Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02314646 2000-07-27
- 1 -
GROOVED CONSTRUCTION LUMBER FOR
CONSTRUCTING LUMBER STRUCTURES
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
A grooved construction lumber element is described
for constructing lumber structures such as portions of a
house frame, building walls, guard rails for decking or
verandas and the like structures wherein lumber pieces are
1o secured at repeat spaced intervals.
BACKGROUND OF. THE INVENTION
In the construction of lumber structures, such as
wood building structures, it is necessary to erect walls,
is flooring, roofing wherein load bearing elements such as
joists, studs, trusses, are secured at substantially
equidistantly spaced intervals. When constructing a wall
with wood framing studs it is necessary to secure the studs
to a top surface of a lower plate at spaced intervals.
20 These spaced intervals are usually measured using a
measuring tape and a pencil mark is made on the plate at the
repeat intervals. These measurements are not always
accurate and subject to human errors as the construction
worker must remember ascending numbers of a predetermined
25 spaced intervals and often makes a human error. and a stud
may be secured at the wrong position and this is detected
later on when it is time to cover the framing with covering
sheet material of predetermined size.
Another disadvantage in the construction of
30 building structures wherein lumber elements must be spaced
at regular intervals is that the butt end of the studs are
usually secured on a side surface of a bottom or top plate
member by nails. Because often construction lumber is not
totally dry the studs will warp longitudinally as they
35 slowly dry and this results in an irregular wall surface.
A still further disadvantage in the construction
of building structures wherein lumber elements must be
CA 02314646 2000-07-27
- 2 -
secured at regular spaced intervals is that such
construction requires skill labor and it can be said to be
time-consuming due to the fact that many measurements need
to be taken not to make errors and when errors occur it is
time-consuming to rectify them. It is also time-consuming
to groove lumber pieces to interconnect butt ends of studs
in a base plate. It is also time-consuming to construct
guard railings where rail posts need to be secured at
regular spaced intervals without error. For these reasons,
l0 it is costly to construct these types of structures.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is a feature of the present invention to
provide a grooved construction lumber element for use in
constructing lumber structures and which substantially
overcomes the above-mentioned disadvantages of the prior
art.
Another feature of the present invention is to
provide a grooved construction lumber element for use in the
construction of building structures and which is comprised
by a straight lumber piece provided with a plurality of
spacing grooves disposed in at least one surface thereof
whereby to permit lumber elements to be secured thereto at
predetermined spaced intervals.
Another feature of the present invention is to
provide a grooved construction lumber element for use in
constructing building structures and comprised of a straight
lumber piece having a plurality of spacing grooves disposed
3o in at least one surface thereof and which permits the butt
end of lumber element to be connected in the grooves and
wherein the grooves substantially arrest the problem of
distortion of the lumber element.
Another feature of the present invention is to
provide a grooved construction element for use in
constructing building structures and wherein such structures
CA 02314646 2002-09-11
- 3 -
may be constructed by unskilled labor and permits near
flawless erection of such building structures.
According to the above features, from a broad
aspect, the present irwention provides a grooved
construction lumber element for. use in constructing lumber
structures. The construction lumber element is comprised
of a straight lumber piece having a plurality of spacing
grooves disposed in at least one surface of the lumber
piece. The spacing grooves have a predetermined depth and
l0 are configured to receive therein an end portion of an
associated further lumber element to construct a specific
structure. At least some of the spacing grooves are
disposed at common spaced intervals.
According to a further broad aspect of the
present invention there is provided a grooved construction
lumber element for use in constructing of habitable lumber
structures. The construction lumber element i.s comprised
of an elongated straight lumber piece of rectangular cross
section and having a top and a bottom parallel side
surfaces and narrow parallel side edge surfaces. A
plurality of rectangular spacing grooves are disposed in
at least one of the top and bottom parallel side surfaces
of the lumber piece and extend between the opposed
parallel side edge surfaces. The spacing grooves have a
predetermined depth and width and are configured to
receive in tight fit a rectangular end portion of an
associated further lumber element of like rectangular
cross-section and extending transverse to the horizontal
surface between the opposed vertical surfaces. The
spacing grooves are connection grooves for connecting
lumber elements to the straight lumber piece at specific
locations to construct an habitable lumber structure. One
or more groups of the spacing grooves are disposed on the
elongated straight lumber piece. Each group has a
different interval spacing of the grooves throughout the
length of a lumber piece. Visual indication means is
affixed on the straight lumber piece adjacent each of the
CA 02314646 2002-09-11
- 3a -
spacing grooves whereby to identify each spacing groove
associated with each group of spacing grooves having a
common width. An end spacing groove is provided at
opposed ends of the straight. lumber piece. The end
spacing groove extends to opposed end edges of the
straight lumber piece and has a width which is half the
width of the other spacing grooves.
According to a further broad aspect of the
present invention there is further provided a grooved
construction lumber element for use in constructing lumber
structures, said construction lumber element being
comprised of an elongated straight lumber piece of
rectangular cross-section and having a plurality of
spacing grooves disposed in at least one of opposed flat
parallel surfaces of said lumber piece between opposed
parallel side edge surfaces, said spacing grooves having a
predetermined depth and width and being configured to
receive therein a rectangular end portion of an associated
further lumber element of like rectangular cross-section
and extending transverse to said horizontal surface
between said opposed vertical surfaces, said spacing
grooves being connection grooves for connecting lumber
elements to said straight lumbex- piece at specific
locations to construct a lumber structure, therebeing one
or more groups of said spacing grooves, each group having
a different interval spacing of said grooves throughout
the length of said lumber piece; Spacing grooves have a
common width, therebeing an end spacing groove at opposed
ends of said straight lumber piece, said end spacing
groove extending to opposed end edges of said straight
lumber piece and having a width which is half the width of
said other sparing grooves, and a transverse saw blade
slit extending across said flat surface and spaced from
each said opposed end edges a distar~ce equal to the width
of said other spacing grocves, said transverse saw blade
slit having the same depth as said grooves and permitting
extension of said end spacing groove by removal of an
CA 02314646 2002-09-11
-3b-
intermediate lumber piece between said end spacing groove
and said slit whereby said end spacing groove may have the
same width as said other spacing grooves.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The preferred embodiments of the present
invention will now be described with reference to the
accompanying drawings in which
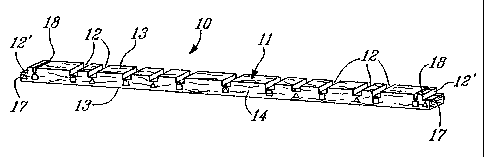
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a grooved
construction lumber element of the present invention for
use in constructing building structures and particularly,
but not exclusively, for erecting wood framed walls;
FIG. 2 is a perspective view of a fragmented end
section of the grooved construction lumber element of
Figure l;
FIG. 3a is a fragmented perspective view showing
a stud butt end secured in the end spacing groove;
FIG. :3b is a fragmented perspective view showing
a butt end of a stud secured in an end spacing groove of
opposed ends of two construction lumber elements of Figure
l;
FIG. 4 is a fragmented perspective view showing a
further grooved construction lumber clement constructed in
accordance with the present invention and herein
represented as a joist support foundation runner;
CA 02314646 2000-07-27
- 4 -
FIG. 5a is a fragmented side view showing an H-
Beam secured in the spacing grooves of a foundation runner
constructed in accordance with the present invention;
FIG. 5b is a view similar to Figure 5a but wherein
the beam is formed by lumber boards secured together;
FIG. 6 is a fragmented side view showing two top
runners secured to one another by two support joists of a
top floor;
FIG. 7 is a fragmented perspective view wherein
l0 the construction lumber element of the present invention is
represented by a stud having spacing grooves formed in one
of the side edge surfaces thereof;
FIG. 8a also shows a stud but wherein the spacing
grooves are formed in opposed flat side surfaces of the
stud;
FIG. Sb is a fragmented perspective view showing a
spacing brace for mounting between an end stud secured in an
expanded end spacing groove;
FIG. 9 is a perspective fragmented view and
2o wherein the groove construction lumber element of the
present invention constitutes a support beam;
FIG. 10 is a simplified side view showing the
construction lumber element of the present invention used in
the construction of roof trusses;
FIG. 11 is a side view of a prefabricated deck
rail constructed in accordance with the present invention;
FIG. 12a is a section side view showing the deck
rail construction;
FIG. 12b is a perspective view showing the
3o construction of the edge floorboard;
FIG. 12c is a fragmented perspective view showing
the construction of the horizontal top rail;
FIG. 12d is a fragmented perspective view showing
the construction of the bottom attachment plate;
FIG. 12e is a fragmented top side view showing
alternative constructions of end sections of the rail posts;
CA 02314646 2000-07-27
- 5 -
FIG. 13 is a simplified fragmented side view
showing the construction of the stair rail using the grooved
construction lumber element of the present invention; and
FIG. 14 is a simplified plan view showing the
construction of a stair side support using a grooved
construction lumber element of the present invention.
DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
l0 Referring now to the drawings and more
particularly to Figures 1 and 2 there is shown generally at
a grooved construction lumber element, constructed in
accordance with the present invention and for use in the
construction of wooden structures, such as building
structures. The construction lumber element is comprised of
a straight lumber piece 11 provided with a plurality of
spacing grooves 12 disposed in a top side surface 13 of the
lumber piece. The spacing grooves 13 are better illustrated
in Figure 2 and as can be seen have a predetermined depth
and are configured, herein rectangular in shape, to receive
therein an end portion of an associated further lumber
element to construct a specific building structure, as will
be described later.
As shown in Figure 1 there are several spacing
grooves formed in the top side surface 13 of the lumber
piece 11 and there are one or more groups of these spacing
grooves, each group having a different interval spacing of
spacing grooves and disposed throughout the length of the
lumber piece 11. In order to identify the grooves of
specific groups there is provided an identification means on
the side surface 14 of the lumber piece 11 and as herein
shown it is provided by a shape symbol 15: As shown in
Figure 1 there are square and triangular symbols wherein all
of the grooves associated with the square symbols have a
predetermined interval spacing, herein 12 inch spacing and
the grooves of the triangular symbol have a spacing of 18
inches. The identification means could also be a color
CA 02314646 2005-03-21
- 6 -
symbol such as a colored dot or it could be a number, such
as the number at 16 shown in Figure 2.
The straight lumber piece 11 may be fabricated
from various types of construction material such as wood,
s plastic, laminates or composites. The lumber pieces are of
rectangular cross-section and defines opposed parallel top
and bottom surfaces 13 and 13' and opposed parallel flat
side edge surfaces 14 and 14'. It is also pointed out that
by using symbol identification means 15 a color-blind person
to could easily identify associated spacing grooves.
It is also pointed out that the spacing grooves 12
have a common width. The end spacing grooves 12' extend to
opposed end edges of the straight lumber piece and have a
width which is half of the width of the other spacing
15 grooves 12. A transverse saw blade slit 18 extends across
the top side surface 13 and spaced from each of the opposed
end edges 17 of the lumber piece 11 a distance equal to the
width of the end grooves 12'. The transverse saw blade slit
18 has the same depth as the spacing grooves and permits
zo extension of the end spacing groove 12' by removal of the
intermediate lumber piece 19 disposed between the end
spacing groove 12' and the slit 18 whereby the end spacing
groove 12' may have the same width as the other spacing
grooves to mount a vertical end stud, such as the stud 20 as
25 shown in Figure 3a.
As shown in Figures 3a and 3b the straight lumber
pieces 11 are herein used as base plate runners utilized in
the framing of walls. The spacing grooves 12' accommodate a
connecting butt end of wall framing studs 20 which are
3o secured in selected ones of the groups of spacing grooves.
As shown in Figure 3b the butt end 20' of the stud 20 is
secured between opposed end spacing grooves 12' of adjacent
lumber pieces 11. When these two end spacing grooves 12'
are disposed side by side they together form a spacing
35 groove equal in width to the standard spacing grooves 12.
CA 02314646 2005-03-21
7 -
Referring now to Figures 4, 5a and 5b the straight
lumber piece is herein constituted by a joist support
foundation runner 21. The foundation runner 21 is provided
with an outer edge groove 22 extending along the entire
length of the foundation runner 21. The outer edge groove
22 has the same depth as the spacing grooves 23 formed in
the top flat side surface 24 of the foundation runner 21 and
are dimensioned, herein substantially of rectangular cross-
section, to receive support end sections 25 of horizontally
to disposed joists 26 or beams 27 and 28 as shown in Figures 5a
and 5b respectively. The outer edge groove 22 accommodates
a lower longitudinal edge portion of an end cap board 29.
Such structure is for framing a floor over a foundation wall
30. As shown in Figure 5a the beam 27 is an I-beam formed
with construction wood pieces or laminated wood pieces. The
beam 28 as shown in Figure 5b is constructed of
interconnected wood planks. The size of the spacing grooves
23 may also vary to accommodate different size of beams or
joists.
2o With reference now to Figure 6 there is shown a
top plate runner 31 secured to the top butt ends of studs 20
and wherein a further plate runner 31' is secured to the top
plate runner but in an inverted manner whereby to receive in
its spacing grooves 12, which are now disposed upwardly, end
z5 portions of floor joists 32. A floor surface material 33 is
secured to the floor joist 32 to start the construction of a
second floor of a building structure. The plate runner 31'
may also support the horizontal cross-connecting piece of a
roof trust. As herein shown some of the spacing grooves 12'
3o are not utilized as they form part of another group of
unselected spacing grooves.
In Figure 7 the straight lumber piece of the
present invention is herein constituted by a stud 35. The
spacing grooves 36 are disposed in one of the side edges 37
CA 02314646 2005-03-21
- 7a -
of the stud 35 to accommodate transverse furring strips 38
to secure an outer wall covering material 39 thereto.
Spacing grooves, herein groove 36' is also disposed in the
opposed side edge surface 37' and it is also used to connect
a furring 38' to secure inner wall boards, such as wall
CA 02314646 2000-07-27
- 8 -
board 40 at a space interval of 4 feet between the lower
edge of the base plate runner 41 and the center of the
furring 38'. It can be appreciated that by providing studs
and runners constructed in accordance with the present
invention that walls are always constructed with the lumber
pieces always perfectly disposed whereby the constructed
walls are always perfectly framed. A saw slit 42 may also
be provided adjacent an end, herein in the top end of the
stud 35 to provide an indication where the stud is to be cut
l0 depending on the desired height of the wall being
constructed.
As shown in Figures 8a and 8b the stud 35 is
provided with spacing grooves 34 in opposed flat side
surfaces 35' thereof and there is at least one groove in
each of the opposed flat side surfaces and aligned with one
another to receive an end portion of a transverse brace
piece 43. Holes 44 may also be formed in the side surfaces
35' to accommodate wiring or piping. Also, shown in Figure
8b the brace element 43, which is herein a rectangular wood
piece, may be provided with a saw blade slit 45 extending
transversely a predetermined distance from an end 46 of the
brace element to allow the removal of an end portion of the
wood brace element to brace an end stud 47 to an adjacent
stud 47', when the end stud 47 occupies the entire end
groove 12'.
As shown in Figure 9 the straight lumber piece of
the present invention is herein constituted as a load
bearing beam 50 with the spacing grooves 51 being disposed
in opposed side surfaces 52 and extending to the top surface
53 of the beam. The spacing grooves 51 are herein shown as
receiving an end portion of a joist 54 for the construction
of a floor.
In Figure 10 the straight lumber piece of the
present invention is herein used in the construction of a
roof trusses 55 with the truss pieces 56 having spacing
grooves 57 on its top edge 58 to receive boards 59 to which
construction sheeting material may be secured. The straight
CA 02314646 2005-03-21
_ g _
lumber piece may also be used in the truss design as the
horizontal cross connecting piece 60 and wherein the spacing
grooves 61 are disposed in a lower side edge 62 thereof. At
least some of the spacing grooves, herein the end grooves
61' are adapted to receive the top plate runners 63 of the
framed wall 64. The intermediate spacing grooves 61 will
receive furring pieces 65 to attach ceiling boards (not
shown) thereto.
Referring now to Figures 11 through 12d there will
to be described the construction of a railed fence for decks,
porches and staircases using a straight lumber piece
constructed in accordance with the present invention. All
the pieces are pre-machined to constitute a prefabricated
kit which is easily assembled by unskilled labor. As shown
in Figure 11 the railed fence is constituted essentially by
a horizontal top rail 70, a bottom attachment plate 71 and
edge floor board 73 and a plurality of rail posts 74 all
interconnected by fasteners 72.
As can be seen more clearly from Figures 12a to
zo 12e the straight lumber piece is herein constituted by the
top rail 70 which is provided with a plurality of spacing
grooves 75 formed in the side surface 76 of the top rail and
extending to lower side edge 77 thereof. The spacing
grooves terminate short of the top side edge 77' and are
herein shown as having a rounded end 78 which is formed by a
router bit head (not shown) which is used to rout these
grooves. The ends 78 of the grooves could also be made
square but this would be more costly to produce and these
are adapted to receive in close fit therein the top end
3o portions 74' of the rails 74. These top end portions may
have the shapes as shown in Figure 12e wherein one could be
round or square to fit within the shaped ends 78 of the
grooves 75, as shown in Figure 12C.
As shown in Figure 12b the bottom attachment plate
3s 73 is also provided with edge spacing grooves 79 which are
spaced at intervals corresponding to the grooves 75 wherein
a portion of the rails 74 will extend through these spacing
CA 02314646 2000-07-27
- 10 -
grooves 79. The edge floorboard 73 is secured adjacent the
top edge of the deck flooring 80, as shown in Figure 12a.
With specific reference to Figure 12d there is
shown the construction of the bottom attachment plate 71.
It also constitutes a straight board piece provided with
spacing grooves 81 and wherein the ends 82 of the spacing
grooves may have a rounded shape or a square shape such as
shown at 82' to accommodate the shape of the rails 74. A
saw blade slit 83 extends from the base 82 and 82' of the
spacing grooves 81 and extend to the lower side edge 84 of
the bottom attachment plate 71. The slits 83 are used to
drain rain water that may have a tendency to accumulate in
these channels. Accordingly, it can be seen that a railing
constructed in accordance with the present invention
provides perfectly aligned rail posts and a perfectly
disposed horizontal top rail. The rail post 74 may be
predrilled, such as shown at 85 to receive the fasteners 72
therein. The top rail 70 could also be predrilled, if
desired.
With reference now to Figure 13 there is shown a
railing for a staircase 86 and constructed substantially in
accordance with the present invention. As hereinshown, the
top rail 87 is provided with spacing grooves 88 disposed
parallel to one another and extending from a lower edge 89
of the rail 87 these are disposed at a transverse angle
which has the same pitch as the pitch of the staircase 86.
The grooves are constructed as with Figure 12c to receive
the top end portions 74' of the rail post 74 therein. The
top portion of the rail posts may be secured in a bottom
rail plank 90 also grooved similarly to that shown in Figure
12d but disposed at an angle or else may be secured directly
to the side edges of the stairs 91.
Figure 14 illustrates a still further embodiment
wherein the side support planks 92 are used to construct
staircases and wherein the grooves 93 are also disposed at
an angle therein to accommodate horizontal stair boards 94.
CA 02314646 2000-07-27
- 11 -
These side supports 92 may be formed with the same stair
rail 87 but used for a different purpose.
It is within the ambit of the present invention to
cover any obvious modifications of the examples of the
preferred embodiment described herein, provided such
modifications fall within the scope of the appended claims.