Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
1
DEVICE FOR STIRRING AND AERATING A LIQUID AND
ELIMINATING
FOAM IN A TANK FOR TREATING SAID LIQUID
The present invention relates to a device for
stirring and aerating a liquid and eliminating foam in
a tank or vat treating this liquid, such as for example
fatty waste products extracted from effluents of town
sewage or agricultural food industries.
As is known, the town sewage effluents which
circulate in discharging pipes such as drains are
collected in purification stations in which there are
carried out various treating operations to purify them
before returning them to the natural medium.
This purification produces by-products related to
iS the purification such as fat, sludges ...
Dumping sites are less and less inclined to accept
this type of products so that the purification stations
must.now be capable of treating them and limiting them
as far as possible.
Thus, the fat trapped at the inlet of the
purification station are poured into a treating tank
such as for example a biological degradation tank which
comprises a mechanical stirrer for stirring the liquid.
Further, the tank may include internally and in
its lower part injection manifolds for injecting air
under pressure into the liquid for aerating and
accentuating the stirring of the liquid.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
2
But this type of aerating and stirring device is
more particularly suitable for fluids which are only
lightly charged, i.e. of low viscosity, and its
efficiency rapidly drops for fluids charged in
particular with fat.
Further, in the course of the treatment of the
liquid, such as for example fatty waste products, with
this type of device there is formed on the surface of
the liquid a
layer of foam which flies away and pollutes the
environment so that it is necessary to provide means
for eliminating this foam floating on the surface of
the liquid in the course of the treatment of the
latter.
Up to the present time, these means have been
formed by stirrers disposed at the level of the surface
of the liquid and adapted to flatten the foam.
But these stirrers are not entirely satisfactory
and a part of the foam flies away and pollutes the
environment.
An object of the invention is to avoid these
drawbacks by proposing a device for stirring and
aerating a liquid, such as for example fatty waste
products extracted from town sewage effluents or
23 agricultural food industries, which permits, with
simple means and a low consumption of energy,
effectively treating this type of liquid and recovering
. . i . . . ,
CA 02276760 2003-01-06
3
the foam floating on the surface of the liquid.
The invention therefore provides a device for
stirring and aerating a liquid and eliminating the foam in
a tank for treating said liquid, comprising inside said
tank:
- a vertical sheath extending in a part of the height
of said tank and comprising, in its upper part, at least a
first opening providing an entry passage for said
liquid and, near the bottom of said tank, at least a
second opening providing an exit passage for said liquid,
- a funnel located around the upper part of said
sheath and connected to said sheath, the upper edge of
said funnel defining with a wall of said tank a free space
for the passage of said liquid,
- a main propeller located inside said sheath below
the bottom of said funnel,
- a vertical shaft driven in rotation, extending
inside said sheath above said propeller and driving the
latter in rotation,
- an anti-vortex means located inside said sheath,
below said propeller,
- means for injecting a gas under pressure in said
sheath, below said anti-vortex means, and
- uniquely static stirring means for stirring said liquid
by turbulence inside said sheath, said static stirring
means being located below said antivortex means.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
4
- means for injecting a gas under pressure into
the sheath below the anti-vortex means.
According to other features of the invention:
- the tank is insulated,
- the device comprises means for regulating the
flow of the liquid and of the foam sucked by the
propeller inside the sheath,
- the- device comprises means for effecting a
static stirring by cavitation of the liquid inside the
sheath and disposed below the anti-vortex means in said
sheath,
- the means for regulating the flow of the liquid
and of the foam sucked by said propeller are formed,
on one hand, by a first sleeve disposed around the
sheath at the level of the first series of ports and,
on the other hand, by a second sleeve disposed around
said sheath at the level of the second series of ports,
the position of said sleeves relative to the
corresponding ports being vertically adjustable,
- the means for effecting a static stirring by
cavitation are formed, on one hand, by a vertical tube
disposed inside the sheath and extending from the
bottom of the tank to below the anti-vortex means and,
on the other hand, by superimposed static obstacles
disposed inside said sheath and fixed to said tube,
- the device comprises a second anti-vortex means
disposed inside the sheath and above the main
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
propeller, said second anti-vortex means being formed
by at least two vertical plates each extended upwardly
by a stiffening rib extending up to the upper end of
said sheath.
5 - the device comprises a liquid accelerator inside
the sheath,
- the device comprises means for aerating the
surface of the liquid inside the tank,
- the device comprises a vortex pump for the
suction of the liquid surface inside the sheath,
disposed above the second anti-vortex means and at the
level of the first series of ports,
- the device comprises a propeller having a single
passage for the suction of the liquid inside the
sheath, disposed above the second anti-vortex means and
at the level of the first series of ports,
- the device comprises a propeller having two
passages for the suction of the liquid inside the
sheath, disposed above the second anti-vortex means and
at the level of the first series of ports.
Further features and advantages of the invention
will be apparent in the course of the following
description with reference to the accompanying
drawings, in which:
- Fig.l is a diagrammatic sectional view of a tank
for treating a liquid provided with a first embodiment
of a device for stirring and aerating said liquid
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
6
according to the invention,
- Fig.2 is a sectional view taken on line 2-2 of
Fig. 1,
- Fig.3 is a diagrammatic sectional view of a tank
S for treating a liquid provided with a second embodiment
of a device for stirring and aerating said liquid
according to the invention,
- Fig.4 is a sectional view taken on line 4-4 of
Fig. 3,
- Fig.5 is a diagrammatic partial sectional view
of a third embodiment of a device for stirring and
aerating the liquid according to the invention,
- Fig.6 is a diagrammatic sectional view of a
liquid accelerator of the stirring and aerating device
according to the invention,
- Fig.7 is a diagrammatic sectional view of means
for aerating the surface of the liquid,
- Fig.8 is a diagrammatic partial sectional view
of a fourth embodiment of a device for stirring and
aerating the liquid according to the invention,
- Fig.9 is a diagrammatic view to a larger scale
of the vortex pump of, the fourth embodiment of the
device according to the invention,
- Fig. 10 is a sectional view taken on line 10-10
of Fig. 9,
- Fig.ll is a diagrammatic partial sectional view
of a fifth embodiment of a device for stirring and
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
7
aerating the liquid according to the invention,
- Fig.12 is a sectional view taken on line 12-12
of Fig.11,
- Fig.13 is a diagrammatic partial sectional view
of a sixth embodiment of a device for stirring and
aerating the liquid according to the invention,
- Fig.14 is a sectional view taken on line 14-14
of Fig. 13.
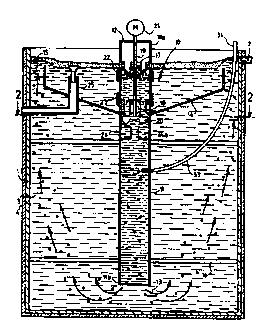
Shown in Figs. 1 and 3 is a tank or vat 1 provided
in its upper part with an inlet 2 for a liquid 3 to be
treated, such as for example fatty effluents extracted
from town sewage effluents.
The treating tank 1 is covered on its outer side
with an insulation 4 and comprises a device, designated
by the general reference numeral 10, for stirring and
aerating the 5 liquid and eliminating the foam.
The device 10 according to the invention, disposed
inside the tank 1, comprises a vertical sheath 11
extending in a part of the height in the tank 1.
The upper end 11a of the sheath 11 is closed by a
plate 12 and the lower end of the sheath 11 is open and
defines with the bottom of the tank 1 a passage 13 for
the liquid 3.
The device 10 further comprises an upwardly
divergent funnel 14 whose upper edge defines with the
wall of the tank 1 a free space 15 for the passage of
the liquid 3 and whose lower edge is connected to the
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
8
sheath 11 at a certain distance from the upper end of
the sheath 11.
The assembly comprising the sheath 11 and the
funnel 14 is fixed inside the tank 1 by suitable
means, such as for example struts 16 which define
therebetween passages for the liquid 3.
The sheath 11 comprises a first series of ports 17
evenly spaced apart on the periphery of the sheath 11
and situated at the level of the liquid in the funnel
14.
This sheath 11 is further provided with a second
series of ports 18 evenly spaced apart on the periphery
of the sheath 11 and situated above the bottom of the
funnel. The device 10 is also provided with means for
sucking the liquid and the foam inside the sheath 11
through the ports 17 and 18 and are formed by a
vertical shaft 19 disposed inside the sheath 11 and
extending from the upper end of the sheath 11 to the
bottom of the funnel 14 and by a main propeller or
screw 20 fixed on the free end of the shaft 19 below
the bottom of the funnel 14.
The diameter of the main propeller 20 is slightly
less than the inside diameter of the sheath 11.
The shaft 19 and the propeller 20 are driven in
rotation by a motor-speed reducer unit 21 which is
fixed to the plate 12 closing the upper end of the
sheath 11.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
9
The device 10 is provided with means for
regulating the flow of the liquid and of the foam
sucked by the main propeller 20 inside the sheath 11
through the ports 17 and 18.
These regulating means comprise, on one hand, a
first sleeve 22 disposed around the sheath 11 at the
level of the first series of ports 17 and, on the other
hand, a second sleeve 23 disposed around the sheath 11
at the level of the second series of ports 18.
The position of each sleeve 22 and 23 relative to
the ports 17 and 18 respectively is vertically
adjustable by suitable clamping means (not shown).
An anti-vortex means 24 is disposed inside the
sheath 11 below the propeller 20 to prevent rotation of
the liquid 3 in the sheath 11.
As shown in Fig. 2, this anti-vortex means 24 is
formed by three vertical plates 24a spaced 120 apart
inside the sheath 11.
The device 10 is also provided with means for
regulating the level of the liquid 3 in the funnel 14
which comprise an overflow pipe 25 disposed inside the
funnel 14 in a vertically adjustable position.
In a second embodiment shown in Fig. 3, the device
10 comprises means 30 for effecting a static stirring
by cavitation of the liquid 3 inside the sheath 11 and
disposed below the anti-vortex means 24 in the sheath.
As shown in Figs. 3 and 4 the means 30 for the
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
static stirring by cavitation of the liquid 3 comprise,
on one hand, a vertical tube 31 disposed inside the
sheath 11 and extending from the bottom of the tank 1
to below the anti-vortex means 24 and, on the other
5 hand, superimposed static obstacles 32 disposed inside
the sheath 11 and fixed on the tube 31.
The tube 31 is fixed to the bottom of the tank 1
by suitable means.
The static obstacles 32 define with the inner wall
10 of the sheath 11 passages for the circulation of the
liquid.
As shown in Fig. 1, the static obstacles 32
arranged along the tube 31, on one hand, below the
anti-vortex means 24 and, on the other hand, in the
lower part of the sheath 11.
For example, the tube 31 comprises in its upper
part below the anti-vortex means 24 two superimposed
static obstacles 32 and in the lower part of the sheath
11 also two superimposed static elements 32.
In a variant, the static obstacles 32 may be
evenly spaced apart throughout the portion of the tube
31 disposed in the sheath 11.
In an embodiment shown in Fig. 3, the static
obstacles 32 are formed by cups whose concavity faces
toward the bottom of the tank 1.
In a variant, the static obstacles 32 may be
formed by discs.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
11
Finally, the device 10 comprises means 33 for
injecting a gas under pressure, such as for example
air, into the sheath 11.
These injecting means 33 are formed by at least
one pipe 34 which opens into the sheath 11 for example
at a level situated below the static elements 32
disposed in the upper part of the tube 31.
The device just described operates in the
following manner.
The liquid 3 to be treated is poured through the
inlet 2 into the tank 1 up to a level above the upper
edge of the funnel 14.
This liquid 3 is also poured into the funnel 14.
The motor-speed reducer unit 21 drives the shaft
1S 19 in rotation which drives the main propeller 20 in
rotation.
Simultaneously, the gas under pressure is injected
into the sheath 11 through the pipes 34.
The rotation of the main propeller 20 causes the
suction of the liquid 3 into the sheath 11 through the
ports 17 and 18 so that this liquid 3 continuously
circulates from the top to the bottom in the sheath 11,
then passes through the space 13 and circulates from
the bottom to the top between the sheath 11 and the
inner wall of the tank 1, and so on.
The anti-vortex means 24 prevents the rotation of
the liquid in the sheath 11 below the propeller 20.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
12
The level of the liquid 3 in the funnel 14 is
below the level of the liquid in the tank 1 and this
level of the liquid in the funnel 14 is regulated by
the overflow pipe 25 so that it is substantially midway
of the height of the ports 17.
Further, owing to the suction created by the
propeller inside the sheath 11, the level of the liquid
in the
sheath 11 is below the level of the liquid in the
funnel 14.
The air driven inside the sheath 11 by the
rotation of the propeller 20 and the gas under pressure
injected into the sheath 11 create gas bubbles which
are dispersed in the liquid 3 in the sheath 11 under
the effect of the rotation of the propeller 20.
During the circulation of the liquid 3 in the
sheath 11, the static obstacles 32 create below each of
the latter a cavitation effect which promotes the
stirring and the aeration of the liquid 3.
These obstacles 32 have the advantage of being
static while promoting the stirring and the aeration of
the liquid in the sheath 11 and prevent the catching of
stringy 5 substances inside the sheath 11.
In this way, the liquid 3 is stirred and the gas
bubbles are divided into micro-bubbles promoting the
dispersion of the gas and consequently the aeration of
the liquid 3.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
13
Between the inner wall of the tank 1 and the
sheath 11, the gas bubbles accelerate the rising of the
liquid and promote the circulation of this liquid in
the tank 1, thereby improving the efficiency.
Thus the liquid to be treated passes several times
through the sheath 11 and therefore undergoes several
oxygenation treatments.
The flow of the liquid 3 may be regulated by
shifting the sleeves 22 and 23 relative to the ports 17
and 18.
The stirring of the liquid 3 by the propeller 20
and the static obstacles 32 causes foam to be formed on
the surface of the liquid 3 in the tank 1.
The rotation of this propeller 20 inside the
sheath 11 produces a pumping effect at the level of the
surface of the liquid 3 in the funnel 14, a suction of
the foam floating on the surface of the liquid and a
drop in the level of the latter in the sheath 11.
The foam is consequently entrained, drowned in and
mixed with the liquid 3 in the tank 1 so that it is
possible to progressively eliminate it.
The position of the sleeves 22 and 23 relative to
the ports 17 and 18 regulates the flow of liquid and
foam 5 sucked inside the sheath 11 by the propeller 20.
The choice of the main propeller 20 and the speed
of rotation of the latter permits adapting the
consumption of energy in accordance with the liquid to
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
14
be treated.
In the case where the device according to the
invention does not include static elements 32 as shown
in Fig. 1, turbulences are created naturally inside the
sheath 11.
But the efficiency is low which is suitable for
liquids only slightly charged.
The static obstacles 32 promote the stirring of
the liquid by cavitation and this improves the
efficiency of the device.
In a variant, the static stirring means with the
cavitation effect are formed by static obstacles fixed
to the inner wall of the sheath 11 and defining an
axial passage for the circulation of the liquid 3.
These static obstacles are evenly spaced apart
throughout the portion of the sheath 11 below the anti-
vortex means 24 or inside the sheath 11, on one hand
below the anti-vortex means, 24 and, on the other hand,
in the lower part of the sheath 11.
In this case also, the static obstacles are formed
for example by cups the concavity of which faces toward
the bottom of tank 1 or by discs.
In a third embodiment shown in Fig. 5, the device
comprises a second anti-vortex means 40 disposed inside
the sheath 11 and above the main propeller 20.
This second anti-vortex means 40 comprises at
least two vertical plates 40a each upwardly extended by
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
a reinforcing rib 41 extending up to the upper end of
the sheath 11.
Preferably, the second anti-vortex means 40 is
formed by four vertical plates 40a evenly spaced apart
5 inside the sheath 11 and each upwardly extended by a
reinforcing rib 41.
In another embodiment shown in Fig. 6, the device
comprises a liquid accelerator inside the sheath 11.
This liquid accelerator comprises a secondary
10 propeller 45 disposed above the second anti-vortex
means 40 and fixed to rotate with the shaft 19.
The secondary propeller or screw 45 has a pitch
oriented in the same direction as the pitch of the main
propeller or screw 20.
1S Further, the liquid accelerator further comprises
an anti-vortex means 46 disposed above the secondary
propeller 45 and inside a cylindrical stack 47.
The stack 47 is fixed to the inner edge of the
reinforcing ribs 41 so as to define with the sheath 11
and between the reinforcing ribs 41 passages 48 for the
liquid.
The secondary propeller 45, the anti-vortex means
46 and the stack 47 are situated between the two series
of ports 17 and 18 which are provided, in this
embodiment, with means for regulating the flow of the
liquid 3 and the flow of the foam sucked inside the
sheath 11.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
16
The rotation of the main propeller 20 causes the
suction of the liquid 3 into the sheath 11 through the
ports 17 and 18 so that this liquid 3 continuously
circulates downwardly in the sheath 11.
Further, owing to the rotation of the secondary
propeller 45, the suction of the liquid 3 into the
sheath 11 through the ports 17 and 18 is accelerated
and a part of the liquid rises through the passages 48
provided between the sheath 11 and the stack 47 which
still further accentuates this phenomenon of the
acceleration of the liquid in the sheath 11.
In this case also, the regulation of the level of
the liquid 3 in the sheath 11 is again achieved by the
position of the sleeves 22 and 23 relative to the ports
17 and 18.
The anti-vortex means 46 prevents the rotation of
the liquid in the stack 47.
This embodiment is in particular suitable for
products which have a particular tendency to foam.
Indeed, owing to the acceleration of the suction
of the liquid 3 inside the stack 47 and the
recirculation of a part of this liquid in the passages
48, the foam floating on the surface of the liquid 3 is
sucked inside the stack 47.
In another embodiment shown in Fig. 7, the device
comprises means for aerating the surface of the liquid
3 in the tank 1.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
17
As shown in this Fig. 7, the means for aerating
the surface of the liquid 3 are formed by a secondary
propeller or screw 50 disposed above the second anti-
vortex means and fixed to rotate with the shaft 19.
This secondary propeller 50 has a pitch which is
inverted relative to the pitch of the main propeller
20.
The means for aerating the surface of the liquid 3
also comprise an anti-vortex means 51 disposed above
the secondary propeller 50 and inside a cylindrical
stack 52.
The stack 52 is fixed to the inner edges of the
reinforcing ribs 48 so as to define with the sheath 11
and said reinforcing ribs 48 passages 55 for the liquid
3.
The secondary propeller 50 and the anti-vortex
means 51 are situated between the two series of ports
17 and 18 and the stack 52 extends substantially from
the median part of the first series of ports 17 to the
upper edge of the second series of ports 18.
A cover 53 is mounted on the shaft 19 above the
upper edge of the stack 52.
The vertical position of the cover 53 is
adjustable in order to define with the upper edge of
the stack 52 an adjustable passage 54.
The rotation of the main propeller 20 sucks liquid
3 through the ports 17 and 18 so that this liquid
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
ig
circulates upwardly in the sheath 11.
Thus a part of the liquid 3 is sucked into the
sheath 11 through the ports 18 and another part of the
liquid is sucked through the ports 17 and circulates
downwardly in the passages 55 defined between the stack
52 and the sheath 11.
Further, in view of the fact that the pitch of the
secondary propeller 50 is inverted relative to the
pitch of the main propeller 20, a part of the liquid is
sucked into the stack 52 in the upward direction and
sprayed into the air on the surface of the liquid 3
inside the funnel 14 in passing through the passage 54.
Thus the spraying of a'part of the liquid permits
aerating the surface of the liquid 3 and consequently a
1s reduction in the formation of foam on this surface.
The anti-vortex means 51 prevents the rotation of
the liquid in the stack 52 above the secondary
propeller 50.
In this embodiment also, the flow of the liquid 3
in the sheath 11 may be regulated by shifting the
sleeves 22 and 23 relative to the ports 17 and 18.
In an embodiment shown in Figs. 8 to 10, the
device comprises a vortex pump 60 for the suction of
the surface of the liquid into the sheath 11.
This vortex pump 60 is disposed above the second
anti-vortex means 40 and at the level of the first
series of ports 17.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
19
This vortex pump 60 is driven in rotation by the
shaft 19 and comprises, on one hand, a circular plate
61 fixed to the shaft 19 and provided on its upper side
with radial and vertical blades 62 and, on the other
hand, a stack 63 fixed to the upper edge of the blades
62.
The assembly comprising the plate 61, the blades
62 and the stack 63 is maintained on the shaft 19 by
means of a sleeve 61a whose position on the shaft 19 is
adjustable.
The sleeve 61a is fixed to the shaft 19 by means
formed for example by a fixing screw (not shown).
As shown in Figs. 8 and 9 the upper edge of the
blades 62 is provided with a ring 64 extending
outwardly of the stack 63.
This stack 63 extends from a position adjacent the
top of the tank 1 substantially from the median part of
the first series of ports 17 to the upper edge of the
blades 62.
The stack 63 defines an inner passage 65 which
communicates in its lower part with the interior of the
sheath 11 through annular passages 66 formed between
the blades 62 and between the ring 64 and the plate 61.
Preferably, the stack 63 is conical and tapers
toward the upper part of the tank 1 as shown in Fig. 9.
In a variant, the stack 63 may be cylindrical.
The blades 62 are planar or curved and preferably
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
three in number angularly evenly spaced apart on the
plate 61 as shown in Fig. 10.
The rotation of the main propeller 20 causes a
suction of the liquid 3 into the sheath 11 through the
5 ports 17 and 18 so that this liquid 3 continuously
circulates downwardly in this sheath.
Further, the rotation of the vortex pump 60 driven
by the shaft 19, i.e. the rotation of the assembly
comprising the plate 61, the blades 62 and the stack
10 63, causes a suction of the surface of the liquid 3
into the passage 65 so that this liquid thereafter
passes through the annular passages 66 and is
reinjected into the tank 1.
In this embodiment, the regulation of the flow of
15 the liquid by means of the sleeves 22 and 23 inside the
sheath 11 is unnecessary.
This embodiment is particularly suitable for
products having a great tendency to foam owing to the
fact that the foam floating on the surface of the
20 liquid 3 is sucked by the vortex pump 60 so that this
foam can be rapidly and effectively eliminated.
In an embodiment shown in Figs. 11 and 12, the
device comprises a single-passage propeller 70 for
sucking the liquid 3 into the sheath 11.
This single-passage propeller 70 is disposed above
the second anti-vortex means 40 and at the level of the
first series of ports 17.
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
21
The single-passage propeller 70 is driven in
rotation by the shaft 19 and comprises, on one hand, a
circular plate 71 fixed to the shaft 19 and disposed
above the level of the liquid 3 in the tank 1 and, on
the other hand, in the liquid 3, a vertical plate 72
forming a spiral and fixed to the lower face of the
plate 71 around the shaft 19.
As shown more particularly in Fig. 12, the plate
72 defines a lateral inlet 73 for the liquid which
extends throughout the height of the plate 72, a
vertical passage 74 for the downward circulation of
this liquid and a lower outlet 75 for the liquid.
The assembly comprising the plate 71 and the
vertical plate 72 is maintained on the shaft 19 by
means of a sleeve 71a whose vertical position on the
shaft 19 is adjustable.
For this purpose, the sleeve 71a is fixed to the
shaft 19 by means formed for example by a fixing screw
(not shown).
The inner edge of the vertical plate 72 includes a
vertical deflector 76 inclined in the direction toward
the center of the spiral formed by the plate 72.
Further, the distance between the plate 72 and the
axis of the shaft 19 progressively decreases as shown
in Fig. 12.
The rotation of the single-passage propeller 70
driven by the shaft 19, i.e. the rotation of the
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
22
assembly comprising the plate 71 and the plate 72, in
the direction indicated by the arrow_in Fig. 12, causes
the suction of the liquid into the interior of the
plate 72 through the lateral inlet 73.
This liquid is stirred inside the vertical passage
74, circulates downwardly in the latter and is
discharged into the sheath through the lower outlet 75.
The deflector 76 improves the stirring of the
liquid in the vertical passage 74 and prevents a return
of the liquid through the lateral inlet 73.
In a last embodiment shown in Figs. 14, the device
comprises a double-passage propeller 80 for the suction
of the liquid 3 into the sheath 11.
This double-passage propeller 80 is disposed above
the second anti-vortex means 40 and at the level of the
first series of ports 17.
The double-passage propeller 80 is driven in
rotation by the shaft 19 and comprises, on one hand, a
circular plate 81 fixed to the shaft 19 and disposed
above the level of the liquid 3 in the tank 1 and, on
the other hand, in the liquid 3, two vertical plates 82
and 83.
The vertical plates 82 and 83 are fixed to the
lower face of the plate 80 and each have the shape of
two half-shells which are in opposed and offset
relation to each other as shown in Fig. 14.
The two plates 82 and 83 define two lateral inlets
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
23
84 and 85 for the liquid, two passages 86 and 87 for
the downward circulation of the liquid and a lower
outlet 88 for the'liquid.
The assembly comprising the plate 81 and the
vertical plates 82 and 83 is maintained on the shaft 19
by means of a sleeve 81a whose vertical position on the
shaft 19 is adjustable.
The sleeve 81 is fixed to the shaft 19 by means
constituted for example by a fixing screw (not shown).
As shown more particularly in Fig. 14, the edge of
each plate 82 and 83 facing toward the passage 86 or 87
defined by the other plate comprises a vertical
deflector respectively 89 and 90.
The rotation of the double-passage propeller 80
driven, by the shaft 19, i.e. the rotation of the
assembly comprising the plate 81 and the two
vertical plates 82 and 83 in the direction indicated by
the arrow in Fig. 14, causes the suction of the liquid
3 through the ports 17.
This liquid enters through the lateral inlet 84
and 85, is stirred inside the passages 86 and 87 and
circulates downwardly in these passages 86 and 87 and
is thereafter discharged into the sheath 11 through the
lower outlet 88.
The deflectors 89 and 90 increase the stirring of
the liquid in the passages 86 and 87 and prevent the
liquid from flowing back through the lateral inlets 84
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
24
and 85.
In these last two embodiments, the regulation of
the flow of liquid by means of the sleeves 22 and 23 of
the sheath 11 is unnecessary and these last two
embodiments are more particularly employed in the case
where the level of- the liquid in the tank 1 is
variable.
To improve the flow of the liquid of the single-
passage propeller 70 or the double-passage propeller
80, a pumping propeller (not shown) may be disposed on
the shaft 19 below the single-passage propeller or
below the double-passage propeller.
The device according to the invention may be
applied for example to the treatment of water, town
effluents, industrial waste waters, fats by
biodegradation, drainage substances, cattle-raising
waste products and generally any biodegradable
industrial products.
The device according to the invention may also be
employed for example in the ozonization of water by an
ozonized gas with or without a catalyst, in the
stabilization of sludges, or may be employed in a
thermophile treatment or for liquids charged with
substances in suspension for example organic or mineral
substances.
The device according to the invention may also be
employed as a reactor operating with a fluidized or
CA 02276760 1999-07-02
moving bed.
The device according to the invention has the
advantage of treating the liquid and simultaneously
progressively eliminating the foam floating on the
5 surface of the liquid in the treating tank and thereby
ensuring that this foam does not pollute the
environment.