Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent: | (11) CA 2219925 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | ANTENNA ELEMENT FOR TWO ORTHOGONAL POLARIZATIONS |
| (54) French Title: | ELEMENT D'ANTENNE DONNANT DEUX POLARISATIONS ORTHOGONALES |
| Status: | Term Expired - Post Grant Beyond Limit |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | MARKS & CLERK |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | 2006-03-14 |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 1996-04-29 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 1996-11-07 |
| Examination requested: | 2003-03-26 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/SE1996/000561 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | SE1996000561 |
| (85) National Entry: | 1997-10-30 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
An antenna element intended for transmission and
reception of orthogonal polarisations having a good
polarisation purity of electromagnetic radiation is
described. It comprises a ground plane and at least one
radiation disc connected to two ports for the supply of a
desired electromagnetic radiation, preferably in the
microwave range. The distance between the ground plane and
the radiation disc is a fraction of the wavelength .lambda. of the
radiation. The antenna element is in particular
characterized in that the ports are located at an electric
distance of 90° from each other and that a quarterwave
transformer is added between the ground plane and the
radiation disc that is shaped so that the transmission line
impedance between the ports is reduced in order to make the
ports radiationally independent of each other.
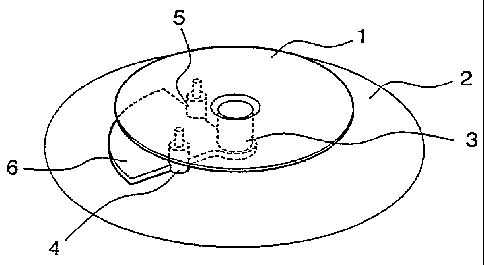
La présente invention concerne un élément d'antenne conçu pour l'émission et la réception de polarisations orthogonales avec une bonne pureté de polarisation du rayonnement électromagnétique. L'élément comprend un plan de sol (2) et au moins un disque de rayonnement (1) connectés à deux orifices (4, 5) fournissant un rayonnement électromagnétique, de préférence dans la gamme des micro-ondes. La distance entre le plan de sol (2) et le disque de rayonnement (1) est une fraction de la longueur d'onde lambda du rayonnement. Cet élément d'antenne est notamment caractérisé par une position des orifices (4, 5) comportant entre eux un écart électrique de 90 DEG , et l'adjonction d'un transformateur quart-d'onde (6) entre le plan de sol (2) et le disque de rayonnement (1), lequel transformateur est configuré de façon que l'impédance propre à la ligne de transmission entre les orifices (4, 5) est réduite, ce qui permet de rendre les orifices indépendants l'un de l'autre en matière de rayonnement.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Inactive: Expired (new Act pat) | 2016-04-29 |
| Letter Sent | 2009-06-19 |
| Inactive: Multiple transfers | 2009-05-08 |
| Letter Sent | 2008-11-21 |
| Grant by Issuance | 2006-03-14 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2006-03-13 |
| Pre-grant | 2005-12-20 |
| Inactive: Final fee received | 2005-12-20 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 2005-07-13 |
| Letter Sent | 2005-07-13 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 2005-07-13 |
| Inactive: IPC removed | 2005-06-06 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2005-06-06 |
| Inactive: Approved for allowance (AFA) | 2005-05-27 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2005-03-24 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2004-09-27 |
| Letter Sent | 2003-04-23 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 2003-03-26 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 2003-03-26 |
| Request for Examination Received | 2003-03-26 |
| Inactive: Single transfer | 1998-03-20 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 1998-02-10 |
| Classification Modified | 1998-02-10 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1998-02-10 |
| Inactive: Courtesy letter - Evidence | 1998-02-03 |
| Inactive: Notice - National entry - No RFE | 1998-01-28 |
| Application Received - PCT | 1998-01-26 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 1996-11-07 |
There is no abandonment history.
The last payment was received on 2005-03-17
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Patent fees are adjusted on the 1st of January every year. The amounts above are the current amounts if received by December 31 of the current year.
Please refer to the CIPO
Patent Fees
web page to see all current fee amounts.
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| RUAG AEROSPACE SWEDEN AB |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| ULF JOSTELL |