Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2325855 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | APPARATUS FOR REMOVING FLUID FROM A FIBROUS WEB |
| (54) French Title: | DISPOSITIF POUR EXTRAIRE UN LIQUIDE D'UNE BANDE FIBREUSE |
| Status: | Deemed Abandoned and Beyond the Period of Reinstatement - Pending Response to Notice of Disregarded Communication |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | SMART & BIGGAR LP |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 1998-03-04 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 1998-10-08 |
| Examination requested: | 2000-09-25 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/US1998/004286 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | WO 1998044193 |
| (85) National Entry: | 2000-09-25 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
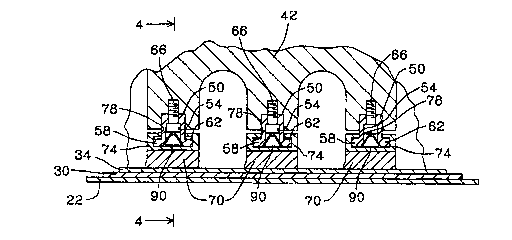
An apparatus for removing fluid from a fibrous web (30) in a papermaking
machine having a machine direction and a cross machine direction, the
apparatus comprising a plurality of generally parallel supports (50) extending
in the cross machine direction, the supports being spaced in the machine
direction, the supports having mounted thereon respective blades (70)
extending in the cross machine direction, the blades being spaced in the
machine direction along a convex path for movement of the web over the blades,
each blade (70) being movable relative to the respective support (50) in a
direction perpendicular to the web such that outward movement of the blade
(70) relative to the support (50) presses the blade against the web (30), and
a control system for exerting, on each of the blades (70), a force in the
direction toward the web (30) so as to press the blade against the web, the
control system being operable to vary the force exerted on each of the blades
(70) independent of the force exerted on the remaining blades.
Dispositif pour extraire un liquide d'une bande (30) fibreuse dans une machine de fabrication de papier présentant un sens machine et un sens transversal. Le dispositif comporte une pluralité de supports (50) sensiblement parallèles, disposés dans le sens transversal et espacés dans le sens machine. Ces supports portent des lames (70) respectives orientées dans le sens transversal, ces lames (70) étant espacées dans le sens machine le long d'une trajectoire convexe pour permettre à la bande de défiler par dessus les lames. Chaque lame (70) est mobile par rapport au support (50) respectif dans une direction perpendiculaire à la bande, de façon que le mouvement de la lame vers l'extérieur par rapport au support (50) presse la lame contre la bande (30). Le dispositif comprend en outre un système de commande pour imprimer à chacune des lames (70) une force en direction de la bande (30) ayant pour effet de presser la lame conte la bande, ce système de commande permettant de faire varier la force exercée sur chacune des lames (70) indépendamment de la force exercée sur les autres lames.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Inactive: IPC from MCD | 2006-03-12 |
| Application Not Reinstated by Deadline | 2005-09-12 |
| Inactive: Dead - No reply to s.29 Rules requisition | 2005-09-12 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2005-03-04 |
| Inactive: Abandoned - No reply to s.29 Rules requisition | 2004-09-10 |
| Inactive: Abandoned - No reply to s.30(2) Rules requisition | 2004-09-10 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2004-03-10 |
| Inactive: S.29 Rules - Examiner requisition | 2004-03-10 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2002-06-28 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2002-06-28 |
| Letter Sent | 2002-06-28 |
| Inactive: Delete abandonment | 2002-06-18 |
| Inactive: Abandoned - No reply to Office letter | 2002-05-07 |
| Inactive: Correspondence - Transfer | 2002-04-26 |
| Inactive: Correspondence - Formalities | 2002-04-26 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2002-03-28 |
| Inactive: Transfer information requested | 2002-02-07 |
| Inactive: Delete abandonment | 2002-02-01 |
| Inactive: Abandoned - No reply to Office letter | 2001-12-27 |
| Inactive: Single transfer | 2001-12-19 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2001-12-11 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2001-12-11 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2001-12-11 |
| Inactive: IPC removed | 2001-12-07 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2001-12-07 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2001-10-30 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2001-01-09 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2001-01-07 |
| Inactive: Courtesy letter - Evidence | 2001-01-02 |
| Inactive: Acknowledgment of national entry - RFE | 2000-12-27 |
| Application Received - PCT | 2000-12-21 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 2000-09-25 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 2000-09-25 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 1998-10-08 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2005-03-04 |
The last payment was received on 2004-02-13
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Please refer to the CIPO Patent Fees web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| MF (application, 3rd anniv.) - standard | 03 | 2001-03-05 | 2000-09-25 |
| Basic national fee - standard | 2000-09-25 | ||
| Request for examination - standard | 2000-09-25 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - standard | 02 | 2000-03-06 | 2000-09-25 |
| Reinstatement (national entry) | 2000-09-25 | ||
| Registration of a document | 2001-09-24 | ||
| Registration of a document | 2001-12-19 | ||
| MF (application, 4th anniv.) - standard | 04 | 2002-03-04 | 2002-02-21 |
| MF (application, 5th anniv.) - standard | 05 | 2003-03-04 | 2003-02-14 |
| MF (application, 6th anniv.) - standard | 06 | 2004-03-04 | 2004-02-13 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD. |
| METSO PAPER INC. |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| RICHARD W. PHILLIPS |