Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO99/06410 1 PCT/US98/16147
HYDROXAMTC ACID SUBSTITUTED FUSED
HFTFROCYCLIC METALLOPROTEINASE INHIBITORS
BACKGROIIND OF THE INVENTION
This application claims the benefit of U.S.
Provisional Application No. 60/054,753 filed August 4,
1997, which is hereby incorporated by reference. The
present invention relates to metalloproteinase
inhibitors and more particularly, relates to novel
compounds, composition and method for prophylaxis and
treatment of inflammation, tissue degradation and the
like. This invention, in particular, relates to novel
hydroxamic acid substituted fused heterocyclic
compounds, compositions containing such compounds and
methods of use of such compounds. The subject invention
also relates to processes for making such compounds as
well as to intermediates useful in such processes.
Metalloproteinase enzymes, such as collagenases
(e. g., MMP-1, MMP-8 and MMP-13), stromelysins (e. g.,
MMP-3, MMP-10, MMp-11 and MMP-7), gelatinases (e. g.,
MMP-2 and MMP-9) and TNF convertase, may contribute to
the onset, etiology, or exacerbate disease states which
are related to connective tissue degradation, secretion
of proinflammatory cytokines and the like. For example,
matrix metalloproteinases, such as collagenases,
stromelysins and gelatinases, are thought to be involved
in the tissue breakdown observed in rheumatoid
arthritis; osteoarthritis; osteopenias (e. g.,
osteoporosis); periodontitis; gingivitis; corneal,
epidermal and gastric ulceration; and tumour metastasis,
invasion and growth; in neuroinflammatory disorders,
such as myelin degradation (e. g., multiple sclerosis).
and in angiogenesis dependent diseases, such as
arthritic conditions; solid tumor growth; psoriasis;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
2
proliferative retinopathies; neovascular glaucoma;
ocular tumours; angiofibromas; and hemangiomas.
Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (TNF-a) is a
proinflammatory cytokine secreted by a variety of cells
including monocytes and macrophages in response to many
inflammatory stimuli (e.g. lipopolysaccharide - LPS) or
external cellular stress (e. g. osmotic shock, peroxide).
Elevated levels of TNF play a major role in mediating
many inflammatory disease states. Elevated levels of
TNF-a may contribute to the onset, etiology, or
exacerbate the following disease states: rheumatoid
arthritis; osteoarthritis; rheumatoid spondylitis; gouty
arthritis; inflammatory bowel disease; adult respiratory
distress syndrome CARDS); psoriasis; Crohn's disease;
allergic rhinitis; ulcerative colitis; anaphylaxis;
contact dermatitis; asthma; antiviral therapy including
those viruses sensitive to TNF-a inhibition - HIV-1,
HIV-2, HIV-3, cytomegalovirus (CMV), influenza,
adenovirus, and the herpes viruses including HSV-1, HSV-
2, and herpes zoster; muscle degeneration; cachexia;
Reiter's syndrome; type II diabetes; bone resorption
diseases; graft vs. host reaction; ischemia reperfusion
injury; atherosclerosis; brain trauma; Alzheimer's
disease; multiple sclerosis; cerebral malaria; sepsis;
septic shock; toxic shock syndrome; fever and mylagias
due to infection.
Several approaches have been taken to block the
effects of TNF-a. One approach involves utilizing
soluble receptors for TNF-a (e. g., TNFR-55 or TNFR-75)
which have demonstrated efficacy in animal models of
TNF-a mediated disease states. A second approach to
neutralizing TNF-a utilizing a monoclonal antibody
specific to TNF-a, cA2, has demonstrated improvement in
swollen joint count in a Phase II human trial of
rheumatoid arthritis (Feldmann et al Immunological
Reviews p.195-223 (1995)).
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
3
The above approaches block the effects of TNF-a by
either protein sequesterazation or receptor antagonism,
but an additional approach to blockade is to intervene
in the cellular secretion of TNF. TNF convertase is
thought to be a metalloproteinase enzyme involved in the
cellular secretion of TNF-a (Mohler et al., Nature
370:218-220, 1994; Gearing et al., Nature 370:555-557,
1994; McGeehan et al., Nature 370:558-561, 1994).
Inhibition of TNF convertase is thought to be an
additional approach to intervene in the cellular
secretion of TNF-a. For example, a metalloproteinase
inhibitor was shown to inhibit cellular secretion of
TNF-a, in vitro and in vivo, which was thought to be due
to inhibition of TNF convertase (McGeehan et al., Nature
370:558-561, 1994). WO 92/02822, WO 94/00555, WO
95/24501, WO 96/41624, WO 98/02557 and US Pat. 5,594,106
(each of which is incorporated herein by reference in
its entirety) describe a TNF-a convertase and methods of
identifying inhibitors thereof. V~Thile evidence as to
the nature of intervention by metalloproteinase
inhibitors in the cellular secretion of TNF-a exists,
additional or alternative mechanisms of action by which
such compounds inhibit TNF secretion may be involved,
such as by intervening at a point on the pathway between
extracellular stimulus and secretion of protein.
Since TNF-a is upstream in the cytokine cascade of
inflammation wherein elevated levels of TNF-a lead to
elevated levels of other cytokines including IL-1, IL-6
and IL-8, inhibiting the secretion of TNF-a may also
reduce levels of other cytokines including but not
limited to IL-1, IL-6 or IL-8.
Further, TNF-a is thought to play a role in head
trauma, stroke, and ischemia. For instance, in animal
models of head trauma (rat), TNF-a levels increased in
the contused hemisphere (Shohami et al J. Cereb. Blood
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
4
Flow Metab. 14:615-619 (1994)). In an model of ischemia
wherein the middle cerebral artery was occluded in rats,
the levels of mRNA of TNF-a increased (Feurstein et al
Neurosci. Lett. 164:125-128 (1993)). Administration of
TNF-a into the rat cortex resulted in significant PMN
accumulation in capillaries and adherance in small blood
vessels. TNF-a promotes the infiltration of other
cytokines (IL-1b, IL-6), and also chemokines, which
promote neutrophil infiltration into the infarct area
(Feurstein Stroke 25:1481-1488 (1994)).
TNF-a may also play a role in promoting certain
viral life cycles and disease states associated with
them. For instance, TNF-a secreted by monocytes induced
elevated levels of HIV expression in a chronically
infected T cell clone (Clouse et al, J. Immunol. 142:431
(1989)). The role of TNF-a in the HIV associated states
of cachexia and muscle degradation has been discussed
(Lahdevirta et al The American J. Med. 85:289 (1988)).
4V0 97/18194 generically discloses N-(substituted-
sulfonyl) thienyl-fused 5-7 membered ring nitrogen
containing heterocycle hydroxamic acid compounds for use
as inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases and TNF
production.
DE 3529960 and DE 3705220 disclose heterocyclic-
fused-tetrahydropyridinyl-2-carboxylic acid derivatives,
such as thieno-fused-tetrahydropyridinyl-2-carboxylic
acid compounds, preparation and use as angiotensin I
converting enzyme inhibitors.
DE 2800596 discloses the preparation and use for
inhibition of agglutination of blood platelets,
erythrocyte adhesion and thrombosis of thieno-fused-
tetrahydropyridinyl-2-carboxylic acid derivatives.
DE 2812950 disclose the preparation and use for
inhibition of agglutination of blood platelets,
erythrocyte adhesion, thrombosis, pain and inflammation
of thieno-fused-dihydropyridinone derivatives.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
DE 2949399 discloses the use of thieno-fused-
tetrahydropyridine derivatives as intermediates in the
preparation of (thieno-fused-tetrahydropyridyl)-fused-
tetrahydrothiazole compounds for use as antiviral,
5 analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory agents.
FR 2457869 discloses the use of thieno-fused-
tetrahydropyridinyl-2-carboxylic acid derivatives as
intermediates in the preparation of (thieno-fused-
tetrahydropyridyl}-fused-pyrazine compounds for use as
sedatives.
WO 96/33172 discloses N-arylsulfonyl and N-
heteroarylsulfonyl substituted 6 membered ring
heterocycle hydroxamic acid derivatives, such as N-
arylsulfonyl- and N-heteroarylsulfonyl-piperidinyl-2-
hydroxamic acid compounds, preparation and use as
inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases and TNF
production.
EP 606046 discloses N-arylsulfonyl and N-
heteroarylsulfonyl substituted 5-6 membered ring
heterocycle hydroxamic acid derivatives, such as N-
arylsulfonyl- and N-heteroarylsulfonyl-piperidinyl-2-
hydroxamic acid compounds and N-arylsulfonyl- and N-
heteroarylsulfonyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolinyl-2-
hydroxamic acid compounds, preparation and use as
inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to selected
metalloproteinase inhibitory compounds, analogs and
pharmaceutically acceptable salts and prodrugs thereof.
The subject compounds are characterized as hydroxamic
acid substituted fused heterocyclic compounds. The
invention compounds useful in the prophylaxis and
treatment of inflammation, tissue degradation and
related diseases. Therefore, this invention also
encompasses pharmaceutical compositions and methods for
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
6
prophylaxis and treatment of inflammation, tissue
degradation and related diseases. The subject invention
also relates to processes for making such compounds as
well as to intermediates useful in such processes.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
In accordance with the present invention, there is
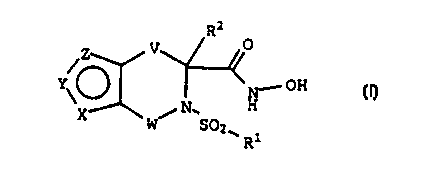
provided a compound of the Formula:
R2
V O
/Z
N,.- OH
Y~ / N. H
W S02w
Ri
(I)
or a pharmacutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein
R1 is (1) an alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl or
heterocyclyl radical optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of -OH, -OR3, -SR3, -S (O) R3, -S (O) 2R3, -C (O) R3 or
-NR3R4, aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl; or
(2) aryl or heteroaryl radicals; wherein the aryl,
heteroaryl, cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl radicals are
3
optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, -OR ,
-SR3, -S (0) R3, -S (O) 2R3, -C (O) R3, -NR3Rq, amino,
alkanoylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkoxycarbonylamino,
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido, alkyl or haloalkyl;
preferably, R1 is (1) an C1-C12 alkyl, C2-C12 alkenyl,
C2-C12 alkynyl, cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl radical
3
optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of -OH, -OR ,
-SR3, -S (O) R3, -S (O) 2R3, -C (O) R3, -NR3R4, aryl,
heteroaryl, cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl; or (2) aryl or
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
7
heteroaryl radicals; wherein the aryl, heteroaryl,
cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl radicals are optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, -OR3, -SR3,
-5 (O) R3, -S (0) 2R3, -C (O) R3, -NR3R4, amino, C1-Cg
alkanoylamino, C1-Cg alkylsulfonylamino, C1-Cg
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-Cg alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-Cg alkyl or C1-Cg haloalkyl of 1-3 halo
radicals;
more preferably, R1 is ( 1 ) an C1-C12 alkyl , C2 -C12
alkenyl, C2-C12 alkynyl, cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl
radical optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of -OH,
-OR3, -SR3, -S (0) R3, -S (O) 2R3, -C (0) R3, -NR3R4, aryl,
heteroaryl, cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl; or (2) aryl or
heteroaryl radicals; wherein the aryl, heteroaryl,
cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl radicals are optionally
3 3
substituted by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, -OR , -SR ,
-S (0) R3, -S (O) 2R3, -C (0) R3, -NR3R4, amino, C1-C4
alkanoylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, C.1-C4
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-C6 alkyl or C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo
radicals;
more preferably, R1 is (1) an C1-C12 alkyl or cycloalkyl
radical optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of -OH,
-OR3, -SR3, -S (0) R3, -S (O) 2R3, -C (O) R3. -NR3R4, aryl,
heteroaryl, cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl; or (2) aryl or
heteroaryl radicals; wherein the aryl, heteroaryl,
cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl radicals are optionally
3 3
substituted by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, -OR , -SR ,
-S (O) R~, -S (O) 2R3, -C (O) R3, -NR3R4, amino, acetyl amino,
methylsulfonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
8
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, C1-C6 alkyl or -CF3
radicals;
more preferably, R is (1) an C1-C12 alkyl or cycloalkyl
radical optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of -OH,
-OR3, -SR3, -S(0)2R3, -NR3R4, aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl
or heterocyclyl; or (2) aryl or heteroaryl radicals;
wherein the aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl and
heterocyclyl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, -OR3, -SR3, -S (O) 2R3, -NR3R4, amino,
acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 aikoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
C1-C6 alkyl or -CF3 radicals;
more preferably, R1 is (1) an C1-C12 alkyl or cycloalkyl
radical optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of -OH,
-OR3, -NR3R4, aryl, heteroaryl or cycloalkyl; or (2) aryl
or heteroaryl radicals; wherein the aryl, heteroaryl and
cycloalkyl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2
radicals of hydroxy, -OR3, -SR3, -S (0) 2R3, -NR3R4, amino,
acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, halo, C1-C6
alkyl or -CF3 radicals;
more preferably, R1 is (1) an C1-C12 alkyl or cycloalkyl
radical optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of -OH,
-OR3, -NR3R4, aryl, heteroaryl; or (2) aryl or heteroaryl
radicals; wherein the aryl, heteroaryl and cycloalkyl
radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of
hydroxy, -OR3, -SR3, -S (0) 2R3, -NR3R4, amino, acetyl amino,
methylsulfonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonyl, halo, C1-C6 alkyl or -CF3 radicals; and
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
9
most preferably, R1 is (1) an C5-C12 alkyl radical
optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of -OH, -OR3 or
3 4
-NR R ; or (2) aryl or heteroaryl radicals optionally
substituted by a hydroxy, -OR3, -SR3, -S (O) 2R3, -NR3R4,
amino, acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, halo, C1-C6
alkyl or -CF3 radical; and
provided that the total number of aryl, heteroaryl,
cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl radicals in R1 is preferably
0-3, more preferably, 0-2, most preferably, 0-1;
3
wherein each R is independently an alkyl, haloalkyl,
aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-alkyl or heteroaryl-alkyl
radical, wherein the aryl and heteroaryl radicals are
optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy,
alkoxy, alkylthiol, amino, alkanoylamino,
alkylsulfonylamino, alkylsulfinyl, alkylsulfonyl,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido,
alkyl, haloalkyl or haloalkoxy;
3
preferably, each R is independently an C1-Cg alkyl, C1-
Cg haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals, aryl, heteroaryl,
aryl-C1-C4-alkyl or heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl radical,
wherein the aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy,
C1-C4 alkylthiol, amino, C1-Cg alkanoylamino, C1-Cg
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1-Cg alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-Cg
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido, C1-Cg alkyl, C1-Cg
haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C8 haloalkoxy of 1-
3 halo radicals;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
3
more preferably, each R is independently an C1-C4
alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals, aryl,
heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C4-alkyl or heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl
radical, wherein the aryl and heteroaryl radicals are
5 optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4
alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol, amino, C1-C4 alkanoylamino, C1-
C4 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido, C1-Cq alkyl, C1-C4
10 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-
3 halo radicals;
more referabl
p y, each R is independently an C1-Cg
alkyl, -CF3, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C4-alkyl or
heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl radical, wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol,
amino, acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino, C1-Cq
alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3;
p y, each R is independently an C1-C4
more referabl
alkyl, -CF3, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C2-alkyl or
heteroaryl-C1-C2-alkyl radical, wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol,
amino, acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3;
more preferably, each R3 is independently an C1-C4
alkyl, -CF3, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C2-alkyl or
heteroaryl-C1-C2-alkyl radical, wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
11
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy, C1-C2 alkylthiol,
amino, acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino, C1-C2
alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonyl, halo, C1-C2 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3;
most preferably, each R3 is independently an C~-C4
alkyl, -CF3, aryl, heteroaryl, arylmethyl or
heteroarylmethyl radical; and
each R~ is independently a hydrogen or alkyl radical;
preferably, each R4 is independently a hydrogen or C1-Cg
20
4
alkyl radical; more preferably, each R is independently
a hydrogen or C1-C4 alkyl radical; most preferably, each
R4 is independently a hydrogen or methyl radical; and
R2 is a hydrogen or alkyl radical; preferably, R2 is a
hydrogen or C1-C4 alkyl radical; more preferably, R2 is
2
a hydrogen or methyl radical; and mast preferably, R is
a hydrogen radical; and
V is -CHR11- or -CHR11-CHR12-; wherein Rii and R12 are each
independently (1) a hydrogen, -OR2o, -SR21, -C (O) R22, -O-
C (O) -NR32R31/ -NR33_C (O) -R31, -NR33-C (0) -OR3o~ -NR33-C (O) -
NR32R31~ -NR33-S (O) 2-R3o~ -NR33-S (0) 2-NR32R31~ aryl or
heteroaryl radical; or (2) an alkyl, alkenyl or alkynyl
zo zi
radical optionally substituted with an -OR , -SR ,
22 32 31 33 31 33 30
-C (0) R , -O-C (O) -NR R , -NR -C (O) -R , -NR -C (O) -OR ,
-NR33-C (O) -NR32R31~ -NR33-S (0) 2-R3o~ -NR33-S (O) 2-NR32R31~
aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, alkoxy, aryloxy, heteroaryloxy,
alkylthiol, amino, alkanoylamino, alkylsulfonylamino,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
12
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido,
alkyl, haloalkyl or haloalkoxy;
preferably, R11 and Rlz are each independently (1) a
20 21 22 32 31 33
hydrogen, -OR , -SR , -C(0)R , -0-C(O)-NR R , -NR -
31 33 30 33 32 31 33
C (O) -R , -NR -C (O) -OR , -NR -C (O) -NR R , -NR -S (O) 2-
R3~, -NR33-S (O) 2-NR3zR31, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or
(2) an C1-Cg alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl
radical optionally substituted with an -OR2~, _SRzl,
22 32 31 33 31 33 30
-C (O) R , -O-C (O) -NR R , -NR -C (O) -R , -NR -C (0} -OR ,
-NR33-C (0) -NR32R31, -NR33_S (0) 2-R3~. -NR33-S (O) 2-NR3zR31I
aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, CI-C4 alkoxy, aryloxy,
heteroaryloxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol, amino, C1-Cg
alkanoylamino, C1-Cg alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, Cl-Cg
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-Cg alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-Cg alkyl, C1-Cg haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-Cg haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals;
more preferably, R11 and R12 are each independently ( 1 ) a
hydrogen, -ORz~, -SR21, -C (O) Rzz, -O-C (O) -NR32R31, -NR33-
C (0) -R31. -NR33-C (0) -OR3~, -NR33-C (0) -NR3zR31, -NR33-S (0) 2-
R3~, -NR33-S (0) 2-NR32R31, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or
(2) an C1-Cg alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl
20 21
radical optionally substituted with an -OR , -SR ,
-C (0) R2z~ -O-C (0) -NR3zR3y -NR33_C (0) -R31, -NR33-C (0) -OR3~,
-NR33-C (0) -NR3zR31~ -NR33_S (0) 2-R3~. -NR33-S (0) 2-NR32R3y
aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
13
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, aryloxy,
heteroaryloxy, C1-CQ alkylthiol, amino, C1-C4
alkanoylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals;
11 12
more preferably, R and R are each independently (1) a
20 21 22 32 31 33
hydrogen, -OR , -SR , -C(0)R , -O-C(O)-NR R , -NR -
31 33 30 33 32 31 33
C (0) -R , -NR -C (O) -OR , -NR -C (O) -NR R , -NR -S (O) 2-
R3o, -NR33-S (O) 2-NR32R31, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or
(2) an C1-Cg alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl
21
radical optionally substituted with an -OR , -SR ,
22 32 31 33 31 33 30
15 -C (O) R , -0-C (O) -NR R , -NR -C (O) -R , -NR -C (O) -OR ,
-NR33-C (0) -NR32R31~ -NR33_S (O) 2_R3o~ -NR33_S (O) 2-NR32R31~
aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, aryloxy,
20 heteroaryloxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol, amino, acetylamino,
methylsulfonylamino, methylsulfinyl, methylsulfonyl, C1-
C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano,
halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
when V is -CHR11-, more preferably, Rll is (1) a
20 21 22 32 31 33
hydrogen, -OR , -SR , -C (0) R , -0-C (0) -NR R , -NR -
C (O) -R31, -NR33-C (O) -OR3o, -NR33-C (0) -NR32R31, -NR33 _ S (O) 2-
R3o, -NR33-S (O) 2-NR32R31, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or
(2) an C1-Cg alkyl or CZ-Cg alkenyl radical optionally
substituted with an -OR2o, -SR21, -C (O) R22, -O-C (O) -
NR32R31, _NR33_C (0) -R31, -NR33-C (O) -OR3o, -NR33-C (O) -NR32R31~
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
14
-NR33-S (O) 2-R3~, -NR33-S (O) 2-NR32R31, aryl or heteroaryl
radical; wherein the aryl and heteroaryl radicals are
optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4
alkoxy, aryloxy, heteroaryloxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol, amino,
acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino, methylsulfinyl,
methylsulfonyl, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or
-OCF3 radicals;
11 20 21
more preferably, R is (1) a hydrogen, -OR , -SR ,
-C (O) R22, -0_C (0) -NR32R31, -NR33_C (O) -R31. -NR33-C (0) -OR3~,
-NR33-C (O) -NR32Rs1~ -NR33_S (0) 2-R3~. -NR33-S (0) 2-NR32R31~
aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-Cg alkyl or C2-
Cg alkenyl radical optionally substituted with an -OR ,
15 -SR21, -C (O) Rz2~ _0_C (0) -NR32R31~ -NR33_C (O) -R31, -NR33-
C (O) -OR3~, -NR33-C (0) -NR32R31~ -NR33_S (0) 2-R3~. -NR33-S (0)2-
32 31
NR R , aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, aryloxy,
20 heteroaryloxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol, methylsulfonyl, halo,
azido, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
more preferably, Rll is (1) a hydrogen, -OR2~, -O-C (O) -
NR32R31, -NR33_C (O) _R31~ -NR33_C (0) -OR3~, -NR33-C (0) -NR32R31~
-NR33-S (O) 2-R3~, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an
C1-Cg alkyl or C2-Cg alkenyl radical optionally
substituted with an -OR2~, -SR21, -C (O) R22, -O-C (O) -
NR32R31/ -NR33_C (0) -R31. -NR33-C (O) -OR3~. -NR33-C (O) -NR32R31~
-NR33-S(O)2-R3~, aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the
aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted
by 1-2 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy, aryloxy,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
heteroaryloxy, C1-C2 alkylthiol, halo, azido, C1-C2
alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; and
most preferably, Rll is (1) a hydrogen, -OR2~, -O-C (O) -
32 31 33 31 33 30 33 32 31
5 NR R , -NR -C (0) -R , -NR -C (0) -OR , -NR -C (O) -NR R ,
-NR33-S (O) 2-R3~, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an
C1-Cg alkyl or C2-Cg alkenyl radical optionally
substituted with an -OR2~, -O-C (O) -NR32R31, -NR33-C (0) -R31,
-NR33-C (O) -OR3~, -NR33-C (0) _NR32R31, _NR33_ S (O) 2-R3~, aryl or
10 heteroaryl radical;
alternatively, when V is -CHR11-CHR12-, more preferably,
Rll is a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl
radical and R12 is (1) a hydrogen, -OR2~, _SR21,
15 -C (0) R22~ -O_C (0) -NR32R31~ -NR33_C (0) -R31. -NR33-C (0) -OR3~,
_NR33-C (O) -NR32R31, -NR33_S (O) 2_R3~. -NR33-S (O) 2-NR32R31~
aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-Cg alkyl or C2-
Cg alkenyl radical optionally substituted with an -OR ,
-SR21, -C (O) R22~ -O-C (O) -NR32R31~ -NR33_C (0) -R31, -NR33-
20 C (0) -OR3~, -NR33-C (0) -NR32R31t -NR33_ S (0) 2-R3~, -NR33-S (O) 2-
32 31
NR R , aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, aryloxy,
heteroaryloxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol, amino, acetylamino,
methylsulfonylamino, methylsulfinyl, methylsulfonyl, C1-
C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano,
halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; or
wherein R12 is a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy or C1-C4
alkyl radical and R11 is (1) a hydrogen, -OR2~, -SR21,
-C (0) R22, _O-C (O) -NR32R31, -NR33-C (O) -R31. -NR33-C (O) -OR3~,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
16
-NR33-C (O) -NR32R31, -NR33_S (O) 2'R3o, -NR33-S (O) 2-NR32Rs1~
aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-Cg alkyl or C2-
Cg alkenyl radical optionally substituted with an -OR ,
-SR21~ -C (O) R22. -0-C (O) -NR32R31~ -NR33_C (0) -R31, -NR33-
33 32 31 33 30 33
5 C(O)-OR , -NR -C(0)-NR R , -NR -S(O)2-R , -NR -S(O)2-
32 31
NR R , aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, aryloxy,
heteroaryloxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol, amino, acetylamino,
10 methylsulfonylamino, methylsulfinyl, methylsulfonyl, C1-
C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano,
halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
more preferably, R11 is a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy
15 or C1-C4 alkyl radical and R12 is (1) a hydrogen, -OR2o,
-SR21~ -C (O)R2z~ -0-C (0) _NR32R31~ _NR33_C (0) -R31, -NR33-
C (O) -OR3o, -NR33-C (0) 'NR32R31, -NR33_ S (0) 2-R3o, aryl or
heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-Cg alkyl or C2-Cg
alkenyl radical optionally substituted with an -OR , -
20 SR21, -C (0) R2z, -0_C (0) -NR32R31, -IVR33_C (O) -R31, -NR33-C (0) -
OR3o, -NR33-C (O) -NR32Rs1, -NR33_S (O) 2'R3o, aryl or
heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and heteroaryl
radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of
hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, aryloxy, heteroaryloxy, C1-C4
alkylthiol, methylsulfonyl, halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl,
12
-CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; or wherein R is a hydrogen,
hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical and R11 is
(1) a hydrogen, -OR2o, -SR21, -C (0) R22, -0-C (O) -NR32R31,
-NR33-C (0) 'R31~ -NR33-C (O) -OR3o, _~33_C (0) -NR32R31~ -NR33-
S(0)2-R3o, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-Cg
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
17
alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl radical optionally substituted with
an -ORzo. -SRzl. -C (O) Rzz, -0-C (O) -NR3zR31, -NR33_C (O) -R31,
-NR33-C (O) -OR3o, -NR33-C (O) -NR32R31, _NR33_S (O) 2-R3o, aryl or
heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and heteroaryl
radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of
hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, aryloxy, heteroaryloxy, C1-C4
alkylthiol, methylsulfonyl, halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl,
-CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
more preferably, R11 is a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-Cq alkoxy
or C1-C4 alkyl radical and Rlz is (1) a hydrogen, -ORzo'
-O-C (0) -NR3zRsi' -NR33_C (0) -R31. -NR33-C (O) -OR3o, -NR33-
C (O) -NR3zR31, -NR33-S (0) 2-R3o, aryl or heteroaryl radical;
or (2) an C2-Cg alkyl or C2-Cg alkenyl radical
optionally substituted with an -ORz~, -SRzl, -C (O) Rzz, -O-
C (O) -NR3zR31, -NR33_C (O) -R31. -NR33-C (0) -OR3o, -NR33-C (O) -
NR3zR31! -NRs3-S (O) 2-R3o, aryl or heteroaryl radical;
wherein the aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally
substituted by 1-2 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy,
aryloxy, heteroaryloxy, C1-C2 alkylthiol, halo, azido,
C1-C2 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; or wherein Rlz is a
hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical
and R11 is (1) a hydrogen, -ORzo, -0-C (0) -NR3zRsy -NR33_
C (O) -R31. -NR33-C (O) -OR3~, -NR33-C (0) -NR3zR31, -NR33_ S (O) 2-
R3o, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-Cg alkyl or
C2-Cg alkenyl radical optionally substituted with an
-ORz~, -SRzl, -C (O) Rzz~ -0-C (O) -NR3zR3y -NR33_C (0) -R31, _
NR33-C (O) -OR3o, -NR33-C (O) -NR3zR31, -NR33_ S (O) 2'R3~. aryl or
heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and heteroaryl
radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of
hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy, aryloxy, heteroaryloxy, C1-C2
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCTNS98/16147
18
alkylthiol, halo, azido, C1-C2 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3
radicals; and
most preferably, R11 is a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy
or C1-C4 alkyl radical and R12 is (1) a hydrogen, -ORZO,
-0-C (0) -NR32R31, -NR33_C (O) -R31. -NR33-C (0) -OR3o, -NR33-
C (O) -NR32R31, -NRss_S (O) 2-R3o, aryl or heteroaryl radical;
or (2) an C1-Cg alkyl or C2-Cg alkenyl radical
optionally substituted with an -ORZO, -O-C (0) -NR32R31,
-NR33-C (O) -R31, -NR33_C (0) -OR3o, -NR33-C (O) -NR32R31, -NR33-
S(O)2-R3o, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or wherein R12 is
a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical
and R11 is (1) a hydrogen, -ORZO, -O-C (O) -NR32R31, -NR3s-
C (0) -R31, -NR33-C (0) -OR3o, -NR33-C (0) -NR32R31, -NR33-S (O) 2-
R3o, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-Cg alkyl or
C2-Cg alkenyl radical optionally substituted with an
-ORZO, -O-C (O) -NR32R31, -NR33_C (O) -R31, -NR33-C (0) -OR3o, _
NR33-C (0) -NR3zR31, -NR3s-S (O) 2-R3o, aryl or heteroaryl
radical;
wherein each R2o is independently a hydrogen, -C (O) RZa,
alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-
alkyl, heteroaryl-alkyl, alkanoyl, aroyl or heteroaroyl
radical; wherein the alkyl and alkenyl radicals are
optionally substituted by -C(0)R22; and wherein the
cycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, alkoxy,
alkylthiol, amino, alkanoylamino, alkylsulfonylamino,
alkylsulfinyl, alkylsulfonyl, alkoxycarbonylamino,
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido, alkyl, haloalkyl or
haloalkoxy;
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
19
preferably, each Rzo is independently a hydrogen, C1-Cg
alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl,
aryl-C1-C4-alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl, C1-Cg alkanoyl,
aroyl or heteroaroyl radical; wherein the alkyl and
alkenyl radicals are optionally substituted by -C(O)Rzz,
and wherein the cycloalkyl, aryl and heteroaryl radicals
are optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy,
C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol, amino, C1-Cg
alkanoylamino, C1-Cg alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, C1-Cg
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-Cg alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-Cg alkyl, C1-Cg haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-Cg haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals;
more referabl 20
p y, each R is independently a hydrogen,
C1-C4 alkyl, C2-C4 alkenyl, cycloalkyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C4-alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl, C1-
C4 alkanoyl, aroyl or heteroaroyl radical; wherein the
alkyl and alkenyl radicals are optionally substituted by
-C(O)Rzz; and wherein the cycloalkyl, aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol,
amino, C1-C4 alkanoylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-
C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals;
more preferably, each R is independently a hydrogen,
C1-C4 alkyl, C2-C4 alkenyl, cycloalkyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C4-alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl, C1-
C4 alkanoyl, aroyl or heteroaroyl radical; wherein the
alkyl and alkenyl radicals are optionally substituted by
-C(O)Rzz; and wherein the cycloalkyl, aryl and
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99106410 PCT/US98/16147
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol,
amino, acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino, methylsulfinyl,
methylsulfonyl, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
5 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or
-OCF3 radicals;
more preferably, each R2~ is independently a hydrogen,
C1-C4 alkyl-C(0)R22, C2-C4 alkenyl, cycloalkyl, aryl,
10 heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C2-alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C2-alkyl or
C1-C4 alkanoyl radical; and wherein the cycloalkyl, aryl
and heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-
2 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, Cl-C4 alkylthiol,
halo, azido, C1-C2 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; and
most preferably, each RZ~ is independently a hydrogen,
C2-C4 alkenyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C2-
alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-CZ-alkyl or C1-C4 alkanoyl radical;
wherein each R21 is independently an alkyl,
alkyl-C(O)R22, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-alkyl or
heteroaryl-alkyl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthiol, amino,
alkanoylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylsulfinyl,
alkylsulfonyl, alkoxycarbonylamino, alkoxycarbonyl,
cyano, halo, azido, alkyl, haloalkyl or haloalkoxy;
referabl 21
p y, each R is independently an C1-C8 alkyl, C1-
Cg alkyl-C(0)R22, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C4-alkyl or
heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol,
amino, C1-Cg alkanoylamino, C1-Cg alkylsulfonylamino, C1-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
21
C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-CQ alkylsulfonyl, C1-C8
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-Cg alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-Cg alkyl, C1-C8 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-Cg haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals;
21
more preferably, each R is independently an C1-C4
alkyl, C1-C4 alkyl-C(O)Rzz, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C4-
alkyl or heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl radical; wherein the
aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, C~,-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthiol, amino, C1-Cq alkanoylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4
haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-
3 halo radicals;
more ref erabl zl
p y, each R is independently an C1-C4
alkyl, C1-C4 alkyl-C(O)Rzz, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C4-
alkyl or heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl radical; wherein the
aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthiol, amino, acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino,
methylsulfinyl, methylsulfonyl, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; and
most preferably, each Rzl is independently an C1-C4
alkyl, C1-C4 alkyl-C(0)Rzz, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C2-
alkyl or heteroaryl-C1-C2-alkyl radical; wherein the
aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted
by 1-2 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C~-C4
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99106410 PCT/US98/16147
22
alkylthiol, halo, azido, C1-C2 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3
radicals;
wherein each R22 is independently a hydroxy, alkoxy,
aryloxy, aryl-alkoxy, heteroaryloxy, heteroaryl-alkoxy
or -NR23Rz4 radical; preferably, each R22 is independently
a hydroxy, C1-Cg alkoxy, aryloxy, aryl-C1-C4-alkoxy,
23 24
heteroaryloxy, heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkoxy or -NR R
radical; more referabl 2z
p y, each R is independently a
hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, aryloxy, aryl-C1-C2-alkoxy,
23 24
heteroaryloxy, heteroaryl-C1-C2-alkoxy or -NR R
radical; and most referabl 22
p y, each R is independently
23 24
a hydroxy or -NR R radical;
wherein R23 is a hydrogen, alkyl, aryl, aryl-alkyl,
heteroaryl or heteroaryl-alkyl radical; preferably, R23
is a hydrogen, C1-Cg alkyl, aryl, aryl-C1-C4-alkyl,
heteroaryl or heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl radical; more
preferably, R23 is a hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl, aryl, aryl-
C1-C2-alkyl, heteroaryl or heteroaryl-C1-C2-alkyl
23
radical; and most preferably, R is a hydrogen, C1-C2
alkyl, aryl, aryl-C1-C2-alkyl, heteroaryl or heteroaryl-
C1-C2-alkyl radical; and
R24 is a hydrogen or alkyl radical; preferably, R24 is a
hydrogen or Cl-C8 alkyl radical; more preferably, R24 is
a hydrogen or C1-C4 alkyl radical; and most preferably,
R24 is a hydrogen or C1-C2 alkyl radical; or
23 24
-NR R represents a heterocyclyl or heteroaryl radical;
23 24
preferably, -NR R represents a heteroaryl radical; and
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
23
wherein the heterocyclyl, aryl and heteroaryl radicals
Of R22, Rz3 and -NR23Ra4 are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthiol, amino,
alkanoyl-amino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylsulfinyl,
alkylsulfonyl, alkoxycarbonylamino, alkoxycarbonyl,
cyano, halo, azido, alkyl, haloalkyl or haloalkoxy;
preferably, 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthiol, amino, C1-Cg alkanoylamino, C1-Cg
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4 alkyl-sulfinyl, C1-C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1-Cg alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-Cg
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido, C1-Cg alkyl, C1-Cg
haloalkyl of 2-3 halo radicals or C1-Cg haloalkoxy of 1-
3 halo radicals; more preferably, 1-3 radicals of
hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol, amino, C1-C4
alkanoylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonyl-amino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals; more
preferably, 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthiol, amino, acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino,
methylsulfinyl, methylsulfonyl, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; more
preferably, 1-2 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthiol, halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3
radicals; and most preferably, 1-2 radicals of hydroxy,
C1-C2 alkoxy, C1-C2 alkylthiol, halo, azido, C1-C2 alkyl,
-CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
15 16 15 16
W-N represents -C(O)-N, -C(0)-CR R -N, -CR R -N or
-CR17R18-CR15R16-N; preferably, W-N represents -C (O) -
15 16 15 16 17 18 15 16
CR R -N, -CR R -N or -CR R -CR R -N; more preferably,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
24
when V is -CHR11-CHR12- , W-N represents -C (O) -N or -
CRlSRls-N; preferably, -CRlSRis-N; provided that the
combined total number of aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl
and heterocyclyl radicals in V and W is 0-3; preferably,
0-2; and more preferably, 0-1;
wherein R15 and R16 are each independently ( 1 ) a
hydrogen, -C(O)Rz2, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2)
an alkyl, alkenyl or alkynyl radical optionally
substituted with an -OR2~, -SR21, -C (O) RZ2, aryl or
heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and heteroaryl
radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of
hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthiol, amino, alkanoylamino,
alkylsulfonylamino, alkylsulfinyl, alkylsulfonyl,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido,
alkyl, haloalkyl or haloalkoxy;
preferably, R15 and R16 are each independently (1) a
hydrogen, -C(O)RZ2, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2)
an C1-Cg alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl radical
optionally substituted with an -OR2~, -SR21, -C (O) Rzzr
aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol,
amino, C1-Cg alkanoylamino, C1-C8 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-
C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, Cl-Cg
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-Cg alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-Cg alkyl, C1-C8 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-Cg haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals;
more preferably, R15 and R16 are each independently (1) a
hydrogen, -C(0)R22, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2)
an C1-Cg alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl radical
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
optionally substituted with an -OR2~, -SR21, -C (O) R22,
aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol,
5 amino, C~-C4 alkanoylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-
C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
azido, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals;
more preferably, R16 iS a hydrogen radical; and R15 is
(1) a hydrogen, -C(O)R22, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or
(2) an C1-Cg alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl
21
radical optionally substituted with an -OR , -SR ,
15 -C(O)R22, aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl
and heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-
3 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthiol,
amino, acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino, methylsulfinyl,
methylsulfonyl, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
20 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3
radicals;
more preferably, R15 is (1) a hydrogen, aryl or
heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-C4 alkyl radical
optionally substituted with an -OR2~, aryl or heteroaryl
radical; wherein the aryl and heteroaryl radicals are
optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C2
alkoxy, C1-C2 alkylthiol, amino, acetylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonyl-amino, halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3
radicals; and
most preferably, R15 is (1) a hydrogen, aryl or
heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-C4 alkyl radical
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
26
optionally substituted with an aryl or heteroaryl
radical; and
wherein Rl~ and R18 are each independently ( 1 ) a
2d 21 22 33 31 33
hydrogen, -OR , -SR , -C(O)R , -NR -C(O)-R , -NR -
C (0) -OR3~, -NR33-C (O) -NR32R31~ -NR33-S (O) 2-R3~. -NR33-S (O) 2-
32 31
NR R , aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an alkyl,
alkenyl or alkynyl radical optionally substituted with
an -OR2~. -SR21. -C (O) R2z~ -NR33-C (O) -R31~ -NR33-C (O) -OR3~,
-NR33-C (O) -NR32R31~ -NR33_S (O) 2-R3~. -NR33-S (O) 2-NR32R31~
aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthiol, amino,
alkanoylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylsulfinyl,
alkylsulfonyl, alkoxycarbonylamino, alkoxycarbonyl,
cyano, halo, azido, alkyl, haloalkyl or haloalkoxy;
pref erably, Rl~ and R18 are each independently ( 1 ) a
hydrogen, -OR2~, -SR21, -C (0) R22. -NR33-C (O) -R31, -NR33-
C (O) -OR3~. -NR33-C (O) -NR32R31~ -NR33_S (0) 2-R3~~ -NR33-S (O) 2-
32 31
NR R , aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-Cg
alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl radical optionally
substituted with an -OR2~, -SR21, -C (O) R22, -NR33-C (O) -R31,
-NR33-C (O) -OR3~, -NR33-C (0) -NR32R31~ -NR33_S (0) 2-R3~. -NR33-
32 31
S(O)2-NR R , aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the
aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthiol, amino, C1-Cg alkanoylamino, C1-Cg
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1-Cg alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-Cg
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido, C1-Cg alkyl, C1-Cg
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
27
haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-Cg haloalkoxy of 1-
3 halo radicals;
more pref erably, Rl~ and R1$ are each independently ( 1 ) a
20 21 22 33 31 33
hydrogen, -OR , -SR , -C(O)R , -NR -C(0)-R , -NR -
C {O) -OR3~, -NR33-C (O) -NR32R31, -NR33_ S (O) 2-R3~~ -NR33-S (O) 2-
32 31
NR R , aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-Cg
alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl radical optionally
substituted with an -OR2~, -SR21, -C (O) R22, -NR33-C (O) -R31,
-NR33-C {0) -OR3~, -NR33-C (0) -NR32R31, -NR33_ S (O) 2-R3o~ -NR33-
32 31
S(O)2-NR R , aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the
aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthiol, amino, C1-C4 alkanoylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4
alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4
haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-
3 halo radicals;
more preferably, R1$ is a hydrogen radical, and R1~ is
(1) a hydrogen, -OR2~, -SR21, -C (O) R22, -NR33-C (O) -R31, -
NR33-C (O) -OR3~, -NR33-C (O) -NR32R31, -NR33_S (0) 2-R3~, -NR33-
32 31
S{0)2-NR R , aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2) an C1-Cg
alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl radical optionally
substituted with an -OR2~, -SR21, -C (0) R22, -NR33-C (0) -R31,
-NR33-C (0) 'OR3~~ -NR33-C (0) -NR32R31~ -NR33_S {0) 2-R3~~ -NR33-
32 31
S(0)2-NR R , aryl or heteroaryl radical; wherein the
aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthiol, amino, acetylamino, methylsulfonylamino,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
28
methylsulfinyl, methylsulfonyl, C1-C4
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl, cyano, halo,
C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
more preferably, R17 is (1) a hydrogen, -OR2~, -NR33-C (O)
R31, -NR33-S (O) 2-R3~, aryl or heteroaryl radical; or (2)
an C1-C4 alkyl radical optionally substituted with an
-NR33-C (O) -R31, -NR33-S (O) 2-R3~, aryl or heteroaryl
radical; wherein the aryl and heteroaryl radicals are
optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of hydroxy, C1-C2
alkoxy, C1-C2 alkylthiol, amino, acetylamino,
methylsulfonyl, C1-C4 alkoxycarbonylamino, halo, C1-C4
alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; and
most preferably, R17 is a hydrogen, hydroxy or C1-C4
alkyl radical; and
15 16 17 18
alternatively, one of -CR R - or -CR R - represent a
cycloalkylene or heterocyclylene radical; and
X is O, Y is CR9and Z is N; or
X is S, Y is CR9and Z is CRl~;
or
X is 0, Y is CR9and Z is N; or
X is S, Y is CR9and Z is CRl~;
or
is 0, X is CR8and Z is CRl~;
Y or
Y is S, X is CR8and Z is CRl~;
or
Z is O, X is N nd i s R9; or
a Y C
Z i S X i CR$and Y i CR9 ;
s , s s or
Z is O, X is N nd i s R9; or
a Y C
is S, X is CR8and Y is CR9;
Z
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT1US98/16147
29
15 16 17 18
preferably, when W-N represents -CR R -N or -CR R -
CR15R16-N, and X is S and Z is CR1~, then at least one of
11 12 15 16 17 18
R , R , R , R , R or R is other than a hydrogen
radical; more preferably, when X is S and Z is CR1~ or
when Z is S and X is CRB, then at least one of R11, R12,
Rls ~ R16 ~ R17 or Rl$ is other than a hydrogen radical;
11 12 15 16 17
more preferably, at least one of R , R , R , R , R or
R18 is other than a hydrogen radical;
wherein Ra, R9 and R1~ are each independently -B-A,
provided that the combined total number of aryl,
a
heteroaryl, cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl radicals in R ,
R9 and R1~ is 0-3; preferably 0-2; and more preferably,
0-1
s
preferably, R is a radical of hydrogen, halo, C1-C2
alkoxy, amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-(C1-C2 alkyl)amino,
C1-C2 alkanoylamino, amidino, amido, carboxy, or C1-C4
alkyl optionally substituted by amino, C1-C2 alkylamino,
di-(C1-C2 alkyl)amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino, hydroxy, C1-
C2 alkoxy, 1-3 halo radicals, amidino, amido or carboxy
radical; more preferably, Ra is a radical of hydrogen,
halo, C1-C2 alkoxy, -CF3 or C1-C4 alkyl optionally
substituted by hydroxy or C1-C2 alkoxy radical; and most
8
preferably, R is a radical of hydrogen, halo, C1-C2
alkoxy, -CF3 or methyl; and
when V is -CHR11- and Z is CRl~, preferably, Rl~ is
11
independently -B-A when R is a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C2
alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical; and when R11 is other than
a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-CZ alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
radical, then Rlo is independently a radical of
hydrogen, halo, C1-C2 alkoxy, amino, C1-C2 alkylamino,
di-(C1-C2 alkyl)amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino, amidino,
amido, carboxy, or C1-C4 alkyl optionally substituted by
5 amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-(C1-C2 alkyl)amino, C1-C2
alkanoylamino, hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy, 1-3 halo radicals,
amidino, amido or carboxy radical;
more preferably, Rlo is independently -B-A when R11 is a
10 hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical;
and when R11 is other than a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C2
alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical, then Rlo is independently
a radical of hydrogen, halo, C1-C2 alkoxy, -CF3 or C1-C4
alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy or C1-C2 alkoxy
15 radical;
more preferably, Rlo is independently -B-A when R11 is a
hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical;
and when R11 is other than a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C2
~o
20 alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical, then R is independently
a radical of hydrogen, halo, C1-C2 alkoxy, -CF3 or
methyl radical;
alternatively, when V is -CHR11-CHR12- and Z is CRlo,
25 preferably, Rlo is independently -B-A when Rll and R12 are
each independently a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy or
C1-C4 alkyl radical; and when R11 or R12 is independently
other than a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy or C1-C4
alkyl radical, then Rlo is independently a radical of
30 hydrogen, halo, C1-C2 alkoxy, amino, C1-C2 alkylamino,
di-(C1-C2 alkyl)amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino, amidino,
amido, carboxy, or C1-C4 alkyl optionally substituted by
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
31
amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-(C1-C2 alkyl)amino, C1-C2
alkanoylamino, hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy, 1-3 halo radicals,
amidino, amido or carboxy radical;
more preferably, R1~ is independently -B-A when R11 and
R12 are each independently a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C2
alkoxy or C1-Cq alkyl radical; and when R11 or R12 is
independently other than a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C2
alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical, then R1~ is independently
a radical of hydrogen, halo, C1-C2 alkoxy, -CF3 or C1-C4
alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy or C1-C2 alkoxy
radical;
more preferably, R1~ is independently -B-A when R11 and
R12 are each independently a hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C2
alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical; and when R11 or R12 is
independently other than a hydrogen, hydroxy, Cz-C2
alkoxy or C1-C4 alkyl radical, then R1~ is independently
a radical of hydrogen, halo, C1-CZ alkoxy, -CF3 or
methyl;
wherein each B is independently a (1) bond; (2) alkyl,
alkenyl or alkynyl radical optionally substituted by (a)
1-3 radicals of amino, alkylamino, dialkylamino,
alkanoylamino, alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino,
hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthio, cyano or halo, and/or (b) 1-
2 radicals of heterocyclyl, aryl or heteroaryl
optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino,
alkylamino, dialkylamino, alkanoylamino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
alkoxy, alkylthio, cyano, halo, alkyl, haloalkyl or
haloalkoxy; (3) heterocyclyl radical optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino, alkanoylamino, alkoxycarbonylamino,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
32
alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthio, cyano,
alkyl, haloalkyl or haloalkoxy; or (4) aryl or
heteroaryl radical optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of amino, alkylamino, dialkylamino,
alkanoylamino, alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino,
hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthio, cyano, halo, alkyl,
haloalkyl or haloalkoxy;
preferably, each B is independently a (1) bond; (2) C1-
Cg alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl radical
optionally substituted by (a) 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-
C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4 alkyl)amino, C1-C5
alkanoylamino, (C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthio, cyano, halo, and/or (b) 1-2 radicals of
heterocyclyl, aryl or heteroaryl optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, cyano, halo, C1-C4 alkyl,
C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C4 haloalkoxy
of 1-3 halo radicals; (3) heterocyclyl radical
optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4
alkylamino, di-(C1-C4 alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino,
(C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino,
hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, cyano, C1-C4
alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-Cg
haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals; or (4) aryl or
heteroaryl radical optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C~
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, cyano, halo, C1-CQ alkyl,
C1-Cg haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C8 haloalkoxy
of 2-3 halo radicals;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
33
more preferably, each B is independently a (1) bond; (2)
C1-Cg alkyl radical optionally substituted by (a) a
radical of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-Cq
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio or cyano and/or (b) 1-3
halo radicals, and/or (c) 1-2 radicals of heterocyclyl,
aryl or heteroaryl optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, cyano, halo, C1-C4 alkyl,
C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C4 haloalkoxy
of 1-3 halo radicals; (3) heterocyclyl radical; or (4)
aryl or heteroaryl radical optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, cyano, halo, C1-C4 alkyl,
C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C4 haloalkoxy
of 1-3 halo radicals;
more preferably, each B is independently a (1) bond; (2)
C1-Cg alkyl radical optionally substituted by (a) a
radical of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, Cl-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, cyano, and/or (b) 1-3
halo radicals, and/or (c) 1-2 radicals of heterocyclyl,
aryl or heteroaryl optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, cyano, halo, C1-C4 alkyl,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
34
-CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; (3) heterocyclyl radical; or (4)
aryl or heteroaryl radical optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonyl-amino, C1-C4 aikylsulfonylamino,
hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, cyano, halo, C1-
C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
more preferably, each B is independently a (1) bond; (2)
C1-C4 alkyl radical optionally substituted by (a) a
radical of amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-(C1-C2
alkyl)amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, hydroxy or C1-C2 alkoxy and/or (b)
1-2 halo radicals, and/or (c) a radical of heterocyclyl,
aryl or heteroaryl optionally substituted by 1-2
radicals of amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-(C1-C2
alkyl)amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C2 alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
C1-C2 alkoxy, C1-C2 alkylthio, halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or
-OCF3 radicals; (3) heterocyclyl radical; or (4) aryl or
heteroaryl radical optionally substituted by 1-2
radicals of amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-(C1-C2
alkyl)amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C2 alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
C1-C2 alkoxy, C1-C2 alkylthio, halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or
-OCF3 radicals;
more preferably, each B is independently a (1) bond; (2)
C1-C4 alkyl radical; or (3) aryl or heteroaryl radical
optionally substituted by a radical of amino, C1-C2
alkylamino, di-(C1-C2 alkyl)amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino,
(C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C2 alkylsuifonylamino,
hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy, C1-C2 alkylthio, halo, C1-C4
alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; and most preferably, each
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
B is independently a bond, C1-C4 alkyl, aryl or
heteroaryl radical; and
each A is independently a (1) hydrogen radical; (2)
5 halo, cyano or nitro radical; (3) -C (O) -R3~, -C (O) -OR31,
32 31 32 32 31 31
-C (O) -NR R or -C (NR ) -NR R radical; (4) -OR , -0-
C (O} -R31, -0-C (O) -NR32R31 or -0-C (O) -NR33-S (O) 2-R3o
radical; (5) -SR31, -S (0) -R3o. -S (0) 2-R3o. -S (O) 2-NR32R3i,
-S (0) 2-NR33-C (0) -R31, -S (0) 2-NR33-C (0) -OR3o or -S (O) 2-NR33-
10 C (O} -NR32R31 radical; or (6} -NR32R31, -NR33-C (0) -R31, -
NR33-C (0) -OR3~. -NR33-C (O) -NR32R3y -NR33_C (NR32) -NR32R3y _
NR33-S (0) 2-R3o or -NR33-S (0) 2-NR32R31 radical;
preferably, each A is independently a (1) hydrogen
15 radical; (2) halo, cyano or nitro radical; (3) -C(O)-
R3o, -C (O) -OR31, -C (0) -NR32R31 or -C (NR32) -NR32R31 radical;
(4) -OR31, -0-C (O) -R31 or -O-C (O) -NR32R31 radical; (5} -
SR31, -S (O) -R3o, -S (O) 2-R3o or -S (O) 2-NR32R31 radical; or
32 31 33 31 33 30 33
(6) -NR R , -NR -C(0)-R , -NR -C(0)-OR , -NR -C(0)-
20 NR32R31~ -NR33_C (NR32) -NR32R31~ -NR33_S (O) 2-R3o or -NR33-
32 31
S(O)2-NR R radical;
more preferably, each A is independently a (1) hydrogen
radical; (2) halo radical; (3) -C (O) -R3o, -C (0) -OR31
25 -C (0) -NR32R31 or -C (NR32) -NR32R31 radical; (4) -OR31
radical; (5) -SR31, -S (0) 2-R3o or -S (O) 2-NR32R31 radical;
or (d) -NR32R31, -NR33_C (O) -R31. -NR33-C (O) -OR3o, -NR33-
32 31 33 30 33 32 31
C(O)-NR R , -NR -S(0)2-R or -NR -S(0)2-NR R radical;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
36
more preferably, each A is independently a (1) hydrogen
radical; (2) halo radical; (3) -C (O) -R3~, -C (O) -OR3y
-C (O) -NR3zR31 or -C (NR32) -NR3zR31 radical; (4) -OR31
radical; (5) -SR31, -S (O) 2-R3~ or -S (O) 2-NR32R31 radical;
or (6) -NR32R31, -NR33-C (O) -R31 or -NR33-S (O) 2-R3~ radical;
and most preferably, each A is independently a hydrogen,
halo, -C (0) -R3~, -C (O) -OR31 or -C (O) -NR32R3i radical;
wherein each R3~ is independently
(1) alkyl, alkenyl or alkynyl radicals optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of -CO2R34, amino,
alkylamino, dialkylamino, alkanoylamino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, N-(alkoxycarbonyl)-N-(alkyl)amino,
aminocarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkoxy,
alkylthio, alkylsulfinyl, alkylsulfonyl, hydroxy, cyano,
halo or aralkoxy, arylalkylthio, arylalkylsulfonyl,
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl or heteroaryl radicals,
wherein the cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl and
heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of amino, alkylamino, dialkylamino,
alkanoylamino, alkoxycarbonyl-amino, alkylsulfonylamino,
alkanoyl, alkoxycarbonyl, hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthio,
alkylsulfinyl, alkylsulfonyl, cyano, halo, alkyl,
haloalkyl or haloalkoxy;
(2) cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl radical optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino, alkanoylamino, alkoxycarbonylamino,
alkylsulfonylamino, alkoxycarbonyl, hydroxy, alkoxy,
alkylthio, cyario, alkyl, haloalkyl or haloalkoxy; or
(3) aryl or heteroaryl radicals optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of amino, alkylamino, dialkylamino,
alkanoylamino, alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino,
alkoxycarbonyl, hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthio, cyano, halo,
azido, alkyl, haloalkyl or haloalkoxy;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
37
preferably, each R is independently
(1) C1-Cg alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-Cg alkynyl radicals
optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of -CO2R34, amino,
C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C~ alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoyl-
5 amino, (C1-C4 alkoxy}carbonylamino, N-((C1-C4 alkoxy)
carbonyl)-N-(C1-C4 alkyl)amino, aminocarbonylamino, Cl-
C4 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, C1-
C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, hydroxy, cyano,
halo or aryl-C1-C4-alkoxy, aryl-C1-C4-alkylthio, aryl-C1-
10 C4-alkylsulfonyl, C3-Cg cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl
or heteroaryl radicals, wherein the cycloalkyl, aryl,
heterocyclyl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino,
di-(C1-C4 alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
15 alkoxy) carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5
alkanoyl, (C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonyl, hydroxy, Cl-C4 alkoxy,
C1-C4 alkylthio, C1-C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4
alkylsulfonyl, cyano, halo, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl
of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo
20 radicals;
(2) cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl radical optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino,
di-(C1-C4 alkyl}amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, (C1-C4
25 alkoxy)carbonyl, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio,
cyano, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals; or
(3) aryl or heteroaryl radicals optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
30 alkyl}amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonyl, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio,
cyano, halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3
halo radicals or Cl-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCTIUS98/16147
38
more preferably, each R3~ is independently
(1) C1-C6 alkyl radicals optionally substituted by 1-3
34
radicals of -C02R , amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonyl-amino, N-((Cz-Cq alkoxy)carbonyl)-N-(C1-
C4 alkyl)amino, aminocarbonylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthio, C1-C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl,
cyano, halo or aryl-C1-C4-alkoxy, aryl-C1-C4-alkylthio,
aryl-C1-Cq-alkylsulfonyl, C3-Cg cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl, aryl or heteroaryl radicals, wherein the
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl and heteroaryl radicals
are optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-
C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4 alkyl)amino, C1-C5
alkanoylamino, (C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkanoyl, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, C1-C4
alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, hydroxy, cyano,
halo, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals;
(2) cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl radical optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino,
di-(C1-C4 alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonyl, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio,
cyano, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals; or
(3) aryl or heteroaryl radicals optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonyl, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
39
cyano, halo, azido, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3
halo radicals or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals;
more referabl 30
p y, each R is independently
(1) C1-C6 alkyl radical optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of -CO2R34, amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonyl-amino, N-((C1-Cq alkoxy)carbonyl)-N-(C1-
C4 alkyl)amino, aminocarbonylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4
alkylthio, C1-C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl,
cyano, halo or aryl-C1-C4-alkoxy, aryl-C1-C4-alkylthio,
aryl-Cl-C4-alkylsulfonyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl, aryl or heteroaryl radicals, wherein the
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl and heteroaryl radicals
are optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-
C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4 alkyi)amino, C1-C5
alkanoylamino, (C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkanoyl, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, C1-C4
alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, hydroxy, cyano,
halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
(2) cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl radical optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino,
di-(C1-C4 alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonyl, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio,
cyano, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C2 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or -OCF3; or
(3) aryl or heteroaryl radicals optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, (C1-C4
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
alkoxy)carbonyl, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio,
cyano, halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
more ref erabl 30
p y, each R is independently
5 (1) -CF3 or C1-C4 alkyl radical optionally substituted
by 1-2 radicals of -CO2R34, amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-
(C1-C2 alkyl)amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonyl-amino, N-((C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonyl)-N-(C1-
C4 alkyl)amino, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy or aryl-C1-C2-
10 alkoxy, heterocyclyl, aryl or heteroaryl radicals,
wherein the heterocyclyl, aryl and heteroaryl radicals
are optionally substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-
C2 alkylamino, di-(C1-C2 alkyl)amino, C1-C2
alkanoylamino, (C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonyl-amino, C1-C5
15 alkanoyl, (C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonyl, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy,
halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
(2) cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl radical optionally
substituted by 1-2 radicals of (C1-C4 alkoxy}carbonyl,
hydroxy or C1-C4 alkyl; or
20 (3) aryl or heteroaryl radicals optionally substituted
by 1-2 radicals of amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-(C1-C2
alkyl}amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino, hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy,
halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals;
25 more referabl 30
p y, each R is independently (1)
heterocyclyl radical optionally substituted by 1-2
radicals of (C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonyl, hydroxy or C1-C4
alkyl; or (2) heteroaryl radicals optionally substituted
by 1-2 radicals of amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-(Cl-C2
30 alkyl)amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino, hydroxy, C~-C2 alkoxy,
halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; and most
referabl 30
p y, each R is independently a heterocyclyl
radical optionally substituted by C1-C4 alkyl;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
41
each R31 is independently hydrogen radical or R3o,
alternatively, more preferably, each R31 is
independently hydrogen radical or (1) -CF3 or C1-C4
alkyl radical optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of
hydroxy, C1-CZ alkoxy or aryl-C1-C2-alkoxy, aryl or
heteroaryl radicals, wherein the aryl and heteroaryl
radicals are optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of
amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-(C1-C2 alkyl)amino, C1-C2
alkanoylamino, (C1-C4 alkoxy) carbonylamino, C1-C5
alkanoyl, (C1-C4 alkoxy)carbonyl, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy,
halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; (2)
cycloalkyl radical optionally substituted by 1-2
radicals of hydroxy or C1-CQ alkyl; or (3) aryl or
heteroaryl radicals optionally substituted by 1-2
radicals of amino, C1-C2 alkylamino, di-(C1-C2 alkyl)
amino, C1-C2 alkanoylamino, hydroxy, C1-C2 alkoxy, halo,
C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; and
most referabl 31
p y, each R is independently hydrogen
radical or (1) C1-C4 alkyl radical optionally
substituted by 1-2 radicals of aryl or heteroaryl
radicals, wherein the aryl and heteroaryl radicals are
optionally substituted by a hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, halo,
C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radical; or (2) cycloalkyl
radical optionally substituted by 1-2 radicals of
hydroxy or C1-C4 alkyl; or (3) aryl or heteroaryl
radicals optionally substituted by a hydroxy, Cl-C2
alkoxy, halo, C1-C4 alkyl, -CF3 or -OCF3 radicals; and
wherein each R32 is independently (1) hydrogen radicals;
(2) alkyl, alkenyl or alkynyl radicals optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino, hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthio, cyano or halo;
or (3) aryl, heteroaryl, arylalkyl, heteroarylalkyl,
heterocyclyl, heterocyclylalkyl, cycloalkyl or
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99!06410 PCT/US98/16147
42
cycloalkylalkyl radicals optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of amino, alkylamino, dialkylamino, hydroxy,
alkoxy, alkylthio, cyano, alkyl, haloalkyl or
haloalkoxy; preferabl 32
y, each R is independently (1)
hydrogen radicals; (2) C1-Cg alkyl, C2-Cg alkenyl or C2-
Ca alkynyl radicals optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4-
alkyl)amino, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio,
cyano or halo; or (3) aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C1-C4-
alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C4-alkyl, heterocyclyl,
heterocyclyl-C1-C4-alkyl, C3-Cg cycloalkyl or Cg-C8-
cycloalkyl-C1-C4-alkyl radicals optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-Cq alkylamino, di-(C1-C4-
alkyl)amino, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio,
cyano, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals
or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals; and most
preferably, each R32 is independently a hydrogen or C1-C4
alkyl radical;
each R33 is independently (1) hydrogen radical; (2)
alkyl radical optionally substituted by a radical of
heterocyclyl, aryl or heteroaryl which is optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino, alkanoylamino, alkoxycarbonylamino,
alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy, alkoxy, alkylthio,
alkylsulfinyl, alkylsulfonyl, cyano, halo, alkyl,
haloalkyl or haloalkoxy; or (3) heterocyclyl, aryl or
heteroaryl radicals optionally substituted by 1-3
radicals of amino, alkylamino, dialkylamino, alkanoyl-
amino, alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
alkoxy, alkylthio, alkylsulfinyl, alkylsulfonyl, cyano,
halo, alkyl, haloalkyl or haloalkoxy; and preferably,
each R33 is independently ( 1 ) hydrogen radical ; ( 2 ) C1- C4
alkyl radical optionally substituted by a radical of
heterocyclyl, aryl or heteroaryl which is optionally
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
43
substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino,
di-(C1-C4 alkyl)amino, Cl-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy) carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino,
hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, C1-C4
alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, cyano, halo, C1-C4
alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C4
haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals; or (3) heterocyclyl,
aryl or heteroaryl radicals optionally substituted by 1-
3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino, di-(C1-C4
alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoyl-amino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl-amino,
hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, C1-C4
alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4 alkylsulfonyl, cyano, halo, C1-C4
alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C4
haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo radicals; more preferably, each
R33 is independently a hydrogen or C1-C4 alkyl radical;
and most preferably, each R33 is independently a
hydrogen or methyl radical; and
each R34 is independently hydrogen, alkyl, heteroaryl,
aryl, arylalkyl or heteroarylalkyl radicals, wherein the
aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally substituted
by 1-3 radicals of cyano, halo, alkyl, amino,
alkylamino, dialkylamino, alkanoylamino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
alkoxy, alkylthio, alkylsulfinyl, alkylsulfonyl,
haloalkyl or haloalkoxy; preferably, each R34 is
independently hydrogen or C1-C4 alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl,
aryl-Cl-C4-alkyl or heteroaryl-C~-C4-alkyl radicals,
wherein the aryl and heteroaryl radicals are optionally
substituted by 1-3 radicals of amino, C1-C4 alkylamino,
di-(C1-C4 alkyl)amino, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, (C1-C4
alkoxy)carbonylamino, C1-C4 alkylsulfonylamino, hydroxy,
C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, C1-C4 alkylsulfinyl, C1-C4
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
44
alkylsulfonyl, cyano, halo, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 haloalkyl
of 1-3 halo radicals or C1-C4 haloalkoxy of 1-3 halo
radicals; and most preferably, each R34 is independently
a hydrogen or C1-C4 alkyl radical.
The symbols used above have the following meanings:
R" Ry O
-CR"Ry- - -C CO) - ' .
f
R
RX N
-NRxRy - ~-N' -C (NR) - -
Ry j..f'
R
i ~/%
-NR- - ~~N~~ -S CO) 2- -
,.~/ ~~.
For example:
R32
N
R31
-NR33-C (NR32) -NR32R31 - ~N~N
R33 R32
0
-O-C (0) -NR33 - S (O) 2-R3o - '~~ ~ N S~ R3o
R33
The compounds of this invention have in general
several asymmetric centers and are depicted in the form
of racemic mixtures. This invention is intended to
encompass racemic mixtures, partially racemic mixtures
and separate enantiomers and diasteromers. Preferably,
the absolute configuration of the hydroxamic acid group
is {R) .
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99!06410 PCT/CJS98/16147
Compounds of interest include the following:
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-
methylaminocarbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
5 tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-phenyl-6-(N-
hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2,-c]-
pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(methoxy
carbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro
thieno- [3,2-c] -pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(ethoxy
carbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(2-pyridyl)-
6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
[3,2-c]-pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(3-pyridyl)-
6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
[3, 2-c] -pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(4-
morpholino carbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(phenoxy
carbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
benzylaminocarbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(3-
phenylpropyl)aminocarbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
phenethyl-N-methylaminocarbonyl)-6-(N-
hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-
ethylaminocarbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(4,4-
dimethylpentyl)aminocarbonyl)-6-(N-
hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridine;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
46
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(4,4-
diphenylbutyl)aminocarbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine;
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-methyl-N-
phenylaminocarbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine;
trans-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-methyl-
N-phenylaminocarbonyl)-6-(N-hydroxyaminocarbonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine;
cis 7-benzylcarbamoyloxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfony)-
25 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
cis 7-phenylcarbamoyloxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
cis 7-methylcarbamoyloxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
cis 7-isopropylcarbamoyloxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6-
hydroxamic acid;
cis 7-(4-phenoxyphenyl)carbamoyloxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6-
hydroxamic acid;
cis 7-(S)-(N-methyl-N-benzylcarbamoyloxy)-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-
c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
cis 7-(4-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyloxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6
hydroxamic acid;
cis 7-phenethylcarbamoyloxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
4-benzyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid;
4-cis-Benzyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid;
4-trans-benzyl-8-(hydroxy)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
47
4-trans-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid;
4-trans-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3,-c)pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid;
4-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid;
4-trans-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid;
4-cis-vinyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid;
4-cis-hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid;
4-trans-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid;
6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid;
4-oxo-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid;
4-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid;
4-cis-methoxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid;
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-trans-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-methyl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid;
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-carboxy-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-carboxy-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid;
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothienof3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
48
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-
(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-
(ethoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-2-yl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-3-yl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-phenyl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
phenylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
(phenylmethyl)aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
phenylmethyl-N-methylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(3-
phenylpropyl)aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(4,4-
diphenylbutyl)aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(3,3-
dimethylbutyl)aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-
(aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-
6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
methylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N,N-
dimethylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
49
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-
(morpholinocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(4-
methylpiperazin-1-ylcarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
(pyridylmethyl)aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
4-benzyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid;
4-cis-benzyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid;
4-traps-benzyl-8-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid;
4-traps-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid;
4-traps-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyisulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3,-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid;
7-cis-(N-methylaminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-prop-2-ylaminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-phenylaminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-{N-(4-methoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
7-cis-(N-(4-phenoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
5 7-cis-(N-(2-biphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(phenylmethyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
10 methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(1(S)-phenylethyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
15 c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(2-phenylethyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(3-methoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(2-methoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(2-chlorophenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(3-chlorophenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(4-chlorophenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7 - cis - (N- (4 - f luorophenyl ) aminocarbonyl ) oxy- 5 - (4 -
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(4-cyanophenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(4-butoxycarbonylphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(4-tolyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
51
7-cis-(N-(3-tolyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-cis-(N-(1-naphthyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid;
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thiazolo[4,5-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
2-(phenylsulfonylamino)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothiazolo[4,5-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothiazolo[4,5-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-(phenylcarbamoyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothiazolo[4,5-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
2-(acetylamino)-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothiazolo[4,5-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
2-(methylcarbamoylamino)-7-(4-fluorophenyl)carbamoyloxy-
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothiazolo
[4,5-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothiazolo
[5,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
2-methyl-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothiazolo[5,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-(phenylcarbamoyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothiazolo[5,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
7-benzyl-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
2-benzoylamino-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothiazolo[5,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
2-methyl-7-(phenylcarbamoyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothiazolo[5,4-c]pyridinyl-6-
hydroxamic acid;
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,2-
c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
52
2-(ethoxycarbonyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrofuro[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrofuro[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-(phenylcarbamoyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
2-methyl-7-(phenylcarbamoyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,2-c]pyridinyl-6-
hydroxamic acid;
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-
c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-(phenylcarbamoyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid;
7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrofuro[3,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno
[3,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid;
7-(phenylcarbamoyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid; and
7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,4-c]pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid.
As utilized herein, the following terms shall have
the following meanings:
~~Alkyl~~, alone or in combination, means a straight-chain
or branched-chain alkyl radical containing preferably 1-
15 carbon atoms (Cl-C15), more preferably 1-8 carbon
atoms (C1-Cg); even more preferably 1-6 carbon atoms
(C1-C6), yet more preferably 1-4 carbon atoms (C1-C4),
still more preferably 1-3 carbon atoms (C1-C3), and most
preferably 1-2 carbon atoms (C1-C2). Examples of such
radicals include methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl,
n-butyl, isobutyl, sec-butyl, tert-butyl, pentyl, iso-
amyl, hexyl, octyl and the like.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
53
"Alkenyl", alone or in combination, means a straight-
chain or branched-chain hydrocarbon radical having one
or more double bonds, preferably 1-2 double bonds and
more preferably one double bond, and containing
preferably 2-15 carbon atoms (C2-C15), more preferably
2-8 carbon atoms (C2-C8), even more preferably 2-6
carbon atoms (C2-C6), yet more preferably 2-4 carbon
atoms (C2-C4), and still more preferably 2-3 carbon
atoms (C2-C3). Examples of such alkenyl radicals
include ethenyl, propenyl, 2-methylpropenyl, 1,4-
butadienyl and the like.
"Alkynyl", alone or in combination, means a straight-
chain or branched chain hydrocarbon radical having one
or more triple bonds, preferably 1-2 triple bonds and
more preferably one triple bond, and containing
preferably 2-15 carbon atoms (C2-C15), more preferably
2-8 carbon atoms (CZ-Cg), even more preferably 2-6
carbon atoms (C2-CS), yet more preferably 2-4 carbon
atoms (C2-C4), and still more preferably 2-3 carbon
atoms (C2-C3). Examples of such alkynyl radicals
include ethynyl, propynyl (propargyl), butynyl and the
like.
"Alkoxy", alone or in combination, means a radical of
the type "R-0-" wherein "R" is an alkyl radical as
defined above and "O" is an oxygen atom. Examples of
such alkoxy radicals include methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy,
isopropoxy, n-butoxy, iso-butoxy, sec-butoxy, tert-
butoxy and the like.
"Alkoxycarbonyl", alone or in combination, means a
radical of the type "R-O-C(0)-" wherein "R-O-" is an
alkoxy radical as defined above and "C(0)" is a carbonyl
radical.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
54
"Alkoxycarbonylamino", alone or in combination, means a
radical of the type "R-0-C(0)-NH-" wherein "R-O-C(0)" is
an alkoxycarbonyl radical as defined above, wherein the
amino radical may optionally be substituted, such as
with alkyl, aryl, aralkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl
and the like.
"Alkylthio", alone or in combination, means a radical of
the type "R-S-" wherein "R" is an alkyl radical as
defined above and "S" is a sulfur atom. Examples of
such alkylthio radicals include methylthio, ethylthio,
n-propylthio, isopropylthio, n-butylthio, iso-butylthio,
sec-butylthio, tert-butylthio and the like.
"Alkylsulfinyl", alone or in combination, means a
radical of the type "R-S(O)-" wherein "R" is an alkyl
radical as defined above and "S(O)" is a mono-oxygenated
sulfur atom. Examples of such alkylsulfinyl radicals
include methylsulfinyl, ethylsulfinyl, n-propylsulfinyl,
isopropylsulfinyl, n-butylsulfinyl, iso-butylsulfinyl,
sec-butylsulfinyl, tert-butylsulfinyl and the like.
"Alkylsulfonyl", alone or in combination, means a
radical of the type "R-S(O)2-" wherein "R" is an alkyl
radical as defined above and "S(0)2" is a di-oxygenated
sulfur atom. Examples of such alkylsulfonyl radicals
include methylsulfonyl, ethylsulfonyl, n-propylsulfonyl,
isopropylsulfonyl, n-butylsulfonyl, iso-butylsulfonyl,
sec-butylsulfonyl, tert-butylsulfonyl and the like.
"Alkylsulfonylamino", alone or in combination, means a
radical of the type "R-S(0)2-NH-" wherein "R-S(0)2-" is
an alkylsulfonyl radical as defined above, wherein the
amino radical may optionally be substituted, such as
with alkyl, aryl, aralkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl
and the like.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
"Aryl", alone or in combination, means a phenyl,
biphenyl or naphthyl radical which is optionally
substituted with one or more substituents selected from
5 alkyl, alkoxy, halogen, hydroxy, amino, azido, nitro,
cyano, haloalkyl, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl, cycloalkyl,
heterocyclo, alkanoylamino, amido, amidino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, N-alkylamidino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino, N-alkylamido, N,N-dialkylamido,
10 aralkoxycarbonylamino, alkylthio, alkylsulfinyl,
alkylsulfonyl and the like. Examples of aryl radicals
are phenyl, p-tolyl, 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-(tert-
butoxy)phenyl, 3-methyl-4-methoxyphenyl, 4-CF3-phenyl,
4-fluorophenyl, 4-chlorophenyl, 3-nitrophenyl, 3-
15 aminophenyl, 3-acetamidophenyl, 4-acetamidophenyl, 2-
methyl-3-acetamidophenyl, 2-methyl-3-aminophenyl, 3-
methyl-4-aminophenyl, 2-amino-3-methylphenyl, 2,4-
dimethyl-3-aminophenyl, 4-hydroxyphenyl, 3-methyl-4-
hydroxyphenyl, 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)phenyl, 1-naphthyl, 2-
20 naphthyl, 3-amino-1-naphthyl, 2-methyl-3-amino-1-
naphthyl, 6-amino-2-naphthyl, 4,6-dimethoxy-2-naphthyl,
piperazinylphenyl and the like.
"Aryl-alkyl", alone or in combination, means an alkyl
25 radical as defined above in which at least one hydrogen
atom, preferably 1-2, is replaced by an aryl radical as
defined above, such as benzyl, 1-, 2-phenylethyl,
dibenzylmethyl, hydroxyphenylmethyl, methylphenylmethyl,
diphenylmethyl, dichlorophenylmethyl, 2-naphthylmethyl,
30 4-methoxyphenylmethyl and the like.
"Aryl-alkoxy°, alone or in combination, means an alkoxy
radical as defined above in which at least one hydrogen
atom, preferably 1-2, is replaced by an aryl radical as
35 defined above, such as benzyloxy, 1-, 2-phenylethoxy,
dibenzylmethoxy, hydroxyphenylmethoxy,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
56
methylphenylmethoxy, dichlorophenylmethoxy, 4-
methoxyphenylmethoxy and the like.
"Aryloxy", alone or in combination, means a radical of
the type "R-0-" wherein "R" is an aryl radical as
defined above.
"Aroyl", alone or in combination, means a radical of the
type "R-C(O)-" wherein "R" is an aryl radical as defined
above and "-C(O)-" is a carbonyl.
"Alkanoyl", alone or in combination, means a radical of
the type "R-C(O)-" wherein "R" is an alkyl radical as
defined above and "-C(0)-" is a carbonyl radical.
Examples of such alkanoyl radicals include acetyl,
trifluoroacetyl, hydroxyacetyl, propionyl, butyryl,
valeryl, 4-methylvaleryl, and the like.
"Alkanoylamino", alone or in combination, means a
radical of the type "R-C(0)-NH-" wherein "R-C(O)-" is an
alkanoyl radical as defined above, wherein the amino
radical may optionally be substituted, such as with
alkyl, aryl, aralkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl and
the like.
"Aminocarbonylamino", alone or in combination, means an
amino substituted carbonyl substituted on a second amino
(ureido) radical, wherein each amino radical may
optionally be mono- or di-substituted, such as with
alkyl, aryl, aralkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl,
alkanoyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aralkoxycarbonyl and the like.
"Benzo", alone or in combination, means the divalent
radical C6H4= derived from benzene.
"Bicyclic" as used herein is intended to include both
fused ring systems, such as naphthyl and b-carbolinyl,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
57
and substituted ring systems, such as biphenyl,
phenylpyridyl, naphthyl and diphenylpiperazinyl.
"Cycloalkyl", alone or in combination, means a saturated
or partially saturated, preferably one double bond,
monocyclic, bicyclic or tricyclic alkyl radical,
preferably monocyclic, containing preferably 3-10 carbon
atoms (C3-C1p), more preferably 3-8 carbon atoms (C3-
Cg), even more preferably 3-6 carbon atoms (C3-C6),
which is optionally be benzo fused and which is
optionally substituted as defined herein with respect to
the definition of aryl. Examples of such cycloalkyl
radicals include cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl,
cyclohexyl, dihydroxycyclohexyl, cycloheptyl,
octahydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl,
dimethoxytetrahydronaphthyl, 2,3-dihydro-1H-indenyl and
the like.
"Cycloalkylene" is a cycloalkyl gem divalent radical,
wherein cycloalkyl is as defined above. Preferably,
cycloalkylene is monocyclic, containing preferably 3-10
carbon atoms (C3-C~o), more preferably 3-8 carbon atoms
(C3-Cg), even more preferably 3-6 carbon atoms (C3-C6).
"Cycloalkylalkyl", alone or in combination, means an
alkyl radical as defined above which is substituted by a
cycloalkyl radical as defined above. Examples of such
cycloalkylalkyl radicals include cyclopropylmethyl,
cyclobutylmethyl, cyclopentylmethyl, cyclohexylmethyl,
1-cyclopentylethyl, 1-cyclohexylethyl, 2-
cyclopentylethyl, 2-cyclohexylethyl,
hydroxycyclopentylpropyl, tetrahydronaphthylpropyl,
cyclohexylbutyl and the like.
"Heteroatoms" means nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur
heteroatoms.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
58
"Heterocyclyl", alone or in combination, means a
saturated or partially unsaturated, preferably one
double bond, monocyclic or bicyclic, preferably
monocyclic, heterocycle radical containing at least one,
preferably 1 to 4, more preferably 1 to 3, even more
preferably 1-2, nitrogen, oxygen or sulfur atom ring
member and having preferably 3-8 ring members in each
ring, more preferably 5-8 ring members in each ring and
even more preferably S-6 ring members in each ring.
"Heterocyclyl" is intended to include sulfone and
sulfoxide derivatives of sulfur ring members and N-
oxides of tertiary nitrogen ring members, and
carbocyclic fused, preferably 3-6 ring carbon atoms and
more preferably 5-6 ring carbon atoms, and benzo fused
ring systems. "Heterocyclyl" radicals may optionally be
substituted on at least one, preferably 1-4, more
preferably 1-3, even more preferably 1-2, carbon atoms
by halogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, oxo, thioxo, aryl,
aralkyl, heteroaryl, heteroaralkyl, amidino, N-
alkylamidino, alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino
and the like, and/or on a secondary nitrogen atom by
hydroxy, alkyl, aralkoxycarbonyl, alkanoyl,
alkoxycarbonyl, heteroaralkyl, aryl or aralkyl radicals.
More preferably, "heterocyclyl", alone or in
combination, is a radical of a monocyclic or bicyclic
saturated heterocyclic ring system having 5-8 ring
members per ring, wherein 1-3 ring members are oxygen,
sulfur or nitrogen heteroatoms, which is optionally
partially unsaturated or benzo-fused and optionally
substituted by 1-2 oxo or thioxo radicals. Examples of
such heterocyclyl radicals include pyrrolidinyl,
piperidinyl, piperazinyl, morpholinyl, thiamorpholinyl,
4-benzyl-piperazin-1-yl, pyrimidinyl, tetrahydrofuryl,
pyrazolidonyl, pyrazolinyl, pyridazinonyl, pyrrolidonyl,
tetrahydrothienyl and its sulfoxide and sulfone
derivatives, 2,3-dihydroindolyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl,
1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolinyl, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
59
oxo-isoquinolinyl, 2,3-dihydrobenzofuryl, benzopyranyl,
methylenedioxyphenyl, ethylenedioxyphenyl and the like.
"Heterocyclylene" is a heterocyclyl gem divalent radical
on a ring carbon atom, wherein heterocyclyl is as
defined above. Preferably, heterocyclylene is a
monocyclic saturated heterocyclic ring system having 5-6
ring members, wherein 1-3, more preferably 1-2, most
preferably 1, ring members are oxygen, sulfur or
nitrogen heteroatoms.
"Heterocyclylalkyl", alone or in combination, means an
alkyl radical as defined above in which at least one
hydrogen atom, preferably 1-2, is replaced by a
heterocyclyl radical as defined above, such as
pyrrolidinylmethyl, tetrahydrothienylmethyl,
piperidinylethyl and the like.
"Heteroaryl", alone or in combination, means a
monocyclic or bicyclic, preferably monocyclic, aromatic
heterocycle radical, having at least one, preferably 1
to 4, more preferably 1 to 3, even more preferably 1-2,
nitrogen, oxygen or sulfur atom ring members and having
preferably 5-6 ring members in each ring, which is
optionally benzo fused or saturated carbocyclic fused,
preferably 3-4 carbon atoms (C3-C4) to form 5-6 ring
membered rings and which is optionally substituted as
defined above with respect to the definitions of aryl
and heterocyclyl. More preferably, "heteroaryl", alone
or in combination, is a radical of a monocyclic or
bicyclic aromatic heterocyclic ring system having 5-6
ring members per ring, wherein 1-3 ring members are
oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen heteroatoms, which is
optionally benzo-fused or saturated C3-C4-carbocyclic-
fused. Examples of such heteroaryl groups include
imidazolyl, 1-benzyloxycarbonylimidazol-4-yl, pyrrolyl,
pyrazolyl, pyridyl, 2-(1-piperidinyl)pyridyl, 2-(4-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
benzyl piperazin-1-yl)-1-pyridinyl, pyrazinyl,
triazolyl, furyl, thienyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, indolyl,
quinolinyl, 1-oxido-2-quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl,
5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolyl, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydroiso-
5 quinolinyl, quinoxalinyl, benzothiazolyl, J3-carbolinyl,
benzofuryl, benzimidazolyl, benzoxazolyl and the like.
"Heteroaroyl", alone or in combination, means a radical
of the type "R-C(O)-" wherein "R" is an heteroaryl
10 radical as defined above and "-C(0)-" is a carbonyl.
"Heteroaryl-alkyl", alone or in combination, means an
alkyl radical as defined above in which at least one
hydrogen atom, preferably 1-2, is replaced by a
15 heteroaryl radical as defined above, such as 3-furyl-
propyl, 2-pyrrolylpropyl, chloroquinolinylmethyl, 2-
thienylethyl, pyridylmethyl, 1-imidazolylethyl and the
like.
20 "Halogen" and "halo", alone or in combination, means
fluoro, chloro, bromo or iodo radicals.
"Haloalkyl", alone or in combination, means an alkyl
radical as defined above in which at least one hydrogen
25 atom, preferably 1-3, is replaced by a halogen radical,
more preferably fluoro or chloro radicals. Examples of
such haloalkyl radicals include 1,1,1-trifluoroethyl,
chloromethyl, 1-bromoethyl, fluoromethyl, difluoro-
methyl, trifluoromethyl, bis(trifluoromethyl)methyl and
30 the like.
"Haloalkoxy", alone or in combination, means an alkoxy
radical as defined above in which at least one hydrogen
atom, preferably 1-3, is replaced by a halogen radical,
35 more preferably fluoro or chloro radicals. Examples of
such haloalkoxy radicals include 2,2,2-trifiuoroethoxy,
chloromethoxy, 2-bromoethoxy, fluoromethoxy, difluoro-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
61
methoxy, trifluoromethoxy, bis(trifluoromethyl)methoxy
and the like.
"Sulfinyl", alone or in combination, means a diradical
of the type "-S(0)-" wherein "S(O)" is a mono-oxygenated
sulfur atom. "Sulfonyl", alone or in combination, means
a diradical of the type "-S(O)z-" wherein "S(O)z" is a
di-oxygenated sulfur atom.
"Leaving group" generally refers to groups readily
displaceable by a nucleophile, such as an amine, a thiol
or an alcohol nucleophile. Such leaving groups are well
known in the art. Examples of such leaving groups
include, but are not limited to, N-hydroxysuccinimide,
N-hydroxybenzotriazole, halides, triflates, tosylates
and the like. Preferred leaving groups are indicated
herein where appropriate.
"Protecting group" generally refers to groups well known
in the art which are used to prevent selected reactive
groups, such as carboxy, amino, hydroxy, mercapto and
the like, from undergoing undesired reactions, such as
nucleophilic, electrophilic, oxidation, reduction and
the like. Preferred protecting groups are indicated
herein where appropriate. Examples of amino protecting
groups include, but are not limited to, aralkyl,
substituted aralkyl, cycloalkenylalkyl and substituted
cycloalkenyl alkyl, allyl, substituted allyl, aryl,
alkoxycarbonyl, aralkoxycarbonyl, silyl and the like.
Examples of aralkyl include, but are not limited to,
benzyl, ortho-methylbenzyl, trityl and benzhydryl, which
can be optionally substituted with halogen, alkyl,
alkoxy, hydroxy, vitro, acylamino, acyl and the like,
and salts, such as phosphonium and ammonium salts.
Examples of aryl groups include phenyl, naphthyl,
indanyl, anthracenyl, 9-(9-phenylfluorenyl),
phenanthrenyl, durenyl and the like. Examples of
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
62
cycloalkenylalkyl or substituted cycloalkylenylalkyl
radicals, preferably have 6-10 carbon atoms, include,
but are not limited to, cyclohexenyl methyl and the
like. Suitable aryl, alkoxycarbonyl and aralkoxy-
carbonyl groups include benzyloxycarbonyl, t-butoxy-
carbonyl, iso-butoxycarbonyl, benzoyl, substituted
benzoyl, butyryl, acetyl, tri-fluoroacetyl, tri-chloro
acetyl, phthaloyl and the like. A mixture of protecting
groups can be used to protect the same amino group, such
as a primary amino group can be protected by both an
aralkyl group and an aralkoxycarbonyl group. Amino
protecting groups can also form a heterocyclic ring with
the nitrogen to which they are attached, for example,
1,2-bis(methylene)benzene, phthalimidyl, succinimidyl,
maleimidyl and the like and where these heterocyclic
groups can further include adjoining aryl and cycloalkyl
rings. In addition, the heterocyclic groups can be
mono-, di- or tri-substituted, such as
nitrophthalimidyl. Amino groups may also be protected
against undesired reactions, such as oxidation, through
the formation of an addition salt, such as
hydrochloride, toluenesulfonic acid, trifluoroacetic
acid and the like. Many of the amino protecting groups
are also suitable for protecting carboxy, hydroxy and
mercapto groups. For example, aralkyl groups. Alkyl
groups are also sutiable groups for protecting hydroxy
and mercapto groups, such as tert-butyl.
Silyl protecting groups are silicon atoms
optionally substituted by one or more alkyl, aryl and
aralkyl groups. Suitable silyl protecting groups
include, but are not limited to, trimethylsilyl,
triethylsilyl, tri-isopropylsilyl, tert-butyldimethyl-
silyl, dimethylphenylsilyl, 1,2-bis(dimethylsilyl)-
benzene, 1,2-bis(dimethylsilyl)ethane and diphenyl-
methylsilyl. Silylation of an amino groups provide
mono- or di-silylamino groups. Silylation of amino-
alcohol compounds can lead to a N,N,O-tri-silyl
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
63
derivative. Removal of the silyl function from a silyl
ether function is readily accomplished by treatment
with, for example, a metal hydroxide or ammonium
flouride reagent, either as a discrete reaction step or
in situ during a reaction with the alcohol group.
Suitable silylating agents are, for example, trimethyl-
silyl chloride, tert-buty-dimethylsilyl chloride,
phenyldimethylsilyl chloride, diphenylmethyl silyl
chloride or their combination products with imidazole or
DMF. Methods for silylation of amines and removal of
silyl protecting groups are well known to those skilled
in the art. Methods of preparation of these amine
derivatives from corresponding amino acids, amino acid
amides or amino acid esters are also well known to those
skilled in the art of organic chemistry including amino
acid/amino acid ester or aminoalcohol chemistry.
Protecting groups are removed under conditions
which will not affect the remaining portion of the
molecule. These methods are well known in the art and
include acid hydrolysis, hydrogenolysis and the like. A
preferred method involves removal of a protecting group,
such as removal of a benzyloxycarbonyl group by
hydrogenolysis utilizing palladium on carbon in a
suitable solvent system such as an alcohol, acetic acid,
and the like or mixtures thereof. A t-butoxycarbonyl
protecting group can be removed utilizing an inorganic
or organic acid, such as HC1 or trifluoroacetic acid, in
a suitable solvent system, such as dioxane or methylene
chloride. The resulting amino salt can readily be
neutralized to yield the free amine. Carboxy protecting
group, such as methyl, ethyl, benzyl, tert-butyl, 4-
methoxyphenylmethyl and the like, can be removed under
hydroylsis and hydrogenolysis conditions well known to
those skilled in the art.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
64
Procedures for preparing the compounds of this
invention are set forth below. It should be noted that
the general procedures are shown as it relates to
preparation of compounds having unspecified
stereochemistry. However, such procedures are generally
applicable to those compounds of a specific
stereochemistry, e.g., where the stereochemistry about a
group is (S) or (R). In addition, the compounds having
one stereochemistry (e.g., (R)) can often be utilized to
produce those having opposite stereochemistry (i.e.,
(S)) using well-known methods, for example, by
inversion.
Preg~ration of Compounds of Formula I
The compounds of the present invention represented
by Formula I above can be prepared utilizing the
following general procedures as schematically shown in
Schemes I and II.
SCHEME I
O O O
V
V R15~ R16 ~ OPl
OP1 Rg~O
R9~ ~~
X NH
X ~2
15 ' 16
R R
0 O
V
9 Z V H.OH g Z OPl
R ~ R ~~ N
N X
X \SO2~ 1 '\~ S02'~ Rl
\ R 15 16
R15 'R16 ~ R R
Compounds of the present invention may be
synthesised using the routes outlined in Schemes I
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
through IV. An appropriately substituted protected (for
example, P1 is a methyl, ethyl, benzyl and the like) or
unprotected (Pl is H) amino acid (1) upon treatment with
appropriately functionalized aldehydes or ketones (2)
5 under acidic conditions (for example see Sola, R. et al,
J. Heterocycles, 1~, 1982), can give the bicyclic
intermediate (3). The acid functionality of the
bicyclic intermediate (3) (when Pl is H) is then be
converted into an ester using standard procedures (for
10 example HC1 and methanol). The protected bicyclic
intermediate (3) is then sulfonylated under Schotten-
Baumann conditions to furnished the sulfonamide (4).
Sulfonamide (4) (when R9 is H) may be halogenated, such
as iodinated, and then carbonylated (See for example
15 Schoenberg, A., et al, J.Org.Chem., ~9, 3318, (1974)))
and subsequently derivatised, amidated (See for example
Corey, E.J. and Hegedus, L.S., J.Am.Chem.Soc., 91, 1233
(1969)), arylated or alkylated (See for example Stille,
J.K., Angew. Int. Ed. Engl., ,~5, 508 (1986)) to yield
20 sulfonamide (4) where R9 is other than H. Sulfonamide
(4) can be readily converted into the corresponding
hydroxamic acids (5) using procedures well known to
those skilled in the art. Alternatively, R11 and/or R12
may be introduced into sulfonamide (4), where R11 and/or
25 R1~ are independently a leaving group (L' and L",
respectively) utilizing suitably functionalized
nucleophilic species (such as RaISH or R'3NHa followed by
reaction with the electrophile R'1N=C=O, R'zR'1N-C (0) -L,
R"-C (0) -L, R'°-SOZ-L, R'ZR31N-SOz-L, and the like) and/or a
30 hydroxy, amino, substituted amino or thiol group
utilizing suitably functionalized electrophilic species
(Such aS R'1N=C=0, R'ZR"N-C (0) -L, R'°-L, Rzz-C (O) -L arid the
like), where L, L' and L" are each a leaving group, such
as chloro, bromo, iodo, mesylate, tosylate and the like.
35 When R11 or R12 is a hydroxy, amino, substituted amino or
thiol group, the groups may require selective protection
and de-protection, using reagents and methods well known
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
66
in the art, in order to avoid producing undesired
reaction products.
SCHEME II
0 OH O
H H2N "
g ~ OH Z ~ OH
R ~ ~ R9
X X NH2
7
O OH O
O ~ ~ OP1
R9 R15 ~ R16 Z OP1
NH R9 ~~
X ~ ~ X NH2
R15 R1s g
pll
OH
R9 OP1 R9
~O N.
N
X S02~ R1 X ~ 502 R1
R15 R16 ~ R15 R16
1~,..~ Ra = - OH
Ra = _ Ri 1
~ Ra = - L
Alternatively, an appropriately substituted
heterocyclic carboxaldehyde (6) (Scheme II) may be
condensed, under basic conditions, with a glycine to
give the hydroxy amino acid (7) (See for example
Dullaghan, M.E. and Nord, F.F., J.Am.Chem.Soc., 73, 5455
(1951)). The hydroxy amino acid (7) is then protected
(for example, esterified) to yield the protected amino
acid (8). Cyclization of the protected amino acid (8)
under acidic conditions with an appropriately
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
67
functionalized aldehyde or ketone (2) can furnish the
bicyclic intermediate (9). Sulfonylation, using
Schotten-Baumann conditions, of the bicyclic
intermediate (9) can give the sulfonamide (10a).
Sulfonamide (10a) can be readily converted into the
corresponding hydroxamic acid (11), where R11 is -OH,
using procedures well known to those skilled in the art.
Alternatively, sulfonamide (10a) may be derivatized by
treatment with a suitably functionalized electrophilic
species, Such aS R'iN=C=0, R'aR'1N-C (O) -L, RZ°-L, R22-C (O) -L
and the like, where L is a leaving group, such as
chloro, bromo, iodo, mesylate, tosylate and the like, to
generate sulfonamide (10b). (See for example Duggan,
M.E. and Imagrire J.S., Synthesis 131 (1989)).
Sulfonamide (10b) can be readily converted into the
corresponding hydroxamic acid (11) using procedures well
known to those skilled in the art. Alternatively, the
hydroxy group of sulfonamide (10a) may be converted into
a leaving group (R8 - L) by treatment with a suitable
agents well known to those skilled in the art, such as
halogenating agents (for example PC15, PBr3, and the
like), mesyl chloride, tosyl chloride, and the like,
where L is a leaving group, such as chloro, bromo, iodo,
mesylate, tosylate and the like, to generate sulfonamide
(lOc). The leaving group (L) of sulfonamide (10c) can
be displaced with a nucleophile, such as R21SH or R3'NH2
followed by reaction with the electrophile R'1N=C=0,
R3~R"N-C (0) -L, R'1-C (O) -L, R'°-SOz-L, R"R'1N-SOz-L, and the
like, to prepare sulfonamide (10b).
SCHEME III
OH 0 R11 p
OH Z OH
R9 ~. R9
NH ~ NH
X 2 X 2
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
68
Alternatively, hydroxy amino acid (7) may be
converted with nucleophiles, electrophiles and the like
as described above or under Mitsonobu conditions to
yield the amino acid intermediate (12) (Scheme III).
The amino acid intermediate (12) may subsequently be
cyclised, sulfonylated and converted to hydroxamic acids
using the aforementioned procedures to give hydroxamic
acid (11).
Alternatively, sulfonamides (l0a) or (lOb) (when R9
is H) may be halogenated, such as iodinated, and then
carbonylated (See for example Schoenberg, A., et al,
J.Org.Chem., ~9, 3318, (1974))) and subsequently
derivatised, amidated (See for example Corey, E.J. and
Hegedus, L.S., J.Am.Chem.Soc., ~,sl, 1233 (1969)),
arylated or alkylated (See for example Stille, J.K.,
Angew. Int. Ed. Engl., ~5, 508 (1986)) to yield
sulfonamides (10a) or (10b) where R9 is other than H.
SCHEME IV
La
0 ~ O
Z V _
OP1 / OP1
Y Y
HN~
W 502 ~ TnT~ S02 \
R1 R1
13 Lb 14
\',' O
0
V V
N~ OH ~ _ OPl
H -(~-
y,~ N~S02 \ X ~ S02 ~ Rl
Rl
I
A second general synthesis useful for the
preparation of the novel compounds of this invention is
illustrated in Scheme IV whereby an appropriately
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
69
substituted heterocycle (13) or (14) is cyclized into
bicyclic intermediate (15) in the presence of a base,
such as KOH in THF, potassium carbonate in DMF, and the
like, where Le and Lb are each a leaving group, such as
chloro, bromo, iodo, mesylate, tosylate and the like, or
-V-La is an appropriately substituted ketone or aldehyde
group, or -V-La or -W-Lb is an appropriately substituted
unsaturated aldehyde, ketone, ester, amide, nitrite or
the like Michael reaction acceptor, or other cyclization
method well known to those skilled in the art.
Alternatively, the bicyclic intermediate (15) can be
prepared in two steps from a protected amino acid (16)
wherein the R1-SOZ- group is introduced after
cyclization with the amino group (-NHZ) (see Scheme V).
8 9 10 11 12 15 16 17 18
When appropriate R , R , R , R , R , R , R , R and R
may be introduced prior to or after the cyclization step
provided the radicals do not interfer with, compete with
or inhibit the cyclization reaction. One skilled in the
art is well versed in such matters and knows when and
how to introduce the various groups and utilize
protecting groups to prevent such deleterious effects.
0 O
V
V
/ OPl /Z OPl
Y~ ~2 ~ y\O .~ 15
NH
W
16 Lb
The intermediates (13), (14) and (16) are readily
prepared from commercially available starting materials,
for example as shown in Scheme VI, wherein P1 and Pz are
protecting groups, La and Lb are leaving groups, A1 is a
radical that can converted into -W-L° and AZ is a radical
that can be converted into -V-La.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
A third general synthesis useful for the
preparation of the novel compounds of this invention
is cyclization reactions, such as Friedel-Crafts and
the like reactions, directly onto the heterocyclic
5 ring as illustrated in Scheme VII, whereby an
appropriately substituted heterocycle (17) or (18) is
cyclized into bicyclic intermediate (15) by
nucleophilic displacement of the leaving group La or
Lb, such as in the presence of acid or a Friedel-Crafts
10 reagent, such as tin chloride, aluminum chloride and
the like, or other nucleophilic reaction conditions,
such as formation of an anion on the ring, for
example, metal halogen exchange and the like. (For an
example of Friedel Crafts reaction, see Frehel, D,
15 Badorc, A., Pereillo, J-M, Maffrand, J-P J Heterocycl
Chem 1985, 22, 1011-1016) In such reactions, -W-Lb and
-V-La are groups containing an electrophilic group,
such as halogen (C1, Br, I), ester, carboxylic acid,
carboxylic acid halide, aldehyde, ketone, nitrile and
20 the like.
SCHEME V~
O
(Me0)2P
_ OP1
O
V
V\ La HN~ P2 ~ OPl
O
O HN.
X A1 X ~W S02w
R
O 13 Lb i
_ OPl La
A2 HN~ ~ O
S02 Z
Y w Ri ,o _ OPi
Y
X W L \X W~N~SO
2~ R
14
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT1US98/16147
71
Heterocycle (17) can be prepared from the
sulfonamide (19) by reaction with Lb-W-L' or Al-L' wherein
A1 is a radical that can be coverted into -W-Lb and
wherein L' is a leaving group similar to L° and Lb.
Sulfonamide (29) can be readily prepared from the
corresponding protected or unprotected amino acid by
reaction with the appropriate sulfonyl chloride (R1-SOZ-
C1) or the like. The amino acid is either commercially
available or is readily prepared from commercially
available starting materials using methods well known to
those skilled in the art.
SCHEME VII
O O
V
OPl ~Z V OPl
\~ HN
X S02 X N
w y,~ ~S02 w
Rl .~Z Lb Rl
15
La La
/Z ~ O V 0
\ -~- OP1 ~Z OPl
X
W HNw ~ \O
502 X ~ S02w
Rl ~ R1
Heterocycle (18) can be prepared by coupling the
electrophile (20) with the sulfonamide (21) in the
presence of a base, such as potassium carbonate and
the like. The radical AZ may be used in place of -V-La
in sulfonamide (21) to avoid reaction of -V-La with the
sulfonamide group, ir~ which event AZ is converted into
-V-La after reaction of the electrophile (20) with the
sulfonamide (21). Electrophiles (20) are either
commercially available or is readily prepared from
commercially available starting materials using
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/1b147
72
methods well known to those skilled in the art.
Sulfonamide (21) can be prepared from the
corresponding protected or unprotected amino acid by
reaction with the appropriate sulfonyl chloride (R1-
S02-Cl) or the like. The amino acid is either
commercially available or is readily prepared from
commercially available starting materials using
methods well knoen to those skilled in the art.
Alternatively, protected or unprotected sulfonamide
intermediate (22), wherein Rb is R11 or a group which can
be converted into R11 during the synthesis of the
compounds of this invention, may be prepared from a
substituted protected carboxylic acid intermediate (23)
(Scheme VIII). The carboxylic acid intermediate (23)
can be selectively reduced to an aldehyde using
appropriate reducing agents, such as DIBAL-H and the
like, which is converted into the sulfonamide imine (24)
by reaction of the aldehyde with the the sulfonamide
R1S02NH2 using reaction conditions well known in the art.
The sulfonamide imine (24) can then be reacted with a
carbon nucleophile which can be converted into a
carboxylic acid or ester, such as cyanide anion followed
by hydrolysis, 1,3-dithiane anion followed by
deprotection and oxidation, and the like, to yield the
protected or unprotected sulfonamide intermediate (22).
The substituted protected carboxylic acid
intermediate (23) is commercially available or may be
readily prepared from commercially available starting
materials using methods well known to those skilled in
the art. For instance, Perkin condensation between
heterocyclic acetic acids and aldehydes to give an
unsaturated acid followed by hydrogenation, Michael
reaction, allylic rearrangement and the like, aldol
condensation, alkylation and the like can be used to
produce intermediate (23) from readily available
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
73
SCHEME VIII
Rb Rb
OP1 H
YO > YO
O ~ O
X X
Rb
0 Rb
OP1
YO
HN~ Y I I
X SO ~" ~O N.
2
~c w R1 X 24 So2~ R
i
SCHEME IX
O 0 OH O
w H w OP1 ~ _ OP1
' S
HN~ HN
S02 502 R
~ Rl ~ OP2 1
OP2
ORc 0 OP3 0
S ~ ~ ~ NHOH S O ~ ' OP1
N~ ~ N
S02 \ S02 \
Ri ~ R2
Rc = _ H
Rc = - C ( 0 ) NR3 2831
Rc = _ R20
starting materials. Alternatively, unsubstituted (i.e.,
R° - H) protected or unprotected carboxylic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
74
intermediate (23) may be alkylated with electrophiles
such as Rb-L, wherein L is a leaving group such as
halogen, mesylate, tosylate, etc.
SCHEME X
O O
Rd V
Y ~ '~ OP1 ~ OP1
Y
HN ~ ~~ HN~
X A1 502 X ~W S02w
~ R1 Lb R1
Rd = - CHO or
- CHR~- CHO
0 O
V V
NHOH Y ~ OP1
N~ ~' ~ / N.
X ~ 502 X
R1 RZ
For example, as shown in Scheme IX, an
appropriately 3,4-substituted thiophene carboxaldehye
(25), wherein Pa is a hydroxy protecting group, may be
condensed, under basic conditions (for example in the
presence of LDA in THF) with a protected N-
sulphonylated glycine (26), wherein P1 is a carboxylic
acid protecting group such as an ester and the like,
to give beta-hydroxy amino acid (27) (see for example
Dikshit, D.K., et al. Tet. Lett. 1988, 29(25), 3109-
3110). The beta-hydroxy amino acid (27) may then be
protected with a hydroxy protecting group P3 such as by
acylation of the beta-hydroxy group and separated into
threo and erythro diastereomers. PZ may then be
removed and Mitsonobu cyclization conditions can give
intermediate (28). P1 may then be removed, a
hydroxamic acid formed and P3 removed to give (29a)
utilizing methodology familiar to one skilled in the
art. Alternatively, (28) may be deprotected to the
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
beta-hydroxy acid and converted to beta-carbamoyl
hydroxamate (29b) or other substituted oxy group
(i.e., -OR'°) compound (29c) again utilizing
methodology familiar to one skilled in the art. This
5 general scheme is also applicable for other
substituted heterocyclic carboxaldehydes as shown in
Scheme X to form six, seven and eight membered
heterocyclic fused compounds (I) of this invention.
Scheme XI illustrates an alternative general
10 synthesis (Claisen ring contraction) useful for the
preparation of the novel compounds of this invention as
illustrated in Scheme IV whereby an appropriately
substituted heterocycle (14) is cyclized into bicyclic
intermediate (15). As shown in Scheme XI, heterocycle
15 (31) can be prepared by coupling electrophile (30),
wherein R8 is - (CHZ)m-L° (m = 0-1) or a group which can be
converted into - (CHZ),~-Le and wherein Rf is W or a group
which can be converted into W during the synthesis of
the compounds of this invention, with the protected N-
20 sulphonylated glycine (26), wherein P1 is a carboxylic
acid protecting group such as an ester and the like,
(for example, a Mitsunobu coupling, Syn. 1981:1-28).
When Re is a leaving group, such as bromine atom, Re can
be converted into -(CH2)m-La by a homologation sequence
25 (for example, for m = 1 and La - Br, Palladium catalyzed
Stille coupling of tributylvinyltin with the heterocycle
(31) (Re - Br), followed by oxidative cleavage (OsO,,
NaIOa) of the resulting vinyl group to form an aldehyde
group (Re - -CHO), reduction with NaBH4 to an alcohol
30 group (Re - -CHZOH), and finally bromination of the
alcohol (NBS and PPh,) to form the desired heterocycle
(32) (m = 1, L8 - Br) ) .
The Z-allylic alcohol (33) can be prepared by
coupling (Z) -Bu3SnCH=CHCHZOTBS, which has been
35 synthesized and utilized in both its protected and
unprotected forms (Corey et al., Tet. Lett. 25:2419-2422
(1984); Jung et al., Tet. Lett. 23:3851-3854 (1982); and
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US9$/16147
76
Stille et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 109:813-817 (1987)),
with heterocycle (32). The coupling can be performed
utilizing PdCl2(PPh3)2 catalyzed Stille reaction (Stille,
Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 25:508-524 (1986); and Stille et
al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 101:4992-4998 (1979)).
Alternatively, (Z) -Bu3SnCH=CHCHZOTBDMS (prepared from
commercially available ethyl cis-3-iodoarylate by
reduction with about two equivalents of DIBAL-H (Beruben
et al., J. Org. them. 60:2488-2501 (1995)) by slow
addition at about -78°C to minimize double bond
isomerization during the reaction followed by gradual
warming to ambient temperature, the resulting iodo-
alcohol is protected as its TBDMS ether and then
subjected to halogen-metal exchange (butyl lithium and
tributyltin chloride, Pearson et al., J. Org. Chem.
59:5662-5671 (1994)) to give the desired (Z)-
Bu3SnCH=CHCHzOTBDMS) is utilized in the coupling
reaction. The Z-allylic alcohol (33) then results
following deprotection of the carboxylic acid (such as
with KOH in THF) and the TMS group (such as with acid)
or the TBDMS group (such as with TBAF in THF).
The lactone (34) is then prepared from the Z-
allylic alcohol (33). Many methods that are available
to form medium to large lactones (Meng et al., "Topics
in Current Chemistry, Ring Closure Methods in the
Synthesis of Macrocyclic Natural Products," Springer-
Verlag (Pub.), Vol. 161 (1991); and Nicolaou,
Tetrahedron 33:683-710 (1977)). For example, the
lactone (34) can be prepared from the Z-allylic alcohol
(33) utilizing Mukaiyama's reagent (Mukaiyama et al.,
Chem. Lett. 1976:49-50; and Mukaiyama, Chem. Int. Ed.
Engl. 18:707-721 (1979)) under high dilution conditions
(Funk et al., J. Org. Chem. 49:4320-4322 (1984); Cooper
et al., J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1987:1220; and
Cooper et al., Tet. Lett. 28:3031 (1987)).
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
77
SCHEME RI
0 O
/Z Re OPl /Z Re OP1
HN.SO ~ Y\O ~ N,
X Rf 2~ X Rf SOz
l b Rl 31 'R1
30 L
HO ~ La 0
O Z
Z ~ / m OP1
/ m OH ~ y\O
y\O ~ N. X Rf ~ N'SOz.
X Rf SOz R1
~R1
33
O 0 /Z
/Z ~m ~ y
yO \
\ X
X fiN
R SOz - R1 3~ ' ~ 02
R1
O
/Z V N.OH
y~ H
\"r /N.
X ~',,~ SOz
I .R1
Claisen ring contraction of the lactone (34) can be
effected by treatment of the lactone with various
combinations of reagents including TBDMSC1/LDA,
TBDMSOTf/LHMDS and TBDMSOTf/KHMDS, such as in THF at
about -78°C (Ireland et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 98:2868-
2877 (1976)) followed by heating the reaction, for
example to reflux, to give the Claisen product as a
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US9$/16147
78
protected carboxylic acid which can be deprotected, such
as with , to yield the heterocycle carboxylic acid (35).
Any silyl ester of the heterocycle carboxylic acid (35)
produced in the reaction can be removed by treatment
with aqueous KZC03 in THF-MeOH to give the free the
heterocycle carboxylic acid (35).
The relative stereochemistry between the vinyl and
carboxylic acid groups of the heterocycle carboxylic
acid (35) may be cis (Abelman et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc.
104:4030-4032 (1982); Funk et al., Tetrahedron 42:2831-
2845 (1986); and Corey et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc.
118:1229-1230 (1996)). The carboxylic acid group of the
heterocycle carboxylic acid (35) or the corresponding
ester can be epimerized, for example by treatment with
base, and the resulting cis and trans diasteriomers can
be separated and the R and S enantiomers can be
separated using methods well known to those skilled in
the art. The 2-trimethylsilylethyl protecting group can
be removed from the carboxylic acid group without
substantial epimerization from the cis stereochemistry
with fluoride in the presence of DMAP. The hydroxamic
acids (I) of this invention can then be prepared from
the heterocycle carboxylic acid (35) using PyBroP,
NHZOH~HCl and Hunigs base in CH2C12.
The alkene group of the heterocycle carboxylic acid
(35) can be functionalize using methods well known in
the art to produce a variety of groups. A recent
methodology described by Suzuki et al. CChem. Rev.
95:2457-2483 (1995)), which involves palladium catalyzed
coupling of alkylborane derivatives with alkenyl or aryl
halides or triflates. For example, coupling of the
hydroboration product of an ester of heterocycle
carboxylic acid (35) with iodobenzene can yield
heterocycles substituted with a phenethyl group. This
functionalization can be carried out in one pot by
hydroboration with 9-BBN in THF, to give a terminally
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
79
substituted alkyl borane that is then treated with
iodobenzene, KZC03 and catalytic PdClz (dppf) .
t
It is apparent from the above description that no
single general synthesis can be used in the preparation
of all of the novel compounds of this invention, because
some of the radicals, well known to those skilled in the
art, will or may have the potential of interfering with,
competing with or inhibiting the some of the reactions
involved in the pathway. However, one skilled in the
art is fully aware of appropriate point in the synthetic
pathway when a radical may be introduced and when
protecting groups can be used.
Sulfonyl halides can be prepared by the reaction of
a suitable alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl and the
like Grignard or lithium reagents with sulfuryl
chloride, or sulfur dioxide followed by oxidation with a
halogen, preferably chlorine. Alkyl, heteroaryl,
heterocyclyl, aryl and the like Grignard or lithium
reagents can be prepared from their corresponding halide
(such as chloro or bromo) compounds which are
commercially available or readily prepared from
commercially available starting materials using known
methods in the art. Alternatively, mercaptans may be
oxidized to sulfonyl chlorides using chlorine in the
presence of water under carefully controlled conditions.
Additionally, sulfonic acids may be converted into
sulfonyl halides using reagents such as PC15, SOC12,
C1C(O)C(O)C1 and the like, and also to anhydrides using
suitable dehydrating reagents. The sulfonic acids are
either commercially available or may be prepared using
procedures well known in the art from commercially
available starting materials. In place of the sulfonyl
halides, sulfinyl halides or sulfenyl halides can be
utilized to prepare compounds wherein the sulfonyl
moiety is replaced by an sulfinyl or thio moiety,
respectively. Arylsulfonic acids, benzo fused
heterocyclyl sulfonic acids or heteroaryl sulfonic acids
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
can be prepared by sulfonation of the aromatic ring by
well known methods in the art, such as by reaction with
sulfuric acid, 503, S03 complexes, such as DMF(S03),
pyridine(S03), N,N-dimethylacetamide(S03), and the like.
5 Preferably, such sulfonyl halides are prepared from such
aromatic compounds by reaction with DMF(S03) and SOC12 or
C1C(O)C(O)Cl. The reactions may be performed stepwise
or in a single pot.
Alkyl sulfonic acids, aryl sulfonic acids,
10 heterocyclyl sulfonic acids, heteroaryl sulfonic acids,
alkylmercaptans, arylmercaptans, heterocyclylmercaptans,
heteroarylmercaptans, alkylhalides, arylhalides,
heterocyclylhalides, heteroarylhalides, and the like are
commercially available or can be readily prepared from
15 starting materials commercially available using standard
methods well known in the art.
Thioether derivatives can be converted into the
corresponding sulfone or sulfoxide by oxidizing the
thioether derivative with a suitable oxidation agent in
20 a suitable solvent. Suitable oxidation agents include,
for example, hydrogen peroxide, sodium meta-perborate,
oxone (potassium peroxy monosulfate), meta-
chloroperoxybenzoic acid, periodic acid and the like,
including mixtures thereof. Suitable solvents include
25 acetic acid (for sodium meta-perborate) and, for other
peracids, ethers such as THF and dioxane, and
acetonitrile, DMF and the like, including mixtures
thereof .
The chemical reactions described above are
30 generally disclosed in terms of their broadest
application to the preparation of the compounds of this
invention. Occasionally, the reactions may not be
applicable as described to each compound included within
the disclosed scope. The compounds for which this
35 occurs will be readily recognized by those skilled in
the art. In all such cases, either the reactions can be
successfully performed by conventional modifications
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
81
known to those skilled in the art, e.g., by appropriate
protection of interfering groups, by changing to
alternative conventional reagents, by routine
modification of reaction conditions, and the like, or
other reactions disclosed herein or otherwise
conventional, will be applicable to the preparation of
the corresponding compounds of this invention. In all
preparative methods, all starting materials are known or
readily prepared from known starting materials.
Prodrugs of the compounds of this invention are
also contemplated by this invention. A prodrug is an
active or inactive compound that is modified chemically
through in vivo physicological action, such as
hydrolysis, metabolism and the like, into a compound of
this invention following adminstration of the prodrug to
a patient. The suitability and techniques involved in
making and using prodrugs are well known by those
skilled in the art. For a general discussion of
prodrugs involving esters see Svensson and Tunek Drug
Metabolism Reviews 165 (1988) and Bundgaard Design of
Prodrugs, Elsevier (1985). Examples of a masked
carboxylate anion include a variety of esters, such as
alkyl (for example, methyl, ethyl), cycloalkyl (far
example, cyclohexyl), aralkyl (for example, benzyl, p-
methoxybenzyl), and alkylcarbonyloxyalkyl (for example,
pivaloyloxymethyl). Amines have been masked as
arylcarbonyloxymethyl substituted derivatives which are
cleaved by esterases in vivo releasing the free drug and
formaldehyde (Bungaard J. Med. Chem. 2503 (1989)).
Also, drugs containing an acidic NH group, such as
imidazole, imide, indole and the like, have been masked
with N-acyloxymethyl groups (Bundgaard Design of
Prodrugs, Elsevier {1985)). Hydroxy groups have been
masked as esters and ethers. EP 039,051 (Sloan and
Little, 4/11/81) discloses Mannich-base hydroxamic acid
prodrugs, their preparation and use.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
82
Without further elaboration, it is believed that
one skilled in the art can, using the preceding
description, utilize the present invention to its
fullest extent. The following preferred specific
embodiments are, therefore, to be construed as merely
illustrative, and not limitative of the remainder of the
disclosure in any way whatsoever.
The following Examples illustrate the preparation
of compounds of the present invention and intermediates
useful in preparing the compounds of the present
invention.
example 1
O
,,~~ N~ OH
S
Me
\ / o
0
Preparation of 5-(4-methoxvghenylsulfonvl)-4 5 6 7-
tetrahvdro-thienof3 2-clQvridine-6iR)-hvrdoxamic acid
S_~.ep A 4 5 6 7 - tetrahydro- thieno f ~ 2 - cl pyridine- 6 f R)
carboxylic acid~HC1
Hydrogen chloride (1N, 0.3 ml, 2.9 mmole) was added into
a mixture of 3-(2-thienyl)-D-alanine(500 mg, 2.9 mmole)
and formaldehyde (375, 0.72 ml, 8.8 mmole) in 5 ml of
water. The reaction mixture was then heated to 90°C for
3 hr. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure to
obtain 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6(R)-
carboxyiic acid hydrochloride salt (450 mg, 91~): 1H NMR
(D20) 8 7.50(d, 1H), 7.00(d, 1H), 4.60(d, 1H), 4.40(d,
1H), 4.38(dd, 1H), 3.62(dd, 1H), 3.39(dd, 1H).
Step B~ methyl 4 5 6 7-tetrahydro-thienof3 2-cl
pvridine-6-carboxvlate~HC1
Hydrogen chloride (gas) was bubbled through a solution of
the carboxylic acid from step A (450 mg, 2.6 mmole) in 20
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
83
ml of methanol for 5 min (until ppt was dissolved). The
reaction mixture was then refluxed at 80oC for 10 hr.
Removal of the solvent under reduced pressure gave methyl
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c] pyridine-6-carboxylate
hydrochloride salt (440 mg, 95~): 1H NMR (D20) S 10.5(bs,
2H), 7.20(s, 1H), 6.70(s, 1H), 4.30-4.60(bm, 3H), 3.85(s,
3H), 3.50(s, 1H), 3.40(s, 1H).
teg C~ methyl 5-!4-methoxyphen~rlsulfonvl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahvdro-thienof3 2-cl~vridine-6-carboxvlate~HC1
A mixture of the methyl ester from step B (390 mg, 2
mmole), 4-dimethylaminopyridine (600 mg, 4.9 mmole) and
4-methoxybenzenesulfonyl chloride (529 mg, 2.6 mmole) in
N,N-dimethylformamide (5 ml) was stirred at 25°C for 3
hr. The N,N-dimethylformamide was then removed under
reduced pressure and the residue was subjected to column
chromatography (ethylacetate:hexane, 1:1) yielding
methyl 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thieno [3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylate hydrochloride salt
(390 mg, 54~): 1H NMR (CDC13, 400 MHz), ppm: 7.78(d,
2H), 7.10(d, 1H), 6.80(d, 2H), 6.70(d, 1H), 5.10(d, 1H),
4.60(d, 1H), 4.30(d, 1H), 3.80(s, 3H),3.50(s, 3H),
3.30(d, 1H), 3.08(d, 1H).
St~,p D~ 5-(4-methoxyphenvlsulfonvl)-4 5.6 7-tetrahvdro-
thienof3 2-clpyridine-6-carboxylic acid
To a solution of the sulfonamide from step C (390 mg,
1.1 mmole) in tetrahydrofuran/water (2 ml each) at 25oC,
was added lithium hydroxide (50 mg, 1.2 mmole) in one
portion. The resulting reaction mixture was then
stirred for 2 hr, followed by neutralization using 2N
hydrochloric acid (1.2 ml). The combined mixture was
then extracted with methylene chloride (30 ml), the
methylene chloride fractions were washed with water (2x5
ml), dried (magnesium sulfate), and the solvent
evaporated to obtain 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
84
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid (200 mg, 51~): 1H NMR (CDC13) 8 10.0(bs, 1H),
7. 8 (d, 2H) , 7.1 (d, 1H) , 6.8 (d, 2H) , 6.6 (d, 1H) , 5.2 (d,
1H), 4.6(d, 1H), 4.3(d, 1H), 3.8(s, 3H), 3.3(d, 1H), 3.0
(dd, 1H) .
.S,~eg E ~ 5 - ( 4 -methoxvpheny~ sul fonyl ) - 4 5 6 7 - tetrahvdro -
thienof3 2-clgvridine-6-hvdroxamic acid
A mixture of the acid from step D (93 mg, 0.26 mmole),
hydroxyamine hydrochloride salt (31 mg, 0.44 mmole), N-
methylmorpholine (0.15 ml, 1.3 mmole) and benzotriazol-
1-yl-oxytripyrrolidinephosphonium hexafluorophosphate
(Py-Bop) (232 mg, 0.44 mmole) in N,N-dimethylformamide
was stirred at 25oC for 4 hr. The solvent was then
removed under reduced pressure and the residue was
subjected to column chromatography (5~ methanol in
methylene chloride) to yield 5-(4-methoxyphenyl
ulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid (45 mg, 71~): 1H NMR (MeOD-d4) 8 7.70(d,
2H), 7.00(d, 1H), 6.80(d, 2H), 6.60(d, 1H }, 4.80(bs,
1H), 4.60(d, 1H), 4.30(d, 1H), 3.80(s, 3H), 3.50(d, 1H),
2.60(bd, 1H); Mass Spec. Calcd. C15H16O5N2S2(M+): 368,
Found(M+1): 369.2 &( M+NH4+): 386.2.
Example 2
Ac0 O
N, OH
I
N' o H OMe
II ~ /
0
Preparation of 5-(4-methoxy'~~nzen~sulfonvl)-4 5 6 7-
~etrahvdro-7-acetoxy-thienof3 2-clpvridine-6-hvdroxamic
acid
Step A~ threo 13-2-thienylserine
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
To a stirred solution of thiophene-2-carboxaldehyde
(44.48, 0.39mo1) in absolute ethanol (80.Om1, 4.9M) was
added glycine (14.8g, 0.20mo1) at ambient temperature.
The resulting suspension was cooled to OoC, at which
5 time a solution of potassium hydroxide (22.2g, 0.39mo1)
in absolute ethanol (120.0, 3.3M) was introduced in a
dropwise manner. Upon complete addition, the reaction
mixture was kept at -10°C for ninety minutes. The
yellow solid which had precipitated during this time was
10 collected via filtration and washed with ethanol. The
solid was dissolved into water (70.Om1) and treated with
glacial acetic acid (l5.Om1). The resulting solution
was stored at -10°C for eighteen hours. The
precipitated product was collected via filtration to
15 give 15.8g (43~) of threo f3-2-thienylserine.
,step B~ 4 5 6 7-tetrahvdro-7-hvdroxy-thienof3 2
cL,~yridine-6-carbox~~ic acid hydrogen sulfate salt
To a stirred solution of threo 13-2-thienylserine (15.8g,
20 84.5mmo1) in 0.25N sulfuric acid (140.Om1) was added 37%
formaldehyde (45.0m1) at ambient temperature. The
resulting mixture was stirred for three days after which
time the product precipitated from solution. The solid
was collected via filtration and washed with water
25 (20m1) to give 5.2g (21~) of 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-7-
hydroxy-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid hydrogen
sulfate salt.
Step C~ 5-(4-methoxyphenYlsulfon~l)-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdro-
30 7-hydroxy-thieno(3 2-clpyridine-6-carboxvlic acid
To a cooled (OoC) suspension of 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-7-
hydroxy-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid hydrogen
sulfate salt (0.778, 2.59mmo1) in 9~ Na2C03 (aq., 6.5m1)
was slowly added a solution of 4-methoxybenzenesulfonyl
35 chloride (0.538, 2.59mmo1) in 1,4-dioxane (6.5m1). Upon
complete addition of the sulfonyl chloride, the cooling
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99106410 PCT/US98/16147
86
bath was removed and the reaction was stirred at ambient
temperature for one hour. The 1,4-dioxane was removed
in vacuo and the remaining residue was diluted with
water and ethyl acetate. The layers were separated.
The aqueous phase was acidified to a pH of about 2 using
2M HC1 and the product was extracted into ethyl acetate
(twice). The combined organics were dried (MgS04),
filtered and concentrated to give 0.44g (46~) of 5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl}-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-7-hydroxy-
thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid: 1H NMR (DMSO-
d6) 8 3.75 (3H), 4.2-4.6 (2H), 4.7-5.0 (2H), 6.8 (1H),
7.2 (1H) , 7.3 (1H) , 7.7 (1H) .
Step D~ 5-(4-methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdro-
7-acetoxv-thienof3 2-cl~vridine-6-carboxylic acid
To a stirred solution of 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-7-hydroxy-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid (0.20g, 0.54mmo1) in pyridine (5.Oml)
was added acetic anhydride (60.Om1, 0.65mmo1) at 0°C
under nitrogen atmosphere. The resulting mixture was
stirred for one hour after which time it was quenched
with water (115.Om1) and ethyl acetate (110.Om1). The
layers were separated and the aqueous phase was
extracted once more with ethyl acetate (110.Om1}. The
combined organics were dried (MgS04), filtered and
concentrated to give the crude product. Purification
via flash column chromatography (silica gel, 10~
methanol/ethyl acetate) afforded 0.198 (86~) of 5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-7-acetoxy-
thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid: 1H NMR (CDC13)
8 2.1 (3H), 3.8 (3H), 4.5-4.6 (2H), 5.2 (1H), 5.9 (1H),
6.7 (1H) , 6.9 (2H) , 7.2 (1H) , 7.8 (2H} , 8.1-8.7 (1H) .
S~~ E 5 ( 4 methoxv»henyl sul f onvl ) - 4 5 6 7 - tet rahydro -
7-acetoxv-thienof3 2-clgyridine-6-hvdroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
87
To a stirred solution of 5-(4-methoxybenzenesulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-7-acetoxy-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid (0.198, 0.46mmo1) in dichloromethane
(20.Om1) was added hydroxylamine hydrochloride (0.77g,
9.20mmo1) at OoC under nitrogen. The resulting mixture
was stirred for five minutes after which time it was
treated with triethylamine (l.Oml, 7.2mmo1) and PyBroP
(Bromo-tris-pyrrolidino-phosphonium hexafluoro-
phosphate, 0.328, 0.69mmo1). The reaction was stirred
for five hours, during which time it had warmed to
ambient temperature, and concentrated. The remaining
residue was purified via column chromatography (silica
gel, 5o methanol/ ethyl acetate) to give 5-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-7-acetoxy-
thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxarnic acid: 1H NMR (CDC13)
b 2.0 (3H), 3.7 (3H), 4.3-4.5 (2H), 4.8 (1H), 5.9 (1H),
6.6 (1H), 6.8 (2H), 7.1 (1H), 7.6 (2H), 10.7 (1H); Mass.
Spec. 444.2 (M+NH4+).
Example 3
HO 0
N~OH
I
OMe
I
0
reparation of 5-(4-methoxwhenvlsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-
tetrahydro-7-hvdroxv-thienof3 2-cltwridine-6-hvdroxamic
acid
To a stirred solution of 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-7-acetoxy-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid (l8.Omg, 0.04mmo1) in methanol (0.5m1,
0.08M) was added 20~ potassium carbonate (aq., 0.5m1).
After stirring at ambient temperature for 2.5 hours, the
methanol was removed in vacuo. The remaining residue
was diluted with water (5.Om1) and ethyl acetate
(l0.Om1). The layers were separated and the aqueous
phase was extracted with ethyl acetate (three times
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
88
l0.Om1). The combined organics were concentrated to
give crude product. Purification via column
chromatography (silica gel, 5~ methanol/ethyl acetate)
gave 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-7-
hydroxy-thieno[3,2-c~pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid as an
off-white solid: 1H NMR (DMSO) 8 3.8 (3H), 5.3-5.9
(4H), 6.8 (1H), 7.1 (2H), 7.4 (1H), 7.7 (2H), 8.5-8.8
(1H); Mass Spec. 385.2 (M+H), 402.0 (M+NH4+).
Examgle 4
HO N~ OH
I
N~ O H OMe
I
0
Preparation of DL-cis 5-(4-methoxy~henvlsulfonvl)-
4 5 6 7-tetrahydro-7-hydrox-y-thienof3 2-clpvridine-6-
hydroxamic acid
Step A~ DL-cis 2-(2-thienvl)serine
To a mechanically stirred solution of 2-thiophene
arboxaldehyde (488.08, 4.35mo1) in absolute ethanol
(900m1) was added glycine (98.5~a purity, 165.88,
2.17mo1). The resulting suspension was cooled to 0°C. A
solution of potassium hydroxide (87.90 purity, 277.68,
4.35mo1) in absolute ethanol (1.3L) was then added
dropwise over 7.5 hours. During this time, the reaction
became homogeneous and shortly after a precipitate
formed. Upon complete addition of the ethanolic KOH
solution, the reaction mixture was stirred for an
additional 0.5 hours and placed in a freezer over night.
The precipitated solid was collected via filtration and
dissolved into water (1L). A sufficient volume of
glacial acetic acid (about 230m1) was added to adjust
the pH to 5.5. The resulting solution was cooled to
induce the precipitation of the desired product. The
solid was collected via filtration to give pure DL-cis
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
89
2 - ( 2 - thienyl ) serine . The NMR (DZO) spectrum was
consistent with the proposed structure.
teg B~ DL-cis 7-hvdroxy-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdro-thienof3 2-
clpyridine-6-carboxvlic acid
To a stirred suspension of DL-cis 2-(2-thienyl)-serine
(116.Og, 0.62mo1) in 0.25N sulfuric acid (2.2L) was
added 37~ formaldehyde (275.Om1) at ambient temperature.
The reaction mixture became homogeneous. After three
days, the precipitated product was collected via
filtration. The pH of the filtrate was adjusted to 5.0-
6.0 using 10N NaOH. The solid product was collected via
filtration. The combined products were dried to give
the desired product. The NMR (DZO) spectrum was
consistent with the proposed structure.
Steg C~ DL-cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenvlsulfonvl)-
d 5 6 7-tetrahvdro-thieno~3 2-clpyridine-6-carboxvlic
acid
A suspension of DL-cis 7-hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid (35.Og, 175.9
mmol) in 9~s sodium carbonate (440.Om1) was cooled to
0°C. To this suspension was added a solution of 4-
methoxybenzenesulfonyl chloride (47.3g, 228.8mmo1) in
1,4-dioxane (440m1) over one hour. Additional 9~ sodium
carbonate was added to maintain a pH=8-9. The reaction
was allowed to stir over night during which time it had
warmed to ambient temperature. The dioxane was removed
and the remaining residue was diluted with water. This
aqueous material was washed with ethyl acetate three
times and then acidified to pH=2 using 2M HCl. The
product was extracted with ethyl acetate (three times).
The combined product extractions were washed
successively with water and brine, then dried (MgS04).
Filtration and concentration yielded DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid as a pink foam. The
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
NMR(CDC13) spectrum was consistent with the proposed
stucture.
Step D~ DL-cis 7-acetoxy-5- (4-methoxyghenylsulfon_yl) -
5 4 5,6,7-tetrahvdrothienof3,2-clpvridine-6-carboxylic
acid
To a stirred solution of DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]
pyridine-6-carboxylic acid (16.5g, 44.9mmo1) in pyridine
10 (440m1) was added acetic anhydride (5.Oml, 53.9mmo1) at
0°C, under argon. After 1.5 hours, the reaction was
diluted with cold water (100m1) then poured into ethyl
acetate (800m1) and chilled 2M HCl (1L). The layers
were separated and the organic was washed twice with
15 chilled 2M HC1 (1L) then twice with cold water (1L).
The organic was then dried (MgSOa), filtered and
concentrated to yield DL-cis 7-acetoxy-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-
6-carboxylic acid. The NMR (CDC1;) spectrum was
20 consistent with the proposed structure.
~ E~ DL-cis 7-Hvdroxy-5-(4-methoxyghenvlsulfonvl)-
4 5 6 7-tetrahvdrothienof3 2-cl~yridine-6-hvdroxamic
acid
25 To a stirred solution of DL-cis 7-acetoxy-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-
6-carboxylic acid (5.3g, 12.9mmo1) in dichloromethane
(60m1) was added oxalyl chloride (12.9m1 of a 2M
dichloromethane solution, 25.8mmo1) at ambient
30 temperature, under argon. One drop of DMF was added to
catalyze the formation of the acid chloride
intermediate. After stirring fox 1.5 hours, the
reaction was cooled to 0°C. A solution of hydroxylamine
hydrochloride (3.6g, 51.6mmo1) and diisopropylethylamine
35 (13.5m1, 77.4mmo1) in THF (50m1) and water (4ml) was
then carefully added in a dropwise manner. Upon
complete addition, the reaction mixture was stirred at
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
91
ambient temperature over night and then poured into
water and dichloromethane. The layers were separated
and the aqueous phase was extracted once with
dichloromethane. The combined organics were washed
twice with 0.5M HC1 (50m1) and dried (MgSOd).
Filtration and concentration gave a brown foam which was
dissolved into methanol (100m1) and diluted with 5~ KZCO,
(100m1). After fifteen minutes, the reaction mixture
was concentrated to low volume. The remaining aqueous
was poured into 0.5M HC1 (pH=1) and dichloromethane.
The layers were separated and the aqueous phase was
extracted twice with dichloromethane. The combined
organics were allowed to stand at ambient temperature.
DL-cis 7-Hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
precipitated as an off-white solid which was collected
via filtration. The NMR (DMSO) spectrum was consistent
with the proposed structure.
Example 5
O
/ 'O O
~ OH
S
N~ ~ ~ OMe
PrgQaration of DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonvloxv)-5-(4-
methoxyphenvlsulfonvl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-f3 2-cl-
pyridinLrl-6-hydroxamic acid
Step A~ DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxv)-5-(4-
methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdrothieno-f3,2-cl-
gyridinvl-6-carboxvlic acid
To a stirred solution of DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-
6-carboxylic acid (88.Omg, 0.24mmo1) in dry DMF (l.5ml)
was added copper (I) bromide (34.0mg, 0.24mmo1) at
ambient temperature. After stirring for five minutes,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/0641P PCT/US98/16147
92
benzyl isocyanate (29.Ou1, 0.24mmo1) was introduced via
syringe. The resulting mixture was stirred for five
minutes and then diluted with water (40m1). The product
was extracted into ethyl acetate (twice). The combined
organics were washed with dilute HC1 (aq.) and dried
(MgSOa). Filtration and concentration gave DL-cis 7-(N-
benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic
acid which was used without further purification.
NMR(CDC13) was consistent with the proposed structure.
Steg B~ DL-cis-7-(N-benzvlaminocarbonvloxv)-5-(4-
methoxvnhenvlsulfonyl)-4 5 6j7-tetrahvdrothi~no-f3 2-cl-
gvridinvl-6-hvdroxamic acid
To a stirred solution of DL-cis 7-(N-benzylamino
carbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid
(0.118, 0.22mmo1) in anhydrous dichloromethane was added
oxalyl chloride (0.22m1, 0.44mmo1) at 0°C, under argon.
One drop of DMF was added to catalyze the formation of
the acid chloride intermediate. After stirring for two
hours, the mixture had warmed to ambient temperature.
The reaction was again cooled to 0°C. A solution of
hydroxylamine hydrochloride (6l.Omg, 0.88mmo1) and
diisopropylethylamine (0.23m1, 1.32mmo1) in THF (0.15m1)
and water (1 drop) was added via syringe (dropwise).
The resulting mixture was stirred for four hours at
ambient temperature and poured into water and
dichloromethane. The layers were separated and the
organic phase was washed with dilute HC1 (aq.) and dried
(MgSO,). Filtration and concentration gave the crude
product. Purification via preparative TLC (silica gel,
10~ methanol/dichloromethane) afforded pure DL-cis 7-(N-
benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid. NMR (DMSO) and MS (M-1 = 516) were consistent
with the proposed structure.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
93
Example 6
O
/_O O
H N. OH
OMe
U
Preparation of DL-cis 7-(N-phenvlaminocarbonyloxv)-5-(4-
methoxvohenylsulfonvl)-4,5.6,7-tetrahvdrothieno-I3,2-cl-
gvridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
~~~p ,F,~ DL-ci~ 7- (N-~henylaminocarbonyloxy) -5- (4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-f3 2-cl-
pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid
Utilizing phenyl isocyanate, DL-cis 7-(N-phenylamino
carbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was
prepared from DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid in the same manner as DL-cis 7-(N-
benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic
acid. DL-cis 7-(N-phenylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was purified via flash
column chromatography (silica gel, 20~ ethyl acetate in
dichloromethane, and 10~ methanol in dichloromethane).
NMR (CDC13) was consistent with the proposed structure.
~tep B~ DL-cis 7-(N-phenylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxvphenylsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrah~,~rothieno-f3 2-cl-
pvridinvl-6-hvdroxamic acid
DL-cis 7-(N-phenylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
hydroxamic acid was prepared in the same manner as DL-
cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
94
hydroxamic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-phenylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-
c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was purified via
preparative TLC (silica gel, 5~ methanol in
dichloromethane). NMR (DMSO) and MS (M-1 = 502) were
consistent with the proposed structure.
Example 7
O
~ O
Mew N/ _ O OH
H N
OMe
Preparation of DL-his 7-(N-methvlaminocarbonvloxv)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdrothieno-f3,2-cl-
pvridinyl-6-hvdroxamic acid
Step A~ DL-cis 7-(N-methvlaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxvnhenvlsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdrothieno-f3 2-cl-
pyridinyl-6-carboxvlic acid
Utilizing methyl isocyanate, DL-cis 7-(N-methylamino
carbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was
prepared from DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid in the same manner as DL-cis 7-(N-
benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic
acid. DL-cis 7-(N-methylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was purified via flash
column chromatography (silica gel, 15~ methanol in
dichloromethane). NMR (CDC1,) was consistent with the
proposed structure.
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
Step B: DL-cis 7-(N-methylaminocarbonvloxv)-5-(4-
methoxy~henvlsulfonvl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-f3 2-cl-
pvridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
DL-cis 7-(N-methylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
5 sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
hydroxamic acid was prepared in the same manner as DL-
cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
hydroxamic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-methylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-
10 (4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-
c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was purified via
preparative TLC (silica gel, 5~ methanol in
dichloromethane). NMR (DMSO) and MS (M-1 = 440) were
consistent with the proposed structure.
Example 8
O
~ O
~N~O ,OH
H S N
OMe
d
Preparation of DL-cis 7-(N-is~propvlaminocarbonyloxv)-5-
(4-methoxvphenylsulfonyl)-4 5 6.7-tetrahvdrothieno-f3.2-
cl-gvridinvl-6-hydroxamic acid
Steg A~ DL-cis 7-(N-isQgro~vlaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxvt~henvlsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-f3 2-cl-
pvridinyl-6-carboxylic acid
Utilizing isopropyl isocyanate, DL-cis 7-(N-isopropyl
aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was
prepared from DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid in the same manner as DL-cis 7-(N-
benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic
acid. DL-cis 7-(N-isopropylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
96
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was purified via flash
column chromatography (silica gel, 20~ ethyl acetate in
dichloromethane, and 10~ methanol in dichloromethane).
NMR (CDC13) was consistent with the proposed structure.
~p B~ DL-cis 7-(N-isoprogylaminocarbonvloxy)-5-(4-
methoxy~~henylsulfonvl)-4 5 6 7-tetrah~drothieno-f3 2-cl-
gyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
DL-cis 7-(N-isopropylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-
c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared in the same
manner as DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-
isopropylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid was purified via preparative TLC (silica gel, 10%
methanol in dichloromethane). NMR (DMSO) and MS (M+1 =
470) were consistent with the proposed structure.
Example 9
0
/ ~ ~ ~.... 0
0 N~OH
I
II ~ ~ OMe
O
prPgaration of DL-cis 7-(N-(4-phenoxyphenvl)amino
c ra_ bonyloxv) -5- (4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl) -4 5 6 7-
tetrahydrothieno-f3 2-cl-gvridinvl-6-hydroxamic acid
~tPp A~ DL-ci~ 7-(N-(4-ohenoxyphenvl)aminocarbonyloxy)-
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-
f3 2-cl-pvridinvl-6-carboxvlic acid
Utilizing 4-phenoxyphenyl isocyanate, DL-cis 7-(N-(4-
phenoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
97
carboxylic acid was prepared from DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid in the same manner as DL-
cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
carboxylic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(4-phenoxyphenyl)amino
carbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was
purified via flash column chromatography (silica gel,
20% ethyl acetate in dichloromethane, and 10% methanol
in dichloromethane).
Step B: DL-cis 7-(N-(4-ghenoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-
5-(4-methoxwhenylsulfonyl)-4,5.6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
f3,2-cl-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
DL-cis 7-(N-(4-phenoxyphenyl}aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared in the same
manner as DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(4-phenoxy
phenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid was purified via preparative TLC (silica gel, 10%
methanol in dichloromethane). NMR (DMSO) and MS (M+1 =
596) were consistent with the proposed structure.
Exa le 10
0
O
N~0 ,OH
H N
H _.
OMe
0
Preparation of DL-cis 7- (N- (1-~henylethyl) amino
carbonvlo~y)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahvdrothieno-f3 2-cl-p,~ridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
98
Step A: DL-cis 7-(N-(1-phenylethyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-4,x,6,7-tetrahydrothieno- 3,2-
cl-pvridinyl-6-carboxylic acid
Utilizing 1-phenylethyl isocyanate, DL-cis 7-(N-(1-
phenylethyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
carboxylic acid was prepared from DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid in the same manner as DL-
cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
carboxylic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(1-phenylethyl)amino
carbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was
purified via flash column chromatography {silica gel,
15~ ethyl acetate in dichloromethane, and 10% methanol
in dichloromethane).
Srep B~ DL-cis 7- LN-(1-phenylethvl)aminocarbonyloxv)-5-
(4-methoxvghenvlsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdrQthieno-f3 2-
cl-pvridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
DL-cis 7-(N-(1-phenylethyl)aminocarbonyloxy}-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared in the same
manner as DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-{4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(1-phenyl
ethyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid was purified via preparative TLC (silica gel, 5~
methanol in dichloromethane). NMR (DMSO) and MS (M+1 =
532) were consistent with the proposed structure.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
99
Examgl a 11
Me / O
~N~O OH
H N~
I
N'~ H -
II ~ ~ OMe
O
Pregaration of DL-cis 7-(N-(4-methoxyphenyl)amino
carbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-4,5,6,7-
tet~ahydrothieno-f3.2-cl-gyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
Steg A: DL-cis 7-(N-(4-methoxyg..henvl)aminocarbonyloxv)-
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
j3,2-cl-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid
Utilizing 4-methoxyphenyl isocyanate, DL-cis 7-(N-(4-
methoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
carboxylic acid was prepared from DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]
pyridine-6-carboxylic acid in the same manner as DL-cis
7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
carboxylic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(4-methoxyphenyl)amino
carbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-(3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was
purified via flash column chromatography (silica gel,
15~ ethyl acetate in dichloromethane, and 10o methanol
in dichloromethane).
Step B~ DL-cis 7- (N- (4-methox~~henyl) aminocarb~nyloxy) -
5-(4-methoxyghenylsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-
f3,2-cl-gvridinyl-6-hvdroxamic acid
DL-cis 7-(N-(4-methoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared in the same
manner as DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-I3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(4-methoxy
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
100
phenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic
acid was purified via preparative TLC (silica gel, 5~
methanol in dichloromethane). NMR (DMSO) and MS (M+1 =
534) were consistent with the proposed structure.
Examble 12
O
0 0
H N.OH
1
N~O ~ OMe
Preparation of DL-cis 7-IN-(~henethyllaminocarbonyloxy)-
5-(4-methoxvt~henylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
~3.2-cl-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
Step A: DL-cis 7- (N- (phenethyl)aminocarbonvloxv) -5- (4-
methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-f3,2-c]-
pvridinyl-6-carboxylic acid
Utilizing phenethyl isocyanate, DL-cis 7-(N-(phenethyl)
aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was
prepared from DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid in the same manner as DL-cis 7-(N-
benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic
acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(phenethyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-
c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was purified via flash
column chromatography (silica gel, 15~ ethyl acetate in
dichloromethane, and 10~ methanol in dichloromethane).
step B~ DL-cis 7-(N-(phenethyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfony,l)-4.5,6,7-tetrahvdrothieno-f3,2-c)-
gvridin~l-6-hvdroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
101
DL-cis 7-(N-(phenethyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared in the same
manner as DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(phenethyl)
aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was
purified via preparative TLC (silica gel, 5o methanol in
dichloromethane). NMR (DMSO) and MS (M+1 = 532) were
consistent with the proposed structure.
Example 13
O
0
N~ O OH
H N~
I
N~ O H OMe
n \ /
0
Preparation of DL-cis 7-(N-cyclohexvlaminocarbonvloxv)-
5-(4-methoxv~henvlsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdrothieno-
~3 2-cl-ovridinvl-6-hydroxamic acid
Step A DL cis 7-(N-cvclohexvlaminocarbonvloxv)-5-(4-
methoxvt~henvlsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdrothieno-(3,2-cl-
pyridinvl-6-carboxvlic acid
Utilizing cyclohexyl isocyanate, DL-cis 7-(N-cyclohexyl
aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was
prepared from DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid in the same manner as DL-cis 7-(N-
benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic
acid. DL-cis 7-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was purified via flash
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
102
column chromatography (silica gel, 105 ethyl acetate in
dichloromethane, and 8~S methanol in dichloromethane).
Ste~g B: DL-cis 7-(N-cyclohexylamino~arbonvloxv)-5-(4-
methoxwhenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-f3,2-cl-
gvridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
DL-cis 7-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared in the same
manner as DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-cyclohexyl
aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
precipitated from dichloromethane. NMR (DMSO) and MS
(M-1 = 508) were consistent with the proposed structure.
example 14
O
O
N~ O ~ OH
H N
I
N' ~ H -
II ~ ~ OMe
0
Preparation of DL-cis 7-(N-(2-
bi~henyl)aminocarbonyloxv)-5-(4-methoxyghenvlsulfonyl)-
4 _5 s 7-~etrahvdrothieno-(3 2-cl-pyridinvl-6-hydroxamic
acid
~tPg A~ DL-cis 7-(N-(2-b~henyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenvlsulfonvl) -4 ~, 6 7-tetra~dro~hieno- f3 2-cl -
pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid
Utilizing 2-biphenylisocyanate, DL-cis 7-(N-(2-biphenyl)
aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was
prepared from DL-cis 7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid in the same manner as DL-cis 7-(N-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
103
benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic
acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(2-biphenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was purified via flash
column chromatography (silica gel, 10~ ethyl acetate in
dichloromethane, and 8~ methanol in dichloromethane).
Steg B: DL-cis 7-(N-(2-biphenyl)aminocarbonvloxy)-5-(4-
methoxvnhenvlsulfonvl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-f3 2-cl-
pvridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
DL-cis 7-(N-(2- biphenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6;7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared in the same
manner as DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(2-biphenyl)
aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was
purified via preparative TLC (silica gel, 5o methanol in
dichloromethane). NMR (DMSO) and MS (M-1 = 578) were
consistent with the proposed structure.
O O
' O ' ~ N~O O ~OH
HS N
OMe
Preparation of DL-cis 7-lN-(4-butoxvcarbonvlnhenvl)
aminocarbonvloxy)-5-l4-methoxwhenylsulfonvl)-4 5 6 7-
t-Pt-rahydrothieno-f3 2-cl-Qyridinyl-6-hvdroxamic acid
~te_p A~ DL-cis 7-(N-(4-butoxycarbonvlt~henyl)amino
carbQnvloxy)-5-(4-methoxvohenylsulfonvl)-4.5,6,7-
Prrahydrothieno-f3 2-cl-gvridinyl-6-carboxylic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99!06410 PCT/US98116147
104
Utilizing 4-butoxycarbonylphenyl isocyanate, DL-cis 7-
(N-(4-butoxycarbonylphenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxy phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-
c]-pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid was prepared from DL-cis
7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid in the
same manner as DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-carboxylic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(4-butoxy
carbonylphenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
carboxylic acid was purified via flash column
chromatography (silica gel, 10~ ethyl acetate in
dichloromethane, and 8~ methanol in dichloromethane).
Step B: DL-cis 7-(N-(4-butoxvcarbonylphenvl)amino
carbonyloxv)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-X3,2-cl-gvridinvl-6-hvdroxamic acid
DL-cis 7-(N-(4-butoxycarbonylphenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-
c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared in the same
manner as DL-cis 7-(N-benzylaminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyi-6-hydroxamic acid. DL-cis 7-(N-(4-butoxy
carbonylphenyl)aminocarbonyloxy)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
hydroxamic acid was purified via preparative TLC (silica
gel, 5~ methanol in dichloromethane). NMR (CD,OD) and
MS (M-1 = 602) were consistent with the proposed
structure.
Examgle 16
HO O
~ OH
N~ ~ H OMe
I
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
105
Preparation of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(~,-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-methylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro thieno-f3.2-cl-pyridinyl-6-~droxamic acid
Step A: cis-7-hvdroxy-5-(4-m~thoxygh~ylsulfonvl)-6-
(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothienof3,2-
cl tavridine
To a solution of cis-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-7-hydroxy-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid (369 mg, 1.0 mmole) in methanol (5.0 mL)
at 0°C was dropwise added (trimethylsilyl)diazomethane
(2.0 M solution in hexane, 1.0 mL, 2.0 mmole). The
reaction mixture was then stirred at that temperature
for 30 min, followed by stirring at 25°C for another 30
min. The solvent was removed by reduced pressure and
the residue was subjected to chromatographic
purification (35~ EtOAc in hexane) giving pure cis-7-
hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-6-(methoxy
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno [3,2-c]pyridine:
White solid; TLC, Rf = 0.5 (40~ EtOAc in hexane); 1H NMR
(CDC13) 8 3.45(s, 3H), 3.82(s, 3H), 4.50(dd, 2H),
5.20(bd, 1H), 5.25(bs, 1H), 6.78(d, 1H), 6.98(d, 2H),
7.22 (d, 1H) , 7.80 (d, 2H) ; MS: Calcd. C16H1,NO6Sz (M') - 383,
Found (M+H)+ - 384.2, (M+rTHd)' - 401.2.
step B~ cis-2-iodo-7-hvdroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenvl
sulfonLrl)-6-(methoxycarbonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno
f3,2-cluvridine
To a solution of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-6-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno
[3,2-c]pyridine (383 mg, 1.0 mmol) in CCla (5.0 mL) and
CHZClZ (1.0 mL) at 25°C was added I2 (140 mg, 0.55 mmol)
in one portion, followed by addition of bis(trifluoro
acetoxy)iodobenzene (237 mg, 0.55 mmol). The reaction
mixture was allowed to stir at that temperature for 3
hr. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and
the residue was subjected to chromatographic
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
106
purification (30~ EtOAc in hexane) to obtain pure cis-2-
iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-6-(methoxy
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro thieno[3,2-c]pyridine:
White solid; TLC, Rf = 0.52 (405 EtOAc in hexane); 1H
NMR (CDC13) 8 3.50(s, 3H), 3.91(s, 3H), 5.00(bt, 1H),
5.15(d, 1H), 6.85(s, 1H), 6.92(d, 2H), 7.78(d, 2H); MS:
Calcd. C16H16NO6SZI (M+) - 509, Found (M+H) ~ - 509 . 8,
( M+NHa ) ' - 5 2 6 . 6 .
Step C: cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)-2-(N-
benzyl -N-methylaminocarbonyl ) - 6 - (methoxycarbon~rl ) -
4,5'~,7-tetrahydrothieno-f3,2-cl-pyriding
A mixture of 2-iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-6-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno
[3,2-c]pyridine (509 mg, 1.0 mmole), N-methyl-N-benzyl
amine (3.0 mL) and nickel tetracarbonyl (0.39 mL, 3
mmole) was stirred well and heated at 55°C under argon
atomsphere for 2 hr. The reaction mixture was then
directly subjected to chromatographic purification (60%
EtOAc in hexane) giving pure cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-methylaminocarbonyi)-6-
(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridine: Oil; TLC, Rf = 0.25(60 EtOAc in hexane); 1H
NMR (CDC13) S 3.05(bs, 3H), 3.45(s, 3H), 3.84(s, 3H),
4.28(bdd, 2H), 4.90(bs, 2H), 5.10(bs, 1H), 5.20(bs, 1H),
5.23 (bs, 1H) , 6.98 (d, 2H) , 7.22 (s, 1H) , 7 .36 (m, 3H) ,
7 .70 (d, 2H) , 7. 80 (d, 2H) ; MS: Calcd. C25Ha6N20,S2 (M+) - 530,
Found (M+H) + - 531. 3 , (M+NHa) ~ - 548 . 0 .
~gp D- cis-7-hvdroxy-5-(4-methoxvnhenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
benzvl-N-methylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahvdrothieno-
f3,2-cl-pyridine-6-carboxvlic acid
To a solution of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-methylaminocarbonyl)-6-(methoxy
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine (530
mg, 1.0 mmole) in THF (4.0 mL) and HZO (4.0 mL) at 25°C
was added LiOH-H20 (124 mg, 3.0 mmole) in one portion.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
107
The reaction mixture was allowed to stir at that
temperature for 1 hr, followed by quenching the reaction
with 1N HCl (3.0 mL, 3.0 mmole) . Dilution with CHZCIz
(100 mL) , washing with H20 (2x10 mL) , dried (MgSOa) ,
filtered and finally, removal of the solvent under
reduced pressure gave crude cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-methylaminocarbonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid which was subjected to the next reaction without
further purification.
Step E: cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methox hy~enylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
benzvl-N-methvlaminocarbonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrah~drothieno-
f3,2-cl-pyridine-6-hvdroxamic acid
To a solution of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-methylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-carboxylic acid (516
mg, 1.0 mmole) in DMF (5.0 mL) at 25°C was sequentially
added hydroxylamine hydrochloride (209 mg, 3.0 mmole),
N,N-diisopropylethylamine (0.7 mL, 4.0 mmole) and Py-
BroP (700 mg, 1.5 mmol). The reaction mixture was then
stirred at that temperature for 2 hr. Standard aqueous
work up (extraction with CHsClz) followed by
chromatographic purification (5~ MeOH in EtOAc) gave
pure cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
benzyl-N-methylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
f3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; TLC,
Rf = 0.5 (10~ MeOH in EtOAc) ; 1H NMR (acetone-d6) 8
3.10(bs, 3H), 3.85(s, 3H), 4.55(bs, 2H), 4.78(bs, 2H),
4.80(s, 1H), 5.05(s, 1H), 7.00(d, 2H), 7.28(m, 6H),
7 . 82 (d, 2H) , 10.30 (bs, 1H) ; MS: Calcd. CZ4HZSN30,S2 (M~) -
531, Found (M+H)' - 532, (M+NH4)' - 549.
Examx~le 17
Preparation of cis-7-hvdroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonvl)-2-ghen~rl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-(3,2-cl-
pyridinvl-6-hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99!06410 PCT/US98/16147
108
H N~OH
I
\ ~ 1 N~O H OMe
,~ II \ /
0
Step A: cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxv-5-f4-methoxvphenyl
sulfonvl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno~3,2-clgyridine-6-
carboxvlic acid
cis-2-Iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid was prepared from cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid in the same manner as cis-2-iodo-7-
hydroxy-5-(4-methoxy phenylsulfonyl)-6-(methoxy
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro thieno[3,2-c]pyridine:
Brown solid; TLC, Rf = 0.5 (20~ MeOH in CHZC12); 1H NMR
(DMSO-ds) b 3.82 (s, 3H) , 4.30 (bs, 2H) , 4.36 (bd, 1H) ,
4.50(bd, 2H), 6.82(s, 1H), 7.02(d, 2H), 7.76(d, 2H}; MS:
Calcd. C15H1aNOsSzI (M') - 495, Found (M-H) ~ - 494.
Step B: cis-7-hydroxy-5-f4-methoxy~he_n_ylsulfonvl)-2-
pphenyl-4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-~3 2-cl-pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid
To a solution of tributylphenyl tin (1.1 g, 3.0 mmole)
in THF at -78°C was dropwise added nBuLi (2M, 1.5 mL,
3.0 mmole). The reaction mixture was then stirred at
that temperature for 10 min, followed by an addition of
ZnCl2 (0.5M, 6.0 mL, 3.0 mmole}. The reaction mixture
was then allowed to slowly warm up to 25°C and was
stirred at that temperature for another 10 min. The
above Zn-reagent was then added into a mixture of cis-2-
iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid (495
mg, 1.0 mmole) and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium
(0) (58 mg, 0.05 mmole) in THF (20 mL) at 25°C and let
the mixture stir at that temperature for another 1 hr.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
109
Standard aqueous work up, extraction with CH2ClZ, removal
of the solvent, and finally, chromatographic
purification (5~ MeOH in CHaCl2) gave pure cis-7-hydroxy-
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-phenyl-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-I3,2-c]-pyridine-6-carboxylic acid:
White solid; TLC, Rf = 0.5 (10~ MeOH in CHzCl2); 1H NMR
(MeOD-d,) b 3.72 (s, 3H) , 4.30 (dd, 2H) , 4.50 (bs, 1H) ,
4.68(bs, 1H), 6.90(m, 3H), 7.10(s, 1H), 7.25(m, 1H),
7.50 (m, 2H) , 7. 88 (m, 2H) ; MS: Calcd. CZIHISNOsS2 (M+) - 445,
Found (M-H)- - 444.2.
step C: cis-7-hvdroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)-2-
phenvl-4,5,6,7-tetrahvdrothieno-f3,2-cl-gyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid
cis-7-Hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-phenyl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid was prepared from cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-phenyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridine-6-carboxylic acid in the same manner as cis-7-
hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-
methylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; TLC, Rf = 0.5
(5~ MeOH in CHaClz) ; 1H NMR (CDC13) 8 3.82 (s, 3H) ,
4.55(dd, 2H), 5.05(bt, 2H), 6.85(s, 1H), 6.92(b, 2H),
7.32(t, 2H), 7.50(d, 2H), 7.80(d, 2H); MS: Calcd.
C2IHZONa06S2 (M') - 460, Found (M-H) - 459 .2 .
Example 18
HO O
~ OH
~I
OMe
~CH3
Preparation of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxvphenyl
sulfonvl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-4.5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
f3,2-cl-pvridine-6-hvdroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
110
Step A~ cis-7-hvdroxv-5-l4-methoxvnhenvlsulfo~vl)-2 6-
bis(methoxvcarbonvl)-4 5 6 7-tetral~ydrothienof3 2-cl
gyridine
Carbon monoxide was bubbled through a mixture of cis-2-
iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-(methoxy
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine (509
mg, 1.0 mmole), triethyl amine (0.15 mL, 1.1 mmole) and
palladium acetate (4.5 mg, 0.02 mmole) in methanol (10
mL) for 10 min. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was
then heated at 70°C for 5 hr. The solvent was removed
under reduced pressure and the residue was subjected to
chromatographic purification (40~ EtOAc in hexane) to
obtain pure cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
2,6-bis(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]
pyridine: Oil; TLC, Rf = 0.45 (50~ EtOAc in hexane); 1H
NMR (CDC13) 8 3.50(s, 3H), 3.84(s, 3H), 3.85(s, 3H),
4.06(d, 1H), 4.08 and 4.62(dd, 2H), 5.20(d, 1H), 6.92(d,
2H) , 7.21 (s, 1H) , 7.78 (d, 2H) ; MS: Calcd. C18H19N08Sz (M')
- 441, Found (M+H)' - 442.2, (M+NH,)' - 459Ø
.Step B: cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxy~~henylsulfonyl)-2-
(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothienof3,2-cl
pyridine-6-carboxylic acid
To a suspension of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2,6-bis(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro
thieno[3,2-c]pyridine (441 mg, 1.0 mmole) in THF (5 mL)
and Hz0 (5 mL) was added LiOH-Hz0 (46 mg, 1.1 mmole) in
one portion. The reaction mixture was allowed to stir
at that temperature for 1 hr until which time the
starting material was consumed. The reaction was then
quenched with 1N HC1 (1.1 mL, 1.1 mmole) to pH = 7. The
solvents were removed under reduced pressure and the
residue was subjected to chromatographic purification
(20~ MeOH in CHaClz) to give pure cis-7-hydroxy-5- (4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid:
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
111
V~hite solid; TLC, Rf = 0.3 (20~ MeOH in CHzCl2) ; ~H NMR
(DMSO-ds) 8 3.75(s, 3H), 3.78(s, 3H), 4.37(dd, 2H),
4.38(bd, 2H), 4.52(bd, 2H), 7.00(d, 2H), 7.50(s, 1H),
7.78 (d, 2H) ; MS: Calcd. C1,H1,NOBSz (M+) - 427, Found (M-H) -
- 426.2, (M+NH4)' - 445.2.
Stex~ C: cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)-2-
(methoxvcarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrot~ienof3,2-c1
gyric~ine-6-hydroxamic acid
cis-7-Hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(methoxy
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c] pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid was prepared from cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c] pyridine-6-carboxylic acid in
the same manner as cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-methylamino carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid:
White solid; TLC, Rf = 0.4 (10 % MeOH in CHzCl2) ; 1H NMR
(MeOD-da) 8 3 . 82 (s, 3H) , 4. 50 (dd, 2H) , 4.75 (bs, 1H) ,
4.86(bs, 1H), 6.96(d, 2H), 7.50(s, 1H), 7.80(d, 2H); MS:
Calcd. C"H18Na08S2 (M~) - 442, Found (M-H) ~ - 441.2.
Example 19
HO
N~OH
I
N\ ~ H -
II ~ ~ OMe
HO O
Preparation of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenvl
sulfonyl)-2-carboxy-4 ~ 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-f3 2-cl-
gyridine-6-hvdroxamic acid
To a suspension of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno
[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid (442 mg, 1.0 mmole) in
THF (5 mL) and Hz0 (5 mL) at 25°C was added LiOH-H20 (84
mg, 2.0 mmole) in one portion. The reaction mixture was
allowed to stir at that temperature for 1 hr at which
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
112
time the starting material was consumed. The reaction
was then quenched with 1N HC1 (2 mL, 2.0 mmole) to pH 7.
The solvents were removed under reduced pressure and the
residue was subjected to chromatographic purification
(40% MeOH in CHZC12) yielding pure cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-carboxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro
thieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid;
TLC, Rf = 0.3 (40% MeOH in CHzCl2) ; 1H NMR (DMSO-ds) 8
3.78(s, 3H), 4.20(bs, 1H), 4.40(dd, 2H), 4.78(bs, 1H),
6.20(bs, 1H), 6.92(bs, 1H), 7.02(bd, 2H), 7.80(d, 2H),
8. 80 (bs, 1H) , 11. 00 (bs, 1H) ; MS: Calcd. C16H16N208S2 (M+) -
428, Found (M-H) - 427.2, (M+NH4)' - 446.
Example 20
HO O
N~OH
S
~I
OMe
CH3
Preparation of cis-7-hydroxy-5-14-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(ethoxvcarbonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-
f3,2-cl-ovridine-6-hydroxamic acid
Utilizing ethanol, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(ethoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared from
cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-
(methoxy carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]
pyridine in the same manner as cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid:
White solid; TLC, Rf = 0.41 (10% MeOH in CHZClz); 1H NMR
(DMSO-d6) b 1.30(t, 3H), 3.81(s, 1H), 4.10(q, 2H),
4.30(dd, 2H), 4.55(d, 1H), 4.90(d, 1H), 7.10(d, 2H),
7.50(s, 1H), 7.72(d, 1H), 7.90(bs, 1H); MS: Calcd.
ClBHZON208Sz (M~) - 456, Found: (M-H) ~ - 455.2, (M+H)' -
457.2, (M+NHa) ~ - 474.2.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
113
example 22
HO
N, OH
I
\ I N\~ H -
\ ~ II ~ ~ OMe
0
Preparation of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-metho~~henyl
sulfonyl)-2-(2-gyridyl)-415,6,7-tetrahydrothi~no-f3,2-
cl-pvridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
Utilizing bromo(2-pyridinyl)zinc, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(2-pyridyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro
thieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared
from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid in the same manner as cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-2-(2-phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; TLC,
Rf = 0.70 (10~ MeOH in CHZC12) ; 1H NMR (acetone-dfi) 8
3.90(s, 3H), 4.60(dd, 2H), 4.95(bd, 1H), 5.00(bd, 1H),
7.05(d, 2H), 7.24(m, 1H), 7.45(s, 1H), 7.76(m, 2H),
7.85 (d, 2H) , 8.50 (d, 1H) ; MS: Caldc. CZ~H19N3O6'~2 (i"I~) - 461,
Found: (M+H)+ - 462Ø
Example 22
HO 0
N, OH
I
N\ ~ H -
I \ ~ OMe
\ O
Preparation of cis-7-hy-droxy-5-(4-methoxy~henvl
sulfonyl) -2- (3-pyridyl) -4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno- f3 2-
cl-wridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid
Utilizing bromo(3-pyridinyl)zinc, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(3-pyridyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro
thieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared
from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
114
acid in the same manner as cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-2-(2-pyridyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; TLC,
Rf = 0.55 (10°s MeOH in CH2C12) ; 1H NMR (acetone-ds) 8
3.92(s, 3H), 4.60(dd, 2H), 4.90(d, 1H), 5.00(bt, 1H),
6.10(d, 1H), 7.10(d, 2H), 7.28(s, 1H), 7.40(dd, 1H),
7.98(d, 1H), 8.20(bs, 1H), 8.52(d, 1H), 8.84(s, 1H),
10.35(bs, 1H); 85(d, 2H), 8.50(d, 1H); MS: Caldc.
CzoH19N306S2 (M~) - 461, Found: (M+H) + - 462 .2 .
Example 23
HO O
N, OH
I
O ~ I N'~ H -
II ~ ~ OMe
0
preparation of cis-7-hvdroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenvl
sulfonyl)-2-(4-morgholinocarbonyl)-4.5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-f3 2-cl_gvridine-6-hydroxamic acid
Utilizing morpholine, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(4-morpholinocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro
thieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared
from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-
(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]
pyridine in the same manner as cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-methylamino
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
hydroxamic acid: White solid; TLC, Rf = 0.40(10 MeOH
in CHZC12) ; 1H NMR (CDC13) 8 3.70 (bs, 8H) , 3 .90 (s, 3H) ,
4.40(dd, 2H), 4.75(bs, 1H), 4.90(bs, 1H), 5.85(bs, 1H),
6.90(d, 2H), 6.95(s, 1H), 7.80(d, 2H), 9.75(bs, 1H); MS:
Caldc. CZOHz3N308S2 (M') - 497, Found: (M+H) a - 498. 0,
( M+NH, ) ' - 515 . 0 .
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
115
Example 24
H O
N~OH
I
N'~ H -
II \ / OMe
O
Preparation of cis-7-hvdro~-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonvl)-2-(phenylmethoxvca~bonyl)-4,5.6,7-
tetrahvdrothieno-f3,2-cl-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
Utilizing benzyl alcohol, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-2-(phenylmethoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid was
prepared from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-6-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno
[3,2-c]pyridine in the same manner as cis-7-hydroxy-5-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid:
Vrhite solid; TLC, Rf = 0 .20 (EtOAc) ; 1H NMR (CDC13) S
3.90(s, 3H), 4.44(dd, 2H), 4.70(bs, 1H), 4.90(bs, 1H),
5.28(s, 2H), 5.30(bs, 1H), 6.98(d, 2H), 7.38(m, 5H),
7.80 (d, 2H) , 9.65 (bs, 1H) ; MS: Caldc. Cz3HzZNZOeSz (M+) -
518, Found: (M+H)' - 519.1, (M+NH')+ - 536Ø
Example 25
HO O
N~OH
I ~ ~ OMe
\ N, H
Preparation of cis-7-hydroxv-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(N-phenylaminocarbonyl)-4,5.6,7-
tetrahvdrothieno-f3,2-cl-twridine-6-hvdroxamic acid
Utilizing aniline, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(N-phenylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro
thieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared
from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
116
(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]
pyridine in the same manner as cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(4-morpholinocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro thieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid:
White solid; TLC, Rf = 0.55 (10~ MeOH in CH2Clz) ; 1H NMR
(acetone-d6) 8 3.70 (s, 3H) , 4.40 (dd, 2H) , 4.70 (s, 1H) ,
4.75(s, 1H), 5.00(bs, IH), 6.90 - 7.70(series of m,
10H) , 9.35 (bd, 1H) ; MS: Caldc. C~2H2oN30,S2 (M') - 503,
Found: (M+H)' - 504 . 0, (M+NHq) ' - 521. 0.
Example 26
HO N~OH
0 ~ I
N' ~ H
I ~ / OMe
H O
Prebaration of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenvl
sulfonyl)-2-(N-benzylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrah_ydrothieno-f3,2-c7-,pyridine-~-hvdroxamic acid
Utilizing benzylamine, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(N-benzylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro
thieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid was prepared
from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-
(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]
pyridine in the same manner as cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(4-morpholinocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid:
White solid; TLC, Rf = 0.50 (10~ MeOH in CH2C12) ; 1H NMR
(CDC13) 8 3.85 (s, 3H) , 4.42 (dd, 2H) , 4.50 (bs, 1H) ,
4.72(bs, 1H), 4.88(bs, 1H), 6.30(bs, 1H), 6.90-7.90
( series of m, 10H) ; MS : Caldc . Cz3H23N;O~Sz (M+) - 517 ,
Found: (M+H); - 518.1, (M+NH4)' - 535.2.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
117
Example 27
HO O
N, OH
\ S
~ ~ ~o~ -
OMe
N
H
Preparation of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxvnhenyl
sulfonvl)-2-(N-(3-phenylpropyl)aminocarbonvl)-4 5 6 7-
tetrahvdrothieno-f3 2-cl-pvridine-6-hydroxamic acid
Utilizing 3-phenylpropylamine, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(3-phenylpropyl)amino
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid was prepared from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine in the same manner as
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(4-
morpholinocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro thieno-f3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; TLC, Rf =
0.60 (10~ MeOH in CH2Cla) ; 1H NMR (CDClj) 8 1.80 (m, 2H) ,
2.58(m, 2H), 3.30(m, 2H), 3.70(bs, 3H), 4.38(bm, 2H),
4 . 70 (bs, 1H) , 4.94 (bs, 1H) , 5.10 (bs, 1H) , 6. 82 (d, 2H) ,
7.00 - 7.20(series of m, 6H), 7.80(d, 2H), 9.90(bs, 1H);
MS: Caldc. CzSHz,N30,S2(M') - 545, Found: (M+H)+ - 546.0,
(M+NH4) + - 563 . 0 .
Example 28
HO
~ OH
S
N' q H -
\ ~ ~ ~ OMe
~CH3 O
Preparation of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)-2-(N-meth~l-N-
lphenethyl ) aminoca~l~on~rl~ - 4 , 5 . 6 . 7 - tetrahydrothieno- f 3 , 2 -
cl-pyridine-6-~ydroxamic acid
Utilizing N-methyl-N-(phenethyl)amine, cis-7-hydroxy-5-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-methyl-N-(phenethyl)amino
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
118
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid was prepared from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine in the same manner as
cis-7-hydroxy-2-(4-morpholinocarbonyl)-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; Rf = 0.20 (5~
MeOH in EtOAc) ; 1H NMR (acetone-ds) b 2.92 (t, 2H) , 3. 12
(bs, 3H), 3.71(t, 2H), 3.88(s, 3H), 4.58(s, 2H), 4.90(s,
1H), 5.05(s, 1H), 7.00(d, 2H), 7.25(m, 6H), 7.80(d, 2H),
7 .90 (bs, 1H) , 10.25 (bs, 1H) ; MS: Calc. CZSH2,N3O,S2 (M') -
545, Found: (M+H) ' - 546. 0, (M+NH,) ~ - 563 .1.
Example 29
HO O
N~OH
I
I N~ ~ H OMe
I \ /
0
p~garation of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-ethvlaminocarbonyl)-4 5 6 7-
tetrahydro thieno-f3 2-cl ~vridine-6-hydroxamic acid
Utilizing N-ethylbenzylamine, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N-ethylaminocarbonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid was prepared from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine in the same manner as
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(4-
morpholinocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; Rf = 0.15
(EtOAc) ; 1H NMR (acetone-ds) 8 1.20 (bm, 3H) , 3.50 (m. 2H) ,
3 .80 (s, 3H) , 4.50 (bs, 1H) , 4.70 (bs, 1H) , 4.85 (bs, 1H) ,
5.00(bs, 1H), 6.90(d, 2H), 7.05(s, 1H), 7.30(m, 5H),
7.78 (d, 2H) , 10.20 (bs, 1H) ; ) ; MS: Calc. C25HZ~N30,Sz (M') -
545, Found: (M+H) ' - 546 . 0, (M+NH4) ' - 563 . 3 .
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
119
Example 30
HO N~ OH
I
N' ~ H
II \ / OMe
N O
H
Preparation of cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenvl
sulfonyl)-2-(N-(4,4-dimethylpentvl)aminocarbonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahvdrothieno-f3,2-cl-pyridine-6-hydroxamic
a i
Utilizing 4,4-dimethylpentylamine, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(4,4-dimethylpentyl)amino
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid was prepared from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine in the same manner as
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(4-
morpholinocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; TLC, Rf =
0.55 (10~ MeOH in CH2C12) ; 1H NMR (CDCl~) b 0.90 (s, 9H) ,
1.15 (bm, 2H) , 1.40 (bm, 2H) , 3 .35 (bm, 2H) , 3 . 80 (s, 3H) ,
4 .32 (bs, 2H) , 4. 80 (bs, 1H) , 4.85 (bs, 1H) , 5.15 (bs, 1H) ,
6.90(d, 2H), 7.10(s, 1H), 7.78(d, 2H), 10.00(bs, 1H);
2 0 MS : Caldc . CZZH29N3O,S2 (M') - 511, Found : (M+H) + - 512 . 2 ,
(M+NH4) + - 529 . 2 .
Example 31
H
~~OH
N'~ ig'~
OMe
N O
H
Preparation of cis-7-hvdroxy-5-(4-methoxvphenyl
sulfonvl)-2-(N-(4 4-diphenylbutyl)aminocarbonvl)-
4 5 6 7-tetrahydrothieno-f3,2-cl-pyridine-6-hvdroxamic
acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
120
Utilizing 4,4-diphenylbutylamine, cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(4,4-diphenylbutyl)amino
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid was prepared from cis-2-iodo-7-hydroxy-
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine in the same manner as
cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-2-(4-
morpholinocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro thieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridinyl-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; Rf = 0.50
(10~ MeOH in CHzCla) ; 1H NMR (acetone-ds) S 1.50 (m, 2H) ,
1.90(m, 2H), 3.35(bm, 2H), 3.70(bm, 1H), 3.92(s, 3H),
4.10(bs, 1H), 4.52(dd, 2H), 4.90(bs, 1H), 5.00(bs, 1H),
6.80-7.90 (series of m, 15H) ; MS: Calc. C31H~1N30,S2 (M+) -
621, Found: (M+H)' - 622.3, (M+NHQ)' - 639.0, (M-H) - -
620Ø
Example ~2
HO O
~ OH
S
~1
OMe
N
,Me
Preparation of cis- and traps-7-hydroxv-5-(4-methoxv
phenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-phenyl-N-methvlaminocarbonvl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-f3,2-c)-pyridine-6-hvdroxamic
acid
Utilizing N-methylaniline, cis- and traps-7-hydroxy-5-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-phenyl-N-methylamino
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]- pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid was prepared from 2-iodo-7-hydroxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-6-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetra
hydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine in the same manner as cis-7-
hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(4-morpholino
carbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro thieno-[3,2-c]-pyridinyl-6-
hydroxamic acid. The diastereoisomers were separated to
yield cis-7-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/Ob410 PCT/US98/16147
121
phenyl-N-methylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-
[3,2-c]-pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; TLC, Rf
- 0.55 (10~ MeOH in EtOAc) ; 1H NMR (acetone-ds) 8 3.36 (s,
3H), 3.85(s, 3H0, 4.30(s, 2H), 4.80(s, 1H), 4.90(s, 1H),
6.45(s, 1H), 7.00(d, 2H), 7.32(d, 2H), 7.40(m, 3H),
7.94 (d, 2H) , 10.25 (s, 1H) ; MS: Calc. C23Hz3N30,SZ (M+) - 517,
Found: (M+H)+ - 517.8, (M+NHQ)' =534.9; and trans-7-
hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-phenyl-N-methyl
aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno-[3,2-c]-
pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid: White solid; TLC, Rf = 0.55
(10o MeOH in EtOAc); 1H NMR (acetone-dfi) 8 3.35(s, 3H0,
3.90(s, 3H0, 4.14(dd, 2H), 4.85(s, 1H), 4.90(s, 1H),
6.40(s, 1H), 7.02(d, 2H0, 7.31(d, 2H0, 7.42(m, 3H0,
7.78 (d, 2H) ; MS: Caldc. Cz3Hz3N3O,SZ (M') - 517, Found:
(M+H)' - 517.9, (M+NH4)' =534.9.
OMe
Preparation of 4-trans-Benzyl-6-(4-methoxvphenyl
sulfonyl)-4.5.6.7-tetrahvdro-thienof2.3.-clpyridine-5-
hydroxamic acid.
Sten A: 3-Phenvl-2-~hien-3-vl-acrylic acid
To a stirred solution of 3-thienylacetic acid (30 g, 211
mmol) in 200 mL acetic anhydride was added triethyl
amine (29.4 mL, 211 mmol) and benzaldehyde (34.2 mL, 336
mmol). The reaction was heated to reflux for two hours
under Argon with stirring. The reaction mixture was
treated with 300 mL water and refluxed for 5 minutes,
followed by cooling to room temperature and then
submerging in an ice bath for 30 minutes. The solid
precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with 600
Example 33
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
122
mL of 50°s aqueous acetic acid and 600 mL of water and
dried overnight in a vacuum dessicator to afford 3-
phenyl-2-thien-3-yl-acrylic acid as a pale tan solid and
used directly in the next step: MS (M+H)+ 231, (M+NH4)+
248. (Das et al., J. Med. Chem. 16(12):1361-1365, 1973)
Step B~ 3-Phenyl-2-thien-3-vl-propionic acid
A suspension of 3-phenyl-2-thien-3-yl-acrylic acid (10.2
g, 44 mmol) in 200 mL of absolute ethanol in a Parr
bottle was degassed by evacuation/purge with Argon
before addition of Wilkinson~s catalyst (1.07 g, 1.2
mmol). The reaction was hydrogenated in a Parr shaker
apparatus with heating to 60-70°C under 50 psi of
hydrogen for 20 hours. The solvent was removed by
rotary evaporation, and the dark residue was dissolved
in 400 mL of 1N sodium hydroxide and washed with 2
portions of 200 mL of ethyl acetate. The aqueous layer
was acidified to pH 2 with 1N aqueous hydrochoric acid
before extracting with 3 portions of 100 mL of ethyl
acetate. The combined organic layers after acid
treatment were dried with sodium sulfate, filtered,
evaporated and dried in vacuo to afford 3-phenyl-2-
thien-3-yl-propionic acid as a tan solid: MS (M-H)- 231
Step-C~ Methyl 3-Phenyl-2-thien-3-yl-propionate
To a solution of 3-phenyl-2-thien-3-yl-propionic acid (9
g, 38.7 mmol) in anhydrous methanol was slowly added
thionyl chloride (1 mL, 13.7 mmol). The reaction was
heated to reflux overnight, followed by removal of
solvent under reduced pressure. The dark residue was
diluted with ethyl acetate, washed with saturated aq
sodium bicarbonate and brine. The organic phase was
dried (sodium sulfate), filtered and evaporated to
afford the methyl ester homogenous by TLC: MS (M+H)+
247, (M+NH4)+ 264
Stets D ~ 3 - Phenyl - 2 - thiophen- 3 -y~nronionaldehvde
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
123
To a stirred cooled (-78°C) solution of methyl 3-phenyl-
2-thien-3-yl-propionate (8.3 8,33.73 mmol) in 65 mL
anhydrous toluene under Argon was added a pre-cooled
(-78°C) solution of diisobutylaluminum hydride (52.5 mL
of a 1 M solution in toluene, 52.5 mmol) dropwise, via
cannula, so the internal temperature of the reaction
does not rise above -65°C. After 25 minutes at -78°C,
TLC indicated complete consumption of methyl ester, and
the reaction was quenched by careful addition of
precooled (-78°C) anhydrous methanol (32.6 mL) dropwise
via cannula, so the internal temperature again does not
rise above -65°C. After warming to ambient temperature
overnight, the reaction was quenched by adding aqueous
citric acid and extracted with ethyl acetate. The
organic layer was washed with water, saturated aqueous
sodium potassium tartrate, dried, filtered and
evaporated to yield a crude product. The product was
purified by silica gel flash chromatography using step
gradient of hexanes/ethyl acetate 9:1; 8:1; 7:1; 3:1 to
afford the aldehyde: MS (M+MeOH+NH4)+ 266
Steb E~ 2-Hydrox~-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-vl-butyronitrile
To a cooled 0°C solution of potassium cyanide (1.95 g,
29.9 mmol) in 1.8 mL water was added ammonium chloride
(1.79 g, 33.5 mmol), concentrated ammonium hydroxide (20
mL, 143.79 mmol), and a solution of 3-phenyl-2-thiophen-
3-yl-propionaldehyde (6.19 g, 29.44 mmol) in 60 mL of
diethyl ether. The mixture was capped tightly before
removing the ice bath and was stirred at room
temperature overnight. The reaction was extracted with
4 portions of 50 mL of diethyl ether and 2 portions of
10 mL of ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers
were dried (magnesium sulfate), filtered and evaporated
to afford crude 2-hydroxy-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-
butyronitrile: MS (M+H)+ 243.
~gp F: 2-Hydroxy-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-butyric acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
124
A suspension of 2-hydroxy-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-
butyronitrile (7.74 g, 29.44 mmol) in 75 mL concentrated
hydrochloric acid was heated to reflux for 2 hours. The
mixture was cooled to room temperature, and treated with
concentrated aq potassium hydroxide to pH 5-6. The
reaction was extracted with several portions of ethyl
acetate, the organic layers were dried, filtered and
evaporated to yield crude 2-hydroxy-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-
yl-butyric acid: MS (M-H)- 261
Step G_Me~hvl 2-hvdroxv-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-vl-butyrate
To a stirred solution of 2-hydroxy-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-
yl-butyric acid (4.2 g, 16 mmol) in 80 mL of methanol
was added 2.5 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, and the
mixture was refluxed for two hours. The solvent was
removed in vacuo, and the residue was dissolved in ethyl
acetate and washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate,
and water. The combined organic phases were dried
(magnesium sulfate), filtered and evaporated to afford
crude product. This was purified by flash
chromatography on silica gel using gradient elution of
hexanes/ethyl acetate 9:1 to 8:1 to afford (a) pure
faster eluting diastereomer as a clear oil, (b} a
mixture of diastereomers and (c) slower eluting
diastereomer as pale yellow oil: MS (M+H)+ 277,
(M+NH4)+ 294
Steg H~ Methyl 2-(4-methoxvohenylsulfonvl)amino-4-
phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-butyrate
To a cooled (0°C) solution of triphenylphosphine (2.91
g, 11 mmol) in 10 mL of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran was
added diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (2.2 mL, 11.2 mmo1)
dropwise with stirring under Argon. After the white
solid complex precipitated, a solution of methyl 2-
hydroxy-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-butyrate (1.38 g, 5,mmol,
faster eluting diastereomer) in 12 mL of tetrahydrofuran
is added dropwise via cannula, followed by a solution of
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
125
N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-p-methoxybenzenesulfonamide
(3.06 g, 10.6 mmol) in 20 mL THF. The yellow-orange
reaction was warmed to ambient temperature and heated to
35°C for four days under an atmosphere of Argon until
all the hydroxy ester was consumed (TLC monitored). The
solvent was removed in vacuo and the off-white foam was
purified by flash chromatography on silica gel using a
gradient of 0-3~ ethyl acetate in 1:1 dichloromethane/
hexanes to afford pure methyl 2-(N-(tert-butoxy
carbonyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)amino)-4-phenyl-3-
thien-3-yl-butyrate as a white foam of a single
diastereomer: MS (M+H)+ 546, (M+NH4)+ 563
To a solution of methyl 2-(N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)amino)-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-
butyrate (910 mg, 1.65 mmol, single diastereomer) in
27.3 mL CHZC12 was added trifluoroacetic acid (13.6 mL).
The reaction was stirred for two hours at room
temperature before removing all volatiles and
azeotroping the residue with 2 by 20 mL portions of
toluene in vacuo to afford crude methyl 2-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)amino-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-butyrate as a
single diastereomer: MS (M+H)+ 446, (M+NH4)+ 463
Step I: Methyl 4-(N-carboxvmethyl-N-(4-methoxyphenvl
sulfonvl~l-amino)-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-vl-butyrate
To a cooled (0°C) solution of the crude methyl 2-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)amino-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-
butyrate (single diastereomer) in 60 mL of
tetrahydrofuran:N,N-dimethylformamide (2:1) was added a
solution of potassium bis-(trimethylsilyl)amide in
toluene (4.64 mL of a 0.5 M solution, 2.32 mmol)
dropwise with stirring under Argon. The solution was
stirred at 0°C for 15 minutes before addition of tert-
butyl bromoacetate (0.342 mL, 2.32 mmol). The reaction
was stirred overnight at ambient temperature, then
worked up by dilution with ethyl acetate and aqueous 2 M
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
126
ammonium chloride. The organic phase was washed with
saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate, dried, filtered
and evaporated to afford crude methyl 2-(N-(tert-
butoxycarbonylmethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
amino)-4-phenyl-3-thiophen-3-yl-butyrate as a mixture of
two diastereomers: MS (M+H)+ 560, (M+NH4)+ 577.
To a cooled (0°C) solution of the crude methyl 2-(N-
(tert-butoxycarbonylmethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
amino)-4-phenyl-3-thiophen-3-yl-butyrate in 50 mL CH2C12
was added 15 mL of trifluoroacetic acid. The reaction
was stirred at 0°C for 3 hours before removing all
volatiles and co-evaporation with 2 portions of 20 mL of
toluene. The crude product was purified by flash
chromatography on silica gel using a gradient of 0-7~
MeOH in CHZClz to afford methyl 4-(N-carboxymethyl-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-amino)-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-
butyrate as a mixture of the two diastereomers: MS
(M+H)+ 504, (M+NH4)+ 521
tep J~ Methvl 4-benzyl-6-(4-methoxvt~henvlsulfonvl)-8-
oxo-5 6 7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3,dlazepine-5-
parboxYlate~ and Methyl 4-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothienof2.3.-clpvridine-5-
carboxylate
To a stirred solution of methyl 4-(N-carboxymethyl-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-amino)-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-
butyrate (476 mg, 0.946 mmol) in 7.7 mL anhydrous
dichloromethane containing 22 uL of N,N-dimethylform-
amide was added oxalyl chloride (180 uL, 2 mmol)
dropwise under Argon. The clear yellow solution turned
turbid with evolution of gas. The reaction was stirred
for 2 hours at room temperature before cooling to -78°C
in an acetone/C02(s) bath. To the reaction was added
tin tetrachloride (151 uL, 1.29 mmol) dropwise. The
reaction turned brownish, and was allowed to warm slowly
overnight with stirring under Argon. To the dark-blue
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
127
reaction mixture was added 1N hydrochloric acid and
dichloromethane, and the aqueous layer was extracted
repeatedly with dichloromethane and ethyl acetate. The
combined organic layers were dried (sodium sulfate),
filtered and evaporated to afford a crude product. This
was purified by flash chromatography on silica gel to
afford the 6-membered ring product methyl 4-benzyl-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2.3.-c]
pyridine-5-carboxylate as a mixture of diastereomers (MS
M+H 458, M+NH4 475) and the 7-membered ring product
methyl 4-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-8-oxo-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-carboxylate
as a mixture of diastereomers (MS (M+H)+ 486, (M+NH4)+
503 ) .
Step K: 4-Benzvl-6-f4-methoxyghenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6.7-
tetrahvdrothienof2.3.-clpvridine-5-hydroxamic acid
To a stirred solution of methyl 4-benzyl-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2.3.-c]
pyridine-5-carboxylate (16.6 mg, 0.036 mmol) in 2 mL of
methanol was added 1 mL of 1N NaOH. The reaction was
stirred overnight at room temperature before removing
the methanol under reduced pressure. The aqueous
solution was acidified with 1N aqueous hydrochloric
acid, and extracted three times with ethyl acetate. The
combined organic layers were dried (sodium sulfate),
filtered, evaporated and dried by co-evaporation with
anhydrous toluene (twice) to afford crude 4-benzyl-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2.3.-c)
pyridine-5-carboxylic acid: MS (M-H}- 442
To a 0°C solution of 4-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2.3.-c]pyridine-5-
carboxylic acid (14 mg, 0.0316 mmol) in 1.5 mL of
dichloromethane was added hydroxylamine hydrochloride
(13.5 mg, 0.194 mmol), PyBroP (Bromo-tris-pyrrolidino-
phosphonium hexafluoro-phosphate, 45 mg, 0.0965 mmol)
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
128
and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (35 uL, 0.201 mmol) with
stirring under Argon. The reaction was warmed slowly to
room temperature overnight. To the reaction was added
1N hydrochloric acid, and the aqueous was extracted with
ethyl acetate. The crude product was purified by flash
chromatography on silica gel using hexanes-ethyl
acetate-acetic acid (5:5:0.1) to afford pure 4-trans-
benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro
thieno[2.3.-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid which was
characterized by NMR analysis to have trans
stereochemistry: (M+H)+ 459, (M+NH4)+ 476
Examgle 34
Alternative Pre~a~ation Qf Methyl 2-(4-methoxvphenyl
sulfonyl)aLnino-4-nhenyl-3-thien-3-yl-butyrate
Step A~ N-(3-Phenyl-2-thien-3-yl-propvlidene)-4-
methoxyphenylsulfonamide
To a solution of 15.0 g 3-phenyl-2-thien-3-yl-propion
aldehyde (69.4 mmol) in 300 mL of anhydrous toluene was
added 12.3 g of freshly activated powdered 5 A sieves,
400 mg of Amberlyst 15 resin and 18.2 g (97.2 mmol, 1.4
eq) of p-methoxyphenylsulfonamide. The reaction was
refluxed with a Dean-stark trap under Argon atmosphere
for two days. The reaction was filtered through a pad
of Celite and the filtrate was evaporated to dryness to
afford N-(3-phenyl-2-thien-3-yl-propylidene)-4-methoxy
phenylsulfonamide: MS (M+H)+ 386, (M+NH4)+ 403
Step B~ N-(1-Cyano-3-,phenyl-2-thien-3-ylpropvl)-4-
mPthoxvohenylsulfonamide
To a stirred solution of N-(3-phenyl-2-thien-3-yl-
propylidene)-4-methoxybenzenesulfonamide (16.6 g, 43.0
mmol) in 200 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide was added
potassium cyanide (18g, 289.7 mmol). The reaction was
stirred overnight at ambient temperature, followed by
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
129
heating to 75°C for two days. The reaction was diluted
with ethyl acetate, washed with 4 portions of 500 mL of
water, and the crude residue after filtration and
evaporation was purified by flash chromatography on
silica gel to afford N-(1-cyano-3-phenyl-2-thien-3-
ylpropyl)-4-methoxyphenylulfonamide as a mixture of
diastereomers: MS (M+H)+ 413, (M+NH4)+ 430
Step C: 2-!4-Methoxyphenvlsulfonylamino)-4-phenvl-3-
thien-3-yl-butyric acid
To a solution of 14.03 g of N-(1-cyano-3-phenyl-2-thien-
3-ylpropyl)-4-methoxyphenylsulfonamide (34.04 mmol) in
600 mL of dioxane was added 1.2 L of concentrated
hydrochloric acid. The reaction was heated to reflux
overnight, and after cooling, 150 mL of 10 N aq sodium
hydroxide was added to the reaction. The reaction
mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate and several
times with dichloromethane. The combined organic phases
were dried, filtered and evaporated to afford the crude
2-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonylamino)-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-
butyric acid as a mixture of diastereomers: MS (M+H)+
432, (M+NH4)+ 449
Step D: Methyl 2-(4-methoxvphenvlsulfonvl)amino-
phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-butyrate
To a solution of the crude 2-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl
amino)-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-butyric acid in 300 mL of
anhydrous methanol was added dropwise 1.5 mL of thionyl
chloride. The reaction was refluxed overnight with
stirring. The solvents were removed by rotary
evaporation, aqueous workup followed by azeotroping with
toluene afforded crude methyl 2-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)amino-4-phenyl-3-thien-3-yl-butyrate as a
mixture of diastereomers: MS (M+H)+ 446, (M+NH4)+ 463
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
130
OMe
Preparation of (+/-)-4-trans-Benzyl-6-(4-methoxy~henyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3-dlazepine-5-
hvdroxamic acid
Step A: Methyl 4-Beg-6-(4-methoxvnhenvlsulfonvl
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2.3-dlazepine-5-carboxvlate
To a stirred solution of methyl 4-benzyl-6-(4-methoxy-
phenylsulfonyl)-8-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno
[2,3,d]azepine-5-carboxylate (52.9 mg, 0.11 mmol) in 3
mL of dichloromethane was added 1.08 mL of trifluoro-
acetic acid, followed by 375 uL of triethylsilane. The
reaction was stirred for two days before removing all
volatiles in vacuo. The residue was dried by co-
evaporation with 2 portions of 10 mL of toluene and
purified by flash chromatography on silica gel to afford
methyl 4-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate: MS
(M+H)+ 472, (M+NH4)+ 489
Step B~ 4-Benzyl-6-(4-methoxyQhenylsulfonyl)-5 6~7 8-
tetra ~rdro-4H-thienof2 3-dlazepine-5-carboxylic acid
To a solution of methyl 4-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylate (24.8 mg, 0.053 mmol) in 2 mL of methanol
was added 2 mL of 1 N NaOH. The solution was stirred
overnight before removing all solvents in vacuo. The
aqueous solution was acidified with 1N hydrochloric acid
and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic phases
were dried, filtered and evaporated to afford crude 4-
benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
Example 35
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99106410 PCT/US98/16147
131
4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid: MS (M-H)-
456
~teb C~ 4-Benzvl-6-(4-methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)-5 6 7 8-
etrahvdro-4H-thienol2~ -~dlazepine-5-hvdroxamic acid
To a solution of 4-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic
acid (22.4 mg, 0.049 mmol) in 2.4 mL of anhydrous
dichloromethane cooled to 0°C was added hydroxylamine
hydrochloride (26 mg, 0.37 mmol), PyBrOP (Bromo-tris-
pyrrolidino-phosphonium hexafluorophosphate, 82 mg,
0.175 mmol), and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (75 uL, 0.43
mmol). The reaction was stirred overnight at room
temperature before adding 1 N hydrochloric acid and
extracting with dichloromethane and ethyl acetate. The
combined organic phases were dried (sodium sulfate),
filtered and evaporated. The crude product was purified
by flash chromatography using hexanes-ethyl acetate-
acetic acid (5:5:0.1) to afford 11.0 mg of pure (+/-)-4-
trans-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid:
MS (M+H)+ 473, (M+NH4)+ 490
OMe
Preparation of (+/-)-4-Benzyl-8-cis-hvdroxv-6-(4-
methoxvohenvlsulfor~yl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahvdro-4H-
~~iPno 2~3,dlazepine-5-hydroxamic acid
step A~ 4-Benzvl-9-(4-methoxy~Ohenylsulfonyl)-11-oxa-3-
thia-9-aza-tricyclof6.2.2.0~-~ldodgca-2(6),4-dien-12-one
Example 36
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/IJS98/16147
132
To a cooled (0°C) suspension of methyl 4-benzyl-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-8-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-carboxylate, as a mixture of two
diastereomers, (83.6 mg, 0.17 mmol) in 8 mL of anhydrous
methanol was added sodium borohydride (3.6 mg, 0.095
mmol). The reaction was stirred for one hour at O°C
before evaporating the methanol under reduced pressure.
The reaction was then partitioned between water and
ethyl acetate, and the crude product after evaporation
of the organic phases was purified by flash
chromatography to afford a diastereomeric mixture of
hydroxy methyl esters and the lactone 4-benzyl-9-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-11-oxa-3-thia-9-aza-tricyclo
[6.2.2.0~-~]dodeca-2(6),4-dien-12-one: (M+H)+ 456,
(M+NH4)+ 473
~~gp B, (+/-) 4-Benzvl-8-cis-hydroxv-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfg~vl)-5.6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thienof2.3,dlazenine-5-hydroxamic acid
To a solution of sodium methoxide (16 mg, 0.29 mmol) in
0.7 mL anhydrous methanol was added hydroxylamine
hydrochloride (20 mg, 0.28 mmol). After 2 hours
stirring at ambient temperature, the solid precipitate
was removed by filtration and the resulting solution was
added to 7-benzyl-9-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-11-oxa-3-
thia-9-aza-tricyclo[6.2.2.0~~~]c~odeca-2(6),4-dien-12-one
(6.3 mg, 0.013 mmol). The solution was stirred
overnight before removing all solvents. The residue was
diluted with ethyl acetate, washed with 1N HC1, dried
(sodium sulfate), filtered and evaporated. The crude
product was purified by flash chromatography to afford
4-benzyl-8-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid as
a single diastereomer: MS (M+H)+ 489, (M+NH4)+ 506
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
133
Example 37
Preparation of: 4-cis-Benzyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno(2,3,dlazepine-5-hydroxamic acid (the other
diastereomer)
Step A: Methyl 4-benzvl-8-hvdroxv-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonvl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahvdro-4H-thi~~a(2,3,dlazepine-5-
carboxylate
A solution of methyl 4-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-8-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno(2,3,-
d]azepine-5-carboxylate (the faster eluting
diastereomer, 330 mg, 0.68 mmol) in 68 mL of anhydrous
tetrahydrofuran was cooled to -78°C before addition of
L-Selectride (0.7 mL of a 1 M solution in
tetrahydrofuran, 0.7 mmol). After 20 minutes stirring
under Argon at -78°C, the reaction was quenched with
saturated aqueous ammonium chloride, then allowed to
warm to room temperature. The reaction was extracted
twice with ethyl acetate and the combined organic layers
were dried over sodium sulfate, filtered, evaporated and
purified by flash chromatography on silica gel (gradient
of 0-10~ ethyl acetate in 1:1 dichloromethane/hexanes)
to afford a faster eluting diastereomer (used
immediately in next step) and slower eluting
diastereomer of methyl 4-benzyl-8-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]
azepine-5-carboxylate: (M-H)- 486.
Step B-1~ 4-benzyl-8-(tert-butyldimethvlsilvloxy)-6-(4-
methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)-5 6'7,8-tetrahvdro-4H-
t-hienof2 3 dlazepine-5-carboxvlic acid (From Step A
Faster Diastereomer)
To a solution of the faster eluting diastereomer of
methyl 4-benzyl-8-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-carboxylate
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
134
(205 mg, 0.42 mmol) in 30 mL of methanol was added 18 mL
of 1N aqueous sodium hydroxide. The reaction was
stirred at room temperature overnight before evaporating
the methanol. The aqueous solution was acidified to pH
4 with 1N hydrochloric acid and extracted with ethyl
acetate several times. The combined organic layers were
dried (sodium sulfate), filtered and evaporated to yield
4-benzyl-8-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid as
a purple oil and dried by co-evaporation with toluene:
(M-H) - 472.
To a suspension of 4-benzyl-8-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid (0.42 mmol) in 20 mL of anhydrous
dichloromethane was added N,N-diisopropylethylamine
(0.63 mL, 0.62 mmol) and tert-butyldimethylsilyl
trifluoromethanesulfonate (0.557 mL, 0.42 mmol). The
solution was stirred overnight at room temperature
before adding saturated aqueous ammonium chloride. The
aqueous layer was extracted with dichloromethane and
ethyl acetate, and the combined organic layers were
dried (sodium sulfate), filtered and concentrated to an
oil. The oil was dissolved in 2.5 mL of methanol and
stirred with 290 mg (2 mmol) of anhydrous potassium
carbonate for 2 hours at ambient temperature. The
methanol was evaporated, aqueous ammonium chloride and
300 uL of glacial acetic acid were added (pH~5), and
extracted with several portions of ethyl acetate. The
combined organic layers were dried, filtered,
concentrated and chromatographed on silica gel (2-mm
Chromatotron plate using a gradient of 20 to 40o ethyl
acetate - 1~ acetic acid in hexanes) to yield a faster
eluting diastereomer and a slower eluting diastereomer
of 4-benzyl-8-(tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy)-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno(2,3,d]
azepine-5-carboxylic acid: (M-H)- 586, (M+NH4)+ 605.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
135
Step B-2~ 4-benzyl-8-(tert-butvldpethylsilvloxy)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thienof2,3,dlazepine-5-carboxvlic acid (From Steg A
Slower Di~stereomer)
Analogous procedures were carried out with the slower
eluting diastereomer of methyl 4-benzyl-8-hydroxy-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno
[2,3,d]azepine-5-carboxylate to yield a single
diastereomer of 4-benzyl-8-(tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy)-
6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3,d3azepine-5-carboxylic acid having an
identical NMR and TLC mobility to the faster eluting
diastereomer of Step B-1.
~t-Pp C-1~ 4-his-benzvl-8-~~s-(tert-butyldimethyl
silyloxy) -6- (4-methoxyphenylsulfonvl) -5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno~2 3 dlaze~ine-5-hydroxamic acid
(From Step B Faster Diastereomer)
4-Benzyl-8-(tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy)-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]
azepine-5-carboxylic acid (the faster eluting
diastereomer, 48 mg, 0.08 mmol) was dried by co-
evaporation with anhydrous toluene and dissolved in 4 mL
of anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide containing 0-tert-
butyldimethylsilyl hydroxylamine (77 mg, 0.52 mmol).
The solution was cooled to -20°C in an ice/methanol
bath. N,N-Diisopropylethylamine (0.075 mL, 0.37 mmol)
was added, followed by HATU (O-7-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-
yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate, 151
mg, 0.39 mmol). The yellow reaction solution was warmed
slowly and stirred overnight under Argon. The reaction
was quenched with saturated ammonium chloride containing
100 uL of acetic acid (pH ~4), and extracted twice with
ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers were dried
(sodium sulfate), filtered, concentrated and purified by
chromatography on silica gel (1-mm Chromatotron plate,
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
136
gradient of 0 to 3 ~ methanol in dichloromethane) to
afford 4-cis-benzyl-8-cis-(tert-butyldimethyl silyloxy)-
6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid.
Step C-2: 4-trans-benzyl-8-(tert-butvldimethvl
silyloxy) -6- (4-methoxyphenvlsulfonvl) -5 6 7 8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno 2 3 dlazepine-5-hydroxamic acid
(From Step B Slower Diastereomer)
Analogous procedures,were carried out with the slower
eluting diastereomer of 4-benzyl-8-(tert-butyldimethyl
silyloxy)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid to
yield 4-trans-benzyl-8-(tert-butyldimethyl silyloxy)-6-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid.
step D-1: 4-cis-benzyl-8-cis-(l~ydroxv)-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonvl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3,~11
~zepine-5-hvdroxamic acid (From Faster Diastereomer of
Step C)
To a solution of tetrabutylammonium fluoride in
tetrahydrofuran (0.5mL of a 1M solution) was added 15 uL
of glacial acetic acid. To a cooled (0°C) solution of
4-cis-benzyl-8-cis-(tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno
[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid (faster eluting
diastereomer, 35.9 mg, 0.06 mmol) in 8.6 mL of anhydrous
THF was added the tetrabutyl ammonium fluoride solution
buffered with acetic acid (0.16 mL, 0.16 mmol). The
reaction was allowed to stir and warm to ambient
temperature for five hours before diluting with ethyl
acetate and washing with saturated ammonium chloride.
The organic layer was dried (sodium sulfate), filtered,
evaporated and purified by silica gel chromatography (1-
mm Chromatotron plate, gr~.dient of 0 to 6~S methanol in
dichloromethane) to afford 4-cis-benzyl-8-cis-(hydroxy)-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
137
6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno
[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: (M-H)- 487, (M+NH4)+
506
Step D-2: 4-traps-benzvl-8-(hvdroxv)-6-(4-methoxvohenvl
sulfonvl)-5,6 7 8-tetrahvdro-4H-thienof2 3 dlazepine-5-
hvdroxamic acid (From Slower Diastereomer of Step C)
Analogous procedures were carried out with the slower
eluting diastereomer of 4-traps-benzyl-8-(tert-butyl
dimethylsilyloxy)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid to
yield 4-traps-benzyl-8-(tert-butyldimethyl silyloxy)-6-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydra-4H-
thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid.
Example 38
Preparation of Methvl 3-(4-Benzyl-thien-3-yl)-2-(tert-
butoxycarbonylamino)propionate
Stgp A~ 4-Benzyl-thio~hene-3-carboxaldeyde
3-Benzyl-4-bromo-thiophene (12.7g, 50.1 mmol) is
dissolved in 100 ml dry diethylether and cooled to
-70°C. Butyllithium (22.0 ml, 2.5 M in Hexane) is added
drop-wise at -70°C and the reaction is stirred for 5
minutes. Dimethylformamide (DMF) is added in one shot
and the reaction mixture is stirred for 15 min. and then
allowed to warm to 0°C. The reaction mixture is
quenched with water and neutralized. The organic phase
is separated and the water phase is extracted twice with
diethylether. The combined organic extracts are dried
with MgSOa, filtered and the solvent is evaporated.
Flash-chromatography, hexane/ethylacetate; 5:1 afforded
the product: Cal. 203.3, found (MH)'203. (MacDowell and
Wisowaty, J. Org. Chem. 1971, 36(26), 3999-4004)
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
138
Step B: Methyl 3-(4-benzvl-thien-3-vl)-2-ftert-
bu~c~xycarbonyl amino)acrvlate
Under an Argon blanket, sodium hydride (493 mg, 12.3
mmol) is suspended in dry hexane (20 ml) and dry
tetrahydrofuran (THF). The suspension is cooled to 0°C.
Methyl tert-butoxycarbonylamino-(dimethoxyphosphoryl)
acetate (3.33 g, 11.2 mmol) is dissolved in dry THF (20
ml) and added drop-wise to the reaction suspension. 4-
Benzyl-thiophene-3-carboxaldeyde (3.69 g, 11.2 mmol) is
dissolved in 20 ml THF and added drop-wise to the
reaction. The reaction is allowed to warm to room
temperature and is stirred for 3 h. After an aqueous
work up, the product is isolated from the organic phase
by flash-chromatography (Hexane/Ethylacetate; 6:1):
Cal. 374.5, found (MH)' 374.
Step C: Methyl 3-(4-Benzvl-thien-3-yl)-2-ltert-
butoxycarbonvlamino)propionate
Methyl 3-(4-benzyl-thien-3-yl)-2-(tert-butoxycarbonyl
amino)acrylate (3.43 g, 9.2 mmo1) is dissolved in 30 ml
benzene/ethanol 4:1. The reaction solution is
hydrogenated under shaking at 50°C at 60 psi using
Chlorotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I) (Wilkinson's
catalyst). Initially, 25~ (160 mg. 0.17 mmol) of the
total amount (640 mg, 0.69 mmol) of the Wilkinson's
catalyst is added and thereafter every 8-10 hours
another 25~ of the catalyst is added. The reaction is
complete after 48 hours. The solvent is evaporated and
the obtained dark oil is purified by flash-
chromatography, Hexane/Ethylacetate (gradient 5-18~):
Cal. 376.5, found (MH); 376.2.
Exam~~ ~ 3 9
4-Hydroxv-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5.6,7-
tetrahydro-thiPnof2,3-clgyridine-5-hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
139
HO
N~OH
I
1 N' ~ H ._
II ~ ~ OMe
O
Under an Argon atmosphere, 4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-
carboxylic acid (70 mg, 0.19 mmol) is dissolved in 3 ml
dimethylformamide (DMF) and cooled to -30°C. O-(tert-
Butyldimethylsilyl)hydroxylamine (36 mg, 0.24 mmol) and
Hunigs Base (50 ul, 0.24 mmol) are added and then O-(7-
azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium
hexafluorophosphate (HATU) (79 mg, 0.21 mmol) is added.
The reaction mixture is stirred for 15 min. and then
allowed to warm to room temp. (about 1h). The solvent
is evaporated at high vacuum and the obtained oil is
purified by flash-chromatography (CHC13/MeOH; 9:1,
followed by CHC13/MeOH, 9:1, cont. 1~ Acetic Acid):
Cal. 385.5, found (MH)'385.2.
Example 40
N,OH
I
H02C ~ I N~~ H -
II ~ ~ OMe
O
Preparation of 2-carboxy-5-(4-methox~rphenvlsulfond)
4,5.6,7-tetrahvdro-thienof2,3-clgyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid
Step A: 2-Iodo-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-4.5,6,7-
tetrahvdro-thienof3.2-clpvridine-6-carboxylic acid
5-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thieno(3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid (1.19 g, 3.4
mmol) is dissolved in 60 ml dry Tetrahydrofuran (THF)
and cooled to -78°C. A solution of lithium
diisopropylamide (3.55 ml, 7.1 mmol) in 5 ml THF is
added drop-wise to the reaction mixture. The reaction
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 14 0 PCT/US98/16147
is stirred for 20 min. Iodine (0.86 g, 3.4 mmol) in 20
ml THF is added drop-wise to the reaction solution. The
reaction is allowed to warm to room temp. (~1h) and is
quenched. with sat. NHQC1-solution. The organic phase is
separated and the water phase is extracted twice with
ethylacetate (50 ml). The water phase is acidified and
extracted one more time with ethylacetate. The combined
organic extracts are washed with sodium thiosulfate
solution, dried with MgS04, filtrated and the solvent is
evaporated in vacuo affording 2-iodo-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid as a yellow foam: ~H NMR (DMSO) 8 7.78
(d, 2H), 7.10(m, 3H), 5.0(d, 1H), 4.55(d, 1H), 4.3(d,
1H), 3.81(s, 3H), 3.2(m, 1H), 2.9(dd, 1H).
Stgp B~ 2-Iodo-5- (4-methoxy-phen~rlsulfonyl) -4 5 6 7-
tetrahvdro-thienof3 2-clovrid~ne-f~-carboxylic acid
benzhvdryloxy-amide
To 2-iodo-5-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid (1.62
g, 3.37 mmol) in 25 ml dry Dimethylformamide (DMF) is
added 0-benzhydryl-hydroxylamine (0.95 g, 4.05 mmol), 1-
hydroxyybenzotriazole (HOBt) (0.52 g, 3.37 mmol) and 1-
(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethyl-carbodiimide hydrogen
chloride (EDC) (0.78 g, 4.05 mmol). The reaction
mixture is stirred for 4 h at room temp. The reaction
mixture is concentrated in vacuo and the residue is
purified by flash chromatography (Hexane/Ethyl acetate;
3:2) affording 2-iodo-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid benzhydryloxy-amide: 1H NMR (DMSO) 8 11.25(s, 1H),
7.68(d, 2H), 7.3(m, 10H), 7.08(m, 3H), 5.75(s, 1H), 4.75
(d, 1H), 4.55(d, 1H), 4.35(d, 1H), 3.85(s, 3H), 2.75 (m,
2H) .
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
141
Step C: 2-(methoxycarbonyl)-5-(4-methoxvnhen~yl
sulfonvl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahvdro-thienof2 3-cl,pvridine-6-
carboxylic acid benzhydryloxy-amide
To 2-iodo-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid
benzhydryloxy-amide (140 mg, 0.21 mmol) in 10 ml
tetrahydrofuran/ methanol (1:1) is added triethylamine
(33 ul, 0.23 mmol) and the reaction solution is
deoxygenated and saturated with Argon. Tetrakis
(triphenylphosphine)palladium (0) (30 mg, 0.02 mmol) is
added and the reaction solution is saturated with carbon
monoxide (CO). The reaction is refluxed over night at
70°C. Evaporation of the solvents and flash-
chromatography (Hexane/Ethylacetate; 3:2) afforded 2-
(methoxycarbonyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid
benzhydryloxy-amide: Cal 593.7, found 592.8.
Step D: 2-lmethoxvcarbonyl)-5-(4-me~ho ~henvl
sulfonvl)-4.5,6,7-tetrahvdro-thienof2,3-clpvridine-6-
hydroxamic acid
To 2-(methoxycarbonyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid benzhydryloxy-amide (53 mg, 0.09 mmol) in
dichloromethane/trifluoroacetic acid (3:1, 4 ml) is
added triethylsilane (14.3 ul, 0.09 mmol) and the
reaction mixture is stirred for 1 h. The solvents are
evaporated and the residue is dissolved in DCM and mixed
with diethylether and hexane. A white precipitate
occurs which is filtered giving 2-(methoxycarbonyl)-5-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid as a white powder: Cal.
427.5, found (MH)' 427.
Step E: 2-carboxy-5-(4-methoxyt~henvlsylfonyl)-4,5,6,7
tetrahydro-thienof2,3-clpyridine-6-hydrc~xamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
I42
2-(Methoxycarbonyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid (20
mg, 0.047 mmol) in 4 ml tetrahydrofuran/water (1:1) is
stirred at room temp. for 1.5 h. The reaction mixture
is acidified with 2N HC1 to pH 3. The organic phase is
separated and the water phase is extracted twice with
ethyl acetate. The solvents are evaporated and the
remaining solid is lyophilized to yield 2-carboxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]
pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid: Cal. 412.5, found (MH)'
413Ø
Example 41
N, OH
\ ~ ' Nw O H OMe
-N fl \ /
0
Prpearation of 5- (4-me~hoxwhenylsulfonyl) -2-gyrid-2-yl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thienof3,2-clpvridine-~-hvdroxamic
ac'
Step A: 5-(4-methoxyghenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-2-yl-
4,5.6,7-tetrahydro-thienof3.2-c~pvridine-6-carboxylic
acid benzhvdryloxy-amide
Under an Argon atmosphere, 2-(tributylstannyl)pyridine
(920 mg, 2.5 mmol) in 10 ml Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is
cooled to -78°C. Butyllithium (1 ml, 2.5M) is added
drop-wise and the reaction mixture is stirred for 10
minutes. A ZnCl solution (5 ml, 0.5 M, 2.5 mmol) is
added. The reaction is allowed to warm room temp. and
added via syringe to 2-iodo-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid benzhydryloxy-amide (550 mg, 0.83 mmol) in 5 ml
THF/1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (4:1) containing 48 mg of
tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium (0). The reaction
mixture is stirred at room temp. for 1 h. 30 ml
Dichloromethane (DCM) and 30 ml sat. NH4C1 solution are
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/1614~
143
added. The organic phase is separated and the water
phase is extracted twice with DCM. The combined organic
fractions are dried with MgS04, followed by filtration,
evaporation of the solvents and flash-chromatography
(Hexane/Ethylacetate; 3:2) to yield 5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-2-pyrid-2-yl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid benzhydryloxy-amide.
Step B: 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl~-2-pyrid-2-yl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno ~,2-clpvridine-6-hvdroxamic
acid
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-2-yl-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid
benzhydryloxy-amide (200 mg, 0.33 mmol) treated in the
same manner as 2-(methoxycarbonyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid benzhydryloxy-amide to afford 5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-2-yl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid: Cal. 445.4,
found (MH)+ 445.8.
Example 42
N, OH
\ ~ ~ N~ ~ H oMe
N"' I \ /
0
Preparation of 5-(4-methoxy~heny~ulfonyl)-2-gvrid-2-yl-
4.5.6,7-tetrahydro-thienof3,2-~]gyridine-6-hvdroxamic
acid
Step A L 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-2-pyrid-3-vl-
4.5,6,7-tetrahydro-thienof~,2-cl~vridine-6-carboxylic
acid benzhydrvloxy-amide
Utilizing 3-(tributylstannyl)pyridine, 5-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-3-yl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno
[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid benzhydryloxy-amide is
prepared from 2-iodo-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
144
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid benzhydryloxy-amide (250 mg, 0.38 mmol) in the same
manner as 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-2-yl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid benzhydryloxy-amide. The product was purified by
flash chromatography (CHC13/MeOH; 19:1).
Step B: 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2~yrid-3-yl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thienof3,2-clpyri~ine-6-hydroxamic
aci
5-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-3-yl-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid was
prepared from 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-3-yl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid benzhydryloxy-amide (100 mg, 0.164 mmol) in the
same manner as 5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-2-yl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid. The product was purified by preparative thin
layer chromatography: Cal. 445.4, found (MH)'446Ø
Example 43
~ HO O
N~OH
O ~ -.
OMe
Pr~aration of 4-Hydroxy-3-benzyl-4-hvdroxv-6-(4-
methoxyghenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thienof2,3-
clpvridine-5-hydroxamic acid
Steo A:- 2-Amino--3-S4-benzvlthien-3-yl) -3-hydroxy-
propionic acid
To 4-benzyl-thiophen-3-carboxaldeyde (3 g, 14.84 mmol)
in 6 ml ethanol is added glycine (557 mg, 7.42 mmol) and
the reaction is cooled to 0°C. A cold solution of KOH
(832 mg, 14.84 mmol) in 4.5 ml ethanol is added in one
shot. The reaction is stirred for 2 h at 0°C and then
kept in a refrigerator over night. Hexane (50 ml) and
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98I16147
145
water (50 ml) are added and then 5 ml 1N HC1. A
precipitate formed between the organic and the water
phase. The suspension is filtered through a fritted
glass funnel and the collected solid is washed with
diethylether to yield 2-amino-3-(4-benzylthien-3-yl)-3-
hydroxy-propionic acid: Cal. 278.3, found (MH)' 278Ø
Step B: 3-Benzyl-4-hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thienof2,3-clpyridine-5-carboxylic acid
2-Amino-3-(4-benzylthien-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-propionic acid
(880 mg, 3.17 mmol) is suspended in 25.4 ml of 0.25 N
sulfuric acid and formaldehyde (2.57 ml, 12.33 M) was
added. The mixture was stirred for 2 h at room temp.
The reaction suspension is then filtered through a small
fritted glass funnel and the obtained white powder is
washed with diethylether and dried at high vacuum to
yield 3-benzyl-4-hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-
c]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid: Cal. 290.3, found (MH)+
290.2.
Step C: 3-Benzyl-4-hvdroxy-6-(4-methox~rphenvlsulfonvl)-
4.5,6,7-tetrahydro-thienof2,3-clgyridine-5-carboxylic
ac'
3-Benzyl-4-hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]
pyridine-5-carboxylic acid (642 mg, l.9 mmol) is
suspended in 8.54 ml of 1M Na2C03-solution. 4-Methoxy
benzenesulfonylchloride in 5 ml dioxane is added drop-
wise at room temperature over a time period of 6 hours.
The reaction suspension is stirred for another 6 h and
is then transferred into a separator funnel and 100 ml
water are added. The water phase is extracted twice
with ethyl acetate. The aqueous layer is acidified (pH
0-1, 6N HC1) and the water phase is extracted three more
times with ethyl acetate. The combined organic extracts
are dried with MgS04 and the solvent is evaporated to
give 3-benzyl-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
146
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylic
acid as an oil: Cal. 458.5, found (M-H)-458.2.
Stets D : 4 -Acetoxv- 3 -benzyl - 4 -hydroxy- 6 - ( 4 -methoxyphenyyi
sulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydro-thienof2 3-clpvridine-5-
carboxylic acid
3-Benzyl-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid (362
mg, 0.85 mmol) is acetylated with acetic anhydride as
described above and is purified by flash-chromatography
(CDC13/MeOH; 4:1) to yield 4-acetoxy-3-benzyl-4-hydroxy-
6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno
[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid: Cal. 500.6, found
(M-H) 500.
Step E: 4-Acetoxy-3-benzyl-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxvohenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thienof2,3-cl~vridine-5-
hvdroxamic acid
A solution of 4-acetoxy-3-benzyl-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]
pyridine=5-carboxylic acid (59 mg, 0.12 mmol) in 4 ml
dichloromethane (DCM) is cooled to 0°C under an Argon
blanket. Hydroxylamine hydrochloride salt (163 mg, 2.35
mmol) is added followed by the drop-wise addition of
triethylamine (246u1, 1.76 mmol). Bromo-tris-
pyrrolidino-phosphonium hexafluorophosphate (PyBrop) (83
mg, 2.35 mmol) is then added. The reaction is stirred
at 0°C for 60 min. The solvents are evaporated and the
residue is purified by preparative thin layer
chromatography (CHC13/MeOH; 9:1) to yield 4-acetoxy-3-
benzyl-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid: Cal.
516.5, found (MH)+515.2.
Stex~ F: 4-Hvdroxy-3-benzyl-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxvnhenyl
sulfonvl)-4.5,6,7-tetrahydro-thienof2,3-cl,pyridine-5-
hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
147
To 4-Acetoxy-3-benzyl-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-
hydroxamic acid (40 mg, 0.097 mmol) in 2 ml methanol is
added 600 ul of a 20~ KZC03-solution. The reaction is
stirred at room temp. for 45 min. The product is
purification by preparative thin layer chromatography
(CHC13/ MeOH; 6:1) to afford 4-hydroxy-3-benzyl-4-
hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thieno [2,3-c]pyridine-5- hydroxamic acid: Cal. 475.5,
found (MH)' 474.8; 1H NMR (DMSO) 8 10.55 (s, 1H) , 8.75 (s,
1H), 7.65 (d, 2H), 7.28 Hz (t, 2H), 7.2 (m, 1H), 7.1 (d,
2H), 7.05 (d, 2H), 6.65 (s, 1H), 5.7 (d, 1H), 4.62 (m,
3H), 4.5 (d, 1H), 3.9 (dd, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H).
Example 44
~H ~ OH
/ ~.,'~N'
I
S~N\q H -
OMe
O
Preparation of cis - (+/ - ) - 4 -Hvdroxv- 6 - ( 4 -methoxypher~yl
sul f onvl ) - 5 , 6 . 7 , 8 - tetrahvdro - 4H - thienoL2 , 3- dl azepine - 5 -
hydroxamic
Step A: Methyl l4-Methox henylsulfonylamino)acetate
Glycine methyl ester hydrochloride (25 g, 0.2 mol) was
dissolved in 200-mL of anhydrous methylene chloride.
The solution was cooled to 0°C on ice. Triethylamine
(40.5 g, 0.4 mol) was added and the solution allowed to
stir for an additional 15 minutes. 4-Methoxybenzene
sulfonyl chloride was added and the reaction allowed to
warm slowly to room temperature and stir overnight. The
reaction mixture was washed twice with 2M ammonium
chloride then brine. The organic layer was dried over
sodium sulfate, filtered, evaporated to dryness and
purified by column chromatography (silica gel, 30~ ethyl
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
148
acetate in hexanes) to yield the product as a white
crystalline solid: MS: (M+H)+ 260, (M+NH4)+ 277.
,~~gp B~ Methvl N-(2-(3-bromothiP~-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-
methoxv ~nylsulfonyl)aminoacetate
To a solution of 3-bromo-2-(2-hydroxyethyl)thiophene
(2.07 g, 10 mmol) in THF (100 mL) was added methyl (4-
methoxyphenylsulfonylamino)acetate (3 g, 11.6 mmol) and
triphenylphosphine (3.18 g, 12.1 mmol). This solution
was then cooled to 0°C and treated over 10 minutes with
diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (2.37 mL, 12 mmol). The
cooling bath was removed and the mixture was stirred for
24 hrs at 25°C. The solvent was removed in vacuo and
the residue was reconstituted in ethyl acetate. The
solution was then washed with saturated aqueous sodium
bicarbonate, HzO, and brine. The organic layer was
dried (NaZSOQ), concentrated, and purified by column
chromatography (silica, 5~ ethyl acetate in toluene) to
give methyl N-(2-(3-bromothien-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate: MS: (M+H)+ 448, 450,
(M+NH4)+ 465, 467; 'H NMR (CDC13) 8 7.78 (d, 2H) , 7.14 (d,
1H), 6.96 (d, 2H), 6.9 (d, 1H), 4.06 (s, 2H), 3.87 (s,
3H), 3.65 (s, 3H), 3.46 (dd, 2H), 3.07 (d, 2H).
~rPo C~ Methyl N-(4-methoxyghenylsulfonyl)-N-(2-(3-
vinylthien-2-yl)ethyl)aminoacetate
Methyl N- (2- (3-bromothien-2-yl) ethyl) -N- (4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate (1.86 g, 4.15 mmol) in
toluene (28 mL) was treated with tributyl(vinyl)tin (3.1
mL, 10.6 mmol). The solution was heated to reflex for 5
minutes and then treated with dichlorbis(triphenyl
phosphine)palladium (II) (250 mg, 0.36 mmol). The
reaction mixture was stirred at reflex for 18 hrs and
then cooled to 25°C. The mixture was diluted with
diethyl ether and treated with 10~ aqueous potassium
fluoride for 30 minutes. Filtration through a plug of
celite removed solids. The liquid phases of the
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99J06410 PCT/US98/16147
149
filtrate were separated and the organic layer was washed
with 10~ aqueous potassium fluoride, dried (Na2SOQ) and
concentrated. The tan oil was purified by flash
chromatography (silica, 25 to 40~ ethyl acetate in
hexanes) to give methyl N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-N-
(2-(3-vinylthien-2-yl)ethyl)aminoacetate; 1H NMR (CDC13)
8 7.75 (d, 2H), 7.13 (d, 1H), 7.05 (d, 1H), 6.94 (d,
2H), 6.64 (dd, 1H), 5.51 (dd, 1H), 5.21 (dd, 1H), 4.00
(s, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.62 (s, 3H), 3.36 (dd, 2H), 3.11
(dd, 2H).
Step D: Methyl N-(2-(3-formylthien-2-vl)ethyl)-N-(4-
methoxvnhenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate
To a solution of methyl N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-N-
(2-(3-vinylthien-2-yl)ethyl)aminoacetate (0.195 g, 0.49
mmol) dissolved in THF and HZO (4:1, 6 mL} was added a
2.5 wt.~ solution of osmium tetroxide in 2-methyl-2-
propanol (0.25 mL, 0.02 mmol) and sodium metaperiodate
(130 mg, 0.6 mmol). The reaction mixture turned black
and a white precipitate formed. The mixture was then
treated with a second portion of sodium metaperiodate
(130 mg, 0.6 mmol) and stirred for 30 minutes at 25 °C.
The THF was then evaporated and the mixture was diluted
with Ha0 and the product was extracted into ethyl
acetate. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried
(MgS04), concentrated and purified by column
chromatography (silica, 25 to 50~ ethyl acetate in
hexanes) to give methyl N-(2-(3-formylthien-2-yl)ethyl}-
N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl) aminoacetate: 1H NMR (CDC13)
8 9.94 (s, 1H), 7.75 (d, 2H), 7.36 (d, 1H), 7.13 (d,
1H), 6.93 (d, 2H), 4.07 (s, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.63 (s,
3H), 3.46 (s, 4H).
~p E; N- (2- (3-formylthien-2-yl)ethvl) -N- (4-
methoxyghenvlsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid
To a solution of methyl N-(2-(3-formylthien-2-yl)ethyl)-
N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate (300 mg, 0.76
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
150
mmol) in THF (8 mL) at 0°C was added 1N aqueous KOH (1
mL, 1 mmol). The reaction mixture was allowed to warm
to 25°C over 1.5 hrs and then the THF was removed in
vacuo. Dilution with H20 was followed by extraction with
ethyl acetate and back extraction of the organic layer
with 0.5N aqueous KOH. The combined aqueous layers were
acidified with 1N aqueous HC1 (to pH 2) to give a white
precipitate that was extracted into ethyl acetate. The
organic layer was dried (Na2SOa) and concentrated to give
N-(2-(3-formylthien-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)aminoacetic acid: 1H NMR (CDC13) b 9.91 (s,
1H), 7.73 (d, 2H), 7.35 (d, 1H), 7.13 (d, 1H), 6.93 (d,
2H), 4.10 (s, 2H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.46 (s, 4H).
Stgp F: tert-butyldimethylsilyl N-(2-(3-formvlthien-2-
Y1)ethvl)-N-l4-methox henylsulfonylLaminoacetate
To a solution of N- (2- (3-formylthien-2-yl) ethyl) -N- (4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid (260 mg, 0.68
mmol) dissolved in dichloromethane and N,N-dimethyl
formamide (7:1, 5.7 mL) was added imidazole (56 mg, 0.82
mmol) and tert-butyldimethylsilyl chloride (124 mg, 0.82
mmol). The reaction mixture was allowed to stir at 25°C
for 1.33 hrs, a white precipitate formed. This mixture
was diluted with diethyl ether and washed with saturated
aqueous potassium bisulfate, saturated aqueous sodium
bicarbonate, and brine. The organic phase was dried
(Na,S04), concentrated, and co-distilled with toluene to
give tert-butyldimethylsilyl N-(2-(3-formylthien-2-yl)
ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate, which
was carried to the next step without further
purification: 1H NMR (CDC13) 8 9.95 (s, 1H) , 7.74 (d,
2H), 7.36 (d, 1H), 7.12 (d, 1H), 6.92 (d, 2H), 4.04 (s,
2H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.48 (m, 4H), 0.89 (s, 9H), 0.21 (2,
6H) .
~tP~ G~ cis-(+/-)-4-(tert-butyldimethylsilanvlo~r)-6-
(4-methox5rohenvlsulfonyl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
151
the eno (2 3 -dl a~ebine- 5 -c~boxylic acid and trans - (+/ - ) -
4-ftert-butvldimethvlsilanylo~)-6-l4-methoxyphenvl
sulfonvl)-5,6,7.8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno(2 3-dlazepine-5-
~arboxylic acid
To a solution of crude tert-butyldimethylsilyl N-(2-(3-
formylthien-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)amino
acetate (313 mg, 0.63 mmol} in THF (5 mL) at -78°C was
added dropwise a 0.5 M solution of KHMDS in toluene (1.4
mL, 0.7 mmol). The reaction mixture was slowly warmed
to -60°C over 1.5 hrs and then diluted with ethyl
acetate. This mixture was poured onto a 1 to 1 mixture
of Ha0 and saturated aqueous ammonium chloride. After
separation the organic layer was washed with HZO and
brine, dried (Na2S0Q) and concentrated. The residue was
purified by column chromatography (silica, 2.5 to 10~
methanol in methylene chloride) to give cis-(+/-)-4-
(tert-butyldimethylsilanyloxy)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid and trans-(+/-)-4-(tert-butyldimethyl
silanyloxy)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid:
MS (cis) : (M+H)+ 498, (M+NH4)+ 515 and MS (trans) : (M+H)+
498, (M+NH4)+ 515.
Steo H: cis-(+,/-)-4-(tert-butyldimethvlsilanyloxv)-6-
Ls4-methox~henyl ul Qnyl)-5,6.7.8-tetrahvdro-4H-
thieno(2.3-dlazenine-5-hydroxamic acid
A solution of cis-(+/-)-4-(tent-butyldimethyl
silanyloxy)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid (50
mg, 0.1 mmol) in CHZC12 (2 mL) at 0°C was treated
sequentially with hydroxylamine hydrochloride (22 mg,
0.32 mmol), diisapropylethylamine (72 ~,L, 0.41 mmol),
and PyBroP (57 mg, 0.12 mmol). The mixture was allowed
to warm to 25°C over 2 hrs and was then concentrated.
The residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate and the
remaining solids were filtered off through a plug of
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
152
cotton. The filtrate was washed with brine, 1N aqueous
HCl, and brine again. The organic phase was then dried
(Na2S04), concentrated, and purified by column
chromatography (silica, 2.5~ methanol in methylene
chloride) to give cis-(+/-)-4-(tert-butyldimethyl
silanyloxy)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid:
MS(cis): (M-H) 511.
Step I~ cis-(+/-)-4-Hydroxv-6-(4-methpxvohenyl
~ulfonvl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2 3-d]azepine-5-
hvdroxamic acid
To a stirred solution of crude cis-(+/-)-4-(tert-butyl
dimethylsilanyloxy)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid (43
mg, 0.084 mmol) dissolved in THF (3 mL) at 0°C was added
a 1 M solution of TBAF in THF (0.17 mL, 0.17 mmol). The
reaction mixture was stirred for 15 minutes and then
diluted with ethyl acetate. This solution was washed
with 1 M aqueous HC1 and H20, dried (NazSOa) and
concentrated. The residue was purified by column
chromatography (silica, 2.5 to 10~ methanol in methylene
chloride) to give cis-(+/-)-4-Hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
hydroxamic acid: MS(cis): (M-H) 397.
Exams a 4 5
OH
OH
/ ~.w~N~
1
S~ N'~ H -
OMe
0
Preparation of trans-(+/-)-4-Hvdroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2 3-dlazPpine-5
hydroxamic acid
trans-(+/-)-4-Hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
153
acid was prepared from trans-(+/-)-4-(tert-butyldimethyl
silanyloxy)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid in
the same manner as cis-(+/-)-4-Hydroxy-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: MS: (M+NH4)+ 416.
Examt~le 46
OMe
Preparation of trans-(+/-)-4-(2-(3 5-Dimethylphenvl)
~thvl)-6-l4-methoxyphen~lsulfonyl)-5 6 7 8-tetrah~dro-
4H-thienof2 3-dlazepine-5-hydroxami~ acid
step A- Methyl N-(2-f3-(3-(tert-butvldimethvlsilanvl
oxv)propenyl)thien-2-yl~ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenvl
sulfonyl)aminoacetate
Methyl N-(2-(3-bromothien-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate (4.83 g, 10.8 mmol) in
toluene (65 mL) was treated with (Z)-1-(tri-n-butyl
stannyl)-3-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]-1-
propene (5.8 g, 12.6 mmol). This solution was heated to
reflux for 5 minutes and then treated with dichlorbis
(triphenylphosphine)palladium (II) (605 mg, 0.86 mmol).
The reaction mixture was stirred at reflux for 2 hrs and
then cooled to 25°C. The mixture was diluted with
diethyl ether and treated with 105 aqueous potassium
fluoride for 1 hr. Filtration through a plug of celite
removed the solids. The liquid phases of the filtrate
were separated and the organic layer was washed with 10~
aqueous potassium fluoride, dried (Na,SOa) and
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
154
concentrated. The tan oil was purified by flash
chromatography (silica, 10 to 25~a ethyl acetate in
hexanes) to give Methyl N-(2-{3-(3-(tert-butyldimethyl
silanyloxy)propenyl)thien-2-yl}ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl) aminoacetate: 1H NMR (CDC13) 8 7.78 (d, 2H) ,
7.09 (d, 1H), 6.96 (d, 2H), 6.89 (d, 1H), 6.29 (m, 1H),
5.76 (m, 1H), 4.33 (dd, 2H), 4.02 (s, 2H), 3.87 (s, 3H),
3.64 (s, 3H), 3.38 (m, 2H), 3.06 (m, 2H).
Step B: N-(2-(3-(3-(tert-butvldimethvlsilanyl
oxvLp~_penyl ) thien- 2 -vl ~ ethyl ) -N- ( 4 -methoxyph~nyl
s~lfonyl)aminoacetic acid
To a stirred solution of methyl N-(2-{3-(3-(tert-butyl
dimethylsilanyloxy)propenyl)thien-2-yl}ethyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate (4.33 g, 8 mmol) in
THF (80 mL) at 0°C was added 1 N LiOH (l2 mL). The
reaction mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C and was
stirred for 3 hrs. The THF was removed under reduced
pressure and the reaction mixture was diluted with water
and acidified with 1N aqueous HC1 (12 mL). The white
precipitate was extracted into ethyl acetate (2x) and
the combined organic layers were dried (NaaSOQ) and
concentrated to give crude N-(2-{3-(3-(tert-butyl
dimethylsilanyl oxy)propenyl)thien-2-yl}ethyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid, which was
carried onto the next step without purification: 1H NMR
(CDC13) 7.77 (d, 2H), 7.10 (d,1H), 6.96 (d, 2H), 6.8E
S
(d, 1H),6.29 (m, 1H), 5.76 (m,1H), 4.33 (d, 2H), 4.00
(s, 2H),3.87 (s, 3H), 3.41 (m,2H), 3.06 (m, 2H).
Step C~ N-(2-f3-(3-hydroxypro~enyl)thien-2-vllethvl)-N-
(4-methoxyl~henylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid
To a stirred solution of crude N-(2-{3-(3-(tert-butyl
dimethylsilanyloxy)propenyl)thien-2-yl}ethyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid (4.4 g, 8 mmol)
in THF (70 mL) at 0°C was added a 1 M solution of TBAF
in THF (16 mL, 16 mmol). The reaction mixture was
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
155
allowed to warm to 25°C and was stirred for 5 hrs. The
THF was removed under reduced pressure and the residue
was redissolved in ethyl acetate. This solution was
washed with 1N aqueous HC1, water, and brine. The
organic phase was then dried (NaaSO,) and concentrated to
give a tan oil, which solidified upon trituration with
diethyl ether. The solid product was collected and
rinsed with cold diethyl ether to give N-(2-{3-(3-
hydroxypropenyl) thien-2-yl}ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl) aminoacetic acid: 1H NMR (CDC13) s 7.75 (d,
2H), 7.11 (d, 1H), 6.96 (d, 2H), 6.85 (d, 1H), 6.38 (d,
1H), 5.84 (m, 1H), 4.29 (d, 2H), 3.95 (s, 2H), 3.86 (s,
3H), 3.43 (m, 2H), 3.07 (m, 2H).
,step D: 10- (4-meth2xy~henylsulfonyl) -9, 10, 11, 12-tetra
hvdro-6H-7-oxa-1-thia-10-aza-cyclop~ntacycloundecen-8-
on
A solution of N-(2-{3-(3-hydroxypropenyl)thien-2-yl}
ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid (1.45
g, 3.5 mmol) in acetonitrile (25 mL) was treated with
triethylamine (3.9 mL, 28.1 mmol). This solution was
slowly added (15 hrs, via syringe pump) to a solution of
2-chloro-1-methylpyridinium iodide in acetonitrile (500
mL) heated at reflux. The reaction mixture was heated
another 5 hrs at reflux and then the acetonitrile was
evaporated. The residue was suspended in ethyl acetate
and the solid by-products were removed via filtration.
The filtrate was concentrated and the crude product was
purified by flash chromatography (silica, 25 to 40~
ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give 10-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-9,10,11,12-tetrahydro-6H-7-oxa-1-thia-10-aza-
cyclopentacycloundecen-8-one: MS: (M+H)+ 394, (M+NH4)+
411.
~te-p E~ tert-butyldimethylsily_1 cis- (+/-) -6- (4-methoxv
ghenylsulfonvl)-4-vinyl-5 6 7 8-tetrahvdro-4H-
thieno~2 3-dlazepine-5-carboxylate and cis- (+/-) -6- (4-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
156
methoxvnhenyl sulfonyl~-4-vinvl-5.6,7.$-tetrahydro-4H-
thienof2.3-dl azepine-5-carboxylic acid
To a solution of 10-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
9,10,11,12-tetrahydro-6H-7-oxa-1-thia-10-aza-
cyclopentacycloundecen-8-one (1.31 g, 3.3 mmol) in THF
(33 mL) at -78°C was added TBSOTf (0.8 mL, 3.5 mmol)
followed immediately by a 0.5 M solution of KHMDS in
toluene (7 mL, 3.5 mmol). The cooling bath was then
removed and the reaction mixture was allowed to warm to
25°C, over 30 minutes. This room temperature mixture
was then heated to reflux for 4 hrs. The mixture was
cooled to 25°C and poured onto a mixture of ethyl
acetate and saturated aqueous NH4C1. The layers were
separated and the organic phase was washed with H20 and
brine and then dried (Na,S04) and concentrated. The
residue was purified by flash chromatography (silica, 25
to 50'-k ethyl acetate in hexanes followed by 5 to 10~
methanol in methylene chloride) to give tert-butyl
dimethylsilyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylate: 1H NMR (CDC13) 8 7.74 (d, 2H), 6.99-6.90
(m, 3H) , 6.81 (d, 1H) , 6.47 (m, 1H) , 5.27 (d, 1H) , 5.23
(d, 1H), 4.90 (d, 1H), 4.02-3.95 (m, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H),
3.55 (m, 1H), 3.13 (m, 1H), 2.94 (m, 1H), 0.84 (s, 9H),
0.07 (s, 3H), 0.04 (s, 3H); and cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno
[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid: MS: (M+H)+ 394,
(M+NH4 ) + 411.
~fi-ep F~ cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxvnhenvlsulfonvl)-4-vinvl-
5.6.7,8-tetrahvciro-4H-~hienof2.3-dlazeoine-5-carboxylic
_~cid
To a solution of tert-butyldimethylsilyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno [2, 3-dJ azepine-5-carboxylate (72 mg, 0.14 mmol) in
methanol and THF (3:1, 2.4 mL) at 0°C was added a
solution of KzCO, (60 mg, 0.43 mmol) in H20 (0.6 mL) .
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
157
The cloudy reaction mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C
over 30 minutes and was then concentrated to 1/4th of
the original volume. Dilution with Hz0 and
acidification with 1N HC1 (to pH 2j gave a white
precipitate that was extracted into ethyl acetate. The
organic phase was dried (Na2S04) and concentrated to give
cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid (57
mg, 0.14 mmol), which was carried to the next step
without further purification: MS: (M+H)+ 394, (M+NH4)+
411.
Step G: Methyl cis-(+/-1-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
vinvl-5.6.7,8-tetrahvdro-4H-thienof2.3-dlazepine-5-
carboxylate
To a solution of crude cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]
azepine-5-carboxylic acid (53 mg, 0.13 mmol) in benzene,
methylene chloride and methanol (3:2:2, 1.75 mL) at 0°C
was added a 2 M solution of TMSCHNz (0.135 mL, 0.27
mmol) in hexanes. The reaction mixture was stirred 15
minutes and then the solvents were removed under reduced
pressure to give methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3
d]azepine-5-carboxylate as a clear oil: MS: (M+H)+ 408,
(M+NH4)+ 425.
~,~~p H- Methvl cis- (+/-) -4- (2- (3 5-dimethvlphenyl)
ethvl)-6-(4-methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)-5.6.7.8-tetrahvdro-
4H-thienof2,3-dlazepine-5-carboxylate
To a solution of methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]
azepine-5-carboxylate (55 mg, 0.13 mmol) in THF (1.25
mL) at 0°C was added a 0.5 M solution of 9-BBN (0.5 mL,
0.25 mmol) in THF. The reaction mixture was allowed to
warm to 25°C over 4 hrs and was then treated
sequentially with PdClz(dppf)~CHZCla (16 mg, 0.02 mmol),
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
158
5-iodo-m-xylene (0.15 mL, 1 mmol), K2C03 (86 mg, 0.62
mmol) , DMF (1 mL) , and H20 (0.1 mL) . After stirring 5
minutes at 25°C, the solution was diluted with diethyl
ether and washed with H20, 1N aqueous HC1, saturated
aqueous NaHC03, and brine. The organic layer was dried
(Na2S04), concentrated, and purified by column
chromatography (silica, 3~ ethyl acetate in toluene) to
give methyl cis-(+/-)-4-(2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)ethyl)-6-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno
[2, 3-d] azepine-5-carboxylate: MS: (M+H)+ 514, (M+NH4)+
531.
SteQ,I: trans-(+/-)-4-(2-13.5-dimethylphenvl)ethyl)-6-
(4-methoxwhenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7.8-tetrahydro-4H-
thienof2,3-dlazepine-5-carboxylic acid
To a solution of methyl cis-(+/-)-4-(2-(3,5-dimethyl
phenyl)ethyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate (25 mg,
0.049 mmol) in THF and HZO (3:1, 2 mL) was added 1N
aqueous LiOH (0.25 mL, 0.25 mmol). The reaction mixture
was heated to reflux for 7 hrs and then the THF was
removed in vacuo. Dilution with H20 followed by
acidification with 1N aqueous HCl gave a white
precipitate that was extracted into ethyl acetate. The
organic layer was then washed with H20 and brine, dried
(Na2S0,) and concentrated to give the crude traps- (+/-) -
4 - ( 2 - ( 3 , 5 - dimethylphenyl ) ethyl ) - 6 - ( 4 -methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid: MS: (M-H) 498.
~tgp J- traps- (+/-,~-4- (2- l3 5-dimethylphenvl) ethyl) -6-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfon~l)-5.6.7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thienof2,3-dlazepin~-5-hvdroxamic acid
A solution of traps-(+/-)-4-(2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)
ethyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid (23 mg, 0.046
mmol) in CHaCl2 (1.5 mL) at 0°C was treated sequentially
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
159
with hydroxylamine hydrochloride (10 mg, 0.14 mmol),
diisopropylethylamine (35 ~.L, 0.2 mmol), and PyBroP (26
mg, 0.056 mmol). The mixture was allowed to warm to
25°C over 2.5 hrs and was then concentrated. The
residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate and the remaining
solids were removed via filtration. The filtrate was
washed with brine, 1N aqueous HC1, and brine again. The
organic phase was then dried (Na~SOa), concentrated, and
purified by column chromatography (silica, 2.5~ methanol
in methylene chloride) to give trans-(+/-)-4-(2-(3,5-
dimethylphenyl)ethyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid: MS: (M+H)+ 515, (M+NH9)+ 532.
Example 47
Prer~ar~tion of Methvl trans-l+/-)-6-(4-methoxvnhenvl
sulfonyl)-4-l3-methylbutyl)-5,6,7.8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno~2,3-dlazeQine-5-carboxylate
To a solution of methyl trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-(3-methylbut-3-enyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate (39 mg, 0.087 mmol)
in benzene (1 mL) was added chlorotris(triphenyl
phosphine)rhodium(I) (16 mg, 0.017 mmol). The reaction
flask was evacuated and flushed with nitrogen (3X) and
hydrogen (3X) each, and finally stirred under an
atmosphere of hydrogen gas for 3 hrs. The solvent was
evaporated in vacuo and the residue was purified by
column chromatography (silica, 15 to 25~ ethyl acetate
in hexanes) to give methyl trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4-(3-methylbutyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-dJazepine-5-carboxylate: MS: (M+H)+ 452,
( M+NH4 ) + 4 6 9 .
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
160
Exam_ble 48
Preparation of Methyl trans - (+/ - ) - 4 - ( 2 - ( 3 - (hvdroxv
methyl)pphenyl}ethyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahvdro-4H-thieno[2,3-dlazepine-5-carboxvlate
Methyl trans-(+/-)-4-(2-(3-formylphenyl)ethyl)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-carboxylate in THF at 0°C was treated with
sodium borohydride to give methyl trans-(+/-)-4-(2-{3-
(hydroxymethyl)phenyl}-ethyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylate: MS: (M+H)+ 516, (M+NH4)+ 533.
Example 49
Utilizing the procedures of Examples 1-48, the
compounds of Table I were prepared.
TABLE I
trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid: MS (M+H) + 487, (M+NH4) + 504 .
trans- (+/-) -6- (4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl) -4- [2- (4-
trifluoromethylphenyl)ethyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: MS (M-H) 553.
trans- (+/-) -4- [2- (4-chlorophenyl)ethyl] -6- (4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]
azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: MS (M+H)+ 521 and 523,
(M+NH4)+ 538 and 540.
trans- (+/-) -6- (4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl) -4- [2- (4-methoxy
phenyl)ethyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]
azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: MS (M+H)+ 517, (M+NH4)+ 534.
trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-[2-(3-methoxy
phenyl)ethyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]
azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: MS (M+H)+ 517, (M+NH4)+ 534.
E-trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-(4-phenyl
but-3-enyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-
5-hydroxamic acid: MS (M+H)+ 513, (M+NH4)+ 530.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
161
trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-(3-methylbut-
3-enyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
hydroxamic acid: MS (M+H)+ 451, (M+NH4)+ 468.
trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-(3-methyl
butyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
hydroxamic acid: MS (M+H)+ 453, (M+NH4)+ 470.
trans - (+/ - ) - 4 - [2 - ( 3 -hydroxymethylphenyl ) ethyl ] - 6 - ( 4 -
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: MS (M+H)+ 517, (M+NHg)+
534.
OMe
Preparation of trans-(+/-)-~,-(4-methoxvnhenylsulfonyl)-
~-(2-methoxyethvl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3-
dlazepine-5-hvdroxamic acid
Step A: Methyl cis- (+/-) -4- (2-hydro~ethyyl) -6- (4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3-
dlazepine-5-carboxylate and 6-(4-methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)-
5,6,6a,9,10,10a- exahydro-4H-8-oxa-3-thia-6-aza-
benz~elazulen-7-one
To a solution of methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-carboxylate (39 mg, 0.096 mmol) in THF (2
mL) at 0°C was added a 0.5 M solution of 9-BBN (0.38 mL,
0.19 mmol) in THF. The reaction mixture was allowed to
warm to 25°C over 2.5 hrs and was then cooled to 0°C.
This solution was slowly treated with Hz0 (1 mL)
followed by NaBO,~4Hz0 and stirred 2.5 hrs. The mixture
was then poured onto a solution of cold brine and
diluted with diethyl ether. After separation, the
organic phase was washed with H20 and brine, dried
(Na2S0,), concentrated, and purified by column
Example 50
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
162
chromatography (silica, 50 to 75~ ethyl acetate in
hexanes) to give the higher Rf 6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl}-5,6,6a,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-8-oxa-3-thia-6-
aza-Benz [e] azulen-7-one: MS: (M+H) i 394, (M+NH9) a 411;
and the lower Rf methyl cis-(+/-)-4-(2-hydroxyethyl}-6-
(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate: MS: (M+H)' 426,
( M+NH, ) + 4 4 3 .
Step B: Methyl cis-(+/-)-6-14-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
(2-methoxyethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetraY~ydro-4H-thienof2,3-
dlazepine-5-carboxylatg
To a vigorously stirred solution of crude methyl cis
(+/-)-4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate
(45 mg, 0.106 mmol} in methylene chloride (1 mL) at 0°C
was added a 48~ aqueous solution of HBFQ (15 ~L, 0.11
mmol). The mixture was treated with a 2 M solution of
TMSCHNz (0.4 mL, 0.8 mmol) in hexanes until TLC (silica,
50~ ethyl acetate in hexanes) anlysis indicated the
starting material had been consumed. The reaction
mixture was stirred a total of 1.5 hrs and was then
diluted with methylene chloride. This mixture was
washed with Hz0 (3X) , dried (NaZSOa) , concentrated, and
purified by column chromatography (silica, 25 to 37.5
ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-
methoxy phenylsulfonyl)-4-(2-methoxyethyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate: MS:
(M+H)' 440, (M+NH')' 457.
~~ep C~ trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxy,~henylsulfonyl)-4-~2-
mPthoxyethvl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2 3-
dlazepine-5-carboxylic acid
To a solution of methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-(2-methoxyethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate (41 mg, 0.09 mmol)
dissolved in THF and HZO (3:1, 2 mL) was added 1N LiOH
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US9$/16147
163
(0.27 mL, 0.27 mmol). The reaction mixture was heated
to reflux for 14 hrs and then the THF was removed in
vacuo. Dilution with H20 followed by acidification with
1N aqueous HC1 gave a white precipitate that was
extracted into ethyl acetate. The organic layer was
then washed with H20 and brine, dried (NaZSOa) and
concentrated to give crude traps-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4-(2-methoxyethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid: MS: (M+H)'
426, (M+NHd) ~ 443 .
Step D: trans-l+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-4-(2-
methoxyethvl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno~2,3-
dlaze~in~-5-hydroxamic acid
A solution of trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
(2-methoxyethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3-d]
azepine-5-carboxylic acid (34 mg, 0.08 mmol) in CHZC12 (2
mL) at 0°C was treated sequentially with hydroxylamine
hydrochloride (18 mg, 0.26 mmol), diisopropylethylamine
(57 ~,L, 0.33 mmol), and PyBroP (45 mg, 0.097 mmol).
This mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C over 1.5 hrs
and was then concentrated. The residue was dissolved in
ethyl acetate and the remaining solids were removed via
filtration. The filtrate was washed with brine, 1 N
HC1, and brine again. The organic phase was then dried
(NasSOa), concentrated, and purified by column
chromatography (silica, 2.5~ methanol in methylene
chloride) to give traps-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-(2-methoxyethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: MS: (M-H) 439.
Example 51
Preparation ofcis- (+/-) -4- f2-hydroxyethvll -6- (4-methoxv
phenylsulfonvl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno(2 3-
3 5 dl azegine- 5 -hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
164
N, OH
I
H
OMe
0
To a solution of 6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,6a,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-8-oxa-3-thia-6-aza-
benz[e]azulen-7-one (15 mg, 0.038 mmol) in
dichloroethane (0.7 mL) was added hydroxylamine
hydrochloride (13 mg, 0.19 mmol), diisopropylethylamine
(35 ~.L, 0.2 mmol), and N,N-dimethylformamide (3 drops).
The reaction mixture was heated to reflux for 8 hrs and
then treated with additional quantities of hydroxylamine
hydrochloride (25 mg, 0.36 mmol) and diisopropylethyl
amine (70 ~L, 0.4 mmol) at reflux. The mixture was
stirred another 1 hr at reflux and then concentrated to
remove the dichloroethane. The residue was dissolved in
ethyl acetate and washed with H20, 1 M aqueous HC1, and
brine. The organic phase was dried (Na2S0,),
concentrated, and purified by column chromatography
(silica, 1:10:190 acetic acid: methanol:methylene
chloride) to give a mixture of higher Rf cis and trans-
(+/-)-4-[2-hydroxy ethyl]-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic
acids and the lower Rf cis-(+/-)-4-[2-hydroxyethyl]-6-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno
[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: MS: (M-H)~ 425.
Examgle 52
/ N~OH
I
S~N~ S H OMe
It
0
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
165
Preparation of cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxy~henylsulfonyl)-4-
vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3-dlazeoine-5-
hydroxamic acid
A solution of cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid (17 mg, 0.043 mmol) in CHZC12 (1 mL) at
0°C was treated sequentially with hydroxylamine
hydrochloride (9 mg, 0.13 mmol), diisopropylethylamine
(30 ~L, 0.17 mmol), and PyBroP (25 mg, 0.054 mmol).
This mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C over 5 hrs and
was then concentrated. The residue was dissolved in
ethyl acetate and the remaining solids were removed via
filtration. The filtrate was washed with brine, 1 M
aqueous HC1, and brine again. The organic phase was
then dried (NazS04), concentrated, and purified by column
chromatography (silica, 5 to 10~ methanol in methylene
chloride to 1:10:90 acetic acid: methanol:methylene
chloride) to give cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
hydroxamic acid: MS: (M-H)- 407.
Examplg 53
O
~ OH
I
N H -
J \ I 1 ~ ~ OMe
O
Preparation of trans- (+/-) -6- (4-methoxtnohenvlsulfonyl) -
4-(ohenylsulfan~lmethyl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-
thienof2 3-dlazpx~ine-5-hYdroxamic acid
.tep A: cis-l+/-)-1-hvdroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxy~yl
~ulfonyl)-1 3a 4 5 6 9b-hexahvdro-2-oxa-7-thia-4-aza-
~yclopentafelazulen-3-one
To a solution of methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d] azepine-5-carboxylate (805 mg, 2 mmol) in THF and H20
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
166
(2:1, 10 mL) was added a 2.5 wt.~ solution of osmium
tetroxide in 2-methyl-2-propanol (0.32 mL, 0.026 mmol)
and 4-methylmorpholine N-oxide (360 mg, 3.1 mmol). The
reaction mixture was stirred for 20 hrs at 25°C. The
THF was then evaporated and the mixture was diluted with
H20. The excess oxidant was reduced with a 0.4 M
aqueous solution of Na2S03 (50 mL) and the product was
extracted into ethyl acetate. The organic layer was
washed with brine, dried (NaaSO,), concentrated and
purified by column chromatography (silica, 50 to 75~
ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give a higher Rf
diasteriomer of cis-(+/-)-1-hydroxymethyl-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-1,3a,4,5,6,9b-hexahydro-2-oxa-7-
thia-4-aza-cyclopenta[e]azulen-3-one: MS: (M+H)' 410,
(M+TTH9)' 427; and a lower Rf diasteriomer of cis- (+/-) -1-
hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-1,3a,4,5,6,9b-
hexahydro-2-oxa-7-thia-4-aza-cyclopenta[e]azulen-3-one:
1H NMR (CDC13) 8 7.66 (d, 2H) , 7.05 (d, 1H) , 6.90 (d,
2H), 6.66 (d, 1H), 5.46 (d, 1H), 4.74 (m, 1H), 4.21 (dd,
1H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 3.81 (dd, 1H), 3.58 (m, 1H), 3.49 (m,
1H), 3.35 (m, 1H), 2.88 (m, 2H), 1.55 (m, 1H).
Step B: cis-(+/-)-4-(1,2-dihydroxyPthyl)-6-(4-
methoxyghenylsulfonvl)-5.6,7.8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3-
dlazepine-5-car$oxylic acid
To a solution of cis-(+/-)-1-hydroxymethyl-4-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-1,3a,4,5,6,9b-hexahydro-2-oxa-7-
thia-4-aza-cyclopenta[e]azulen-3-one, a mixture of
diastereomers, (375 mg, 0.92 mmol) in THF and HZO (3:1,
12 mL) at 0°C was added 1N aqueous LiOH (2.25 mL, 2.25
mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred 15 minutes and
then the THF was removed in vacuo. Dilution with H20
followed by acidification with 2 M aqueous HCl (to pH 2)
gave a white precipitate that was extracted into ethyl
acetate (2X). The organic layers were combined and
washed with HZO and brine. The ethyl acetate phase was
then dried (NazSOa) and concentrated to give crude cis-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
167
(+/-)-4-(1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid: 1H NMR (DMSO-d6) 8 12.55 (bs, 1H), 7.73
(d, 2H), 7.11 (d, 1H), 7.05 (d, 2H), 6.82 (d, 1H), 5.56
(d, 1H), 4.55 (m, 1H), 4.26 (m, 1H), 3.87 (m, 1H), 3.80
(s, 3H), 3.51 (m, 1H), 3.35-3.17 (m, 2H), 3.01 (d, 1H),
2.84 (dd, 1H), 2.69 (m, 1H). The crude product could be
crystallized from methylene chloride to give a pure
white solid, free of residual acid, which can induce
relactonization in subsequent steps.
Step C: (+/-)-1-hvdroxv-4-(4-methoxyghenylsulfonvl)-
1.3a.4,5.6.9b-hexahydro-2-oxa-7-thia-4-aza-
cyclopenta[e]azulen-3-one
To a solution of cis-(+/-)-4-(1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid, a single diastereomer, (37
mg, 0.087 mmol) dissolved in THF (1 mL) at 0°C was added
a 0.38 M solution of sodium metaperiodate (0.5 mL, 0.19
mmol) in HzO. After 5 minutes a white precipitate
formed. The reaction mixture was stirred a total of 15
minutes and then concentrated. The residue was poured
onto a mixture of ethyl acetate and H,0 and then
separated. The organic layer was washed with brine,
dried (Na2S0a) and concentrated to give (+/-)-1-hydroxy-
4-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-1,3a,4,5,6,9b-hexahydro-2-
oxa-7-thia-4-aza-cyclopenta[e]azulen-3-one as a 4 to 1
mixture: 1H NMR (CDC13, data only given for the major
isomer) 8 7.71 (d, 2H), 7.07 (d, 1H), 6.92 (d, 2H), 6.79
(d, 1H), 5.73 (s, 1H), 5.60 (d, 1H), 4.19 (bs, 1H), 3.96
(d, 1H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 3.85 (m, 1H), 3.48 (m, 1H),
3.00-2.88 (m, 2H).
Step D: cis-(+/-)-4-hydrox5rnnethyl-6-(4-methoxvnhenvl
sulfon~l)-5.6.7.8-tetrahvdro-4H-thiQno(2.3-dlazepine-5-
carbox~lic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
168
To a solution of 1-hydroxy-4-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
1,3a,4,5,6,9b-hexahydro-2-oxa-7-thia-4-aza-cyclopenta
[e]azulen-3-one (as a 4 to 1 mixture of lactols) (30 mg,
0.076 mmol) in THF (1.5 mL) at 0°C was added sodium
borohydride (4 mg, 0.1 mmol). The reaction mixture was
stirred 30 minutes and then concentrated. The residue
was reconstituted in ethyl acetate and washed with 1N
aqueous HC1 and HaO. The organic layer was then dried
(Na2S0,) and concentrated to give a 10 to 1 mixture of
cis-(+/-)-4-hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic
acid and the corresponding 'y-lactone: MS: (M+H)+ 398,
( M+NHa ) ~ 415 . .
Step E~ Methyl cis-l+/-)-4-h~droxy_methyl-6-(4-methoxv
p enylsulfonvl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienol2 3-
dlazepine-5-carboxylate
To a solution of the 10 to 1 mixture of cis-(+/-)-4-
hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid and
the corresponding y-lactone (30 mg, 0.076 mmol) in
benzene and methanol (2:1, 1.5 mL) at 0°C was added a 2
M solution of TMSCHN, (0.1 mL, 0.2 mmol) in hexanes.
The reaction mixture was stirred 15 minutes and then the
solvents were removed under reduced pressure to give a 5
to 1 mixture of methyl cis-(+/-)-4-hydroxymethyl-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-carboxylate and the corresponding y-lactone:
1H NMR (CDC13) 8 7.78 (d, 2H) , 6.98 (d, 1H) , 6.96 (d,
2H), 6.81 (d, 1H), 5.35 (d, 1H), 4.34-4.20 (m, 2H), 4.05
(m, 1H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 3.47 (m, 1H), 3.40 (s, 3H), 3.34
(m, 1H), 3.11 (m, 1H), 2.94 (dd, 1H), 1.95 (dd, 1H).
+ -6- 4- 1 n
phenylsulfanvlmethyl-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2 3-
dl azepine- 5 - carboxylate and methy~L trans - (+/ - ) - 6 - ( 4 -
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
169
methoxwhenylsulfonvl)-4-ohenvlsulfanylmet 1-5 6 7 8-
tetrahvdro-4H-thienof2,3-dlaze~2~ne-5-carboxvlate
To a solution of the 5 to 1 mixture of methyl (+/-)-4-
hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate and the
corresponding y-lactone (40 mg, 0.097 mmol) in THF (1
mL) was added diphenyl sulfide (62 mg, 0.28 mmol) and
tri-n-butylphosphine (0.1 mL, 0.4 mmol). The solution
was stirred 15 hrs at 25°C. TLC analysis (505 ethyl
acetate in hexanes) indicated residual starting
materials present so the mixture was heated to reflux
and additional quantities of diphenyl sulfide (40 mg,
0.18 mmol) and tri-n-butylphosphine (0.05 mL, 0.2 mmol)
were added. The reaction mixture was heated at reflux
for 8 hrs and then cooled anddiluted with diethyl ether.
This solution was washed with H20 and brine, dried
(NaZSO,) and concentrated. The crude product was
purified by column chromatography (silica, 15 to 25~
ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give methyl cis and trans-
(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenylsulfanyl
methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylate as a 2.5 to 1 mixture: MS: (M+H)' 504,
( M+NHQ ) + 5 21 .
Step G~ trans- (+/-) -6- (4-methoxy)~henylsulfonyl) -4-
phenylsulfanvlmethvl-5,6,7,8-tetrahvdro-4H-thienof2,3-
dlaz~pine-5-carboxylic acid
A mixture of methyl cis and trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4-phenylsulfanylmethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate was
hydrolyzed with 1N LiOH as described above to give
trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenylsulfanyl
methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid as a single isomer: MS: (M-H)- 488.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
170
Step H: trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxvbenz~nesulfonyl)-4-
henylsulfanylmethyl-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2 3-
dlazepine-5-hydroxamic acid
Trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenylsulfanyl
methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
hydroxamic acid was prepared from trans-(+/-)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenylsulfanylmethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid in
the same manner as trans-(+/-)-4-[2-(3,5-dimethyl
phenyl)-ethyl]-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid:
MS: (M+H)+ 505, (M+NH,)+ 522.
~xamble 54
HO O
/ N~ OH
S L/N 0 H -
OMe
I I
O
Preparation of trans-(+/-)-4-hydrox et 1-6-(4-
methox~phenvlsulfonyl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahy~o-4H-thienof2 3-
dl azegine- 5 -hvdroxamic acid
~.~e_p A~ Methyl traps-(+/-)-4-(1 2-dihydroxvethyl)-6-(4-
mPthoxyghenylsulfon~rl)-5 6 7 8-tetrah~dro-4H-thienof2 3-
dl aze~i.ne- 5 - carboxvlate
Methyl trans-(+/-)-4-(1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]
azepine-5-carboxylate, as a mixture of diastereomers,
was prepared from methyl traps-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]
azepine-5-carboxylate in the same manner as cis-(+/-)-1-
hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-1,3a,4,5,6,9b-
hexahydro-2-oxa-7-thia-4-aza-cyclopenta[e]azulen-3-one.
Diastereomer products, epimeric at the secondary alcohol
center: MS (isomer 1) : (M+H)' 442, (M+NH4)i 459; MS
(isomer 2) : (M+H)' 442, (M+NH,)' 459.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
171
Step B: Methyl trans-(+/-)-4-formvl-6-(4-methoxvphenvl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahvdro-4H-thieno~2,3-d azepine-5-
carboxvlate
Methyl trans-(+/-)-4-formyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate
was prepared from methyl traps-(+/-)-4-(1,2-dihydroxy
ethyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate, a mixture of
diastereomers, in the same manner as (+/-)-1-hydroxy-4-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-1,3a,4,5,6,9b-hexahydro-2-oxa-
7-thia-4-aza-cyclopenta[e]azulen-3-one: 1H NMR (CDC13,)
8 9.83 (s, 1H), 7.78 (d, 2H), 7.03 (d, 1H), 6.97 (d,
2H), 6.79 (d, 1H), 5.77 (d, 1H), 4.45 (d, 1H), 3.87 (s,
3H), 3.85 (m, 1H), 3.54 (s, 3H), 3.30 (m, 1H). 2.98 (m,
1H) , 2.86 (m, 1H) .
tep C~ Methyl trans-(+/-)-4-hydroxymethvl-6-(4-methoxv
ghenvlsulfonyl) -5~ 6 7 8-tetral!~ydro-4H-thieno f2 3-
dlazepine-5-carboxvlate
Methyl trans-(+/-)-4-hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylate was prepared from methyl traps-(+/-)-4-
formyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate in the same manner
as cis-(+/-)-4-hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid: MS: (M+H)' 412, (M+NH,)+ 429.
~rPp D Met~l traps-(+/-)-4- pert-butyldimethvlsilanyl
~ymethvl)-6-(4-methoxyghenylsulfonvl)-5 6 7,8-
tetrahvdro-4H-thienof2 3-dlaz~pine-5-carboxylat~
To a solution of methyl traps-(+/-)-4-hydroxymethyl-6-
(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate (36 mg, 0.088 mmol)
in N,N-dimethylformamide (0.5 mL) at 0°C was added
imidazole (7 mg, 0.1 mmol) and tert-butyldimethylsilyl
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
172
chloride (15 mg, 0.1 mmol). The reaction mixture was
allowed to warm to 25°C and was stirred 6 hrs. This
mixture was diluted with diethyl ether and washed with
saturated aqueous potassium bisulfate, saturated aqueous
sodium bicarbonate, and brine. The organic phase was
dried (Na2S0,) and concentrated to give methyl trans-(+/-
-4-(tert-butyldimethylsilanyl oxymethyl)-6-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno [2, 3-d] azepine-5-carboxylate: 'H NMR (CDC13) 8
7.81 (d, 2H), 6.94 (d, 2H), 6.91 (d, 1H), 6.79 (d, 1H),
5.43 (d, 1H), 3.91 (dd, 1H), 3.87 (m, 1H), 3.86 (s, 3H),
3.75 (m, 1H), 3.68 (m, 1H), 3.51 (s, 3H), 3.26 (m, 1H),
3.03 (m, 1H), 2.78 (m, 1H), 0.90 (s, 9H), 0.05 (s, 3H),
0.01 (s, 3H).
Stex~ E~ trans- (+/-) -4- (tert-butyldimethylsilanyloxy
methyl)-6-(4-methoxy~~hen~lsulfonYl)-5 6 7,8-tetrahvdro-
4H-thienof2 3-dlazepine-5-carboxy_lic acid
Trans-(+/-)-4-(tert-butyldimethylsilanyloxymethyl)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid was prepared from methyl
trans-(+/-)-4-(tert-butyldimethylsilanyloxymethyl)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-carboxylate in the same manner as trans-
(+/-)-4-(2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)ethyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid: MS: (M+H)+ 512, (M+NHQ)+ 529.
Step F trans (+/ )-4-(tgrt-butvldimethylsilanyloxv
methyl)-6-(4-methoxvi~henvlsulfonyl)-5 6,7 8-tetrahydro-
4H-thieno~2 3-dlazegine-5-hvdroxamic acid
Trans-(+/-)-4-(tert-butyldimethylsilanyloxymethyl)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid was prepared from trans-
(+/-)-4-(tert-butyldimethylsilanyloxymethyl)-6-(4-
methoxy phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno
[2,3-d] azepine-5-carboxylic acid in the same manner as
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
173
traps - (+/ - ) - 4 - ( 2 - ( 3 , 5 - dimethylphenyl ) ethyl ) - 6 - ( 4 -
methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]
azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: MS: (M+H)~ 527, (M+NH~)' 544.
Step G: trans-(+/-)-4-hydroxyethyl-6-(4-methoxvohenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetra~dro-4H-thienof2,3-dlazepine-5-
hydroxamic acid
Trans-(+/-)-4-hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid was prepared from traps-(+/-)-4-(tert-butyldimethyl
silanyloxymethyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid in
the same manner as N-(2-{3-(3-hydroxypropenyl)thien-2-
yl}ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid.
The crude product was purified by trituration with
diethyl ether to an off-white solid: MS: (M-H)~ 411.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
174
Examt~le 55
S N, OH
I
N~ O H
II ~ ~ 0Me
HO O
Preparation of cis-(+/-)-4-Hvdroxv-6-(4-m~thoxyphenyl
sulfonvl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3-dlazepine-7-
hvdroxamic acid
Stets A: M~ h~2-amino-3-thien-2-vl-t~ropionate~HC1
3-(2-Thienyl)-DL-alanine (0.486 g, 2.84 mmoL) was
suspended in methanol (4 mL) and hydrogen chloride gas
was introduced into the mixture at 25°C until a clear
solution formed. The solution was diluted with
additional methanol (8 mL) and heated at reflux for 22
hrs. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and
the resulting residue was reconstituted in methanol and
the solvent was again removed under reduced pressure.
The white solid was purified by recrystallization from
methanol-ether to give methyl 2-amino-3-thien-2-yl-
propionate~HC1: 1H NMR (DzO, 400 MHz), ppm: 7.50 (d, 1H),
7.00 (d, 1H), 4.60 (d, 1H), 4.40(d, 1H). 4.38 (dd, 1H),
3.62 (dd, 1H), 3.39 (dd, 1H).
~rPp B Meth5rl 2 (4 methoxwhenylsulfonylamino) -3-thien-
2-yl-propionate
To a solution of methyl 2-amino-3-thiophen-2-yl-
propionate~HC1 (1 g, 4.51 mmoL) in N,N-dimethylformamide
(10 mL) at 0°C was added diisopropylethylamine (1.7 mL,
9.8 mmoL), 4-methoxybenzenesulfonyl chloride (1.12 g,
5.4 mmoL) and a catalytic amount of 4-
dimethylaminopyridine (55 mg, 0.45 mmoL). The reaction
mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C and was stirred for
1.5 hrs. The mixture was then poured onto HZO and ethyl
acetate and separated. The organic phase was washed
with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate, 1 M aqueous
HC1, and brine, dried (NaZSO,), and concentrated to give
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
175
methyl 2-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonylamino)-3-thien-2-yl-
propionate: MS: (M+H)+ 356, (M+NH4)+ 373.
Step C: Methyl 2-(N-(tert-butoxvcarbonv~met yl)-N-(4-
methoxy~henylsulfonvl)amino)-3-thien-2-yl-propionate
To a solution of methyl 2-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonylamino)-3-thien-2-yl-propionate
(1.82 g, 5.13 mmoL) in N,N-dimethylformamide (12 mL) was
added tert-butyl bromoacetate (0.8 mL, 5.4 mmoL) and
potassium carbonate (0.78 g, 5.6 mmoL). The reaction
mixture was heated to 70°C for 1 hr and was then poured
onto H20 and ethyl acetate and separated. The organic
phase was dried (Na,S04) and concentrated to give methyl
2-(N-(tert-butoxycarbonylmethyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)amino)-3-thien-2-yl-propionate,
which was carried to the next step without further
purification: 1H NMR (CDC13, 400 MHz), ppm: 7.82 (d,
2H), 7.10 (dd, 1H), 6.92 (d, 2H), 6.85 (dd, 1H), 6.77
(d, 1H), 4.55 (dd, 1H), 4.05 (ABq, 2H). 3.84 (s, 3H),
3.49 (s, 3H), 3.33 (dd, 1H), 3.15 (dd, 1H), 1.44 (s,
9H) .
~~p D ~ Methyl 2 - (N- (carbox5rnnethyl ) -N- (4 -methoxvbhenvl
sulfonyl)amino)-'~ thien-2-vl-propionate
To a solution of crude methyl 2-(N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl
methyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)amino)-3-thien-2-yl-
propionate in methylene chloride (22 mL) at 0°C was
added trifuoroacetic acid (7 mL). The reaction mixture
was stirred for 1 hr at 0°C, concentrated and co-
evaporated with toluene. The residue was purified by
column chromatography (silica, 5 to 10~ methanol in
methylene chloride to give methyl 2-(N-(carboxymethyl)-
N-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)amino)-3-thien-2-yl-
propionate: 1H NMR (CDC13, 400 MHz), ppm: 7.74 (d, 2H),
7.02 (d, 1H), 6.85 (d, 2H), 6.76 (bs, 1H), 6.69 (bs,
1H), 4.62 (m, 1H), 4.04 (m, 2H), 3.77 (s, 3H), 3.53 (s,
3H), 3.36 (m, 1H), 3.17 (m, 1H).
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
176
Step E: Methvl l+/-)-6-(4-methQxvphenylsulfonyl)-4-oxo-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2.3-dlazepine-7-carboxvlate
To a solution of methyl 2-(N-(carboxymethyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)amino)-3-thien-2-yl-propionate
(1.5 g, 3.63 mmoL) in methylene chloride (18 mL) at 0°C
was added oxalyl chloride (0.4 mL, 4.59 mmoL), and a
catalytic amount of N,N-dimethylformamide (0.1 mL). The
reaction mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C over 1.5
hrs and was then cooled to -10°C and treated with a
solution of tin(IV) tetrachloride (0.55 mL, 4.7 mmoL) in
methylene chloride (5 mL). The reaction mixture was
allowed to warm to -3°C over 2.5 hrs, diluted with
methylene chloride and washed with 1N aqueous HCl. The
organic layer was then dried (MgSO,), concentrated, and
purified by column chromatography (silica, 50o ethyl
acetate in hexanes) to give methyl (+/-)-6-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-carboxylate: MS: (M+H)+ 396,
2 0 ( M+NH4 ) + 413 .
Step F~ Methyl ci~-(+/-)-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenvl
sulfonyl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2 3-dlazepine-7-
car oxyl~te
Methyl cis-(+/-)-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-carboxylate
was prepared from methyl (+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-7-carboxylate in the same manner as cis-(+/-)-
4-hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid.
The product was purified by column chromatography
(silica, 2.5~ methanol in methylene chloride): MS:
(M+H)+ 398, (M+NH4)+ 415.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
177
Steg G: cis-(+/-)-4-Hydroxy-6-(4-methoxvohenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahvdro-4H-thienof2,3-dlazepine-7-carboxylic
aci
Methyl cis-(+/-)-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-carboxylate
was hydroyzed with aqueous LiOH as described above to
give cis-(+/-)-4-Hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-carboxylic
acid: MS: (M+H)+ 384, (M+NH4)+ 401.
Step H: 9-(4-methoxv~ohenylsulfonyl)-11-oxa-5-thia-9-aza-
tricyclo [6.2.20°'°1 dodeca-2 (6) , 3-dien-12-one
A solution of cis-(+/-)-4-Hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-
carboxylic acid (100 mg, 0.26 mmoL) in N,N-dimethyl
formamide (5 mL) was treated with 1-hydroxybenzotriazole
hydrate (40 mg, 0.3 mmoL). The solution was cooled to
0°C and treated with 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-
ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (55 mg, 0.29 mmoL). The
reaction mixture was allowed to warm to 20°C and was
stirred for 1.5 hrs. This mixture was diluted with
ethyl acetate and washed with saturated aqueous NaHC03,
0.5 M aqueous HC1, and water. The organic phase was
dried (NaZS04) and concentrated to give the 9-(4-
methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-11-oxa-5-thia-9-aza-
tricyclo [6.2.20°'°] dodeca-2 (6) , 3-then-12-one: 'H NMR
(CDC13, 400 MHz), ppm: 7.75 (d, 2H), 7.17 (d, 1H), 6.98
(d, 2H), 6.81 (d, 1H), 5.38 (dd, 1H), 5.00 (dd, 1H),
3.90 (m, 1H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 3.57 (dd, 1H), 3.52 (dd,
1H) , 3.41 (dd, 1H) .
Step I~ cis-(+/-)-4-H d'L roxy-6-(4-methoxvt~henylsulfonyl)-
5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2 3-dlazepine-7-hvdroxamic
acid
cis-(+/-)-4-Hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid was
prepared from 9-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-11-oxa-5-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCTNS98/16147
178
thia-9-aza-tricyclo [6.2.20°'°] dodeca-2 (6) , 3-dien-12-one
in the same manner as cis-(+/-)-4-[2-hydroxyethyl]-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid. The product was purified
by column chromatography (silica, 2.5 to 5% methanol in
methylene chloride): MS: (M+H)+ 399, (M+NH4)+ 416.
Example 56
N, OH
I
Nw 0 H -
II ~ / OMe
Me0 O
Preparation of cis-(+/-)-4-methoxv-6-(4-methoxvphenvl
sulfonyl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienoL2.3-dlazepine-7-
hvdroxamic acid
cis-(+/-)-4-Methoxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid was
prepared from methyl cis-(+/-)-4-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]
azepine-7-carboxylate in the same manner as traps-(+/-)-
6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-(2-methoxyethyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-dlazepine-5-hydroxamic acid:
MS (M+H)+ 413.
Examplg 57
OMe
0 O
S N, OH
I
N~ 0 H -
II ~ /
Preparation of (+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-4-oxo
~ 6 7 8-tetrahvdro-4H-thieno(2 3-dlazepine-7-hvdroxamic
ac'
(+/-)-6-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-oxo-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid was
prepared from methyl (+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
179
carboxylate in the same manner as trans-(+/-)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-(2-methoxyethyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid:
MS (M+H) + 397, (M+NH4) + 414 .
Example 5 8
OMe
0
S N, OH
I N,o g
l
Preparation of (+/-)-6-(4-methoxyghenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3-dlazegine-7-hydroxamic
acid
Step A: Methyl (+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7.8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-dlazepine-7-carboxylate
Methyl (+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-oxo-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-carboxylate (70 mg,
0.18 mmoL) was treated with trifluoroacetic acid (0.27
mL, 3.54 mmoL) and triethylsilane (0.085 mL, 0.531 mmoL)
at 25°C. The reaction mixture was heated to 50°C for 45
minutes, cooled to 25°C, and then concentrated. The
residue was co-evaporated with toluene (2X) and purified
by column chromatography (silica, 25~ ethyl acetate in
hexanes) to give methyl (+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-
carboxylate: 'H NMR (CDC13, 400 MHz), ppm: 7.78 (d, 2H),
6.97 (d, 1H), 6.95 (d, 2H), 6.69 (d, 1H), 5.11 (dd, 1H),
3.95 (dt, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.58 (s, 3H), 3.49 (dd,
1H), 3.45 (m, 1H), 3.30 (dd, 1H), 2.97 (m, 1H), 2.86 (m,
1H) .
Step B: (+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5.6.7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno(2,3-dlazs~ine-7-hydroxamic acid
(+/-)-6-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid was prepared from
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
180
methyl (+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-carboxylate in the
same manner as trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4-(2-methoxyethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid: MS (M-H) 381.
Example 59
N, OH
I
H
/ OMe
O
Preparation of f+/-)-3-benzyl-6-(4-methoxvt~henvl
sulfonyl)-5 6 7 8-tetrahvdro-4H-thienof2 3-dlazepine-7-
hvdroxamic acid
Step A~ Methyl (+/-)-3-(4-ben~lthien-3-vl)-2-(N-
(carboxy~ethYl)-N-(4-metho~yphenylsulfonvl)amino)
propionate
Methyl (+/-)-3-(4-benzylthien-3-yl)-2-(N-
(carboxymethyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)amino)propionate is prepared from
methyl 3-(4-benzylthien-3-yl)-2-aminopropionate in the
same manner as methyl 2-(N-(carboxymethyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)amino)-3-thiophen-2-yl-propionate:
MS: (M+H)+ 504, (M+NH4)+ 521.
Step B~ Methyl (+/-)-3-benzvl-6-(4-methoxyphenvl
sulfonyl)-8-oxo-5 fZ 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno(2,3-
d_1 azepine- 5 - carboxylate and methyl (+/ - ) - 3 -benzvl - 6 - ( 4 -
methoxvnhenylsulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydro-thieno[2 3-
~Zpvridine-5-carboxylate
To a solution of methyl (+/-)-3-(4-benzylthien-3-yl)-2-
(N-(carboxymethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)amino)
propionate (0.755 g, 1.5 mmoL) in toluene (9.5 mL) at
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/1614~
181
0°C was added oxalyl chloride (0.17 mL, 1.95 mmoL) and a
catalytic amount of N,N-dimethylformamide (0.012 mL).
The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C over 2
hrs and was then heated to reflux and treated with a
tin(IV) tetrachloride (0.228 mL, 1.95 mmoL). The
reaction mixture was heated for 20 minutes, poured onto
ethyl acetate and 1N aqueous HC1 and then separated.
The organic layer was washed with brine, dried (MgSOd),
concentrated, and purified by column chromatography
(silica, 0 to lea methanol in methylene chloride) to give
methyl (+/-)-3-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-8-
oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylate: MS: (M+H)+ 486, (M+NH4)+ 503; and methyl
(+/-)-3-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylate: MS:
(M+H)+ 458, (M+NH4)+ 475.
Steg C~ (+/-)-3-benzvl-6-(4-methoxvnhenvlsulfonvl)-
~ 8 tetrahydro-4H-thienof2 3-dlazepine-7-hydroxamic
ac'
(+/-)-3-Benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid was
prepared from methyl (+/-)-3-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-8-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-carboxylate in the same manner as (+/-)-6-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid: MS: (M+H)+ 473,
(M+NH4)+ 490.
Example 60
~ ,OH
~ ~N\o ~ -
S~' ~ ~ OMe
O
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
182
Preparation of (+/-)-3-benzyl-6-(4-methoxvbhenvl
sulfonyl)-4 5 6 7-tetrahydro-thienof2 3-clpvridine-5-
hvdroxamic acid
(+/-)-3-Benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c)pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid was
prepared from methyl (+/-)-3-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-
carboxylate in the same manner as trans-(+/-)-6-(4-
methoxybenzenesulfonyl)-4-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid:
MS: (M+H)+ 459, (M+NH4)+ 476.
Example 61
N, OH
OMe
Preparation of cis- and trans-(+/-)-5-(4-methoxvphenvl
sulfonvl) 4-phenethyl-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdro-thienof3 2-
cltwridine-6-hydroxamic acid
Step A' Methvl (+/-)-2-(3-ghenvlpronionvlamino)-3-
thien-2-yl-propionate
A suspension of methyl 2-amino-3-thiophen-2-yl-
propionate~HCl (3.5 g, 15.8 mmoL) in dichloromethane (25
mL) was treated with an aqueous (10 mL) solution of KZC03
(4.6 g, 33.3 mmoL). This two phase mixture was cooled
to 0°C and treated with a solution of hydrocinnamoyl
chloride (2.6 mL, 17.5 mmoL) in dichloromethane (15 mL).
The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C over 3
hrs. The mixture was diluted with dichloromethane and
washed with water. The aqueous phase was re-extracted
with dichloromethane and the combined ogranic phases
were dried (Na2S09) and concentrated. The white solid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
183
was purified by recrystallization from ethyl acetate-
ether to give methyl (+/-)-2-(3-phenylpropionylamino)-3-
thien-2-yl-propionate: 1H NMR (CDC13, 400 MHz), ppm:
7.15-7.35 (m, 6 H), 6.9 (m, 1 H), 6.6 (d, 1 H), 6.0 (d,
1 H), 4.9 (m, 1 H), 3.75 (s, 3 H), 3.35 (d, 2 H), 3.0
(m, 2 H) , 2.55 (m, 2 H) .
Step B: Methvl cis-(+/-)-4-phenethyl-6,7-dihydro-
thienof3,2-clpyridine-6-carboxylate
A solution of methyl (+/-)-2-(3-phenylpropionylamino)-3-
thien-2-yl-propionate (1.7 g, 5.4 mmoL) in acetonitrile
(55 mL) was treated with POC13 (9 mL, 97 mmoL) and then
heated at reflux for 6 hrs. The reaction mixture was
concentrated under reduced pressure and then
reconstituted in ethyl acetate. This solution was
washed with saturated aqueous NaHC03 (2 times), water,
and brine. The organic phase was then dried (Na2SOa) and
concentrated to give methyl cis-(+/-)-4-phenethyl-6,7-
dihydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylate, which was
carried onto the next step without purification.
Sten C: Methyl cis-(+/-)-4-phenethvl-4,5.6.7-
tetrahydro-thienof3,2-clpvridine-6-carboxYlate
A solution of methyl cis-(+/-)-4-phenethyl-6,7-dihydro-
thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylate (0.222 g, 0.74 mmoL)
in methanol (5 mL) was treated with Pt02 (53 mg, 0.23
mmoL) . The ~Sask was evacuated and flushed with
nitrogen (3X) and hydrogen (3X). The reaction mixture
was then placed under an atmosphere of Ha for 1 hr. The
mixture was diluted with MeOH, filtered through a pad of
celite, concentrated, and purified by flash
chromatography (silica, 255 ethyl acetate in hexanes) to
give methyl cis-(+/-)-4-phenethyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylate: MS: (M+H)+ 302,
(2M+H)' 603.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
184
Steg p: cis-(+/-)-4-phenethyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thienof3.2-clpvridine-6-carboxylic acid
A solution of methyl cis-(+/-)-4-phenethyl-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylate (3.47 g,
11.5 mmoL) in methanol (30 mL) was cooled to 0°C and
treated with 1N aqueous NaOH (11.8 mL). The reaction
mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C and was stirred for
5 hrs. The methanol was removed under reduced pressure
and the reaction mixture was diluted with water (100 mL)
and acidified with 1N aqueous HC1 (to pH 8). This
solution was cooled to 0°C and the resulting solid was
isolated by filtration to give cis-(+/-)-4-phenethyl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid: MS: (M+H)~ 288.
tep E~ cis- (+/-) -5- (4-methoxyphenvlsulfqnyl) -4-
,phenethyl-4 5 6 7-tetraY~ydro-thienof3 2-clpvridine-6-
carboxylic acid
A suspension of cis-(+/-)-4-phenethyl-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid (3.14
g, 10.9 mmoL) in 9~S aqueous NazC03 (13.6 mL, 11.6 mmoL)
was cooled to 0°C and treated with a solution of 4-
methoxybenzene sulfonyl chloride (3.12 g, 15.1 mmoL) in
1,4-dioxane (18 ml). The reaction mixture was allowed
to warm to 25°C and was stirred for 5 hrs. The 1,4-
dioxane was removed under reduced pressure and the
reaction mixture was diluted with water and ethyl
acetate. Filtration of the aqueous layer yielded
recovered starting material. The aqueous filtrate was
then treated with solid Na2C03 (0.8 g) and was used to
extract the original organic phase. The organic layer
was again extracted with 1~ aqueous NaZCO, (2X) and the
aqueous layers were combined and acidified with 1N
aqueous HC1 (to pH 2). The resulting suspension was
extracted with ethyl acetate (2X), and the organic
phases were combined, dried (Na2S0a), and concentrated to
give cis-(+/-)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
185
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic
acid, which was carried onto the next step without
purification: 1H .NMR (CDC13, 400 MHz) , ppm: 7.66 (d,
2H), 7.1-7.3 (m, 5 H), 7.06 (d, 1 H), 6.86 (d, 2 H),
6.73 (d, 2 H), 5.16 (m, 1 H), 4.84 (dd, 1 H), 3.82 (s,
3H), 3.3 (dd, 1 H), 3.0 (m, 1 H), 2.8 (m, 1 H), 2.59
(dd, 1 H) , 1.97 (m, 2 H) .
Step F: cis and trar~s-(+/-)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4-~henethyl-4;5,6,7-tetrahvdro-thieno(3,2-clpyridine-6-
carboxylic acid benzhydryloxy-amide
A solution of cis- and trans-(+/-)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid (5:3)(300 mg, 0.656 mmoL)
in N,N-dimethylformamide (8 mL) was treated with O-
benzhydryl-hydroylamine (166 mg, 0.834 mmoL) and 1-
hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate (116 mg, 0.858 mmoL). This
solution was cooled to 0°C and treated with 1-(3-
dimethylaminoprpyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
(154 mg, 0.803 mmoL). The reaction mixture was allowed
to warm to 25°C and was stirred for 8 hrs. This mixture
was diluted with ethyl acetate and washed with saturated
aqueous NaHCO,, 0.5N aqueous HC1, water, and brine. The
organic phase was dried (NazS04), concentrated, and
purified by flash chromatography (silica,
dichloromethane) to give the higher Rf cis-(+/-)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid benzhydryloxy-
amide and the lower Rf trans-(+/-)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid benzhydryloxy-amide:
MS (cis) : (M+H)+ 639, (M+NHa)' 656 and MS (trans) : (M+H)'
639, (M+NHQ)+ 656.
Step G~ cis and trans-(+/-)-5-(4-methoxvphenylsulfonyl)-
4-p-henethyl-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdro-thieno(3 2-clpyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
186
A solution of cis-(+/-)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
phenethyl-4,5,6,?-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
carboxylic acid benzhydryloxy-amide (228 mg, 0.357 mmoL)
in dichloromethane (6 mL) was cooled to 0°C and treated
with trifluoroacetic acid (6 mL), followed by dropwise
treatment with triethylsilane (0.12 mL, 0.75 mmoL). The
reaction mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C over 1 hr,
concentrated and the residue was co-distilled with
toluene. The crude reaction product was then purified
by flash chromatography (silica, 5~S methanol in
dichloromethane) to give the higher Rf cis-(+/-)-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-
thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hyrdoxamic acid and the lower Rf
trans-(+/-)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid: MS (cis) : (M+H); 473, (M+NH4)+ 490 and MS (trans)
(M+H) ' 473, (M+NH,)' 490.
Example 62
Utilizing the procedures of Example 61, the
compounds of Table II were prepared.
TABLE II
cis-(+/-)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-methyl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid: MS (M+H)+ 383, (M+NH4)+ 400.
trans-(+/-)-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-methyl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid: MS (M+H)+ 383, (M+NH4)+ 400.
cis-(+/-)-4-benzyl-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-
hydroxamic acid: MS (M+H)+ 459, (M+NH4)+ 476.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
187
Example 63
0
~ OMe
~S OMe
ii
0
Preparation of Methyl 6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-4-
vin~rl-4,5,6,7-tetrahvdrQ-thienof2.3-clpyridine-5-
carboxvlate
Methyl 6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylate was
prepared from 3-bromo-2-(2-hydroxymethyl)thiophene and
methyl (4-methoxyphenylsulfonylamino)acetate in the same
manner as methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylate was prepared: MS: (M+NH4)+ 411.2.
prpgaration of trans-(+/-Z-6-(4-methoxvbhenylsulfonvl)-
4-phenethvl-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2 3-dlazepine-
5-hydroxamic acid
ctpg A~ Methvl (4-methoxyphenvlsulfonylamino)acetate
Glycine methyl ester hydrochloride (20 g, 0.16 mol) was
suspended in dichloromethane (320 mL), cooled to 0°C,
and treated with diisopropylethylamine (69.4 mL, 0.4
mol). The resulting solution was allowed to stir for 15
minutes and was then treated with 4-methoxybenzene
sulfonyl chloride (31 g, 0.15 mol) suspended in
dichloromethane (165 mL). This reaction was allowed to
Example 64
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
188
warm slowly to room temperature and stirred overnight.
The reaction mixture was washed with 2 M aqueous HC1
(3X), saturated aqueous NaHC03 (3X), and brine. The
organic layer was dried (MgSO,) and concentrated to
yield sulfonamide as a white crystalline solid: Rf=0.09
(silica, 10~ ethyl acetate in toluene); mp 60-62°C; MS
(ESI, positive) m/z 260 (M+H), 277 (M+NH4); HRMS (EI+}
for C1oH13N05 (M+) , calcd 259.0514, found 259.0508; Anal.
Calcd for C1oH13N05: C, 46.33; H, 5.05; N, 5.40. Found:
C, 46.32; H, 5.33, N, 5.44.
SteQ B~ Methyl N-(2-(3-bromothioghen-2-vl)ethvl)-N-(4-
metho_~rr~henvlsulfonvl) aminoacetate
A solution of triphenylphosphine (12.3 g, 46.9 mmol) in
THF (400 mL) was cooled to 0°C and treated with
diisopropylazodicarboxylate (9.2 mL, 46.8 mmol). To
this was added 2-(3-bromothiophen-2-yl)ethanol (Keegstra
et al., Tetrahedron 48:3633-3652 (1992)) (9.65 g, 46.6
mmol), followed by methyl (4-methoxyphenylsulfonylamino)
acetate (15.1 g, 58.3 mmol). The resulting solution was
warmed to ambient temperature and stirred for 24 h. TLC
(silica, 10~ ethyl acetate in toluene) indicated
starting materials remained so additional quantities of
triphenylphosphine (5.9 g, 22.5 mmol) and diisopropyl
azodicarboxylate (4.1 mL, 20.8 mmol) were added and the
mixture was stirred another 1 h. The solvents were
evaporated and the residue was purified by column
chromatography (silica 5~ ethyl acetate in toluene)
followed by trituration with 5~ ethyl acetate in hexanes
to give the desired product as a white solid. This
product could be recrystallized from ethyl acetate-
hexanes; Rf=0.4 (silica, 10~ ethyl acetate in toluene);
mp 79-80°C (ethyl acetate-hexanes); MS (ESI, positive)
m/z 448 (M+H, '9BR) , 450 (M+H, 8lBr) , 465 (M+NHd, "Br) ,
467 (M+NH4, elBr) ; HRMS (FAB) for C16H,9NOSSzBr (M+H, '9Br) ,
calcd 447.9915; Anal. Calcd for C16Hi8NO5S2Br: C, 42.86;
H, 4.05; N, 3.12. Found: C, 42.88; H, 3.94; N, 3.10.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/U598/16147
189
Step C: Methyl N- (2- (3- (3- (tert-butyldimethylsilanvl
oxy)propenvl)thiophen-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonvl)aminoacetate
Methyl N-(2-(3-bromothiophen-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate (2.38 g, 5.3 mmol) was
dissolved in toluene (35 mL) and treated with (Z)-
nBu3SnCHCHCH20Si'BuMe2 (Jung et al. , Tet. Lett. 23:3851-
3854 (1982)). This solution was heated to reflex for 5
minutes and then treated with dichlorobis(triphenyl
phosphine)palladium (II) (289 mg, 0.4 mmol). The
reaction mixture was stirred at reflex for 1.5 h and
then cooled to 0°C. The mixture was diluted with
diethyl ether and stirred vigorously with 10~ aqueous
potassium fluoride for 1 hr. Filtration through a plug
of celite removed the solid by-products. The liquid
phases of the filtrate were separated and the organic
layer was washed with 105 aqueous potassium fluoride,
dried (NaaS04) and concentrated. The tan oil was
purified by flash chromatography (silica, 10 to 15~
ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give the desired product as
a yellow oil: Rf=0.25 (silica, 25~ ethyl acetate in
hexanes); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 557 (M+NHQ); Anal.
Calcd for CZSH3,N06SzSi: C, 55.63; H, 6.91; N, 2.59.
Found: C, 55.52; H, 6.94; N, 2.46.
Step D ~ N- ( 2 - ( 3 - ( 3 -Hydroxvorogenyl ) thiophen- 2 -vl )
ethyl) -N- (4-methoxvyhenvlsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid
To a stirred solution of methyl N-(2-(3-(3-(tert-
butyldimethylsilanyloxy)propenyl)thiophen-2-yl)ethyl)-N-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate (4.33 g, 8 mmol)
dissolved in THF (8mL) at 0°C was added 1 M aqueous KOH
(12 mL). The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to
25°C and was stirred for 3 h. The THF was removed under
reduced pressure and the reaction mixture was diluted
with water and acidified with 1 N HC1 (12 mL). The
white precipitate was extracted into ethyl acetate (2X)
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
190
and the combined organic layers were dried (Na2S04) and
concentrated to give crude N-(2-(3-(3-(tert-butyl
dimethylsilanyloxy)propenyl)thiophen-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid (4.4 g), which
was carried onto the next step without purification:
Rf=0.6 (silica, 10% methanol in dichloromethane with 10
acetic acid); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 543 (M+NH4); MS
(ESI, negative) m/z 524 (M-H). To a stirred solution of
the crude carboxylic acid dissolved in THF (70mL) at 0°C
was added a 1 M solution of TBAF in THF (16 mL, 16
mmol). The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C
and was stirred for 5 h. The THF was removed under
reduced pressure and the residue was redissolved in
ethyl acetate. This solution was washed with 1 N HCl,
water and brine. The organic phase was then dried
(NaZSO,) and concentrated to give a tan oil, which
solidified upon trituration with diethyl ether. The
solid product was collected on a buchner funnel and
rinsed with cold diethyl ether to give the desired
product as a light tan solid in a 20 to 1 ratio of cis
to trans isomers. Data for the major (cis) isomer:
Rf=0.37 (silica, 10~s methanol in dichloromethane with 1 0
acetic acid); mp 109.5-115°C (ethyl acetate-hexanes); MS
(ESI, positive) m/z 394 (M-H20+H) , 429 (M+NH4) ; MS (ESI,
negative) m/z 410 (M-H) ; HRMS (FAB- ) for ClBH~aNO6S~ (M-H) ,
calcd 410.0732, found 410.0718; Anal. Calcd for C18
Hz1N06S2: C, 52.24; H, 5.14; N, 3.40. Found: C, 52.25;
H, 4.83; N, 3.33.
St°n F~ ~ 0- 14-Methoxvphenylsulfonyl) -9 10 1~ 12-
tetrahvdro-6H-7-oxa-1-thia-10-aza-cvclopenta
cvcloundecen-8-one
A solution of N-(2-(3-(3-hydroxypropenyl)thiophen-2-yl)
ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid, a
20:1 mixture of cis to trans isomers (1.45 g, 3.5 mmol)
dissolved in acetonitrile (25 mL) was treated with
triethylamine (3.9 mL, 28.1 mmol). This solution was
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
191
slowly added (15 hrs, via syringe pump) to a solution of
2-chloro-1-methylpyridinium iodide (3.6 g, 14.1 mmol) in
acetonitrile (500 mL) heated at reflux. The reaction
mixture was heated another 5 hrs at reflux and then the
acetonitrile was evaporated. The residue was suspended
in ethyl acetate and the solid by-products were removed
via filtration. The filtrate was concentrated and the
crude product was purified by flash chromatography
(silica, 25 to 40~ ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give the
desired product as a white solid. This product could be
recrystallized from ethyl acetate-hexanes: Rf=0.43
(silica, 50~ ethyl acetate in hexanes); mp 138.5-140°C
(ethyl acetate-hexanes); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 394
(M+H) , 411 (M+NHq) ; HRMS (EI+) for C18H19N05S2 (M+) , calcd
393.0705, found 393.0701; Anal. Calcd for C18H19NOSSz: C,
54.94; H, 4.87; N, 3.56. Found: C, 54.93; H, 4.85; N,
3.56.
Step F~ Methyl cis- (+/-) -6- (4-methoxwhenvlsulfonvl) -4-
Vsnyl-5 6 7 8-tetrahvdro-4H-thienof2 3-dlazegine-5-
carboxylate
To a solution of 10-(4-methoxyphenyisulfonyl)-
9,10,11,12-tetrahydro-6H-7-oxa-1-thia-10-aza-cyclopenta
cycloundecen-8-one (1.31 g, 3.3 mmol) dissolved in THF
(33 mL) at -78°C was added TBSOTf (0.8 mL, 3.5 mmol)
followed immediately by a 0.5 M solution of KHMDS in
toluene (7 mL, 3.5 mmol). The cooling bath was then
removed and the reaction mixture was allowed to warm to
25°C, over 30 minutes. The mixture was then heated to
reflux for 4 hrs. The mixture was cooled to 25°C and
poured onto a mixture of ethyl acetate and saturated
aqueous NH4C1. The layers were separated and the
organic phase was washed with H20 and brine, dried
(Na2S04) and concentrated. The residue was purified by
flash chromatography (silica, 25 to 50~ ethyl acetate in
hexanes followed by 5 to 10o methanol in methylene
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
192
chloride) to give tert-butyldimethylsilyl cis-(+/-)-6-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl}-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate as a clear oil:
Rf=0.66 (silica, 50o ethyl acetate in hexanes,
decomposed on silica gel plate) ; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDC13)
87.74 (m, 2H), 6.95-6.90 (m, 3H), 6.81 (d,J=5.0 Hz 1H},
6.47 (m, 1H), 5.27 (d,J=10 Hz, 1H, 5.23 (d,J=17.5 Hz,
1H), 4.90 (d,J=3 Hz, 1H), 4.02-3.95 {m, 2H), 3.85 (s,
3H), 3.55 (m, 1H}, 3.13 (m, 1H), 2.94 (m, 1H), 0.84 (s,
9H) , 0.07 (s, 3H) , 0.04 (s, 3H) ; 1H NMR (400 MHz, THF-d8)
57.73 {m, 2H), 7.00 (m, 2H), 6.99 (d, 1H), 6.80 (d,J=5
Hz, 1H), 6.55 (ddd,J=17.0, 10.0, 9.0 Hz, 1H), 5.22
(d,J=10 Hz, 1H), 5.21 (dd,J=17.0, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 4.93
(d,J=2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.97-3.91 (m, 2H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.51
(m, 1H), 3.06 (m, 1H), 2.93 {m, 1H), 0.85 (s, 9H), 0.06
(s, 3H), 0.05 (s, 3H); and cis-(+/-}-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid, as a tan foam:
Rf=0.35 (silica, 10~ methanol in dichloromethane); MS
(ESI, positive) m/z 394 (M+H), 411 (M+NH,). To a
solution of tert-butyldimethylsilyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate (72 mg, 0.14 mmol)
dissolved in methanol and THF (3:1, 2.4 mL) at 0°C was
added a solution of KZC03 (60 mg, 0.43 mmol) in H20 ( .6
mL). This cloudy reaction mixture was allowed to warm
to 25°C, over 30 minutes, and was then concentrated to
1/4t'' of the original volume. Dilution with HZO and
acidification with 1 N HC1 (to pH 2) gave a white
precipitate that was extracted into ethyl acetate. The
organic phase was dried (Na2S0,) and concentrated to give
the additional cis-(+/-}-6-{4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid, which was carried to the next step
without further purification. To a solution of the
carboxylic acid (323 mg, 0.82 mmol) dissolved in benzene
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
193
and methanol (2:1, 9 mL) at 0°C was added a 2 M solution
of TMSCHNz in hexanes ( 0 . 82 mL, 1. 64 mmol ) . The
reaction mixture was stirred 15 minutes and then the
solvents were removed under reduced pressure. The
residue was purified by flash chromatography (silica, 25
to 38~ ethyl acetate in hexanes followed by 5 to 10~
methanol in methylene chloride) to give the desired
product as a white solid: Rf=0.47 (silica, 50~ ethyl
acetate in hexanes) and Rf=0.51 (silica, 10o ethyl
acetate in toluene); mp 112-113°C; MS (ESI, positive)
m/z 408 (M+H) , 425 (M+NHq) ; HRMS (EI+) for C,9HuN05S2
(M+), calcd 407.0861, found 407.0848; Anal. Calcd for
C19HZ1NOSS2: C, 56.00; H, 5.19; N, 3.44. Found: C,
56.15; H, 4.88; N, 3.34.
Step G: Methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-4-
phenethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno(2,3-dlazepine-5-
carboxylate
To a solution of methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
d]azepine-5-carboxylate (77 mg, 0.19 mmol) dissolved in
THF (3 mL) at OgC was added a 0.5 M solution of 9-BBN in
THF (0.625 mL, 0.31 mmol). The reaction mixture was
allowed to warm to 25°C, over 3.5 hrs, and was then
treated sequentially with PdCl2(dppf)~CH2C12 (18 mg, 0.02
mmol) , iodobenzene (0.17 mL, 1.5 mmol) , KZC03 (108 mg,
0 . 7 8 mmol ) , DMF ( 1 mL) , and Hz0 ( 0 .15 mL) . Af ter
stirring 1 h at 25~C the solution was diluted with
diethyl ether and washed with HzO, 1 N HCl, saturated
aqueous NaHC03, 10~ aqueous NaZS03, and brine. The
organic layer was dried (NazS04), concentrated, and
purified by column chromatography (silica, 3~ ethyl
acetate in toluene) to give the desired product as a
white foam: Rf=0.47 (silica, 10~ ethyl acetate in
toluene); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 486 (M+H), 503 (M+NH4);
HRMS (EI+) for CZSHz,NOSS, (M+) , calcd 485.1331, found
485.1282.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
194
tep H: trans-(+/-)-6-(4-Methoxvr~henvlsulfonyl)-4-
phenethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2,3-dlazepine-5-
carboxvlic acid
To a solution of methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-
dJazepine-5-carboxylate (95 mg, 0.2 mmol) dissolved in
THF and HZO (3:1, 4 mL) was added 1 M aqueous LiOH (0.6
mL, 0.6 mmol). The reaction mixture was heated to
reflux for 18 h and then the THF was removed in vacuo.
Dilution with HZO followed by acidification with 2 N HC1
(to pH 2) gave a white precipitate that was extracted
into ethyl acetate. The organic layer was then dried
(Na2SOd), concentrated, and purified by column
chromatography (silica, 5 to 10o methanol in
dichloromethane) to give the desired product as a white
foam: Rf=0.5 (silica, 10~s methanol in dichloromethane) ;
mp 177-178°C (CHC13) ; MS (ESI, positive) m/z 489 (M+NH4)
MS (ESI, negative) m/z 470 (M-H); HRMS (FAB+) for
CaaHz6NO5SZ (M+H) , calcd 472.1252, found 472.1262.
Step I- trans- (+/-) -6- (4-Methoxy~henvlsulfonyl) -4-
phenethvl-5 6 7 8-tetrahydro-4H-thienof2 3-dlaze_pine-5-
hvdroxamic acid
A solution of trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
phenethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid (48 mg, 0.1 mmol) dissolved in CH2C1~ (5
mL) at O~C was treated sequentially with hydroxylamine
hydrochloride (28 mg, 0.4 mmol), diisopropylethylamine
(90 uL, 0.52 mmol), and PyBroP (59 mg, 0.13 mmol). This
mixture was allowed to warm to 25qC over 1.5 hrs and was
then concentrated. The residue was dissolved in ethyl
acetate and the remaining solids were removed via
filtration. The filtrate was washed with brine, 1 N
HC1, and brine again. The organic phase was then dried
(NazSO,), concentrated, and purified by column
chromatography (silica, 2.5~ methanol in methylene
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
195
chloride) to give the desired product as a white foam.
This product could be recrystallized from diethyl ether-
hexanes: Rf=0.5 (silica, 7.5~ methanol in
dichloromethane); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 504 (M+NHq); MS
(ESI, negative) m/z 485 (M-H) ; HRMS (FAB+) for Ca4HZ,N205S2
(M+H), calcd 487.1361, found 487.1381; Anal. Calcd for
CzaHzsNzOsSz: C, 59.24; N, 5.76. Found: C, 59.46; H,
5.34; N, 5.58.
Example 65
OMe
0
Preparation of trans-(+/-)-6-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahvdro-4H-thienof2,3-dlazeoine-5-
carboxvlic acid and its methyl ester
To a solution of the methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d)azepine-5-carboxylate (365 mg, 0.9 mmol)
dissolved in THF and HZO (3:1, 16 mL) at ambient
temperature was added a 1 M aqueous solution of LiOH
(2.7 mL, 2.7 mmol). This solution was heated to reflux
for 18 h and then cooled to room temperature. The THF
was removed in vacuo and the resulting aqueous solution
was diluted with HZO and acidified with 2 N HCl (to
pH2). The cloudy mixture was extracted into ethyl
acetate (2X) and the combined organic layers were dried
(NaZSO,), filtered and concentrated to give the desired
product as a tan solid: Rf=0.35 (silica, 10~ methanol
in dichloromethane); MS (ESI, negative) m/z 392 (M-H).
To confirm that the base had indeed induced
epimerization, the methyl ester of the trans carboxylic
acid was prepared. To a solution of trans carboxylic
acid (280 mg, 0.71 mmol) dissolved in benzene and
methanol (2:1, 10.5 mL) at O~C was added a 2 M solution
O
OH
S ~ NHS
I I
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
196
of TMSCHN2 (1.05 mL, 2.1 mmol) in hexanes. The reaction
mixture was stirred 15 minutes and then the solvents
were removed under reduced pressure. The residue was
purified by flash chromatography (silica, 0.5~ methanol
in methylene chloride) to give the trans methyl ester as
a white foam: Rf=0.68 (silica, 75~ ethyl acetate in
hexanes) and Rf=0.46 (silica, 10~ ethyl acetate in
toluene; MS (ESI, positive) m/z 408 (M+H), 425 (M+NHQ);
HRMS (EI+) for C,9H21NO5S2 (M+) , calcd 407.0861, found
407.0881.
Example 66
1 (CH3 ) 3
OMe
0
O
OCH2CH2 S
S ~ NHS
II
Preparation of 2-(trimethvlsilvl)ethyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-
mPthoxyDhenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5 6 7.8-tetrahvdro-4H-
thienof2 3-dlazepine-5-carboxylate
A solution of cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylic acid (33 mg, 0.08 mmol) in CHzCla (1 mL) was
treated with a catalytic amount of DMAP followed by the
2-(trimethylsilyl)ethanol (12 mL, 0.08 mmol). This
solution was then cooled to O~C and treated with DCC (17
mg, 0.08 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred 1 h at
OqC and then poured onto a mixture of CH2C12 and 0.1 N
HC1. The aqueous layer was extracted with additional
CHZC12 and the combined organic layers were washed with
brine, dried (MgS04), and concentrated. The residue was
purified by column chromatography (silica, 15~ ethyl
acetate in hexanes) to give the desired product as a
clear oil in a 10 to 1 ratio of cis to trans isomers.
Data for the major cis isomer: Rf=0.78 (silica, 5
methanol in dichloromethane); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 494
( M+H ) , 511 ( M+NHQ ) .
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
197
Example 67
OMe
O
O
OH
S ~ NHS
I I
Preparation of cis-l+/-)-6-(4-methoxvohenvlsulfonyl)-4-
vinyl-5,6,7.8-tetrahvdro-4H-thienof2,3-dlazepin~-5-
carboxvlic acid
To a solution of 2-(trimethylsilyl)ethyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate (7 mg; 10:1 mixture
of cis and trans isomers) dissolved in THF (0.75 mL),
cooled to O~C, was added a 1 M solution of TBAF in THF
(20 uL). This solution was stirred for 20 minutes and
then concentrated. The residue was dissolved in EtOAc
and washed with 0.1 N HC1. The aqueous layer was back
extracted with EtOAc and the combined organic layers
were washed with brine, dried (MgSO,), and concentrated
to give the desired carboxylic acid. The 1H NMR
indicated a 10:1 mixture of cis and trans isomers, with
the major compound NMR matching that of the previously
prepared carboxylic acid.
OMe
Preparation of trans-(+/-)-7-l4-methoxy~hen_ylsulfonvl)-
5-phenethvl-4,5,6,7.8,9-hexa drothienof2,3-d]azocine-6-
hydroxamic acid
Example 68
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
198
~~tep A~ Methyl N- (4-methoxy~ylsu onyl) -N- (2- (3-
vinvlthiophen-2-yl)ethyl)aminoacetate
A solution of methyl N-(2-(3-bromothiophen-2-yl)ethyl)-
N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate (5.5 g, 12.3
mmol) in toluene (75 mL) was treated with
tributylvinyltin (9 mL, 30.8 mmol) and then heated to
reflux. The hot solution was treated with dichloro
bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) (625 mg, 0.89 mmol)
and stirred at reflux for 24 h. Proton NMR analysis of
the reaction mixture indicated starting material
remained so an additional quantity of dichloro
bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) (600 mg, 0.85 mmol)
was added and the mixture was stirred another 7 h at
reflux. After cooling to ambient temperature, the
mixture was diluted with diethyl ether and stirred
vigorously with 10o aqueous potassium fluoride for 1 hr.
Filtration through a plug of celite removed the solid
by-products. The liquid phases of the filtrate were
separated and the organic layer was washed with 10~
aqueous potassium fluoride, dried (Na,S04) and
concentrated. The residue was purified by flash
chromatography (silica, 25 to 40~ ethyl acetate in
hexanes) to give the desired product as a yellow solid:
Rf = 0.45 (silica, 50o ethyl acetate in hexanes); mp 69-
72 °C; MS (ESI, positive) m/z 396 (M+H), 413 (M+NHq);
HRMS (FAB+) for C18HZ1NOSS2 (M+H) , calcd 396 . 0939 , found
396.0950; Anal. Calcd for C18HZ1NOSS2:C, 54.66; H, 5.35; N,
3.54. Found: C, 54.85; H, 5.31; N, 3.43.
Step B- Methyl N- (2- (3-formylt~ionhen-2-~1) -ethyl) -N-
~4-methoxvnhenylsulfon~l)aminoacetate
To a solution of methyl N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-N-
(2-(3-vinylthiophen-2-yl)ethyl)aminoacetate (3.25 g, 8.2
mmol) dissolved in THF and Hz0 (4:1, 85 ml) was added to
a 2.5 wt.~ solution of osmium tetroxide in 2-methyl-2-
propanol (4.1 ml, 0.33 mmol) and sodium metaperiodate
(2.2 g, 10.3 mmol). The mixture was then treated with a
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
199
second portion of sodium metaperiodate (2.2 g, 10.3
mmol) and stirred for 1 h, at 25°C. The THF was then
evaporated and the mixture was diluted with H20 and the
product was extracted into ethyl acetate (2X). The
combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried
(MgS04), concentrated and purified by column
chromatography (silica, 25 to 50~ ethyl acetate in
hexanes) to give the desired product as a light tan
solid: Rf = 0.3 (silica, 50~ ethyl acetate in hexanes);
mp 79-81°C; MS (ESI, positive) m/z 398 (M+H), 415
(M+NHQ) ; HRMS (FAB+) for Cl~HZONO6S2 (M+H) , calcd 398.0732,
found 398.0747; Anal. Calcd for C1,H19NO6Sz: C, 51.37; H,
4.82; N, 3.52. Found: C, 51.36; H, 4.48; N, 3.50.
Step C: Methyl N-(2-(3-(hydroxymethyl)thiophen-2-yl)-
ethvl)-N-(4-methoxy~henylsulfonyl)aminoacetate
To a solution of methyl N-(2-(3-formylthiophen-2-yl)-
ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate (1.43 g,
3.6 mmol) dissolved in methanol and dichloromethane
(3:1) 36 ml) was added the NaBH4 (138 mg, 3.65 mmol).
The mixture was stirred at ambient temperature for 30
minutes and then concentrated in vacuo. The residue was
dissolved in dichloromethane and washed with 1 N HC1 and
HZO. The organic layer was dried (Na,SO,), concentrated,
and purified by column chromatography (silica, 50 to 750
ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give the desired product as
a white solid: Rf = 4.6 (silica, 75~ ethyl acetate in
hexanes); mp 83-85 °C; MS (ESI, positive) m/z 382 (M+H-
H20) , 417 (M+NHQ) ; HRMS (FAB+) for Cl,HzoNO5S2 (M+H-H20) ,
calcd 382.0783, found 382.0814; Anal. Calcd flor
C1,H21N06Sz: C, 51.11; H, 5.30; N, 3.51. Found: C, 50.95;
H, 5.20; N, 3.46.
~teg D~ Methyl N- (2- (3- (bromomethvl) thio~hen-2-yl) -
ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate
To a solution of methyl N-(2-(3-(hydroxymethyl)thiophen-
2-yl)-ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
200
(0.97 g, 2.43 mmol) dissolved in dichloromethane (21
ml), cooled to -30~C, was added PPh3 (795 mg, 3 mmol)
and recrystallized NBS (550 mg, 3.1 mmol). This
solution was stirred for 30 minutes, diluted with
diethyl ether, and then washed with saturated aqueous
sodium carbonate. Addition of HZO was required to
dissolve solids that had formed during the wash. The
organic layer was washed with a l~ solution of Na2S03 (93
ml) and brine, dried (Na2SOa~ concentrated, and purified
by column chromatography (silica, 25 to 38~ ethyl
acetate in hexanes) to give the desired product as a
white solid. This product could be recrystallized from
ethyl acetate-hexanes: Rf = 0.63 (silica, 755 ethyl
acetate in hexanes); mp 73-74~C (ethyl acetate in
hexanes) ; Anal. Calcd flor Cl,HzoNOSSZBr: C, 44.16; H,
4.36; N, 3.03. Found: C, 44.05; H, 4.30; N, 2.98.
Sip E~ Methyl N- (2- (3- (4- (tert-butyldimethvl
silanyloxy)but-2-enyl)thiophen-2-vl)ethvl)-N-(4-
~~hoxyphenvlsulfonyl)aminoacetate
Methyl N-(2-(3-(4-(text-butyldimethylsilanyloxy)but-2-
enyl)thiophen-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
aminoacetate was prepared from methyl N-(2-(3-(bromo
methyl)thiophen-2-yl)-ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
aminoacetate (1.26 g, 2.7 mmol) according to the same
procedure used for the preparation of methyl N-(2-(3-(3-
(tert-butyldimethyl silanyloxy)propenyl)thiophen-2-
yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxy phenylsulfonyl)aminoacetate,
using (Z)"Bu3SnCH=CHCHZOSi'BuMe2 (20:1; Z:E) , and
PdCl2 (PPh3) 2 (150 mg, 0.21 mmol) in toluene (30 ml) . The
residue was purified by flash chromatography (silica,
25~ ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give the desired
product as a tan oil in a 20:1 ratio of cis to trans
isomers. Data for the major (cis) isomer: Rf = 0.28
(silica, 50~ ethyl acetate in hexanes); MS (ESI,
positive) m/z 554 (M+H), 571 (M+NHa); HRMS (FAB+) for
Ca6H4pNO6SzSi (M+H) , calcd 554.2066, found 554.2051; Anal.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
201
Calcd for CZ6H39NO6SzSl: C, 56.39; H, 7.10; N, 2.53. Found:
C, 56.60; H, 7.06; N, 2.33.
Step F: N-(2-(3-(3-Hydr~ybut-2-enyl)thiophen-2-vl)
ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)am_inoacetic acid
N-(2-(3-(3-Hydroxybut-2-enyl)thiophen-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid was prepared from
methyl N-(2-(3-(4-(tert-butyldimethylsilanyloxy)but-2-
enyl)thiophen-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
aminoacetate (20:1 (Z: E) mixture, 1.07 g, 1.93 mmol)
according to the same procedure used for the preparation
of N- ( 2 - ( 3 - ( 3 -Hydroxypropenyl ) thiophen- 2 -yl ) ethyl ) -N-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid, using 1 N KOH
(3 ml) dissolved in THF (20m1) . The N- (2- (3- (4- (tert-
butyldimethylsilanyloxy)but-2-enyl)thiophen-2-yl)ethyl)-
N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid intermediate
(1.05 g) (Rf = 0.6 (silica, 10% methanol in
dichloromethane with 1% acetic acid); MS (ESI, negative)
m/z 424 (M-Si'BuMez) , 538 (M-H) ; HRMS (FAB+) for
2O CZ~H38NO6S2S1 (M+H) , calcd 540.1910, found 540.1885) was
treated with a 1 M solution of TBAF in THAF in THF (3.7
ml) dissolved in THF (20 ml). After trituration with
ether and recrystallization of the filtrates from
dichloromethane-hexanes, the desired product was
obtained as a tan solid in a 10 to 1 ratio of cis to
trans isomers. Data for the major (cis) isomer: R~ _
0.34 (silica, 10% methanol in dichloromethane with 1%
acetic acid); mp 109-110.5~C (dichloromethane-hexanes);
MS (ESI, positive) m/z 443 (M+NHa); MS (ESI, negative)
m/z 424 (M-H) ; HRMS (FAB+) for Cl9Ha'NO6S2 (M+H) , calcd
426.1045, found 4.26.1056; Anal. Calcd for Cl9Hz;N06S2: C,
56.63; H, 5.45; N, 3.29. Found: C, 53.48; H, 5.38; N,
3.29.
~tPp G~ 11-(4-Methoxyphenvlsulfonvl)-4 7 10 11 12 13-
hexahydro-8-oxa-1-t~ia-llaza-cyclo en,acvlododecen-9-one
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
202
11-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,7,10,11,12,13-hexahydro-
8-oxa-1-thia-llaza-cyclopentacylododecen-9-one was
prepared from N-(2-(3-(3-Hydroxybut-2-enyl)thiophen-2-
yl) ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid
(10:1 Z:E mixture, 0.57 g, 1.34 mmol) according to the
same procedure used for the preparation of 10-(4-
Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-9,10,11,12-tetrahydro-6H-7-oxa-1-
thia-10-aza-cyclopenta cycloundecen-8-one, using 2-
chloro-1-methylpridinium iodide (1.37 g, 5.36 mmol), and
triethylamine (1.5 ml, 10.8 mmol) in CH3CN (200 ml).
The residue was purified by flash chromatography
(silica, 25 to 50~ ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give the
desired product as a white solid in a 9 to 1 ratio of
cis to traps isomers. This product could be
recrystallized from ethyl acetate-hexanes. Data for the
major (cis) isomer: Rf = 0.38 (silica, 50°s ethyl acetate
in hexanes); mp 134-135~C (ethyl acetate-hexanes); MS
(ESI, positive) m/z 408 (M+H), 425 (M+NHa); HRMS (E1+)
for C19Hz1NO5Sz (M+) , calcd 407.0861, found 407.0892; Anal .
Calcd for C,9HZ1NOSS2; C, 56.00; H, 5.19; N, 3.44. Found:
C, 56.24; H, 5.14; N, 3.41.
Steg H~ Methyl cis-l'+/-)-7-(4-methoxvnhenylsulfonyl)-5-
vinvl-4 5 6 7 8 9-hexahydrothienof2 3-dlazocine-6-
carboxylate
To a solution of a 9:1 Z:E mixture of 11-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-4,7,10,11,12,13-hexahydro-8-oxa-1-thia-
11-aza-cyclopentacylododecen-9-one (748 mg, 1.84 mmol)
dissolved in THF (18 ml) at -78°C was added TBSOTf (0.63
ml, 2.7 mmol) followed immediately by a 0.5 M solution
of KHMDS in toluene (5.5 ml, 2.7 mmol). The reaction
mixture was allowed to warm to about 0°C, over 10
minutes. The reaction mixture was then dilute with
diethyl ether and poured onto pH 7 aqueous buffer
solution. After addition of small volume of brine, the
layers were separated and the organic layer was washed
with brine, dried (MgSO,) and concentrated to remove the
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
203
THF and diethyl either. This solution was diluted with
additional toluene (l3ml) and heated to 95°C for 2 h.
The reaction mixture was then concentrated and the
residue was dissolved in THF (2.5 ml) and methanol (10
ml) and treated with a 10% aqueous solution of K2C03 (5.2
ml, 3.8 mmol). The mixture was stirred 1.5 h at room
temperature and then concentrated to remove the THF and
methanol. The residual aqueous mixture was diluted with
H20 and acidified with 2 N HCI (to pH 2) to give a white
precipitate that was extracted into ethyl acetate. The
organic phase was washed with brine, dried (NazS04) and
concentrated to give cis-(+/-)-7-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5-vinyl-4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydrothieno[2,3-
d]azepine-6-carboxylic acid which was carried to the
next step without further purification. A solution of
the crude acid (860 mg) dissolved in benzene and
methanol (2:1, 22 ml) at 0°C was added to a 2 M solution
of TMSCHNZ in hexanes ( 1. 5 ml , 3 mmol ) . The reaction
mixture was stirred 15 minutes and then the solvents
were removed under reduced pressure. The reside was
purified by flash chromatography (silica, 25~ ethyl
acetate in hexanes) to give the desired product.
Recrystallization from dichloromethane-hexanes gave the
crude product as a white solid: Rf= 0.50 (silica, 500
ethyl acetate in hexanes); Rf= 0.38 (silica, 10~ ethyl
acetate in toluene}; mp 105-107°C (dicloromethane-
hexanes); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 422 (M+H), 439
(M+NHa) ; HRMS (EI+) for C2oH23NO5Sz (M+) , calcd 421.1018,
found 421.1025; Anal. Calcd for CzoH23NO5S2: C, 56.99; H,
5.50; N, 3.32. Found: C, 56.96; H, 5.58; N, 3.39.
Step I ~ Methyl ~~rans ~+/ - ) - 7 - ( 4 -methoxyghenylsul fond )
5-phenethvl-4 5 6 7 8 9-hexahydro-thienof2 3-dlazocine-
~- carbQ~3rlate
Methyl trans-(+/-)-7-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5-
phenethyl-4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydro-thieno[2,3-d]azocine-6-
carboxylate was prepared from methyl cis-(+/-)-7-(4-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
204
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5-vinyl-4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydro
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-6-carboxylate (30 mg,71 mmol)
according to the same procedure used for the preparation
of methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
phenethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-
carboxylate, using a 0.5 M solution of 9-BBN in THF
(2.25 mL, 1.13 mmol) dissolved in THF (7 ml). This was
followed by the addition of PdCl2(dppf)~CHZC12 (56 mg, 69
~.mol) , iodobenzene (0.66 ml, 5.9 mmol) , KZC03 (390 mg,
2.83 mmol) , DMF (3 mL) , and H20 (0.6 mL) . The residue
was purified by flash chromatography (silica, 3~ ethyl
acetate in toluene) to give the desired product as a
dark oil: Rf = 0.46 (silica, 10~ ethyl acetate in
toluene); MS (positive) m/z 500 (M+H), 517 (M+NHa); HRMS
(EI+) for CZ6Hz9N05SZ (M+) , calcd 499.41487, found
499.1446. This material was carried onto the next step
without further purification.
~~ep J~ trans-(+/-)-7-(4-Methoxyghenvlsulfonvl)-5-
phenethvl-4 5 6 7 8 9-hexa~dro-thieno[2 3-dlazocine-6-
carboxylic acid
Trans-(+/-)-7-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5-phenethyl-
4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydro-thieno[2,3-d]azocine-6-carboxylic
acid was prepared from methyl trans-(+/-)-7-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5-phenethyl-4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydro-thieno
[2,3-d]azocine-6-carboxylate (350 mg) according to the
same procedure used for the preparation of trans-(+/-)-
6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid,
using 1 N LiOH (3.45 mL, 3.45 mmol) dissolved in THF:H20
(3:1, 24 mL). The THF was removed in vacuo and the
solids that remained in the aqueous layer were collected
by filtration. These solids were suspended in water
treated with 1 N HC1 (to pH 2), and extracted into ethyl
acetate. The organic layer was dried (NaZS04) and
concentrated to give the desired product as a white
foam: Rf = 0.46 (silica, 10~ methanol in
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
205
dichloromethane); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 503 (M+NHa); MS
(ESI, negative) m/z 484 (M-H) ; HRMS (EI+) for CZSH2~NOSSz
(M+), calcd 485.1331, found 485.1332; Anal. Calcd for
C25Hz7NO5S2: C, 61.83; H, 5.60; N, 2.88. Found: C,
61.86; H, 5.81; N, 2.69.
Step K: trans-(+/-)-7-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5-
~henethyl-4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahvdrothienof2,3-dlazocine-6-
hvdroxamic acid
trans-(+/-)-7-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5-phenethyl-
4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydrothieno[2,3-d]azocine-6-hydroxamic
acid was prepared from trans-(+/-)-7-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5-phenethyl-4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydrothieno[2,3-
d]azocine-6-carboxylic acid (75 mg, 0.16 mmol) according
to the same procedure used for the preparation of trans-
(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid,
using hydroxylamine hydrochloride (79 mg, 1.1 mmol),
diisopropylethylamine (265 uL, 1.52 mmol), and PyBroP
(176 mg, 0.38 mmol) dissolved in dichloromethane (3 mL).
The residue was purified by column chromatography
(silica, 2.5~s methanol in methylene chloride) to give
the desired product as a white foam: Rf= 0.57 (silica,
7.55 methanol in dichloromethane); MS (positive) m/z 501
(M+H), 518 (M+NHa); MS (negative) m/z 499 (M-H); HRMS
(FAB+) for Ca5H29N2O;S2 (M+H) , calcd 501.1518, found
501.1528; Anal. Calcd for CZSHzeNz05S2: C, 59.98; H, 5.64;
N, 5.60. Found C, 59.91; H, 5.71; N, 5.44.
Example 69
O
1 0 OH
S~N~S ~ ~ OMe
O
Preparation of trans-(+/-)-7-(4-Methoxyghenylsulfonyl)-
5-vinyl-4 5 6 7 8 9-hexahydrothienof2 3-dlazepine-6-
carbox~lic acid and its methyl ester
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
206
trans-(+/-)-7-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5-vinyl-
4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydrothieno[2,3-d]azepine-6-carboxylic
acid was prepared from methyl cis-(+/-}-7-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5-vinyl-4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydrothieno[2,3-
d]azepine-6-carboxylate (28 mg, 66 mmol) according to
the same procedure used for preparation of traps-(+/-)-
6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid, using a 1M
aqueous solution of LiOH (0.2 ml, 0.2 mmol) dissolved in
THF and Hz0 (3:1, 2 ml) to yield the desired product as
a white foam: Rf = 0.5 (silica, 10% methanol in
dichloromethane); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 408 (M+H},
(M+NH4); MS (ESI, negative) m/z 406 (m-H); HRMS (E1+)
for C19HZ1NOSSz (M+) , calcd 407.0861, found 407.0852. In
order to confirm that the base has indeed induced
epimerization, the methyl ester of the traps carboxylic
acid was formed according to the same procedure used for
the preparation of methyl traps-(+/-)-6-(4-
Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylate, using a 2 M solution
of TMSCHN2 in hexanes (24 uL, 48 mmol) dissolved in
benzene and methanol (2:1, 1.5 ml). The residue was
purified by flash chromatography (silica, 25o ethyl
acetate in hexanes) to give the desired ester as a white
foam: Rf = 0.50 (silica 50~ ethyl acetate in hexanes);
MS (ESI, positive) m/z 422 (M+H) , 439 (M+NH,) ; HRMS
(EI+) for CZOH23NO5Sz (M+) , calcd 421.1018, found 421.1035.
Exam_nle 70
Preparation of traps-l+/-)-6-(4-Methoxvnhenvlsulfonvl)-
4-vinyl-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdrothienof2 3-clgvri ine-5-
hvdroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
207
Steo A: (3-Bromothiophen-2-yl)methanol
To a solution of the 3-bromo-2-formyl-thiophene (15 g,
78.5 mmol) dissolved in methanol and dichloromethane
(3:2, 785 mL) was added the NaBH4 (1.4 g, 38.2 mmol) in
two portions. The mixture was stirred for 20 minutes,
treated with 2 N HC1 (10 mL), and then concentrated in
vacuo. The residue was partitioned between ethyl
acetate and HZO. After separation, the aqueous layer
was re-extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined
organic layers were washed with 1 N HC1 and brine, dried
(MgS04), and concentrated to give the desired product as
a yellow oil: RF= 0.35 (silica 20°s ethyl acetate in
hexanes); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 211 (M+NH4).
Steg B- Methyl N-(3-Bromothio"phen-2-yl)methyl-N-(4-
methoxyphenvlsulfonyl)aminoacetate
A solution of triphenylphosphine (30.9 g, 118 mmol) in
THF (250 mL) was cooled to 0°C and treated with
diisopropylazodicarboxylate (23.2 mL, 118 mmol). A
precipitate formed as the reaction mixture stirred for
minutes. To this was added (3-bromothiophen-2-
yl)methanol {15.1 g) dissolved in THF (80 mL), followed
by addition of the methyl N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
25 aminoacetate (30.5 g, 118 mmol) dissolved in THF (155
mL). The resulting solution was warmed to ambient
temperature and stirred for 24 h. The solvent was
evaporated in vacuo and the residue was purified by
flash chromatography (silica, 0 to 1~ acetone in
30 toluene) to give the desired product as a yellow solid.
Trituration of this solid with hexanes gave a white
solid: Rf= 0.5 (silica, 5~ acetone in toluene); mp 96-
99qC; MS (ESI, positive) m/z 434 (M+H, '9Br), 436 (M+H,
e'Br) , 451 (M+NH4, "Br) , 453 (M+NH4, 8'Br) ; HRMS (FAB+) for
C15H1,NOSS,Br (M+H, '9Br) , calcd 433.9732, found 433.9729;
Anal. Calcd for C15H,6NOSSzBr: C, 41.48; H, 3.71; N, 3.22.
Found: C, 41.60; H, 3.65; N, 3.20.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
208
Step C~ Methyl N- (3- (3- (tert-Butvldimethylsilanyloxy~ -
propenyl)thiophen-2-vl)methvl)-N-(4-methoxvnhenyl
~ulfonvl)aminoacetate
Methyl N-(3-(3-(tent-Butyldimethylsilanyloxy)-
propenyl)thiophen-2-yl)methyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)aminoacetate was prepared from methyl N-(3-
bromothiophen-2-yl)methyl-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)
aminoacetate (1.56 g, 3.6 mmol) according to the same
procedure used for the preparation of methyl N-(2-(3-(3-
(tert-butyldimethylsilanyl oxy)propenyl)thiophen-2-
yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl sulfonyl)aminoacetate,
using (Z) -"Bu,SnCHCHCH20Si'BuMe2 (20:1; Z:E) and
PdCl2 (PPh3) z (202 mg, 0:29 mmol) in toluene (21 mL) . The
residue was purified by flash chromatography (silica, 10
to 25~ ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give the desired
product as a yellow oil in a 20:1 ratio of cis to trans
isomers. Data for the major (cis) isomer: Rf= 0.2
(silica, 20~ ethyl acetate in hexanes); MS (ESI,
positive) m/z 543 (M+NHa) ; Anal . Calcd for Ca4H35NO6S2Si
C, 54.83; H, 6.71; N, 2.66. Found: C, 55.00; H, 6.85;
N, 2.66.
Step D~ N-((3-(3-Hydroxypropenyl)thiophen-2-vl)methyl)-
N-(4-methoxyphen~lsulfonvl)aminoacetic acid
N-((3-(3-Hydroxypropenyl)thiophen-2-yl)methyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid was prepared from
methyl N-(3-(3-(tert-butyldimethylsilanyloxy)-
propenyl)thiophen-2-yl)methyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)aminoacetate (20:1 (Z: E) mixture, 1.55 g, 2.95
mmol) according to the same procedure used for the
preparation of N-(2-(3-(3-(tert-butyldimethylsilanyloxy)
propenyl)thiophen-2-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)aminoacetic acid, using 1 N KOH (4.4 M1)
dissolved in THF (31 ml). The crude acid was carried
onto the next step without purification: Rf - 0.5
(silica, 105 methanol in dichloromethane); MS (ESI,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
209
negative) m/z 396 (M-Si'BuMe2) , 510 (M-H) . N- ( (3- (3-
Hydroxypropenyl)thiophen-2-yl)methyl)-N-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid was obtained
according to the same procedure used for the preparation
of N-(2-(3-(3-hydroxypropenyl)thiophen-2-yl) ethyl)-N-
(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid, using the
crude carboxylic acid (1.27 g) and a 1 M THF solution of
TBAF (5 ml) dissolved in THF (23 ml). The residue was
purified by flash chromatography (silica, ethyl acetate
to 10~ methanol in ethyl acetate with 1~ acetic acid) to
give the desired product as a tan solid in a 10 to 1
ratio of cis to traps isomers. Data for the major (cis)
isomer: Rf = 0.25 (silica, 10~ methanol in
dichloromethane); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 415 (M+H); MS
(ESI, negative) m/z 396 (M-H) ; HRMS (FAB+) for Cl~HZON06Sz
(M+H), calcd 298.0732, found 398.0806; Anal. Calcd for
C1,H19NO6SZ:C, 51.37; H, 4.82; N, 3.52. Found: C, 51.17; H,
4.94; N, 3.49.
teQ,E~ 10-(4-Methoxyghenvlsulfonyl)-9 10 11 12-
~etrahvdro-6H-7oxa-1-thia-10-aza-cyclopentacycloundecen-
8-one
10-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-9,10,11,12-tetrahydro-6H-
7oxa-1-thia-10-aza-cyclopentacycloundecen-8-one was
prepared from N-((3-(3-Hydroxypropenyl)thiophen-2-yl)
methyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)aminoacetic acid
(10:1 (Z:E) mixture, 1.44 g, 3.6 mmol) according to the
same procedure used for the preparation of 10-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-9,10,11,12-tetrahydro-6H-7-oxa-1-thia-
10-aza-cyclopentacycloundecen-8-one, using 2-chloro-1-
methylpyridinium iodide (3.6 g, 14.1 mmol), and
triethylamine (3.9 mL, 28.1 mmol) in CH3CN (518 mL).
The residue was purified by flash chromatography
(silica, 25 to 40% ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give the
desired product as a white solid. This product could be
recrystallized from ethyl acetate-hexanes: Rf= 0.42
(silica, 50~s ethyl acetate in hexanes); mp 144-145pC
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
210
(ethyl acetate-hexanes); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 380
(M+H) , 397 (M+NH4) ; HRMS (EI+) for C1~H1~NOSSz: C, 53. 81;
H, 4.52; N, 3.69. Found: C, 53.92; H, 4.39; N, 3.64.
step F~ Methvl cis- (+/-) -6- (4-metho~r~henylsulfonyl) -4-
vinyl-4 5 6 7-tetrahvdro-thienof2 3-clgvridine-5-
carboxylate
Methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylate
was prepared from 10-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
9,10,11,12-tetrahydro-6H-7oxa-1-thia-10-aza-
cyclopentacycloundecen-8-one (325 mg, 0.86 mmol)
according to the same procedure used for the preparation
of methyl cis-(+/-)-7-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5-vinyl-
4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydrothieno[2,3-d]azocine-6-carboxylate,
using TBDMSOTf (0.3 mL, 1.3 mmol), and a 0.5 M toluene
solution of KHMDS (2.6 ml, 1.3 mmol) dissolved in THF
(10 ml). After the buffered aqueous work-up, TLC
indicated a mixture of the silyl ketene acetal (Rf =
0.66, silica, 50~ ethyl acetate in hexanes) and the
silyl ester (Rf = 0.66, silica, 505 ethyl acetate in
hexanes). This was followed by treatment of the above
solution with additional toluene (8 ml) and heating to
80~C for 1 h. The reaction mixture was then
concentrated to give the crude silyl ester, which was
dissolved in a mixture of methanol-THF (3:3:1, 6.5 ml)
and treated with a 10o aqueous solution of KZC03 (2.4 ml,
1.7 mmol). This gave the crude carboxylic acid (Rf =
0.32, silica, 10~ methanol in dichloromethane), which
was dissolved in benzene-methanol (2:1, 15 ml) and
treated with a 2 M solution of TMSCHNZ in hexanes (0.6
ml, 1.2 mmol), according to the same procedure
referenced above. The residue was purified by flash
chromatography (silica, 25~ ethyl acetate in hexanes) to
give the desired product as a white solid. This
material could be recrystallized from dichloromethane-
hexanes: RE = 0.52 (silica, 50~ ethyl acetate in
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
211
hexanes); mp 110-112pC (dichloromethane-hexanes); MS
(ESI, positive) m/z 394 (M+H), 411 (M+NHa); HRMS (FAB+)
for ClBHZONOSSz (M+H) , calcd 394.0783 found 394.0724; Anal
Calcd C18H19NOSSz: C, 54.94; H, 4.87; N, 3.56. Found: C,
55.06; H, 4.86; N, 3.62.
Step G: trans- (+/-) -6- l4-Methoxwhenylsulfonvl) -4-
vinvl-4,~,6,7-tetrahvdrothieno(2,3-clpyridine-5-
carboxylic acid
trans-(+/-)-6-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid was
prepared from methyl cis-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-4-vinyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3-
c]pyridine-5-carboxylate (138 mg, 0.35 mol) according to
the same procedure used for the preparation of trans-
(+/-)-6-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-carboxylic acid,
using a 1 M aqueous solution of LiOH (1.05 ml, 1.05
mmol) dissolved in THF and HZO (3:1, 8 ml) . This gave
the desired product as a white foam: Rf = 0.25 (silica,
10o methanol in dichloromethane); MS (ESI, positive) m/z
380 (M+H), 397 (M+NH,); MS (ESI, negative) m/z 378 (M-H)
HRMS (FAB+) for CzoH~3NO5S~ (M+H) , calcd 380.0626, found
380.0681. The cis acid (6 mg, 5~) was also obtained as
a clear oil: Rf = 0.32 (silica, 10~ methanol in
dichloromethane); MS (ESI, positive) m/z 380 (M+H), 397
(M+NHa); MS (ESI, negative) m/z 378 (M-H).
Steg H~ trans-(+/-)-6-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonvl)-4-
vinyl-~5 6,7-tetrahvdrothienof2,3-cltwridine-5-
hydroxamic acid
trans-(+/-)-6-(4-Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid was
prepared from trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-
vinyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-
carboxylic acid (60 mg, 0.16 mmol) according to the same
procedure used for the preparation of trans-(+/-)-6-(4-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
212
Methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid, using
hydroxylamine hydrochloride (33 mg, 0.47 mmol),
diisopropylethylamine (110 ~1, 0.63 mmol), and PyBroP
(90 mg, 0.19 mmol} dissolved in dichloromethane (3 ml).
The residue was purified by column chromatography
(silica, 2.5 to 5~ methanol in methylene chloride) to
give the desired product as a white foam. This material
could be triturated with diethyl ether and then
recrystallized from dichloromethane-hexanes to give pure
product: Rf = 0.44 (silica, 105 methanol in
dichloromethane); mp 145.5-147.5QC; MS (ESI, negative)
m/z 393 (M-H}; MS (ESI, negative) m/z 393 (M-H) (FAB+)
for C1,H19NaO5S2 (M+H) , calcd 395.0735, found 395.0721.
Exa~~le 71
Utilizing the procedures of Examples 1-70, the compounds
of Table III can be prepared.
TABLE III
4-trans-isopropyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno(2,3,-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-trans-isopropyl-6-(4-chlorophenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3,-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-trans-phenethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3,-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-trans-phenethyl-6-(4-fluorophenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3,-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-trans-hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2,3,-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic
acid
4-traps-(4-biphenylbenzyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thieno[2,3,-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic
acid
4-traps-isopropyl-6-(4-chlorophenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
213
4-trans-butyl-6-(4-chlorophenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-trans-(4-bromobenzyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid
4-trans-(4-fluorobenzyl)-6-(4-fluorophenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid
4-trans-isobutyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl}-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-
hydroxamic acid
4-cis-isobutyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-
hydroxamic acid
4-trans-(4-phenylbenzyl)-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]
azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-cis-(4-phenylbenzyl)-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5
hydroxamic acid
4-trans-(4-pyridinebenzyl)-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-cis-(4-pyridinebenzyl)-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxy
phenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]
azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-trans-(4-bromobenzyl)-6-(3-chlorophenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid
4-traps-(4-fluorobenzyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid
4-traps-isobutyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-nitrophenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-
hydroxamic acid
4-cis-isobutyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(3-chlorophenylsulfonyl}-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid
4-traps-(4-phenylbenzyl)-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(3-
pyridinephenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
214
4-cis-(4-phenylbenzyl)-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(3-chlorophenyl
sulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-
hydroxamic acid
4-trans-(4-pyridinebenzyl)-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(2-
fluorophenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3,dlazepine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-cis-(4-pyridinebenzyl)-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-
nitrophenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H
thienoC2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
Example 72
Using the procedures of the above general descriptions
and the above examples, the compounds of Tables IV-X can
be prepared.
TABLE IV
Rli
OH
R9~~ ~ H
812
R1
Rs Rii
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(0)- (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Me0-C(O)- (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(O)- (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- (cis)HO-
C (O) -
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(O)- (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(0)- (cis)HO-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCTlUS98/16147
215
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- (cis)HO-
NH-C (O) -
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) (cis)HO-
(Me) N-C (0)
-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzEtN-C(0)- (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl (cis)HO-
pentyl ) NHC
(O) -
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-diphenyl (cis)HO-
butyl ) NHC
(O) -
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- PhMeN-C(0)- (cis)HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- PhMeN-C(O)- (trans}HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- BzNH-C(0)-O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- MeNH-C(0)-O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- i-propylNH-
C (0) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
C (O) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (1-Ph-ethyl)
NH-C (O) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
C (O) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (2-Ph-ethyl)
NH-C (O) -O-
C-H S phenyl H- HO-
C-H S 4-CN-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4- (Me-C(0) - H- HO-
NH}-Ph-
C-H S 4-i-propyl-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4-Et-Ph- H- HO-
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
216
C-H S 4-t-butyl-Ph- H- H-
C-H S n-dodecyl H- HO-
C-H S n-octyl H- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-SOz-NH- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- MeC(0)-NH- HO-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- Me0-C(O)-NH- (4-F-Ph)NH-
C (O) -0-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- methyl H-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-C(O)-NH- HO-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- benzyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(0)-O-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
C-H 0 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- H-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
C-H 0 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(0)-O-
C-H 0 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(O)-0-
S C-H 4-MeS-Ph- BzMeN-C(0)- HO-
S C-H 4-C1-Ph- phenyl Ph-SOZ-NH-
S C-H 4-CF30-Ph- Me0-C(0)- 2-thienyl-S-
S C-H 5-benzo- HO-C(0)- HO-
dioxolyl
S C-H 4-Me-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl MeS-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
217
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
S C-H n-dodecyl Bz0-C(O)- HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- 3-thienyl-NH-
C (O) -O-
S C-H 2-furyl Bz-NH-C (0) - HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- 2-pyridyl-NH-
NH-C (O) - C (0) -O-
S C-H 4-Ph0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) HO-
(Me) N-C (O)
-
S C-H 4-pyridyl BzEtN-C(O)- propargyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl 2-thienyl-O-
pentyl)NHC(0)-
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl HO-
O C-H 5-benzofuranyl 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(O)- HO-
0 C-H 5-benzo- Ph-NH-C(O)- (1-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(O)-O-
0 C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
O C-H 4-Ph0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- HO-
NH-C (O) -
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) vinyl
(Me) N-C (0)
-
O C-H n-dodecyl BzEtN-C(0)- HO-
0 C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl PhNH-C(0)-0-
pentyl ) NHC
(O) -
N S 4-morpholino phenyl PhNH-C(O)-0-
N S 2-naphthyl 3-pyridyl MeNH-C(O)-O-
N S 3,4-dimethoxy- 4-morpholino- i-propylNH-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
218
phenyl C (O) - C (0) -O-
S N 4-piperidinyl- Bz0-C(O)- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
butyl C (0) -0-
S N 6-benzo- Ph-NH-C(0)- 2-thienyl-NH-
dioxanyl C (O) -O-
S N 4-hydroxy- 2-pyridyl-NH- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
cyclohexyl C (0) - C (O) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(O)- 3-(3-furyl)-
butyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-acetamido- 4-methyl-
phenyl pentyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 2-MeS-ethyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
ethyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-chlorobenzyl 4-pyrid-3-yl-
butyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-pyridyl 3-hydroxy-
butyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-CHZ-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(0)- 2-(pyrid-3-yl-
C (0) -NH) -ethyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl 2-(2-thienyl-
thio)ethyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- PhNH-C(O)-
C (O) - methyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 3-MeS-propyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- 2-phenoxyethyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- 3-pyrid-3-yl-
propyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl-NH- iso-butyl
C (O) -
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
217
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
219
OH
N~
H
R9
2
R1
X Z R1 R9 Ril
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C (O) - HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
C-H S 4-CF30-Ph- 3-pyridyl H-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me-Ph- Ph-NH-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 3-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzEtN-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl HO-
pentyl ) NHC
(0) -
C-H S 4-Cl-Ph- PhMeN-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 2-thienyl PhMeN-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- BzNH-C(O)-0-
C-H S 3,4-dimethoxy- H- PhNH-C(O)-0-
phenyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
C (O) -0-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- i-propylNH-
TABLE V
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
220
C (0) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- MeNH-C(O)-O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (1-Ph-ethyl)
NH-C (0) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
C (0) -O-
C-H S 5-benzo- H- (2-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(0)-O-
C-H S phenyl H- vinyl-
C-H S 4-CN-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4- (Me-C (0) H- HO-
-
NH ) - Ph -
C-H S 4-i-propyl-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4-Et-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4-t-butyl-Ph- H- H-
C-H S n-dodecyl H- HO-
C-H S n-octyl H- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-SOZ-NH- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- MeC(0)-NH- HO-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- Me0-C(0)-NH- (4-F-Ph)NH-
C (O) -O-.
S N 4-Me0-Ph- methyl H-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-C(0)-NH- HO-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- benzyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
221
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(O)- H-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(0)-O-
S C-H 4-MeS-Ph- BzMeN-C(O)- HO-
S C-H 4-C1-Ph- phenyl Ph-SOZ-NH-
S C-H 4-CF30-Ph- Me0-C(0)- thienyl-S-
S C-H 5-benzo- HO-C(0)- HO-
dioxolyl
S C-H 4-Me-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl MeS-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
S C-H n-dodecyl Bz0-C(O)- HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(0)- thienyl-NH-
C (O) -O-
S C-H furyl Bz-NH-C(0)- HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- 2-pyridyl-NH-
NH-C (O) - C (O) -O-
S C-H 4-Ph0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) HO-
(Me) N-C (O)
-
S C-H 4-pyridyl BzEtN-C(0)- propargyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl thienyl-0-
pentyl) NHC
(0) -
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl HO-
O C-H 5-benzofuranyl 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(O)- HO-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
222
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
O C-H 5-benzo- Ph-NH-C(O)- (1-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(O)-O-
0 C-H 4-Ph0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- HO-
NH-C (0) -
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) vinyl
(Me) N-C (O)
-
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
pentyl ) NHC
(O)
O C-H n-dodecyl BzEtN-C(O)- HO-
N S 4-morpholino phenyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
N S 2-naphthyl 3-pyridyl MeNH-C(0)-O-
N S 3,4-dimethoxy- 4-morpholino- i-propylNH-
phenyl C (O) - C (O) -O-
S N 4-piperidinyl- Bz0-C(0)- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
butyl C (O) -O-
S N 6-benzo- Ph-NH-C(O)- thienyl-NH-
dioxanyl C (O) -O-
S N 4-hydroxy- 2-pyridyl-NH- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
cyclohexyl C (O) - C (O) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C (O) - 3- (3-furyl)
-
butyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-acetamido- 4-methyl-
phenyl pentyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 2-MeS-ethyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(0)-
ethyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-chlorobenzyl 4-pyrid-3-yl-
butyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-pyridyl 3-hydroxy-
butyl
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
223
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
methyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(O)- 2-(pyrid-3-yl-
C (O) -NH) -ethyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl 2-(2-thienyl-
thio)ethyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 3-MeS-propyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- PhNH-C(0)-
C{O)- methyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- 2-phenoxyethyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(0)- 3-pyrid-3-yl-
propyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl-NH- iso-butyl
C (O) -
TABLE VI
R12
N~ OH
H
R9
'1
R
R1 ~ L.
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
C-H S 4-CF30-Ph- 3-pyridyl H-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
224
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 3-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzEtN-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl HO-
pentyl) NHC (O)
-
C-H S 4-C1-Ph- PhMeN-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 2-thienyl PhMeN-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- BzNH-C(O)-O-
C-H S 3,4-dimethoxy- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
phenyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- MeNH-C(0)-0-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- i-propylNH-
C (O) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
C (0) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (1-Ph-ethyl)
NH-C (O) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
C (0) -O-
C-H S 5-benzo- H- (2-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(0)-0-
C-H S phenyl H- vinyl-
C-H S 4-CN-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4- (Me-C (O) H- HO-
-
NH)-Ph-
C-H S 4-i-propyl-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4-Et-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4-t-butyl-Ph- H- H-
C-H S n-dodecyl H- ~ HO-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
225
C-H S n-octyl H- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-SOZ-NH- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- MeC(O)-NH- HO-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- Me0-C(0)-NH- (4-F-Ph)NH-
C (O) -O-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- methyl H-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-C(O)-NH- HO-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- benzyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(0)-0-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(O)- H-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
S C-H 4-MeS-Ph- BzMeN-C(0)- HO-
S C-H 4-Cl-Ph- phenyl Ph-S02-NH-
S C-H 4-CF30-Ph- Me0-C (O) - thienyl-S-
S C-H 5-benzo- HO-C(O)- HO-
dioxolyl
S C-H 4-Me-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl MeS-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
S C-H n-dodecyl Bz0-C(0)- HO-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
226
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- thienyl-NH-
C (O) -O-
S C-H furyl Bz-NH-C(0)- HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- 2-pyridyl-NH-
NH-C (O) - C (O) -O-
S C-H 4-Ph0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) HO-
(Me) N-C (O)
-
S C-H 4-pyridyl BzEtN-C(O)- propargyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl thienyl-O-
pentyl ) NHC
(O)
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl HO-
0 C-H 5-benzofuranyl 4-marpholino- HO-
C (O) -
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(O)- HO-
O C-H 5-benzo- Ph-NH-C(O)- (1-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(0)-0-
0 C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(0)- HO-
O C-H 4-Ph0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- HO-
NH-C (0) -
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) vinyl
(Me) N-C (0)
-
O C-H n-dodecyl BzEtN-C(0)- HO-
0 C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl PhNH-C(0)-0-
pentyl ) NHC
(0) -
N S 4-morpholino phenyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
N S 2-naphthyl 3-pyridyl MeNH-C(0)-O-
N S 3,4-dimethoxy- 4-morpholino- i-propylNH-
phenyl C (O) - C (0) -0-
S N 4-piperidinyl- Bz0-C(0)- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
butyl C(0)-O-
*rB
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
227
S N 6-benzo- Ph-NH-C(O)- thienyl-NH-
dioxanyl C(O)-0-
S N 4-hydroxy- 2-pyridyl-NH- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
cyclohexyl C (O) - C (O) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(O)- 3-(3-furyl)-
butyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-acetamido- 4-methyl-
phenyl pentyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 2-MeS-ethyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
ethyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-chlorobenzyl 4-pyrid-3-yl-
butyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-pyridyl 3-hydroxy-
butyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
methyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(O)- 2-(pyrid-3-yl-
C (O) -NH) -ethyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl 2-(2-thienyl-
thio)ethyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- PhNH-C(O)-
C (O) - methyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 3-MeS-propyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- 2-phenoxyethyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(0)- 3-pyrid-3-yl-
propyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl-NH- iso-butyl
C (0) -
TABLE VII
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
228
R11
N, OH
H
R9 ~X~ ~
2
~
1
R
X Z
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
C-H S 4-CF30-Ph- 3-pYridyl H-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 3-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- BzEtN-C(O)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl HO-
pentyl ) NHC
(0)
C-H S 4-C1-Ph- PhMeN-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 2-thienyl PhMeN-C(0)- HO-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- BzNH-C(O)-0-
C-H S 3,4-dimethoxy- H- PhNH-C(0)-0-
phenyl
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- MeNH-C(0)-O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- i-propylNH-
C (0) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
229
C (O) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (1-Ph-ethyl)
NH-C (O) -O-
C-H S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
C (O) -O-
C-H S 5-benzo- H- (2-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(O)-O-
C-H S phenyl H- vinyl-
C-H S 4-CN-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4- {Me-C(O) - H- HO-
NH ) - Ph -
C-H S 4-i-propyl-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4-Et-Ph- H- HO-
C-H S 4-t-butyl-Ph- H- H-
C-H S n-dodecyl H- HO-
C-H S n-octyl H- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- ph-SOZ-NH- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- MeC(O)-NH- HO-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- Me0-C(0)-NH- (4-F-Ph)NH-
C (O) -0-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- methyl H-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-C(0)-NH- HO-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- benzyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(0)-O-
S N 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
N S 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
230
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(O)- H-
C-H 0 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
C-H O 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
S C-H 4-MeS-Ph- BzMeN-C(O)- HO-
S C-H 4-C1-Ph- phenyl Ph-S02-NH-
S C-H 4-CF30-Ph- Me0-C(O)- thienyl-S-
S C-H 5-benzo- HO-C(O)- HO-
dioxolyl
S C-H 4-Me-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl MeS-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
S C-H n-dodecyl Bz0-C(O)- HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- thienyl-NH-
C (O) -O-
S C-H furyl Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- 2-pyridyl-NH-
NH-C (0) - C (0) -0-
S C-H 4-pyridyl BzEtN-C(0)- propargyl
S C-H 4-Ph0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) HO-
(Me) N-C (0)
-
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl thienyl-O-
pentyl ) NHC
(0) -
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl HO-
0 C-H 5-benzofuranyl 4-morpholino- HO-
C (0) -
0 C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(0)- HO-
O C-H 5-benzo- Ph-NH-C(0)- (1-Ph-ethyl)
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
231
thiazolyl NH-C(O)-O-
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
O C-H 4-Ph0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- HO-
NH-C (O) -
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) vinyl
(Me) N-C (O)
-
O C-H n-dodecyl BzEtN-C(0)- HO-
O C-H 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl PhNH-C(0)-O-
pentyl) NHC (0)
-
N S 4-morpholino phenyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
N S 2-naphthyl 3-pyridyl MeNH-C(O)-O-
N S 3,4-dimethoxy- 4-morpholino- i-propylNH-
phenyl C (O) - C (O) -O-
S N 4-piperidinyl- Bz0-C(0)- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
butyl C(O)-0-
S N 6-benzo- Ph-NH-C(0)- thienyl-NH-
dioxanyl C(O)-O-
S N 4-hydroxy- 2-pyridyl-NH- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
cyclohexyl C (O) - C (O) -O-
C-HS 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(O)- 3-(3-furyl)-
butyl
C-HS 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 2-MeS-ethyl
C-HS 4-Me0-Ph- 4-acetamido- 4-methyl-
phenyl pentyl
C-HS 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(0)-
ethyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-chlorobenzyl 4-pyrid-3-yl-
butyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- 4-pyridyl 3-hydroxy-
butyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/L1S98/16147
232
methyl
S C-H 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(0)- 2-(pyrid-3-yl-
C (O) -NH) -ethyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl 2-(2-thienyl-
thio)ethyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- PhNH-C(O)-
C (O) - methyl
N S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 3-MeS-propyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(O)- 2-phenoxyethyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- 3-pyrid-3-yl-
propyl
S N 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl-NH- iso-butyl
C (0) -
TABLE VIII
Rlo R11 O
OH
O ~ N
H
w
S02
R1
S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
S 4-CF30-Ph- 3-pYridyl H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (0) -
S 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(O)- HO-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
233
S 4-Me-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- HO-
S 3-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl HO-
pentyl ) NHC
(O) -
S 4-C1-Ph- PhMeN-C(O)- HO-
S 2-thienyl PhMeN-C(O)- HO-
S 4-MeO-Ph- H- BzNH-C(O)-O-
S 3,4-dimethoxy- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
phenyl
S 4-MeO-Ph- H- MeNH-C(O)-O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- i-propylNH-
C (O) -0-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
C (O) -O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (1-Ph-ethyl)
NH-C (O) -O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
C (o) -o-
S 5-benzo- H- (2-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(O)-O-
S phenyl H- vinyl-
S 4-CN-Ph- H- HO-
S 4 - (Me-C (O) H- HO-
-
NH)-Ph-
S 4-i-propyl-Ph- H- HO-
S 4-Et-Ph- H- HO-
S 4-t-butyl-Ph- H- H-
S n-dodecyl H- HO-
S n-octyl H- H-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
234
S 4-Me0-Ph- ph-SOZ-NH- H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- MeC(O)-NH- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- Me0-C(O)-NH- (4-F-Ph)NH-
C (O) -O-
O 4-Me0-Ph- methyl H-
O 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-C(O)-NH- HO-
O 4-Me0-Ph- H- benzyl
O 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
O 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
0 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
O 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
O 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- H-
O 4-MeS-Ph- BzMeN-C(0)- HO-
O 4-C1-Ph- phenyl Ph-SOZ-NH-
0 4-CF30-Ph- Me0-C(0)- thienyl-S-
O 5-benzo- HO-C(O)- HO-
dioxolyl
0 4-Me-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
O 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl MeS-
O 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
0 n-dodecyl Bz0-C(0)- HO-
0 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(0)- thienyl-NH-
C (0) -0-
0 furyl Bz-NH-C(0)- HO-
O 4-Me0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- 2-pyridyl-NH-
NH-C (O) - C (0) -O-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
235
S 4-Ph0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) HO-
(Me) N-C (0)
-
S 4-pyridyl BzEtN-C(O)- propargyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl thienyl-O-
pentyl ) NHC
(0) -
S 5-benzofuranyl 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
S 5-benzo- Ph-NH-C(O)- (1-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(O)-O-
S 4-Ph0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- HO-
NH-C (O) -
S 4-Me0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) vinyl
(Me) N-C (O)
-
S n-dodecyl BzEtN-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl PhNH-C(0)-O-
pentyl ) NHC
(O) -
S 4-morpholino phenyl PhNH-C(0)-O-
S 3,4-dimethoxy- 4-morpholino- i-propylNH-
phenyl C (O) - C (O) -O-
S 4-piperidinyl- Bz0-C(O)- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
butyl C (O) -O-
S 6-benzo- Ph-NH-C(0)- thienyl-NH-
dioxanyl C (O) -0-
S 2-naphthyl 3-pyridyl MeNH-C(0)-0-
S 4-hydroxy- 2-pyridyl-NH- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
cyclohexyl C (0) - C (0) -0-
S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(0) - 3- (3-furyl)
-
butyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-acetamido- 4-methyl-
phenyl pentyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 2-MeS-ethyl
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
236
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
ethyl
O 4-Me0-Ph- 4-chlorobenzyl 4-pyrid-3-yl-
butyl
O 4-Me0-Ph- 4-pyridyl 3-hydroxybutyl
O 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
methyl
O 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(0)- 2-(pyrid-3-yl-
C (O) -NH) -ethyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl 2-(2-thienyl-
thio)ethyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 3-MeS-propyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- PhNH-C(0)-
C (0) - methyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- 2-phenoxyethyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- 3-pyrid-3-yl-
propyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl-NH- iso-butyl
C (0) -
TABLE IX
R11
~. OH
~ S H
Y
02
R1
W
Y R, R R
S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(0)- HO-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
237
S 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
S 4-CF30-Ph- 3-PYridyl H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
S 4-Me-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- HO-
S 3-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(0)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl HO-
pentyl ) NHC
(O) -
S 4-Cl-Ph- PhMeN-C(0)- HO-
S 2-thienyl PhMeN-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- BzNH-C(O)-O-
S 3,4-dimethoxy- H- PhNH-C(O)-0-
phenyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- MeNH-C(O)-O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- i-propylNH-
C (O) -O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
C (O) -O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (1-Ph-ethyl)
NH-C (0) -0-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
C (0) -0-
S 5-benzo- H- (2-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(0)-0-
S phenyl H- vinyl-
S 4-CN-Ph- H- HO-
S 4 - (Me-C (O) H- HO-
-
NH) -Ph-
S 4-i-propyl-Ph- H- HO-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
238
S 4-Et-Ph- H- HO-
S 4-t-butyl-Ph- H- H-
S n-dodecyl H- HO-
S n-octyl H- H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- ph-SOZ-~- H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- MeC(O)-NH- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- Me0-C(0)-NH- (4-F-Ph)NH-
C (O) -O-
O 4-Me0-Ph- methyl H-
O 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-C(0)-NH- HO-
0 4-Me0-Ph- H- benzyl
0 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
0 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(0)-O-
0 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(0)-O-
O 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
O 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- H-
O 4-MeS-Ph- BzMeN-C(O)- HO-
0 4-C1-Ph- phenyl ph-SOZ-NH-
O 4-CF30-Ph- Me0-C (O) - thienyl-S-
O 5-benzo- HO-C(0)- HO-
dioxolyl
O 4-Me-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
0 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl MeS-
0 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
0 n-dodecyl Bz0-C(O)- HO-
O 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- thienyl-NH-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
239
C (O) -O-
O 4-Me0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- 2-pyridyl-NH-
NH-C (O) - C (O) -O-
O furyl Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Ph0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) HO-
(Me) N-C (O)
-
S 4-pyridyl BzEtN-C(O)- propargyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl thienyl-0-
pentyl ) NHC
(0)
S 5-benzofuranyl 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
S 5-benzo- Ph-NH-C(O)- (1-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(O)-O-
S 4-Ph0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- HO-
NH-C (0) -
S 4-Me0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) vinyl
(Me) N-C (O)
-
S n-dodecyl BzEtN-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl PhNH-C(0)-0-
pentyl ) NHC
(0) -
S 4-morpholino phenyl PhNH-C(O)-0-
S 2-naphthyl 3-pyridyl MeNH-C(0)-0-
S 3,4-dimethoxy- 4-morpholino- i-propylNH-
phenyl C (O) - C (0) -0-
S 4-piperidinyl- Bz0-C(O)- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
butyl C (0) -O-
S 6-benzo- Ph-NH-C(0)- thienyl-NH-
dioxanyl C (0) -O-
S 4-hydroxy- 2-pyridyl-NH- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
cyclohexyl C (O) - C (O) -0-
S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(0)- 3-(3-furyl)-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
240
butyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-acetamido- 4-methyl-
phenyl pentyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 2-MeS-ethyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
ethyl
O 4-Me0-Ph- 4-chlorobenzyl 4-pyrid-3-yl-
butyl
O 4-Me0-Ph- 4-pyridyl 3-hydroxy-
butyl
0 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
methyl
0 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(O}- 2-(pyrid-3- yl-
C (0) -NH) -ethyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl 2-(2-thienyl-
thio) ethyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 3-MeS-propyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- PhNH-C(O)-
C(O)- methyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(0)- 2-phenoxyethyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(0)- 3-pyrid-3-yl-
propyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl-NH- iso-butyl
C (O)
TABLE X
v12
to ~\N~OH
H
Y ~ 802
R1
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
241
Ri Rio Ria
S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(0)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- HO-C(0)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
S 4-CF30-Ph- 3-pYridyl H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (0) -
S 4-Me0-Ph- Bz0-C(0}- HO-
S 4-Me-Ph- Ph-NH-C(0)- HO-
S 3-Me0-Ph- Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl HO-
pentyl) NHC
(O) -
S 4-C1-Ph- PhMeN-C(O)- HO-
S 2-thienyl PhMeN-C(O)- HO-
S 3,4-dimethoxy- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
phenyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- BzNH-C(O)-0-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- i-propylNH-
C (O) -O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Ph0-Ph)NH-
C (0) -O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- MeNH-C(0}-O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (1-Ph-ethyl}
NH-C (O) -O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
C (0) -0-
S 5-benzo- H- (2-Ph-ethyl)
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
242
thiazolyl NH-C(O)-O-
S phenyl H- vinyl-
S 4-CN-Ph- H- HO-
S 4- (Me-C (0) H- HO-
-
NH) -Ph-
S 4-i-propyl-Ph- H- HO-
S 4-Et-Ph- H- HO-
S 4-t-butyl-Ph- H- H-
S n-dodecyl H- HO-
S n-octyl H- H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- ph-S02-NH- H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- MeC(0)-NH- HO-
S 4-Me0-Ph- Me0-C(O)-NH- (4-F-Ph)NH-
C (O) -O-
O 4-Me0-Ph- methyl H-
0 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-C(0)-NH- HO-
0 4-Me0-Ph- H- benzyl
O 4-Me0-Ph- H- HO-
O 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-O-
0 4-Me0-Ph- methyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
0 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- H-
0 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C (0) - H-
O 4-MeS-Ph- BzMeN-C(0)- HO-
O 4-C1-Ph- phenyl ph-S02-NH-
4-CF30-Ph- Me0-C (O) - thienyl-S-
0 5-benzo- HO-C(0)- HO-
dioxolyl
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
243
O 4-Me-Ph- 2-pyridyl HO-
0 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl MeS-
O 4-Me0-Ph- 4-morpholino- HO-
C (0) -
O 4-Me0-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- thienyl-NH-
C (O) -O-
O n-dodecyl Bz0-C(0)- HO-
O furyl Bz-NH-C(O)- HO-
0 4-Me0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- 2-pyridyl-NH-
NH-C (0) - C (O) -O-
S 4-Ph0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) HO-
(Me) N-C (O)
-
4-pyridyl BzEtN-C(0)- propargyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl thienyl-O-
pentyl)NHC(0)
-
S 5-benzofuranyl 4-morpholino- HO-
C (O) -
S 5-benzo- Ph-NH-C(O)- (1-Ph-ethyl)
thiazolyl NH-C(O)-O-
S 4-Ph0-Ph- 3-Ph-propyl- HO-
NH-C (0) -
S 4-Me0-Ph- (2-Ph-ethyl) vinyl
(Me) N-C (O)
-
S 4-Me0-Ph- (4,4-dimethyl PhNH-C(O)-O-
pentyl ) NHC
(O) -
S n-dodecyl BzEtN-C(O)- HO-
S 4-morpholino phenyl PhNH-C (O)
-~O-
S 2-naphthyl 3-pyridyl MeNH-C(0)-0-
S 3,4-dimethoxy- 4-morpholino- i-propylNH-
phenyl C(O)- C(O)-0-
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
244
S 4-piperidinyl- Bz0-C(O)- (4-PhO-Ph)NH-
butyl C (O) -O-
S 6-benzo- Ph-NH-C(O)- thienyl-NH-
dioxanyl C (O) -O-
S 4-hydroxy- 2-pyridyl-NH- (4-Me0-Ph)NH-
cyclohexyl C (O) - C (O) -O-
S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 2-MeS-ethyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- BzMeN-C(O)- 3-(3-furyl)-
butyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 4-acetamido- 4-methyl-
phenyl pentyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
ethyl
0 4-Me0-Ph- 4-chlorobenzyl 4-pyrid-3-yl-
butyl
O 4-Me0-Ph- 4-pyridyl 3-hydroxybutyl
O 4-Me0-Ph- H- PhNH-C(O)-
methyl
O 4-MeO-Ph- HO-C(O)- 2-(pyrid-3-yl-
C(0)-NH)-ethyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- phenyl 2-(2-thienyl-
thio)ethyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 3-pyridyl 3-MeS-propyl
S 4-MeO-Ph- 4-morpholino- PhNH-C(O)-
C (O) - methyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- Et0-C(O)- 2-phenoxyethyl
S 4-MeO-Ph- Ph-NH-C(O)- 3-pyrid-3-yl-
propyl
S 4-Me0-Ph- 2-pyridyl-NH- iso-butyl
c (o) -
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
245
Example 73
The following assays are in vitro assays which were
used to characterize the ability of compounds of this
invention to inhibit the production of TNF-a by
monocytes following LPS stimulation, Human Monocyte TNF
Convertase Assay, Human Neutrophil Collagenase Assay and
Human Fibroblast Stromelysin Assay.
Lipopolysaccharide-activated monocyte TNF production
assay
Isolation of monocvtes
Test compounds were evaluated in vitro for the
ability to inhibit the production of tumor necrosis
factor (TNF) by monocytes activated with bacterial
lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Fresh residual source
leukocytes (a byproduct of plateletpheresis) were
obtained from the local blood bank and peripheral blood
mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated by density
gradient centrifugation on Ficol-Paque Plus (Pharmacia).
PBMCs were suspended at 2 x 106/ml in DMEM supplemented
to contain 2o FCS (10 mM), 0.3 mg/ml glutamate, 100 U/ml
penicillin G and 100 mg/ml streptomycin sulfate
(complete media). Cells were plated into Falcon
flatbottom 96 well culture plates (200 ul/well) and
cultured overnight at 37oC and 6~ C02. Nonadherent
cells were removed by washing with 200 ul/well of fresh
medium. Wells containing adherent cells (~70~
monocytes) were replenished with 100 ul of fresh medium.
Preparation of test compound stock solutions
Test compounds were dissolved in DMS. Compound
stock solutions were prepared to an initial
concentration of 10 - 50 ~,iM. Stocks were diluted
initially to 20 - 200 ~.iM in complete media. Nine two-
fold serial dilutions of each compound were then
prepared in complete medium.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
246
Treatmentof cells with test compounds and activation of
TNF production with lipopolysaccharide
One hundred microliters of each test compound
dilution were added to microtiter wells containing
adherent monocytes and 100 ul complete medium.
Monocytes were cultured with test compounds for 60 min
at which time 25 ul of complete medium containing 30
ng/ml lipopolysaccharide from E. coli K532 were added to
each well. Cells were cultured an additional 4 hrs.
Culture supernatants were then removed and TNF present
in the supernatants was quantified using an ELISA.
TNF ELISA
Flat bottom 96 well Corning High Binding ELISA
plates were coated overnight (4oC) with 250 uL/well of 3
ug/ml murine ant i human TNFa MAb (R&D Systems #MAB210).
Wells were then blocked 1 h at room temperature with 200
uL/well of CaCl2-free ELISA buffer supplemented to
contain 20 mg/ml BSA (standard ELISA buffer: 20 mM, 150
mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 0.15 mM thimerosal, pH 7.4).
Plates were washed and replenished with 100 ul of test
supernatants (diluted 1:3) or standards. Standards
consisted of eleven 1.5-fold serial dilutions from a
stock of 1 ng/ml recombinant human TNF (R&D Systems).
Plates were incubated at room temperature for 1 h on
orbital shaker (300 rpm), washed and replenished with
100 ul/well of 0.5 ug/ml goat anti-human TNFa (R&D
systems #AB-210-NA) biotinylated at a 4:1 ratio. Plates
were incubate for 40 min, washed and replenished with
100 ul/well of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated
streptavidin (Jackson ImmunoResearch #016-050-084) at
0.02 pg/ml. Plates were incubated 30 min, washed and
replenished with 200 ul/well of 1 mg/ml of p-nitrophenyl
phosphate. After 30 min, plates were read at 405 nm on
a Vmax plate reader.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
247
Data analysis
Standard curve data were fit to a second order
polynomial and unknown TNFa concentrations determined
from their OD by solving this equation for
concentration. TNF concentrations were then plotted vs.
test compound concentration using a second order
polynomial. This equation was then used to calculate
the concentration of test compounds causing a 50~
reduction in TNF production.
Human Monocyte TNF Convertase Assay
TNF convertase activity is demonstrated by
hydrolytic cleavage of a dinitrophenyl (DNP)-labeled
peptide substrate between amino acids Ala and Val.
Dependent on the purity of the TNF convertase used in
the reaction, hydrolysis of incorrectly clipped DNP-
peptides are also possible. Human monocyte TNF
convertase activity is determined by using DNP-labeled
peptide substrate (1) Dnp-SPLAQAVRSSSR-CONH2; and
clipped peptides: (2) DNP-SPLAQ-COON (incorrectly
clipped between Gln and Ala); (3) DNP-SPLAQA-COON
(correctly clipped); and (4) DNP-SPLAQAV-COOH
(incorrectly clipped between Val and Arg).
Full length and clipped DNP-peptides are separated
and quantitated using reversed phase HPLC, monitoring at
350 nM (where dinitrophenyl absorbs). Inhibitors of TNF
convertase in the reaction are detected by a decrease in
peak height of peptide 3 and an increase in peak height
of peptide 1. Inhibition is calculated as percent of
control by comparing peak height of peptide 3 in samples
with no inhibitors (control conditions) and peak height
of peptide no. 3 in samples with inhibitors.
Typically, compounds at 2 mM in DMSO are first
diluted 1:11.8 in 40 mM Tris, pH 7.5. A further 1:17
dilution of the compound occurs in the final reaction
mixture. This reaction mixture contains 2.5~L of the
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/IJS98/16147
248
diluted compound, 20 ~.L of peptide 1, and 20 ~,L of TNF
convertase. This results in a compound concentration of
~.tM, 0.5~ DMSO, in the final reaction volume. Compounds
are initially screened at 10 uM and selected compounds are
5 further assayed to determine an ICSO~
Human Neutrophil Collagenase Assay
Human neutrophil collagenase (HNC) activity is
determined by using fluorogenic peptide substrate Dnp-
10 Pro-b-Cyclohexyl-Ala-Gly-Cys(Me)-His-Ala-Lys-(N-
methylanthranilic acid)-NHz. The N-terminus Dnp group
and the C-terminus N-methyl-anthranilyl moiety (Nma) are
fluorescence self-quenching until the peptide is cleaved
at the Gly-Cys(me) bond. The fluorescence from the
cleavage products is measured on a Bio-Tek Instrument
FL500 fluorescence micro-plate reader (excitation at 360
nm, emission at 460 nm). The assay is performed in a
96-well plate (in duplicate), and the Km = 51 nM for the
substrate, and Ki = 722 nM for Actinonin have been
determined. The test compounds (at 100, 33 & 10 mM) are
compared for their inhibition of HNC activity on the
substrate against the activity of Actinonin and Ki's
were determined on selected compounds.
Human Fibroblast Stromelysin Assay
Human fibroblast stromelysin (HFS) activity is
determined by using fluorogenic peptide substrate Dnp-
Pro-b-Cyclohexyl-Ala-Gly-Cys(Me)-His-Ala-Lys-(N-
methylanthranilic acid)-NH2. The N-terminus Dnp group
and the C-terminus N-methyl-anthranilyl moiety (Nma) are
fluorescence self-quenching until the peptide is cleaved
at the Gly-Cys(me) bond. The fluorescence from the
cleavage products is measured on a Bio-Tek Instrument
FL500 fluorescence micro-plate reader (excitation at 360
nm, emission at 460 nm). The assay is performed in a
96-well plate (in duplicate), and the Km = 51 nM for the
substrate, and Ki = 722 nM for Actinonin (an inhibitor
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
249
of enzyme activity; Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, MO;
A6671) have been determined as the standard control.
The test compounds (at 100, 33 & 10 mM) are compared for
their inhibition of HFS activity on the substrate
against the activity of Actinonin and Ki's were
determined on selected compounds.
Inhibition of LPS-Induced TNF-a production in mice
Male DBA/1LACJ mice were dosed with vehicle or test
compounds in a vehicle (the vehicle consisting of 0.5~
tragacanth in 0.03 N HC1) prior to lipopolysaccharide (2
mg/kg, I.V.) injection. Ninety minutes after LPS
injection, blood was collected and the serum was
analyzed by ELISA for TNF levels.
The following compounds had a TNF convertase, HNC
and/or HFS inhibition activity ICso of less than luM:
4-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-traps-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-cis-vinyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-cis-hydroxymethyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-traps-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid
4-oxo-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-
thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid
4-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid
4-cis-methoxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-7-hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
250
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-trans-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-methyl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-carboxy-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-carboxy-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid
5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-
(methoxycarbonyl)-4,5.6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-
(ethoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-2-yl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-pyrid-3-yl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-phenyl-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
phenylaminocarbonyl)-4,5.6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
(phenylmethyl)aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-
phenylmethyl-N-methylaminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/LJS98/16147
251
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(3-
phenylpropyl)aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothien[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-(N-(4,4-
diphenylbutyl)aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl}-2-(N-(3,3-
dimethylbutyl)aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-
(aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-
6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-hydroxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-2-
(morpholinocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
4-benzyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid
4-cis-benzyl-8-cis-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid
4-trans-benzyl-8-hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3,d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid
4-trans-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro-4H-thieno[2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic acid
4-trans-benzyl-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydro-thieno[2,3,-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-
4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic
acid
7-cis-(N-methylaminocarbonyl}oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-prop-2-ylaminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-cyclohexylaminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/1614~
252
7-cis-(N-phenylaminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(4-methoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(4-phenoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(2-biphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(phenylmethyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis- (N- (1 (S) -phenyl ethyl) aminocarbonyl) oxy-5- (4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(2-phenylethyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(3-methoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(2-methoxyphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(2-chlorophenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(3-chlorophenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(4-chlorophenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis- (N- (4-fluorophenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5- (4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
cJpyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis- (N- (4-cyanophenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5- (4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
253
7-cis-(N-(4-butoxycarbonylphenyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(4-tolyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(3-tolyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
7-cis-(N-(1-naphthyl)aminocarbonyl)oxy-5-(4-
methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno(3,2-
c]pyridine-6-hydroxamic acid
trans-(+/-)-7-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-5-phenethyl-
4,5,6,7,8,9-hexahydrothieno[2,3-d]azocine-6-hydroxamic
acid
trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-vinyl-4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-hydroxamic acid
trans-(+/-)-6-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenethyl-
5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-thieno(2,3-d]azepine-5-hydroxamic
acid
Selected compounds from this invention have
demonstrated antiinflammatory properties in a adjuvant
arthritis model. Also, selected compounds from the
class have shown in vivo activity in a LPS mouse model
in which serum levels of TNF-a were reduced in the
presence of compounds of this invention.
Methods of Treatment
All of the compounds of this invention are useful
in the prophylaxis and treatment of TNF-a mediated
disease states. The compounds are also useful in the
prophylaxis and treatment of disease states in which HNC
and/or HFS play a role. Preferably, the compounds of
this invention are useful in the prophylaxis and
treatment of rheumatoid arthritis; osteoarthritis;
rheumatoid spondylitis; gouty arthritis; inflammatory
bowel disease; adult respiratory distress syndrome
CARDS); psoriasis; Crohn's disease; allergic rhinitis;
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
254
ulcerative colitis; anaphylaxis; contact dermatitis;
asthma; antiviral therapy including those viruses
sensitive to TNF-a inhibition - HIV-1, HIV-2, HIV-3,
cytomegalovirus (CMV), influenza, adenovirus, and the
herpes viruses including HSV-1, HSV-2, and herpes
zoster; muscle degeneration; cachexia; Reiter's
syndrome; type II diabetes; bone resorption diseases;
graft vs. host reaction; ischemia reperfusion injury;
brain trauma; atherosclerosis; Alzheimer's discease;
multiple sclerosis; cerebral malaria; sepsis; septic
shock; toxic shock syndrome; fever and mylagias due to
infection.
The present invention provides a method of treating
a disease state in which TNF-a, HNC and/or HFS levels
are elevated which comprises administering an effective
amount of a compound of this invention. Compounds of
this invention are of use in the prophylaxis and acute
or chronic therapy of any disease state in a human, or
other mammal, which is exacerbated by or mediated by
elevated or unregulated TNF-a, HNC and/or HFS by
mammal's cells. More preferably, this invention relates
to a method of lowering the levels of TNF-a in a mammal
in need thereof which comprises administering an
effective dose of a compound of this invention or a
pharmaceutical composition thereof. In addition, this
invention relates to a method of lowering the activity
levels of HNC and/or HFS in a mammal in need thereof
which comprises administering an effective dose of a
compound of this invention or a pharmaceutical
composition thereof.
A compound of this invention or a pharmaceutical
composition thereof is useful in the treatment or
prophylaxis of a number of disease states including
rheumatoid arthritis; osteoarthritis; rheumatoid
spondylitis; gouty arthritis; inflammatory bowel
disease; adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS);
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98116147
255
psoriasis; Crohn's disease; allergic rhinitis;
ulcerative colitis; anaphylaxis; contact dermatitis;
asthma; antiviral therapy including those viruses
sensitive to TNF-a inhibition - HIV-1, HIV-2, HIV-3,
cytomegalovirus (CMV~, influenza, adenovirus, and the
herpes viuses including HSV-1, HSV-2, and herpes zoster;
muscle degeneration; cachexia; Reiter's syndrome; type
II diabetes; bone resorption diseases; graft vs. host
reaction; ischemia reperfusion injury; atherosclerosis;
brain trauma; Alzheimer's disease; multiple sclerosis;
cerebral malaria; sepsis; septic shock; toxic shock
syndrome; fever and mylagias due to infection.
Pharmaceutical Compositions
This invention further relates to the use of a
compound of this invention in the manufacture of a
medicament for the prophylaxis and treatment, either
acutely or chronically, of TNF-a mediated disease
states. In addition, the compounds of this invention
are useful in the manufacture of a medicament for
treating disease states in which HNC and/or HFS play a
role.
This invention also relates to a pharmaceutical
composition comprising a compound of this invention and
a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and if desired
other active ingredients. The compounds of this
invention are administered by any suitable route,
preferably in the form of a pharmaceutical composition
adapted to such a route, and in a dose effective for the
treatment intended. Therapeutically effective doses of
the compounds of the present invention required to
arrest the progress or prevent tissue damage associated
with the disease are readily ascertained by one of
ordinary skill in the art.
For the prophylaxis and treatment of disease
states, the compounds of the present invention may be
administered orally, parentally, or by inhalation spray,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
256
rectally, or topically in dosage unit formulations
containing conventional pharmaceutically acceptable
carriers, adjuvants and vehicles. The term parenteral
as used herein includes, subcutaneous, intravenous,
intramuscular, intrasternal, infusion techniques or
intraperitoneally.
The amount of active ingredient that may be
combined with the carrier materials to produce a single
dosage form will vary depending upon the host treated
and the particular mode of administration.
The dosage regimen for treating a disease state
with the compounds of this invention and/or compositions
of this invention is based on a variety of factors,
including the type of disease, the age, weight, sex and
medical condition of the patient, the severity of the
condition, the route of administration, pharmacological
considerations such as the activity, efficacy,
pharmacokinetic and toxicology profiles of the
particular compound employed, whether a drug delivery
system is utilized and whether the compound is
administered as part of a drug combination. Thus the
dosage regimen may vary widely. Dosage levels of the
order from about 0.01 mg to 80 mg per kilogram of body
weight per day, preferably from about 0.5 mg to 30
mg/kg, more preferably from about 1 mg to 15 mg/kg are
useful for all methods of use disclosed herein. The
pharmaceutically active compounds of this invention can
be processed in accordance with convential methods of
pharmacy to produce medicinal agents for administration
to patients, mammals including humans.
For oral administration, the pharmaceutical
composition may be in the form of, for example, a
capsule, a tablet, a suspension, or liquid. The
pharmaceutical composition is preferably made in the
form of a dosage unit containing a given amount of the
active ingredient. For example, these may contain an
amount of active ingredient from about 1 to 250 mg,
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
257
preferably from about 25 to 150 mg. A suitable daily
dose for a human or other mammal may vary widely
depending on the condition of the patient and other
f actors .
The compounds of this invention may also be
administered by injection as a composition with suitable
carriers including saline, dextrose, or water. The
daily parenteral dosage regimen wll be from about 0.1 to
about 80 mg/kg of total body weight, preferably from
about 0.5 to about 30 mg/kg, and more preferably from
about 1 mg to 15 mg/kg.
Injectable preparations, for example, sterile
injectable aqueous or oleaginous suspensions may be
formulated according to the known art using suitable
dispersing or wetting agents and suspending agents. The
sterile injectable preparation may also be a sterile
injectable solution or suspension in a nontoxic
parenterally acceptable diluent or solvent, for example,
as a solution in 1,3-butanediol. Among the acceptable
vehicles and solvents that may be employed are water,
Ringer's solution, and isotonic sodium chloride
solution. In addition, sterile, fixed oils are
conventionally employed as a solvent or suspending
medium. For this purpose any bland fixed oil may be
employed including synthetic mono- or diglycerides. In
addition, fatty acids such as oleic acid find use in the
preparation of injectables.
Suppositories for rectal administration of the drug
can be prepared by mixing the drug with a suitable
nonirritating excipient such as cocoa butter and
polyethylene glycols which are solid at ordinary
temperatures but liquid at the rectal temperature and
will therefore melt in the rectum and release the drug.
A suitable topical dose of compounds of this
invention is 0.1 mg to 150 mg administered one to four,
preferably two or three times daily. For topical
administration, the active ingredient may comprise from
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
258
0.001 to 10~ w/w, e.g. from 1~ to 2~ by weight of the
formulation, although it may comprise as much as 10~
w/w, but preferably not more than 5~ w/w, and more
preferably from 0.1~ to 1~ of the formulation.
Formulations suitable for topical administration include
liquid or semi-liquid peparations suitable for
penetration through the skin such as liniments, lotions,
ointments, creams, or pastes and drops suitable for
administration to the eye, ear, or nose.
For administration, the compounds of this invention
are ordinarily combined with one or more adjuvants
appropriate for the indicated route of administration.
The compounds may be admixed with lactose, sucrose,
starch powder, cellulose esters of alkanoic acids,
stearic acid, talc, magnesium stearate, sodium,
magnesium oxide, sodium and calcium salts of phosphoric
and sulphuric acids, acacia, gelatin, sodium alginate,
polyvinylpyrrolidine, and/or polyvinyl alcohol, and
tableted or encapsulated for conventional
administration. Alternatively, the compounds of this
invention may be dissolved in saline, water,
polyethylene glycol, propylene glycol, ethanol, corn
oil, peanut oil, cottonseed oil, sesame oil, benzyl
alcohol, and/or various buffers. Other adjuvants and
modes of administration are well known in the
pharmaceutical art. The carrier or diluent may include
time delay material, such as glyceryl monostearate or
glyceryl distearate alone or with a wax, or other
materials well known in the art.
The pharmaceutical compositions may be made up in a
solid form including granules, powders or suppositories
or in a liquid form such as solutions, suspensions, or
emulsions. The pharmaceutical compositions may be
subjected to conventional pharmaceutical operations such
as sterilization and/or may contain conventional
adjuvants, such as preservatives, stabilizers, wetting
agents, emulsifiers, buffers, etc.
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
259
Solid dosage forms for oral administration may
include capsules, tablets, pills, powders, and granules.
In such solid dosage forms, the active compound may be
admixed with at least one inert diluent such as sucrose
lactose or starch. Such dosage forms may also comprise,
as in normal practice, additional substances other than
inert diluents, e.g., lubricating agents such as
magnesium stearate. In the case of capsules, tablets,
and pills, the dosage forms may also comprise buffering
agents. Tablets and pills can additionally be prepared
with enteric coatings.
Liquid dosage forms for oral administration may
include pharmaceutically acceptable emulsions,
solutions, suspensions, syrups, and elixirs containing
inert diluents commonly used in the art, such as water.
Such compositions may also comprise adjuvants, such as
wetting agents, emulsifying and suspending agents, and
sweetening, flavoring, and perfuming agents.
Compounds of the present invention can possess one
or more asymmetric carbon atoms and are thus capable of
existing in the form of optical isomers as well as in
the form of racemic or nonracemic mixtures thereof. The
optical isomers can be obtained by resolution of the
racemic mixtures according to conventional processes,
for example by formation of diastereoisomeric salts by
treatment with an optically active acid or base.
Examples of appropriate acids are tartaric,
diacetyltartaric, dibenzoyltartaric, ditoluoyltartaric
and camphorsulfonic acid and then separation of the
mixture of diastereoisomers by crystallization followed
by liberation of the optically active bases from these
salts. A different process for separation of optical
isomers involves the use of a chiral chromatography
column optimally chosen to maximize the separation of
the enantiomers. Still another available method
involves synthesis of covalent diastereoisomeric
molecules by reacting compounds of Formula I with an
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
260
optically pure acid in an activated form or an optically
pure isocyanate. The synthesized diastereoisomers can
be separated by conventional means such as
chromatography, distillation, crystallization or
sublimation, and then hydrolyzed to deliver the
enantiomerically pure compound. The optically active
compounds of Formula I can likewise be obtained by
utilizing optically active starting materials. These
isomers may be in the form of a free acid, a free base,
an ester or a salt.
The compounds of the present invention can be used
in the farm of salts derived from inorganic or organic
acids. These salts include but are not limited to the
following: acetate, adipate, alginate, citrate,
aspartate, benzoate, benzenesulfonate, bisulfate,
butyrate, camphorate, camphorsulfonate, digluconate,
cyclopentanepropionate, dodecylsulfate, ethanesulfonate,
glucoheptanoate, glycerophosphate, hemisulfate,
heptanoate, hexanoate, fumarate, hydrochloride,
hydrobromide, hydroiodide, 2-hydroxy-ethanesulfonate,
lactate, maleate, methanesulfonate, nicotinate,
2-naphthalenesulfonate, oxalate, palmoate, pectinate,
persulfate, 3-phenylpropionate, picrate, pivalate,
propionate, succinate, tartrate, thiocyanate, tosylate,
mesylate and undecanoate. Also, the basic nitrogen-
containing groups can be quaternized with such agents as
lower alkyl halides, such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, and
butyl chloride, bromides, and iodides; dialkyl sulfates
like dimethyl, diethyl, dibutyl, and diamyl sulfates,
long chain halides such as decyl, lauryl, myristyl and
stearyl chlorides, bromides and iodides, aralkyl halides
like benzyl and phenethyl bromides, and others. Water or
oil-soluble or dispersible products are thereby
obtained.
Examples of acids which may be employed to form
pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts include
such inorganic acids as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric
CA 02297988 2000-O1-25
WO 99/06410 PCT/US98/16147
261
acid and phosphoric acid and such organic acids as
oxalic acid, malefic acid, succinic acid and citric acid.
Other examples include salts with alkali metals or
alkaline earth metals, such as sodium, potassium,
calcium or magnesium or with organic bases.
While the compounds of the invention can be
administered as the sole active pharmaceutical agent,
they can also be used in combination with one or more
other agents. When administered as a combination, the
therapeutic agents can be formulated as separate
compositions which are given at the same time or
different times, or the therapeutic agents can be given
as a single composition.
The foregoing is merely illustrative of the
invention and is not intended to limit the invention to
the disclosed compounds. Variations and changes which
are obvious to one skilled in the art are intended to be
within the scope and nature of the invention which are
defined in the appended claims.
From the foregoing description, one skilled in the
art can easily ascertain the essential characteristics
of this invention, and without departing from the spirit
and scope thereof, can make various changes and
modifications of the invention to adapt it to various
usages and conditions.