Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02301350 2000-03-20
UNIVERSAL VTOL POWER AND
ROTOR SYSTEM MODULE ..
This application is related to and claims priority from U.S. Patent
Application Serial No. 09!045,991 filed March 23, 1998 which is incorporated .
herein by reference.
BACKGROUND
This invention broadly relates to aerial vehicles having vertical
takeoff/landing (VTOL) capability, of which helicopters are a common type,
! 0 and of which the described VTOL aircraft has a particularly useful
capability
as an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) , sometimes referred to as a "drone"
aircraft.
More particularly, the invention is a common universal power drive and
lifting rotor system module from which various types of single and multiple
! 5 rotor VTOL aircraft can be produced. The simplicity and versatility of the
power drive and lifting rotor system module of the invention is such that it
has
a particular adaptation to providing VTOL UAV aircraft of several types that
are highly suitable to carrying out military and commercial surveillance
missions.
There is a particular need for a portable, remotely controlled VTOL
UAV platform carrying visual and sensing recording devices for performing a.
variety of military and commercial missions including transmitting or
recording
visual and other ground data information that is not readily available or
possible
by other means. The capability of recently developed, simple and lightweight
devices for recording and transmitting a wide variety of visual and other data
is such that their usefulness can be greatly expanded by mounting them on a
portable and remotely controlled VTOL UAV aircraft platform. Typical
missions for such VTOL UAV units would be aerial intelligence gathering and
CA 02301350 2000-03-20
reconnaissance, commercial cinematography, news coverage, aerial mapping,
law enforcement and anti-terrorism augmentation, border patrol, disaster..
assessment, environmental assessment, utility inspection and maintenance, etc.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The invention provides a universal power drive and lifting rotor system
unit or module suitable for powering a variety of types of VTOL aircraft
including both single and multiple rotor type VTOL aircraft, and both single
rotor convention and compound helicopters.
The invention further provides a system capable of rapid assembly and
disassembly into small modules for man portable transport andlor rapid
maintenance without the use of hand tools.
The invention incorporates VTOL power producing and lifting rotor
systems and their interconnections on and within a component support airframe.
I 5 The component support airframe is configured for the detachable attachment
of
an engine and VTOL augmentation framework. The lifting rotor assembly and
transmission are mounted on the component support airframe and receive power
from a power train comprising a main drive shaft detachably coupled to the
engine and extending within the component support airframe. The main drive
O shaft and transmission are adapted for detachable connection to a drive
shaft of
a rotor torque compensating means mounted on any one of the VTOL.
conversion auxiliary frameworks affixed to the module component support
airframe. Thus, a variety of types of VTOL aircraft can be powered by
attaching the versatile power drive and rotor system module to an auxiliary
?s framework on which is mounted the particular type of rotor torque
compensating system utilized on the specific type of VTOL aircraft being
produced.
-2-
CA 02301350 2000-03-20
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is a side elevation of one embodiment of the invention. ..
Figure 2 is a side elevation of a second embodiment of the invention.
Figure 3 is a side elevation of a third embodiment of the invention.
Figure 4 is an illustration of an embodiment of a quick disconnect
fastener for use with the invention.
Figure 5 is an illustration of another embodiment of a quick disconnect
fastener for use with the invention.
Figure 6 is an illustration of another embodiment of a quick disconnect
I c~ fastener for use with the invention.
Figure 7 is an illustration of another embodiment of a quick disconnect
fastener for use with the invention.
Figure 8 is an illustration of another embodiment of a quick disconnect
fastener for use with the invention.
Figure 9 is an illustration of another embodiment of a quick disconnect
fastener for use with the invention.
Figure 10 is a side elevation of one embodiment of a coupling for use
with the invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
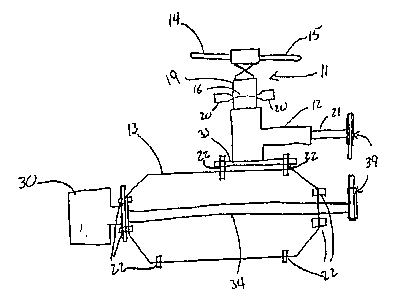
The module 10 utilized to power various types of VTOL aircraft.
subsequently described is illustrated in Figure 1, in which a lifting rotor
assembly 11 and transmission 12 are mounted onto a component support
airframe 13 on which the components of the module are supported.
Components of module 10 are preferably connected using quick disconnect
fasteners 22. Fasteners 22 preferably provide a self aligning interface for
the
components of module 10 and allow quick connection and removal without use
-3-
CA 02301350 2000-03-20
of hand tools.
The rotor assembly 11 is preferably of a conventional nature with rotor
blades 14, 15 supported thereon. Rotor assembly 11 may also be multibladed,
may be bearingless, or may employ a hollow main rotor shaft or other
apparatus commonly known or used in the art. The main rotor interface of
rotor assembly 11 is preferably easily adaptable to accommodate a variety of
rotor head designs (including fully articulated, bearingless, teetering, off-
set
teetering, and co-axial designs) capable of providing variable rigidity in
flapping and movement. This flexible design has a direct impact on the
I c> suitability of rotary wing aircraft to perform successful launch and
retrieval in
heaving, pitching, and rolling conditions on a boat landing or when landing on
ground inclines. The pitch of the rotor blades 14, 15 is preferably controlled
by a linkage arrangement of a swash plate assembly 19 actuated by servo
motors 20 and of which the details will not be described as being well known
I S in the art. Rotor assembly 11 is also preferably configured for quick
disconnection and connection at point 16 using quick disconnect fasteners.
The rotor transmission 12 is preferably driven by a power input shaft 21
which preferably extends from the transmission 12. The power input shaft 21
is preferably adapted for detachable connection to the main power drive shaft
~c~ 34 and for receiving an external rotatable shaft (not shown). The
component
supporting airframe 13 of the module on which the lifting rotor assembly 11.
and transmission 12 and other components of the module are supported is
preferably a cylindrical composite airframe structure which provides fuel
storage as well as allows for increased space for payloads. This provides an
s innovative solution to the traditional design compromise over the location
of the
fuel tank vis-a-vis other supporting structures by actually making the fuel
tank
the airframe. Engine 30 is preferably mounted on airframe 13 using quick
-4-
CA 02301350 2000-03-20
disconnect fasteners 22.
The support airframe 13 is preferably provided with bolt holes (not
shown) and other facilities for attaching augmentation auxiliary framework
using quick disconnect fasteners 22. The rotor assembly 11 and transmission
12 are preferably supported by a base plate 33 fastened to the lower side of
the .
transmission housing 23 and to the component support airframe 13 using quick
disconnect fasteners 22. The component support airframe 13 preferably
provides space in which various control and operational components required
for operation of a VTOL may be stowed and for which the consumption of fuel
o does not adversely affect the balance of the aircraft during operation.
A main power drive shaft 34 extending longitudinally of the component
support airframe 13 is preferably supported for rotation in the airframe
structure. One end of the drive shaft 34 is preferably detachably connected to
the engine 30 by a flexible coupling (not shown) that de-links axially.
A preferred powering unit mounted on the component support airframe
13 is a two-stroke air cooled engine with twin opposed cylinders. A more
preferable powering unit is a diesel engine, but other engines suitable for
mounting on the front end of the airframe 13 could be utilized. Preference for
a two-stroke engine is discussed below with respect to module 10 being used to
p) power a dual rotor configured VTOL aircraft. Auxiliary power for the module
may be provided using one or more generators (not shown). It is preferred
that a combination starterlgenerator is used to provide both auxiliary power
and
starter capability. Use of a combination starterlgenerator also provides
benefits
in terms of reduced weight.
Rotational power of the main drive shaft 34 is preferably transferred to
the transmission power input shaft 21 by means of a pulley and belt drive
arrangement 39. The pulley-belt drive arrangement 39 is one preferred
-5-
CA 02301350 2000-03-20
embodiment as being light and effective. Gear trains and other well known
power transfer apparatus may be utilized for power transmission. The maim
drive shaft 34 is also preferably adapted for detachable connection to an
external rotatable shaft of a VTOL augmentation auxiliary framework. This
s can be accomplished using a splined coupling (not shown) to allow for quick
connection and disconnection to the transmission power input shaft 21 or other
external rotatable shafts. A centrifugal clutch (not shown) may be
incorporated
with the main drive shaft 34 for selectively connecting and disconnecting the
main drive shaft 34 from the transmission power input shaft 21.
p The versatility of the above described module 10 for powering a variety
of types of VTOL aircraft, particularly VTOL UAV aircraft (drone helicopters)
is demonstrated in the following descriptive matter relating to the
illustrations
of Figures 2 and 3. Figure 2 illustrates the module of the invention powering
a VTOL aircraft having a tail mounted torque compensating rotor. Referring
I 5 now to Figure 2, a main drive shaft clutch assembly extension 60 is
detachably
attached to the module component supporting airframe 13 by quick disconnect
fasteners 22 or other attaching components. VTOL augmentation framework
45 is connected to clutch assembly extension 60 using quick disconnect
fasteners 22. The augmentation framework 45 contains a torque compensating
c) rotor (counter torque rotor) 49. A counter torque rotor drive shaft 50 is
preferably supported for rotation within the augmentation framework 45 and is.
.
operatively connected to rotate the counter torque rotor 49. Counter torque
rotor drive shaft 50 is preferably also detachably connected to the main power
drive shaft 34. The counter torque rotor drive shaft 50 is preferably a
floating
?s thin-walled drive shaft. Augmentation framework 45 preferably comprises a
tail boom section 45a detachably connected to a tail section 45b with quick
disconnect fasteners 22.
-6-
CA 02301350 2000-03-20
An undercarriage 51 is preferably configured with a landing support 52
connected thereto using quick disconnect fasteners 22. The undercarriage 51
is attached to the module 13 using the quick disconnect fasteners 22. The
undercarriage illustrated in Fig. 2 is one suitable for a VTOL UAV type
aircraft. If the module 10 is of a size and power suitable for powering pilot
controlled aircraft, the undercarriage structure and configuration would
conform
more closely to a conventional VTOL fuselage.
In a preferred embodiment of the invention an exhaust boom support
structure is used to reduce the thermal heat signature and muffle the exhaust
I () sound signature. The augmentation framework 45 (and 59 discussed below)
structure provides valuable space aboard the aircraft which can reduce noise
pollution in commercial environments and increase survivability and stealth in
war or near war environments. Accordingly, the augmentation framework 45
is preferably used for exhaust baffling to reduce the sound signature.
~ 5 A particularly useful VTOL configuration utilizing a pair of the modules
of the invention for powering a twin rotor VTOL aircraft is illustrated in
Figure 3. By interconnecting a pair of modules 10 of the invention in a back-
to-back arrangement, the payload is considerably more than can be carried by
a single module configuration, the lifting rotor torque generated by one
module
o being counteracted by the other module. This configuration is also
preferable
when one engine fails to operate, for whatever reason, as the other engine can
still apply power to both rotor systems permitting safe recovery of the
aircraft.
Referring to Figure 3, an augmentation framework 59 is configured for rapid
detachable connection to the module component support airframe 13 via quick
disconnect fasteners 22. A connecting drive shaft 61 is detachably connected
to the transmission input shafts 21 of the respective modules 10. The tandem
rotor configuration of the VTOL aircraft of Figure 3 requires the lifting
rotors
CA 02301350 2000-03-20
11 of the respective back-to-back arranged modules 10 rotate in opposite
directions. e.g., the engine 30 of the left side module 10 rotates clockwise
as
viewed from the front side of the engine and the engine 30 of the right side
module 10 rotates counterclockwise as viewed from the front side of the
engine.
Two-stroke engines are preferred since two-stroke engines have the
characteristic of operating in either direction with no change to the timing
or
other operative components of the engine. A two-stroke engine operates in the
same direction in which it is started. Hence, an operative configuration of
the
described tandem rotor VTOL aircraft of Figure 3 ,powered by a pair of
I c~ modules of the invention connected back-to-back in the manner described
is
easily achieved by starting the respective engines of the pair of modules in
opposite directions. Four-stroke~engines may be utilized, but require a
different
timing adjustment of each of the respective engines and other modifications.
It is preferred that engine timing is electromagrietically switched using a
I s plurality of Hall effect sensors mounted on the rotating components of the
engine, thereby eliminating the need for manual timing adjustments.
The embodiment shown in Figure 3 can be modified to include a third
engine (not shown) mounted on or within augmentation framework 59 to
provide additional payload capacity. The third engine is preferably connected
0 to the augmentation framework 59 using quick disconnect fasteners.
As previously indicated, the space provided on and around the module.
component support airframe 13 is available for installation of components
involving operative control of the module lifting rotor assembly 11 and
operative control of VTOL augmentation framework mounted flight control
units. The present invention is adapted to powering VTOL UAV aircraft. The
described VTOL embodiments of Figures 2 and 3 are of this unmanned type
preferably include equipment which establishes remote control of the aircraft
_g_
CA 02301350 2000-03-20
from the ground. An example of such equipment is disclosed in U.S. Patent
3,096,046 which is incorporated herein by reference. ..
Figures 4 _and S illustrate two embodiments of the quick disconnect
fasteners 22 which can be used to connect landing support 52 to undercarriage
51. Figure 6 shows an embodiment of quick disconnect fastener 22 which can
be used to connect augmentation framework 45 to main drive shaft clutch
assembly extension 60. Figure 7 shows an embodiment of the quick disconnect
fastener 22 which can be used to connect transmission 12 to component support
air frame 13. Figures 8 and 9 show an embodiment of quick disconnect
I U fastener 22 which can be used to connect tail boom section 45a to main
drive
shaft clutch assembly extension. 60. Figure 10 shows an embodiment of a
coupling which may be used to~ connect main drive shaft 34 to transmission
power input shaft 21 or counter torque rotor drive shaft 50.
It should be understood that the foregoing disclosure involves preferred
I 5 embodiments of the invention and that numerous modifications or
alterations
therein may be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the
invention as set forth in the appendant claims.
-9-