Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02204700 1997-0~-07
Field of Invention
This invention relates to dikes. In particular, this invention relates to a
portable dike which can be erected as a water barrier where required in areas
anticipating flood conditions and anchored to the ground to prevent floodwater from
flowing onto protected lands, and a method of constructing such a dike.
Background of the Invention
Flooding is a major problem in many parts of the world. Particularly after
a spring thaw or persistent rain, rivers and lakes which overflow can crest at a height
many metres higher than their normal waterline. In bad flood conditions it is not only
low lying areas which are affected, and even structures built on high ground can be
susceptible to tremendous water damage. Floods cause the loss of many lives and
homes, necessitate mass evacuations, and cause damage to property often reaching into
the billions of dollars. However, because extensive flooding is relatively rare it is not
practical or desirable to build permanent dikes around water sources such as rivers,
lakes, reservoirs etc., for cost, accessibility and environmental reasons.
Often floods can be predicted well in advance, and steps can be taken to
reduce or eliminate the flow of floodwater onto lands desired to be protected.
Conventionally this entails building sandbag dikes, which in a typical situationinvolves scores or even hundreds of individuals filling sandbags, conveying them to
the required location and stacking them to erect the dike. This consumes an enormous
number of man-hours, and presents additional problems. The construction of a
sandbag dike is very time consuming so it must be started well in advance of the flood.
In some areas the sand must be transported to the dike site from a remote source.
There is a practical height limit to sandbag dikes constructed in this fashion, and in
many cases the dike ends up being unstable because the individuals (usually
volunteers) erecting it were not trained in proper sandbag dike construction
techniques.
The present invention overcomes these disadvantages by providing a
portable dike which can be erected quickly and which can be disassembled and moved
~ CA 02204700 1997-0~-07
from site to site with relative ease and haste. Minimal training is required to construct
the dike of the invention, and it can be erected by a small number of individuals in
response to predicted flooding.
The invention accomplishes this by providing a portable dike formed
from dike sections each comprising an inflatable bladder and an anchoring flap affixed
to a lower portion of the bladder and extending along the ground on the floodwater
side of the dike, to anchor the dike section to the ground. The bladder is inflated to the
required height with water pumped from the water source. A series of such dike
sections are anchored end-to-end to construct a dike of the required length. In the
preferred embodiment the ends of the dike sections interlock to form a watertight seal.
The present invention thus provides a portable dike section comprising
an inflatable, substantially fluid-impermeable bladder, and an anchoring flap affixed to
a lower portion of the bladder for anchoring the bladder to the ground, wherein the
bladder can be inflated to form a substantially waterproof dike section.
The present invention further provides a dike comprising a plurality of
dike sections, each dike section comprising an inflatable, substantially fluid-
impermeable bladder, and an anchoring flap affixed to a lower portion of the bladder
for anchoring the bladder to the ground, wherein the bladder can be inflated to form a
substantially waterproof dike section such that a plurality of dike sections anchored
end-to-end form a substantially waterproof dike.
The present invention further provides a method of constructing a dike
from a plurality of portable dike sections, each dike section comprising an inflatable,
substantially fluid-impermeable bladder and an anchoring flap affixed to a lowerportion of the bladder for anchoring the bladder to the ground, comprising the steps of
anchoring a series of the dike sections end-to-end, and inflating the bladders with water
wherein the bladders can be inflated to form substantially waterproof dike sections, a
plurality of dike sections being anchored to the ground end-to-end form a substantially
waterproof dike.
CA 02204700 1997-0~-07
Brief Description of the Drawin~
In drawings which illustrate by way of example only a preferred
embodiment of the invention,
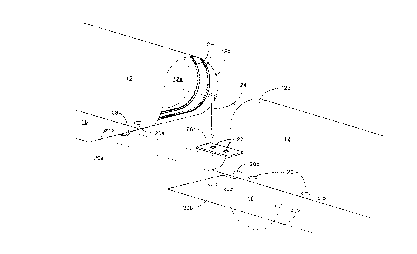
Figure 1 is a partially cutaway elevation of a preferred embodiment of the
portable dike of the invention anchored to the ground adjacent to a river bank,
Figure 2 is a perspective view of the dike of Figure 1,
Figure 3 is a top plan view of a dike section in the dike of Figure 2,
Figure 4 is an exploded perspective view of adjacent inflated sections in
the dike of Figure 2,
Figure 5 is a partial enlarged elevation of the anchoring flap,
Figure 6 is a partial cross-sectional elevation of a dike section, and
Figure 7 is a schematic elevation of a deflated dike section partially
unrolled from a reel for construction of the dike of Figure 2.
Detailed Description of the Invention
Figures 1 and 2 illustrate a water source 2 and a dike 8 of the invention
anchored to the adjacent ground 6. In the illustrated embodiment the water source 2 is
a river, but the water source 2 could be lake, canal, reservoir or any other natural or
artificial source of water and the invention is not intended to be restricted in this
respect. Figure 1 illustrates the normal waterline for the water source 2 at 2a and an
anticipated floodwater waterline at 2b.
The dike 8 consists of adjacent dike sections 10, each anchored to the
ground 6 and inflated with a fluid, preferably water from the water source 2. However,
it is contemplated within the invention that other fluids, including gases such as air or
helium, may be suitable for inflating the dike sections 10.
CA 02204700 1997-0~-07
-- 4 --
In the preferred embodiment each dike section 10 comprises a bladder 12
and an anchoring flap 16. The bladder 12 is formed from a bladder wall 12b and end
faces 12a composed of a strong, flexible, substantially fluid-impermeable membrane
material that can retain the weight of fluid required to inflate it to the required height
and is preferably resistant to being pierced or punctured by floating debris on the
floodwater (water source 2) side of the dike 8.
Examples of suitable membrane materials may be rubber, Tedlar
(Trademark), or a water-impermeable vinyl coated polyester fabric such as UnitexUltralon #4 (Trademark). The bladder 12 may also be reinforced with a flexible fabric or
fibre mesh (not shown). Many flexible fluid-impermeable membrane materials are
available which are sufficiently strong to retain a large volume of a water, and for
larger applications the membrane can be doubled or reinforced with a synthetic fibre
mesh such as Kevlar (Trademark) for additional strength and puncture resistance. (It
will be appreciated that the term "fluid-impermeable" is used herein relative to the
fluid intended to be used to inflate the bladder 12, which in the preferred embodiment
is water).
The dike sections 10 can be formed to any practical length, up to 100 feet or
more, and can extend up to 10 feet in height when filled (to retain 6 to 7 feet of
floodwater), depending upon the size of and materials selected for the bladder 12. The
construction and selection of materials having the required characteristics for a bladder
12 of the desired size, and the manner of seaming the end faces 12a to the bladder wall
12b, is well known to those skilled in the art.
A filling opening 14 is provided in the bladder 12, preferably near the top
adjacent to one end of the bladder 12. The filling opening 14 is provided with aconventional watertight closure (not shown) and optionally an adaptor (not shown)
for attachment to a hose 4a from a water pump 4.
An anchoring flap 16 extends from a lower portion of the bladder 12. In
the preferred embodiment the anchoring flap 16 is formed integrally with the bladder
12 from a single sheet of membrane material, as shown in Figure 1, by folding the
membrane material over itself and bonding, welding or otherwise suitably affixing the
. CA 02204700 1997-0~-07
folded end of the membrane material to the proximal edge of the flap 16, as at 15 in
Figure 1. This forms a teardrop-shaped bladder wall 12a to which the end faces 12a are
affixed to form a substantially fluid-impermeable bladder 12.
Alternatively, the bladder 12 can be formed as a separate fluid-
impermeable tube and the anchoring flap 16 may be affixed to the bottom of the bladder
12. In this embodiment the flap 16 may be formed from the same material as the
bladder 12, but it will be appreciated that the anchoring flap 16 does not need to be as
flexible as the bladder 16 (although this may be advantageous in many circumstances
such as where the dike 8 is laid over relatively rough terrain).
The anchoring flap 16 extends along the ground 6 on the floodwater side
of the bladder 12, and is anchored to the ground 6 using pegs or spikes 24. The
anchoring flap 16 is preferably provided with preformed holes 20 for this purpose, to
facilitate a uniform distribution of the spikes 24 and thus distribute the tensile force of
the floodwater along the flap 16 more evenly. To resist tearing of the flap 16 around
the spikes 24, rigid (for example metal) reinforcing plates 26 are provided with holes 27
in alignrnent with the holes 20 in the anchoring flap 16. For large applications the
reinforcing plates 26 can be 3 feet in length, preferably with a pair of holes 27 spaced
apart to be coincident with pairs of holes 20 in the anchoring flap 16. In the preferred
embodiment the anchoring flap 16 is provided with two rows of holes 20, one of which
extends along the portion where the membrane material overlaps the flap 16 forming
the seam for the bladder wall 12b, as seen in Figure 1, for additional reinforcement of
this seam.
The anchoring flap 16 may be provided with ribs or recesses (not shown)
to accommodate the reinforcing plates 26. In alternative embodiments the reinforcing
plates 26 may be unnecessary, for example if large-headed spikes 24 are used, the
anchoring flap 16 is constructed from a particularly strong material or suitablereinforcement is designed into the anchoring flap 16 itself.
To resist water seepage underneath the dike section 10, the reinforcing
plates 26 should be anchored as flat as possible against the anchoring flap 16. The distal
end of the anchoring flap 16 is preferably buried in a trench and backfilled, as shown at
CA 02204700 1997-0~-07
the left hand side of Figure 1. Further, in the preferred embodiment a hooked flange
28, best seen in Figure 5, extends along the bottom face of the anchoring flap 16 parallel
to the bladder 12. The flange 28 may be formed integrally with the anchoring flap 16,
affixed to the flap 16 or fitted into a slot provided in the flap 16. The flange 28
protrudes toward the floodwater side of the dike 8, so that as the floodwater rises and
the pressure of seepage toward the bladder 12 increases the flange 28 splays away from
the anchoring flap 16, which increases the pressure of the flange 28 against the ground
6. The flange 28 thus acts as a gasket which expands against the ground as the water
pressure increases due to rising floodwater. This effect is enhanced by the weight of the
floodwater on the anchoring flap 16, which presses the flange 28 tightly against the
ground 6.
The invention further provides means for interlocking the ends of
adjacent dike sections 10 together to form a watertight seal. In each dike section 10 a
protruding end 12d of the bladder 12 extends beyond the anchoring flap 16, as shown at
the left hand side in Figure 3. At the other end of the bladder 12 the end face 12a is
recessed, so that the end portion of the bladder wall 12b forms a sleeve 12c which
overhangs the end of the bladder 12, as shown at the right hand side in Figure 3.
When the dike sections 10 are laid for filling, the protruding end 12d of the bladder 12
of a deflated dike section 10 is inserted into the sleeve 12c of an inflated dike section 10,
and inflation of the deflated bladder 12 causes the protruding end 12d of the bladder 12
to distend within the sleeve 12c, thus locking it into position.
To facilitate the proper positioning of adjacent dike sections 10 the
anchoring flap 16 includes a portion 16a which is separated from the bladder wall 12b,
as at 17 in Figure 3, and which overlaps the anchoring flap 16 of the adjacent dike
section so that a single spike 24 simultaneously anchors the overlapping ends of both
anchoring flaps 16, as shown in Figure 4.
To ensure a watertight seal between dike sections 10, the sleeve 12c is
provided with hooked flanges 29, best seen in Figure 6, which function in the same
fashion as the hooked flange 28. The hooked flanges 29 circumscribe the interior of the
sleeve 12c, preferably at two locations as shown in Figures 4 and 6, and the flanges 29
protrude toward the exposed seam between adjacent bladders 12. The flanges 29 act as
CA 02204700 1997-0~-07
gaskets between the protruding end 12d of one bladder 12 and the sleeve 12c in which it
is disposed, so that water seeping into the sleeve 12c is prevented from seeping between
the two adjacent bladder faces 12a. As in the case of the flange 28, when the water
pressure increases the flanges 29 splay open, increasing the force of the seal.
In a further embodiment another anchoring flap 18 may optionally be
affixed to the bladder 12 to extend along the ground 6 on the dry side of the dike 8, as
shown in phantom in Figure 1, to resist oscillation and surging of the bladder 12 under
fast-flowing flood conditions. However, the anchoring flap 18 would not need to be as
wide as the anchoring flap 16 which preferably provides a broad surface area in contact
with the floodwater, taking advantage of the weight of the floodwater to anchor the
dike 8 more firmly, as explained below.
In operation, the deflated dike sections 10 are transported by truck 40 or
other suitable transportation means to the predicted site of the flood, with the dike
sections 10 preferably being rolled onto reels 42, as shown in Figure 7, to facilitate
unloading. The first dike section 10 is unrolled with its anchoring flap 16 facing the
ground 6. The dike section 10 is laid along the dike path and the anchoring flap 16 is
spiked to the ground 6 using spikes 24 through reinforcing plates 26 (transported with
the rolled dike sections 10) and the holes 20 in the anchoring flap 16. The last hole 20a
(closest to the periphery at the sleeve 12c end of the dike section 10, as seen in Figure 4)
is left open until the next dike section 10 is laid. The first dike section 10 is inflated by
filling the bladder 12, preferably with water, which can be pumped from the water
source 2 by a pump 4 (which may be located on the truck 40) through the opening 14 in
the bladder 12. As the bladder 12 inflates the bladder 12 starts to rise, until the desired
height is reached.
The second dike section 10 is then laid end-to-end beside the first dike
section 10 along the dike path. The separate portion 16a of the anchoring flap 16 of the
second dike section 10 is laid over the the anchoring flap 16 of the first (inflated) dike
section 10 so that the hole 20b overlies the hole 20a (see Figure 4), a reinforcing plate 26
is placed over the holes 20a, 20b and a spike 24 is driven through the overlaying holes
20a, 20b to secure the two dike sections 10 together. The remainder of the anchoring
flap 16 of the second dike section 10 is spiked to the ground 6 using spikes 24 through
CA 02204700 1997-0~-07
reinforcing plates 26 (except for the last hole 20a), and the protruding end 12d of the
second dike section 10 is inserted into the sleeve 12c of the first dike section 10. The
second dike section 10 is inflated in the same manner as the first, and as the protruding
end 12d of the bladder 12 inflates within the sleeve 12c of the first dike section 10 it
becomes locked in position, integrating the dike sections 10 to provide an effective
watertight seal therebetween.
The remaining dike sections 10 are erected in a similar fashion, the
protruding end 12d of each bladder 12 in turn locking into the sleeve 12c of thepreviously inflated dike section 10, to create a dike 8 of unlimited length.
As the floodwater rises the weight of the floodwater on the anchoring
flaps 16 anchors the dike 8. Water seepage between dike sections 10 is resisted by the
expansion of the flanges 29. Water seepage beneath the anchoring flaps 16 is resisted by
the buried distal ends of the anchoring flaps 16, the pressure of the reinforcing plates 26
against the ground 6 and the expansion of the flange 28.
When the floodwater has receded the dike 8 can be disassembled by
deflating the bladders 12 through their filling openings 14, either by siphoning or with
the assistance of a pump 4, and removing the spikes 24. The dike sections 10 areflattened and rolled onto reels 42 (which may require motorized or mechanical
assistance depending upon the size of the deflated dike sections 10). The rolled dike
sections 10 can then be relocated to another flood site or stored for future use.
A preferred embodiment of the invention having been described above by
way of example only, it will be apparent to those skilled in the art that certain
modifications and adaptations may be made without departing from the scope of the
invention. For example, without limiting the foregoing, depending upon the required
size of the dike 8 it may be unnecessary to use reinforcing plates 26, and depending
upon the type of terrain on which the dike 8 is erected it may be unnecessary to bury
the distal end of the anchoring flaps 16 and/or include a flange 28 beneath the
anchoring flaps 16. The inflatable bladder 12 and anchoring flap 16 can be formed
integrally or separately, and their respective shapes are a matter of choice. It is
preferable that the bladders 12 be inflated with water from the water source 2, due to its
CA 02204700 1997-0~-07
abundance and immediate availability, however any other fluid suitable for inflating
the bladders 12 can be used instead of water. All of these features have been described
in the context of the preferred embodiment, and the invention is not intended to be
limited except as set out in the appended claims.