Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2221829 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | METHOD FOR PROTECTING SOFTWARE |
| (54) French Title: | METHODE DE PROTECTION DE LOGICIELS |
| Status: | Deemed Abandoned and Beyond the Period of Reinstatement - Pending Response to Notice of Disregarded Communication |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | SMART & BIGGAR LP |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (22) Filed Date: | 1997-11-21 |
| (41) Open to Public Inspection: | 1998-05-22 |
| Examination requested: | 1997-11-21 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | No |
|---|
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
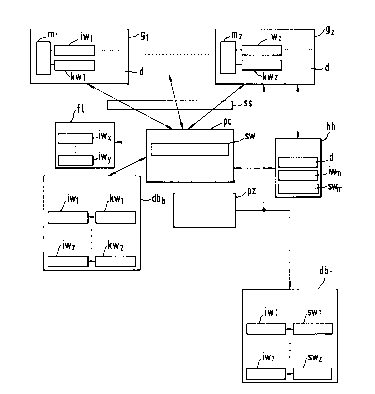
For safe-guarding that a software package produced by a
manufacturer can be used only by someone acquiring it
together with an individual device ((g1;gz) of the same
manufacturer and for inhibiting the device owner to acquire
further devices of the same type without assuming the
obligation of also having to acquire the software package
which is necessary for each further device, the following
software protecting method is disclosed: The software (sw)
is installed in a computer (pc) of the owner. Each device
(g1;gz) is assigned by the manufacturer an individual
identification word (iw1;iwz) which differs from the respective
identification words of all the other devices. This word is
stored in a nonvolatile memory (m1;mz) of the device. By
means of a processor (pz), a key word (kw1;kwz) is formed
by the manufacturer from the identification word (iw1;iwz)
using an encryption algorithm and the key word is stored in
the memory (m1;mz) of the device. The identification words
are listed, together with the associated key word, in a
database (dbb) of the device owner and in a database (dbh)
of the software manufacturer. Whenever one of the devices
is started up the software checks, whether the identification
word stored in its memory is present in the owner database
and, if so, whether the key word associated with this
identification word is present in the owner database,
if the identification word is not present therein, whether
a correct key word is stored in the device memory. If so,
the software stores the key word and the associated
identification word in the owner database and enables the
electronic control of the device. If not so, the software
creates an error list of those identification words with
which an incorrect key word is associated and does not
enable the electronic control of the device.
L'invention est une méthode de protection de logiciels servant à garantir qu'un progiciel produit par un constructeur donné ne puisse être utilisé par quelqu'un qui en aurait fait l'acquisition avec un dispositif particulier (g1;gz) du même constructeur, et à empêcher le propriétaire de ce dispositif d'acquérir d'autres dispositifs du même type sans faire l'acquisition du progiciel pour chacun de ces autres dispositifs. Dans cette méthode, le logiciel (sw) est installé sur l'ordinateur (PC) du propriétaire. Le constructeur attribue à chaque dispositif (g1;gz) un mot d'identification particulier (iw1;iwz). Ce mot est conservé dans une mémoire non volatile (m1;mz) incorporée au dispositif. En utilisant un processeur (pz), le constructeur forme un mot clé (kw1;kwz) à partir du mot d'identification (iw1;iwz) en se servant d'un algorithme de chiffrement et ce mot clé est stocké dans la mémoire (m1;mz) du dispositif. Les mots d'identification sont listés avec les mots clés connexes dans une base de données (dbb) du propriétaire du dispositif et dans une base de données (dbh) du constructeur du logiciel. Quand l'un des dispositifs est mis en fonction, le logiciel vérifie si le mot d'identification stocké dans sa mémoire se trouve dans la base de données du propriétaire et, si tel est le cas, si le mot clé connexe est présent dans cette même base de données; si le mot clé connexe ne s'y trouve pas, le logiciel vérifie si le mot clé approprié se trouve dans la mémoire du dispositif. Si tel est le cas, le logiciel stocke ce mot clé et le mot d'identification connexe dans la base de données du propriétaire et valide le contrôleur électronique du dispositif. Si le mot clé ne se trouve pas dans la mémoire, le logiciel dresse la liste des mots d'identification auxquels un mot clé incorrect est associé et ne valide pas le contrôleur électronique du dispositif.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Inactive: IPC expired | 2013-01-01 |
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Application Not Reinstated by Deadline | 2001-01-19 |
| Inactive: Dead - No reply to s.30(2) Rules requisition | 2001-01-19 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2000-11-21 |
| Inactive: Abandoned - No reply to s.30(2) Rules requisition | 2000-01-19 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 1999-10-19 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 1998-05-22 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1998-03-27 |
| Classification Modified | 1998-03-27 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 1998-03-27 |
| Filing Requirements Determined Compliant | 1998-02-12 |
| Letter Sent | 1998-02-12 |
| Inactive: Filing certificate - RFE (English) | 1998-02-12 |
| Application Received - Regular National | 1998-02-11 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 1997-11-21 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 1997-11-21 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2000-11-21 |
The last payment was received on 1999-07-21
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Please refer to the CIPO Patent Fees web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application fee - standard | 1997-11-21 | ||
| Registration of a document | 1997-11-21 | ||
| Request for examination - standard | 1997-11-21 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - standard | 02 | 1999-11-22 | 1999-07-21 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| ENDRESS + HAUSER WETZER GMBH + CO. KG |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| ALFRED UMKEHRER |