Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
INPROVED WEATHERPROOFING FOR SHEET METAL ROOFING
INTRODUCTION
The present invention relates to sheet metal roofing;
and, more particularly, is concerned with preparing
composite-coated flat-rolled mild steel and fabricating
unitary roof covering structures whlch contribute
lightweight, durable and weathertight roof protection.
SU~ RY OF THE IN~JENTION
Preparation of flat-rolled steel substrate includes
selecting thickness gauge, developing mechanical properties
for desired strength while enabling fabrication, surface
corrosion protection, and can include embossing and
decorative coating prior to fabrication into unitary roof
covering structures. Such selection, preparation and
fabrication provides:
i. for ease of roofing assembly,
ii. resistance to surface corrosion,
iii. an interfitting arrangement which resists
subsurface entry of liquids from climatic
--1--
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
precipitation, along with
iv. a tortuous path for subsurface circulation
of air which is free of liquids from climatic
precipitation, and
v. a rigid high-strength roofing assembly with
provisions for reception of accessories which enhance
installation or roof operating efficiency.
The above and other advantages and contributions are
considered in more detail during the description of
specific embodiments of the invention, presented with
references to the accompanying drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
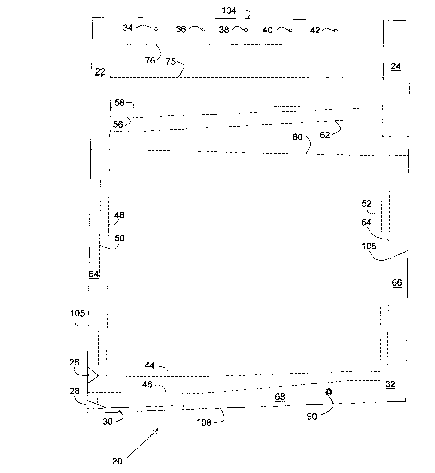
FIG. 1 is an outer-surface plan view of a unitary
blank, as cut from continuous strip after being prepared to
provide surface protection and desired mechanical
properties, and showing line markings for carrying out
fabrication of a- unitary roof covering structure of the
invention;
FIG. 2 is a plan view of the embodiment of FIG. 1 for
describing cutting away portions of such blank in
accordance with the invention;
FIG. 3 is an outer-surface plan view. of a roof
covering structure fabricated in accordance with the
lnventlon;
FIG. 4 is an enlarged cross-sectional view, taken
along line 4-4 of FIG. 3, for describing folding over sheet
metal portions forming vertically-extending slots for
interfitting roof covering structures along lateral sides
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
of a viewable ~tab~ portion of those structures, during
assembly of a horizontally-oriented course in accordance
with the invention;
FIG. 5 is an enlarged cross-sectional view for
describing folded-over sheet metal portions forming
interfitting slots, which extend horizontally above and
below a viewable "tab" portion and are used for vertical
direction assembly and horizontal alignment of unitary roof
covering structures of the invention, such view being taken
along line 5-5 of FIG. 3;
FIG. 6 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of such
interfitting slots of FIG. 5, as shown along line 6-6 of
FIG. 3;
FIG. 7 is an outer-surface plan view of a pair of
unitary roof covering structures of the invention for
describing a side-by-side interlocking relationship of such
structures along a horizontally-oriented course;
FIG. 8 is an outer-surface plan view for depicting a
staggered relationship of interfitting edge portions during
assembly of a second course of roof covering structures,
located next-adjacent vertically of the horizontally-
oriented course of FIG. 7, in accordance with the
invention;
FIG. 9 is an enlarged cross-sectional view, taken
along the line 9-9 of FIG. 8, for describing interfitting
assembly of a pair of such unitary structures, positioned
in vertically-adjacent relationship, in accordance with the
invention;
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
.
FIG. 10 is an enlarged cross-sectional partial view,
taken along line 10-10 of FIG. 7, for describing
interfitting lateral edges of a pair of such unitary
structures, as assembled along a horizontally-oriented
S course, in accordance with the invention;
FIG. 11 is an enlarged cross-sectional partial view of
such pair of unitary roof covering structures approaching
such interfitting, shown in FIG. 10, for describing
dimensional provisions made during fabrication for ease of
assembly in accordance with the invention;
FIG. 12 is a cross-sectional view of a pair of such
unitary roof covering structures, taken along the line 12-
12 of FIG. 8, for describing a feature of the invention
which facilitates desired assembly of those structures, in
accordance with the invention;
FIG. 13 is a cross-sectional view of such pair of
unitary structures, taken along the line 13-13 of FIG. 8,
for describing verti.cal assembly of roof covering
structures and provisions for attaching accessories in
accordance with the invention, and
FIG. 14 is a perspective view of a unitary roof
covering structure of the invention in the form of a panel
in which the viewable portion presents the appearance of a
plurality of individual "tabs" or shingles.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
Sheet metal of prepared thickness gauge and mechanical
properties for fabricating unitary roof covering structures
is composite-coated. Blanking, cutting and folding steps
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
of the invention contribute interfitting slots which are
weathertight and easily assembledi and the interfitting
slots, as fabricated and assembled, provide for subsurface
air circulation while creating a barrier to subsurface
entry of liquids from climatic precipitation.
The unitary roof covering structures of the invention
can be fabricated to present a single viewable "tab" (which
is often referred to as the "shingle" after roofing is
installed), or as unitary panels each providing the
appearance of a plurality of individual tabs (or shingles).
Such panels are joined and interfitted along four linear
edges of the panel, in the same manner as a single viewable
"tab" embodiment of the invention is interfitted, and each
provides the same weathertight features.
Flat-rolled mild steel is selected in a thickness
gauge range of about .01" to about .03" for economy,
impact-resistance, and control of tensile strength and
ductility for embossing and fabrication. Such steel is
selectively work-hardened by cold-rolling to provide
desired tensile strength and hardness while maintaining
desired fabricating properties.
Surface coatings are selected which protect against
surface corrosion so as to maintain structural integrity
and to maintain surface appearance characteristics over
extended time periods. Significant reductions in roofing
weight, when compared to commercially available asphalt
roofing materials, are provided; for example, the weight of
a square (10 ft. x 10 ft.) using the invention with .020"
--5--
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
thickness gauge steel (.020") is approximately 113 pounds;
whereas, a "three tab - 25 year guarantee" asphalt-based
roof covering for such a square has a weight of
approximately 238 pounds.
Inorganic corrosion protection for the flat-rolled
steel surface is selected from the group consisting of
aluminum, copper, hot-dipped tin/zinc alloys, hot-dipped
galvanized (including Galfan~ and Galvalume~, available
from Weirton Steel Corp., Weirton, WV 26062), Tin Mill
coatings such as electrolytic tin, zinc, TFS or chrome-
oxide, and metal coatings applied to mild steel by
particulate metal-spray coating, as disclosed in copending
and co-owned U.S. Patent -Application (Serial No.
60/053,787), filed July 25, 1997, entitled "Metal Spray-
Coated Flat-Rolled Mild Steel And Its Manufacture."
Chemical passivating treatment of flat-rolled steel
surface, or of a coating metal surface, is selectively
carried out to enhance adhesion of a paint or polymeric
finish which is selected for decorative and color purposes
for certain of the corrosion-protective metal coatings.
Polymeric coating application methods-are selected from the
group consisting of polymers in a solvent carrier, solid
polymers applied as a powder or laminate, extruded
polymers, or other suitable methods for applying a
substantially uniform thickness polymer coat to corrosion-
protected flat-rolled steel.
Embossing of the sheet metal, or at least an exposed
"tab" portion, of a unitary roof covering structure of the
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
invention helps to compensate for temperature-related
expansion and contraction of the flat-rolled steel
substrate. Acceptable embossed appearance features are
shown in co-owned and copending U.S. Design Patent
Applications 29/067,466 and 29/067,465, filed March 4,
1997, which are incorporated herein by reference; however,
the present invention is not limited to those embossing
designs.
Unitary sheet metal blanks for a single viewable tab
embodiment, or for a panel embodiment with the appearance
of multiple individual tabs, can be cut from continuous
strip composite-coated flat-rolled steel. To facilitate
fabrication, selective embossing and a limited number of
steps (as indicated in the fabrication process) can be
carried out while the sheet metal is in continuous-strip
form.
In the above and following description of roof
covering structures of the invention, directional
references, such as vertical or horizontal, find their
basis in relation to directions for making an installation,
along an inclined support surface for receiving a roof
covering. Unitary roof covering structures of the
invention are located side-by-side to form a horizontally-
oriented course; and, such courses are assembled, one above
the other, in a vertical direction, from rain gutter level
of such inclined surface toward the apex (or "ridge")
thereof. Such directional orientations are also used in
describing the unitary roof covering structures of the
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
invention.
Unitary sheet metal blank 20 of FIG. 1 has a generally
rectangular configuration along its upper perimeter, with
a trapezoidal configuration along its lower perimeter. Use
of that trapezoidal configuration enables the roof covering
structures to be fabricated to provide barriers to entry of
liquid from climatic precipitation, and to provide for
interfitting in a manner such that viewable portions
(single "tab" or multiple tabs in a panel) of such
structures present a horizontal appearance in an assembled
roof.
Assembly of horizontally-oriented courses is shown and
described from left to right. Provision for assembly in
the opposite direction (right to left) can be provided
based on present teachings. The lateral sides of a unitary
roof covering structure are fabricated to be parallel to
each other.
In order to prevent access of subsurface liquid, an
added fold-over layer of sheet metal is located to act as
a barrier to liquid entry at the distal ends of
horizontally-extending slots. Also, air access is
provided, as described in more detail later herein.
During fabrication, those portions of unitary blank 20
which are to be cut away are shown as solid lines in FIG.
1; and locations for folding over of sheet metal are
indicated by interrupted lines. At the latter locations,
the sheet metal is folded over to form linearly-extended
slotted openings (slots), contiguous to each linear
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
dimension of a generally rectangular viewable tab, for
interfitting roof covering structures with adjacent roof
covering structures located both horizontally and
vertically.
In FIG. 1, right-angle corner portions 22, 24, near
the upper portion of the blank are outlined in solid lines
and are cut away. Angled sections 26, 28, at the lower
left portion of the blank, lower edge section 30, and
trapezoidally-shaped corner portion 32, shown in solid
lines, are also cut away. Further, apertures 34-42, near
the upper edge of the blank, are formed prior to folding
over sheet metal during fabrication of a unitary roof
covering structure.
Cutting away steps, forming of such apertures, and
selective embossing can be carried out while composite-
coated f-lat rolled steel is in continuous-strip form, which
facilitates fabrication of production quantities.
The trapezoidal configuration is introduced along the
lower edge of unitary blank 20 of FIG. l; and, has its
effect above that perimeter.
Dimensions of a specific embodiment of the invention,
included below, contribute to the description and
understanding of functions achieved by use of the
trapezoidal shape.
Vertically-adjacent interrupted lines, which are shown
in pairs in FIG. 1, provide for folding over of sheet metal
during fabrication to form an elongated slot which is
accessible along its opening for interfitting with a slot
_ g _
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
of an adjacent structure during asse~bly. After folding
over of sheet metal along such pairs of interrupted lines,
to form a slot, the closed end of the slot has a
substantially semicircular, or arcuate, shape in cross
section.
As located, that semicircular shape helps to define the
portion of the unitary structure, referred to as the
viewable tab portion, which remains in view after assembly.
Such pairs of interrupted lines are indicated as 44
and 46 (near the bottom edge of blank 20), 48 and 50 (near
the left edge of the blank), 52 and 54 (near the right
edge); with 56, 58, 60 and 62 located in an area
approaching the upper portion of blank 20.
Unitary blank 20, with cut-away sections removed, is
shown in FIG. 2; interrupted lines remain as they were
shown in FIG. 1. Roof covering structure 63 of the
invention, as it appears subse~uent to cutting away of such
portions and subsequent to folding over of sheet metal to
form slots for interfitting with other such structures, is
shown in FIG. 3. FIGS. 1- 3 are plan views of the outer
surface of the blank and fabricated structure. A single
viewable tab embodiment is shown and described initially;
details of that fabrication are applicable to structures
having a panel configuration, as later shown, in which the
viewable portions present a plurality of tabs; and, Table
I dimensions refer to such a panel embodiment.
Folding over of sheet metal to form lateral edge slots
is first carried out along vertically-oriented fold lines
--10--
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
48-50 and 52-54 (FIGS. 1 and 2). Section 64 (along the
left edge of roof covering structure 63 of FIG. 3) is
folded-over so as to be substantially parallel with the
plane of remaining sheet metal of unitary blank 20; and, is
positioned on the underside of such remaining sheet metal
blank. The metal, which had been between interrupted lines
48 and 50 (FIG. 1) after folding over of section 64, has a
semicircular cross-sectional shape which connects
subsurface section 64 with the remaining sheet metal roof
covering structure 63 and comprises the closed end of the
otherwise open linearly-extended slot, and has a mid-point
which defines one lateral side (65, FIG. 3) of the viewable
tab portion of the unitary structure 63. The orientation
of such folded-over section 64 is better seen in FIG. 4,
which is an enlarged cross-sectional view taken at line 4-4
of FIG. 3.
Section 66 (near the right edge of blank 20 in FIGS.
1 and 2) is folded-over so as to be substantially parallel
with the plane of remaining sheet metal of the blank; and,
is positioned on the outer surface edge of the roof
covering structure being fabricated.- The section between
interrupted lines 52 and 54 of FIGS. 1 and 2 is fabricated
with a semicircular cross-sectional shape, connecting
planar section 66 with the remaining roof covering
structure. Folded-over section 66 is located at the
opposite lateral edge with respect to section 64, as shown
in cross section in FIG.- 4, and mid-point 67, FIG. 3,
defining the lateral side of the viewable tab portion at
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
that location.
Reference points designated 48, 50 and 52, 54 in FIG.
4 refer, respectively, to the locations where interrupted
lines 48, 50 and 52, 54 were located in FIGS. 1 and 2.
Folded-over sections 64, 66 establish linearly-extended
slots along the lateral edges of roof covering structure
63, which provide for interfitting of horizontally-adjacent
roof covering structures of the invention as those
structures are assembled along a horizontally-oriented
course. The relative movement between roof covering
structures, for purposes of interfitting those slots during
assembly, is considered later and described in more detail.
Folding over of sheet metal along rem~;n'ng pairs of
interrupted lines, shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, comprises a
second stage of the fabrication which differs from the
fabrication of the vertically-disposed folded-over sections
64 and 66 of FIG. 4. The latter are uniformly-spaced from
the main body of the unitary structure along each such
linearly-extended lateral slot, as indicated by the cross-
sectional view of FIG. 4.
The trapezoidal configuration is utilized in forming
slots which extend horizontally and which are located at
the upper and lower perimeter of the viewable tab. Those
slots result from folding over sheet metal at pairs of
interrupted lines (44, 46 and 56, 58 of FIGS. 1 and 2).
Those pairs of interrupted lines have substantially
parallel portions only at locations contiguous to their
distal ends. An intermediate portion, between those distal
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
,
ends, is transitional and can have varying cross-sectional
geometry.
The substantially uniform cross-sectional geometry
established near each such distal end provides for nested
interlocking of slots of adjacent roof covering structures
at those ends. Also, an added thickness of folded-over
sheet metal is made at those locations to provide a barrier
to entry of precipital liquids. Compensation for that
added folded-over sheet metal, as taught herein, avoids a
stepped relationship between adjacent roof covering
structures along a horizontally-oriented course, which
would otherwise be cumulative; and, provides a
substantially horizontal presentation for viewable tabs
along the length of the course.
The differing cross-sectional dimensional relationship
(geometry), in approaching each distal end of the upper and
lower horizontally-extending slots, is shown in FIGS. 5 and
6. The dimensional relationship of the slot near one
distal end is presented in FIG. 5; and a substantially
uniform width portion at the opposite distal end is shown
in FIG. 6. A cross-sectional dimensional transition exists
intermediate those two locations which are taken at 5-5 and
6-6, respectively, of FIG. 3.
The length of the substantially uniform geometry near
each distal end of the slots provides for ease of assembly,
as the adjacent unitary roof covering structures must slide
in relation to each other in making a lateral edge
interfitting (described in relation to FIGS. 10 and 11) as
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
such covers are assembled along a horizontal course.
Section 68, along the lower edge at unitary blank 20
of FIGS. 1 and 2, is folded over so as to be substantially
parallel with the plane of the remaining shingle structure
blank and to have a position on the undersurface of the
remaining blank. - A cross-sectional view of folded-over
section 68, along the lower perimeter of the viewable tab,
as taken at a location indicated by line 5-5 in FIG. 3, is
shown in FIG. 5; and a cross-sectional view of section 68,
as viewed at a location indicated by line 6-6 of FIG. 3, is
- shown in FIG. 6.
Reference points 44 and 46 in FIGS. 5 and 6 represent
lines 44 and 46, respectively, of FIGS. 1-2. The
difference in slot cross-sectional geometry, dimension, in
each of the substantially uniform slot width portions at
each distal end of such lower perimeter slot, is also
indicated by the differing dimensions between lines 44 and
46 in the views of FIGS. 1 and 2.
The differing slot widths near distal ends, as lines
44 and 46 become near parallel, make sliding assembly
easier in assembling a horizontally-oriented course while
providing a rigid and weathertight fit with improved
nesting at those distal ends; the near parallel
relationship at those distal ends is also shown by the data
in Table 1.
Upper horizontally-extending interfitting slots are
also formed by folding over multiple sheet metal layers
along two pairs of interrupted lines, 56, 58 and 60, 62,
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
respectively, of FIGS. 1-2. The cross-sectional
dimensional relationship of those upper horizontally-
extending slots near their distal ends are also shown in
the enlarged cross-sectional views of FIGS. 5 and 6. The
pairs of fold lines are referenced by points 56, 58, and
60, 62, respectively, in those FIGS. The substantially
uniform cross-sectional dimensional relationship (geometry)
established near distal end portions helps to provide for
ease of sliding movement for interfitting of lateral edge
slots mentioned earlier.
Such upper multiple-layer slots (formed by folding
over sheet metal at 56, 58 and 60, 62) separate the unitary
structure 63 into: (i) a viewable tab portion 70 (FIGS. 5
and 6) which, after assembly, remains exposed and visible,
and (ii) an upper lapped portion 72 which is overlapped and
not visible after assembly. Portion 72 is covered by tab
portion 70 of a next vertically-adjacent roof covering
structure. Embossed or contoured portions, as disclosed in
co-owned, copending design patent applications referenced
above, can be limited to such viewable portion (70) where
a deep embossing pattern would not interfere with folding
over of sheet metal or with interfitting of slots.
However, a shallow embossing pattern (depth between about
0.005" to about 0.01") can be carried out on the entire
surface of the blank, before stamping or cutting the roof
covering structure, and has certain advantages.
Apertures 34-42, for placement of fasteners, are
located in top edge section 73 of covered portion 72. An
-15-
CA 02242478 l998-08-l8
offset 74 iS formed in covered portion 72 by bending the
metal at interrupted bend lines 75 and 76 of FIGS. 1-2
(which also appear as reference points 75 and 76 of FIGS.
5 and 6). The angled relationship o~ the sheet metal
between 75 and 76 allows the full fastener section 73 to
contact the understructure support for securing the unitary
roof covering structure in place, by nailing or other
fastening means, while angled offset 74 provides for
absorbing forces which may be encountered during assembly
which otherwise could tend to distort such a unitary
structure as secured by fastener means.
Assembly proceeds in the direction from left to right
along a horizontally-oriented course in FIG. 7. A left
lateral edge slot of roof covering structure 77 iS
interfitted in the right lateral edge slot of roof covering
structure 78 (reference is also made to FIG. 4 and later
FIGS. 10. 11). Structure 78, which has been at least
partially fastened to supporting understructure, receives
the left lateral edge (section 66 of FIG. 4) by relative
sliding movement of unitary roof covering structure 77 as
the two unitary structures are assembled in side-by-side
relationship as shown in the general arrangement view of
FIG. 7.
After completion or partial completion of a
horizontally-oriented course, a new course, vertically
above the first course, can be initiated, as shown in
general arrangement view of FIG. 8, and in the enlarged
cross-sectional view of FIG. 9. Structure 79 for such a
-16-
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
; . .
new course is placed in staggered relationship to the
vertically-oriented lateral edge slots of FIG. 7. The
staggered location is at approximately one-half the
horizontally-oriented dimension of the next vertically
adjacent roof covering structure. Such staggered
placement, indicated by FIG. 8, continues throughout each
new vertically-located course.
Referring to FIGS. 9-12, FIG. 9, an enlarged cross-
sectional partial view taken along line 9-9 of FIG. 8, and
FIG. 10, a cross-sectional partial view taken along line
10-10 of FIG. 7, show the interfitting relationships
carried out as roof covering structures are being
assembled. The horizontally-extending sheet metal slots
are interfitted vertically resulting in the orientation of
FIG. 9. The vertically-oriented lateral edge slots (FIG.
10) are interfitted by relative sliding movement in. a
horizontal direction.
The roof covering structure 77 being placed in FIG. 7
must be able to move laterally to provide an interfitting
relationship of each vertical lateral edge slot of the two
unitary structures (77, 78). That relative movement is
determined by the amount of sliding.movement necessary for
interfitting the vertically-oriented sections 64 and 66, as
shown in FIG. 10. The total distance provided for ease of
assembly, shown at 82 in FIG. 11, equals the sum of the
distance between:
i. an edge of section 64 and a mid-point of the
semicircular fold between interrupted lines 48 and 50
-17-
-
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
,
(indicated at 80 in FIG. 11), and
ii. an edge of section 66 and a mid-point of the
semicircular fold between interrupted lines 52 and 54
(indicated at 81 in FIG. 11).
To provide for ease of alignment and interfitting
relative movement of roof covering structures, portions of
the horizontally-extending slots, near each distal end, are
made with a uniform cross-sectional dimensional
relationship (geometry) approximately equal to dimension 82
indicated in FIG. 11. In general, the enlarged dimensional
relationship at the left distal end of the unitary
structures (FIG. 5) extends substantially the full length
of the transition zone intermediate both uniform cross-
sectional distal ends.
The interfitting configurations of slot means allow
movement of air, but prevent subsurface access by
precipitation liquid. The configuration of the added
folded sheet metal near each distal end of the
horizontally-extending slots prevents siphoning of water
which could otherwise take place through metal surfaces
positioned in closely spaced relationship. Air gaps are
indicated in FIGS. 9 and 10 at 84 and 86, respectively. A
separation gap of about 0.125" prevents such siphoning of
liquids. Dimensional relationships are tabulated below for
a specific embodiment in Table I.
Additional features which assist in obtaining the
desired configuration of sheet metal folds for forming
interlocking slots include a triangular-shaped cut-out
-18-
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
section 26, shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, and selecting
dimensions for section 66 relative to fold lines 60 and 62.
Cutting away of over-layered sheet metal at distal ends of
the horizontally-extending slots prevents buckling of the
metal. Such buckling could result in an irregular arc
shape at a slot fold which could prevent proper
interfitting and nesting. In the selected embodiment of
Table I, cut-out section 26 has a 90~ angle at its
intersection with fold line 44. For the same buckling-
prevention reason, the barrier layer of sheet metal at theright distal end of the upper horizontally-extending slot
need only extend about ninety degrees (90~) into the closed
arcuate end of the slot at that location; that is, about
half-way between reference points 56 and 58 of FIG. 6~
Another feature of the invention provides for
temporarily holding a roof covering structure in position,
during assembly, until fastener means are in place for
securing the roof covering to the understructure. Such
holding function utilizes at least one detent, located in
roof covering structure section 68, near the right lateral
edge of the unitary structure, as shown at 90 of FIGS. 1-3,
7-8, and in cross-sectional view in FIG. 12. Such detent
restricts the width of the slot at a selected area and
temporarily positions a unitary structure, being added to
a course, until fastener means are in place.
An aid for alignment of roof covering structures in a
course, during assembly, enables sighting the right lateral
edge of an assembled shingle through an aperture which is
-19 -
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
strategically located in a unitary roof covering structure
being added to a course. Such edge positioning at a
boundary of such aperture is shown at aperture 34 in FIG.
7; in such figure, the edge which is sighted is designated
92.
In a preferred method of the invention, fasteners
presenting a threaded shaft are used for securing roof
covering structures to a roof support surface. Sizing of
such fasteners provides a root diameter for the fastener
which is substantially equal to the diameter of the
apertures; such a size relationship increases protection
against high wind forces.
In an additional feature, a provision is made in
interfitting horizontally-oriented folded-over metal for
insertion of support means for roofing accessories such as
snow guards, or for roof jacks used for support of
equipment used during roof covering. A cut-out section, 30
of FIG. 1, provides clearance required for insertion of
sheet metal for roofing accessories or support means.
Snow guard 94 is shown installed at such lower
horizontally-extended slot in the cross-sectional view of
FIG. 13. Such cross-sectional view is taken along line 13-
13 of FIG. 8. Support arm means 96, for snow guard 94, is
interfitted between the lower folded-over sheet metal by
inserting its U-shaped upper portion over offset edge 98,
as indicated in FIG. 13. The snow guard 94 is connected to
support means 96 by fastener means 100. Such support means
can be utilized for other roofing accessories, or
-20-
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
installation equipment, and can vary in width (indicated at
102 of FIG. 8) to provide desired support strength. When
used for support of equipment used for installation, such
as roof jacks, the support means width dimension can extend
twelve inches or more. Such support means width dimension
determines the horizontal dimensions of cut-out section 30
(FIG. 1). Such section is formed with a dimension
extending centrally of the structure along its bottom edge,
which is at least equal to the width of the support means,
and provides clearance for the thickness gauge of the sheet
metal of support 96.
In addition, the cross-sectional configuration of the
lower folded-over section (defined by fold lines 44 and
46), at the left of the unitary structure, extends toward
the opposite distal end of the slot a distance which
provides for support 96, and that cross-sectional
dimensional geometry can extend to the uniform width
portion between lines 44 and 46 of FIG. 6.
An important contribution of the invention takes into
consideration the thickness of folded-over liquid barrier
metal distal end slot means. Without alignment features of
the invention, the cumulative effect of those sheet metal
barriers (twice coated metal thickness gauge for each
assembled unitary roof covering structure) would distort
the orientation of the viewable tabs along a horizontally-
oriented course. The appearance of non-alignment of
viewable tab portions would be accentuated by the length of
the course. The use of the trapezoidal configuration fold
-21-
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
lines, described above, maintains a horizontal appearance
for the viewable tabs.
In a specific embodiment of the trapezoidal
configuration, top edge 104 (FIGS. 1 and 2) is
perpendicular to mutually parallel lateral edges 105 and
106. However, bottom edge 108 is angled in relation to
such parallel lateral edges, and lateral edge 105 is longer
than lateral edge 107. The folding over of sheet metal, as
described, takes advantage of that trapezoidal
configuration such that the assembled roof covering
structures present a substantially horizontal orientation
for the viewable portions of the roof covering structures
along a horizontally-oriented course, and such viewable
portions appear substantially rectangular in shape.
- CA 02242478 1998-08-18
TABLE I
Specific Embodiment of Sheet Metal Roof Panel Structure
Material
Sheet Metal Material .023" galvanized steel
Sheet Metal Coating .0016" polyrner
Sheet Metal Embossing .009" depth texture
Dimensions of Blank (FIG. 1~
Top Edge (104) 37.302"
Bottom Edge (108) 37.303"
Left Edge (105) 16.326"
Right Edge (106) 16.032"
Diameter of Apertures 0.156"
Center of Apertures from Top Edge 0.284"
Section 22 (horizontal x vertical) 0.391" x 2.771"
Section 24 (horizontal x vertical) 0.561" x 2.458
Section 32 (horizontal x vertical) 0.561" x 0.822"
Section 30 (horizontal x vertical) 12.00 " x 0.050
Section 28 (length, angle) 0.391 ", 60~ 22'
Section 26 (angle at fold line 44) 90~
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
TABLE I
Specific Embodiment of Sheet Metal Roof Panel Structure
TABLE I (continued)
Location of Fold Lines (Distance From Top Edqe 104, FIG. 1)
Line 76 Left 0.560"
Right 0.48"
Line 75 Left 1.25"
Right 1.18"
Line 58 Left 1.903"
Right 1.813"
Line 56 Left 2.099"
Right 1.843"
Line 62 Left 2.402"
Right 2.079"
Line 60 Left 2.771"
Right 2.838"
Line 44 Left 15.551"
Right 15.399"
Line 46 Left 15.904"
Right 15.577"
Location of Vertically-Oriented Fold Lines Near
Left Lateral Edqe (Distance From Edqe 105, FIG. 1)
Line 50 0.226"
Line 48 0.391"
Location of Vertically-oriented Fold Lines Near
Riqht Lateral Ed~e (Distance From Edqe 106, FIG. 1)
Line 54 0.396"
Line 52 0.561"
.
--24--
CA 02242478 1998-08-18
.. . .
For purposes of disclosing concepts of the invention
dimensional data, geometrical relationships and materials
of specific embodiments have been described; and it should
be recognized that, in the light of the above description,
changes in those specifics can be made while relying on the
concepts taught; therefore, in construing the scope of the
present invention, reference should be made to the appended
claims.