Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02269357 1999-04-20
WO 98118227 PCTIFI97/00612
PROCEDURE AND SYSTEM FOR ADAPTING A DATA LINK
CONNECTION BETWEEN A REMOTE WORKSTATION AND AN
AUTOMATIC CALL ALLOCATION SYSTEM
The present invention relates to a procedure
as defined in the preamble of claim 1 and to a system
as defined in the preamble of claim 5 for connecting a
remote workstation to an automatic call allocation
system.
An automatic call allocation system is used
IO in modern communication systems, especially in so-
called service telephone exchanges, which are provided
with certain automatic functions to facilitate cus-
tomer service. Via an automatic call allocation sys-
tem, calls made to service numbers are directed to
service operators connected to the call allocation
system.
Generally, in addition to a voice connection,
the operators also use a computer terminal through
which they can communicate e.g. via a local network
with a database to read data that they need in custo-
mer service. The equipment used by the operator in
this work is called a workstation, which may be an as-
sembly consisting of a computer and devices connected
to it to allow the setup of a voice connection. There-
fore, a possibility of transmitting both data and call
signals between the workstation and the call allocati-
on system may be required.
In most cases a call allocation system is
implemented in the area of a single telephone exchan-
ge, a so-called host exchange, so the connections bet-
ween the workstation and the call allocation system
can be effected using a non-standardized, producer-
specific communication protocol. If a workstation is
to be placed at a distance from the host exchange, to
establish a remote workstation, then the connection
between the call allocation system and the workstation
1 IN
CA 02269357 1999-04-20
WO 98f18227 PCTJFI97/00612
2
at least up to the host exchange must be set up using
a standard communication protocol.
Patent specification EP 376 527 presents a
prior-art automatic call allocation system in which a
remote workstation is connected to a host exchange via
a standardized communication protocol, e.g. an ISDN
multi-service protocol. In this case, the automatic
call allocation system has to convert and adapt the
ISDN signals proceeding from the remote workstation so
that they accord with the communication protocol used
by the workstations connected directly to the automa-
tic call allocation system.
A problem here is that each time new worksta
tions are added to the system, changes must be made in
the automatic call allocation system software in the
host exchange. At the same time, use of the system
must be restricted during the software update. Moreo-
ver, a remote workstation places a larger load on the
processing capacity of the automatic call allocation
system than a normal workstation communicating di-
rectly with the host exchange.
The object of the present invention is to
eliminate the problems described above. A specific ob-
ject of the present invention is to produce a new type
of procedure and system for setting up a data link
connection between a remote workstation and an automa-
tic call allocation system without making changes in
the software of the automatic call allocation system.
As for the features characteristic of the
present invention, reference is made to the claims.
In the procedure of the invention for adap-
ting a data link connection between a remote worksta-
tion and an automatic call allocation system connected
to a host exchange, a data link connection from the
remote workstation to the host exchange is generally
set up according to a first communication protocol.
The connection is preferably set up via an ISDN
CA 02269357 1999-04-20
WO 98/18227 PCT/FI97/00612
3
(Integrated Services Digital Network) network, in
which it is possible to use e.g. SS7 signalling
(Signalling System 7) in accordance with the ITU-T re-
commendations. According to the invention, the automa-
tic call allocation system is provided with an adap
' ter, and a data link connection is set up between the
adapter and the remote workstation, preferably in ac
cordance with a first communication protocol. In addi
tion, a data link connection is set up between the au
tomatic call allocation system and the adapter in ac-
cordance with a second communication protocol. Furt-
her, according to the invention, the adapter is used
to match the first and second communication protocols
between the automatic call allocation system and the
remote workstation, the communication signals
transmitted according to the first communication pro-
tocol between the remote workstation and the adapter
and the communication signals transmitted according to
the second communication protocol between the adapter
and the automatic call allocation system being conver-
ted by means of the adapter so as to match them to
each other.
In a preferred embodiment of the invention,
the data link connection between the remote workstati
on and the adapter is set up via a local exchange, in
which case the data link connection between the remote
workstation and the local exchange and between the lo-
cal exchange and the host exchange is set up according
to a first communication protocol. On the other hand,
the data link connection between the remote workstati-
on and the adapter can be set up by using a router ar-
ranged to match the interface between the adapter and
the communication protocol used, in which case it will
be possible to use a data Link connection and communi-
cation protocol independent of the telephone network
for the transmission of both data and voice.
CA 02269357 1999-04-20
WO 98/18227 PCT/FI97/00612
4
The adapter is preferably connected to the
host exchange via a 2B+D link capable of transmitting
both voice and data, in which case the data link con-
nection between the remote workstation and the adapter
is set up via the first B channel of the 2B+D link and
using the associated D channel signalling, while the
data link connection between the adapter and the host
exchange is set up via the second B channel and the
associated D channel signalling. In another embodi-
ment, a plurality of 2B+D links are provided between
the adapter and the host exchange. In this case, a
single adapter can be used to connect several remote
workstations to an automatic call allocation system.
The system of the invention for adapting a
data link connection between a remote workstation and
an automatic call allocation system connected to a
host exchange comprises a data link connection between
the remote workstation and the host exchange, in which
a first communication protocol is used. The first data
link connection is preferably set up via an ISDN net-
work. According to the invention, the system comprises
an adapter included in the automatic call allocation
system, and a data link connection is set up between
the adapter and the remote workstation preferably ob-
serving the first communication protocol. In addition,
a data link connection is set up between the automatic
call allocation system and the adapter in accordance
with a second communication protocol, the communicati-
on signals consistent with the first communication
protocol between the remote workstation and the adap
ter and the communication signals consistent with the
second communication protocol between the adapter and
the automatic call allocation system being converted
by means of the adapter so as to match them to each
other.
As compared with prior art, the present in-
vention has the advantage that the connection of a new
_. _._
CA 02269357 1999-04-20
WO 98118227 PCTIFI97100612
remote workstation to the system can be practically be
carried out in a way corresponding to the connection
of a workstation that communicates directly with the
host exchange. Therefore, connecting a new remote
5 workstation does not involve any laborious updating of
software in the automatic call allocation system, nor
does it add to the load on the processing capacity of
the system more than a normal workstation does.
In the following, the invention will be de-
scribed by the aid of a few examples of its embodi-
ments by referring to the attached drawing, in which
Fig. 1 presents a system according to the
present invention; and
Fig. 2 presents a flowchart representing the
operation of the system in Fig. 1.
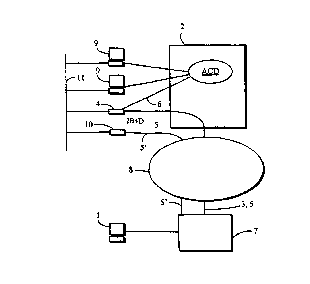
Fig. 1 presents a diagrammatic example of a
system according to the invention. The system compri-
ses a host exchange 2, which may be a normal telephone
exchange provided with the functions required by an
automatic call allocation system ACD. Connected to the
subscriber ports (not shown) of the host exchange 2
are two workstations 9 for operator use. In the commu-
nication between the workstation 9 and the ACD, a pro-
tocol defined by the manufacturer of the system is us-
ed. Fig. 1 further shows an adapter 4 connected to the
host exchange 2 via a 2B+D interface so that one of
the B channels is used to set up a data link connecti-
on 5 via an ISDN network 8 to a remote workstation 1
while the other B channel is used to set up a data
link connection 6 to the automatic call allocation
system ACD. Further, the remote workstation 1 is con-
nected to a local exchange 7, which may be located in
any part of the world. From the local exchange 7, a
data link connection 5 is set up to the host exchange
2 and to the adapter 4 via the ISDN network 8. In ad-
dition, the system presented in Fig. 1 comprises a ro-
uter 10, which can alternatively be used to set up a
CA 02269357 1999-04-20
WO 98/18227 PCTIFI97/00612
6
data link connection 5' . In this case, the communica-
tion protocol used may be e.g. the TCP/IP protocol
(Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol). The
router is used to adapt e.g. TCP/IP signalling into a
form acceptable to the adapter 4 and the automatic
call allocation system.
Fig. 1 further shows an LAN network 11 (Local
Area Network), which is a local network used in data
communication. An LAN network is a network with a high
transmission capacity, usually owned by a company or
institution and used for internal data communication
within a relatively small, geographically limited
area. The network consists of workstations and ser-
vers. The router 10 is connected to the LAN 11, so a
link between the adapter 4 and the remote workstation
1 can be set up directly by forming e.g. a TCP/IP con-
nection from the remote workstation directly to the
router 10 and further via the LAN to the adapter 4.
Such a connection can be set up using a data network
independent of the telephone network, e.g. a packet-
switched data network.
Referring to Fig. 1 and 2, a preferred embo-
diment example of the operation of the system of the
invention will now be described. When the operator of
a remote workstation 1 starts working, he/she logs in
(log-in procedure) into the automatic call allocation
system ACD. At this time, a data link connection 5 is
set up between the remote workstation 1 and the adap-
ter 4, unless a connection has already been set up.
The data link connection setup is performed as a nor-
mal ISDN connection setup by having the remote
workstation 1 call the subscriber number of the adap-
ter 4. The remote workstation 1 sends a SETUP message
to the local exchange 7. In the SETUP message, the
called-party number is the subscriber number of the
adapter 4. With the SETUP message, a UUS information
packet containing the required log-in data is
....~...._.... ,_.. ._........... ...... .... . i. . , ~ ..... ..
CA 02269357 1999-04-20
WO 98/18227 PCT/FI97/006I2
7
transmitted. When the local exchange 7 receives the
SETUP message, it generates and send into the ISDN
network an IAM message based on the SETUP message; the
IAM message contains the same data as the SETUP
message . The network 8 routes the call to the adapter
' as a normal ISDN call.
When the host exchange 2 receives the call,
it reserves one of the B channels in the 2B+D interfa-
ce connecting it to the adapter 4 and sends a SETUP
message to the adapter. The message contains the re-
quired log-in data in its UUS information element.
When the adapter 4 receives the data, it generates a
new SETUP message and sends it to the ACD function of
the host exchange 2. The message contains the data re-
quired for log-in in the same format in which a
workstation 9 connected to the ACD would send it.
From now on, the ACD directs calls via the
adapter to the remote workstation just as it would di-
rect calls to local workstations. The ACD sees the
adapter 4 in the same way as it sees a workstation 9
connected to the host exchange. Adding a remote
workstation concept to the ACD does not require any
updating of software in the host exchange 2 or any ot-
her network elements of the telephone network.
When a call comes via the ACD function and it
is directed via the adapter 4 to a remote workstation
1, the operation of the adapter is as follows. For the
incoming ACD call, the host exchange reserves the ot-
her free B channel in the 2B+D interface connecting it
to the adapter 4. One of the B channels was already
reserved earlier, when the remote workstation 1 logged
in into the ACD. In other words, among the interfaces
in the exchange, the adapter reserves only one 2B+D
interface for each remote workstation.
The adapter 4 receives the SETUP message,
which contains call data needed by the remote worksta-
tion 1 as well as data relating to display control in
CA 02269357 1999-04-20
WO 98/18227 PCT/FI97100612
8
the remote workstation. The adapter converts these da-
ta for the UUS information element and transmits them
further in a USER INFORMATION message to the remote
workstation. A data link connection 5 between the re-
mote workstation 1 and the adapter 4 was already set
up at log-in time, so it need not be set up again at
this stage.
As the call progresses, the host exchange
transmits messages in accordance with DSS1 signalling
(Digital Signalling System 1), from which a USER INFO
message is generated when necessary and transmitted to
the remote workstation 1. The adapter 4 takes care of
the control of DSS1 messages all the time during the
connection. When the remote workstation 1 answers the
call, it generates a USER INFO message for the adap-
ter. When the adapter 4 receives the USER INFO
message, it connects the B channel going to the remote
workstation 1 and the B channels of the incoming call
and sends a CONNECT message to the host exchange 2,
whereupon the voice connections are made and the
subscriber being served and the remote workstation 1
can hear each other.
When the remote workstation 1 wishes a . g . to
transfer a call to another subscriber, the action is
as follows. In the USER INFO message, the remote
workstation 1 sends information indicating that it
wants to make an inquiry call to another subscriber.
The message contains the information needed for call
setup, such as the subscriber number. The adapter 4
receives this information in the USER INFO message.
Further, the adapter 4 generates an inquiry all con-
nection request to the host exchange just as a local
exchange would do. The adapter 4 converts the required
information obtained from the signalling messages con-
cerning the inquiry call connection request into a
USER INFO message and transmits it to the remote
workstation 1. When the called subscriber of the in-
CA 02269357 1999-04-20
WO 98/18227 PCT/FI97/00612
9
quiry call answers, the remote workstation 1 can re-
quest call transfer. The remote workstation generates
from the request a USER INFO message, which is sent to
the adapter. In the DSS1 message, the call transfer
request is passed to the host exchange, which carries
out the call transfer and releases the remote worksta-
tion 1.
When the host exchange 2 releases the remote
workstation 1, either after a transfer or a normal
call, a disconnection request is sent in accordance
with the DSS1 protocol to the adapter 4, which informs
the remote workstation 1 about the disconnection via a
USER INFO message. The adapter takes care of discon-
nection according to the DSS1 protocol of the link to
the host exchange 2. The host exchange frees the adap
ter 4 from the call and releases one of the B channels
and adds the remote workstation 1 to the queue of free
workstations in the ACD function. The remote worksta
tion 1 is now ready to receive new calls or to initia
to calls itself.
When the remote workstation 1 starts a call
setup procedure itself, the data required for the con-
nection are transmitted in USER INFO messages to the
adapter. The adapter 4 sends a SETUP message to the
host exchange 2. The adapter 4 has converted the in-
formation needed for call setup that it has received
in the USER INFO message, and included it in the SETUP
message. The host exchange 2 reserves a B channel in
the 2B+D interface connecting to the adapter 4 and re-
moves the remote workstation 1 from the queue of free
workstations. When the adapter 4 receives acknowledge-
ment of receipt of the SETUP message, it connects the
B channel coming from the remote workstation 1 and the
B channel reserved for the new call, whereupon the re-
mote workstation can hear the signals and messages re-
lating to call setup.
CA 02269357 1999-04-20
WO 98118227 PCTIFI97I00612
When the operator at the workstation stops
working, he/she logs out from the system (log-out pro-
cedure), whereupon the remote workstation sends to the
adapter a USER INFO message indicating that the opera-
s for has stopped working . The adapter transmits a log-
out procedure to the ACD. When the log-out procedure
has been carried out in the ACD, the adapter 4 discon-
nects the voice connection reserved in the log-in pro-
cedure between the remote workstation 1 and the adap-
10 ter, unless the connection is still needed. Generally,
it can be stated that the setup/disconnection of a da-
ta link connection is largely dependent both on the
start-up procedure (starting of software) and on the
shut-down procedure (shutting down of the software) of
the remote workstation. After this, the remote
workstation 1 functions like a normal ISDN terminal
device, until a new log-in procedure is carried out.
The invention is not limited to the examples
of its embodiments described above, but instead many
variations are possible within the framework of the
inventive idea defined by the claims.
.._........ T r . ... . . . .......