Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02324460 2000-09-19
1
FUNGICIDE MIXTURES BASED ON TRIPLE OXIME
ETHER DERIVATIVES AND INSECTICIDES
The present invention relates to mixtures for controlling harmful
fungi and insects, which [lacuna]
a) phenylacetic acid derivatives of the formula I
Rs
R2 m
R~ ,N ~ ,O
O ~N
(I).
~N R
i
O, Rs
in which the substituents and the index have the following
meaning:
X is NOCH3, CHOCH3 or CHCH3;
Y is oxygen or NR;
R1, R independently of one another are each hydrogen or
C1-C4-alkyl;
R2 is cyano, nitro, trifluoromethyl, halogen, C1-C4-alkyl
or C1-C4-alkoxy;
m is 0, 1 or 2, where the radicals R2 may be different if
m is 2;
R3 is hydrogen, cyano, C1-C4-alkyl, C1-C4-haloalkyl or
C3-C6-cycloalkyl;
R4, R6 independently of one another are each hydrogen,
CA 02324460 2000-09-19
1a
are CI-CIO-alkyl, C3-C6-cycloalkyl, C2-CIO-alkenyl,
CZ-CIO-alkynyl, CI-CIO-alkylcarbonyl,
C2-CIO-alkenylcarbonyl, C3-Cio-alkynylcarbonyl or
CI-CIO-alkylsulfonyl, where these radicals may be
partially ar fully halogenated or may carry one to
three of the following groups: cyano, nitro, hydroxyl,
mercapto, amino, carboxyl, aminocarbonyl,
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
2
aminothiocarbonyl, halogen, C1-C6-alkyl,
C1-C6-haloalkyl, C1-C6-alkylsulfonyl,
C1-C6-alkylsulfoxyl, Cl-C6-alkoxy, C1-C6-haloalkoxy,
C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C6-alkylthio, C1-C6-alkylamino,
di-C1-C6-alkylamino, C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl,
di-C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl,
C1-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl,
di-C1-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl, C2-C6-alkenyl,
C2-C6-alkenyloxy, C3-C6-cycloalkyl, C3-C6-cycloalkyloxy,
heterocyclyl, heterocyclyloxy, benzyl, benzyloxy, aryl,
aryloxy, arylthio, hetaryl, hetaryloxy and hetarylthio,
where the cyclic groups for their part may be partially
or fully halogenated or may carry one to three of the
following groups: cyano, nitro, hydroxyl, mercapto,
amino, carboxyl, aminocarbonyl, aminothiocarbonyl,
halogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-haloalkyl,.
C1-C6-alkylsulfonyl, C1-C6-alkylsulfoxyl,
C3-C6-cycloalkyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C1-C6-haloalkoxy,
C1-C6-alkyloxycarbonyl, C1-C6-alkylthio,
C1-C6-alkylamino, di-C1-C6-alkylamino,
C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl, di-C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl,
C1-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl,
di-C1-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl, CZ-C6-alkenyl,
CZ-C6-alkenyloxy, benzyl, benzyloxy, aryl, aryloxy,
arylthio, hetaryl, hetaryloxy, hetarylthio or
C(=NORM)-An-Re;
are aryl, arylcarbonyl, arylsulfonyl, hetaryl,
hetarylcarbonyl or hetarylsulfonyl, where these
radicals may be partially or fully halogenated or may
carry one to three of the following groups: cyano,
nitro, hydroxyl, mercapto, amino, carboxyl,
aminocarbonyl, aminothiocarbonyl, halogen, C1-C6-alkyl,
C1-C6-haloalkyl, C1-C6-alkylcarbonyl,
C1-C6-alkylsulfonyl, C1-C6-alkylsulfoxyl,
C3-C6-cycloalkyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C1-C6-haloalkoxy,
C1-C6-alkyloxycarbonyl, C1-C6-alkylthio,
C1-C6-alkylamino, di-C1-C6-alkylamino,
C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl, di-C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl,
C1-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl,
di-C1-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl, C2-C6-alkenyl,
CZ-C6-alkenyloxy, benzyl, benzyloxy, aryl, aryloxy,
hetaryl, hetaryloxy or C(=NORM)-An-Re;
RS is hydrogen,
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
3
is C1-C6-alkyl, CZ-C6-alkenyl, CZ-C6-alkynyl, where the
hydrocarbon radicals of these groups may be partially
or fully halogenated or may carry one to three of the
following radicals: cyano, vitro, hydroxyl, mercapto,
amino, carboxyl, aminocarbonyl, aminothiocarbonyl,
halogen, C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl,
di-C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C6-alkylaminothio-
carbonyl, di-Cz-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl,
C1-C6-alkylsulfonyl, C1-C6-alkylsulfoxyl, C1-C6-alkoxy,
C1-C6-haloalkoxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C6-alkylthio,
C1-C6-alkylamino, di-C1-C6-alkylamino, C2-C6-alkenyloxy,
C3-C6-cycloalkyl, C3-C6-cycloalkyloxy, heterocyclyl,
heterocyclyloxy, aryl, aryloxy, aryl-C1-C4-alkoxy,
arylthio, aryl-C1-C4-alkylthio, hetaryl, hetaryloxy,
hetaryl-C1-C4-alkoxy, hetarylthio,
hetaryl-C1-C4-alkylthio, where the cyclic radicals for
their part may be partially or fully halogenated and/or
may carry one to three of the following groups: cyano,
vitro, hydroxyl, mercapto, amino, carboxyl,
aminocarbonyl, aminothiocarbonyl, C1-C6-alkyl,
C1-C6-haloalkyl, C1-C6-alkylsulfonyl,
C1-C6-alkylsulfoxyl, C3C6-cycloalkyl [sic),
C1-C6-alkoxy, C1-C6-haloalkoxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl,
C1-C6-alkylthio, C1-C6-alkylamino, di-C1-C6-alkylamino,
C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl, di-C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl,
C1-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl,
di-C1-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl, CZ-C6-alkenyl,
CZ-C6-alkenyloxy, benzyl, benzyloxy, aryl, aryloxy,
arylthio, hetaryl, hetaryloxy, hetarylthio and
C(=NORM)-An-Re;
is C3-C6-cycloalkyl, C3-C6-cycloalkenyl, heterocyclyl,
aryl, hetaryl, where the cyclic radicals may be
partially or fully halogenated or may carry one to
three of the following groups: cyano, vitro, hydroxyl,
mercapto, amino, carboxyl, aminocarbonyl,
aminothiocarbonyl, halogen-, C1-C6-alkyl,
C1-C6-haloalkyl, C1-C6-alkylsulfonyl,
C1-C6-alkylsulfoxyl, C3-C6-cycloalkyl, C1-C6-alkoxy,
C1-C6-haloalkoxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C6-alkylthio,
C1-C6-alkylamino, di-C1-C6-alkylamino,
C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl, di-C1-C6-alkylaminocarbonyl,
C1-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl,
di-C1-C6-alkylaminothiocarbonyl, C2-C6-alkenyl,
Cz-C6-alkenyloxy, benzyl, benzyloxy, aryl, aryloxy,
hetaryl and hetaryloxy;
i
005048890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
4
where
A is oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen and where the nitrogen
carries hydrogen or C1-C6-alkyl;
n is 0 or 1;
R~ is hydrogen or C1-C6-alkyl and
RB is hydrogen or C1-C6-alkyl,
and their salts,
and
b) at least one insecticide selected from insecticides of the
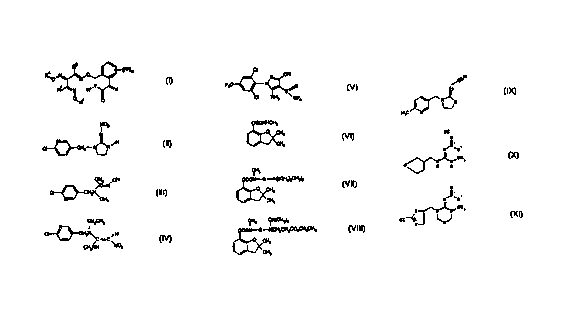
formulae II to XI
N02
N
N- ~ ,H (II)
H - N_ 'N
CI ~ ~ C 2
U
3o CH3 RCN
N (IIZ)
CI }-CH2N
N \CH3
CH2CH3 _
N
CI CH2N~C -C ~ H ( Iv)
CH3NH
005048890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
CI
N CN
5 F3C ~ ~ N ~ ,O (v)
~S ~
CI NH2 ~ CF3
to OCONHCH3
O CHs
(vi)
CH3
CH3
OCON-S -N[(CH2)3CH~]2
\ 0 CH3 ( vi z )
CH3
CH3 CH(CH~2
OCON-S -NCH2CH2C02CH2CH3
(vzzi)
\ 0 CH3
CH3
~N
N
\ N (zx
)
4o H3C N
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
6
0
n .,
N~N~O_
~ ~CH3
N_ _N
0\ I H H
(X)
O
II.
N~N~O_
~ CH
S N~N~ 3 (XI)
C1--C~ ~OJ
N
It is an object of the present invention to provide mixtures
which, on the one hand, have good fungicidal activity, in
particular against fungal diseases in rice and, on the other
hand, good insecticidal activity. Since in the climatic regions
in which rice is cultivated, harmful insects are usually also
encountered in great numbers, a combination of fungicidal and
insecticidal activity is desirable.
we have found that this object is achieved by the mixtures
claimed in claim 1.
The compounds of the formula I and their preparation are known
per se and described in the literature (WO 97/15,552).
The insecticides of the formulae II to IX [sic] are also known
and described in the literature. Additionally, they are
commercially available under the trade names mentioned below in
brackets:
II: EP-A 192,060, common name: imidacloprid (trade name:
Admire~, Gaucho~, from Bayer);
III: common name: acetamiprid (trade name: Mospilan~, from
Nippon Soda);
IV: CAS RN 120738-89-8, common name: nitenpyram (trade name:
Bestgard~, from Takeda Chemicals);
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-o9-i9
V: Colliot et al., Proc. Br. Conf. Dis. ~,, (1992), 29, common
name: fipronil (trade name: Regent~, from Rhone-POUlenc);
VI: US 3,474,170; US 3,474,171 and DE-C 1,493,646; common name:
5 carbofuran (trade name Curaterr~, from Bayer; Furadan~,
from FMC);
VII: Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. ~ (1979), 557, common name:
carbosulfan (trade name: Marshall~, from FMC);
VIII: FR-A 2,489,329; Proc. Int. Congr. Plant Prot. 10th,
(1983), 360, common name: benfuracarb (trade name: Oncol~,
from Otsuka; Furacon~, from Siapa Chem.);
IX: CAS RN 111 988-49-9, common name: thiacloprid (development
product from Bayer); .
X: Proc. of the 1998 Brighton Conference "Pests and Diseases",
Vol. 1, pp. 21-26 (MTI 446, from Mitsui);
XI: Proc. of the Brighton Conference on Pests and Diseases,
Vol. 1, pp. 27-36 (CGA 293 343, from Novartis).
Owing to their C=C and C=N double bonds, the preparation of the
compounds I may yield E/2 isomer mixtures which can be separated
into the individual compounds in a customary manner, for example
by crystallization or chromatography.
However, if the synthesis yields isomer mixtures, a separation is
generally not necessarily required since in some cases the
individual isomers can be converted into one another during the
preparation for use or upon use (for example under the action of
light, acids or bases). Similar conversions may also occur after
use, for example in the treatment of plants in the treated plant
or in the harmful fungus or animal pest to be controlled.
with regard to the C=X double bond, preference is given to the E
isomers of the compounds I (configuration based on the -OCH3 or
the -CH3 group in relation to the -C02R1 group) with respect to
their activity.
With regard to the -C(R3)=NOCH2- double bond, preference is given
to the cis isomers of the compounds I (configuration based on the
radical R3 in relation to the -OCH2- group) with respect to their
activity.
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
8
In the definitions of the compounds I given at the outset,
collective terms were used which generally represent the
following groups:
Halogen: fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine;
Alkyl: straight-chain or branched alkyl groups having 1 to 4, 6
or 10 carbon atoms, for example C1-C6-alkyl such as methyl, ethyl,
propyl, 1-methylethyl, butyl, 1-methylpropyl, 2-methylpropyl,
1,1-dimethylethyl, pentyl, 1-methylbutyl, 2-methylbutyl,
3-methylbutyl, 2,2-dimethylpropyl, 1-ethylpropyl, hexyl,
1,1-dimethylpropyl, 1,2-dimethylpropyl, 1-methylpentyl,
2-methylpentyl, 3-methylpentyl, 4-methylpentyl,
1,1-dimethylbutyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 1,3-dimethylbutyl,
2,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,3-dimethylbutyl, 3,3-dimethylbutyl,
1-ethylbutyl, 2-ethylbutyl, 1,1,2-trimethylpropyl,
1,2,2-trimethylpropyl, 1-ethyl-1-methylpropyl and
1-ethyl-2-methylpropyl;
Haloalkyl: straight-chain or branched alkyl groups having 1 to 6
carbon atoms, it being possible for some or all of the hydrogen
atoms in these groups to be replaced by halogen atoms as
mentioned above, for example C1-C2-haloalkyl, such as
chloromethyl, dichloromethyl, trichloromethyl, fluoromethyl,
difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, chlorofluoromethyl,
dichlorofluoromethyl, chlorodifluoromethyl, 1-fluoroethyl,
2-fluoroethyl, 2,2-difluoroethyl, 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl,
2-chloro-2-fluoroethyl, 2-chloro-2,2-difluoroethyl,
2,2-dichloro-2-fluoroethyl, 2,2,2-trichloroethyl and
pentafluoroethyl;
Cycloalkyl: monocyclic alkyl groups having 3 to 6 carbon ring
members, for example cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl and
cyclohexyl;
Alkenyl: straight-chain or branched alkenyl groups having 2 to 6
or 10 carbon atoms and a double bond-in any position, for example
C2-C6-alkenyl, such as ethenyl, 1-propenyl, 2-propenyl,
1-methylethenyl, 1-butenyl, 2-butenyl, 3-butenyl,
1-methyl-1-propenyl, 2-methyl-1-propenyl, 1-methyl-2-propenyl,
2-methyl-2-propenyl, 1-pentenyl, 2-pentenyl, 3-pentenyl,
4-pentenyl, 1-methyl-1-butenyl, 2-methyl-1-butenyl,
3-methyl-1-butenyl, 1-methyl-2-butenyl, 2-methyl-2-butenyl,
3-methyl-2-butenyl, 1-methyl-3-butenyl, 2-methyl-3-butenyl,
3-methyl-3-butenyl, 1,1-dimethyl-2-propenyl,
1,2-dimethyl-1-propenyl, 1,2-dimethyl-2-propenyl,
1-ethyl-1-propenyl, 1-ethyl-2-propenyl, 1-hexenyl, 2-hexenyl,
~ CA 02324460 2000-09-19
0050/48890
9
3-hexenyl, 4-hexenyl, 5-hexenyl, 1-methyl-1-pentenyl,
2-methyl-1-pentenyl, 3-methyl-1-pentenyl, 4-methyl-1-pentenyl,
1-methyl-2-pentenyl, 2-methyl-2-pentenyl, 3-methyl-2-pentenyl,
4-methyl-2-pentenyl, 1-methyl-3-pentenyl, 2-methyl-3-pentenyl,
3-methyl-3-pentenyl, 4-methyl-3-pentenyl, 1-methyl-4-pentenyl,
2-methyl-4-pentenyl, 3-methyl-4-pentenyl, 4-methyl-4-pentenyl,
1,1-dimethyl-2-butenyl, 1,1-dimethyl-3-butenyl,
1,2-dimethyl-1-butenyl, 1,2-dimethyl-2-butenyl,
1,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl, 1,3-dimethyl-1-butenyl,
1,3-dimethyl-2-butenyl, 1,3-dimethyl-3-butenyl,
2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl, 2,3-dimethyl-1-butenyl,
2,3-dimethyl-2-butenyl, 2,3-dimethyl-3-butenyl,
3,3-dimethyl-1-butenyl, 3,3-dimethyl-2-butenyl,
1-ethyl-1-butenyl, 1-ethyl-2-butenyl, 1-ethyl-3-butenyl,
2-ethyl-1-butenyl, 2-ethyl-2-butenyl, 2-ethyl-3-butenyl,
1,1,2-trimethyl-2-propenyl, 1-ethyl-1-methyl-2-propenyl,
1-ethyl-2-methyl-1-propenyl and 1-ethyl-2-methyl-2-propenyl;
Alkynyl: straight-chain or branched alkynyl groups having 2 to 10
carbon atoms and a triple bond in any position, for example
CZ-C6-alkynyl, such as ethynyl, 2-propynyl, 2-butynyl, 3-butynyl,
1-methyl-2-propynyl, 2-pentynyl, 3-pentynyl, 4-pentynyl,
1-methyl-2-butynyl, 1-methyl-3-butynyl, 2-methyl-3-butynyl,
1,1-dimethyl-2-propynyl, 1-ethyl-2-propynyl, 2-hexynyl,
3-hexynyl, 4-hexynyl, 5-hexynyl, 1-methyl-2-pentynyl,
1-methyl-3-pentynyl, 1-methyl-4-pentynyl, 2-methyl-3-pentynyl,
2-methyl-4-pentynyl, 3-methyl-4-pentynyl, 4-methyl-2-pentynyl,
1,1-dimethyl-2-butynyl, 1,1-dimethyl-3-butynyl,
1,2-dimethyl-3-butynyl, 2,2-dimethyl-3-butynyl,
1-ethyl-2-butynyl, 1-ethyl-3-butynyl, 2-ethyl-3-butynyl and
1-ethyl-1-methyl-2-propynyl;
Heterocyclyl or heterocyclyloxy, heterocyclylthio and
heterocyclylamino: three- to six-membered saturated or partially
unsaturated mono- or polycyclic heterocycles which contain one to
three heteroatoms selected from a group consisting of oxygen,
nitrogen and sulfur and which are attached to the skeleton
directly or (heterocyclyloxy) via an oxygen atom or
(heterocyclylthio) via a sulfur atom or (heterocyclylamino) via a
nitrogen atom, such as, for example, 2-tetrahydrofuranyl,
oxiranyl, 3-tetrahydrvfuranyl, 2-tetrahydrothienyl,
3-tetrahydrothienyl, 2-pyrrolidinyl, 3-pyrrolidinyl,
3-isoxazolidinyl, 4-isoxazolidinyl, 5-isoxazolidinyl,
3-isothiazolidinyl, 4-isothiazolidinyl, 5-isothiazolidinyl,
3-pyrazolidinyl, 4-pyrazolidinyl, 5-pyrazolidinyl,
2-oxazolidinyl, 4-oxazolidinyl, 5-oxazolidinyl, 2-thiazolidinyl,
4-thiazolidinyl, 5-thiazolidinyl, 2-imidazolidinyl,
0050/48890
CA 02324460 2000-09-19
4-imidazolidinyl, 1,2,4-oxadiazolidin-3-yl,
1,2,4-oxadiazolidin-5-yl, 1,2,4-thiadiazolidin-3-yl,
1,2,4-thiadiazolidin-5-yl, 1,2,4-triazolidin-3-yl,
1,3,4-oxadiazolidin-2-yl, 1,3,4-thiadiazolidin-2-yl,
5 1,3,4-triazolidin-2-yl, 2,3-dihydrofur-2-yl, 2,3-dihydrofur-3-yl,
2,3-dihydrofur-4-yl, 2,3-dihydrofur-5-yl, 2,5-dihydrofur-2-yl,
2,5-dihydrofur-3-yl, 2,3-dihydrothien-2-yl,
2,3-dihydrothien-3-yl, 2,3-dihydrothien-4-yl,
2,3-dihydrothien-5-yl, 2,5-dihydrothien-2-yl,
10 2,5-dihydrothien-3-yl, 2,3-dihydropyrrol-2-yl,
2,3-dihydropyrrol-3-yl, 2,3-dihydropyrrol-4-yl,
2,3-dihydropyrrol-5-yl, 2,5-dihydropyrrol-2-yl,
2,5-dihydropyrrol-3-yl, 2,3-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl,
2,3-dihydroisoxazol-4-yl, 2,3-dihydroisoxazol-5-yl,
4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl, 4,5-dihydroisoxazol-4-yl,
4,5-dihydroisoxazol-5-yl, 2,5-dihydroisothiazol-3-yl,
2,5-dihydroisothiazol-4-yl, 2,5-dihydroisothiazol-5-yl,
2,3-dihydroisopyrazol-3-yl, 2,3-dihydroisopyrazol-4-yl,
2,3-dihydroisopyrazol-5-yl, 4,5-dihydroisopyrazol-3-yl,
4,5-dihydroisopyrazol-4-yl, 4,5-dihydroisopyrazol-5-yl,
2,5-dihydroisopyrazol-3-yl, 2,5-dihydroisopyrazol-4-yl,
2,5-dihydroisopyrazol-5-yl, 2,3-dihydrooxazol-3-yl,
2,3-dihydrooxazol-4-yl, 2,3-dihydrooxazol-5-yl,
4,5-dihydrooxazol-3-yl, 4,5-dihydrooxazol-4-yl,
4,5-dihydrooxazol-5-yl, 2,5-dihydrooxazol-3-yl,
2,5-dihydrooxazol-4-yl, 2,5-dihydrooxazol-5-yl,
2,3-dihydrothiazol-2-yl, 2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl,
2,3-dihydrothiazol-5-yl, 4,5-dihydrothiazol-2-yl,
4,5-dihydrothiazol-4-yl, 4,5-dihydrothiazol-5-yl,
2,5-dihydrothiazol-2-yl, 2,5-dihydrothiazol-4-yl,
2,5-dihydrothiazol-5-yl, 2,3-dihydroimidazol-2-yl,
2,3-dihydroimidazol-4-yl, 2,3-dihydroimidazol-5-yl,
4,5-dihydroimidazol-2-yl, 4,5-dihydroimidazol-4-yl,
4,5-dihydroimidazol-5-yl, 2,5-dihydroimidazol-2-yl,
2,5-dihydroimidazol-4-yl, 2,5-dihydroimidazol-5-yl,
2-morpholinyl, 3-morpholinyl, 2-piperidinyl, 3-piperidinyl,
4-piperidinyl, 3-tetrahydropyridazinyl, 4-tetrahydropyridazinyl,
2-tetrahydropyrimidinyl, 4-tetrahydropyrimidinyl,
5-tetrahydropyrimidinyl, 2-tetrahydropyrazinyl,
1,3,5-tetrahydrotriazin-2-yl, 1,2,4-tetrahydrotriazin-3-yl,
1,3-dihydrooxazin-2-yl, 1,3-dithian-2-yl, 2-tetrahydropyranyl,
1,3-dioxolan-2-yl, 3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyridin-2-yl,
4H-1,3-thiazin-2-yl, 4H-3,1-benzothiazin-2-yl,
1,1-dioxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrothien-2-yl, 2H-1,4-benzothiazin-3-yl,
2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3-yl, 1,3-dihydrooxazin-2-yl, 1,3-dithian-2-yl;
005048890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
IZ
Aryl or aryloxy, arylthio, arylcarbonyl and arylsulfonyl:
aromatic mono- or polycyclic hydrocarbon radicals which are
attached to the skeleton directly or (aryloxy) via an oxygen atom
(-O-) or (arylthio) a sulfur atom (-S-), (arylcarbonyl) via a
carbonyl group (-CO-) or (arylsulfonyl) via a sulfonyl group
(-SOZ-), for example phenyl, naphthyl and phenanthrenyl or
phenyloxy, naphthyloxy and phenanthrenyloxy and the corresponding
carbonyl and sulfonyl radicals;
Hetaryl or hetaryloxy, hetarylthio, hetarylcarbonyl and
hetarylsulfonyl: aromatic mono- or polycyclic radicals which,
beside carbon ring members, can additionally contain one to four
nitrogen atoms or one to three nitrogen atoms and one oxygen or
one sulfur atom or one oxygen or one sulfur atom and which are
attached to the skeleton directly or (hetaryloxy) via an oxygen
atom (-o-) or (hetarylthio) a sulfur atom (-S-),
(hetarylcarbonyl) via a carbonyl group (-CO-) or
(hetarylsulfonyl) via a sulfonyl group (-SOZ-), for example
- 5-membered heteroaryl, containing one to three nitrogen
atoms: 5-membered heteroaryl groups which, beside carbon
atoms, can contain one to three nitrogen atoms as ring
members, for example 2-pyrrolyl, 3-pyrrolyl, 3-pyrazolyl,
4-pyrazolyl, 5-pyrazolyl, 2-imidazolyl, 4-imidazolyl,
1,2,4-triazol-3-yl and 1,3,4-triazol-2-yl;
- 5-membered heteroaryl, containing one to four nitrogen atoms
or one to three nitrogen atoms and one sulfur or oxygen atom
or one oxygen or one sulfur atom: 5-membered heteroaryl
groups which, beside carbon atoms, can contain one to four
nitrogen atoms or one to three nitrogen atoms and one sulfur
or oxygen atom or one oxygen or sulfur atom as ring members,
for example 2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl,
2-pyrrolyl, 3-pyrrolyl, 3-isoxazolyl, 4-isoxazolyl,
5-isoxazolyl, 3-isothiazolyl, 4-isothiazolyl, 5-isothiazolyl,
3-pyrazolyl, 4-pyrazolyl, 5-pyrazolyl, 2-oxazolyl,
4-oxazolyl, 5-oxazolyl, 2-thiazoiyl, 4-thiazolyl,
5-thiazolyl, 2-imidazolyl, 4-imidazolyl,
1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl, 1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl,
1,2,4-thiadiazol-3-yl, 1,2,4-thiadiazol-5-yl,
1,2,4-triazol-3-yl, 1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl,
1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl, 1,3,4-triazol-2-yl;
- benzo-fused 5-membered heteroaryl, containing one to three
nitrogen atoms or one nitrogen atom and/or one oxygen or
sulfur atom: 5-membered heteroaryl groups which, beside
carbon atoms, can contain one to four nitrogen atoms or one
0~5~/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
12
to three nitrogen atoms and one sulfur or oxygen atom or one
oxygen or one sulfur atom as ring members, and in which two
adjacent carbon ring members or one nitrogen and one adjacent
carbon ring member may be bridged by a buta-1,3-dien-1,4-diyl
group;
- 5-membered heteroaryl bonded via nitrogen and containing one
to four nitrogen atoms, or benzo-fused 5-membered heteroaryl,
bonded via nitrogen and containing one to three nitrogen
atoms: 5-membered heteroaryl groups which, beside carbon
atoms, can contain one to four nitrogen atoms and one to
three nitrogen atoms, respectively, as ring members, and in
which two adjacent carbon ring members or one nitrogen and
one adjacent carbon ring member can be bridged by a
buta-1,3-dien-1,4-diyl group, these rings being attached to
the skeleton via one of the nitrogen ring members;
6-membered heteroaryl containing one to three and one to four
nitrogen atoms, respectively: 6-membered heteroaryl groups
which, beside carbon atoms, can contain one to three and one
to four nitrogen atoms, respectively, as ring members, for
example 2-pyridinyl, 3-pyridinyl, 4-pyridinyl, 3-pyridazinyl,
4-pyridazinyl, 2-pyrimidinyl, 4-pyrimidinyl, 5-pyrimidinyl,
2-pyrazinyl, 1,3,5-triazin-2-yl, 1,2,4-triazin-3-yl and
1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl;
- benzo-fused 6-membered heteroaryl containing one to four
nitrogen atoms: 6-membered heteroaryl groups in which two
adjacent carbon ring members can be bridged by a buta-
1,3-dien-1,4-diyl group, for example quinoline, isoquinoline,
quinazoline and quinoxaline,
and the corresponding oxy, thio, carbonyl or sulfonyl groups.
Hetarylamino: aromatic mono- or polycyclic radicals which, beside
carbon ring members, can additionally contain one to four
nitrogen atoms or one to three nitrogen atoms and one oxygen or
one sulfur atom and which are attached to the skeleton via a
nitrogen atom.
The specification ~~partially or fully halogenated~~ is meant to
express that some or all of the hydrogen atoms in the groups thus
characterized may be replaced by identical or different halogen
atoms as mentioned above.
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
a
13
With respect to their biological activity, preference is given
to compounds of the formula I in which m is 0.
Likewise, preference is given to compounds of the formula I in
which R1 is methyl.
Besides, preference is given to compounds I in which R3 is
hydrogen, cyano, cyclopropyl, methyl, ethyl, 1-methylethyl or CF3.
Moreover, preference is given to compounds I in which R3 is
methyl.
Besides, preference is given to compounds I in which R3 is cyano.
Furthermore, preference is given to compounds I in which R3 is
cyclopropyl.
Additionally, preference is given to compounds I in which R3 is
CF3.
Additionally, preference is given to compounds I in which RS is
hydrogen, cyclopropyl, methyl, ethyl, isopropyl, unsubstituted or
substituted aryl or hetaryl.
Moreover, preference is given to compounds I in which RS is
methyl.
Additionally, preference is given to compounds I in which RS is
ethyl.
Moreover, preference is given to compounds I in which R5 is
isopropyl.
Moreover, preference is given to compounds I in which R5 is
cyclopropyl.
Moreover, preference is given to compounds I in which R5 is CF3.
Additionally, preference is given to compounds I in which RS is
unsubstituted or substituted aryl or hetaryl.
Additionally, preference is given to compounds I in which R5 is
unsubstituted or substituted pyridyl, pyrimidyl, pyrazinyl,
pyridazinyl or triazinyl.
~~50/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
r
14
Additionally, preference is given to compounds I in which R5 is
unsubstituted or substituted furyl, thienyl or pyrrolyl.
Additionally, preference is given to compounds I in which R5 is
unsubstituted or substituted oxazolyl, thiazolyl, isoxazolyl,
isothiazolyl, pyrazolyl or imidazolyl.
Additionally, preference is given to compounds I in which RS is
unsubstituted or substituted oxdiazolyl [sic], thiadiazolyl or
triazolyl.
Moreover, preference is given to compounds I in which R5 is phenyl
which is unsubstituted or carries one or two of the following
groups: nitro, cyano, hydroxyl, amino, aminocarbonyl,
15' aminothiocarbonyl, halogen, C1-C4-alkyl, C1-C4-haloalkyl,
C1-C4-alkoxy, CZ-C4-haloalkoxy, C1-CQ-alkylamino,~
di-C1-C4-alkylamino, C1-C4-alkylsulfonyl, C1-C4-alkoxycarbonyl,
C1-C4-alkylaminocarbonyl or di-C1-C4-alkylaminocarbonyl.
Moreover, preference is given to compounds I in which R4 is
hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C2-C6-alkenyl, C2-C6-alkynyl, allyl,
arylalkyl, hetarylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, hetaryloxyalkyl, aryl or
hetaryl.
Additionally, preference is given to compounds I in which R4 is
C1-C6-alkyl.
Further preferred compounds I are disclosed in WO 97/15,552.
The compounds I which are contained in the mixtures according to
the invention have excellent activity against a broad range of
phytopathogenic fungi, in particular against fungi from the
classes of the Ascomycetes, Deuteromycetes, Phycomycetes and
Basidiomycetes.
They are especially important for controlling a large number of
fungi in a variety of crop plants, such as cotton, vegetable
species (for example cucumbers, beans, tomatoes, potatoes and
cucurbits), barley, grass, oats, bananas, coffee, maize, fruit
species, rice, rye, soya, grapevine, wheat, ornamentals, sugar
cane, and a variety of seeds.
They are particularly suitable for controlling the following
phytopathogenic fungi: Erysiphe graminis (powdery mildew) in
cereals, Erysiphe cichoracearum and Sphaerotheca fuliginea in
cucurbits, Podosphaera leucotricha in apples, Uncinula necator in
grapevines, Puccinia species in cereals, Rhizoctonia species in
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
cotton, rice and lawns, Ustilago species in cereals and sugar
cane, Venturia inaequalis (scab) in apples, Helminthosporium
species in cereals and rice, Septoria nodorum in wheat, Botrytis
cinera [sic] (gray mold) in strawberries, vegetables, ornamentals
5 and grapevines, Cercospora arachidicola in groundnuts,
Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides in wheat and barley,
Pyricularia oryzae in rice and lawns, Phytophthora infestans in
potatoes and tomatoes, Plasmopara viticola in grapevines,
Pseudoperonospora species in hops and cucumbers, Alternaria
10 species in vegetables and fruit, Mycosphaerella species in
bananas and Fusarium and Verticillium species.
The compounds of the formulae II to IX [sic] are used for
controlling animal pests from the class of the insects, arachnids
15 and nematodes. They can be employed in crop protection and in the
hygiene, stored-product and veterinary sector for controlling
animal pests. In particular, they are suitable for controlling
the following animal pests:
~ insects from the order of the lepidopterans (Lepidoptera), e.g.
Agrotis ypsilon, Agrotis segetum, Alabama argillacea,
Anticarsia gemmatalis, Argyresthia conjugella, Autographa
gamma, Bupalus piniarius, Cacoecia murinana, Capua reticulana,
Cheimatobia brumata, Choristoneura fumiferana, Choristoneura
occidentalis, Cirphis unipuncta, Cydia pomonella, Dendrolimus
pini, Diaphania nitidalis, Diatraea grandiosella, Earias
insulana, Elasmopalpus lignosellus, Eupoecilia ambiguella,
Evetria bouliana, Feltia subterranea, Galleria mellonella,
Grapholitha funebrana, Grapholitha molesta, Heliothis armigera,
Heliothis virescens, Heliothis zea, Hellula undalis, Hibernia
defoliaria, Hyphantria cunea, Hyponomeuta malinellus, Keiferia
lycopersicella, Lambdina fiscellaria, Laphygma exigua,
Leucoptera coffeella, Leucoptera scitella, Lithocolletis
blancardella, Lobesia botrana, Loxostege sticticalis, Lymantria
dispar, Lymantria monacha, Lyonetia clerkella, Malacosoma
neustria, Mamestra brassicae, Orgyia pseudotsugata, Ostrinia
nubilalis, Panolis flammea, Pectinophora gossypiella, Peridroma
saucia, Phalera bucephala, Phthorimaea operculella,
Phyllocnistis citrella, Pieris brassicae, Plathypena scabra,
Plutella xylostella, Pseudoplusia includens, Rhyacionia
frustrana, Scrobipalpula absoluta, Sitotroga cerealella,
Sparganothis pilleriana, Spodoptera frugiperda, Spodoptera
littoralis, Spodoptera litura, Thaumatopoea pityocampa, Tortrix
Viridana, Trichoplusia ni and Zeiraphera canadensis,
~ beetles (Coleoptera), e.g. Agrilus sinuatus, Agriotes lineatus,
Agriotes obscurus, Amphimallus solstit:ialis, Anisandrus dispar,
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
i
16
Anthonomus grandis, Anthonomus pomorum, Atomaria linearis,
Blastophagus piniperda, Blitophaga undata, Bruchus rufimanus,
Bruchus pisorum, Bruchus lentis, Byctiscus betulae, Cassida
nebulosa, Cerotoma trifurcata, Ceuthorrhynchus assimilis,
Ceuthorrhynchus napi, Chaetocnema tibialis, Conoderus
vespertinus, Crioceris asparagi, Diabrotica longicornis,
Diabrotica 12-punctata, Diabrotica virgifera, Epilachna
varivestis, Epitrix hirtipennis, Eutinobothrus brasiliensis,
Hylobius abietis, Hypera brunneipennis, Hypera postica, Ips
typographus, Lema bilineata, Lema melanopus, Leptinotarsa
decemlineata, Limonius californicus, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus,
Melanotus communis, Meligethes aeneus, Melolontha hippocastani,
Melolontha melolontha, Oulema oryzae, Ortiorrhynchus [sic]
sulcatus, Otiorrhynchus ovatus, Phaedon cochleariae,
Phyllotreta chrysocephala, Phyllophaga sp., Phyllopertha
horticola, Phyllotreta nemorum, Phyllotreta striolata, Popillia
japonica, Sitona lineatus and Sitophilus granaria,
~ dipterans (Diptera), e.g. Aedes aegypti, Aedes vexans,
Anastrepha ludens, Anopheles maculipennis, Ceratitis capitata,
Chrysomya bezziana, Chrysomya hominivorax, Chrysomya
macellaria, Contarinia sorghicola, Cordylobia anthropophaga,
Culex pipiens, Dacus cucurbitae, Dacus oleae, Dasineura
brassicae, Fannia canicularis, Gasterophilus intestinalis,
Glossina morsitans, Haematobia irritans, Haplodiplosis
equestris, Hylemyia platura, Hypoderma lineata, Liriomyza
sativae, Liriomyza trifolii, Lucilia caprina [sic], Lucilia
cuprina, Lucilia sericata, Lycoria pectoralis, Mayetiola
destructor, Musca domestica, Muscina stabulans, Oestrus ovis,
Oscinella frit, Pegomya hysocyami, Phorbia antiqua, Phorbia
brassicae, Phorbia coarctata, Rhagoletis cerasi, Rhagoletis
pomonella, Tabanus bovinus, Tipula oleracea and Tipula
paludosa,
~ thrips (Thysanoptera), e.g. Frankliniella fusca, Frankliniella
occidentalis, Frankliniella tritici, Scirtothrips citri, Thrips
oryzae, Thrips palmi and Thrips tabaci,
~ hymenopterans (Hymenoptera), e.g. Athalia rosae, Atta
cephalotes, Atta sexdens, Atta texana, Hoplocampa minuta,
Hoplocampa testudinea, Monomorium pharaonis, Solenopsis
geminata and Solenopsis invicta,
~ heteropterans (Heteroptera), e.g. Acrosternum hilare, Blissus
leucopterus, Cyrtopeltis notatus, Dysdercus cingulatus,
Dysdercus intermedius, Eurygaster integriceps, Euschistus
impictiventris, Leptoglossus phyllopus, Lygus lineolaris, Lygus
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
17
pratensis, Nezara viridula, Piesma quadrate, Solubea insularis
and Thyanta perditor,
~ homopterans (Homoptera), e.g. Acyrthosiphon onobrychis, Adelges
laricis, Aphidula nasturtii, Aphis fabae, Aphis pomi, Aphis
sambuci, Brachycaudus cardui, Brevicoryne brassicae, Cerosipha
gossypii, Dreyfusia nordmannianae, Dreyfusia piceae, Dysaphis
radicola, Dysaulacorthum pseudosolani, Empoasca fabae,
Macrosiphum avenae, Macrosiphum euphorbiae, Macrosiphon rosae,
Megoura viciae, Metopolophium dirhodum, Myzodes persicae, Myzus
cerasi, Nilaparvata lugens, Pemphigus bursarius, Perkinsiella
saccharicida, Phorodon humuli, Psylla mali, Psylla piri,
Rhopalomyzus ascalonicus, Rhopalosiphum maidis, Sappaphis male,
Sappaphis mali, Schizaphis graminum, Schizoneura lanuginosa,
Trialeurodes vaporariorum and Viteus vitifolii,
~ termites (Isoptera), e.g. Calotermes flavicollis, Leucotermes
flavipes, Reticulitermes lucifugus and Termes natalensis,
~ orthopterans (Orthoptera), e.g. Acheta domestica, Blatta
orientalis, Blattella germanica, Forficula auricularia,
Gryllotalpa gryllotalpa, Locusta migratoria, Melanoplus
bivittatus, Melanoplus femur-rubrum, Melanoplus mexicanus,
Melanoplus sanguinipes, Melanoplus spretus, Nomadacris
septemfasciata, Periplaneta americana, Schistocerca americana,
Schistocerca peregrine, Stauronotus maroccanus and Tachycines
asynamorus,
~ Arachnoidea, such as arachnids (Acarina), e.g. Amblyomma
americanum, Amblyomma variegatum, Argas persicus, Boophilus
annulatus, Boophilus decoloratus, Boophilus microplus,
Brevipalpus phoenicis, Bryobia praetiosa, Dermacentor silvarum,
Eotetranychus carpini, Eriophyes sheldoni, Hyalomma truncatum,
Ixodes ricinus, Ixodes rubicundus, Ornithodorus moubata,
Otobius megnini, Paratetranychus pilosus, Dermanyssus gallinae,
Phyllocoptruta oleivora, Polyphagotarsonemus latus, Psoroptes
ovis, Rhipicephalus appendiculatus; Rh:ipicephalus evertsi,
Sarcoptes scabiei, Tetranychus cinnabarinus, Tetranychus
kanzawai, Tetranychus pacificus, Tetranychus telarius and
Tetranychus urticae,
~ nematodes such as root knot nematodes, e.g. Meloidogyne hapla,
Meloidogyne incognita, Meloidogyne javanica, cyst-forming
nematodes, e.g. Globodera rostochiensis, Heterodera avenae,
Heterodera glycines, Heterodera schachtii, Heterodera trifolii,
stem eelworms and foliar nematodes, e.g. Belonolaimus
longicaudatus, Ditylenchus destructor, Ditylenchus dipsaci,
Heliocotylenchus multicinctus, Longidorus elongatus, Radopholus
,
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
18
similis, Rotylenchus robustus, Trichodorus primitivus,
Tylenchorhynchus claytoni, Tylenchorhynchus dubius,
Pratylenchus neglectus, Pratylenchus penetrans, Pratylenchus
curvitatus and Pratylenchus goodeyi.
The application rate of active ingredient for controlling animal
pests is under field conditions usually from 0.01 to 2.0,
preferably 0.02 to 1.0, kg/ha.
The mixtures according to the invention are particularly
preferably utilizable for controlling plant diseases and harmful
insects in rice.
The compounds I and at least one of the compounds II to XI can be
applied simultaneously, either together or separately, or in
succession, the sequence, in the case of separate application,
generally not having any effect on the control results.
Depending on the nature of the desired effect, the application
rates of the mixtures according to the invention are, in
particular in agricultural crops, from 0.01 to 8 kg/ha,
preferably from 0.1 to 5 kg/ha, in particular from 0.5 to
3.0 kg/ha.
In the case of the compounds I, the application rates are from
0.01 to 2.5 kg/ha, preferably from 0.05 to 2.5 kg/ha, in
particular from 0.1 to 1.0 kg/ha.
For seed treatment, the application rates of the mixture are
generally from 0.001 to 250 g/kg of seed, preferably 0.01 to
100 g/kg, in particular 0.01 to 50 g/kg.
If phytopathogenic harmful fungi are to be controlled, the
separate or joint application of the compounds I and at least one
of the compounds II to XI or of the mixtures of the compounds I
and at least one of the compounds II to IX [sicj is effected by
spraying or dusting the seeds, the plants or the soils before or
after sowing the plants, or before or after plant emergence.
The mixtures according to the invention can be formulated for
example in the form of ready-to-spray solutions, powders and
suspensions or in the form of highly concentrated aqueous, oily
or other suspensions, dispersions, emulsions, oil dispersions,
pastes, dusts, materials for broadcasting or granules, and
applied by spraying, atomizing, dusting, broadcasting or
watering. The use form depends on the intended purpose; in any
case, it should ensure as fine and uniform a distribution as
OOSO/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
19
possible of the mixture according to the invention.
The formulations are prepared in a known manner, for example by
expanding the active ingredient with solvents and/or carriers, if
desired by use of emulsifiers and dispersants. If the diluent
used is water, it is also possible to use other organic solvents
as auxiliary solvents. Suitable auxiliaries are essentially:
solvents, such as aromatics (for example xylene), chlorinated
aromatics (for example chlorobenzenes), paraffins (for example
mineral oil fractions), alcohols (for example methanol, butanol),
ketones (for example cyclohexanone), amines (for example
ethanolamine, dimethylformamide) and water; carriers, such as
natural ground minerals (for example kaolins, clays, talc, chalk)
and ground synthetic minerals (for example finely divided silica,
silicates); emulsifiers, such as nonionic and anionic emulsifiers
(for example polyoxyethylene fatty alcohol ethers,
alkylsulfonates and arylsulfonates), and dispersants, such as
lignosulfite waste liquors and methylcellulose.
Suitable surfactants are the alkali metal salts, alkaline earth
metal salts and ammonium salts of aromatic sulfonic acids, e.g.
ligno-, phenol-, naphthalene- and dibutylnaphthalenesulfonic
acid, and of fatty acids, alkyl- and alkylarylsulfonates, alkyl,
lauryl ether and fatty alcohol sulfates, and salts of sulfated
hexa-, hepta- and octadecanols, or of fatty alcohol glycol
ethers, condensates of sulfonated naphthalene and its derivatives
with formaldehyde, condensates of naphthalene or of the
naphthalenesulfonic acids with phenol and formaldehyde,
polyoxyethylene octylphenol ether, ethoxylated isooctyl-, octyl-
or nonylphenol, alkylphenol or tributylphenyl polyglycol ethers,
alkylaryl polyether alcohols, isotridecyl alcohol, fatty alcohol
ethylene oxide condensates, ethoxylated castor oil,
polyoxyethylene alkyl ethers or polyoxypropylene [sic], lauryl
alcohol polyglycol ether acetate, sorbitol esters, lignosulfite
waste liquors or methylcellulose.
Powders, materials for broadcasting and dusts can be prepared by
mixing or jointly grinding the compounds I and at least one of
the compounds II to XI or the mixture of the compounds I and at
least one of the compounds II to XI with a solid carrier.
Granules (e.g. coated granules, impregnated granules or
homogeneous granules) are usually prepared by binding the active
ingredient, or active ingredients, to a solid carrier.
Fillers or solid carriers are, for example, mineral earths, such
as silica gel, silicic acids, silica gels (sic], silicates, talc,
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
kaolin, limestone, Lime, chalk, bole, loess, clay, dolomite,
diatomaceous earth, calcium sulfate, magnesium sulfate, magnesium
oxide, ground synthetic materials, and fertilizers, such as
ammonium sulfate, ammonium phosphate, ammonium nitrate, ureas,
5 and products of vegetable origin, such as cereal meal, tree bark
meal, wood meal and nutshell meal, cellulose powders or other
solid carriers.
The formulations generally comprise 0.1 to 95% by weight,
10 preferably 0.5 to 90% by weight, of one of the compounds I and at
least one of the compounds II to XI or of the mixture of the
compounds I and at least one of the compounds II to XI. The
active ingredients are employed in a purity of from 90% to 100%,
preferably 95% to I00% (according to NMR or HPLC spectrum [sic]).
The compounds I and at least one of the compounds II to XI, the
mixtures or the corresponding formulations are applied by
treating the harmful fungi, their habitat or the plants, seeds,
soils, areas, materials or spaces to be kept free from them with
a fungicidally effective amount of the mixture, or of the
compounds I and at least one of the compounds II to XI in the
case of separate application.
Application can be effected before or after attack by the harmful
fungi.
Examples of such preparations comprising the active ingredients
are:
I. A solution of 90 parts by weight of the active ingredients
and 10 parts by weight of N-methylpyrrolidone; this
solution is suitable for use in the form of microdrops;
II. A mixture of 20 parts by weight of the active ingredients,
80 parts by weight of xylene, 10 parts by weight of the
adduct of 8 to 10 mol of ethylene oxide and 1 mol of oleic
acid N-monoethanolamide, 5 parts by weight of the calcium
salt of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, 5 parts by weight of
the adduct of 40 mol of ethylene oxide and 1 mol of castor
oil; a dispersion is obtained by finely distributing the
solution in water;
III. An aqueous dispersion of 20 parts by weight of the active
ingredients, 40 parts by weight of cyclohexanone, 30 parts
by weight of isobutanol, 20 parts by weight of the adduct
of 40 mol of ethylene oxide and 1 mol of castor oil;
IV. An aqueous dispersion of 20 parts by weight of the active
ingredients, 25 parts by weight of cyclohexanol, 65 parts
by weight of a mineral oil fraction of boiling point 210 to
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
21
280~C, and 10 parts by weight of the adduct of 40 mol of
ethylene oxide and 1 mol of castor oil;
V. A mixture, ground in a hammer mill, of 80 parts by weight
of the active ingredients, 3 parts by weight of the sodium
salt of diisobutylnaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid, 10 parts by
weight of the sodium salt of a lignosulfonic acid from a
sulfite waste liquor and 7 parts by weight of pulverulent
silica gel; a spray mixture is obtained by finely
distributing the mixture in water;
VI. An intimate mixture of 3 parts by weight of the active
ingredients and 97 parts by weight of finely divided
kaolin; this dust comprises 3% by weight of active
ingredient;
VII. An intimate mixture of 30 parts by weight of the active
ingredients, 92 parts by weight of pulverulent silica gel
and 8 parts by weight of paraffin oil which had been
sprayed onto the surface of this silica gel; this
formulation imparts good adhesion to the active ingredient;
VIII. A stable aqueous dispersion of 40 parts by weight of the
active ingredients, 10 parts by weight of the sodium salt
of a phenolsulfonic acid/urea/formaldehyde condensate, 2
parts by weight of silica gel and 48 parts by weight of
water; this dispersion rnay be diluted further;
IX. A stable oily dispersion of 20 parts by weight of the
active ingredients, 2 parts by weight of the calcium salt
of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, 8 parts by weight of fatty
alcohol polyglycol ether, 20 parts by weight of the sodium
.salt of a phenolsulfonic acid/urea/formaldehyde condensate
and 88 parts by weight of a paraffinic mineral oil.
The synergistic activity of the mixtures according to the
invention can be demonstrated by the following experiments:
The active ingredients, separately or together, are formulated as
a 10% emulsion in a mixture of 63% by weight of cyclohexanone and
27% by weight of emulsifier, and correspondingly diluted with
water to the desired concentration.
Evaluation is carried out by determining the infected leaf areas
in percent. These percentages are converted into efficacies. The
efficacy (W_) is calculated as follows using Abbot's formula:
W = (1 - a) ~100/(3
a corresponds to the fungal infection of the treated plants in
% and
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
o-
22
corresponds to the fungal infection of the untreated
(control) plants in %
An efficacy of 0 means that the infectian level of the treated
plants corresponds to that of the untreated control plants; an
efficacy of I00 means that the treated plants were not infected.
The expected efficacies of the mixtures of the active ingredients
were determined using Colby's formula (R.S. Colby, weeds ~5,
20-22 (1967)] and compared with the observed efficacies.
Colby's formula: E = x + y - x~y/100
E is the expected efficacy, expressed in % of the untreated
control, when using the mixture of the~active ingredients A
and B at the concentrations a and b
x is the efficacy, expressed in % of the untreated control,
when using active ingredient A at the concentration a
y is the efficacy, expressed in % of the untreated control,
when using active ingredient B at the concentration b
Use Example 1 - Activity against Pyricularia oryzae (protective)
Leaves of potted rice seedlings c.v. "Tai-Nong 67" were sprayed
to runoff point with an aqueous preparation of active ingredient
which had been prepared from a stock solution comprising 10% of
active ingredient, 63% of cyclohexanone and 27% of emulsifier.
The following day, the plants were innoculated with an aqueous
spore suspension of Pyricularia oryzae. The test plants were
subsequently placed in climatized chambers at 22-24~C and 95-99%
relative atmospheric humidity for 6 days. The extent of the
development of the disease on the leaves was then determined
visually.
The visually determined values for the percentage of diseased
leaf area were converted into efficacies as percent of the
untreated control. An efficacy of 0 means the same disease level
as in the untreated control, an efficacy of 100 means 0% disease.
The expected efficacies for active ingredient combinations were
determined using Colby's formula (Colby, S. R.: "Calculating
synergistic and antagonistic responses of herbicide
combinations", Weeds 15, pp. 20-22, 1967) and compared with the
observed efficacies.
As component a), use was made of the following compound I':
I
0050/48890 CA 02324460 2000-09-19
t
23
CH3
HaC.O. Nw y
(I')
CH3 ~ N ,~ CH3
H C
3
The test results are shown in Tables 1 and 2 below:
Table 1:
Ex. Active ingredient Conc. in ppm Efficacy in % of
the untreated
control
1C None (100% diseased) 0
2C Compound I' 2.0 20
0.5 0
3C Compound II 2.0 0
0.5 0
4C Compound V 2.0
0.5 0
Table 2:
Ex. Mixture according to Observed Calculated
the efficacy efficacy *1
invention (conc. in ppm)
5 2 ppm I' + 2 ppm II 50 % 20 %
6 0.5 ppm I' + 0.5 ppm 30 % 10 %
II
7 2 ppm I ' + 2 ppm V 4 0 % 2 0 %
8 0.5 ppm I' + 0.5 ppm 25 % 10 %
V
*)
calculated
using
Colby's
formula
The test results show that for all mixing ratios, the observed
efficacy is higher than the efficacy which had been calculated
beforehand using Colby's formula.