Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02315952 2000-08-11
A TURBO TCM SCHEME WITH LOW COMPLEXITY
This invention relates to the field of communication systems and in particular
to a system and method
for improving transmission rate and loop reach in xDSL systems.
BACKGROUND OF INVENTION
There have been a number of proposals to apply powerful turbo coding/decoding
technique [ 1 ] to
G.lite and G.dmt to improve transmission rate and loop reach. Among them,
there are two typical turbo
TCM (Trellis Coded Modulation) schemes. One is the symbol-level turbo TCM,
which was proposed
by [2] and evaluated by Alcatel [3). The other one is the bit-level turbo TCM,
proposed by Mitsubishi
and Vocal Technologies [4]-[6). Mitsubishi uses the JPL (Jet Propulsion Lab)
design [7], and Vocal
Technologies uses conventional R=1/2 coding rate turbo codes but with a lot of
puncturing and
mapping schemes for different constellation size of QAM modulation.
Referring to Figure 1 there is shown a block diagram of a turbo TCM proposed
by Vocal technologies.
Information bits are encoded by two parallel-concatenated systematical
recursive convolutional (SRC)
encoders with an interleaves between the inputs of the SRC encoders. The two
encoders are identical
and have a coding rate of R=1/2. The respective sets of parity bits output
from the encoders are
punctured in a predetermined pattern in order to reduce the parity overhead.
Then the systematical
information bits and parity bits are grouped and subsequently mapped into a
QAM constellation.
Although the turbo TCM shown in figure has very good error performance, its
has some drawbacks.
These are 1 ) All information bits are passed into the convolutional encoder
for protection, therefore the
number of trellis transitions is very large and the decoder is very
complicated; 2) The puncturing and
mapping patterns are different for different constellation sizes of QAM, which
lead to high
implementation complexity; and 3) High coding rate can not be obtained for
large constellation size
because over-puncturing will damage the code, and therefore high data rate can
not be achieved.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
An advantage of the present invention is a universal turbo TCM, which has not
only good error
performance but also has very low decoder complexity.
In accordance with this invention there is provided a A turbo TCM encoder
system comprising:
1
CA 02315952 2000-08-11
(a) a pair of systematical recursive convolutional (SRC) encoders for
generating parity bits from input
bits;
(b) an interleaver for interleaving input bits to the encoders;
(c) a puncture unit for determining a puncture rate of the parity bits in
response to to an even and odd
number of information bits;
(d) a bit grouping module for receiving the punctured bits and the input bits
and grouping the bits for
mapping into a symbol.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
A better understanding of the invention will be obtained by reference to the
detailed description below
in conjunction with the following drawings.
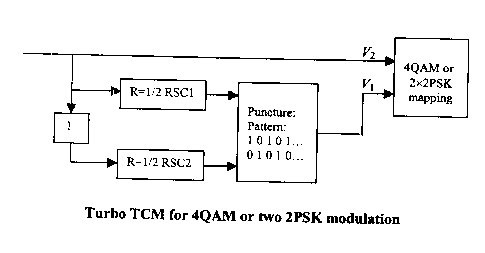
1. Turbo TCMEncoder with coding rate R=Il2 for 4.QAM or a grog o two 2QAM
As shown in Figure 2, this turbo TCM encoder is used to transmit lbit in 4QAM
symbol or in two
2QAM symbols. For each information bit, two parity bits are generated by two
systematical recursive
convolutional (SRC) encoders. 'The parity bits generated by each SRC encoder
are punctured
?0 alternatively, i.e., one half of the total parity bits are punctured. The
overall coding rate is R=1/2. For
each information bit v2 , one parity bit vl is generated. (vl , v2 ) are
mapped into one 4QAM symbol
using Gray mapping.
2. Turbo Encoder with coding rate R j2+2k~4+2k) for MQAM (M>16~
As shown in Figure 3, this turbo TCM encoder is used to transmit even number
information bits in one
QAM symbol. For every two information bits (v3 , v4 ) passed into SRC
encoders, four parity bits are
generated by two SRC encoders. The parity bits generated by each SRC encoder
will be punctured
alternatively, i.e., one half of the total parity bits are punctured. For
every two information bits
(v3 , v4 ) , two parity bits (v, , v2 ) are generated. (v1, V2 ,..., V2m ) are
mapping into one QAM symbol
using set-partition mapping [8] and Gray mapping. This mapping is preferred to
be operated in one
dimension, i.e., two halves of (vl, v2,..., v2m ) are mapped into two 2m -ASK
signals.
Applications: 1) 2/4 16QAM; 2) 4/6 64QAM; 3) 6/8 256QAM; 4) 8/10 1024QAM; 5)
10/12
4096QAM; 6) 12/ 14 163 84QAM.
2
CA 02315952 2000-08-11
3. Turbo Encoder with coding rate R ~3+2k~(4+2 ~ for MQAM (M>16,~
As shown in Figure 4, this turbo TCM encoder is used to transmit odd number
information bits in one
QAM symbol. For every 3 information bits passed into the two SRC encoders, 6
parity bits are
generated by the two SRC encoders. The parity bits generated by each SRC
encoder will be punctured
with the puncturing rate 5/6, i.e., 5 from 6 parity bits are punctured. For
every three information bits
(v2 , v3 , v4 ) , one parity bit vl are generated. (vl , V2 ,..., v2m ) are
mapped into one QAM symbol using
set-partition mapping and Gray mapping. This mapping is preferred to be
operated in one dimension,
i.e., two halves of (vl , v2 ,..., v2m ) are mapped into two 2 "' -ASK
signals.
Applications: 1) 3/4 16QAM; 2) 5/6 64QAM; 3) 7/8 256QAM; 4) 9/10 1024QAM; 5)
11/12
4096QAM; 6) 13/14 16384QAM.
4.1. Uniaue Mappin>? Schemes~(1) mixed Gray m~nin are set~artition mapping
In order to achieve better error performance and low decoder complexity, an
unique mapping scheme
is used. The mapping of (vl , v2,..., v2m ) into 22"' -QAM is operated by
mapping each half of
(vl , v2 ,..., v2,~ ) into one 2 m -ASK signal. For example, (vl , v3 ,...,
v2m-I ) is mapped into one 2 m -ASK
signal and (v2, V,I,..., V2m ) is mapped into another 2m -ASK signal. Figure 5
shows this unique
mapping (set-partition plus Gray mapping) for 4-ASK and 8-ASK. For 4-ASK, it
is Gray mapping. For
8-ASK, the first most significant bit is set partition mapping and the two
least significant bits are Gray
mapping. For general 2m -ASK, the first (m-2) most significant bits are set
partition mapping and the
two least significant bits are Gray mapping. Suppose that BI , B2 ,..., B2,"
are a mapping for 2 m -ASK
(m> 1 ), where Bk (1 < k <_ 2'~ ) is a m-bit string, then the mapping for
2'"+I -ASK can be generated by
1BI ,1B2 ,...,lB2m ,OBI ,OB2 ,...,OB2," , i.e., append 1 bit to all BI , B2
,..., B2m to get first half and append
Obit to all BI , B2 ,..., B2m to get the second half.
4.2. Unigue Mapping Schemes: (2) Concatenated Gray moping
Both the coded bits such as (vl , v3 ) or (v2 , v4 ) and uncoded bits such as
(vs , v~ ,..., v2m-I ) or
(v6 , vg ,..., v2m ) are Gray mapping, and then they are concatenated. For
example, m = 4 , both (v~ , v3 )
3
CA 02315952 2000-08-11
and (vs, v~ ) are Gray mappings as shown in Figure 5(a). The concatenated Gray
code is as shown in
Figure 5(c). The two least significant bits are the Gray mapping of coded bits
(v, , v3 ) , which will
repeat every four mappings. The two most significant bits are the Gray mapping
of the uncoded bits
(v5 , v~ ) , which are same for each group of 4 mappings.
S. An Universal Implementation of Turbo TCMEncoderfor MOAM
Figure 6 shows a universal implementation scheme for the above turbo TCM
encoders. The (a, b) data
paths in Figures 3 to 4 are combined if the interleaver provides that the bits
at even number positions
are interleaved to even number positions and the bits at odd number positions
are interleaved to odd
number positions. The puncture rate for each SRC encoder is either P=1/2 or
P=5/6, which is
controlled by the even/odd number of information bits. Finally, the bits
passed into SRC encoders and
their parity bits are grouped into 4-bit by 4-bit for MQAM(M>4), or are
grouped into 2-bit by 2-bit for
4QAM.
Y