Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
TRICYCLIC 3-OXO-PROPANENITRILE COMPOUNDS
The present invention relates to novel tricyclic 3-oxo-propanenitrile
compounds, to a
process for their preparation, to pharmaceutical compositions containing them
and to
their use in therapy.
The compounds of the invention act as inhibitors of Kynurenine-3-hydroxylase
(KYN-
OH), an enzyme which forms part of the metabolic pathway of kynurenine.
It is well known that through the kynurenine pathway, tryptophan metabolism
gives rise
1 o to the formation of 3-hydroxy-kynurenine(3-OH-KYN) and quinolinic acid
(QUIN), on
the one side, and kynurenic acid (KYNA), on the other side, as shown in Figure
1. (The
legend to Figure 1 is to be found on the last page of the experimental part of
the
specification).
KYNA is endowed with neuroprotective properties (J. Neurosci. 1990,10,2965-
2973),
whereas QUIN is a potent neurotoxin which has been implicated in the
pathogenesis of
a variety of neurological disorders (Life Sci. 1984,35,19-32; Nature,
1986,321,168-171;
Science, 1983,219,316-318).
Increased concentrations of QUIN have also been indicated as responsible for
neurological disorders accompanying many infections and inflammatory diseases
2 0 including Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) (Ann. Neurol.
1991,29,202
209).
One of the main strategies, aimed at altering the KYNA/QUIN balance blocking 3-
OH-
KYN and QUIN's production and increasing KYNA production, entails inhibition
of
key enzymes of the kynurenine (KYN) pathway, among which Kynurenine-3-
hydroxylase (KYN-OH) is of~rimary importance.
Consequently, there is a need in therapy of compounds able of inhibiting this
enzyme.
The compounds of the present invention fulfill such a need.
Accordingly, the present invention provides novel txicyclic 3-oxo-
propanenitrile
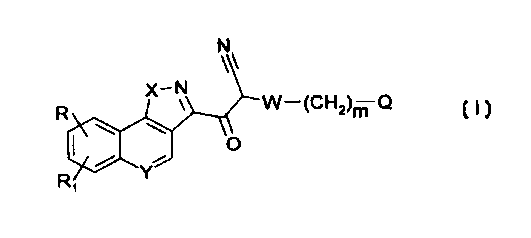
compounds of formula (I)
N
W-(CHZ)m Q
3 0 ~~ (I)
wherein
Y represents a nitrogen atom or a CH or N-oxide group;
X represents an oxygen atom or NR2 wherein R2 represents C~-C6 alkyl, benzyl,
pyridyl
3 5 or phenyl, the phenyl being unsubstituted or substituted by one or two
substituents
chosen independently from halogen, trifluoromethyl, C~-C6 alkyl, C,-C6 alkoxy,
vitro,
amino, formylarnino and C2-C$ alkanoylamino;
each of R and R, is independently hydrogen, halogen, CF3, C~-C6 alkyl,
hydroxy, C,-C6
alkoxy, C3-C4 alkenyloxy, vitro, amino, formylamino, C2-Cg alkanoylamino or C2-
Cs
4 o alkanoyloxy;
m is zero or an integer of I to 6;
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
2
Q is C,-C,4 alkyl, phenyl or unsaturated pentatomic heteromonocyclic ring
containing
two or three heteroatoms chosen from oxygen, sulphur and nitrogen, wherein the
phenyl
ring and the heteromonocyclic ring are unsubstituted or substituted by one or
two
substituents chosen independently from halogen, CF3, C,-C6 alkyl, hydroxy, C1-
C6
alkoxy, nitro, amino, formylamino, C2-C8 alkanoylamino or C2-C8 alkanoyloxy;
and W
represents a -CONH-, -S02- or -CO- group.
The present invention also includes within its scope the pharmaceutically
acceptable
salts, and all possible isomers, stereoisomers and opti al isomers and their
mixtures, and
both the metabolites and the pharmaceutically acceptable bio-precursors
(otherwise
1 o known as pro-drugs) of the compounds of the invention.
It has to be noticed that the compounds of formula (I) may be represented also
by a
tautomeric structure, namely the enol structure of formula (Ia)
R~ _ .~ ~~W ~CHz~m Q
R~ '
(Ia)
wherein
X, Y, R, R,, m, Q and W are as defined above.
However, the compounds of formula (Ia), which fall within the scope of the
present
invention too, are described in the present specification either as compounds
of formula
(I) or of formula (Ia) as more convenient or appropriate in the art.
2 o The alkyl, alkanoyloxy, alkoxy and alkanoylamino groups may be branched or
straight
chain groups.
A C,-C,4 alkyl group is preferably a C,-C6 alkyl group.
Representative examples of C,-C~ alkyl groups include C,-C4 alkyl groups such
as
methyl, ethyl, n- and iso-propyl, n-,
2 5 iso-, sec- and tert-butyl.
Representative examples of C,-C6 alkoxy groups include C,-C4 alkoxy groups
such as
methoxy or ethoxy.
Representative examples of C2-C8 alkanoylamino include C2-C4 alkanoyl groups
such as
acetylamino or propionylamino.
3 o Representative examples of C2-C8 alkanoyloxy include C2-C4 alkanoyl groups
such as
acetoxy or propionyloxy.
A C3-C4 alkenyloxy group is preferably allyloxy.
When Q is a heteromonocyclic ring as defined above it is preferably chosen
from
oxazole, isoxazole, thiazole, pyrazole, imidazole, 1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-
triazole, 1,2,4
3 5 oxadiazole and 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
A halogen atom is fluorine, bromine, chlorine or iodine; in particular
chlorine or
fluorine.
Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds of the invention include
base
addition salts with inorganic bases, e.g. sodium, potassium, calcium and
aluminium
4 o hydroxydes or with organic bases, e.g. lysine, triethylamine,
triethanolamine,
dibenzyiamine, methylbenzylamine, di-(2-ethyl-hexyl)-amine, piperidine, N-
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCTIEP98/06051
3
ethylpiperidine, N,N-diethylaminoethylamine, N-ethyl-morpholine, p-
phenethylamine,
N-benzyl-~3-phenethylamine, N-benzyl-N,N-dimethylamine and the other
acceptable
organic amines.
Preferred compounds of the invention are the compounds of formula (I) wherein:
Y represents a nitrogen atom or a CH group;
X is oxygen or NR2 wherein R2 represents C,-C4 alkyl or phenyl unsubstituted
or
substituted by one or two substituents selected independently from halogen,
trifluoromethyl, C,-C4 alkyl, C,-C4 alkoxy and nitro;
each of R and R~ independently is hydrogen, nitro, halogen, trifluoromethyl,
C,-C4 alkyl
or C ~ -C4 alkoxy;
m is zero or 1;
Q is C,-C4 alkyl or a phenyl ring unsubstituted or substituted by one or two
substituents
selected from halogen, trifluoromethyl, nitro, C,-C4 alkyl and C,-C4 alkoxy;
W is a -CONH-, -S02- or -CO- group;
and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
Examples of preferred compounds of the invention are the following:
2-ciano-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-acrylamide:
2-cyano-3-(8-fluoro-1-methyl-1 H-benzolgl indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-3-(9-chloro-1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2 0 2-cyano-3-(9-methoxy-1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-ben2olglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
2 5 propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-nitro-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-
oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-methyl-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
3 o propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-chloro-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
N-butyl-2-cyano-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionamide;
N-benzyl-2-cyano-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolgl indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionamide;
35 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-{1-phenyl-1H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-acrylamide;
2-cyano-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-pyrazolol4,3-clquinolin-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-3-( 1-phenyl-1 H-pyrazolol4,3-clquinolin-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-N-phenyl-acrylamide,
2-cyano-3-(8-fluoro-isoxazolof 2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
4 o 2-cyano-3-(9-chloro-isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-3-(9-methoxy-isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolo12,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
4 5 2-cyano-N-(3-nitro-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolol2, l -alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolo12,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-methyl-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolol2,1-a)naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
2-cyano-N-(3-chloro-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
N-benzyl-2-cyano-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionamide;
N-butyl-2-cyano-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionamide;
2-benzoyi-3-( 1-methyl- I H-benzo(gl indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-(4-methoxy-benzoyl)-3-{1-methyl-IH-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(4-fluoro-benzoyl)-3-( 1-methyl- I H-benzof g)indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-vitro-benzoyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-trifluoromethyl-benzoyl)-3-( 1-methyl-I H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-methyl-benzoyl)-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-(3-chloro-benzoyl)-3-(I-methyl-I H-benzolglindazol-3-y()-3-oxo-
propionitrile:
2-benzoyl-3-(8-fluoro-1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-benzoyl-3-(9-chloro-1-methyl- I H-benzo(gl indazo I-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzoyl-3-(9-methoxy-I-methyl-1 H-benzolg(indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-benzoyl-3-(isoxazolol2,I-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-(4-methoxy-benzoyl}-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-(4-fluoro-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitri(e;
2-(3-vitro-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolof 2, I -alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-trifluoromethyl-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2 0 2-(3-methyl-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2, I -alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-chloro-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2, I -alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzoyl-3-(8-fluoro-isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl}-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-benzoyl-3-(9-chloro-isoxazolol2, I-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-benzoyl-3-(9-methoxy-isoxazolo(2,1-a(naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile:
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-(4-methoxy-benzenesulfonyl)-3-( 1-methyl-I H-benzo(g)indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(4-fluoro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-( I-methyl-I H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-{3-vitro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(1-methyl-IH-benzolg(indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-trifluorornethyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-( 1-methyl-I H-benzo(gl indazol-3-yl)-
3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-methyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-( I -methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-chloro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-{1-methyl-IH-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(8-fluoro-1-methyl-1 H-benzolg(indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(9-chloro-1-methyl-I H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(9-methoxy-I -methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
4 0 propionitrile;
2-(4-methoxy-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2, I-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(4-fluoro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-vitro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2, I -alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-trifluoromethyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolo12,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-
oxo-
4 5 propionitrile;
2-(3-methyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-chioro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(8-fluoro-isoxazolo(2, I -alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99116753 PCT/EP98/06051
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(9-chloro-isoxazolo(2, I -alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(9-methoxy-isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
and
2-benzenesulfony l-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-a(naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
S and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
A further object of the present invention is also to provide a compound of
formula (I) as
defined above, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use as an
active
therapeutic substance, in particular as kynurenine-3-hydroxylase enzyme
inhibitor.
Object of the present invention is also the use of a compound of formula (I),
as defined
1 o above, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture
of a
medicament for use as kynurenine-3-hydroxylase enzyme inhibitor.
The present invention also provides a method of treating a mammal, including
human,
in need of a kynurenine-3-hydroxylase inhibitor, such method comprising
adminstering
thereto a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I), as
defined
above. or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
The compounds of the invention and the salts thereof can be obtained, for
instance, by a process comprising:
a) reacting a compound of formula (II)
X-N
R i \ z
J (II)
Y
R~
wherein X, R and R, are as defined above, Y represents a nitrogen atom or a CH
group
and Z is a derivative of a carboxy group,with a compound of formula (III)
~N
(III)
w~(CH2)m Q
2 5 wherein m, Q and W are as defined above, thus obtaining a compound of
formula (I) in
which Y represents a nitrogen atom or a CH group; or
b) reacting a compound of formula (IV)
X-N
R \ CN
'O
R, Y (I~
3 0 wherein
X, R and R, are as defined above and Y represents a nitrogen atom or a CH
group, with
a compound of formula (V) or (VI)
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
6
Q-(CH2) m Z Q-(CH2)m N--__C_-_O
(Vl)
wherein Q, m and Z are as defined above, so obtaining a compound of formula
(I)
wherein W is a -CO- or a -CONH- group respectively and Y represents a nitrogen
atom
or a CH group; or
c) oxidizing a compound of formula (I) wherein Y is a nitrogen atom into the
corresponding compound of formula (I) in which Y is a N-oxide group; and, if
desired
converting a compound of formula (I) into another compound of formula {I),
and/or, if
desired, converting a compound of formula (I) into a salt thereof, and/or, if
desired,
1 o converting a salt of a compound of formula (I) into a free compound of
formula (I),
and/or, if desired, separating a mixture of isomers of a compound of formula
(I) into the
single isomers.
The above process-variants a), b) and c) are analogy processes which can be
carried out
according to well known methods in the art.
When Z is a derivative of a carboxy group, it is preferably a reactive
derivative thereof,
for example a halocarbonyl group, preferably a chlorocarbonyl group, or a CZ-
C~
alkoxycarbonyl group, preferably a C2-C3 alkoxycarbonyl group.
The reaction between a compound of formula (II) wherein Z is a reactive
derivative of a
carboxy group and a compound of formula (III) can be carned out, for example,
in the
2 o presence of a strong base such as sodium hydride, potassium t-butoxide,
thallous
ethoxide, in an inert solvent such as 1,2-dimethoxyethane, dioxane,
dimethylformamide,
at a temperature ranging from about 0°C to about 100°C.
The reaction between a compound of formula (IV) and a compound of formula (V)
or
(VI) can be carried out, for example, in the presence of a base such as sodium
hydride or
2 5 triethylamine, in an inert solvent such as toluene, dioxane,
tetrahydrofuran,
dimethylformamide, dichloromethane, at a temperature varying between about
0°C and
about 100°C.
The conversion of a compound of formula (I) wherein Y is a nitrogen atom into
the
corresponding compound of formula (I) in which Y is a N-oxide group may be
3 o performed by treatment, for example, with m-chloroperbenzoic acid or
perbenzoic acid
in a solvent such as dichloromethane or with H202 in acetic acid.
Also the optional conversion of a compound of formula (I) into another
compound of
formula (I) can be carried out according to known methods. For example,in a
compound
of formula (I) a nitro group may be converted into an amino group by
treatment, for
3 5 example, with stannous chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid, using,
if necessary,
an organic cosolvent such as acetic acid, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran at a
temperature
varying between room temperature and about 100°C. Furthermore, for
example, an
amino group may be converted into a formylamino or a C2-Cg alkanoylamino
group, for
example by reacting with formic acid or with the suitable C2-Cg
alkanoylanhydride
4 o without any solvent or in an organic solvent such as dioxane,
dimethylformamide,
tetrahydrofuran, usually in the presence of a base such as pyridine or
triethylamine, at a
temperature varyng between about 0°C and about 100°C.
The optional salification of a compound of formula (I) as well as the
conversion of a salt
into the free compound and the separation of a mixture of isomers into the
single
4 5 isomers may be carried out by conventional methods.
The compounds of formula (II) as herein defined are novel compounds and are a
further
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
7
object of the present invention.
A compound of formula (II), wherein Z is a C2-C~ alkoxycarbonyl group, can be
otbained for instance by aromatization of a compound of formula (VII)
X-N
R ~~ z
i (VII)
R A
wherein
R, R, and X are as defined above and A is a NH or CH2 group. Aromatization
reaction
may be accomplished using quinones such as, e.g. chloroanil (2,3,x,6-
tetrachloro-1,4-
benzoquinone) or DDQ (2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone), in a solvent
such
as toluene, dioxane, at a temperature varying between about room temperature
arid
about 120°C. Aromatization reaction, wherein Y is a nitrogen atom, can
be simply
performed warming a compound of formula (VII) in an organic solvent such as
dimethylformamide.
A compound of formula (VII) may be prepared, for example, by reacting a
compound of
formula {VIII)
O
R COCOOR3
A (VIII
R~
wherein
R, R~ and A are as defined above and R3 is a lower alkyl, e.g. C~-C6 alkyl,
preferably
C1-C2 alkyl, with a compound of formula (IX)
H-X-NH2 (IX)
wherein X is oxygen or NR2 wherein R2 is as defined above.
The reaction between a compound of formula (VIII) and a compound of formula
(IX)
may be carried out, for example, in an organic solvent such as C,-C6 alkyl
alcohol,
2 5 dioxane, tetrahydrofuran, dimethylformamide, acetic acid, at a temperature
varying
between about 0°C and about 150°C, in the presence or in the
absence of a suitable acid,
e.g. methanesulfonic acid.
A compound of formula (II), wherein Z is halocarbonyl, preferably
chlorocarbonyl, may
be prepared, for example, by reacting the corresponding compound of formula
(II),
3 o wherein Z is carboxy, with the suitable acid halide, for example oxalyl
chloride, thionyl
chloride, PC13, PBr3, in an inert solvent such as ether, benzene,
dichloromethane,
dioxane or without any solvent, at a temperature varying between about
0°C and about
100°C. The compounds of formula (II), wherein Z is carboxy may be
prepared, for
example, by hydrolysis of the corresponding compounds of formula (II) wherein
Z is
3 5 C2-C~ alkoxycarbonyl, according to standard methods well known in the art,
for
example, by basic hydrolysis, carried out e.g. by treatment with sodium or
potassium
hydroxide in a solvent such as water, C2-C6 alkyl alcohol, dioxane,
dimethylformamide
and their mixtures, at a temperature varying between about 0°C and
about 50°C.
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
8
Compounds of formula (III) are, in some cases, commercially available
products, or
may be prepared by methods well known in the art.
Also the compounds of formula (IV) as herein defined are novel compounds and
are a
further object of this invention.
A compound of formula (IV) can be obtained by process a) above, for example,
by
reacting a compound of formula {II), wherein Z is C2-C~ alkoxycarbonyl, with
acetonitrile, in the presence of a strong base e.g. sodium hydride, potassium
tert-
butoxide, in an inert organic solvent such as benzene, dioxane,
tetrahydrofizran, at a
temperature varying between about 0°C and about 100°C.
1 o A compound of formula (VIII) may be prepared, for example, by reacting a
compound
of formula (X)
O
R
~ ~ (x)
R ~ _A
wherein
R, R, and A are as defined above, with a compound of formula (XI)
COOR4
COOR5 (XI)
wherein
each of R4 and R5, being the same or different, is C,-C6 alkyl, preferably
methyl or
2 0 ethyl.
The reaction between a compound of formula (X) and a compound of formula {XI)
may
be carried out, for example, in the presence of a strong base such as sodium
methoxide,
sodium ethoxide, sodium hydride, potassium tert-butoxide, in an organic
solvent such as
C,-C6 alkyl alcohol, benzene, dioxane, dimethylformarnide, at a temperature
varying
2 5 between about 0°C and about 100°C. When in the compounds of
formula (X) Y
represents a nitrogen atom, it needs to be protected before submitting these
compounds
to the hereabove illustrated reaction. This group may be protected before
being reacted
and then deprotected according to methods well known in organic chemistry, for
example, by reacting with p-toluensulfonylchloride in pyridine at a
temperature varying
3 o between 0°C and about 120°C and then by treatment with
methanesulfonic acid and
anisole at a temperature ranging from about 0°C to about 60°C.
The compounds of formula (V), (VI), (X) and (XI) are known compounds and may
be
prepared by conventional methods: in some cases they are commercially
available
products.
3 5 When in the compounds of the invention and the intermediate products
thereof, groups
are present which may interfere with the hereabove illustrated reactions, they
may be
protected before the reactions take place and then deprotected at the end of
the reactions,
according to well known methods in organic chemistry.
4 0 Pharmacol_o~v
The compounds of the invention are active as kynurenine-3-hydroxylase enzyme
inhibitors and therefore are useful in the prevention and/or treatment of
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
9
neuropathological processes, related to a deranged production of QUIN and/or 3-
OH-
KYN due to excessive activation of neuro-transmission mediated by excitatory
amino
acid receptors andlor oxidative stress. Examples of such neuropathological
processes are
neurodegenerative pathologies including, e.g. Huntington's chorea, Alzheimer's
disease,
Parkinson's disease, olivoponto cerebellar atrophy, non-Alzheimer's demential,
including the dementia like syndrome caused by Acquired Immunodeficiency
Syndrom
(AIDS), multi-infarctual dementia, cerebral amyotrophic lateral sclerosis,
cerebral
ischemia, cerebral hypoxia, spinal and head trauma, and epilepsy.
A human or animal in need of a kynurenine-3-hydroxylase enzyme inhibitor can
1 o thus be treated by a method which comprises the administration thereto of
a
therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention or a salt
thereof. The
condition of the human or animal can thereby be improved.
The efficacy of the compounds of the invention in the inhibition of the enzyme
kynurenine-3-hydroxylase was evaluated e.g., in rat liver mitochondria)
extract
following the method reported below, according to the procedure described in
"Analytical Biochem. ( 1992), 205, 257-262", with minor modifications.
The assay for kynurenine 3-hydroxylase is based on the enzymatic synthesis of
tritiated
water during the hydroxylation reaction. Radiolabeled water was quantified
following
selective adsorption of the isotopic substrate and its metabolite with
activated charcoal.
2 o Rat liver mitochondria) extract was used as enzymatic preparation for this
assay.
The assay for kynurenine 3-hydroxylase activity was carned out at 37°C
for a time of 30
min. The reaction mixture of a total volume of 100 ml was constituted of 44 mg
of
suspended extract, 100 p.M Tris/Cl- buffer pH 8.1, 10 PM EDTA, 100 ~M KCI, 0.8
pM
NADPH, 0.025 ~M L-Kynurenine, 0.5 pCi L-(3,5 3H)Kynurenine { 10 Ci/p.mo1) and
10
pl of different concentration of inhibitor solutions. After the incubation,
the reaction
was terminated by the addition of 1 pl of 7.5% (W/v) activated charcoal,
vortexed and
centrifuged for 7 min..
A 500 p.l aliquot of supernatant was counted by scintillation, spectroscopy in
5 p.l of
liquid scintillation.
3 o The obtained results, which have been reported in the following Table 1,
demonstrate
the efficacy of the representative compound of the invention 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-
3-( 1-
methyl-I-H-benzo[gJindazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-acrylamide sodium salt (internal
code
PNU-168754 A).
Table 1
KYN-3-OH-inhibition
Compound ICSo
PNU-168754 A 0.04 p.M
The dosage level, suitable for administration to a mammal, e.g.: to humans,
depends on the age, weight, conditions of the patient and on the
administration route;
for example, the dosage adopted for oral administration e.g. for the
representative
4 o compound of the invention PNU 168754 may range from about 10 to about S00
mg pro
dose, from 1 to 5 times daily.
The compounds of the invention can be administered in a variety of dosage
forms,
e.g. orally, in the form of tablets, capsules, sugar or film coated tablets,
liquid solutions
or suspensions; rectally in the form of suppositories; parenterally, e.g.
intramuscolarly,
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
or by intravenous and/or intrathecal and/or intraspinal injection or infusion.
The invention includes also pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound
of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in association
with a
pharmaceutically acceptable excipient (which can be a carrier or a diluent).
5 The pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of the invention
are
usually prepared following conventional methods and are administered in a
pharmaceutically suitable form.
For example, the solid oral forms may contain, together with the active
compound,
diluents, e.g. lactose, dextrose, saccharose, sucrose, cellulose, corn starch
or potato
10 starch; lubricants, e.g. silica, talc, stearic acid, magnesium or calcium
stearate. and/or
polyethylene glycols; binding agents, e.g. starches, arabic gum, gelatin,
methylcellulose,
carboxymethylcellulose or polyvinyl pyrrolidone; disaggregating agents, e.g. a
starch,
alginic acid, alginates or sodium starch glycolate; effervescing mixtures:
dyestuffs;
sweeteners; wetting agents such as lecithin, polysorbates, laurylsulphates:
and, in
general, non-toxic and pharmacologically inactive substances used in
pharmaceutical
formulations. Said pharmaceutical preparations may be manufactured in known
manner,
for example, by means of mixing, granulating, tabletting, sugar-coating, or
film-coating
processes.
The liquid dispersions for oral administration may be e.g. syrups, emulsions
and
2 0 suspensions.
The syrups may contain as carrier, for example, saccharose or saccharose with
glycerine
and/or mannitol and/or sorbitol.
The suspensions and the emulsions may contain as carrier, for example, a
natural gum,
agar, sodium alginate, pectin, methylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose, or
polyvinyl
2 5 alcohol.
The suspension or solutions for intramuscolar injections may contain, together
with the
active compound, a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, e.g. sterile water,
olive oil,
ethyl oleate, glycols, e.g. propylene glycol, and, if desidered, a suitable
amount of
lidocaine hydrochloride. The solutions for intravenous injections or infusions
may
3 0 contain as carrier, for example, sterile water or preferably they may be
in the form of
sterile, acqueous, isotonic saline solutions or they may contain as a carrier
propylene
glycol.
The suppositories may contain together with the active compound a
pharmaceutically
acceptable carrier, e.g. cocoa butter, polyethylene glycol, a polyoxyethylene
sorbitan
3 5 fatty acid ester surfactant or lecithin.
The following examples illustrate but do not limit the invention.
Example 1
4 0 ~I
To a solution of sodium ethoxide (4.49 g; 0.066 mol) in anhydrous ethanol (SO
ml)
cooled at about 10°C, a- tetralone (8.77 g; 0.06 mol), dissolved in
anhydrous ethanol
(10 ml), was added under stirring under inert atmosphere. After a few minutes
diethyl
oxalate (8.76 g; 0.06 mol) was added and the reaction mixture was kept under
stirring
4 5 for 2h 30 min at about 40°C. After cooling the suspension thus
obtained was diluted
with ice water and then acified to pH 4 with 0.1 N HCI. The product was
extracted with
ethyl acetate and the organic solutions collected, washed with water until
neutral and
then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Evaporation of the solvent to
dryness in
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCTIEP98/06051
11
vacuo gave 14 g (95 %) of crude hydroxy-(1-oxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-naphthalen-2-
ylidene)-acetic acid, ethyl ester, a brown oil, which was used without further
purification. N.M.R. (CDCl3) 8 ppm: 1.4 (t, 3H, -C02CH2~i~), 3.0 (s, 4H, -
CH2CH2-),
4.4 (q, 2H, -C02~i~CH3), 7.2-8.1 (m, 4H, phenyl protons).
Analogously, the following products can be prepared:
(7-fluoro-1-oxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-naphthalen-2-ylidene)-hydroxy-acetic acid,
ethyl ester;
(8-chloro-I-oxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-naphthalen-2-ylidene)-hydroxy-acetic acid,
ethyl ester;
and
{8-methoxy-I-oxo-3,4-dihydro-IH-naphthalen-2-ylidene)-hydroxy-acetic acid,
ethyl
ester.
Example 2
Preparation of I-meth 1-4.5-di vdro-IH-benzolglin a~.~le-'i-carbOgy ' . a~'
,ghy
Methylhydrazine (3.6 ml; 0.068 mol) was added under stirring to a solution of
hydroxy-
( 1-oxo-3,4-dihydro-1 H-naphthalen-2-ylidene)-acetic acid, ethyl ester ( 15.0
g; 0.061
mol) in acetic acid ( 100 ml) at room temperature (exotermic reaction). The
reaction
mixture was stirred without cooling for 7 h and was then diluted with ice
water (200
ml). The products (both isomers} were extracted with ethyl acetate (300 ml),
the organic
solution was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and the solvent was
evaporated. The
desired isomer (Rf <} was separated by flash chromatography on silica gel with
a
gradient of 20-SO% AcOEt in hexane as eluent. Evaporation of the purified
fractions
gave 8.3 g {53%) of I-methyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-benzolglindazole-3-carboxylic
acid, ethyl
ester, m.p. 115-116°C.
N.M.R. (CDC13) b ppm: 1.4 (t, 3H, -C02CH2~~), 2.9-3.1 (m, 4H, -CH2CH2-), 4.2
(s,
3H, -N-CH3), 4.4 (q, 2H, -C02~i~CH3), 7.2-7.6 (m, 4H, phenyl protons).
Analogously, the following products can be prepared:
8-fluoro-1-methyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-benzo(glindazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl
ester;
9-chloro-1-methyl-4,S-dihydro-1H-benzolglindazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl
ester;
9-methoxy-1-methyl-4,5-dihydro-IH-benzolglindazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl
ester;
3 o and
1-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-benzolg)indazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester: m.p.
156-
159°C.
Example 3
Preparation of 1-methyl-1H-benzolglinda?nIP-3-c~~x3rlic acid,~y c Pr
1-Methyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-benzolglindazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester (6.0
g; 0.023
mol) and 10.63 g (0.046 mol) of DDQ in 100 ml of dioxane was refluxed for 7h,
cooled,
filtered, and the solvent evaporated. The residue was dissolved in benzene,
washed
twice with I U% NaOH, three times with water, dried (sodium sulfate) and the
solvent
evaporated to give 4.94 g (83%) of 1-methyl-1H-benzolglindazole-3-carboxylic
acid,
ethyl ester, m.p. 122-123°C.
N.M.R. (CDC13) 8 ppm: I .5 (t, 3H, -C02CH2~~), 4.55 (q, 2H, -C02~~CH3), 4.65
(s,
3H, -N-CH3), 7.6-8.5 (m, 6H, aromatic protons).
Analogously, the following products can be prepared:
8-fluoro-1-methyl-IH-benzolglindazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester;
9-chloro-I-methyl-1H-benzolg)indazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester;
9-methoxy-1-methyl-1H-benzolglindazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester; and
1-phenyl-1H-benzolglindazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester: m.p. 143-
145°C.
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
12
Example 4
p-Toluensulfonyl chloride (12.83 g, 0.067 mol) was added portionwise to a
solution of
4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-quinoline (9.00 g, 0.061 moI) in pyridine (87 ml)
maintained
under magnetic stirring at room temperature. The reaction mixture was refluxed
for
about 8 hours, cooled at room temperature, and poured into water (300 ml); the
resulting
solid was filtered, washed with water and dried in vacuum at 60°C. The
title compound
was obtained as a beige solid {13.5 g, 75%), m.p. 138-141 °C.
to
Example S
p~naration of hydroxy-[4-oxo-1-lp-toluensulfonyl -l~ 2.4-dih3r ro-1H- uinolin-
'i-
~ lir_ dene]-acetic acid,~yl ester.
Diethyl oxalate ( 12.76 ml, 0.094 mol) was added dropwise to a solution of
sodium
ethylate (8.16 g, 0.120 mol) in dry benzene (150 ml) maintained under nitrogen
atmosphere; the mixture was heated to reflux for about 10 minutes. After
cooling at 0
3°C with an ice-water bath, a solution of N-p-toluensulfonyl-4-oxo-
1,2,3,4-tetrahydro
quinoline (13.5 g, 0.045 mmol) in THF (300 ml) was added dropwise. The
reaction
mixture was allowed to warm at room temperature and stirred for about 4 hours.
It was
2 0 then diluted with water (300 ml), acidified to pH S-6 with N HCl and
extracted with
ethyl acetate (4X200 ml); the organic layers were combined, washed with water
until
neutral, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under vacuum to
yield
the title compound as an orange solid (17 g, 94%), m.p. 11 S-120°C.
N.M.R. (CDC13) 8 ppm: 7.8 (m, 2H); 7.65 (m, 1H); 7.4 (m, 1H); 7.23 (d, 2H);
7.08 (d,
2H); 5 (s, 2H, N~~); 4.45 (q, 2H, O~~CH3); 2.31 (s, 3H, CH3); 1.46 (t, 3H,
OCH2~~).
Example 6
3 0 3-carbox~ Ir is arid. ethyl ester.
Methylhydrazine {4.S 1 ml, 0.0848 mol) was added dropwise to a solution of
hydroxy-
[4-oxo-1-(p-toluensulfonyl)-2,4-dihydro-1 H-quinolin-3-ylidene]-acetic acid,
ethyl ester
( 17 g, 0.0424 mol) in glacial acetic acid ( 180 ml) at room temperature; the
reaction
mixture was heated at 50°C for about 10 hours, cooled at room
temperature, diluted
3 5 with water (200 ml) and extracted with ethyl acetate (3X200 ml). The
organic layers
were combined, washed with brine (200 ml), dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate
and
concentrated under vacuum. The residue was flash chromatographed on silica gel
using
cyclohexane/ethyl acetate 20-40 as eluent to separate the two regioisomers
(about 1:1
ratio): the title compound was obtained as a light yellow solid (7.S g, 43%),
m.p. 165-
40 168°C.
N.M.R. (CDC13) b ppm: 7.87 (m, 1 H); 7.45 (m, 3H); 7.12 (d, 2H); 6.89 (d, 2H);
5.05 (s,
2H, N~~); 4.47 (q, 2H, O~~CH3); 3.8 {s, 3H, N~j3); 2.25 (s, 3H, CH3); 1.47 (t,
3H,
OCH2~H~).
4 5 Example 7
Preparation of 1-meth 1-4.5-di dro- -pj4,~~~P,~'~-ca ' aciy
etj~yl ester.
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
13
A solution of 5-(p-toluensulfonyl)-1-methyl-4,5-dihydro-IH-pyrazolo[4,3-
cJquinoline-
3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester {7 g, 0.0170 mol), methanesulphonic acid (27.7
ml) and
anisole (5.55 ml, 0.0511 mol) was maintained under magnetic stirring at
50°C for about
hours; it was then diluted with ice-water ( 100 ml) and basified with N NaOH:
the
5 aqueous mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3X150 ml). The organic
layers were
combined, washed with water until neutral, with brine, dried over anhydrous
sodium
sulfate and concentrated under vacuum. The residue was slurried with methanol,
filtered
and dried in vacuum at 45°C to give a light yellow solid (4.7 g) which
was used in the
next step without any further purification, m.p. 206-210°C.
1 o N.M.R. (CDCl3) 8 ppm: 7.5 (m, 1 H); 7 (m, 1 H); 6.6 (m, 2H); 6. I (broad
s, 1 H, NH);
4.55 (d, 2H, N~~); 4.27 (q, 2H, O~j~CH3); 4.1 (s, 3H, N~~); 1.3 (t, 3H,
OCH2~~).
Example 8
Preparation of 1-methyl-1H-pyrazolo(4.3-c]~uinoline-3-carbon, liv c ac'~d, et
3r1 ester
1-Methyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl
ester (4.7g,
0.0170 mol) was dissolved in DMF (130 ml) and heated to 100°C for about
32 hours.
The reaction mixture was diluted with water (250 ml) and extracted with ethyl
acetate
(3X200 ml); the aqueous layer was added with NaCI and extracted with ethyl
acetate
(2X100 ml). The organic layers were combined, washed with water (300 ml),
dried over
2 o anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under vacuum. The residue was
slurried
with diethyl ether and filtered to yield the title compound as a colorless
solid (2.5 g,
58%), m.p. 123-125°C.
N.M.R. (CDC13) 8 ppm: 9.67 (s, IH, NCH); 8.38 (m, 2H); 7.8 (m, 2H); 4.61 (s,
3H,
NCH3); 4.58 {q, 2H, O~i~CH3); 1.52 (t, 3H, OCH2~~).
Example 9
Preparation of 3-(1-me yl-1H-ben?.olglinda?.ol-3-yl - -oxo-pro ioni rile.
To a suspension of 55% sodium hydride (1.03 g; 0.024 mol) in anhydrous dioxane
(20
ml), 1-methyl-IH-benzolglindazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester (3.0 g; 0.012
mol) and
3 o then anhydrous acetonitrile (20 ml} were added under stirring at room
temperature, in
inert atmophere. The reaction mixture was heated to about 55°C, under
stirnng, and
then kept at that temperature for 30 min. After cooling, the suspension was
diluted with
ice water obtaining a solution that was acidified to pH 4 with 2N HCI. The
precipitate
was filtered, washed with water until neutral and then dried in vacuo at
SO°C.
3 5 Crystallization from dichloromethane/isopropyl ether gave 2.18 g (74%) of
3-( I -methyl-
1H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile, m.p. >220°C.
N.M.R. (DMSO) 8 ppm: 4.6 (s, 3H, -N-CH3), 4.7 (s, 2H,-COCH2CN), 7.6-8.6 (m,
6H,
aromatic protons).
Analogously, the following products can be prepared:
40 3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]quinolin-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
3-( 1-phenyl-1 H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]quinolin-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
3-(8-fluoro-1-methyl-1 H-benzolgl indazol-3-yl}-3-oxo-propionitrile;
3-(9-chloro-1-methyl-I H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
3-(9-methoxy-1-methyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile; and
45 3-(I-phenyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile: m.p. 151-
156°C.
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/Ob051
14
Example 10
Preyaration of 2-c3rano- - ~ ro ~r_-~(1-methyrl-1H-benzolgfindazol-3-yil-N-
phe~,~-
ac~rlamide.
To a suspension of 3-(1-methyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile
(2.80 g;
0.011 mol) in dimethylformamide (60 ml), triethylamine (1.7 ml; 0.012 mol) was
added
under stirring, at room temperature obtaining a solution. Phenylisocyanate (
1.3 ml;
0.012 mol) diluted with dimethylformamide (2 ml) was added and the rection
mixture
was allowed to react at room temperature for 30 min. The solution was
acidified to pH 2
with 2N HCl and diluted with ice water. The precipitate was filtered, washed
with water
1 o until neutral and then dried in vacuo at 50°C. Trituration in MeOH
(40 ml) gave 3.10 g
(75%) of 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-
acrylamide, m.p. 263°C (dec.).
N.M.R. (DMSO) S ppm: 4.6 (s, 3H, -N-CH3), 7-8.6 (m, I 1H, aromatic protons),
11.1 (s,
1H, -CO-NH-Ph).
Analogously, the following products can be prepared:
2-cyano-3-(8-fluoro-1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-3-(9-chloro-1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-3-(9-methoxy-1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2 0 2-cyano-N-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl}-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-{3-vitro-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-3-(I-methyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl}-3-
oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-methyl-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl- I H-benzolglindazol-3-yl}-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-chloro-phenyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
3 0 propionamide;
2-cyano-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-pyrazolol4,3-cJquinolin-3-yl )-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide:
m.p. 250°C (dec.);
2-cyano-3-( 1-phenyl-1 H-pyrazolo14,3-clquinolin-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide:
m.p. 260-263°C;
N-butyl-2-cyano-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionamide;
N-benzyl-2-cyano-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionamide; and
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(I-phenyl-IH-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-acrylamide;
m.p.
252°C (dec.).
4 0 Example 11
Hydroxylamine hydrochloride (2.48 g; 0.036 mol} was added under stirring to a
solution
of hydroxy-(1-oxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-naphthalen-2-ylidene)-acetic acid, ethyl
ester (8.0 g;
0.032 mol) in acetic acid (50 ml) at room temperature. The reaction mixture
was stirred
4 5 at about 60°C for 8 h and, after cooling, was then diluted with ice
water (250 ml). The
precipitate was filtered, washed with water and then dried in vacuo at
30°C to give 5.2 g
(66%) of 4,5-dihydro-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl
ester, m.p.
84-87°C.
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCTIEP98/06051
N.M.R. (CDC13) 8 ppm: 1.4 (t, 3H, -C02CH2~~), 2.9-3.2 (m, 4H, -CH2CH2-), 4.5
(q,
2H, -C02~~CH3), 7.2-7.8 (m, 4H, phenyl protons).
Analogously, the following products can be prepared:
8-fluoro-4,5-dihydro-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl
ester;
5 9-chloro-4,5-dihydro-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl
ester; and
9-methoxy-4,5-dihydro-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl
ester.
Example 12
Preparation of isoxazolo(2.1-a]~nhthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester.
10 4,5-Dihydro-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester (3.0
g; 0.012
mol) and 5.6 g (0.024 rnol) of DDQ in 50 ml of dioxane was refluxed for 12 h,
cooled,
filtered, and the solvent evaporated. The residue was dissolved in benzene.
washed
twice with 10% NaOH, three times with water, dried (sodium sulfate) and the
solvent
evaporated. The residue was triturated in MeOH to give 1.44 g (48%) of
isoxazolo[2,1-
15 a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester, m.p. 95-97°C.
N.M.R. (CDC13) 8 ppm: 1.5 (t, 3H, -C02CH2~~), 4.6 (q, 2H, -C02~~CH3), 7.7-8.5
(m, 6H, aromatic protons).
Analogously, the following products can be prepared:
8-fluoro-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester;
2 0 9-chloro-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester; and
9-methoxy-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester.
Example 13
Preparation of 3-~(isoxazolo12.1-alnanhthalen-3-~l-3-oxo-pronionitrile.
To a suspension of 55% sodium hydride (0.51 g; 0.012 mol) in anhydrous dioxane
(10
ml), isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester ( 1.40 g;
0.006 mol) and
then anhydrous acetonitrile (10 ml) were added under stirring at room
temperature, in
inert atmophere. The reaction mixture was heated to about 55°C, under
stirring, and
then kept at that temperature for 30 min. After cooling, the suspension was
diluted with
3 o ice water obtaining a solution that was acidified to pH 4 with 2N HCI. The
precipitate
was filtered, washed with water until neutral and then dried in vacuo at
30°C. The
product was purified by flash chromatography on silica gel with
dichloromethane as
eluent to give 0.78 g (57%) of 3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile,
m.p. 183-184°C.
3 5 N.M.R. (DMSO) 8 ppm: 4.4 (s, 2H,-COCH2CN), 7.7-8.5 (m, 6H, aromatic
protons).
Analogously, the following products can be prepared:
3-(8-fluoro-isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
3-(9-chloro-isoxazolol2,1-a)naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile; and
3-(9-methoxy-isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile.
Example 14
Preparation of 2-cvano-3-h dro v-3-(isoxazolol?" 1-alnap halen-_ -yl)-N- hn
envl-
~ylamide.
To a solution of 3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile (0.75
g; 0.003
4 5 mol) in dimethylformamide (8 ml), triethylamine (0.49 ml; 0.003 mol) was
added under
stinring, at room temperature. Phenylisocyanate (0.36 ml; 0.003 mol) diluted
with
dimethylfomamide (0.5 ml) was added and the rection mixture was allowed to
react at
room temperature for lh 30 min. The solution was acidified to pH 2 with 2N HCl
and
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
16
diluted with ice water. The precipitate was filtered, washed with water until
neutral and
then dried in vacuo at 30°C. Trituration in MeOH (20 ml) gave 0.93 g
(82%) of 2-
cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-N-phenyl-acrylamide, m.p.
231-
233°C (dec.).
N.M.R. (DMSO) b ppm: 6.9-8.5 (m, I 1H, aromatic protons), I 1.9 (s, 1 H, -CO-
NH-Ph).
Analogously, the following products can be prepared:
2-cyano-3-(8-fluoro-isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-3-(9-chloro-isoxazoio(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-y()-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-3-(9-methoxy-isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-N-phenyl-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl}-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-vitro-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolol2,1-a)naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionarnide;
2-cyano-N-(3-methyl-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-a)naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
2-cyano-N-(3-chloro-phenyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionamide;
N-benzyl-2-cyano-3-(isoxazolol2,l-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionamide; and
N-butyl-2-cyano-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionamide.
Example 15
Preparation of 2-benzn3r~1-me hyl-1H-berLOlglind ~~nl ~-. - -ox~propioni rile
To a solution of 3-(1-methyl-1H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile
(0.50 g;
0.002 mol) in dichloromethane (20 ml), triethylamine (0.31 ml; 0.002 mol) was
added
2 5 under stirring, at room temperature. Benzoyl chloride (0.23 ml; 0.002 mol)
was added
and the reaction mixture was allowed to react at room temperature for 1 h. The
solution
was washed with water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then
evaporated. The
residue was purified by flash chromatography on silica gel using
dichloromethane/AcOEt 98:2 as eluent. The purified fractions were collected
and
3 0 evaporated to dryness. The residue was triturated in MeOH (6 ml)to give
0.35 g (50%)
of 2-benzoyl-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile.
Analogously, the following products can be prepared:
2-(4-methoxy-benzoyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzofglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(4-fluoro-benzoyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
3 5 2-(3-vitro-benzoyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-( 3-trifluoromethyl-benzoyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-methyl-benzoyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-chloro-benzoyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
40 2-benzoyl-3-(8-fluoro-1-methyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzoyl-3-(9-chloro-1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-benzoyl-3-(9-methoxy-1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitril
e;
2-benzoyl-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-(4-methoxy-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
4 5 2-(4-fluoro-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-vitro-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-(3-trifluoromethyl-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-a)naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-methyl-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/I6753 PCT/EP98/06051
17
2-(3-chloro-benzoyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2, I -alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzoyl-3-(8-fluoro-isoxazolof2,1-a)naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
2-benzoyl-3-(9-chloro-isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile;
and
2-benzoyl-3-(9-methoxy-isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile.
Example 16
Preparation of 1-methyl-IH-benzo(g(inda'ole-3-carboxylic arid
1-Methyl-1H-benzo(g)indazole-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester (I.SO g; 0.006
mol) was
heated at the reflux temperature for 4h 30 min with a 0.1 N KOH solution in
95%
1 o methanol (70 ml; 0.007 mol). After cooling the precipitate was collected
by filtration,
washed with 95% ethanol and dissolved in water. The solution was acidified to
pH 3
with 2N HCl and the precipitate was filtered, washed with water until neutral
and then
dried in vacuo at 50°C to give 1.19 g (89%) of I-methyl-IH-
benzolglindazole-3-
carboxylic acid.
Analogously the following products can be prepared:
8-fluoro-I-methyl-IH-benzo(g)indazole-3-carboxylic acid;
9-chloro-l-methyl-1H-benzo(g)indazole-3-carboxylic acid;
9-methoxy-I-methyl-IH-benzo(g)indazole-3-carboxylic acid;
8-fluoro-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid;
2o 9-chloro-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid;
9-methoxy-isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid; and
isoxazolo[2,1-a]naphthalene-3-carboxylic acid.
Example 17
2 5 Preparation of 2-benzenesulfo~yj~~ 1-me~;~,y~ - n~ (glindazol 3 y].) oxo
propionitriie.
1-Methyl-1H-benzo(glindazole-3-carboxylic acid (0.40 g; 0.002 mol) was reacted
with
thionyl chloride (0.42 g; 0.004 mol) in anhydrous dioxane (6 ml) at the reflux
temperature for 1.5 hours. After cooling the solution was evaporated to
dryness in vacuo
3o and the crude I-methyl-IH-benzo(glindazole-3-carbonyl chloride was
dissolved in
anhydrous dioxane ( 1 S ml). This solution was added under stirring at room
temperature
under inert atmosphere to the suspension of the carbanion obtained by
treatment of
(phenylsulfonyl)acetonitrile (0.35 g; 0.002 mol) with 55% sodium hydride (0.12
g;
0.003 mol) in anhydrous dioxane (25 ml}; the reaction mixture was allowed to
react at
3 5 room temperature for 1.5 hours and was then acidified to pH 2 with 2N HCl
and diluted
with ice water. The product was extracted with ethyl acetate and the organic
solutions
collected, washed with water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then
evaporated.
The residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate (50 ml) and extracted twice with
0.1 N NaOH
(20 ml). The alkaline solutions were collected, acidified to pH 3 with 2N HCl
and then
4 0 extracted three times with ethyl acetate. The organic solutions were
collected, washed
with water and then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Evaporation of the
solvent to
dryness gave 0.31 g (45%) of 2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(I-methyl-1H-benzo(g)indazol-
3-yl}-
3-oxo-propionitrile.
Analogously the following products can be prepared:
4 5 2-(4-methoxy-benzenesulfonyl)-3-( I -methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-
oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(4-fluoro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(g)indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
18
2-(3-vitro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-trifluoromethyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(g)indazol-3-yl)-3-
oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-methyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-( I -methyl-1 H-benzo(g)indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-chloro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolg) indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-( 8-fluoro-1-methyl-1 H-benzo(g) indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-{9-chloro- I -methyl- I H-benzo(g)indazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(9-methoxy-I-methyl-1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(4-methoxy-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-a(naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(4-fluoro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolo)2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl}-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-vitro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-trifluoromethyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-a)naphthalen-3-yl)-3-
oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-methyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-{isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-(3-chloro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-a)naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(8-fluoro-methoxy-isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
2 0 propionitrile;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(9-chloro-isoxazolo)2,1-a)naphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(9-methoxy-isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yt)-3-oxo-
propionitrile;
and
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-3-oxo-propionitrile.
Example 18
Preparation of 2-cvano-3-hyrdrox3r-~ 1-methyl-1 H-ben~.nig '
acrvlamide, odi ~ m salt.
2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzo(g)indazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-acrylamide
(2.75
3 o g; 0.0075 mol) was suspended in ethanol (180 mL) and 0.1 N NaOH (75 mL;
0.0075
mol) was added. The solution so obtained was evaporated to dryness to afford
the
desired compound, m.p. 311°C (dec.). C22H~SN4Na02; required: C= 67.69;
H= 3.87; N=
14.35; found: C=67.45; H=3.90; N=14.28.
Analogously the following derivatived can be prepared:
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(8-fluoro-I-methyl-1H-benzofglindazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(9-chloro-1-methyl-1 H-benzo(g)indazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(9-methoxy-1-methyl-1 H-benzo(gl indazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-
4 0 acrylamide, sodium salt;
N-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-( I -methyl-1 H-benzo(g)indazol-3-yl)-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
N-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
N-(3-vitro-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzo(g)indazol-3-yl)-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
N-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-I H-
benzo(g)indazol-3-
yl)-acrylamide, sodium salt;
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
I9
N-( 3-methyl-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(g( indazol-3-yl
)-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
N-(3-chloro-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-I H-benzo(g(indazol-3-yl)-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
N-butyl-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-acrylamide,
sodium
salt;
N-benzyl-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-( I-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-acrylamide.
sodium salt;
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-{ I -phenyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-acrylamide,
sodium salt: m.p. 220°C (dec.);
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-pyrazolo(4,3-clquinolin-3-yI)-N-phenyl-acry
lamide,
sodium salt: m.p. 210°C (dec.);
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-( I -phenyl-1 H-pyrazolol4,3-clquinolin-3-yl)-N-phenyl-
acrv lamide,
sodium salt;
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-N-phenyl-acrylamide,
sodium
salt: m.p. 195°C (dec.);
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(8-fluoro-isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-N-phenyl-
acrylamide.
sodium salt;
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(9-chloro-isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-N-phenyl-
acrylamide,
2 o sodium salt;
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(9-methoxy-isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-N-phenyl-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
N-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
2 5 N-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
N-(3-vitro-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo(2, I -alnaphthalen-3-yl}-
acrylamide,
sodium salt;
N-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-
yl)-
3 0 acrylamide, sodium salt;
N-(3-methyl-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
N-(3-chloro-phenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-
acrylamide, sodium salt;
3 5 N-benzyl-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazoloft,1-a)naphthalen-3-yl)-acrylamide,
sodium
salt;
N-butyl-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo(2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-acrylamide,
sodium
salt;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(glindazol-3-yl)-
acrylonitrile,
4 o sodium salt;
2-(4-methoxy-benzenesulfonyl}-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzo(g(indazol-3-yl)-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-{4-fluoro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-hydroxy-3-(1-methyl-1 H-benzo(g(indazol-3-yl)-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
45 2-(3-vitro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-hydroxy-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzofg(indazol-3-yl)-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-(3-trifluoromethyl-benzenesulfony!)-3-hydroxy-3-( I -methyl-1 H-
benzolglindazol-3-
yl)-acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
2-(3-methyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolgl indazol-3-y I
)-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-(3-chloro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl )-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
5 2-benzenesulfonyl-3-hydroxy-3-(8-fluoro-1-methyl- 1H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-hydroxy-3-(9-chloro-1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl )-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-hydroxy-3-(9-methoxy-1-methyl-1 H-benzolglindazol-3-yl)-
1 o acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-{4-methoxy-benzenesulfonyl)-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl )-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-(4-fluoro-benzenesulfonyl}-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolol2, I-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
15 2-(3-nitro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo12,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-(3-trifluoromethyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo12,1-alnaphthalen-
3-yl}-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-(3-methyl-benzenesulfonyl)-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo12,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-
2 o acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-(3-chloro-benzenesulfonyl)-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazoio12,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-hydroxy-3-(8-fluoro-isoxazolol2,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl )-
acrylonitrile,
sodium salt;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-hydroxy-3-{9-chloro-isoxazolo12,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt;
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-hydroxy-3-{9-methoxy-isoxazolo12,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-
acrylonitrile, sodium salt; and
2-benzenesulfonyl-3-hydroxy-3-(isoxazolo12,1-alnaphthalen-3-yl)-acrylonitrile.
sodium
3 0 salt.
Example 19
Capsule, each weighting 0.23 g and containing 50 mg of the active substance
can be
prepared as follows:
3 5 Composition for 500 capsules:
2-cyano-3-hydroxy-3-( 1-methyl-1-H-benzo[g]indazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-acrylamide
sodium salt 25 g
Lactose 80
Corn starch 5 g
4 0 Magnesium stearate 5 g
This formulation can be incapsulated in two hard gelatin capsules of two
pieces, each
with each capsule weighing
0.23 g.
4 5 Example 20
Intramuscular injection of 50 mg/ml
A pharmaceutical injectable composition can be manifactured dissolving 50 g 2-
cyano-
3-hydroxy-3-(1-methyl-1-H-benzo[g]indazol-3-yl}-N-phenyl-acrylamide sodium
salt in
CA 02302025 2000-02-25
WO 99/16753 PCT/EP98/06051
21
sterile propyleneglycol (1000 ml) and sealed in 1-5 ml ampoules.
Legend to Figure 1
IDO = Indolamineoxigenase
KYN = Kynurenine
KYN-OH = Kynurenine-3-hydroxylase
KYNA = Kynurenic acid
3-OHAA = 3-hydroxy anthranilic acid
KYNase = Kynureninase
QUIN = Quinolinic acid
3-HAO = 3-hydroxy anthranilic acid deoxygenase
KAT = kynurenine amino transferase
3-OH-KYN = 3-Hydroxy-kynurenine