Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02216922 1997-09-29
WO 96!31310 PCTISE96100447
1
A SAW AXLE AND A SAW BLADE WHICH CAN BE FITTED ONTO
THE AXLE
The present invention relates to a.saw axle for floatingly
supporting a plurality of saw blades, which are caused to
~ 5 rotate with the axle by. virtue of a form-locking effect
achieved between the outer contour of the axle and corre~-
sponding holes in respective saw blades. The invention als«
relates to a saw blade for use with such an axle.
Circular saws that are used to saw logs and blocks into
smaller dimensions include a plurality of axle-mounted saga
blades. The saw blades are usually fitted floatingly on thc=
axle, i.e. are loosely displaceable thereon, therewith
simplifying relative positional changes between the blades
for adaptation to different blade settings, among other
things. Each blade is guided by outer blade guides which
coact with said blade and which can be moved between differ--
ent blade positions along the axle.
The blades are dogged by the rotating axle through the medium
of splines, the axle being provided with a plurality o:E
radially outwardly projecting splines which extend axially
along the axle, wherein the blades are provided with corre-
sponding recesses for coaction with the axle-mounted splines,:
see US-A-3,516,460, for instance.
One drawback with the use of splines is that the blades area
liable to wear grooves in the splines at those regions wherEs
the blades are in contact therewith. This can cause problems
when wishing to move floatingly-mounted blades through a very
short distance to a new blade setting, since the grooves tend
to return the blades to their old setting and therewith make
it difficult to finely adjust the blade settings.
Furthermore, when a plurality of splines are used the'
attachment is not statically determined, since it is not.
CA 02216922 2000-02-17
2
known whether or not the blade has contact with all splines
when a sawing operation is started.
A conventional splined axle is relatively expensive to
renovate, since it is necessary to remove the entire axle
and possibly send the axle to a workshop to be reground,
which is an expensive exercise.
One object of the present invention is to provide an axle on
which saw blades can be floatingly-mounted and which
provides statically determined contact with respective saw
blades.
Another object is to provide such an axle which can be
manufactured at relatively low cost, which is easy to grind
and whose surfaces can be readily treated, and which can be
renovated in a cost-effective manner when so required.
Still another object of the invention is to provide a saw
blade that can be mounted on an inventive axle.
Summary of the Invention
In accordance with one aspect of the present invention there
is provided a saw axle in combination with a plurality of
saw blades, said saw axle floatingly supporting the
plurality of saw blades, which are coupled with the axle for
rotation therewith by a form fit between an outer contour of
the axle and matingly configured centre holes in respective
saw blades, wherein: a) both the outer contour of the axle
and a contour of the centre hole in each saw blade present,
exclusively, three symmetrical arcuate main Bides of uniform
CA 02216922 2000-02-17
2a
length for obtaining a statically determined three-point
contact between axle and blades; b) the three sides have the
shape of circular arcs having a same, constant radius of
curvature; c) the centres of the arcs form respective
corners of an equilateral triangle; d) a centre of said
triangle is coincident with a centre axis of said axle; and
e) the coupling between the axle and the blades is
exclusively provided by the matingly configured outer
contour of the axle and the centre hole of the blades
without the use of any expandable fasteners.
In accordance with another aspect of the present invention
there is provided a saw blade in combination with and
floatingly fitted to a saw axle and coupled with the axle
for rotation therewith by a form fit between an outer
contour of the axle and a matingly configured centre hole in
the saw blade, wherein: a) said centre hole defines,
exclusively, three symmetrical arcuate main sides of uniform
length and arcuate transitions therebetween; b) the three
sides have the shape of circular arcs having a same,
constant radius of curvature; c) the centres of the arcs
form respective corners of an equilateral triangle; d) a
centre of said triangle is coincident with a centre axis of
said axle; and e) the coupling between the axle and the
blade is exclusively provided by the matingly configured
outer contour of the axle and the centre hole of the blade
without the use of any expandable fasteners.
In accordance with the invention, the first object is
achieved with a saw axle of the kind defined in the
introduction which is characterized in that both the outer
contour of the axle and the contour of the blade-mounting
. CA 02216922 2000-02-17
2b
hole present three main sides for achieving statically
determined three-point contact between axle and blade.
As a result of this three-point contact, the blades will be
self-centred relative to their rotational axes while being
easily adjusted to desired positions in the longitudinal
direction of the axle. A three-sided axle constructed with
the invention is relatively easy to produce and treat.
The three Bides of the axle are suitably arcuate in shape,
e.g. circular-arcuate, with the centres of respective arcs
lying at the corners of an equilateral triangle.
CA 02216922 1997-09-29
W O 96131310 PCTlSE96I00441
3
According to one preferred embodiment, the three arcuat:e
sides merge together via arcuate parts whose radius of
curvature is smaller than the radius of curvature of the main
sides. Despite having three sides, an axle of this construe-
tion will have high mechanical strength while requiring th.e
r
provision of only relatively small holes in the saw blade,
meaning that the available useful saw radius of the blade
will be relatively large.
In a particularly preferred embodiment, the axle comprises
a core axle and a sleeve non-rotatably mounted thereon,
wherein the outer contour of said sleeve presents said three
main surfaces for coaction with corresponding main surfaces
of respective blade-mounting holes.
When renovating an axle of this construction, all that is
needed is to remove the sleeve from the axle and to send tha
sleeve to a workshop for re-grinding, if necessary.
The core axle and the inner surface of the sleeve ar~~
preferably circular in shape, wherein the sleeve is held
firmly to the axle with the aid of at least one clamping
joint. The sleeve may be provided with passageways through
which oil under pressure can be delivered to a space between
the core axle and the sleeve for separating the same in an
axial direction.
This thus facilitates fitting of the sleeve to the axle anc~
its removal therefrom, therewith also facilitating renovation
of the sleeve, among other things.
Other features of an inventive saw axle and an inventive saw
blade will be apparent from the following Claims.
The invention will now be described in more detail with.
reference to an exemplifying embodiment thereof and also with
reference to the accompanying drawings, in which
CA 02216922 1997-09-29
WO 96/31310 PCT/SE96/00447
4
Fig. 1 is a partially sectioned view of one embodiment of an
inventive axle comprised of a core axle and a surrounding
sleeve; s
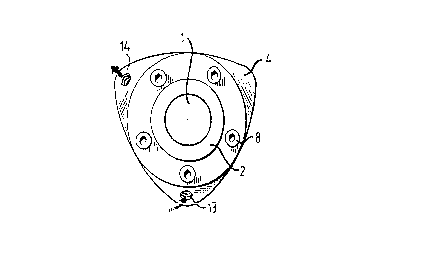
Fig. 2 is an end view ofl.the axl.e_ shown in Fig. l, as seen
in the direction of the arrows It-II; and
Fig. 3 illustrates an inventive saw blade which can be fitted
to the axle shown in Figs. 1 and 2.
Fig. 1 illustrates a core axle 1 having a conically tapering
end-part or trunnion 2 which is intended to be supported in
a bearing, not shown. The inner end 3 of the axle is rotat-
ably mounted in a saw frame (not shown) and driven in a
desired, conventional manner. The core axle is surrounded by
an outer axle sleeve 4 provided with a through-penetrating
bore for accommodating the core axle 1. The bore has a
circular cross-section of different diameters over different
parts in accordance with the different parts of the core axle
Z, which also has a circular cross-sectional shape.
As will be seen from Fig. 2, the outer contour of the sleeve
4 comprises three main sides which in the case of the
illustrated embodiment are comprised of circular-arcuate
surfaces whose centres are located at the corners of an
equilateral triangle located inwardly of the arcs. The
arcuate main Bides merge with one another via circular
arcuate parts of smaller radius of curvature, the centres of
said parts also lying at the corners of the equilateral
triangle.
One of the advantages afforded is that as a result of the
outer configuration of the sleeve, the stress concentrations
therein will be low and the fatigue strength of the sleeve
commensurately high. The use of such an outer profile for a
saw axle on which inventive saw blades 17 having a centre
hole 18 adapted to the profile of the sleeve (see Fig. 3) are
CA 02216922 1997-09-29
W O 96131310 PCTlSE96/00445'
floatingly-mounted provides significant advantages. As tree
axle and the mounting holes in the saw blades have three main
sides, the positions of the blades will always be statical7.y
determined as a result of said three-point contact. The saw
y 5 blades are thus self-centering around the rotational axiss.
The arcuate abutment surfaces o~ the axle and the blade:-
mounting hole respectively also results in successive contacts
over a longer distance than that achieved with conventional
splines. This results in a larger abutment and force-tran.-
mission surface and therewith less risk of grooves being worn
in the outer surface of the sleeve 4 among other things, such
grooves otherwise making it difficult to finely adjust the
settings of the blades, as mentioned above.
An axle according to the Fig. 1 embodiment also provides the
advantage that in the event of any damage, it is only
necessary to draw the sleeve 4 from the axle 1 and send the
sleeve to a workshop for renovation. The sleeve 4 is secured
to the core axle 1 to this end with the aid of a clamping
joint 5, which may be of any convenient, known kind. In the
illustrated case, the clamping joint includes two conical,
flanged sleeves 6, 7 which are displaced relative to one
another with the aid of tightening screws 8 which function
to tighten the sleeve 4 on the axle 1. The reference numeral
9 identifies a spacing ring which functions to prevent
undesirable movement between the various elements.
The sleeve 4 includes parts 10, 11 which have a centering
function in coaction with the core axle 1, wherein a certain
amount of clearance exists between the sleeve and the axle
along the part 12 intermediate of said centering parts 10,
11. The space provided by this clearance is connected to oil
inlet and oil outlet passageways 13 and 14 respectively,
wherein oil is also delivered through said space to a
circumferentially extending groove 15 via a passageway 1~
provided in the inner surface of the sleeve 4.
CA 02216922 1997-09-29
WO 96/31310 PCT/SE96/00447
6
When wishing to remove the sleeve from the core axle 4, e.g.
for renovating purposes, a pressure oil source is connected
to the passageway 13 and air is allowed to pass out through '
the passageway 14 at the same time. The pressure exerted by
the oil will cause the sleeve 4 to be pushed from the core
axle 1 to the right in Fig. 1.'The sleeve 4 can thus be
removed easily from the axle 1 with the axle left mounted in
the machine. Only the journal bearing coacting with the
trunnion 2 need be swung to one side. When the sleeve has
been renovated, the sleeve can be readily refitted to the
axle 1 and clamped firmly thereto with the aid of the
clamping joint 5. The invention thus simplifies renovation
of the axle and substantially reduces the costs entailed
thereby.
An axle that is constructed in accordance with the aforegoing
is easier to manufacture than conventional splined axles.
Scratches and the like can also be ground or polished away
and surface coatings applied more easily than in the case of
conventional splined axles, due to the smooth and even
surfaces of the inventive axle. The use of a three-sided axle
having rounded or cut corners provides the advantages of
static determined contact with the holes in the saw blades
while retaining the largest possible "useful" blade radius
to enable logs and blocks of large dimensions to be sawn. A
purely triangular shape would greatly reduce the maximum
sawing measurement.
The invention has been described in the aforegoing with
reference to a preferred embodiment thereof where the axle
comprises a core axle and a sleeve surrounding the axle. It ,
lies within the purview of the invention, however, to provide
a solid saw axle with the aforedescribed outer contour so as ,
to obtain the desired three-point contact and to dispense
with the use of a surrounding sleeve.
CA 02216922 1997-09-29
WO 96131310 PCT/SE96/0044'1
7
It will be understood that the sides of the three-sided
axle/sleeve may have a curvature other than a purely circular
curvature, as may also the transitions between the main sides
of the axle/sleeve. The use of rounded transitions between
A 5 said Bides, however, is~~advantageous from the aspect of
stress concentrations in comparison with abrupt transitions,
although such transitions are nevertheless conceivable. It
will also be understood that when a sleeve is used, the
manner in which the sleeve is held firmly on the core axle
and the forms of the coating parts may be varied as desired
without departing from the scope of the inventive concept.
The blade toothing may also be varied in accordance with the
use for which the blade is intended.