Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 PCT/DK96/00186
A conveyor device running on rails
The present invention concerns a rail-travelling conveyor
device to be advanced supported on two mutually parallel
rails and comprising a carrier frame, a load compartment
substantially firmly connected with the carrier frame,
said load compartment being arranged at least partly be-
low the rails, said load compartment having a maximum ex-
tent in the longitudinal direction of the rails, a plu-
rality of driving wheels engaging the rails, and at least
one motor which is connected with the conveyor device and
which drives at least one driving wheel. In this connec-
tion, "firmly" means that, when being advanced, the load
compartment is connected with the carrier frame in such a
manner that the location of its centre of gravity sub-
stantially cannot change with respect to the carrier
frame, i.e. the load compartment cannot pivot freely like
a pendulum.
Conveyor devices which travel on rails and are used e.g.
to feed viscous masses through production systems, are
generally known. The conveyor devices may be advanced
supported by rail systems, which comprise a single rail
or two rails extending mutually in parallel, and which
are either supported by columns or are suspended from an
overhead structure. The rail systems used may be provided
with upward gradients in the longitudinal direction, as
required, and may comprise curved track segments and
switches allowing the travelling direction of the con-
veyor devices to be changed.
Whether one rail system or another is selected for a
given production system usually depends on the occurring
loads from the conveyor devices and on the mutual loca-
tion of the production buildings. Further, the selection
may determined by the simplicity with which the load com-
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 PCT/DK96/00186
2
partments of the conveyor devices must be capable of be-
ing filled with the viscous mass. Particularly in connec-
tion with rail systems having two rails extending mutu-
ally in parallel, it is possible to fill the conveyor de-
vices from a position centrally above the load compart-
ment, without the access to the access opening of the
load compartment being blocked by a rail.
An example of a known conveyor device of the type de-
scribed in the opening paragraph has been manufactured by
the applicant. This known conveyor device is used par-
ticularly in production systems for the production of
cast concrete objects. In such production systems, the
casting of the concrete objects is usually performed in a
separate production building which is located at a dis-
tance from the production area where the wet concrete is
produced. It is thus necessary to be able to transport
the liquidconcrete rapidly and reliably from one loca-
tion to another, and this is expediently done by means of
the described, known conveyor device, whose load compart-
ment is filled at a filling station in the production
building.
However, with this known conveyor device which is ad-
vanced supported by two mutually parallel rails, special
measures have to be taken when the conveyor devices are
to travel through curves. For the conveyor device to
travel through curves and bends, the rotational shafts
are mounted so as to be rotatable also with respect to
the load compartment about a vertical axis, thereby
avoiding derailing of the conveyor devices in the bends. Thus, the conveyor
devices have conventionally been pro-
vided with two separate (two-wheeled) bogies arranged in front of and behind
the load compartment and connected
with the carrier.frame of the conveyor device by means of
a complicated pivot joint. A separate drive means in the
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 3 PCT/DK96/00186
form of a motor on the bogie has moreover been mounted in
order to propel the conveyor device. In situations where
it is necessary to connect all the driving wheels with a
drive means, it is thus necessary to mount a drive means
= 5 on each bogie.
The complicated pivot joint between the bogies and the
need for two separate drive means, however, have made the
production of the described conveyor devices difficult
and more expensive, and, accordingly, an object of the
present invention is to provide a simplified conveyor de-
vice, which must also be capable of being advanced
through bends without any risk of derailing. Further, the
conveyor device must also be capable of being produced at
a lower cost than the known conveyor devices and moreover
be cheaper to operate and maintain.
This is achieved according to the invention by means of a
conveyor device of the type described in the opening
paragraph, said conveyor device being characterized by
each driving wheel having a separate rotational shaft
connected with the carrier frame, said rotational shafts
having rotational axes fixed with respect to the carrier
frame, said rotational shafts being arranged within the
said maximum extent of the load compartment in the longi-
tudinal direction of the rails, and by guide means for
guiding the conveyor device through bends.
When the driving wheels are provided with separate rota-
tional shafts located within the said maximum extent of
the load compartment in the longitudinal direction, and
= when guide means are provided for guiding the conveyor
device through curves, while the rotational shafts have
~ rotational axes fixed with respect to the carrier frame,
it has surprisingly been found that -it is possible to
drive the conveyor devices through bends without any risk
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 PCT/DK96/00186
4
of derailing, with an uncomplicated and low-cost bearing
structure, while still providing unobstructed access to
the load compartment during filling. As the load compart-
ment is arranged at least partly below the rails, so that 5 the centre of
gravity is located below the driving
wheels, the conveyor device does not tend to tilt during
acceleration and deceleration. Thus, it is an essential
feature of the invention to avoid a structure with drive
shafts that extend between the rails and may thus inter-
fere with the filling of the load compartment or with the
storage of the viscous mass in the load compartment,
while still allowing the conveyor device to be driven
through bends.
The invention moreover allows the driving wheels to be
arranged close to each other in the longitudinal direc-
tion, so that the conveyor devices can follow the rails
in bends and curves with an even smaller risk of derail-
ing.
The invention provides special advantages when the load
compartment has an access opening, particularly a filling
opening, arranged at a position between and preferably
also above the rails, and optionally a discharge opening
disposed at a distance below the rails, as the filling
opening may preferably have the same dimensions as the
load compartment.
When, as stated in claim 3, the conveyor device is pro-
vided with respective drives extending at least partly
along respective longitudinal sides of the load compart-
ment, said respective drives connecting at least one re-
spective driving wheel with a drive means, it is possible
to connect the driving wheels with a single propelling
device which may be arranged in front of or behind the
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 PCT/DK96/00186
load compartment, and which has a drive take-off that may
extend to the longitudinal sides of the load compartment.
In a particularly expedient embodiment, the guide means
5 may moreover be arranged on the front and rear ends, re-
spectively, of the carrier frame with respect to the di-
rection of travel and may engage the rails to guide the
conveyor device through the curves.
In a further embodiment, the conveyor device may comprise
four driving wheels and support means arranged on the
front and rear ends, respectively, of the carrier frame
with respect to the travelling direction to prevent tilt-
ing of the conveyor device under special loads, as, in
that case, the support means will provide a support
against the rails. This embodiment is particularly expe-
dient in situations where the driving wheels are arranged
two and two above each rail with a relatively small mu-
tual spacing. It is also possible to use the support
means when just two driving wheels are used.
According to special embodiments of the invention, the
guide means and/or the support means may comprise a car-
rier element having two separate guide wheels and support
wheels, respectively, said carrier element itself being
mounted for rotation about an axis which extends perpen-
dicularly to the rotational axes of the driving wheels.
This enables the guide wheels and the support wheels to
yield when moving through bends. The respective carrier
elements may be arranged for rotation about a common
shaft in a particularly advantageous manner, thereby pro-
viding a particularly simplified structure.
It is moreover within the scope of the invention to ad-
vance the conveyor devices in engagement with rail sys-
tems, where the inner or the outer rails in the curves
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 PCT/DK96/00186
6
are provided with a coating of a material of low friction
on the travelling surfaces. Hereby, e.g. errors in the
travelling geometry may be avoided.
The invention will be described more fully below with
reference to a non-limiting embodiment shown in the draw-
ing. Fig. 1 schematically shows a known conveyor device, seen
in perspective view,
fig. 2 schematically shows a conveyor device according to
the invention, seen in perspective view,
fig. 3 is a front view of a carrier frame for a conveyor
device according to the invention, supported by two par-
allel rails,
fig. 4 is a top view of the carrier frame illustrated in
fig. 3,
fig. 5 is a lateral view of the carrier frame illustrated
in fig. 3,
fig. 6 is a lateral enlarged view of a carrier element
according to the invention,
fig. 7 schematically shows the conveyor device according
to the invention when travelling through a bend.
Fig. 1 schematically shows a known conveyor device 10,
which is marketed by the applicant. The conveyor device
is used particularly in production systems for producing
cast concrete objects and is advanced supported by two
mutually parallel rails 1, 2. The conveyor device com-
prises a carrier frame 8, which is firmly connected with
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 PCT/DK96/00186
7
a load compartment 5 having a first or upper opening lo-
cated in a plane above the rails, said load compartment
5, as indicated in broken line, extending at a distance
~ below the plane of the rails and being provided with a
second or lower opening (not shown), which may be
blocked, and which is used for emptying the load compart-
ment. The conveyor device is moreover provided with four
driving wheels 3 connected in pairs with rotational
shafts, which extend transversely between the rails, and
which are arranged in front of and behind the load com-
partment. To enable the conveyor device to travel through
bends and curves, each of the rotational shafts is
mounted forrotation with respect to the load compartment
5 about a vertical axis 6 so as to avoid derailing of the
conveyor devices in the bends. Basically, this results in
a structure with two separate bogies which are connected
with the carrier frame of the conveyor device by means of
a pivot joint 6. A separate drive means in the form of a
motor which drives the wheels, and a brake are mounted on
each bogie.
Fig. 2 schematically shows an embodiment of a conveyor
device 20 according to the invention. The conveyor device
travels on two parallel rails 21, 22, which may particu-
larly be formed as I profiles having an upwardly directed
engagement flange, which expediently forms a carrier face
for the driving wheels and support means described below.
The rails moreover have a web part which may expediently
form an engagement face for the guide means also de-
scribed below. As will appear, the conveyor device is
,
particularly expedient for use in connection with rail
systems having curved rail segments of the type shown in
fig. 2.
The conveyor device 20 is constructed with a carrier
frame 25 firmly connected with a load compartment 26,
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 PCT/DK96/00186
8
which has an upper filling opening and a lower discharge
opening 30 provided at a level below the rails. The con-
veyor device is used particularly expediently in systems
where viscous masses, such as liquid concrete in particu-
lar, are to be conveyed rapidly and reliably from one lo-
cation to another, said load compartment being filled from above at a filling
station and emptied at an empty-
ing station located at e.g. floor level below the load
compartment and between the rails. The shown load com-
partment 26 has an extent L in the longitudinal direction
of the rails and may optionally be provided with parti-
tions (not shown) which divide the load compartment into
independent cells. The conveyor device is additionally
provided with four driving wheels 36, of which only two
are shown in the figure, and which, in pairs, engage the
upper flange of a respective rail 21, 22. The driving
wheels may advantageously be constructed as rubber
wheels, as the deformation of the rubber material facili-
tates the travel of the conveyor device through curves.
To ensure free access from above to the load compartment,
each driving wheel has a separate rotational shaft, which
is mounted on the carrier frame 25, and which extends on
the outer side of the boundary walls of the load compart-
ment 26. The rotational shafts are fixed with respect to
the carrier frame, in the sense that the driving wheels
cannot be steered to provide a change in the direction of
travel of the conveyor device. It is an essential feature
of the invention that the driving wheels 36 are arranged
along the extent L of the load compartment 26, preferably
relatively close to the line of symmetry at L/2, so that
only a limited displacement of the wheels transversely to ~
the rails will take place in bends, thereby obviating de-
railing of the conveyor device when it travels through
the curve shown. The carrier frame 25 moreover mounts a
drive motor (drive means) 35 connected by means of suit-
able drives with the driving wheels to drive these.
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 PCT/DK96/00186
9
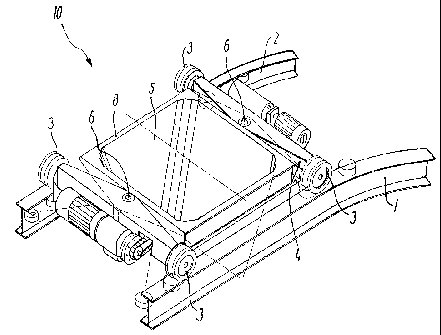
Reference is now made to figs. 3-5 which show an embodi-
ment of a carrier frame 25 for the conveyor device of the
invention in greater detail. The carrier frame is com-
posed of two parallel and longitudinal beams 28 and de-
fine a rectangular area in which a load compartment may
be mounted. For clarity, the load compartment is not
shown, but it will be appreciated that a load compartment
is preferably firmly connected with the carrier frame 25
between the beams 27, 28 to be arranged at least partly
below the rails 21, 22, as the load compartment 25 is to
be filled from above from a position between the rails. A
propelling motor 35 is mounted on one of the transverse
beams 28 of the carrier frame. As mentioned above, two
mutually spaced driving wheels 36 are mounted along each
of the longitudinal beams 27, and, according to the in-
vention, these driving wheels have individual, separate
rotational shafts 37 which are mounted on the beams.
As appears from fig. 5 in particular, the propelling mo-
tor 35 is connected to the driving wheels by means of re-
spective drives 39, each drive extending at least partly
along an associated longitudinal beam 27. It is hereby
possible to drive the conveyor device by means of a
single propelling motor which can drive all the driving
wheels, while the conveyor device may be advanced through
curves by guide means 40, which are preferably arranged
on the front and rear ends, respectively, of the carrier
frame 25 with respect to the direction of travel at a
distance from the driving wheels, and which can engage
the vertical web part of each rail 21, 22. Preferably,
drives are provided along both longitudinal beams so that
all driving wheels may be driven, but in some situations
it may be relevant not to drive all the drawing wheels.
Each guide means 40 may engage a rail either directly or
indirectly and comprises a carrier element 44 in the ex-
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 PCT/DK96/00186
ample shown. The carrier element 44, shown in greater de-
tail in fig. 6, carries a pair of rotatable guide wheels
40', 40" and is rotatable itself with respect to the car-
rier frame about a vertical axis 42.
5
To ensure that the conveyor device does not tilt during e.g. fast
accelerations or decelerations in those cases
where the driving wheels are arranged very close to each
other on each longitudinal beam 27, the carrier f.rame is
10 moreover provided with support means 46, which are like-
wise arranged on the front and rear ends, respectively,
of the carrier frame with respect to the direction of
travel. Like in the example shown, the support means 46
may be formed by a carrier element 47, which carries a
pair of rotatable support wheels 46', 46", and which is
rotatable with respect to the carrier frame about the
said, vertical axis 42. As will be seen from fig. 6, the
carrier element 47 of the support means 46 may be con-
nected with the carrier element 44 of the guide means 40
by a connecting part 100, which results in a quite simple
structure. As appears from fig. 3 in particular, the con-
necting part 100 is angled. The carrier elements 44, 47
and the connecting part 100 are connected with a pipe
section 105, which is received in a bushing 110 mounted
on the carrier frame. A spring device 120 is received be-
tween an end face 115 in the bushing and an engagement
face in the pipe section to provide for spring cushioning
of the conveyor device and to allow unobstructed movement
of said device through upward and downward gradients
along the path of travel. The pipe section 105 can rotate
about the vertical axis 42 by means of a pin connection
130.
.
Fig. 7 schematically shows a conveyor device according to
the invention when travelling through a bend. In the fig-
ure the rails 21, 22 are just illustrated with their web
CA 02217881 1997-10-09
WO 96/33897 PCT/DK96/00186
11
part. As appears, the guide wheels 40 engage the outer
rail 22, thereby guiding the conveyor device through the
bend, as the driving wheels 36 will be displaced slightly
transversely to the upper horizontal flange of the rail.
To minimize motion of the conveyor device transversely to
the rails in the bend, the web part of the internal rail
22 has welded thereon a supplementary flange part, which
is so adapted that also the internal guide wheels engage
the rail. This results in extremely reliable travel of
the conveyor device through the bend. As appears, the
carrier elements 44 will adjust themselves tangentially
to the rails at any time.
EXAMPLE
The conveyor device shown in fig. 2 was constructed with
a frame having a length dimension L of 2200 mm and a
transverse dimension of 2000 mm. The load compartment 26,
which was connected with the frame, had an opening at the
upper side of the frame with a length dimension of 1500
mm and a transverse dimension of 1500 mm, and extended at
a distance of 1100 mm below the rails and was provided
with a discharge opening at this location. The conveyor
device was advanced on rails by means of two pairs of
driving wheels 36, each pair of driving wheels being ad-
vanced on the upper flange of a respective rail. The
driving wheels had a diameter of 320 mm and were mounted
with a mutual centre distance (shaft distance) of 500 mm
on each side of the line of symmetry of the frame.