Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02258062 2004-02-11
RESISTANCE DEVICE
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
For an exercising apparatus using atmospheric pressure (i.e.,
vacuum means) as the source of resisting force, the major
advantage is to reduce the total weight of the apparatus compared
to an apparatus using gravity force (e.g., weight stacks) as the
source of resisting force.
For example, such apparatus like U.S. Pat. No. 5,336,150, "Lever
Resistance Selection Mechanism for Strength Training" and U.K.
Pat. Application GB2267224A, "Exercising Device " reveal
solutions for adjusting the resistance. Although U.S. Pat. No.
5,336,150 and U.K. Application GB2267224A disclose several
types of resistance adjusting means, none of these resistance
adjusting means can allow a user to adjust the level of resistance
with a quick and easy process.
Therefore, a resistance device using atmospheric pressure as the
source of resisting force with resistance adjusting means which
can easily adjust the level of resisting force is necessary.
SUMMARY AND OBJECTS OF THE INVENTION
The present invention which pertains to a resistance device
installed in an exercising apparatus comprises a plurality of
resistance elements, a force transmission means and a resistance
adjusting means. Through the force transmission means, a user
1
CA 02258062 2004-02-11
may apply an exercising force to the resistance elements which
in general provides a resisting force. Each resistance element
comprises a vacuum chamber and an air passage which is
connected to the vacuum chamber. The vacuum chamber can be
expanded opposing atmospheric pressure which accordingly
produces a resisting force and said air passage makes it possible
to introduce air into the vacuum chamber in which case the
corresponding resistance element will be disabled. By operating
the resistance adjusting means which controls the close /open of
the air passage of respective resistance elements, the user may
adjust the level of the total resistance. Each resistance element
may be designed to provide an amount of resisting force different
to that of each other. By arranging different combinations of
enabled resistance elements for selection, it is possible to
provide more levels of resistance than the number of resistance
elements.
It is an object of the present invention to provide a resistance
device for an exercising apparatus of which the level of
resistance can be quickly and conveniently adjusted.
A further object of the present invention is to provide a
resistance adjusting means which not only can adjust the level of
resisting force but also can be used to release (disable) the
resistance.
z
CA 02258062 2004-02-11
Another object of the present invention is to use a few of the
resistance elements to achieve many different levels of
resistance. For example, four resistance elements each provide
Kg, 20 Kg, 40 Kg, and 80 Kg resistance force. By controlling
5 the enabled or disabled status of these four resistance elements,
fifteen different levels (10 Kg, 20 Kg, . . . 150 Kg, each level has
10 Kg difference) of resistance can be provided. For example a
130 Kg resistance is provided by three enabled resistance
elements, 10 Kg, 20 Kg, 40 Kg, and 80 Kg, and one disabled
10 resistance element, 20 Kg.
Other advantages of the present invention will become apparent
during the course of the following description.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG. 1 is an elevational view of the first embodiment of the
present invention applied in an exercising apparatus.
FIG. 2A is an exploded view of the first embodiment regarding
the resistance elements of the present invention.
FIG. 2B is an enlarged cross-section of the one-way valve
described in the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 3 is an exploded view of a preferred embodiment of the
resistance adjusting means of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a cutaway view of FIG. 3.
FIG. 5 is a top plan view of FIG. 3.
FIG. 6 is an exploded view of the second embodiment regarding
the resistance elements of the present invention.
3
CA 02258062 2004-02-11
FIG. 7 illustrates a way in which the cylinder walls in FIG. 2A
can be combined as a single piece.
FIG. 8 illustrates a way in which the cylinder walls in FIG. 6 can
be combined as a single piece.
FIG. 9 is a cutaway view of the third embodiment regarding the
resistance elements of the present invention.
FIG. 10 is a perspective view of the fourth embodiment
regarding the resistance elements of the present invention.
FIG. 11 is a cutaway view of the fifth embodiment regarding the
resistance elements of the present invention.
FIG. 12 is an exploded view of the sixth embodiment regarding
the resistance elements of the present invention.
FIG. 13 is another view of FIG. 12.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED
EMBODIMENTS
The present invention will now be described, by way of example,
with reference to the accompanying diagrammatic drawings. FIG.
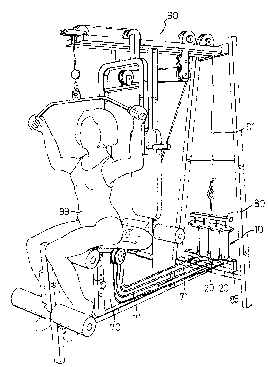
1 gives a comprehensive illustration of how the present invention
is applied to an exercising apparatus 90. The resistance device 10
comprises a plurality of resistance elements 20, a force
transmission means 80 and a resistance adjusting means 70.
Through the force transmission means 80, a user 99 can apply an
exercising force to the resistance elements 20 which provide a
resisting force. By operating the resistance adjusting means 70,
the user 99 can adjust the total resistance to a desired level. The
fixing means 85 fix the resistance device 10 on the exercising
4
CA 02258062 2004-02-11
apparatus 90. To let the user 99 access the resistance adjusting
means 70 within a short distance, the extension tubes 71 connect
the resistance elements 20 and the resistance adjusting means 70.
During operation, the user 99 applies an exercising force to draw
the resistance elements 20 through a wire 91 and the force
transmission means 80.
Referring to FIG. 2A regarding the first embodiment of the
present invention, each resistance element 20 is a cylinder 40
(the cross-section is not limited to a circular shape), which
comprises a piston head 43 and a piston rod 44. All the cylinders
40 are mounted on the fixing base 46 (i.e., the fixing means 85)
which includes the end covers 42 as a part. The fixing base 46 is
then fastened to the exercising apparatus 90 by bolts 47. Each
end cover 42 at least has an air passage 21 to which an extension
tube 71 is hermetically connected. At the top end of each
cylinder 40 is fastened a top cover 41 and all the top covers 41
are combined together. Each top cover 41 has an axial through
hole 412. The piston rods 44 extend from the piston heads 43
through the through holes 412 and are fixed to a pulling member
45 (i.e. force transmission means 80.) The pulling member 45 is
then connected to a wire 91 by an eyebolt 451.
The edge of each piston head 43 sealingly engages the inner wall
of cylinder 40 to resist passage of air in the cylinder 40 so that a
vacuum chamber 30 is formed between the piston head 43 and
the end cover 42. Further, an air passage 21 is connected with
5
CA 02258062 2004-02-11
the vacuum chamber 30. Because such cylinders 40 uses
atmospheric pressure as the source of resisting force is a prior
art (e.g. U.S. Pat. No. 5,336,150), the theory and detail
description will not be discussed hereafter. The amount of
resisting force provided by a cylinder 40 is depended on the
cross-sectional area (F=P*A).
Referring now to FIGS. 3, 4 and 5, in a preferred embodiment,
the resistance adjusting means 70 mainly comprise a valve seat
72 and a valve cap 73. A bolt 75 is sequentially inserted through
the axle holes 731, 721 and a spring 752 and then screws in a nut
751, to revolvably secure the valve cap 73 onto the valve seat 72.
A plurality of protrusions 722 and depressions 732 are provided
respectively on the surface of the valve seat 72 and on the
corresponding positions on the valve cap 73, so that the user can
turn the valve cap 73 stepwise. Of course, the protrusions 722
and depressions 732 may be provided at other appropriate
portions of the valve seat 72 and valve cap 73 respectively or
vice versa. The resistance adjusting means 70 is mounted on the
exercising apparatus 90 through a connecting arm 77 by
fastening member 771.
The purpose of the resistance adjusting means 70 is to
selectively close or open the air passages 21 of the resistance
elements 20. The mechanism will be described hereafter. The
valve seat 72 comprises a plurality of air gateways 76 which are
respectively hermetically connected to the air passage 21 of the
6
CA 02258062 2004-02-11
vacuum chambers 30 by extension tubes 71. The valve cap 73
comprises a plurality of valve sets 79 and each of valve sets 79
represents a level of resistance. Each valve set 79 is preferably
provided with a unique combination of openings 74 which are
respectively located opposed to the associated gateways 76 of the
valve seat 72 when this valve set 79 connects to the gateways 76.
All the openings 74 can communicate with the atmosphere. A
valve set 79 may be provided with no opening 74, like valve set
79a illustrated in FIG. 5. So if valve set 79a is switched to
connect to the gateways 76, the air passages 21 of all the
resistance elements 20 are closed, which means that all the
resistance elements 20 are enabled and the total resistance is the
aggregate of that provided by every resistance element 20. For
another instance, when the valve set 79b which has two middle
openings, is switched to connect to the gateways 76, two
resistance elements 20 associated to these openings are disabled
because the vacuum chambers 30 of these two resistance
elements 20 communicate with the atmosphere. Therefore, the
total resistance provided by selecting valve set 79b is smaller
than by selecting valve set 79a. Of course, the resistance
adjusting means 70 may be of other forms, for example, solenoid
valves combined with an electric circuit to control the open or
close status of air passages 21.
Also referring to FIG. 2A again, each top cover 41 may include
some small holes 411 to prevent the outside air from quickly
flowing into the cylinder 40. Therefore, when a user 99 releases
7
CA 02258062 2004-02-11
his/her force after the piston heads 43 were pulled up, the piston
heads 43 will not quickly drop down to injure the user 99. With
the design of some small holes 411, the top covers 41 should
further have one-way valves 48 so that when a user 99 pulls up
the piston head 43, the exhaust air can pass through the one-way
valves 48 easily. FIG. 2B is a cross-section of a typical one-way
valve 48 which consists of a cap 481 and openings 482.
Referring to FIG. 6, the second embodiment of the present
invention, the resistance elements 20 are arranged symmetrically
in pairs except the one in the center. Both resistance elements 20
of a pair (for example, 20a and 20b) are identical and set to be
enabled or disabled simultaneously by the resistance adjusting
means 70. Therefore, all the resisting forces provided by the
resistance elements 20 are balanced during operation without any
torque.
FIGS. 7 and 8 shows that the cylinders 40 corresponding FIGS.
2A and 6 may be also manufactured as a joined single piece.
Referring to FIG. 9, in a third embodiment of the present
invention, the cylinders 40 are arranged coaxially, in which case
at least two piston rods 44 must be provided for each piston head
43 except the one in the center.
Referring to FIG. 10, in the fourth embodiment of the present
invention, each resistance element 20 is a flexible, variable
8
CA 02258062 2004-02-11
length bellows-like sidewall 60 with two end covers 61, 62. The
inside of bellows-like sidewall 60 is a vacuum chamber 30 with a
variable volume. The prior art of bellows-like vacuum resistance
device has been disclosed in U.S. Pat. Nos., 3,884,463 and
5,356,361. The end cover 61 and 62, each being a single piece
shared by all the resistance elements 20, also act respectively as
the force transmission means 80 and the fixing means 85. FIG.
11 shows a variation of the fourth embodiment, wherein the
flexible side walls 60 are arranged coaxially.
FIGS. 12 and 13 illustrate the sixth embodiment of the present
invention, wherein the resistance elements 20 are circular
chambers 50 in annular shape and coaxially arranged. Each
circular chamber 50 comprises two side walls 51, an end cover
59, a rotary disc 55, a fixing plate 56, and a rectangular piston
plate 53 which is perpendicularly fixed on the rotary disc 55 and
originally located contiguous to the end cover 59. The side walls
51 and the end covers 59 are tightly fixed on the fixing plate 56
(they may be also manufactured as a joined single piece). On the
fixing plate 56 and adjacent to the end covers 59, a series of air
passages 21 and a series of small holes 561 are provided
respectively on the same side as the piston plates 53 and on the
other side of the end covers 59. The small holes 562 may be
disposed on the rotary disc 55 and adjacent to the piston plates
53 on the opposite side to the end covers 59, replacing or
cooperating with the small holes 561. The functions of the small
holes 561, 562 and of the air passages 21 which are hermetically
9
CA 02258062 2004-02-11
connected to the extension tubes 71, have been described
hereinbefore, please refer to the description of the first
embodiment.
With the piston plates 53 being sealingly inserted into the
circular chamber 50, the rotary disc 55 is sealingly and
revolvably secured to the side walls 51, end covers 59 and fixing
plate 56 combined by a bolt 57, a spring 572 and a nut 571. The
rotary disc 55 and the fixing plate 56 also act respectively as the
force transmission means 80 and the fixing means 85. The rotary
disc 55 can be drawn to revolve by a wire 54 connected to and
wound on its periphery, thereby moves the piston plates 53 away
from the end covers 59, forming and expanding a vacuum
chamber 30 therein-between. The mechanism of gaining a desired
resistance is the same as described hereinbefore.
It is to be understood that the drawings and associated
descriptions are for the purpose of illustration only, and are not
intended as a definition of the limits and scope of the present
invention. Any modifications or variations without departing
from the spirit of the present invention are included in the scope
of the present invention as defined by the following claims.