Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
-- 1 --
METHOD OF STRAIGHTENING ANNULAR METALLIC SHEETS
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the invention
The present invention relates to a method of
straightening annular metallic sheets. More particularly,
the present invention relates to a method of straightening
blanks made of aluminum or an aluminum alloy used for a
magnetic disk substrate for computer.
2. Description of the Related Art
An annular metallic sheet having a hole pierced at
the center thereof such as a blank used for a magnetic
disk substrate made of aluminum or an aluminum alloy is
prepared in general by stamping a rolled sheet into an
annular disk. This as-stamped blank has a convex or
concave curved shape. A magnetic disk substrate is
required to have a very high flatness, so that is it
necessary to straighten the as-stamped blank to remove
strain caused by stamping.
A commonly adopted method of straightening a blank
known as the pressure-annealing method comprises, for
example, placing a plurality of blanks to be straightened
between flat stools, piling a'plurality of such
assemblies, and annealing the same while vertically
applying a pressure.
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication No. 61-44162
discloses a method of straightening a blank comprising the
steps of piling blanks on a lower stool connected to
vertically movable pressing means, raising the same,
charging the same into an induction heating furnace, and
applying a pressure by bringing the same into contact
under a pressure with an upper stool formed integrally
with the heating furnace. Japanese Unexamined Patent
Publication No. 62-240112 discloses a method comprising
the steps of piling a plurality of blanks on a lower
stool, placing an upper stool onto the blanks, holding the
blanks, and heating and annealing the blanks while
applying a pressure to the upper and the lower stools via
a heat resistant spring. While it is the general practice
to use flat stools for holding the piled blanks in
between, a method is available of using stools tapered
into a concave or a convex shape (see Japanese Unexamined
Patent Publication No. 5-263201). In addition, there is
proposed a method comprising the steps, upon stamping a
blank, of pressing the blank at the center to cause the
same to deform into a wide frustconical shape, thereby
causing a uniform plastic deformation by such expansion,
eliminating slight strain under the effect of this plastic
elongation, and then conducting annealing under pressure
(see Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication No. 6-285554).
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
In these conventional straightening methods of
blanks, however, blanks are piled so that the convex side
is in contact with the concave side for each blank, and
the thus piled blanks are pressure-annealed for
straightening.
In this manner of piling a plurality of blanks so
that a convex side is in contact with a concave side, the
contact area between blanks is large and the apparent
blank thickness is regarded as the lamination thickness of
the piled sheets, thus leading to a very large pressing
force required for straightening. Furthermore, the blank
after straightening may show an insufficient flatness.
The present invention was developed to solve the
problems described above, and has an object to provide a
method of straightening annular metallic sheets, which
requires only a slight pressing force for straightening
annular metallic sheets, permits easy straightening, and
gives a product excellent in flatness.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
To achieve the foregoing object, the present
invention provides a method of straightening annular
metallic sheets, comprising the steps of putting a
plurality of annular metallic sheets to be straightened
each having a convex and a concave sides one on top of the
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
other; sandwiching the annular metallic sheets between
stools having flat surfaces; and annealing the plurality
of annular metallic sheets via the stools while applying a
pressure; wherein at least part of the plurality of
annular metallic sheets are piled by bringing a convex
side into contact with another convex side and a concave
side, with another concave side, and the thus piled sheets
are annealed while applying a pressure. Lamination of the
annular metallic sheets so that a convex side is in
contact with another convex side and a concave side is in
contact with another concave side and the pressure-
annealing reduce the pressing force required for
straightening the annular metallic sheets, permit easy
straightening and give an excellent flatness of
straightening, with reduced damage and wear and a longer
service life of jigs used for straightening.
When applying this method, the annular metallic
sheets may be piled by bringing a convex side into contact
with another convex side and a concave side, with another
concave side one by one, or by bringing a convex side into
contact with another convex side and a concave side, with
another concave side to form a unit, and bringing a convex
side of this unit into contact with a convex side of
another unit and a concave side of the unit, with another
concave side of another unit. This permits effective
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
straightening of many annular metallic sheets with a
satisfactory flatness without largely increasing the
pressing force.
In the method of straightening annular metallic
sheets of the present invention as described above, an
elastic force of a heat resistant elastic material is
utilized as the pressing force. By using the elastic
force of the heat resistant elastic material for pressing,
differences in expansion and contraction with temperature
between the annular metallic sheets and the tightening
jigs are absorbed, and it is possible to apply constantly
a uniform pressing force during annealing, thus permitting
stable straightening.
Now, the method of the present invention will be
described further in detail with reference to the
drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is a descriptive view illustrating an
embodiment of lamination of annular metallic sheets
adopted in the method of straightening annular metallic
sheets of the present invention;
Fig. 2 is a descriptive view of a pressure-annealing
step of annular metallic sheets adopting the embodiment of
lamination shown in Fig. l; and
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
Fig. 3 is a descriptive view illustrating another
embodiment of lamination of annular metallic sheets.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
The annular metallic sheets used in the present
invention are blanks made of aluminum or an aluminum alloy
used for a magnetic disk substrate for computer. The
blank has a thickness within a range of from 0.4 to 2.5
mm, depending upon the material and the diameter of the
magnetic disk substrate.
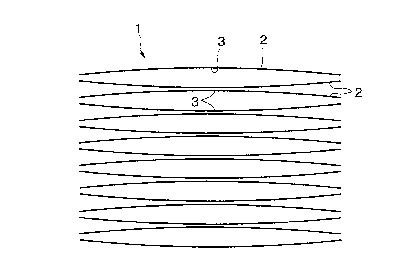
The blank 1 is formed by a known stamping process,
and has a convex side 2 and a concave side 2. As shown in
Fig. 1, a plurality of blanks 1 are piled with a convex
side 2 thereof in contact with another convex side 2 and a
concave side 3 thereof in contact with another concave
side 3. Fig. 1 shows a case where the blanks are piled
one by one alternately in a sequence of a back, a face, a
back and then a face. As shown in Fig. 2, a block 4a
comprising a plurality of piled blanks as shown in Fig. 1
is placed on a lower stool 10 having a flat surface lOa.
Then, an intermediate stool 9a (spacer) having flat upper
and lower surfaces is placed on this block 4a, and then,
another block 4b comprising a plurality of similarly piled
blanks is placed on the intermediate stool 9a.
Furthermore, blocks 4c and 4d and intermediate stools 9c
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
and 9d are alternately piled, and an upper stool 8 having
a flat surface 8 is placed on the final block 4e. A
prescribed pressing force is applied onto the surface of
the blank 1 via a spring 11 which is made of a heat
resistant elastic material by means of a screw stock 12
fixed to the lower stool 10 and a nut 13 screw-engaging
with the screw stock 12. The thus formed assembly is
charged into an annealing furnace (not shown), and
pressure-annealed at a prescribed temperature for a
prescribed period of time, for example, at a temperature
of over 300~C, or preferably, at a temperature within a
range of from 350 to 360~C for a sufficient period of
time, for example, from 5 to 6 hours.
In the foregoing embodiment, the number of blanks in
a block and the pressing force are appropriately selected,
depending upon the material of the blank, thickness or
diameter thereof. While a case with five blocks has been
described in this embodiment, the present invention is not
limited to this, but the number of blocks is appropriately
selected, as in the case of the number of blanks and the
pressing force, depending upon the material of the blank,
thickness or diameter thereof. The stool is made of
aluminum or an aluminum alloy and must have a flatness at
least higher than the flatness of the blank after
straightening. The spring 11 must be heat-resistant,
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
keeping elasticity at an annealing/holding temperature
within, for example, a range of from 350 to 360~C, and
should be made of a material such as an alloy tool steel
or a heat-resistant spring steel. The shape thereof is
not limited to a helical shape, but it may be any other
shape.
By piling the blanks 1, with a convex side 2 in
contact with another convex side 2 and a concave side 3 in
contact with another concave side 3, and applying
pressure-annealing, the pressing force required for
straightening the blanks 1 is reduced, leading to an easy
straightening, and an excellent flatness is available,
with reduced damage or wear of jigs used for straightening
and a longer service life of the jigs.
In addition, pressing by the utilization of an
elastic force of the heat-resistant spring 11 absorbs the
difference in expansion and contraction caused by
temperature between the blanks 1 and the tightening jigs
during annealing in the annealing furnace, thus permitting
application of a constant pressing force during annealing,
resulting in a stable straightening.
Fig. 3 is a descriptive view illustrating another
embodiment of lamination of the annular metallic sheets
shown in Fig. 1. According to this embodiment, a
plurality of blanks which are piled annular metallic
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
sheets are placed between stools having flat surfaces.
Upon annealing the plurality of blanks while pressing
them, a plurality of, for example, five blanks 1 piled
with a convex side 2 in contact with a concave side 3 are
considered as a unit, and units are piled with a concave
side 7 of the unit 5a in contact with a concave side 7 of
the unit 5b, and with a convex side 6 of the unit 5b in
contact with a convex side 6 of the unit 5c. In this
manner, units are piled by bringing into contact concave
sides 7 with concave sides 7 of the units 5c to 5f, and
convex sides 6 with convex sides 6. In other words, a
plurality of blanks 1 are piled by bringing into contact
the sides of the same direction of strain, and units are
piled with the convex sides in contact with the convex
sides and with the concave sides 7 in contact with the
concave sides 7.
This manner of piling with convex sides in contact
with convex sides and concave sides in contact with
concave sides of units and pressure-annealing the units as
in this embodiment gives a larger pressing force than in
the manner of bringing a convex side into contact with a
convex side, and a concave side, with a concave side one
by one as shown in Fig. 1. It permits however more
effective straightening of many blanks under a smaller
pressing force, with a better flatness, than in the
' CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
-- 10 --
conventional method bringing a convex side into contact
with a concave side.
Now, an example showing the effect of straightening
by the method of straightening annular metallic sheets of
the present invention and a comparative example showing
the effect of straightening by the conventional method for
comparison will be described.
EXAMPLE
Thirty blanks each comprising 4.5 wt.% Mg, 0.06 wt.~
Cu and the balance Al and incidental impurities having an
outside diameter of 95 mm, an inside diameter of 25 mm and
a thickness of 0.8 mm were piled, as shown in Fig. 1, by
bringing a convex side into contact with a convex side and
a concave side, with a concave side of the blank one by
one, into a block. Five such blocks were inserted between
a lower stool, an intermediate stool (spacer) and an upper
stool in a five-layer lamination. This resulted in 150
blanks in total. The spacer in this case had a diameter
of 110 mm and a thickness of 20 mm, and was made of S55C.
A nut was tightened and vertical pressing was applied.
The tightening torque at the moment when gaps between
piled blanks were eliminated was measured with a torque
wrench to determine a tightening pressure: this gave a
result of 200 kgf/cm2. When a tightening pressure of 100
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
kgf/cm2 was additionally applied, the blanks showed a
surface pressure of 2 kgf/cm2. Three sets of such blanks
were provided, and an annealing treatment was applied at
an annealing/holding temperature of 350~C for a holding
time of five hours.
Flatness of the 420 straightened blanks (excluding
the first blanks in contact with the steels) was measured
by counting fringes by means of a known optical
interference fringe gauge. A concentric fringe pattern on
the blank is the ideal one, and in this case, one fringe
corresponds to 1 ,um. For the blanks before annealing, the
foregoing gauge showed unmeasurable result because of
range over. The results included an average value x = 4.8
,um and a standard deviation ~ = 0.54 ,um.
COMPARATIVE EXAMPLE
For comparison purposes, 30 blanks obtained in the
same process as that of the blanks used in the Example
were piled by bringing a convex side into contact with a
concave side, and the piled blanks were placed between
stools similar to those used in the Example into five-
layer lamination. Thus three sets of 150 blanks in total
were prepared. Further, a tightening nut was tightened,
and a vertical pressure was applied. At the moment when
gaps between the piled blanks were eliminated, the
CA 02206108 1997-0~-26
pressing force was measured with a torque wrench. A
pressing force of 800 kgf/cm2 resulted. In addition, a
tightening pressure of 100 kgf/cm2 was added. This gave a
blank surface pressure of 6 kgf/cm2. Three sets of such
blanks were prepared, and an annealing treatment was
applied at an annealing/holding temperature of 350~C for a
holding time of five hours.
Measurement of the flatness of 420 blanks excluding
the first ones in contact with the stools, in the same
manner as in the Example, by means of a flatness measuring
gauge gave results including an average value x = 7.2 ,um
and a standard deviation ~ = 0.73 ,um.
These results of measurement of flatness suggest that
the blanks in the Example are largely improved in terms of
flatness over the blanks in the Comparative example, with
smaller variations. Further, the pressing force for
pressure-straightening the blanks was reduced to a third
that in the Comparative Example.
The present invention has been described in detail by
means of the Examples shown in the drawings. The present
invention is not however limited to these Examples, but it
is needless to mention that diverse and various variations
are possible by making various modifications without
deviating from the spirit of the present invention.
According to the present invention, it is possible to
CA 02206108 1997-05-26
obtain annular metallic sheets easily straightened with a
small pressing force and excellent in flatness.