Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 022330~4 1998-03-24
INJECIION-FOAMED PRODUCT AND MANUFACI~URING l\lETHOD THE~EOF
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an injection-foamed product having a
different material portion and a manufacturing method thereof
An injection-foaming method comprises steps of filling up a mixture
of resin such as ethylene vinylacetate copolymer (EVA) and a foamin g agent
in a cavity having a desired shape which is formed in a mold, maintainin,
the mixture in the cavity at about 170-190~ C for about 6-10 minutes and
then opening the mold to obtain an inJection-foamed product which is
expanded by 30% or more compared with the size of the cavity by the
expansion of foaming gas from the foaming agent. The injection-foaming
method, which has been developed recently, is not yet prevailing. Howe\,-er,
since the injection-foaming, method can promptly and easily provide a foamed
product having various shapes and properties, the application thereof is
expected to be widely extended.
The injection-foamed product is actively employed as parts for shoes,
particularly sports shoes, such as a mid-sole and an out-sole. Recently, an
integral sole for shoes has been developed in the shape of the
injection-foamed product.
ln conventional sports shoes, an out-sole of rubber is attached onto
the lower surface of a mid-sole of a foaming material such as polyurethane,
as disclosed in U. S. Patent No. 4,245,406. However, the above-described
injection-foaming method can form the mid-sole and the out-sole into one
integral piece, thereby to reduce the weight of the product and increase the
productivity, resulting in decreasing a manul'acturin~ cost.
CA 022330S4 1998-03-24
However, in the injection-foaming method, since the material is
supplied into a cavity of a mold in a fluid state and undergoes a
cross-linking reaction for a predetermined time to obtain the injection-foamed
product, the fluid material has inevitably homogeneous. Therefore, the
product is generally monotonous in properties such as color, density and
hardness thereof. Further, the injection-foamed substance is typically inferior
to a injection-molded substance or rubber in anti-abrasiveness. In these
respects, it will be preferable if the injection-foaming method can provide an
injection-foamed product having at least a different material portion to obtain
different colors, densities or hardnesses.
SUMMARY OF THE IN~,TENTION
It is an object of the present invention to provide an injection-foamed
product having a different material portion and a manufacturing method
thereof.
To accomplish the above object, there is provided a method for
manufacturing an injection-foamed product having a different material portion,
comprising the steps of: preparing a main material mixture containing a
main resin and a foaming agent; preforming an auxiliary material piece
containing an auxiliary resin which can cross-link with the main resin and
having a property different from a property of the main material mixture;
forming an auxiliary cavity region in a cavity of a mold for
injection-foaming; placinl the auxiliary material piece in the auxiliary cavity
region; filling up the main material mixture in a fluid state in the cavity;
maintaining the main material mixture and the auxiliary material piece in the
cavity under a predetermined temperature and pressure for a predetermined
- 2
CA 022330~4 1998-03-24
time, and opening the mold to obtain the injection-foamed product.
It is preferable that the main material mixture and the auxiliary
material piece have the same resin and are different from each other in at
least one of color, density and hardness. The same resin may preferably be
EVA.
Here, the auxiliary material piece may further contain the foaming
agent and is preformed at a temperature lovver than a foaming temperature of
the foaming agent.
To accomplish the above object, there is also provided an
injection-foamed product having a different material portion manufactured
according to the following method: preparing a main material mixture
containing a main resin and a foaming agent; preforming an auxiliary
material piece containin~ an auxiliary resin which can cross-link with the
main resin and having a property different from a property of the main
material mixture; .forming an auxiliary cavity re~ion in a cavity of a mold
for injection-foaming; placing the auxiliary material piece in the auxiliary
cavity region; filling up the main material mixture in a fluid state in the
cavity; maintaining the main material mixture and the auxiliary material
piece in the cavity under a predetermined temperature and pressure for a
predetermined time; and opening the mold to obtain the injection-formed
product.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The above object and advantage of the present invention will become
apparent by describing in detail a preferred embodiment thereof vvith reference
to the accompanying drawiny,s in which:
CA 022330S4 1998-03-24
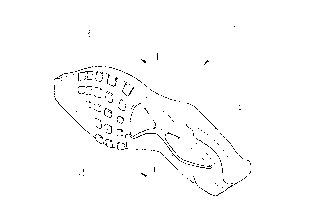
Fig. 1 shows a perspective view of a sole for shoes as one
application of an injection-foamed product according to the present invention,
Fig. 2 shows a sectional view taken along a line II-II in Fig. l;
Fig. 3 shows a sectional view of a mold for explaining an
injection-foamed product manufacturing method according to the present
invention;
Fi~,. 4 shows a plan view of a lower die in Fig. 3; and
Figs. 5 to 7 show sectional views of the mold in Fig. 3, for
sequetltially explaining the method accordin~, to the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTlON OF THE INVENTION
Referring to Figs. I and 2, a sole 1, for example, for sports shoes as
one application of an injection-foamed product having different material
portions according to the present invention has an integral shape in contrast
to the conventional sports shoes in which a mid-sole and an out-sole are
separately formed.
The sole I includes a main material portion 2 occupying most of the
sole I and f rst and second auxiliary material portions 3 and 4 occupying a
part of the lower surface of the sole 1. The main material portion 2 and the
first and second auxiliary material portions 3 and 4 contain resin materials
which can cross-link with each other under a predetermined condition. It is
preferable that the resin materials are identical with each other. Preferably,
one of polyurethane, polystyrene, EVA, PVC and TPR (thermoplastic rubber),
particularly EVA may be used for the resin materials.
The main material portion 2 and the first and second auxi]iary
material portions 3 and 4 may have different densities, hardnesses, elasticities
CA 022330~4 1998-03-24
or colors by adjusting contents and kinds of foaming agents or additives
contained in the main and auxiliary materials. For example, an auxiliary
material portion having higher anti-abrasiveness, density or hardness than the
main material portion can be applied to a heel region of a sole. Auxiliary
material portions having different colors allow a injection-foamed product to
be designed with two-tone or multi-tone color.
Fi~g. 3 shows a sectional view of a mold 10 for forming the sole ]
having the auxiliary material portions 3 and 4 and Fig. 4 is a plan view of a
lower die in Fig. 3. Here, the shape of a cavity 13 formed in the mo]d 10
is simplil'ied as compared with the sole I shown in Fig. 1, for convenience
of description.
The mold 10 includes a lower die 12 formed with the cavity 13 at
an upper surface thereof, and an upper die 14 for coverin(l' the cavity 13..
The lovver and upper dies 12 and 14 moves toward and away from each
other by a driving means (not shown) to close and open the cavity 13.
Referring to Figs. 3 and 4, in the cavity 13 of the lower die 12, frst
and second auxiliary cavity regions 15 and 17 are formed for forming the
first and second auxiliary material portions 3 and 4 of the sole 1. The
auxiliary cavity regions 15 and 17 are partitioned by respective partitioning
walls 16 and 18, which protrude upward from the bottom of the cavity 13,
from the residual cavity region. A main material runner 21 is formed at the
lower die 12 to connect a main material inlet 20 to the inside of the cavity
13. The main material supplied to the main material inlet 20 can flow
through the main material runner 21 into the cavity ]3
A manufacturing method of the sole I having the different material
portions will be hereinafter described with reference to Fj J,C~ 5 to 7
CA 022330~4 1998-03-24
First of all, a main material mixture for the main material region 2 is
prepared. The main material mixture contains a resin as a main ingredient
and a foaming agent. The resin can be selected from one of polyurethane,
polystyrene, EVA, PVC and TPR.
Auxiliary material pieces for the auxiliary material portions 3 and 4
are preformed in a solid state. The auxiliary material pieces contain a resin
as a main ingredient which can easily cross-link with, prel'erably is identical
with, the resin of the main material mixture. Particularly EVA is most
preferable for the main ingredients of the main material mixture and auxiliary
material pieces.
The material for the auxiliary material pieces may contain a foaming
agent. In this case, the auxiliary material pieces must be formed at a
temperature lower than an active temperature of the foaming agent to be
foamed in the cavity 13 of the mold l O together with the main material
mixture. The main material mixture is different from the auxiliary material
pieces in the content of the foaming agent or in the kind of the additives
contained therein, so that the fabricated sole 1 has the auxiliary material
portions with densities, hardnesses or colors different from those of the main
material portion.
In a state that the upper die 14 have moved away from the lower die
12 to open the cavity 13, the preformed auxiliary material pieces 3a and 4a
for the first and second auxiliary material portions 3 and 4 are placed in the
first and second auxiliary cavity regions ] 5 and 17, respectively. Then, the
upper die 14 descends to close the cavity 13, as shown in Fig S. After the
cavity 13 of the lower die 12 is closed by the upper die 14, the main
material mixture is supplied into the cavity ] 3 throu~h the main material
CA 022330~4 1998-03-24
runner 21 to f111 up the cavity 13, as shown in Fig. 6.
The main material mixture and the auxiliary material pieces 3a and 4a
are maintained together in the cavity 13 at about 170-1 90~ C for about 6-10
minutes. The main material mixture cross-links internally. Also, boundary
surfaces of the auxiliary material pieces 3a and 4a with respect to the main
material mixture are activated and the cross-linking reaction occurs between
the main material mixture and the boundary surfaces and to integrally
incorporate the main material and the auxiliary material pieces 3a and 4a.
After a predetermined time, the upper die 14 ascends by the driving
means to open the cavity 13. At this time, the integrally incorporated
materials rapidly expand by the expansion of foaming gas from the forming
agents in the materials and escape from the cavity 13 to form the sole 1, as
shown in Fig. 7. The thus-formed sole 1 passes through a process such as a
trimming to be formed into a completed product. The completed sole 1
includes the main material portion 2 and the first and second auxiliary
material portions 3 and 4, which are different from each other in colors,
densities or hardnesses according to the selection of the composition of the
auxiliary material pieces 3a and 4a.
As described above, according to the manufacturing method of the
present invention, injection-foamed products having different portions with
various properties such as color, density and hardness can be easily and
eff1ciently obtained in a single mold.