Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02275544 1999-06-11
-1-
TITLE
A Lebetin Peptide which inhibits Platelet Aggregation
DESCRIPTION
The invention relates to a peptide derived from lebetin, and to its use in
methods for
the treatment of thrombosis or thromboembolism.
Several components isolated from snake venom, e.g. platelet aggregation
inhibitors,
phospholipases and ADPases, thrombin-like enzymes and fibrinolytic enzymes,
affect
hemostasis by interfering with the coagulation and platelet aggregation
processes.
Platelet aggregation involves a complex network of cell surface adhesion
proteins, one
of which is GPIIb/IIIa. GPIIb/IIIa binds fibrinogen and this binding is
inhibited by
proteins ( "disintegrins") isolated from snake venom and containing an RGD
sequence.
Fibrinogen-GPIIb/IIIa interaction is the final step of a complex cascade of
biochemical
reactions and cell morphological changes, including activation of platelets
which
become competent to bind fibrinogen, changes in shape, secretion of the
granular
content and aggregation. These events are induced by platelet aggregation
agonists and
each of these may be a target for anti-aggregation agents.
Barbouche et al (FEBS Letters 392 (1996) 6-10] have recently isolated a new
inhibitor
of platelet aggregation from Vipera lebetina venom. This isolate, lebetin,
lacks the
RGD sequence of the disintegrins. Lebetin is composed of two groups of related
peptides, lebetin 1 and lebetin 2. Lebetin 1 is a mixture of two proline and
lysine rich
peptides, one (sLla) of 13 amino acid residues and the other (sL113) of 12
amino acid
residues, the same sequence but lacking the N-terminal glycine of sLla. sLla
and
sL113 have the following amino acid sequences:
sLl« GDNKPPKKGPPNG (SEQ ID NO 1), and
sL113 DNKPPKKGPPNG (SEQ ID NO 2).
Lebetin 2 also consists of two peptides, one of 38 amino acid residues (sL2a)
and the
other of 37 amino acid residues (sL213) . sL2a has sL 1 a at its N-terminal
and a 25
amino acid residue peptide with one disulphide bridge at its C-terminal. sL213
has the
same sequence but lacking the N-terminal glycine of sL2a.
The invention provides a peptide (hereinafter called sLl ;~) having the amino
acid
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02275544 1999-06-11
_7_ . .
sequence NKPPKKGPPNG (SEQ ID NO 3).
sLly has proven more effective as an inhibitor of platelet aggregation than
native
lebetin 1 or its components sLla and sL113.
The invention also includes within its scope a modified sLly peptide in which
one or
more of the amino acid residues is a D-amino acid residue. D amino acids last
longer in
vivo because they are harder for peptidase to cut, but the L amino acids have
better
activity.
Moreover, peptide analogues, synthetic constructs using the carbon skeleton of
peptides
but omitting the -CONH- peptide bonds, can be employed in place of peptides.
Thus, it
should be understood that the invention also includes within its scope a
modified sLl°~
peptide in which at least one of the amino acid residues is replaced by its
decarboxamido analogue. It is believed that such peptide analogues will be
more
resistant to peptidase and last longer in vivo.
Synthetic methods
1. Manual Synthesis of the lebetin 1 peptides using Boc-chemistry
The synthetic lebetin 1 peptides sLl a (Glyl-Gly 13), sL113 (Asp2-Gly 13) and
sLly
(Asn3-Gly 13) were assembled manually by the solid phase technique (R. B.
Merrifield,
1986) on Boc-aminoacyl-Pam resin (0.5 mmol, substitution 0.67-0.82 mequiv of
amino
group per gram). The following side-chain protecting groups for trifunctional
Boc-amino acids were used: cyclohexyl (CHex) for Asp, 2-chlorobenzyloxy (C1Z)
for
Lys and 2-bromocarbobenzoxy (BrZ) for Tyr. The synthesis cycle used for
incorporation of each Boc-amino acids was: ( 1 ) dichloromethane (DCM) wash,
(2 x
0.5 min); (2) 65 % trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in DCM for deprotection step, 2
min and
13 min; (3) DCM wash, 0.6 min; isopropanol wash, 0.5 min; (4) DCM wash, (2 x
0.5
min); (5) N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) wash, (2 x 0.5 min); (6) Boc amino acid (4
equiv) and PyBOP (4 equiv) in NMP and (7) diisopropylethylamine (DIEA) (8
equiv)
for Boc-as coupling, 3 min; and (8) two NMP washes, 1 min. Each coupling step
was
monitored by using the qualitative ninhydrin test and recoupling was performed
as
necessary. Unreacted amino groups detected by ninhydrin after two consecutive
couplings were blocked by acetylation withy 50 % acetic anhydride in DCM for
10 min.
At the end of the assembly and after the last deprotection step, the peptidyl
resin was
dried under vacuum. The high hydrogen fluoride (HF) procedure was achieved for
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02275544 1999-06-11
-3-
deprotection and cleavage from the resin using 10 % p-cresol per volume as a
scavenger. After removal of HF in vacuo, the resin was washed with cold
diethylether
and the peptide extracted with water. The crude peptides were purified by
reversed-phase preparative medium-pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC)
(Labomatic, C 18 HD-SIL 15-22 ~cm, 26 x 313 mm) using a 90-min linear Gradient
of
acetonitrile in 0.1 % (by vol . ) TFA/H~ O from 0 to 30 % , at a flow rate of
10 mllmin
with UV detection at 206 nm. The homogeneity of the fractions was assessed by
analytical HPLC (Merck, C 18 Lichrospher, 4 x 125 mm). Fractions containing
homogeneous peptides ( > 99 % ) were pooled and lyophilized.
Experimental Results
Platelets were prepared from 0.2M EDTA treated blood samples. Human platelets
were
prepared as follows: blood was collected in vials containing a sodium citrate/
dextrose
( 1: 5 v/v j mixture from a donor who had not taken any drug for at least 1
week.
Platelets were resuspended in Tyrod's buffer pH 7.4 at a final concentration
of 3 x 108
cells/ml prior to the assay which was performed at 37°C with stirring
in an
aggregometer. For anti-aggregation activity assays, washed platelets ( 1.2 x
108
cells/400 ~1) were incubated at 37 ° C for 2 min with peptides, and
then stimulated with
the agonist. The aggregation was monitored by recording the change in light
transmission. The concentration of peptide giving 50 %o inhibition of platelet
aggregation (ICSo) was determined from the dose responsive curve.
1. In vitro anti platelet a~Rre~ation by lebetins.
Rabbit platelets (3 x 108 cells/ml) were incubated with lebetin 1 for 2
minutes at 37 ° C .
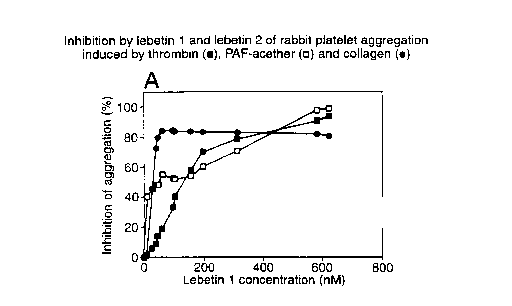
Agonists were then added. Figure 1 shows the inhibition by native lebetin 1 of
rabbit
platelet aggregation induced by 0.04 IU/ml thrombin (plotted as ~, 10-7 M
PAF-acether (plotted as D) and 5 ~,g/ml collagen (plotted as ~). Rabbit
platelet
aggregation induced by thrombin, PAF-acether and collagen was inhibited by
lebetin 1
with ICSOS of 125, 48 and 27 nM respectively.
Human platelets (3 x 108 cells/ml) were incubated with native lebetin 1
(plotted as ~ in
Figure 2) for 2 minutes at 37°C. Thrombin was then added. Native
lebetin 1 inhibited
thrombin induced aggregation of human platelets with an ICSO of 590 nM.
Rabbit platelets (3 x 108 cells/ml) were incubated with sLla (plotted as 1 in
Figure 3),
sL113 (plotted as 1 in Figure 3) and sLly (plotted as ~ in Figure 3) for 2
minutes at
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02275544 1999-06-11
_4- " .
37°C. 0.04 IU/ml Thrombin was then added. Rabbit platelet aggregation
induced by
thrombin was inhibited by sLla, sL113 and sLly with ICSOS of 23, 10 and 7 nVI
respectively.
Rabbit platelets (3 x 10g cells/ml) were incubated with sLla (plotted as 1 in
Figure
4A), sL113 (plotted as ~ in Figure 4B) or sLly (plotted as ~ in Figure 4A) for
2
minutes at 37°C. 5 ~,g/ml of collagen was then added.
Human platelets (3 x 10g cells/ml) were incubated with sLla (plotted as 1 in
Figure
SA), sL113 (plotted as ~ in Figure 5A) or sLly (plotted as ~ in Figure SB) for
2
minutes at 37°C. 0.04 IU/ml Thrombin was then added. Human platelet
aggregation
induced by thrombin was inhibited by sLla, sL113 and sLly with ICSOS of 140,
32 and
3 nl~i respectively.
Results are shown in the Figures as mentioned above, and also in the Table
below.
TABLE
Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation induced by Thrombin
Rabbit Human
Platelets Platelets
Optimal Optimal
ICSO ICSO
Inhibition Inhibition
Concentration Concentration
( % (~)
)
(~)
Lebetin 125 - - 590 - -
1
sLla 23 50 106 140 55 170
sL113 10 87 106 32 49 170
sLly 7 93 33 3 73 8
sLly appeared to be about 20 (ICSO=7nM) and 200 (ICSO=3nM) times more active
than native lebetin 1 for the inhibition of either rabbit (ICSo=125nM) or
human
(ICSO=590nM) platelet aggregation (induced by thrombin) respectively. sLly was
also
notably more active than sLla or sL113 on both rabbit and human platelets.
2. Inhibition by lebetins of collagen-induced thrombocytopenia in rats
sLla (plotted as D in Figure 6), sL113 (plotted as O in Figure 6) or sLl~~
(plotted as O
in Figure 6) were injected into the left jugular vein of anesthetised rats.
After 2
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02275544 1999-06-11
minutes, 1 mg/kg body weight of collagen was injected into the jugular, and 1
minute
later blood was sampled from the right carotid and platelet rich plasma was
prepared.
The percentage of inhibition is the ratio of platelet counts in rats which
received
lebetins against those which received saline solution. The EDSOS were 10.7,
3.2 and 3.1
nmol/kg for sLla, sL113 and sLll respectively.
3. Study of toxicity in vivo
sLly (100 ~cg) was devoid of toxicity in Swiss mice (20 ~ 2 g) after injection
whether
intracerebroventricularly, intraperitoneally or subcutaneously.
These results suggest that sLly will be useful for the treatment of thrombosis
or
thromboembolism in veins and arteries, and accordingly the invention further
provides
a method for the treatment of thrombosis or thromboembolism in the veins or
arteries
of a patient, the method comprising administering to the patient an effective
amount of
the peptide sLly. In particular, it is envisaged that the method of treatment
will be
suitable for anti-thrombotic therapy in animals and humans for venous
thrombosis,
coronary ischaemic event, pulmonary embolism, and in the pre-operative,
operative
and post-operative periods of endovascular examination and of cardiovascular
surgery.
It is also envisaged that the peptide sLly will be useful for prophylactic
anticoagulant
therapy including the prevention of restenosis after transluminal angioplasty,
for the
development of coagulation tests and platelet functional exploration, and for
vascular
imaging by the injection of tracers.
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02275544 1999-06-11
-6-
SEQUENCE LISTING
(1) GENERAL INFORMATION:
(i) APPLICANT:
(A) NAI1~IE: Armel S.A.
(B) STREET: 50 rue Basse
(C) CITY: Steinsel
(E) COUNTRY: Luxembourg
(F) POSTAL CODE (ZIP): L-7307
(ii) TITLE OF INVENTION: A Lebetin Peptides which inhibits Platelet
Aggregation
(iii) NUMBER OF SEQUENCES: 3
(iv) COMPUTER READABLE FORM:
(.A) MEDIUM TYPE: Floppy disk
(B) COMPUTER: IBM PC compatible
(C) OPERATING SYSTEM: PC-DOS/MS-DOS
(D) SOFTWARE: Patentln Release #1.0, Version #1.30 (EPO)
(vi) PRIOR APPLICATION DATA:
(A) APPLICATION NUMBER: GB 9627116.8
(B) FILING DATE: 31-DEC-1996
(2) INFORMATION FOR SEQ ID NO: 1:
(i) SEQUENCE CHARACTERISTICS:
(A) LENGTH: 13 amino acids
(B) TYPE: amino acid
(C) STRANDEDNESS:
(D) TOPOLOGY: linear
(ii) MOLECULE TYPE: peptide
(xi) SEQUENCE DESCRIPTION: SEQ ID NO: 1:
Gly Asp Asn Lys Sro Pro Lys Lys Gly PrOo Pro Asn Gly
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02275544 1999-06-11
(2) INFORMATION FOR SEQ ID NO: 2:
(i) SEQUENCE CHARACTERISTICS:
(A) LENGTH: 12 amino acids
(B) TYPE: amino acid
(C) STRANDEDNESS:
(D) TOPOLOGY: linear
(ii) MOLECULE TYPE: peptide
(xi) SEQUENCE DESCRIPTION: SEQ ID NO: 2:
Asp Asn Lys Pro Pro Lys Lys Gly Pro Pro Asn Gly
1 5 10
(2) INFORMATION FOR SEQ ID NO: 3:
(i) SEQUENCE CHARACTERISTICS:
(A) LENGTH: 11 amino acids
(B) TYPE: amino acid
(C) STRANDEDNESS:
(D) TOPOLOGY: linear
(ii) MOLECULE TYPE: peptide
(xi) SEQUENCE DESCRIPTION: SEQ ID NO: 3:
Asn Lys Pro Pro Lys Lys Giy Pro Pro Asn Gly
1 5 10
AMENDED SHEET