Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2216627 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR CHECKING SECURITY DOCUMENTS |
| (54) French Title: | METHODE ET APPAREIL POUR VERIFIER LES DOCUMENTS DE SECURITE |
| Status: | Deemed Abandoned and Beyond the Period of Reinstatement - Pending Response to Notice of Disregarded Communication |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | SMART & BIGGAR LP |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 1996-03-29 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 1996-10-03 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/DE1996/000598 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | WO 1996030879 |
| (85) National Entry: | 1997-09-26 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
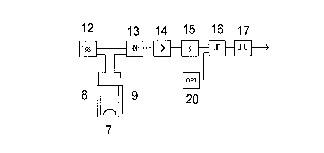
The invention concerns a method and devices for checking security documents.
According to this process which uses known capacitive coupling, electrical
signals are transmitted by transmitting antennae via electrically conductive
security features to receiving antennae and amplified. The amplitude responses
and time characteristics of the electrical signals are then evaluated and
compared with existing signal responses, by being converted into signal
responses having easily comparable parameters. In order to enable the testing
arrangement to be specifically selective, a selective amplifier is
additionally coupled to the evaluation electronics. Currency-specific
definition by means of the evaluation electronics according to the invention
is attained in that, for a given currency, a time limit of the test signal
amplitude can be determined by means of controllers, for example, this time
limit differing from the duration of the amplitude response of all the other
currencies.
L'invention concerne un procédé et des dispositifs permettant de vérifier des documents de sécurité. Selon le procédé de vérification de documents de sécurité, qui fait appel au couplage capacitif connu en soi, il est prévu que des signaux électriques émanant d'antennes émettrices soient transmis à des antennes réceptrices par le biais de caractéristiques de sécurité électroconductrices, et amplifiés. Ces signaux sont ensuite évalués d'après leur réponse d'amplitude et leur réponse en temps, et comparés à des courbes de signaux existantes, par conversion en courbes de signaux présentant des paramètres facilement comparables. Afin de parvenir à une sélectivité spécifique du dispositif de vérification, un amplificateur sélectif est en outre couplé à l'unité électronique d'évaluation. On parvient à une définition propre à la monnaie à l'aide de l'unité électronique d'évaluation, du fait qu'une limite de temps de l'amplitude du signal de vérification différant de la durée de la réponse d'amplitude de toutes les autres monnaies, peut être déterminée par exemple à l'aide de contrôleurs.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Sorry, the description for patent document number 2216627 was not found. Text is not available for all patent documents. The current dates of coverage are on the Currency of Information page
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Inactive: IPC expired | 2016-01-01 |
| Inactive: IPC expired | 2016-01-01 |
| Inactive: IPC expired | 2016-01-01 |
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Time Limit for Reversal Expired | 2004-03-29 |
| Application Not Reinstated by Deadline | 2004-03-29 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2003-03-31 |
| Inactive: Abandon-RFE+Late fee unpaid-Correspondence sent | 2003-03-31 |
| Letter Sent | 2000-05-01 |
| Reinstatement Requirements Deemed Compliant for All Abandonment Reasons | 2000-04-18 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2000-03-29 |
| Inactive: Single transfer | 1998-03-16 |
| Inactive: Applicant deleted | 1998-02-18 |
| Inactive: Correspondence - Formalities | 1997-12-24 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1997-12-16 |
| Classification Modified | 1997-12-16 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 1997-12-16 |
| Inactive: Courtesy letter - Evidence | 1997-12-09 |
| Inactive: Notice - National entry - No RFE | 1997-12-03 |
| Application Received - PCT | 1997-12-01 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 1996-10-03 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2003-03-31 | ||
| 2000-03-29 |
The last payment was received on 2002-02-11
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Please refer to the CIPO Patent Fees web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic national fee - standard | 1997-09-26 | ||
| Registration of a document | 1998-03-16 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - standard | 02 | 1998-03-30 | 1998-03-23 |
| MF (application, 3rd anniv.) - standard | 03 | 1999-03-29 | 1999-02-05 |
| MF (application, 4th anniv.) - standard | 04 | 2000-03-29 | 2000-04-18 |
| Reinstatement | 2000-04-18 | ||
| MF (application, 5th anniv.) - standard | 05 | 2001-03-29 | 2001-01-19 |
| MF (application, 6th anniv.) - standard | 06 | 2002-03-29 | 2002-02-11 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| WHD ELEKTRONISCHE PRUFTECHNIK GMBH |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| FRANK PUTTKAMMER |
| TORSTEN WOLF |