Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02300243 2008-05-01
Description
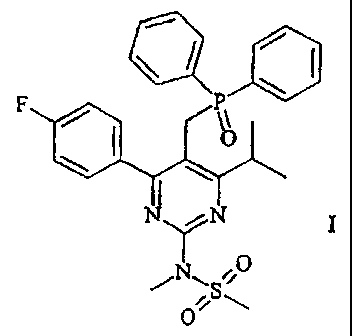
The present invention relates to a process for preparing N-[5-
(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-
methylmethanesulphonamide
~-
\
~
PO
N
Yo
The N-[5-(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluoro- phenyl)-6-
isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-methylmethane-sulphonamide (I) preparable according
to the invention is an intermediate for the preparation of pharmaceutically
active
compounds, for example of HMG-Co A reductase inhibitors (Bioorg. Med. Chem.
1997, 5, 437).
It was the object of the invention to provide better access to the
abovementioned
intermediate.
The object was achieved by the novel process according to an aspect of the
invention, in which there is provided a process for preparing N-[5-
(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-
methylmethanesulphonamide of the formula (I) is prepared by reacting [4-(4-
fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-methylsullphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-
yl]methanol of the formula (II)
CA 02300243 2000-03-09
2
F OH
n
0
/N~'S,
Oi \
with chlorodiphenylphosphine.
An important advantage of the synthesis according to the invention is its
industrial
applicability.
[4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol of the formula (II) can be
obtained in a simple manner by reducing the corresponding ester, for example
with
diisobutylaluminium hydride (EP-A 0521471).
The reaction of the [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol of the formula (II) with
chlorodiphenylphosphine can be carried out either directly or via prior
deprotonation.
Preference is given to the direct reaction with chlorodiphenylphosphine and
subsequent treatment with a base.
According to the "deprotonation" variant, the [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-
2-
(N-methyl-N-methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl] methanol of the formula (II)
is advantageously treated with a deprotonating agent which is familiar to the
person skilled in the art, preferably with an alkali metal hydride or an
alkali metal
hexaalkyldisilazane.
Preference is given to using sodium hydride. The deprotonation is usually
carried
out at room temperature. This is followed by the reaction with
chlorodiphenylphosphine.
CA 02300243 2008-05-01
, . . . .
3
The reaction with chlorodiphenylphosphine is advantageously carried out at a
temperature between 80 C and 200 C.
The chlorodiphenyiphosphine can act directly as solvent. However, it is
possible to
use additionally a very high-boiling. inert solvent, such as, for example,
toluene or
xylene or decalin, and the respective isomer mixtures.
The reaction can be carried out, in the presence of a catalyst.
Suitable catalysts are iodine, an alkali metal iodide, such as, for example,
sodium
iodide or potassium iodide, an alkali metal halide, such as, for example,
methyl
iodide or ethyl iodide, or a dihaloalkane, such as, for example,
dibromomethane.
Preference is given to using an alkali metal iodide.
The amount of catalyst is usually chosen in the range from I mol% to 20 mol%,
based on the alcohol of the formula II used.
The reaction according to the direct variant is advantageously carried out at
a
temperature of from -20 C to 130 C, preferably at from +20 C to 120 C.
Corresponding to the "deprotonation" variant described above, the
chlorodiphenylphosphine can act in the direct variant directly as solvent.
However,
in addition, it is possible to use a very high-boiling inert solvent, such as,
for
example, toluene or xylene or decalin, and the respective isomer mixtures.
Following the reaction with chlorodiphenylphosphine, the reaction mixture is
treated with a base.
Suitable bases are the alkali metal hydroxides, such as, for example, aqueous
solutions of sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, or alkali metal
carbonates,
such as sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate. If appropriate, a customary
phase-transfer catalyst, such as, for example, a tetraalkylammonium halide,
can be
employed to accelerate the reaction with the base. Good results can also be
obtained by using crown ethers.
CA 02300243 2000-03-09
4
After the reaction has ended, the N-[5-(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-
fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide of the
formula I can be isolated from the mixture in a manner known to a person
skilled
in the art, for example by extraction from the reaction mixture using a
suitable
solvent, and by crystallization.
Examples
Example 1
N-[5-(Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-
2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide
1.00 g (2.83 mmol) of [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol was initially charged in 5 ml of
cis/trans-decalin and admixed with 204 mg (4.68 mmol) of sodium hydride (55%
dispersion in mineral oil). After 30 min at room temperature, 680 mg (2.93
mmol)
of chlorodiphenylphosphine were added with vigorous stirring over a period of
6
min. The mixture was admixed with 52.2 mg (0.35 mmol) of sodium iodide and
heated at 184 - 186 C for 2 h 15 min. After cooling to room temperature, 50 ml
of
38 - 40% strength sodium bisulphite solution and 50 ml of ethyl acetate were
added. The organic phase was separated off and the aqueous phase was extracted
with 50 ml of ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases were dried over
magnesium sulphate and concentrated under reduced pressure. This gave 1.74 g
of
crude product which was purified by silica gel chromatography (mobile phase: n-
hexane/ethyl acetate 1:2). This gave 382.4 mg (25.1%) of N-[5-
(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl] -N-
methylmethanesulphonamide in the form of a colourless solid. (Melting point
184
- 185 C)
1 H NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): 1.11 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 6H);
CA 02300243 2000-03-09
3.28 (sept, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H);
3.40 (s, 3H);
3.51 (s, 3H);
4.05 (d, J 12.6 Hz, 2H);
7.07 (t, J 8.9 Hz, 2H);
7.35 (m, 2H);
7.42 (m, 4H);
7.5 - 7.9 (m, 6H).
13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 100 MHz): g= 21.52 (q);
29.12 (td);
31.94 (d);
33.07 (q);
41.53 (q);
114.50 (sd);
115.03 (dd);
128.54 (dd);
130.21 (dd);
130.84 (dd);
131.64 (dd);
133.41 (sd);
134.51 (sd);
156.54 (sd);
162.10 (sd);
165.86 (sd);
176.49 (sd).
CA 02300243 2008-05-01
. . , .
. =
6
Example 2
N-[5-(Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-
2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide
282.8 mg (0.80 mmol) of [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol were initially charged in 4.5 ml
of xylene (isomer mixture) and admixed with 55 mg (1.30 mmol) of sodium
hydride (55% dispersion in mineral oil). After 35 min, 185 mg (0.84 mmol) of
chlorodiphenylphosphine in 1.5 ml of xylene were added at room temperature
with
vigorous stirring over a period of 5 min, and the mixture was subsequently
heated
at 135 C for 20 h. After cooling to room temperature, the mixture was admixed
with 15 ml of water and extracted with 10 ml of ethyl acetate. The organic
phase
was separated off and the aqueous phase was extracted with 2 x 10 ml of ethyl
acetate. The combined organic phases were subsequently dried (MgSO4) and
concentrated under reduced pressure. This gave 510 mg of crude product which
was purified by silica gel chromatography (mobile phase: n-hexane/ethyl
acetate
1:2, then ethyl acetate), and 230 mg (53.5%) of N-[5-
(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-
methylmethanesulphonamide were isolated in the form of a colourless solid.
Example 3
N-[5-(Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-
2 5 2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide
512 mg (1.45 mmol) of [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol were initially charged in 8 ml of
toluene and admixed with 96 mg (2.20 mmol) of sodium hydride (55% dispersion
in mineral oil). After 1 h, 333.5 mg (1.44 mmol) of chlorodiphenyiphosphine in
2.5 ml of toluene were added at room temperature with vigorous stirring over a
I i II
CA 02300243 2000-03-09
7
period of 5 min. The mixture was admixed with 28.7 mg (0.19 mmol) of sodium
iodide and heated at 108 C for 22 h. After 6 h, a further 28.7 mg (0.19 mmol)
of
sodium iodide were added. After cooling to room temperature, the mixture was
admixed with 30 ml of 38 - 40% strength sodium bisulphite solution and
extracted
with 50 ml of ethyl acetate. The organic phase was separated off and the
aqueous
phase was extracted with 50 ml of ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases
were subsequently concentrated under reduced pressure. This gave 740 mg of
crude product which was purified by silica gel chromatography (mobile phase:
ethyl acetate), and 212.7 mg (27.3%) of N-[5-(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-
fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide were
isolated in the form of a colourless solid.
Example 4
N-[5-(Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-
2-yl] -N-methylmethanesulphonamide
502.6 mg (1.42 mmol) of [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol were initially charged in 8 ml of
xylene (isomer mixture) and admixed with 96.6 mg (2.21 mmol) of sodium
hydride (55% dispersion in mineral oil). After 1 hour, 340.8 mg (1.47 mmol) of
chlorodiphenylphosphine in 2.5 ml of xylene were added at room temperature
with
vigorous stirring over a period of 5 min. The mixture was admixed with 34.6 mg
(0.23 mmol) of sodium iodide and heated at 136 C for 19 h. After 3 h, a
further
25.1 mg of sodium iodide were added. After cooling to room temperature, the
mixture was admixed with 30 ml of dilute sodium bisulphite solution and
extracted
with 50 ml of ethyl acetate. The organic phase was separated off and the
aqueous
phase was extracted with 50 ml of ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases
were subsequently concentrated under reduced pressure. This gave 906 mg of
crude product which was purified by silica gel chromatography (mobile phase:
ethyl acetate), and 315.9 mg (41.3%) of N-[5-(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-
CA 02300243 2000-03-09
8
fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide were
isolated in the form of a colourless solid.
Example 5 (direct reaction)
N-[5-(Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-
2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide
With ice-bath cooling, 1.05 g (2.95 mmol) of [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-
(N-methyl-N-methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol were initially
charged in 7 g of toluene and admixed with stirring with 820 mg (3.69 mmol) of
chlorodiphenylphosphine. The mixture was heated at 108 C for 3 h. After
cooling
to room temperature, 553 mg (4.43 mmol) of aqueous potassium hydroxide
solution (45% strength) and 97.5 mg (0.29 mmol) of tetrabutylammonium bromide
were added, and the mixture was stirred vigorously at 60 C for 1 h. The heat
source was removed and the reaction mixture, which was still warm, was admixed
with 20 ml of water. The mixture was slowly cooled to 4 C, and the
precipitated
solid was filtered off. The product was washed with cold water and toluene and
dried under reduced pressure at 40 C. 1.04 g(64.1 %; content: 97.6%) of N-[5-
2 0 (diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-
N-
methylmethanesulphonamide were isolated in the form of a colourless solid.
Example 6 (direct reaction)
N-[5-(Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-
2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide
2.03 g (5.69 mmol) of [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol were initially charged in 13 g of
toluene and, with ice-bath cooling, admixed with 1.67 g (7.51 mmol) of
chlorodiphenylphosphine in 2 g of toluene. The mixture was heated at 111 C
for
2.5 h. After cooling to room temperature, 1.08 g (8.66 mmol) of a 45% strength
CA 02300243 2000-03-09
9
potassium hydroxide solution and 175 mg (0.574 mmol) of tetrabutylammonium
chloride were added, and the mixture was stirred vigorously at 60 C for 2 h.
30 ml
of water were added to the warm reaction mixture. The mixture was briefly
stirred
at 60 C and slowly cooled to 4 C, and the precipitated solid was filtered off.
The
product was washed with cold water (10 ml) and cold toluene (10 ml) and dried
under reduced pressure at 40 C. 2.66 g(84.1%; content: 96.6%) of N-[5-
(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-
methylmethanesulphonamide were isolated in the form of a colourless solid.
Example 7 (direct reaction)
N-[5-(Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-
2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide
2.02 g (5.69 mmol) of [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol were initially charged in 13.1 g
of
toluene and, with ice-bath cooling, admixed with 1.67 g (7.51 mmol) of
chlorodiphenylphosphine in 1.9 g of toluene. The mixture was heated at 109 C
for
3 h. After cooling to room temperature, 590 mg (8.94 mmol) of solid potassium
hydroxide and 159 mg (0.582 mmol) of 18-crown-6 were added, and the mixture
was stirred vigorously at 60 C for 3.5 h. 30 ml of water were added to the
warm
reaction mixture. The mixture was briefly stirred at 60 C and slowly cooled to
4 C, and the precipitated solid was filtered off. The product was washed with
cold
water (10 ml) and cold toluene (10 ml) and dried under reduced pressure at 40
C.
1.82 g (59.5%; content: 95.9%) of N-[5-(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-
fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide were
isolated in the form of a colourless solid.
CA 02300243 2000-03-09
Example 8 (direct reaction)
N- [5-(Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-
2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide
5
2.02 g (5.69 mmol) of [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol were initially charged in 13.1 g
of
toluene and, with ice-bath cooling, admixed with 1.71 g (7.69 mmol) of
chlorodiphenylphosphine in 1.9 g of toluene. The mixture was heated at 111 C
for
10 2.5 h. After cooling to room temperature, 1.17 g (8.78 mmol) of 30%
strength
sodium hydroxide solution and 182 mg (0.597 mmol) of tetrabutylammonium
chloride were added, and the mixture was stirred vigorously at 60 C for 3.5 h.
30 ml of water were added to the warm reaction mixture. The mixture was
briefly
stirred at 60 C and slowly cooled to 4 C, and the precipitated solid was
filtered
off. The product was washed with cold water (10 ml) and cold toluene (10 ml)
and
dried under reduced pressure at 40 C. 2.18 g (71.3%; content: 97.3%) of N-[5-
(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-
methylmethanesulphonamide were isolated in the form of a colourless solid
(melting point 184 - 185 C).
Example 9 (direct reaction)
N-[5-(Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-
2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide
A suspension of 9.29 g (26.3 mmol) of [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-
methyl-N-methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol in 26 g of toluene was,
with ice-bath cooling, admixed with 7.64 g (34.4 mmol) of
chlorodiphenylphosphine. After rinsing with a little toluene, the mixture was
heated at 111 C for 2 h. After cooling to room temperature, 4.94 g of a 45%
strength potassium hydroxide solution and 873 mg (2.71 mmol) of
tetrabutylammonium bromide were added, and the mixture was stirred vigorously
CA 02300243 2000-03-09
11
at 60 C for I h. 100 ml of water were added to the warm reaction mixture. The
mixture was briefly stirred at 60 C and slowly cooled to 4 C, and the
precipitated
solid was filtered off. The product was washed with cold water (30 ml) and
cold
toluene (30 ml) and dried under reduced pressure at 40 C. 11.74 g (78.4%;
content:
94.4%) of N-[5-(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-
isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide were isolated in the
form of a colourless solid.
Example 10 (direct reaction without phase-transfer catalyst)
N-[5-(Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-
2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide
2.03 g (5.69 mmol) of [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]methanol were initially charged in 13 g of
toluene and, with ice-bath cooling, admixed with 1.69 g (7.60 mmol) of
chlorodiphenylphosphine in 1.9 g of toluene. The mixture was heated at 109 C
for
2.5 h. After cooling to room temperature, the mixture was admixed with 1.09 g
(8.74 mmol) of a 45% strength potassium hydroxide solution and stirred
vigorously at 60 C for 2 h 45 min. 30 ml of water were added to the warm
reaction
mixture. The mixture was briefly stirred at 60 C and slowly cooled to 4 C, and
the
precipitated solid was filtered off. The product was washed with cold water
(10 ml)
and cold toluene (10 ml) and dried under reduced pressure at 40 C. 2.44 g
(76.8%;
content: 99.1 %) of N-[5-(diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-
2 5 isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide were isolated in the
form of a colourless solid.
CA 02300243 2000-03-09
12
Example 11 (direct reaktion)
N-[(5-Diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorphenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-
yl]-N-methylmethanesulphonamide
A solution of 60.08 g (0.170 mol) [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-
N-
methylsulphonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl] methanol in ca. 485 ml of toluene was
admixed at 60 C with 42.55 g (0.192 mol; content 99,7%)
chlorodiphenylphosphine. The mixture was stirred for 2.5 h and then added to a
mixture of 70.66 g of a 20 % strength potassium hydroxide solution and 5.04 g
(0.017 mol) tetrabutylammonium chloride at 60 C. The resulting reaction
mixture
was stirred for another 2 h at 60 C. Then 215 ml of water and 108 ml of
toluene
were added. The aqueous phase was separated off at 80 C. The organic phase
was
extracted twice with 2 x 215 ml of hot water. Residual water of the organic
phase
was removed azeotropicly. The mixture was slowly ( 2 h) cooled to 0 C and the
precipitated solid was filtered off. The product was washed twice with 2 x 160
ml
of toluene and dried under reduced pressure at 40 C. 81.94 g (89.7%) N-[(5-
diphenylphosphinoylmethyl)-4-(4-fluorphenyl)-6-isopropylpyrimidin-2-yl]-N-
methylmethanesulphonamide were isolated in the form of a colourless solid
[content (HPLC): 100%].