shaft, means for
selectively rotating the second shaft so as to, when selectively rotated in a first direction, force the
first and second wedges towards the center position, and when selectively rotated in a second
direction counter to the first direction so as to force the first and second wedges away from the
center position, an actuator urges the first and second sawguides slidably towards each other along
the first shaft against the first and second wedges, respectively, whereby translation of the first and
second wedges along the second shaft by reason of selective rotation of the second shaft causes
relative longitudinal translation between the first and second sawguides on the first shaft.
Le dispositif de commande à distance de sélection de la position des guides-lames, pour les scies alternatives circulaires à lames multiples montées sur le mandrin de la scie, comporte un premier arbre, tel qu'un guide-chaîne, se prolongeant le long d'un premier axe habituellement parallèle au mandrin de la scie. Un premier guide-lame et un deuxième guide-lame coulissent longitudinalement sur le premier arbre sur les côtés opposés du premier coin et du deuxième coin. Les coins sont montés par vissage à gauche et à droite respectivement, sur un deuxième arbre tournant et se trouvant entre le premier guide-lame et le deuxième guide-lame le long d'un deuxième axe habituellement perpendiculaire au premier axe. Le deuxième arbre est fixé au premier coin et au deuxième coin par des tourillons filetés tout en étant centré et ancré en rotation entre le premier guide-lame et le deuxième guide-lame. Le premier coin et le deuxième coin sont vissés sur le deuxième arbre et font face aux sommets du premier coin et du deuxième coin les plus rapprochés d'une position centrale le long du deuxième arbre. Le dispositif comporte également des moyens pour faire tourner individuellement le deuxième arbre de sorte que, quand l'arbre tourne dans un sens, il force le premier coin et le deuxième coin vers le centre, et lorsque l'arbre tourne dans l'autre sens, il écarte le premier coin et le deuxième coin du centre. Un actionneur fait coulisser le premier guide-lame et le deuxième guide-lame l'un vers l'autre le long du premier arbre et contre le premier coin et le deuxième coin respectivement. Par conséquent, le déplacement du premier coin et du deuxième coin le long du deuxième arbre, à cause de la rotation sélective du deuxième arbre, entraîne le déplacement longitudinal relatif entre le premier guide-lame et le deuxième guide-lame sur le premier arbre.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Inactive: Office letter | 2005-10-19 |
| Inactive: Correspondence - Transfer | 2005-09-06 |
| Inactive: Correspondence - Transfer | 2003-09-08 |
| Letter Sent | 2003-08-20 |
| Time Limit for Reversal Expired | 2003-04-16 |
| Letter Sent | 2002-11-15 |
| Letter Sent | 2002-11-15 |
| Inactive: Multiple transfers | 2002-09-26 |
| Letter Sent | 2002-04-16 |
| Letter Sent | 2001-10-24 |
| Grant by Issuance | 2000-07-18 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2000-07-17 |
| Inactive: Inventor deleted | 2000-06-28 |
| Inactive: Inventor deleted | 2000-06-28 |
| Inactive: Inventor deleted | 2000-06-28 |
| Inactive: Received pages at allowance | 2000-04-11 |
| Pre-grant | 2000-04-11 |
| Inactive: Final fee received | 2000-04-11 |
| Letter Sent | 1999-10-27 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 1999-10-18 |
| Letter Sent | 1999-10-18 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 1999-10-18 |
| Inactive: Approved for allowance (AFA) | 1999-10-04 |
| Inactive: Status info is complete as of Log entry date | 1999-10-04 |
| Inactive: Application prosecuted on TS as of Log entry date | 1999-10-04 |
| Letter Sent | 1999-08-18 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 1999-04-14 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 1999-04-14 |
| Extension of Time for Taking Action Request Received | 1999-04-14 |
| Inactive: Correspondence - Prosecution | 1998-01-21 |
| Inactive: Correspondence - Transfer | 1998-01-21 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 1997-10-18 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 1997-08-06 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1997-08-06 |
| Inactive: Filing certificate - No RFE (English) | 1997-07-11 |
| Filing Requirements Determined Compliant | 1997-07-11 |
| Inactive: Correspondence - Formalities | 1997-06-10 |
There is no abandonment history.
The last payment was received on 1999-04-14
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Please refer to the CIPO Patent Fees web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application fee - standard | 1997-04-16 | ||
| Registration of a document | 1997-04-16 | ||
| MF (application, 4th anniv.) - standard | 04 | 2001-04-16 | 1999-04-14 |
| MF (application, 3rd anniv.) - standard | 03 | 2000-04-17 | 1999-04-14 |
| Request for examination - standard | 1999-04-14 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - standard | 02 | 1999-04-16 | 1999-04-14 |
| Registration of a document | 1999-09-17 | ||
| Final fee - standard | 2000-04-11 | ||
| Registration of a document | 2001-05-24 | ||
| Registration of a document | 2002-09-26 | ||
| Registration of a document | 2003-07-17 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| COE NEWNES/MCGEHEE ULC |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| JOHN SERGEANT |
| STEVEN W. MICHELL |
| WILLIAM R. NEWNES |