Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02326263 2004-07-12
-1-
NONWOVEN FABRIC OF POLYPROPYLENE FIBER
This invention' relates to a nonwoven fabric made of
continuous polypropylene fiber and to a process for making the
same.
Japanese Patent No. 2887611 describes a process for
making a nonwoven fabric of continuous microfibers having a
fineness less than 1 denier. According to the process described
in this Patent, continuous microfibers are stretched once on
a step of melt spinning and then stretched again until its
fineness is reduced to a desired value. The continuous
microfibers having a fineness thereof reduced in this manner
are collected and bonded together, for example, by adhesion to
obtain the desired nonwoven fabric.
The prior art described above offers a nonwoven fabric
compris ing continuous microfibers of a fineness sufficiently
reduced to ensure a comfortable soft touch. This invent ion aims
to add this comfortable soft touch nonwoven fabric with a high
breakin g extens ion .
The object set forth above is achieved by a first aspect
of this invention relating to the product, on one hand, and by
CA 02326263 2000-11-17
-2-
a second aspect of this invention relating to the process for
making this product.
Specifically, the object set forth above is achieved,
according to its first aspect, by an improvement in the
nonwoven fabric made of continuous polypropylene fiber.
The improvement according to the first aspect of this
invention is in that the continuous f fibers have a f fineness of
0.006 - 5.8 deniers, a birefringence of o.019 - 0.030 and a
tensile breaking extension of 100 - 300 % wherein the fibers
are subjected to substantially mechanical entanglement to
maintain the form of a nonwoven fabric.
According to one preferred embodiment of the first aspect,
said nonwoven fabric has a tensile strength of 1 - 3 g/d.
The object set forth above is achieved, according to the
second aspect of this invention, by an improvement in the
process for making a nonwoven fabric comprising the steps of
stretching the continuous polypropylene fibers extruded from
a plurality of nozzle orifices, accumulating the continuous
ploypropylene fibers on a belt travelling in one direction and
entangling the continuous fibers together to obtain a desired
form of a nonwoven fabric.
The improvement according to the second aspect of this
invention is in by that the process comprises the steps of
CA 02326263 2000-11-17
-3-
heating a region of an extruder in the vicinity of said nozzle
substantially at a temperature of said continuous fibers being
extruded in molten state, guiding the continuous fibers through
guide passage of a sucker extending through between in- and
outlet thereof and being supplied with compressed air at the
normal temperature discharged in a direction defined from the
inlet toward the outlet, stretching the continuous fibers along
a path extending between the nozzle and the sucker and thereby
reducing a fineness of the continuous fibers, and orienting
polypropylene molecules sufficiently to obtain a desired
birefringence.
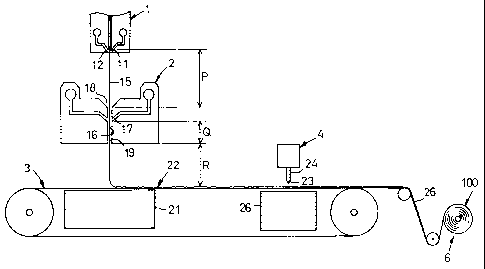
Fig. 1 is a diagram schematically illustrating the
process for making a nonwoven fabric.
Details of a nonwoven fabric and a process for making the
same according to this invention will be more fully understood
from the description given hereunder with reference to the
accompanying drawing.
Fig. 1 is a diagram schematically illustrating the
process for continuously making nonwoven fabric 100 using a melt
spinning machine 1, a sucker 2, an endless belt conveyor 3, a
high pressure water jet ejector 4 and a take-up roller 6.
CA 02326263 2004-07-12
-4-
The melt spinning machine 1 includes a material feed
hopper and a screw feed extruder ( not shown ) , the latter being
provided at its forward end with spinning nozzle 11 and hot blast
blow-off orifices 12 on both sides of the nozzle 11. As material,
polypropylene having MFR, for example, of 10 - 80 g/10 min is
used. 600 orifices of the nozzle 11 each having an orifice
diameter, for example, of 0.35 mm are arranged in line at the
orifice pitch of 1 mm in a direction perpendicular to the plane
of the drawing. Continuous polypropylene fiber 15 is discharged
through each of these orifices of the nozzle 11 at a rate of
0.13 - 0.40 g/min/nozzle. The blow-off orifices 12 breathe out
hot blast substantially at the same temperature as a temperature
of polypropylene being discharged in molten state, i.e., at a
temperature of approximately 230°C on the assumption that
polypropylene is discharged through the nozzle 11 at a
temperature of approximately 230°C. The hot blast is breathed
out at a rate of 1 - 3 Nm'/min and prevents polypropylene being
extruded from being rapidly cooled.
The sucker 2 has guide passage 16 for the continuous
fibers 15 and blow-off orifices 17 opening into the guide
passage 16 from both sides thereof to breathe out compressed
air at the normal temperature. The guide passage 16 has an inlet
18 and an outlet 19 for the continuous fibers 15. The sucker
CA 02326263 2000-11-17
-5-
2 is positioned so that a distance P between the nozzle 11 and
the inlet 18 of the sucker 2 is 500 mm or less, preferably 100
- 300 mm. The continuous fibers 15 travelling over the distance
P preferably have a temperature falling nearly to the melting
point thereof as the continuous fibers 15 reach the inlet 18.
Over a distance Q between the blow-of f orif ices 17 and the outlet
19, the continuous fibers 15 are supplied with compressed air
at the normal temperature breathed out toward the outlet 19.
The distance Q is preferably in a range of 20 - 500 mm and the
expression "normal temperature" used herein should be
understood to be the temperature in a range of 10 - 50°C . The
compressed air is of 0.5 - 2 kgf/cm~G and supplied at a flow
rate of Nm'/min. The continuous fibers 15 entering the guide
passage 16 are quenched by the compressed air at the normal
temperature nearly to the normal temperature and, at the same
time, stretched appropriately to achieve a fineness of 0.006-
5.8 deniers and a birefringence ~n of 0.019 - 0.030. After
stretched in this manner, the continuous fibers 15 preferably
have a tensile strength of 1 - 3 g/d.
The endless conveyor belt 3 has its width extending in
the direction orthogonal to the plane defined by the drawing.
A distance R between the nozzle 11 and the conveyor belt 3 is
dimensioned preferably in a range of 300 - 1500 mm, more
CA 02326263 2000-11-17
-6-
preferably in a range of 400 - 600 mm by correspondingly
adjusting the distances P and Q. The conveyor belt 3 travels
rightward as viewed in the drawing at a speed of 2 - 8 m/min.
The conveyor belt 3 is made of material having a breathable
nature and a suction box 21 is opposed to the sucker 2 with this
conveyor belt 3 therebetween. The continuous fibers 15
emerging from the outlet 19 swing transversely as well as
longitudinally of the conveyor belt 3 under the effect of
compressed air andsuction.Consequently,the continuous fibers
15 are accumulated on the conveyor belt 3 in an irregular pattern
to form web 22.
The high pressure water jet ejector 4 has single or dual
or more nozzle arrays) 24 each comprising a plurality of
orifices 23 arranged in line transversely of the conveyor belt
3 at a pitch of 0.3 - 3 mm and a suction box 26 opposed to these
nozzle array( s ) with the conveyor belt 3 therebetween. In the
case of dual nozzle arrays 24, for example, the orifices 23 of
the first array may stabilize texture of the web 22 by ejecting
water jet streams of 20kgf/cmZ and the orifices 23 of the second
array serve may partially orienting the continuous fibers 15
so as to extend in a travelling direction of the web 22 or may
partially intertwine the continuous fibers 15 with one another
to improve a tensile strength of the web 22. The web 22 may
CA 02326263 2000-11-17
be subsequently dried on a step of drying ( not illustrated ) to
form nonwoven fabric 26 which is, in turn, taken up by the take-up
roller 6 in the form of a roll.
The continuous fibers 15 and the nonwoven fabric 26
obtained through the above-mentioned series of steps under
operating conditions as will be described have presented
physical properties as follow:
(Operating conditions)
Resin used as the starting material: Polypropylene (MFR = 70
g/10 min)
Spinning nozzle:
Orifice diameter: 0.35 mm
Number of orifices: 600
Orifice pitch: 1 mm
Temperature: 230°C
Discharge: 0.13 g/min/nozzle
Hot blast:
Temperature: 230°C
Flow rate: 1.5 Nm'/min
Compressed air at the normal temperature:
Pressure: 1.0 kgf/cmsG
Flow rate: 6.0 Nm'/min
Conveyor belt:
CA 02326263 2000-11-17
_g_
Distance from the spinning nozzle: 490 mm
Travelling speed: 4.4 m/min
High pressure water jet ejection:
First array: at a pressure of 20 kgf/cm2
Second array: at a pressure of 100 kgf/cm~
(Physical properties of the continuous fibers)
Average f fiber diameter : 8 . 9 ,c.Lm ( 0 . 51 d )
Standard deviation of the fiber diameter: 1.03
Tensile strength: 1.72 g/d
Tensile breaking extension: 6.38 mm
Condition of tension:
Distance between chucks: 0 mm
Tensile speed: 10 mm/min
Birefringence (On): 0.027
(Physical properties)
Hasis weight: 34.2 g/m~
Thickness (under a measuring load of 3 g/cm~): 0.48 mm
Tensile strength in MD (machine direction): 16550 g/width of
50 mm)
Tensile breaking extension in MD: 193 %
Tensile strength in CD (cross direction): 8248 g/width of 50
mm
Tensile breaking extension in CD: 197 %
CA 02326263 2000-11-17
-9-
Condition of tension:
Distance between chucks: 10 mm
Tensile speed: 10 mm/min
As will be apparent from the physical properties of the
continuous fibers and the nonwoven fabric as indicated above,
the novel process for making a nonwoven fabric enables the
continuous fibers 15 to have a relatively small fineness, e.g.,
of 0.006 - 05.8 d and, at the same time, enables unevenness
possibly occurring in the fineness to be alleviated. The
continuous fibers 15 obtained by such a novel process are
practically free from heat-sealing with one another but only
mechanically entangled with one another throughout the process
to form the nonwoven fabric 26. In addition, such mechanical
entanglement is not tight because the fiber is continuous, so
these continuous fibers 15 moderately restrict their relative
movement. The nonwoven fabric 26 made of such continuous fibers
15 offer soft and comfortable touch. The continuous fibers 15
appropriately stretched to obtain a birefringence of 0.019
-0.030 have a high breaking extension since a degree at which
the polypropylene molecules have been stretched is not so high
that a stretchability of the continuous fibers 15 might be
significantly restricted thereby. For example, a tensile test
with 0 mm distance between chucks indicated that the continuous
CA 02326263 2000-11-17
-10-
fibers 15 as a typical embodiment of this invention can be
stretched to 6.38 mm. The nonwoven fabric 26 formed by
mechanically entangling such continuous fibers 15 with one
another under the effect of high pressure water jet streams has
a breaking extension as high as 100 - 300 % in MD as well as
in CD because of a high breaking extension of the continuous
fibers 15 and a moderate intertwining among these fibers 15.
The nonwoven fabric 26 as one embodiment of this invention has
a breaking extension of 193 % in MD and a breaking extension
of 197 % in CD.
The nonwoven fabric 26 obtained by the novel process is
useful not only as disposable sanitary articles such as
disposable diapers, sanitary napkins or disposable gowns to be
used on the medical site but also as filters, wet wipes or the
like.
The process according to this invention makes it possible
to obtain a nonwoven fabric made of polypropylene having a
fineness of 0.006 - 5.8 deniers, a birefringence of 0.019 - 0.030
and a tensile strength of 1 - 3 g/d. In this nonwoven fabric,
a degree at which the polypropylene molecules are oriented in
the course of spinning the continuous fibers is relatively low
and, in addition, the continuous fibers are intertwined one with
another not so tightly that they might significantly restrict
CA 02326263 2000-11-17
-11-
their relative movement. Such continuous fibers offer a
comfortable soft touch and a high breaking extension.