Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2247322 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | METHOD OF CORRECTING THE DETERMINATION OF WORKPIECE AND TOOL POSITIONS IN MACHINE TOOLS |
| (54) French Title: | PROCEDE DE CORRECTION DE POSITIONNEMENT DE PIECES ET D'OUTILS DANS DES MACHINES-OUTILS |
| Status: | Deemed Abandoned and Beyond the Period of Reinstatement - Pending Response to Notice of Disregarded Communication |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | MARKS & CLERK |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 1997-01-17 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 1997-09-04 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/EP1997/000188 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | WO 1997031751 |
| (85) National Entry: | 1998-08-24 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
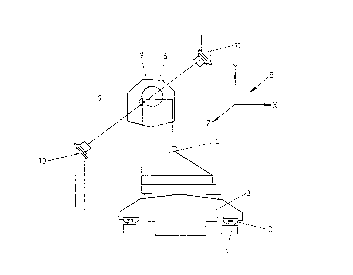
The invention concerns a method of correcting the determination of positions
of workpieces and tools which can be moved relative to one another in machine
tools, in particular CNC machining centres, by means of measuring systems
internal to the machines. Machining inaccuracies caused by changes in the
positions of the workpiece and/or tool owing to heat in the working region of
the tool can be avoided if the workpiece and tool are moved with associated
measuring points or measuring edges through a stationary optical test barrier,
simultaneously or at short intervals one after the other. If the test barrier
is interrupted, the respective positions of the workpiece and tool are
determined by means of the measuring system internal to the machine. The
positions determined are compared with stored positions determined during a
previous measurement, and the difference between the determined position and
the stored position is used to correct the machine control. The invention
further concerns a machine for carrying out the method.
L'invention concerne un procédé de correction de positionnement de pièces et d'outils pouvant se déplacer les uns par rapport aux autres dans des machines d'usinage, notamment des centres d'usinage à commande numérique par calculateur, à l'aide de systèmes de mesure internes. Des imperfections d'usinage dues à des modifications de position de pièces et/ou d'outils inhérentes à des contraintes d'ordre thermique peuvent être évitées dans la zone de travail de l'outil, si la pièce et l'outil sont déplacés simultanément ou successivement à un court intervalle à travers une barrière de mesure optique fixe. En cas d'interruption de la barrière de mesure, chaque position de la pièce ou de l'outil est détectée à l'aide du système de mesure interne. Les positions détectées sont comparées à des positions mémorisées lors d'une mesure antérieure et les différence entre la position détectée et la position mémorisée sert à corriger la commande de la machine. L'invention concerne en outre une machine d'usinage appropriée pour mettre ledit procédé en oeuvre.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Application Not Reinstated by Deadline | 2002-01-17 |
| Time Limit for Reversal Expired | 2002-01-17 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2001-01-17 |
| Inactive: Single transfer | 1999-01-13 |
| Classification Modified | 1998-11-13 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1998-11-13 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 1998-11-13 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 1998-11-13 |
| Inactive: Courtesy letter - Evidence | 1998-11-03 |
| Inactive: Notice - National entry - No RFE | 1998-10-28 |
| Application Received - PCT | 1998-10-26 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 1997-09-04 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2001-01-17 |
The last payment was received on 2000-01-05
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Please refer to the CIPO Patent Fees web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic national fee - standard | 1998-08-24 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - standard | 02 | 1999-01-18 | 1999-01-11 |
| Registration of a document | 1999-01-13 | ||
| MF (application, 3rd anniv.) - standard | 03 | 2000-01-17 | 2000-01-05 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| HULLER HILLE GMBH |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| HORST SANZENBACHER |
| KARLHERMANN SUS |
| SOREN WELB |
| WOLFGANG HORN |