Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02314165 2000-07-13
SOUNDPROOFING PANEL FOR ACOUSTIC BARRIERS
The present invention relates to a soundproofing
panel for acoustic barriers.
In particular, the present invention relates to a
panel for acoustic barriers used to prevent the
propagation of pollutant sound waves in open spaces, to
which application the following description refers purely
by way of example.
As is known, the propagation of pollutant sound
waves in open spaces - such as along motorways or
railways, around building sites or factories - is
currently prevented using acoustic barriers comprising a
number of sound-absorbing and/or soundproofing panels
placed adjacent to one another on supporting frames to
form a substantially vertical wall surrounding, normally
seamlessly, the pollutant sound source.
Currently used sound-absorbing and/or soundproofing
panels are rectangular, and are defined by a
parallelepiped-shaped outer box shell normally made of
zinc plated, painted sheet metal and filled with glass
wool or similar. The outer box shell is formed by fitting
CA 02314165 2000-07-13
2
together two half-shells, and mainly provides for
soundproofing, while the filler material mainly provides
for sound absorption.
The main drawback of currently used sound-absorbing
and/or soundproofing panels is their inability to adapt,
or rather be "tuned°, to the characteristics, i.e. the
frequency spectrum, of the incident sound wave, so as to
maximize shielding capacity. The characteristics of the
pollutant sound wave, in fact, vary according to the
t0 pollutant sound source (moving vehicles and trains,
machinery, etc.), whereas the curve representing
attenuation of the incident sound wave as a function of
the frequency of the sound-absorbing and/or soundproofing
panel is of a given fixed shape (continuous line in
l5 Figure 3 ) .
It is an object of the present invention to provide
a panel for acoustic barriers, designed to eliminate the
aforementioned drawbacks.
According to the present invention, there is
20 provided a panel for acoustic barriers, characterized by
being defined exclusively by a sheet having, on one of
the two lateral surfaces, a number of longitudinal sound
breaking fins parallel to and facing one another, and
each for breaking the front of the incident sound.wave.
25 A non-limiting embodiment of the present invention
will be described by way of example with reference to the
accompanying drawings, in which:
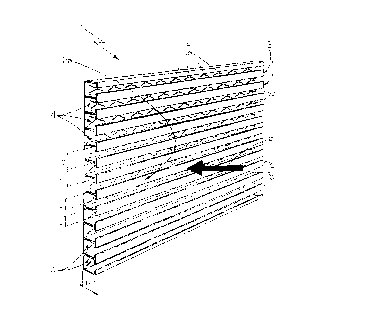
Figure 1 shows a schematic view in perspective of a
CA 02314165 2000-07-13
3
soundproofing. panel for acoustic barriers, in accordance
with the teachings of the present invention;
Figure 2 shows a larger-scale detail of Figure 1;
Figure 3 shows a number of frequency versus
attenuation curves obtainable using the Figure 1
soundproofing panel;
Figures 4 and 5 show views in perspective of two
variations of the Figure l soundproofing panel.
Number 1 in Figures 1 and 2 indicates as a whole a
l0 soundproofing panel particularly suitable for forming
acoustic barriers for preventing the propagation of
pollutant sound waves in preferably, though not
necessarily, open spaces.
Soundproofing panel 1 is defined by a sheet 2
having, on one of the two lateral surfaces, a number of
longitudinal sound-breaking fins 3 parallel to and facing
one another, and each for breaking the front F of the
incident sound wave.
In the example shown, sheet 2 is made of metal, such
as steel or aluminium, possibly painted and/or zinc
plated to withstand atmospheric agents, but may obviously
also be made of plastic material or similar.
Longitudinal sound-breaking fins 3 are T-shaped in
section and equally spaced over the whole of lateral
surface 2a of sheet 2 to define a number of open gaps 4
for preventing propagation of the incident sound wave, in
the same way as currently marketed double glazing. Being
located side by side and full of air, in fact, gaps 4
CA 02314165 2000-07-13
4
define a layer of air, which simultaneously provides for
soundproofing and sound absorption, in the same way as
the layer of air trapped between the two panes of glass
of a double-glazed window. Gaps 4 also act as sound boxes
by more effectively attenuating a given sound frequency
spectrum depending on the geometric dimensions of gaps 4.
With reference to Figure 2, in the example shown,
sheet 2 has a fretted profile, so that longitudinal
sound-breaking fins 3 are defined by the stiffening ribs
l0 of sheet 2, and sheet 2 may thus be obtained directly by
subjecting a flat rolled section to a succession of
rolling, die-forming operations or similar production
process.
Finally, sheet 2 preferably, though not necessarily,
comprises a number of stiffening drawings 5, which are X-
shaped in the example shown, are equally spaced along the
back of gaps 4, and provide for increasing the structural
rigidity of sheet 2 and the soundproofing capacity of
panel 1 by raising the natural resonance frequency of
sheet 2. Obviously, the dimensions and distribution of
drawings 5 may vary to adjust the natural resonance
frequency of sheet 2 as required.
In the Figure 4 variation, soundproofing panel 1
also comprises a number of inserts 9 made of
soundproofing and/or sound-absorbing material, and each
housed inside a respective gap 4 on the panel. Inserts 9
extend the full length of respective gaps 4, may vary in
thickness according to their position on soundproofing
CA 02314165 2000-07-13
panel 1, and are all preferably, though not necessarily,
made of the same soundproofing and/or sound-absorbing
material.
In the example shown, each insert 9 is retained
5 inside respective gap 4 by a retaining grille 10 inserted
inside gap 4, directly over insert 9. Each grille on
soundproofing panel 1 is obviously fitted between the two
longitudinal sound-breaking fins 3 defining respective
gap 4, to prevent insert 9 from falling out when
soundproofing panel 2 is set up.
In the Figure 5 variation, sheet 2 of soundproofing
panel 1 also comprises a number of preferably, though not
necessarily, semispherical auxiliary drawings 11
appropriately distributed along the back of gaps 4. The
concavity of each drawing 11 may selectively face inwards
or outwards of soundproofing panel 1, i.e. inwards or
outwards of respective gap 4, so as to vary the total
volume of each gap 4 of soundproofing panel 1 as
required. The number, depth, shape and arrangement of
auxiliary drawings 11 may obviously vary inside each gap
4.
The above solution provides for adjusting, at the
production stage of soundproofing panel 1, the
attenuation characteristic of each gap 4 on soundproofing
panel 1 independently of the others. As stated, each gap
4 acts as a sound box for more effectively attenuating a
given sound frequency spectrum, depending on the
geometric dimensions, i.e. volume, of gap 4.
CA 02314165 2000-07-13
6
Operation of soundproofing panel 1 is easily
deducible' from the foregoing description with no further
explanation required.
It should be pointed out, however, that tests have
shown that, by appropriately varying the distance d
between adjacent longitudinal sound-breaking fins 3, the
height h of longitudinal sound-breaking fins 3, and the
width 1 of the heads of longitudinal sound-breaking fins.
3, the attenuation curve of soundproofing panel 1 can be
adjusted as a function of frequency, so as to °tune" the
response of the panel to the characteristics of the
incident sound wave.
The dimensions and distribution of longitudinal
sound-breaking fins 3, in fact, determine the dimensions
t5 of gaps 4, which, acting as sound boxes, provide for more
effectively attenuating a given sound frequency spectrum.
Figure 3 shows, as a function of frequency, the
attenuation curve Ao(f) of a conventional panel
(continuous line), and the attenuation curves A1(f),
A2(f), A3(f) of three different geometric configurations
of soundproofing panel 1 (dash lines).
In the event soundproofing panel 1 is equipped with
inserts 9, attenuation curve A(f) may obviously also be
adjusted using different soundproofing and/or sound-
absorbing materials for inserts 9.
The advantages of soundproofing panel 1 will be
clear from the foregoing description: it is now possible
to produce acoustic barriers specially designed to
CA 02314165 2000-07-13
7
attenuate the sound waves generated by specific pollutant
sound sources. This may obviously also be achieved using
adjacent soundproofing panels 1 with appropriately
differing attenuation curves.
A further advantage of soundproofing panel 1 as
described and illustrated above lies in it being much
cheaper to produce than currently used panels, by having
no sound-absorbing filler material.
Clearly, changes may be made to acoustic barrier
soundproofing panel 1 as described and illustrated herein
without, however, departing from the scope of the present
invention.