Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
1
A WRAPPING MACHINE FOR WRAPPING AN ARTICLE
AND A RELATED METHOD
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a wrapping machine for wrapping five
surfaces of an article except the bottom thereof, and a method to do the
same. More particularly, the machine and the method of the present
invention are useful for wrapping an article having a variable length such as
1o a bundle of lumber, plywood or the like, or a pile of other products, or a
single article.
BACKGROUND
A very significant proportion of lumber and construction panels are
15 currently shipped and stored in bundles or piles wrapped in a waterproof
envelope in order to provide a protection against alterations due to weather
conditions and stabilise the humidity level.
Traditionally, the placement and folding of the wrapper sheet has
2o mostly been carried-out in a semi-automatic fashion, a web like material
being supplied from a material roll positioned above the article to be
wrapped. Also, prefabricated plastic envelopes (bags) are currently used to
speed-up the wrapping operation. The bag is generally installed from the top
of the bundle, thus protecting the top and the sides of the bundle, while
25 allowing some air circulation through the bottom. In this latter case, the
envelope is manually secured to the bundle by stapling into the wood
pieces. In this case, the operation is still quite expensive since extensive
manpower is still required and the cost of the envelopes is relatively high.
3 o Many automated solutions have been proposed in the prior art to
wrap palletised articles in a plastic film or web. However, most of these
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
2
solutions perform the wrapping operation by rotating a narrow plastic film
roll around the load on a spiral path. Such techniques are not practical for
elongate articles such as lumber bundles and do not provide automatic
installation of a top web member nor yield a neat result.
It is also known in the art to use an automated system to slide a
bundle of lumber into a bag that is then manually closed and sealed at one
end. The economic performance of that process is still limited since
expensive large prefabricated bags are required in a wide range of sizes,
1o thus also resulting in inventory concerns.
Also known in the art, there is the U.S. patent 5,657,608 which
discloses a fully automated method for wrapping a parallelepipedly shaped
article such as a bundle of lumber, using a web like material supplied from
a roll located over the article. The wrapper material is dispensed and folded
around the article in a continuous process by the relative movements of a
backing means and the article, plus the movement of the article with
respect to spring loaded rollers as folding members. The principal
embodiments of that invention as described show several limitations and
2 o drawbacks. The main drawback is certainly the fact that the process must
be continuous, so that a new set-up is required after each time an incoming
article does not require wrapping, that situation occurring frequently since
only a part of lumber shipments must be wrapped. It shall also be noted that
the folding caused by the rollers is not precisely controlled and will
generally
yield a poor looking result and very visible folding lines on the long sides
of
the article. That poor looking result is also subject to be emphasised by the
presence of static electricity in plastic based wrapper material. Moreover,
it is worth indicating that it is generally not acceptable to apply adhesive
all
over the article to hold the web in place. Another obvious limitation of that
3 o process is that the article is moved back and forth a few times to
complete
the wrapping. Since the contemplated articles are long and heavy, a lot of
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
3
time and energy is required.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is directed to a wrapping machine and a related
method that overcome the above-mentioned drawbacks.
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a
wrapping machine for wrapping an article located in a wrapping area,
comprising:
to - web delivering means for delivering a web;
- first clamping means for clamping a first end of the web extending
from the web delivering means;
- first moving means for moving the first clamping means;
- cutting means for cutting the web extending from the web
delivering means and therefor providing a web piece for wrapping the
article;
- second clamping means for clamping a second end of the web piece
that is a free end opposite to said first end;
- second moving means for moving the second clamping means;
2 0 - fastening means for fastening the web piece on the article; and
a controller for controlling the web delivering means, the first and
second clamping means, the first and second moving means, the cutting
means, and the fastening means following a predetermined sequencing
program in such a way that, in operation, the web piece is moved and put
2 5 down over the article by means of the first and second clamping means and
the first and second moving means, and is fastened to the article by means
of the fastening means.
In accordance with the present invention, there is also provided a
3 o method for wrapping an article, comprising the steps of:
a) delivering a web by means of a web delivering means;
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
4
b) clamping a first end of the web extending from the web delivering
means by means of a first clamping means;
c) moving said first end away from the delivering means by means of
the first clamping means;
d) after step (c), cutting the web extending from the web delivering
means and therefor providing a web piece for wrapping the article;
e1 clamping a second end of the web piece that is a free end opposite
to said first end by means of a second clamping means;
f) moving and putting down the web piece over the article by means
of the first and second clamping means; and
g) after step (f), fastening the web piece on the article.
Advantageously, the machine and the method of the present
invention provide an automatic adjustment of the length of the article.
According the method and the machine of the invention, it is not
necessary to move the article during its wrapping which is very
advantageous for heavy article.
The present invention has also the advantage of providing a fully
automated machine with a very high level of control and accuracy.
A preferred embodiment of the invention has a further advantage of
providing a clean and neat appearance of the wrapped article with the web
folded only at the ends of the article and no apparent folding line.
The invention and its advantages will be better understood after
reading the non restrictive description of a preferred embodiment of the
3 o present invention. This description is given with reference to the
appended
drawings.
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 a side view of a wrapping machine according to a preferred
embodiment of the present invention, with the working environment.
5
Figure 2 is a top view of the wrapping machine shown in figure 1
which does not have the crane-and winch assembly.
Figure 3 is a front view of the first assembly of the machine shown
1 o in figure 1, where the first pivoting frame is missing for sake of
clarity.
Figure 4 is a front view of the first pivoting frame of the first
assembly of the machine shown in figure 1.
Figure 5 is a side view of the first pivoting frame shown in figure 4.
Figure 6 is rear view of the second assembly of the machine shown
in figure 2, where the second pivoting frame is missing for sake of clarity.
2 o Figure 7 is a front view of the second pivoting frame of the second
assembly of the machine shown in figure 1.
Figure 8 is a side view of the second pivoting frame shown in
figure 7.
Figure 9 is a side view of the third assembly of the machine shown
in figure 1.
Figure 10 is a rear view of the web delivering means, the cutting
3 o means and a portion of the third assembly shown in figure 9.
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
6
Figure 1 1 is a top view of the web delivering means shown in figure
10.
Figure 12 is a side view of a portion of the web delivering means
shown in figures 10 and 1 1.
Figure 13 is a side view of the second assembly of the machine
shown in figure 1, where the second pivoting frame is in an horizontal
position.
to
Figure 14 is a side view of the second assembly shown in figure 13,
except that the second pivoting frame is in a diagonal position.
Figure 15 is a side view of the second assembly shown in figures 13,
except that the second pivoting frame is in a vertical position.
Figure 16 is a side view of the first assembly of the machine shown
in figure 1, where the first pivoting frame is in an horizontal position.
2o Figure 17 is a side view of the first assembly shown in figure 16,
except that the first pivoting frame is in a diagonal position.
Figure 18 is a side view of the first assembly shown in figures 16 and
17, except that the first pivoting frame is in a vertical position.
Figure 19 is a front view of a portion of the third assembly shown in
figures 9 and 10, showing a portion the retractable supporting means.
Figure 20 is a side view of a portion of the third assembly shown in
3 o figure 10, showing the retractable supporting means being in an horizontal
position in relation with the cutting means.
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
7
Figure 21 is a side view of a portion of the third assembly shown in
figure 9, where a tension relief roller is in a back position and in a front
position.
Figure 22 is a side view of a clamp of the first clamping means
shown in figures 16, 17 and 18, where a jaw of the clamp in is an open
position and a closed position.
to Figure 23 is a top view of the clamp shown in figure 22.
Figure 24 is side view of a clamp of the second clamping means
shown in figures 13, where two jaws of the clamp are in open position and
in closed position.
Figure 25 is a top view of the clamp of figure 24.
Figure 26 is a diagram of the controller.
2 o Figure 27 is a perspective view of a wrapping machine according to
a preferred embodiment of the present invention, showing the article
partially covered by the web and the working environment.
Figure 28 is a perspective view of a wrapping machine according to
a preferred embodiment of the present invention, showing the article
partially wrapped by the web piece and the working environment.
Figure 29 is a perspective view of a wrapping machine according to
a preferred embodiment of the present invention, showing the article
3 o completely wrapped by the web piece and the working environment.
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
8
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF
A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT OF THE INVENTION
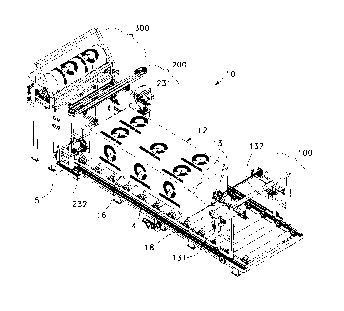
Referring to figures 1, 2, 27, 28 and 29, we will now generally
describe a wrapping machine 10 for wrapping an article 1 located in a
wrapping area 17. The wrapping machine 10 according to the present
invention comprises web delivering means for delivering a web 9; first
clamping means for clamping a first end 14 of the web 9 extending from the
web delivering means; first moving means for moving the first clamping
to means; and cutting means for cutting the web 9 extending from the web
delivering means and therefor providing a web piece 12 for wrapping the
article 1. The machine 10 further comprises second clamping means for
clamping a second end 15 of the web piece 12 that is a free end opposite
to said first end 14; second moving means for moving the second clamping
means; fastening means for fastening the web piece 12 on the article 1; and
a controller 50 illustrated in figure 26. The controller is for controlling
the
web delivering means, the first and second clamping means, the first and
second moving means, the cutting means, and the fastening means
following a predetermined sequencing program in such a way that, in
2 o operation, the web piece 12 is moved and put down over the article 1 by
means of the first and second clamping means and the first and second
moving means, and is fastened to the article 1 by means of the fastening
means.
We will now describe three assemblies of the machine 10 that are
structurally in relation with the above mentioned means and indicated in
figures 1, 2 and 29.
More particularly, the first moving means comprise a first assembly
3 o 100 on which the first clamping means is mounted, and a first sliding
means for sliding the first assembly 100 along the wrapping area 17. The
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
9
first sliding means are controlled by the controller 50 illustrated in figure
26.
The second moving means comprise a second assembly 200 on which the
second clamping means is mounted, and a second sliding means for sliding
the second assembly 200. The second sliding means being controlled by the
controller 50. The machine further comprises a third assembly 300 on
which the web delivering means and the cutting means are mounted.
Referring to figures 1, 2, 3 and 29, the first sliding means for sliding
the first assembly 100 comprise a pair of rails 4 parallel to opposite sides
1 o of the wrapping area 17, and sliding members 102 mounted under the first
assembly 100 and for slidably engaging the rails 4. The sliding motion of the
first assembly 100 on the rails 4 is driven by the motor 6.
Referring to figures 1, 2, 6 and 29, the second sliding means for
sliding the second assembly 200 comprise a pair of rails 5 parallel to
opposite sides of the wrapping area 17, and sliding members 202 mounted
under the second assembly 200 for slidably engaging the rails 5. The sliding
motion of the second assembly 200 on the rails 5 is driven by the powered
cylinder 326 indicated in figure 1.
We will now describe staplers which are among many tools that
could be used to fasten the web piece 12 to the article 1 shown in figure
28 and 29. It should be noted that the wrapping machine 10 of the
invention has been designed for wrapping a pile of lumbers and.
consequently it is not a problem to staple a web to the pile of lumbers.
However, the machine 10 of the invention is very useful to wrap many
other type of article on which it may not be suitable to staple. In this case,
other fastening means may be used such as adhesive material, fusion
3 o processing with heat stem, thermosealing, or the like.
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
Referring to figures 1, 4, 5 and 28 and 29, the fastening means
comprise a front stapler 137 mounted on the first assembly 100 for stapling
the web piece 12 to a front surface 20 of the article 1, and a third moving
means for moving the front stapler 137 along the front surface 20 of the
5 article 1. The third moving means are mounted on the first assembly 100,
and comprise a first powered cylinder 1 18 for moving horizontally the front
stapler 137, and two second powered cylinders 114 et 1 15 for moving the
same vertically and being perpendicular to the first powered cylinder 1 18.
The third moving means further comprise front stapler detecting means for
to detecting a position of the front stapler 137 along each of said cylinders.
The front stapler detecting means comprises one detector 133 shown in
figure 4, for detecting the position of the front stapler 137 along the
cylinder 118, and another detector 134 for detecting the position of the
front stapler 137 along the cylinders 1 14 and 1 15. Both detectors 133 and
134 provide an output signal to the controller 50 illustrated in figure 26.
Referring to figures 1, 7, 8, 28 and 29, the fastening means further
comprise a rear stapler 239 mounted on the second assembly 200 for
stapling the web piece 12 to a back surface 21 of the article 1, and a fourth
2 o moving means for moving the rear stapler 239 along the back surface 21
of the article 1. The fourth moving means are mounted on the second
assembly 200, and comprise a first powered cylinder 219 shown in figure
7, for moving horizontally the rear stapler 239, and two second powered
cylinders 221 and 222 shown in figure 8, for moving the same vertically
and being perpendicular to the first powered cylinder 219. The fourth
moving means further comprise rear stapler detecting means for detecting
a position of the rear stapler 239 along each of said cylinders. The rear
stapler detecting means comprise one detector 234 shown in figure 7, for
detecting the position of the rear stapler 239 along the cylinder 219, and
3 o another detector 233 for detecting the position of the rear stapler 239
along
the cylinders 221 and 222. Each detector and powered cylinder mentioned
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
11
above and hereinafter are preferably a linear encoder and a pneumatic
rodless linear cylinder with magnetic piston. Both detectors 233 and 234
provide an output signal to the controller 50 illustrated in figure 26.
Referring to figures 1, 3, 28 and 29, the fastening means further
comprise two side staplers 135 and 136 mounted respectively on opposite
sides of the first assembly 100 for fastening side portions 16 of the web
piece 12 to side surfaces 22 of the article 1.
1 o Referring again to figure 1, we will now describe article detectors of
the machine 10 further comprises a conveyor 2 controlled by the controller
50 for conveying the article 1 within a wrapping area 17, and first detecting
means 8 mounted on the second assembly 200, for detecting a back
surface 21 of the article 1 and providing an output signal to the controller
50 illustrated in figure 26. The controller 50, in operation, controls the
conveyor 2 to align the back surface 21 of the article 1 with a proper
location in the wrapping area 17. The machine further comprises second
detecting means 143 mounted on the first assembly 100, for detecting a
front surface 20 of the article 1 and providing an output signal to the
2 o controller 50 which, in operation, controls the first moving means to move
the first clamping means away from the web delivering means at a specific
distance which is in relation with the length of the article 1 so that the
cutting means is in a proper position to cut a web piece 12 having a size
adapted to cover a top surface 23, a front surface 20, a back surface 21
and two opposite side surfaces 22 of the article 1.
The article 1 may slide on the conveyor 2. Consequently, it is planned
that the machine 10 can comprise an alignment system for aligning the
article with the conveyor 2 before conveying it in the wrapping area 17.
Since the machine 10 is designed for wrapping a bundle of lumbers
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
12
among others and such bundle may has an end of wood extending out, it
planned that the machine 10 can comprises a trimming system for cutting
such end of wood. A end of wood extending out the article 1 could interfere
with the wrapping processing.
We will now describe different elements mounted on the third
assembly 300. Referring now to figures 1, 2, 9 to 12, the web delivering
means has a roll support composed of two cradle rollers 306 and 307, for
supporting a roll of web 305 from which the web 9 is delivered.
to
Referring more particularly to figures 27 and 28 and according to the
preferred embodiment of the invention, the web 9 in the roll 305 has two
opposite side portions 30 fold under a central portion 31 thereof, where the
central portion has a width determining the width of the roll 305 which is
slightly superior to the width of the top surface 23 of the article 1. The
fold
side portions 30 of the web 9 fold under the central portion 31 of the web
9 are indicated on the roll 305 in figure 28 with dotted lines. It should be
understood that the web 9 can be in a roll without being fold as explained
above. In such a case, the roll of web would be as long as the width of the
2 o web and adapters could be provided for avoiding interference between the
web from the roll and the second assembly 200. It should be understood
also that it is not necessary that the web is delivered from a roll, since the
web could be fold up in a pile or in any other form.
Referring to figures 1 and 9, the machine preferably further comprises
an over head crane-and-winch assembly 304 for supplying a spare roll of
web 323 to a base 327. It is to be understood that other lifting apparatus
can be used in replacement of the crane-and-winch assembly 304 such as
an elevator. The base 327 is pivotally mounted on the third assembly 300
3 o and can be raise up by means of the powered cylinders 328 and 329 for
pushing the spare roll of web 323 on the cradle rollers 306 and 307.
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
13
Referring more particularly to figures 9 and 21, the web delivering
means comprises advantageously a tension relief roller 308 to make sure
that the web 9 is delivered equally from side-to-side of the roll 305. The
tension relief roller 308 has a sliding bushing 338 on each extremity thereof,
which is slidably engaged on a guiding shaft 339 and is driven by the
powered cylinder 337.
Referring now to figures 9 and 12, the web delivering means further
to comprise a motorised upper drive roller 309 and a lower roller 310 for
squeezing the web 9 extending from the roll 305 between them and pulling
out the web 9 from the roll 305 by the motion of the motorised upper drive
roller 309. The web delivering means also comprise a shelf 313 for
separating the central portion 31 of the fold web 9 from the side portions
thereof. Such separation is particularly useful for allowing the first and
second clamping means to clamp only locations on the central portion 31
of the web 9.
Referring to figures 10, 12, 19, 20 and 28, the cutting means is
2o preferably a circular rotary blade 317, and the shelf 313 of the web
delivering means has a slot 320 for allowing the rotary blade 317 to go
through. Since the central portion 31 of the web 9 slides above the shelf
313 and the rotary blade 317 engages the slot 320, the central portion 31
is cut all way long when the rotary blade 317 is moved from side-to-side of
the shelf 313. The rotary blade 317 is driven laterally along the powered
cylinder 319 shown in figure 10, 1 1 and 12.
To make sure that the side portions 30 of the web 9, shown in figure
28, is cut at the same time than the central portion thereof, the third
3 o assembly 300 is provided with retractable supports 324 and 325 and
powered cylinders 334 and 335 for driving them as illustrated in figures 10
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
14
and 19. The retractable support 324 and 325 have an upper concave
surface 340 which is align with the path of the rotary blade 317 so that,
when the retractable supports 324 and 325 are raised up against the shelf
313, the blade 317 engages the concave surface 340 and cut the side
portions 30 of the web 9 slid between the shelf 313 and the retractable
supports 324 and 325.
We will now describe clamps of the machine 10. Referring now to
figure 4, 27 and 28, the first clamping means comprise a pair of clamps
l0 104 and 105 for clamping two points on the first end 14 of the web 9 that
are spaced apart by a distance corresponding to a width of the top surface
23 of the article 1 and centrally located along the first end 14 of the web
9.
Referring to figure 7, 27 and 28, the second clamping means
comprise a pair of clamps 204 and 205 for clamping two points on the
second end 15 of the web piece 12 that are spaced apart by a distance
corresponding to the width of the top surface 23 of the article 1 and
centrally located along the second end 15.
Referring now to figures 24 and 25, the second moving means also
comprise third pivoting means for pivoting the clamps 204 and 205 around
an horizontal axis parallel to the back surface 21 of the article 1 shown in
figure 1. Figures 24 and 25 show only clamp 204 since clamps 204 and
205 are preferably identical. More particularly, the third pivoting means
comprise a powered rotary cylinder for each jaw of each clamp 204 and
205. Each clamp 204, 205 has a longer jaw 224 and a shorter jaw 225
which are driven respectively by the powered rotary cylinder 227 and 228.
3 o Figures 22 and 23 show only clamp 104 since clamps 104 and 105
are preferably identical. Each of clamps 104, 105 has a fixed jaw 145, a
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
pivoting jaw 144 and a powered rotary cylinder 146 for driving the pivoting
jaw 144.
We will now describe different elements mounted on the first
5 assembly 100. Referring more particularly to figures 1, 16, 17 and 18, the
first moving means comprise preferably a first pivoting frame 106 pivotally
mounted on the main frame 101 of the first assembly 100, and first
pivoting means for pivoting the first pivoting frame 106 between an
horizontal position (shown in figure 16) higher than the height of the front
1o surface 20 of the article 1 and a vertical position (shown in figure 18)
parallel to the front surface 20 of the article 1. An intermediate position of
the first pivoting frame 106 is illustrated in figure 17.
As shown in figure 4, the first pivoting frame 106 has a "C" shaped
15 frame on which are mounted the first clamping means, the front stapler 137
and the third moving means for moving the front stapler 137.
The main frame 101 of the first assembly 100 has a substantially
"H" shape as illustrated in the side views of figures 16 to 18. The main
2 o frame 101 constitute two "H" shaped frames interconnected by an upper
part and a lower part thereof as shown in the front view of figure 3. The
first pivoting frame 106 is pivotally mounted on each opposite "H" shaped
frame of said main frame 101 by means of a bracket 103 which may rotate
around the pivot 109. The rotation of the brackets 103 is driven by the first
pivoting means which comprise two powered cylinders 107 and 108 on the
opposite "H" shaped frames of the main frame 101 respectively.
Referring more particularly to figures 5 and 16, the first moving
means further comprise translating moving means for translating the clamps
3 0 104 and 105 of the first clamping means along the first pivoting frame
106.
The translating means comprise a powered cylinder 116 or 117 for
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
16
translating each clamp 104 or 105 respectively.
We will now describe different elements of the second assembly
200. Referring more particularly to figures 1, 13, 14 and 15, the second
moving means comprise preferably a second pivoting frame 206 pivotally
mounted on the main frame 201 of the second assembly 200, and second
pivoting means for pivoting the second pivoting frame 206 between an
horizontal position (shown in figure 13) higher than the height of the back
surface 21 of the article 1 and a vertical position (shown in figure 15)
l0 parallel to the back surface 21 of the article 1. An intermediate position
of
the second pivoting frame 206 is illustrated in figure 14.
As shown in figure 7, the second pivoting frame 206 has a "C"
shaped frame on which are mounted the second clamping means, the rear
stapler 239 and the fourth moving means for moving the rear stapler 239.
The main frame 201 of the second assembly 200 has a substantially
"b" shape as illustrated in the side views of figures 13 to 15. The main
frame 201 constitute two "b" shaped frames interconnected by an upper
2 0 part and a lower part thereof as shown in the front view of figure 6. The
second pivoting frame 206 is pivotally mounted on each opposite "b"
shaped frame of said main frame 201 by means of a bracket 203 which
may rotate around the pivot 209. The rotation of the brackets 203 is driven
by the second pivoting means which comprise two powered cylinders 207
and 208 on the opposite "b" shaped frames of the main frame 201
respectively.
Referring more particularly to figures 1, 6 and 13, the second moving
means further comprise fifth moving means for moving the second pivoting
3 o frame 206 vertically with respect to the second assembly 200. The fifth
moving means comprise vertical threaded shafts 235 and 236 passing
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
17
through the opposite "b" shaped frames of the main frame 201 respectively.
The fifth moving means further comprise a motor 238 for driving the
threaded shafts 236 and indirectly the threaded shafts 235.
Referring now more particularly to figures 6 and 13, it should be
understood that the dimensions the machine 10, shown in figure 1, may
vary in order to wrap different sizes of article 1. It is also contemplated
that
the machine 10 can adapt itself to a variable width and height of the article
1 to be wrapped could also be constructed. The pivots 109 and 209 could
to be mounted on linear jacks or the like such as electric motorized screws so
that the pivots 109 and 209 can be aligned with the top surface 23 of the
article 1 detected by an optical or proximity sensor. Should the variations
of the dimensions of the article 1 be such that the width of the web 9
would need to be reduced to avoid the web 9 to exceed below the article
1, the machine 10 can comprise a pair of laterally adjustable rotary blades
installed under the shelf 313 to cut the excess of web 9 symmetrically on
side portions 30 of the web 9 , shown in figure 28. With the machine 10
being so adapted, it can comply with a wide range of article sizes, since the
width of the web 9 is selected with respect of the width of the article 1 to
2 0 be wrapped.
We will now describe the blowers of the machine 10 according to
the preferred embodiment of the invention. Referring to 28, the machine 10
comprises folding means for folding the web piece 12 around the article 1
so that the resulting wrapped article has a clean and neat appearance. The
folding means hereinafter described are designed more particularly for
wrapping a parallelepipedly shaped article 1.
Referring to figures 3, 16, 17, 18, 28 and 29, the preferred folding
3 o means comprise two blowers 131 and 132 mounted respectively on the
opposite "H" shaped frames of the main frame 101 of the first assembly
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
18
100 for blowing corners 18 of the first end 14 of the web piece 12 towards
each other while the clamps 104 and 105 of the first clamping means
having the first end 14 of the web piece 12 clamped therein move from an
initial position to a final position located on a lower edge of the front
surface
20 of the article 1. The final and fold position of the corners 18 is shown
in figure 29 and the diagonal dotted lines illustrate folded lines 13 in the
web piece 12. The movement of the clamps 104 and 105 between the
initial position and the final position located on a lower edge of the front
surface 20 is essentially driven by the powered cylinders 107 and 108
1 o which pivot the first pivoting frame 106 around the pivot 109 and is
illustrated the sequence of figures 16, 17 and 18.
Referring to figures 6, 13, 14, 15, 28 and 29, the preferred folding
means further comprise two blowers 231 and 232 mounted respectively on
the opposite "b" shaped frames of the main frame 201 of the second
assembly 200 for blowing corners 19 of the second end 15 of the web
piece 12 towards each other while the clamps 204 and 205 of the second
clamping means having the second end 15 of the web piece 12 clamped
therein move from an initial position to a final position located on a lower
2 o edge of the back surface 21 of the article 1. The movement of the clamps
204 and 205 between the initial position and the final position located on
a lower edge of the back surface 21 is essentially driven by the powered
cylinders 207 and 208 which pivot the second pivoting frame 206 around
the pivot 209 and is illustrated the sequence of figures 13, 14 and 15.
Basically, the action of the blowers 131, 132, 231 and 232 is push the
corners 18 and 19 under a central portion of the first and second ends 14
and 15 located between the clamps 104, 105 and the clamps 204, 205
respectively. The movement of the clamps 104, 105, 204 and 205
sandwiches the corners 18 and 19 under the central portions of the first and
3 o second end 14 and 15. After the web folding, the web piece 12 is fasten
to the article 1 as above described.
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
19
Many types of folding means may be designed without departing
from the scope of the invention to carry out the folding of the web piece 12
such as using retractable arms or the like for folding the corners 18 and 19
of the web piece 12 as described above.
We will now describe the anti-static electrode 312 of the machine
10, shown in figure 1, according to the preferred embodiment of the
invention and we will refer more particularly to figures 9, 12 an 20. Many
1o kind of web 9 as the one shown in figure 27, may be used such as fabric,
plastic film and the like. The choice of the type of web 9 depends on the
type of article 1 to be wrapped and the necessity to be permeable, semi-
permeable or impermeable. Using certain kinds of web 9 with the wrapping
machine 10 can results in creation of static electricity. Such static
electricity
in mainly generate by the web delivering means and can interfere with
positioning and folding of the web piece 12 over the article 1. In order to
overcome this inconvenient, the machine 10 further comprises an anti-static
electrode 312 located at an exit point of the web 9 from the web delivering
means. Thus, the contact of the web with the electrode 312 is done just
2 o before the web 9 leaves the web delivering means. More particularly, the
electrode 312 is located at an external extremity of the shelf 313. Other
devices can be used for overcome this inconvenient such as static
eliminating brush and tinsel. A grounded tinsel wire in conductive copper
strands has been used for such purpose.
Referring to figure 26, the controller 50 receives input signals from
the detector 8 for detecting the front surface 20 of the article 1, the
detector 143 for detecting the back surface 21 of the article 1, the
detectors 133 and 134 for detecting the position of the front stapler 137,
3 o the detectors 233 and 234 detecting the position of the rear stapler 239.
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
Still referring to figure 26, the controller 50 transmits output signals
to the motor 7 of the conveyor 2, the motor 6 for sliding the first assembly
100, the cylinders 107 and 108 for pivoting the first pivoting frame 106,
the cylinders 1 16 and 1 17 for the translation of the clamps 104 and 105,
5 the rotary cylinders 146 of the clamps 104 and 105, the first cylinder 1 18
for moving horizontally the front stapler 137, the second cylinders 1 14 and
1 15 for moving vertically the front stapler 137, the front stapler 137, the
side stapler 135 and 136, the cylinder 326 for sliding the second assembly
200, the cylinders 207 and 208 for pivoting second pivoting frame 206, the
l0 rotary cylinders 227 and 228 of the clamps 204 and 205, the first cylinder
219 for moving horizontally the rear stapler 239, the rear stapler 239, the
second cylinders 221 and 222 for moving vertically the front stapler 239,
the blowers 131, 132, 231 and 232, the motorized upper drive roller 309,
the cylinder 334 and 335 for pivoting the retractable support 324 and 325,
15 the circular rotary blade 317 and the cylinder 319 for sliding the blade
317.
The present invention also provides a method for wrapping an article
1 which will be now described with references to figures 9, 27, 28 and 29.
The method of the invention is preferably perform with the machine 10
2o above-described. The machine 10 necessitates an initial preparation for
being ready to perform the method for wrapping. Referring to figure 9, the
initial preparation includes installing a roll 305 of web 9 of the cradle
rollers
306 and 307, slipping the web 9 from the roll 305 between the cradle
rollers 306 and 307, in front of a guiding roll 330, behind the tension relief
roller 308, between the lower roller 310 and the motorized upper drive roller
309, and around the shelf 313 where the fold side portions 30 of the web
9 is slid under the shelf 313 and the central portion 31 thereof is slid over
the shelf 313.
3 o Still referring to figure 9, the method is fully automated and
comprises the step 1a) of delivering a web 9 by means of a web delivering
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
21
means. The action of the motorized upper drive roller 309 pushes the web
9 until it extends out the shelf 313.
Referring to figure 17, the method further comprises the step (b) of
clamping a first end 14 of the web 9 extending from the shelf 313 by
means of the clamps 104 and 105, and the following step (c) of moving
away from the shelf 313, the clamps 104 and 105 having the first end 14
clamped therein. According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, in
the step (cl, the first end 14 is moved away from the shelf 313 at a specific
to distance which is in relation with the length of the article 1 so that the
rotary blade 317 is in a proper position to cut a web piece 12 having a size
adapted to cover a top surface 23, a front surface 20, a back surface 21
and two opposite side surfaces 22 of the article 1. For practical purpose,
the second pivoting frame 206 is raised up by means of the motor 238 and
the threaded shafts 235 and 236, shown in figures 13 and 27, in order to
clear a sufficient space for allowing the first assembly 100 to slide under it
and the clamps 204 and 205 to reach the web 9 extending out the shelf
313 and perform step (b).
2 o Referring to figures 9 and 20, the method further comprises the step
(d), executed after step (cl, of cutting the web 9 extending from the lower
roller 310 and the motorized upper drive roller 309 and therefor providing
a web piece 12, shown in figure 28, for wrapping the article 1.
Advantageously, the clamps 204 and 205 are also used to stabilized the
web 9 during the cutting step (d). To do so, the method further comprises,
before step (dl, the step (x) of moving the clamps 204 and 205 in proximity
of the rotary blade 317; and the step (y) of squeezing the second end 15 of
the web piece 12 between the longer jaws 224 (shown in figures 24 and
25) of the clamps 204 and 205 and the shelf 313 by engaging the two
3 o cavities 321 and 322 (shown in figure 1 1 ) provided in the shelf 313.
Therefor, the step (d) further comprises the step (z) of maintaining the
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
22
squeezing action of step (y) for stabilizing the web 9 during the cutting
action. It should be understood that the step (x) of moving the clamps 204
and 205 in proximity of the rotary blade 317 comprises the step of lowering
the second pivoting frame 206 since it has been raised up for allowing step
(b).
Referring to figure 27, the method further comprises the step (e)
which follows step (d), of clamping a second end 15 of the web piece 12
that is a free end opposite to said first end 14 and that has been generated
l0 by the cutting step (d) with the clamps 204 and 205. In the case that the
step (z) is performed, the shorter jaws 225 stayed in the open position are
ready to pivot towards the respective longer jaws 224 and therefor clamp
the second end 15 in order to perform step (e).
Referring to figures 13 to 18, 27 and 28, the method further
comprises the step (f), which follows step (e), of moving and putting down
the web piece 12 over the article 1 by moving the clamps 104 and 105 and
moving the clamps 204 and 205. According to a preferred embodiment of
the invention, the step (f) comprises the sub-step (f-1 ) of pivoting the
clamps 104 and 105 to bring the first end 14 of the web piece 12 at a
lower edge of the front surface 20 of the article 1; and the sub-step (f-2);
which is performed during step (f-1 ), of blowing corners 18 of the first end
14 of the web piece 12 towards each other while the clamps 104 and 105
having the first end 14 of the web piece 12 clamped therein move from an
initial position to a final position located on a lower edge of the front
surface
20 of the article 1. In sub-step (f-1 ), it should be understood that the
action
of pivoting the clamps 104 and 105 is executed by pivoting the first
pivoting frame 106 by means of the powered cylinders 107 and 108. The
step (f) further comprises the sub-step (f-3) of pivoting the clamps 204 and
3 0 205 to bring the second end 15 of the web piece 12 at a lower edge of the
back surface 21 of the article 1; and (f-4), which is performed during step
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
23
(f-3), of blowing corners 19 of the second end 15 of the web piece 12
towards each other while the clamps 204 and 205 having the second end
15 of the web piece 12 clamped therein move from an initial position to a
final position located on a lower edge of the back surface 21 of the article
1. In sub-step (f-3), it should be understood that the action of pivoting the
clamps 204 and 205 is executed by pivoting the second pivoting frame 206
by means of the powered cylinders 207 and 208. For practical purpose, the
sub-step (f-3) comprise a prior step of moving the second assembly 200
away from the third assembly 300 by means of the powered cylinder 326
to in order that the shelf 313 would not interfere with the second pivoting
frame 206 when it pivots. Advantageously, the sub-steps (f-1 ) and (f-3) are
executed simultaneously in order to reduce time consuming.
Referring to figures 3, 14, 17 and 28, the method further comprises
the step (g), executed after step (f), of fastening the web piece 12 on the
article 1. Still according to the preferred embodiment, the step (g) comprises
the sub-step (g-1 ) of fastening the web piece 12 to the front surface 20 and
back surface 21 of the article 1 by means of the front stapler 137 and the
rear stapler 239; the sub-step (g-2) of conveying the article 1 away from the
2 o wrapping area 17; and the sub-step (g-3), executed during sub-step (g-2),
of fastening the web piece to the two opposite sides of the article by means
of the two side staplers 135 and 136. An other way to fasten the web
piece 12 to the side surfaces 22 of the article 1 could be to slide the first
assembly 100 towards the back surface 21 of the article 1. As above
mentioned, it is not necessary to move the article 1 for wrapping it.
However it is less time consuming the fasten side surfaces 22 thereof while
conveyed out the wrapping area 17.
It should be understood that he steps of the above described method
3 o may be executed in a different sequence and some of them may be
executed simultaneously.
CA 02277565 1999-07-15
24
While embodiments of this invention have been illustrated in the
accompanying drawings and described above, it will be evident to those
skilled in the art that changes and modifications may be made therein
without departing from the essence of this invention. All such modifications
or variations are believed to be within the scope of the invention as defined
by the claims appended hereto.