Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
r
a
DEMANDES OU BREVETS VOLUMINEUX
LA PRESENTS PART1E DE CETTE DEMANDS OU CE BREVET
COMPREND PLUS D'UN TOME.
CECt EST LE TOME '/ DE y
NOTE: ~ Pour les tomes additionels, veuillez contacter le Bureau canadien des
brevets
JUMBO APPLICATIONS/PATENTS
THIS SECTION OF THE APPL1CATIONIPATENT CONTAINS MORE
THAN ONE VOLUME
THtS IS VOLUME ~ , OF
NOTE: For additional volumes please contact the Canadian Patent Office
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- I -
BRIDGED HETEROCYCI~IC DERIVATIVES
This application claims the benefit of the filing date
of Provisional U.S. Patent Application No. 60/101,077,
filed on September 18, 1998, and U.S. Patent Application
No. 09/159,105, filed September 23, 1998, the entire
contents of which are herein incorporated by reference.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of Invention
This invention relates generally to novel bridged
heterocyclic compounds, and their preparation and use for
preventing and/or treating neurological disorders,
including physically damaged nerves and neurodegenerative
diseases; for treating alopecia and promoting hair growth;
for treating vision disorders and/or improving vision; and
for treating memory impairment and/or enhancing memory
performance in an animal requiring or benefitting from such
treatment, using low molecular weight, small molecule
bridged heterocyclic derivative compounds.
Descris~tion of Related Art
A. Neuroimmunophilins
The peptidyl-prolyl isomerases ("PPIases") are a
family of ubiquitous enzymes which catalyze the
interconversion of cis and trans amide bond rotamers
adjacent to proline residues in peptide substrates. See,
for example, Galat, A., Eur. J. Biochem. (1993) 216:689-707
and Kay, J.E., Biochem. J. (1996) 314:361-385. The PPIases
have been referred to as "immunophilins" because of their
interaction with certain immunosuppressant drugs.
Schreiber, S.L., Science (1991) 251:283-287; Rosen, M.K.
and Schreiber, S.L., Angew. Chem. Intl. Ed. Engi. (1992)
31:389-400.
The PPIase, cyclophilin A, was found to be the
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 2 -
intracellular protein target for the potent
immunosuppressant drug cyclosporin A. Subsequently, the
structurally unrelated macrolide immunosuppressant FK506
was discovered to bind to a different PPIase enzyme which
was named FK506-binding protein, or FKBP. Rapamycin,
another macrolide drug which is a structural analogue of
FK506, also interacts with FKBP.
All three of these drugs bind to their respective
immunophilins and inhibit the respective PPIase activities.
However, inhibition of immunophilin enzymatic activity is
not the cause of the observed immunosuppressive effects.
Binding of the drugs to the immunophilins results in the
formation of "activated complexes", which interact with
downstream proteins to inhibit proliferation of
T-lymphocytes. Schreiber, supra; Rosen, et al., supra. In
the case of FK506, binding to FKBP results in a drug-
protein complex which is a potent inhibitor of the calcium-
calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase, calcineurin.
Bierer, B.E., Mattila, P.S., Standaert, R.F., Herzenberg,
L.A., Burakoff, S.J., Crabtree, G., Schreiber, S.L., Proc.
Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (1990) 87:9231-9235; Liu, J., Farmer,
J.D., Lane, W.S., Friedman, J., Weissman, I., Schreiber,
S.L.; Cell (1991) 66:807-815.
Neither FK506 or FKBP alone appreciably inhibits
calcineurin's activity. Inhibiting calcineurin blocks the
signaling pathway by which the activated T-cell receptor
causes transcription of the gene for interleukin-2,
inhibiting the immune response. Despite the structural
dissimilarity between FK506 and cyclosporin A (and
cyclophilin and FKBP), the cyclosporin A-cyclophilin
complex also inhibits calcineurin, and thus cyclosporin A
and FK506 have the same mechanism of action.
On the other hand, while rapamycin and FK506 have
similar structures and bind to the same immunophilin
(FKBP), rapamycin's mechanism of action is different from
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 3 -
that of FK506. The complex of FKBP12 with rapamycin
interacts with a protein called FRAP, or RAFT, and in so
doing blocks the signal pathway leading from the IL-2
receptor on the surface of T-cells to promotion of entry
into the cell cycle in the nucleus. Sabatini, D.M.,
Erdjument-Bromage, H., Lui, M.; Tempst, P., Snyder, S.H.,
Cell (1994) 78:35-43; Brown, E.J., Albers, M.W., Shin,
T.B., Ichikawa, K., Keith, C.T., Lane, W.S., Schreiber,
S.L. Nature (1994) 369:75-758; Brown, E.J., Beal, P.A.,
Keith, C.T., Chen, J., Shin, T.B., Schreiber, S.L., Nature
(1995) 377:441-446.
Thus, all three drugs produce the same effect --
suppression of T-cell proliferation -- but do so by
inhibiting distinct signal transduction pathways. The
introduction of cyclosporin("CsA") marked a breakthrough in
organ transplantation, and the drug became a major
pharmaceutical product. The subsequent discovery of
rapamycin ("Rapamycin") and FK506 further fueled interest
in the cellular basis of the actions of these drugs. The
discovery of the interaction of the immunophilins with CsA,
FK506 and Rapamycin led to research on the mechanistic
basis of immunophilin-mediated immunosuppression.
B. Immunophilins and the Nervous System
Because the initial interest in the immunophilins was
largely driven by their role in the mechanism of action of
the immunosuppressant drugs, most of the original studies
of these proteins and their actions focused on the tissues
of the immune system. In 1992, it was reported that levels
of FKBP12 in the brain were 30 to 50 times higher than in
the immune tissues. Steiner, J.P., Dawson, T.M., Fotuhi,
M., Glatt, C.E., Snowman, A.M., Cohen, N., Snyder, S.H.,
Nature (1992) 358:584-587. This finding suggested a role
for the immunophilins in the functioning of the nervous
system. Both FKBP and cyclophilin were widely distributed
in the brain and were found almost. exclusively within
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 4 -
neurons. The distribution of the immunophilins in the
brain closely resembled that of calcineurin, suggesting a
potential neurological link. Steiner, J.P., Dawson, T.M.,
Fotuhi, M., Glatt, C.E., Snowman, A.M., Cohen, N., Snyder,
S.H., Nature (1992) 358:584-587; Dawson, T.M., Steiner,
J.P., Lyons, W.E., Fotuhi, M., Blue, M., Snyder, S.H.,
Neuroscience (1994) 62:569-580.
Subsequent work demonstrated that the phosphorylation
levels of several known calcineurin substrates were altered
in the presence of FK506. Steiner, J.P., Dawson, T.M.,
Fotuhi, M., Glatt, C.E., Snowman, A.M., Cohen, N., Snyder,
S.H., Nature (1992) 358:584-587. One of the proteins
affected by FK506 treatment, GAP-93, mediates neuronal
process elongation. Lyons, W.E., Steiner, J.P., Snyder,
S.H., Dawson, T.M., J. Neurosci. (1995) 15:2985-2994. This
research revealed that FKBP12 and GAP-43 were upregulated
in damaged facial or sciatic nerves in rats. Also, FKBP12
was found in very high levels in the growth cones of
neonatal neurons. FK506 was tested to determine whether or
not it might have an effect an nerve growth or
regeneration. In cell culture experiments with PC12 cells
or sensory neurons from dorsal root ganglia, FK506 promoted
process (neurite) extension with subnanomolar potency.
Lyons, W.E., George, E.B., Dawson, T.M., Steiner, J.P.,
Snyder, S.H., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (1994)
91:3191-3195. Gold et al. demonstrated that FK506
functioned as a neurotrophic agent .in vivo. In rats with
crushed sciatic nerves, FK506 accelerated nerve
regeneration and functional recovery. Gold, B.G., Storm-
Dickerson, T., Austin, D.R., Restorative Neurol. Neurosci.,
(1994) 6:287; Gold, B.G., Katoh, K., Storm-Dickerson, T.J,
Neurosci. (I995) 15:7509-7516. See, also, Snyder, S.H.,
Sabatini, D.M., Nature Medicine (1995) 1:32-37
(regeneration of lesioned facial nerves in rats augmented
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 5 -
by FK506).
Besides FK506, rapamycin and cyclosporin also produced
potent neurotrophic effects in vitro in PC12 cells and
chick sensory neurons. Steiner, J.P., Connolly, M.A.,
Valentine, H.L., Hamilton, G.S., Dawson, T.M., Hester, L.,
Snyder, S.H., Nature Medicine (1997) 3:421-428. As noted
above, the mechanism for immunosuppression by rapamycin is
different than that of FK506 or cyclosporin. The
observation that rapamycin exerted neurotrophic effects
similar to FK506 and cyclosporin suggested that the nerve
regenerative effects of the compounds are mediated by a
different mechanism than that by which they suppress T-cell
proliferation.
Analogues of FK506, rapamycin, and cyclosporin which
bind to their respective immunophilins, but are devoid of
immunosuppressive activity, are known in the art. Thus,
the FK506 analogue L-685,818 binds to FKBP but does not
interact with calcineurin, and is therefore
nonimmunosuppressive. Dumont, F.J., Staruch, M.J., Koprak,
S.L., J. Exp. Med. (1992) 176:751-760.
Similarly, 6-methyl-alanyl cyclosporin A (6-[Me]-ala-
CsA) binds to cyclophilin but likewise lacks the ability to
inhibit calcineurin. The rapamycin analogue WAY-124,466
binds FKBP but does not interact with RAFT, and is likewise
nonimmunosuppressive. Ocain, T.D., Longhi, D., Steffan,
R.J., Caccese, R.G., Sehgal, S.N., Biochem. Biophys. Res.
Commun. (1993) 192:1340-1346; Sigal, N.H., Dumont, F.,
burette, P., Siekierka, J.J., Peterson, L., Rich, D., J.
Exp. Med. (1991) 173:619-628. These nonimmunosuppressive
compounds were shown to be potent neurotrophic agents in
vitro, and one compound, L-685,818, was as effective as
FK506 in promoting morphological and functional recovery
following sciatic nerve crush in rats. Steiner, J.P.,
Connolly, M.A., Valentine, H.L., Hamilton, G.S., Dawson,
T.M., Hester, L., Snyder, S.H., Nature Medicine (1997)
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 6 -
3:421-428. These results demonstrated that the
neurotrophic properties of the immunosuppressant drugs
could be functionally dissected from their immune system
effects.
Published work by researchers studying the mechanism
of action of FK506 and similar drugs had shown that the
minimal FKBP-binding domain of FK506 (as formulated by Holt
et al., BioMed. Chem. Lett. (1994) 4:315-320) possessed
good affinity for FKBP. Hamilton et al. proposed that the
neurotrophic effects of FK506 resided within the
immunophilin binding domain, and synthesized a series of
compounds which were shown to be highly effective in
promoting neurite outgrowth from sensory neurons, often at
picomolar concentrations. Hamilton, G.S., Huang, W.,
Connolly, M.A., Ross, D.T., Guo, H., Valentine, H.L.,
Suzdak, P.D., Steiner, J.P.; BioMed. Chem. Lett. (1997).
These compounds were shown to be effective in animal models
of neurodegenerative disease.
C. FKBP12 Inhibitors/Liaands
A number of researchers in the early 1990s explored
the mechanism of immunosuppression by FK506, cyclosporin
and rapamycin, and sought to design second-generation
immunosuppressant agents that lacked the toxic side effects
of the original drugs. A pivotal compound, 506BD (for
"FK506 binding domain"--see Bierer, B.E., Somers, P.K.,
Wandless, T-J., Burakoff, S.J., Schreiber, S.L., Science
(1990) 250:556-559), retained the portion of FK506 which
binds FKBP12 in an intact form, while the portion of the
macrocyclic ring of FK506 which extends beyond FKBP12 in
the drug-protein complex was significantly altered. The
finding that 506BD was a high-affinity ligand for, and
inhibitor of, FK506, but did not suppress T-cell
proliferation was the first demonstration that the
immunosuppressant effects of FK506 were not simply caused
by rotamase activity inhibition.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US9$/25577
In addition to various macrocyclic analogues of FK506
and rapamycin, simplified compounds which represent the
excised FKBP binding domain of these drugs were synthesized
and evaluated. Non-macrocyclic compounds with the
FKBP-binding domain of FK506 excised possess lower affinity
for FKBP12 than the parent compounds. Such structures
still possess nanomolar affinity for the protein. See,
e.g., Hamilton, G.S., Steiner, J.P., Curr. Pharm. Design
(1997) 3:405-428; Teague, S.J., Stocks, M.J., BioMed.
Chem. Lett., (1993) 3:1947-1950; Teague, S.J., Cooper,
M.E., Donald, D.K., Furber, M., BioMed. Chem. Lett. (1994)
4:1581-1584.
Holt et al. published several studies of simple
pipecolate FKBP12 inhibitors which possessed excellent
affinity for FKBP12. In initial studies, replacement of
the pyranose ring of FK506 mimetics demonstrated that
simple alkyl groups such as cyclohexyl and dimethylpentyl
worked well in this regard. Holt et al., BioMed. Chem.
Lett. (1994) 4:315-320. Simple compounds possessed good
affinity for FKBP12 (Ki values of 250 and 25 nM,
respectively). These structures demonstrated that these
simple mimics of the binding domain of FK506 bound to the
immunophilin in a manner nearly identical to that of the
corresponding portion of FK506. Holt, D.A., Luengo, J.I.,
Yamashita, D.S., Oh, H.J., Konialian, A.L., Yen, H.K.,
Rozamus, L.W., Brandt, M., Bossard, M.J., Levy, M.A.,
Eggleston, D.S., Liang, J., Schultz, L.W.; Stout, T.J.;
Clardy, I., J. Am. Chem. Soc. (1993) 115:9925-9938.
Armistead et al. also described several pipecolate
FKBP12 inhibitors. X-ray structures of the complexes of
these molecules with FKBP also demonstrated that the
binding modes of these simple structures were related to
that of FK506. Armistead, D.M., Badia, M.C., Deininger,
D.D., Duffy, J.P., Saunders, J.O., Tung, R.D., Thomson,
J.A.; DeCenzo, M.T.; Futer, 0., Livingston, D.J., Murcko,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
_ $ _
M.A., Yamashita, M.M., Navia, M.A., Acta Cryst. (1995)
D51:522-528.
As expected from the noted effector-domain model,
FKBP12 ligands lacking an effector element were inactive as
immunosuppressant agents, failing to suppress lymphocyte
proliferation both in vitro and in vivo.
D. Neuroprotective/Neuroregenerative Effects of FKBP12
Ligands
Steiner et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,696,135 (issued
December 9, 1997) describe the neurotrophic actions of a
large number of compounds such as those described above.
Cultured chick sensory neurons were used as an in vitro
assay to measure the ability of compounds to promote
neurite outgrowth (fiber extension) i.n neurons. Compounds
were also tested for their ability to bind to FKBP12 and
inhibit its enzymatic (rotamase) activity. As the data
demonstrate, many of these compounds were found to be ,
extremely potent nerve growth agents, promoting fiber
extension from cultured neurons with half-maximal effects
seen in some cases at picomolar concentrations. The effects
of these simple FKBP12 ligands on nervous tissue are
comparable to, or in some cases more potent than, FK506
itself.
Some of the compounds were also shown to promote
regrowth of damaged peripheral nerves in vivo. Steiner,
J.P., Connolly, M.A., Valentine, H.L., Hamilton, G.S.,
Dawson, T.M., Hester, L., Snyder, S.H., Nature Medicine
(1997) 3:421-428. In whole-animal experiments in which the
sciatic nerves of rats were crushed with forceps and
animals treated with these compounds subcutaneously, there
was found significant regeneration of damaged nerves
relative to control animals, resulting in both more axons
in drug-treated animals and axons with a greater degree of
myelination. Lesioning of the animals treated only with
vehicle caused a significant decrease in axon number (500
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 9 -
decrease compared to controls) and degree of myelination
(90% decrease compared to controls). Treatment with the
FKBP12 ligands resulted in reduction in the decrease of
axon number (25o and 5o reduction, respectively, compared
to controls) and in the reduction of myelination levels
(65% and 50~ decrease compared to controls). Similar
results were subsequently reported by Gold et al. Gold,
B.G., Zeleney-Pooley, M., Wang, M.S., Chaturvedi, P.;
Armistead, D.M., Exp. Neurobiol. (1997) 147:269-278.
ZO Several of these compounds were shown to promote
recovery of lesioned central dopami.nergic neurons in an
animal model of Parkinson's Disease. Hamilton, G.S.,
Huang, W., Connolly, M.A., Ross, D.T., Guo, H., Valentine,
H.L., Suzdak, P.D., Steiner, J.P., BioMed. Chem. Lett.
(1997). N-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
(~~MPTP") is a neurotoxin which selectively destroys
dopaminergic neurons. Gerlach, M., Riederer, P., Przuntek,
H., Youdim, M.B., Eur. J. Pharmacol. (1991) 208:273-286.
The nigral-striatal dopaminergic pathway in the brain is
responsible for controlling motor movements.
Parkinson's Disease is a serious neurodegenerative
disorder resulting from degeneration of this motor pathway.
Lesioning of the nigral-striatal pathway in animals with
MPTP has been utilized as an animal model of Parkinson's
Disease. In mice treated with MPTP and vehicle, a
substantial loss of 60-700 of functional dopaminergic
terminals was observed as compared to non-lesioned animals.
Lesioned animals receiving FKBP12 ligands concurrently with
MPTP showed a striking recovery of TH-stained striatal
dopaminergic terminals, as compared with controls,
suggesting that FKBP12 ligands may possess potent
neuroprotective and neuro-regenerative effects on both
peripheral as well as central neurons.
Other compounds which have an affinity for FKBP12 may
also possess neurotrophic activities similar to those
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 10 -
described above. For example, one skilled in the art is
referred to the following patents and patent applications
for their teaching of neurotrophic compounds which are
lacking immunosuppressive activity:
Hamilton et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,614,547
(March 25, 1997);
Steiner et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,696,135 (Dec.
9, 1997 ) ;
Hamilton et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,721,256 (Feb.
24, 1998);
Hamilton et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,786,378 (July
28, 1998);
Hamilton et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,795,908 (Aug.
18, 1998);
Steiner et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,798,355
(August 25, 1998);
Steiner et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,801,197 (Sept.
1, 1998); and
Li et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,801,187 (Sept. 1,
1998)
These molecules are effective ligands for, and
inhibitors of, FKBP12 and are also potent neurotrophic
agents in vitro, promoting neurite outgrowth from cultured
sensory neurons at nanomolar or subnanolar dosages.
Additionally, as noted, compounds which possess
immunosuppressive activity, for example, FK506, CsA and
Rapamycin, among others, also may possess a significant
level of neurotrophic activity. Thus, to the extent that
such compounds additionally may possess activities,
including neurotrophic activities, such compounds are
intended to be included within the term
"sensorineurotrophic compound" as used herein. The
following publications provide disclosures of compounds
which presumably possess immunosuppressive activities, as
well as possibly other activities, and are likewise
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 11 -
intended to be included within the term
"sensorineurotrophic compound" as used herein:
Armistead et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,192,773
(March 9, 1993);
Armistead et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,330,993
(July 19, 1994);
Armistead et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,516,797 (May
14, 1996);
Armistead et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,620,971
(Apr. 15, 1997);
Armistead et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,622,970
(Apr. 22, 1997);
Armistead et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,665,774
(Sept. 9, 1997); and
Zelle et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,780,484 (July
14, 1998) .
The neuroregenerative and neuroprotective effects of
FKBP12 ligands are not limited to dopaminergic neurons in
the central nervous system. In rats treated with
para-chloro-amphetamine ("PCA"), an agent which destroys
neurons which release serotonin as a neurotransmitter,
treatment with an FKBP ligand was reported to exert a
protective effect. Steiner, J.P., Hamilton, G.S., Ross,
D.T., Valentine, H.L., Guo, H., Connolly, M.A., Liang, S.,
Ramsey, C., Li, J.H., Huang, W., Howorth, P.; Soni, R.,
Fuller, M., Sauer, H., Nowotnick, A., Suzdak, P.D., Proc.
Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (1997) 94:2019-2024. In rats lesioned
with PCA, cortical density of serotonin fibers was reduced
90o relative to controls. Animals receiving the ligand
showed a greater serotonin innervation in the cortex-
serotonergic innervation in the somatosensory cortex was
increased more than two-fold relative to lesioned, non-drug
treated animals.
Similarly, such ligands have been shown to induce
sprouting of residual cholinergic axons following partial
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 12 -
transection of the fimbria fornix in rats. Guo, H.,
Spicer, D.M., Howorth, P., Hamilton, G.S., Suzdak, P.D,
Ross, D.T., Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. (1997) 677.12. The
transection produced a 75-80o deafferentiation of the
hippocampus. Subcutaneous administration of the FBKP12
ligand produced a four-fold sprouting of spared residual
processes in the CA1, CA3 and dentate gyrus regions of the
hippocampus, resulting in significant recovery of
cholinergic innervation in all three regions as quantitated
by choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) density.
Taken together, the data in the noted references
indicate that certain ligands for FKBP 12, preferably those
which are non-immunosuppressive, comprise a class of potent
active neurotrophic compounds which have been referred to
as "neuroimmunophilins" or "neuroimmunophilin ligands" with
potential for therapeutic utility in the treatment or
prevention of neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, in the
context of the present invention, a sensorineurotrophic
compound is meant to encompass those compounds which have
been designated as neuroimmunophilins and which also may
have, but are not required to have, binding affinity for an
FKBP. The ultimate mechanism of action and whether or not
such compounds also possess other activity such as, for
example, immunosuppressive activity, is not determinative
of whether the compound is neurotrophic, promotes hair
growth, regenerates vision, or improves memory for purposes
of the invention, as long as the compound in question
possesses the desired effect on nerve cells, hair
follicles, eye tissues, or brain cells.
Until the present invention, none of the prior work
disclosed the use of the disclosed compounds in the
treatment or prevention of neurological disorders,
alopecia, vision disorders, memory impairment, and
associated diseases. As described in more detail below,
the present invention is directed to such uses. To better
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 13 -
understand the invention, the following discussion on
preventing and/or treating neurological disorders,
including physically damaged nerves and neurodegenerative
diseases, and for treating memory impairment and/or
enhancing memory performance; for treating alopecia and
promoting hair growth; and for treating vision disorders
and/or improving vision; is provided:
1. Preventing And/or Treating Neurological Disorders
It has been found that picomolar concentrations of an
immunosuppressant such as FK506 and rapamycin stimulate
neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells and sensory nervous, namely
dorsal root ganglion cells (DRGs). Lyons et al., supra. In
whole animal experiments, FK506 has been shown to stimulate
nerve regeneration following facial nerve injury and
results in functional recovery in animals with sciatic
nerve lesions.
Several neurotrophic factors effecting specific
neuronal populations in the central nervous system have
been identified. For example, it has been hypothesized
that Alzheimer' s disease results from a decrease or loss of
nerve growth factor (NGF). It has thus been proposed to
treat Alzheimer's patients with exogenous nerve growth
factor or other neurotrophic proteins such as brain derived
nerve factor (BDNF), filial derived nerve factor, ciliary
neurotrophic factor, and neurotropin-3 to increase the
survival of degenerating neuronal populations.
Clinical application of these proteins in various
neurological disease states is hampered by difficulties in
the delivery and bioavailability of large proteins to
nervous system targets. By contrast, immunosuppressant
drugs with neurotrophic activity are relatively small and
display excellent bioavailability and specificity.
However, when administered chronically, immunosuppressants
exhibit a number of potentially serious side effects
including nephrotoxicity, such as impairment of glomerular
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 14 -
filtration and irreversible interstitial fibrosis (Kopp et
al., 1991, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1:162); neurological
deficits, such as involuntary tremors, or non-specific
cerebral angina such as non-localized headaches (De Groen
et al., 1987, N. Engl. J. Med. 31'7:861); and vascular
hypertension with complications resulting therefrom (Kahan
et al., 1989 N. Engl. J. Med. 321: 1725).
Accordingly, there is a need for small-molecule
compounds which are useful for neurotrophic effects and for
treating neurodegenerative disorders.
2. Treating Alopecia and Promotina Hair Growth
Hair loss occurs in a variety of situations. These
situations include male pattern alopecia, alopecia senilis,
alopecia areata, diseases accompanied by basic skin lesions
or tumors, and systematic disorders such as nutritional
disorders and internal secretion disorders. The mechanisms
causing hair loss are very complicated, but in some
instances can be attributed to aging, genetic disposition,
the activation of male hormones, the loss of blood supply
to hair follicles, and scalp abnormalities.
The immunosuppressant drugs FK506, rapamycin and
cyclosporin are well known as potent T-cell specific
immunosuppressants, and are effective against graft
rejection after organ transplantation. It has been
reported that topical, but not oral, application of FK506
(Yamamoto et al., J. Invest. Dermatol., 1994, 102, 160-164;
Jiang et al., J. Invest. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 523-525) and
cyclosporin (Iwabuchi et al., J. Dermatol. Sci. 1995, 9,
64-69) stimulates hair growth in a dose-dependent manner.
One form of hair loss, alopecia areata, is known to be
associated with autoimmune activities; hence, topically
administered immunomodulatory compounds are expected to
demonstrate efficacy for treating that type of hair loss.
The hair growth stimulating effects of FK506 have been the
subject of an international patent filing covering FK506
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00116603 PCT/US98/25577
- 15 -
and structures related thereto for hair growth stimulation
(Honbo et al., EP 0 423 714 A2). Honbo et al. discloses
the use of relatively large tricyclic compounds, known for
their immunosuppressive effects, as hair revitalizing
agents.
The hair growth and revitalization effects of FK506
and related agents are disclosed in many U.S. patents
(Goulet et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,258,389; Luly et al.,
U.S. Patent No. 5,457,111;~Goulet et al., U.S. Patent No.
5, 532, 248; Goulet et al. , U. S. Patent No. 5, 189, 042; and Ok
et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,208,241; Rupprecht et al., U.S.
Patent No. 5,284,840; Organ et al., U.S. Patent No.
5,284,877). These patents claim FK506 related compounds.
Although they do not claim methods of hair revitalization,
they disclose the known use of FK50Fi for effecting hair
growth. Similar to FK506 (and the claimed variations in
the Honbo et al. patent), the compounds claimed in these
patents are relatively large. Further, the cited patents
relate to immunomodulatory compounds for use in autoimmune
related diseases, for which FK506's efficacy is well known.
Other U.S. patents disclose the use of cyclosporin and
related compounds for hair revitalization (Hauer et al.,
U.S. Patent No. 5,342,625; Eberle, U.S. Patent No.
5,284,826; Hewitt et al., U.S. Patent No. 4,996,193).
These patents also relate to compounds useful for treating
autoimmune diseases and cite the known use of cyclosporin
and related immunosuppressive compounds for hair growth.
However, immunosuppressive compounds by definition
suppress the immune system and also exhibit other toxic
side effects. Accordingly, there is a need for non
immunosuppressant, small molecule compounds which are
useful as hair revitalizing compounds.
Hamilton and Steiner disclose in U.S. Patent No.
5,614,547 novel pyrrolidine carboxylate compounds which
bind to the immunophilin FKBP12 and stimulate nerve growth,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 16 -
but which lack immunosuppressive effects . Unexpectedly, it
has been discovered that these non-immunosuppressant
compounds promote hair growth with an efficacy similar to
FK506. Yet their novel small molecule structure and non-
immunosuppressive properties differentiate them from FK506
and related immunosuppressive compounds found in the prior
art.
3. Treating Vision Disorders And/or Improving Vision
The visual system is composed of the eyes, ocular
adnexa and the visual pathways. Dysfunction of the visual
system may lead to permanent or temporary visual
impairment, i.e, a deviation from normal in one or more
functions of the eye. Visual impairment manifests itself
in various ways and includes a broad range of visual
dysfunctions and disturbances. Without limitation, these
dysfunctions and disturbances include partial or total loss
of vision, the need for correction of visual acuity for
objects near and far, loss of visual field, impaired ocular
motility without diplopia (double vision), impaired or
skewed color perception, limited adaptation to light and
dark, diminished accommodation, metamorphopsic distortion,
impaired binocular vision, paresis of accommodation,
iridoplegia, entropion, ectropion, epiphora, lagophthalmos,
and scarring. See Physicians' Desk Reference (PDR) for
Ophthalmology, 16th Edition, 6:47 (1988). The visual
system may be adversely affected by various ophthalmologic
disorders, diseases, injuries, and complications,
including, without limitation, genetic disorders; disorders
associated with aging or degenerative diseases; disorders
correlating to physical injury to the eye, head, or other
parts of the body resulting from external forces; disorders
resulting from environmental factors; disorders resulting
from a broad range of diseases; and combinations of any of
the above.
The visual system is a complex system composed of
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 17 -
numerous components. Visual impairment can involve the
entire visual system, any one component, or any combination
of components, depending upon the precise nature of the
circumstances. The eye is composed of a lens, which is
suspended in the zonules of Zinn and is focused by the
ciliary body. The ciliary body also secretes aqueous
humor, which fills the posterior chamber, passes through
the pupil into the anterior chamber, then drains primarily
via the canal of Schlemm. The iris regulates the quantity
of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of its
central opening, the pupil. A visual image is focused onto
the retina, the fovea centralis being the retinal area of
sharpest visual acuity. The conjunctiva is the mucus
membrane which lines the eyelids and the eyeball, and ends
abruptly at the limbus conjunctivae, the edge of the
conjunctiva overlapping the cornea. The cornea is the
clear, transparent anterior portion of the fibrous coat of
the eye; it is important in light refraction and is covered
with an epithelium that differs in many respects from the
conjunctival epithelium.
The retina is the innermost, light sensitive portion
of the eye, containing two types of photoreceptors, cones,
which are responsible for color vision in brighter light,
and rods, which are essential for vision in dim light but
do not perceive colors. After light passes through the
cornea, lens system, and the vitreous humor, it enters the
retina from the inside; that is, it passes through the
ganglion cells and nerve fibers, the inner and outer
plexiform layers, the inner and outer nuclear layers, and
the internal and external limiting membranes before it
finally reaches the layer of photoreceptors located near
the outside of the retina, just inside the outermost
pigment epithelium layer. The cells of the pigment
epithelium layer act as an anatomical barrier to liquids
and substances located outside of the eye, forming the
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 fCT/US98/25577
- 18 -
"blood-retina" barrier, and provide nourishment, oxygen, a
source of functionally useful substances like vitamin A,
and phagocytosis of decomposition products to photoreceptor
cells. There is no anatomical connection between the
pigment epithelium and the photoreceptor layer, permitting
separation of the layers in some pathological situations.
When rods or cones are excited by light, signals are
transmitted through successive neurons in the retina
itself, into the optic nerve fibers, and ultimately to the
cerebral cortex. Both rods and cones contain molecules
that decompose on exposure to light and, in the process,
excite the nerve fibers leading from the eye. The molecule
in rods is rhodopsin. The three light-sensitive molecules
in cones, collectively called iodopsin, have compositions
only slightly different from that of rhodopsin and are
maximally excited by red, blue, or green light,
respectively.
Neither rods nor cones generate action potentials.
Rather, the light-induced membrane hyperpolarization
generated in the outer, photosensitive segment of a rod or
cone cell is transmitted from the outer segment through the
inner segment to the synaptic body by direct conduction of
the electrical voltage itself, a process called
electrotonic conduction. At the synaptic body, the
membrane potential controls the release of an unknown
transmitter molecule. In low light, rod and cone cell
membranes are depolarized and the rate of transmitter
release is greatest. Light-induced hyperpolarization
causes a marked decrease in the release of transmitter
molecules.
The transmitters released by rod and cone cells induce
signals in the bipolar neurons and horizontal cells. The
signals in both these cells are also transmitted by
electrotonic conduction and not by action potential.
The rod bipolar neurons connect with as many as 50 rod
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
19 -
cells, while the dwarf and diffuse bipolar cells connect
with one or several cone cells. A depolarizing bipolar
cell is stimulated when its connecting rods or cones are
exposed to light. The release of transmitter molecules
inhibits the depolarizing bipolar cell. Therefore, in the
dark, when the rods and cones are secreting large
quantities of transmitter molecules, the depolarizing
bipolar cells are inhibited. In the light, the decrease in
release of transmitter molecules from the rods and cones
reduces the inhibition of the bipolar cell, allowing it to
become excited. In this manner, both positive and negative
signals can be transmitted through different bipolar cells
from the rods and cones to the amacrine and ganglion cells .
As their name suggests, horizontal cells project
horizontally in the retina, where they may synapse with
rods, cones, other horizontal cells, or a combination of
cells types. The function of horizontal cells is unclear,
although some mechanism in the convergence of photoreceptor
signaling has been postulated.
All types of bipolar cells connect with ganglion
cells, which are of two primary types. A-type ganglion
cells predominately connect with rod bipolar cells, while
B-type ganglion cells predominately connect with dwarf and
diffuse bipolar cells. It appears that A-type ganglion
cells are sensitive to contrast, light intensity, and
perception of movement, while B-type ganglion cells appear
more concerned with color vision and visual acuity.
Like horizontal cells, the Amacrine cells horizontally
synapse with several to many other cells, in this case
bipolar cells, ganglion cells, and other Amacrine cells.
The function of Amacrine cells is also unclear.
The axons of ganglion cells carry signals into the
nerve fiber layer of the eye, where the axons converge into
fibers which further converge at the optic disc, where they
exit the eye as the optic nerve. The ganglion cells
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 20 -
transmit their signals through the optic nerve fibers to
the brain in the form of action potentials. These cells,
even when unstimulated, transmit continuous nerve impulses
at an average, baseline rate of about 5 per second. The
visual signal is superimposed onto this baseline level of
ganglion cell stimulation. It can be either an excitatory
signal, with the number of impulses increasing above the
baseline rate, or an inhibitory signal, with the number of
nerve impulses decreasing below the baseline rate.
As part of the central nervous system, the eye is in
some ways an extension of the brain; as such, it has a
limited capacity for regeneration. This limited
regeneration capacity further complicates the challenging
task of improving vision, resolving dysfunction of the
visual system, and/or treating or preventing ophthalmologic
disorders. Many disorders of the eye, such as retinal
photic injury, retinal ischemia-induced eye injury, age-
related macular degeneration, free radical-induced eye
diseases, as well as numerous other disorders, are
considered to be entirely untreatable. Other
ophthalmologic disorders, e.g., disorders causing permanent
visual impairment, are corrected only by the use of
ophthalmic devices and/or surgery, with varying degrees of
success.
The immunosuppressant drugs FK506, rapamycin, and
cyclosporin are well known as potent T-cell specific
immunosuppressants, and are effective against autoimmunity,
transplant or graft rejection, inflammation, allergic
responses, other autoimmune or immune-mediated diseases,
and infectious diseases. It has been disclosed that
application of Cyclosporin, FK-506, Rapamycin, Buspirone,
Spiperone, and/or their derivatives are effective in
treating some ophthalmologic disorders of these types.
Several ophthalmologic disorders or vision problems are
known to be associated with autoimmune and immunologically-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 21 -
mediated activities; hence, immunomodulatory compounds are
expected to demonstrate efficacy for treating those types
of ophthalmologic disorders or vision problems.
The effects of FK506, Rapamycin, and related agents in
the treatment of ophthalmologic diseases are disclosed in
several U.S. patents (Goulet et al., U.S. Patent No.
5,532,248; Mochizuki et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,514,686;
Luly et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,457,111; Russo et al., U.S.
Patent No. 5, 441, 937; Kulkarni, U. S. Patent No. 5, 387, 589;
Asakura et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,368,865; Goulet et al.,
U.S. Patent No. 5,258,389; Armistead et al., U.S. Patent
No. 5, 192, 773; Goulet et al. , U. S. Patent No. 5, 189, 042;
and Fehr, U.S. Patent No. 5,011,844). These patents claim
FK506 or Rapamycin related compounds and disclose the known
use of FK506 or Rapamycin related compounds in the
treatment of ophthalmologic disorders in association with
the known immunosuppressive effects of FK506 and Rapamycin.
The compounds disclosed in these patents are relatively
large. Further, the cited patents relate to
immunomodulatory compounds limited to treating autoimmunity
ar related diseases, or immunologically-mediated diseases,
for which the efficacy of FK506 and Rapamycin is well
known.
Other U.S. patents disclose the use of cyclosporin,
Spiperone, Buspirone, their derivatives, and other
immunosuppressive compounds for use in the treatment of
ophthalmologic diseases (Sharpe et al., U.S. Patent No.
5,703,088; Sharpe et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,693,645;
Sullivan, U.S. Patent No. 5,688,765; Sullivan, U.S. Patent
No. 5, 620, 921; Sharpe et al. , U. S. Patent No. 5, 574, 041;
Eberle, U.S. Patent No. 5,284,826; Sharpe et al., U.S.
Patent No. 5,244,902; Chiou et al., U.S. Patent Nos.
5,198,454 and 5,194,434; and Kaswan, U.S. Patent No.
4,839,342). These patents also relate to compounds useful
for treating autoimmune diseases and cite the known use of
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 22 -
cyclosporin, Spiperone, Buspirone, their derivatives, and
other immunosuppressive compounds in treating ocular
inflammation and other immunologically-mediated
ophthalmologic diseases.
The immunosuppressive compounds disclosed in the prior
art suppress the immune system, by definition, and also
exhibit other toxic side effects. Accordingly, there is a
need for non-immunosuppressant, small molecule compounds,
and compositions and methods for use of such compounds,
that are useful in improving vision; preventing, treating,
and/or repairing visual impairment or dysfunction of the
visual system; and preventing, treating, and/or resolving
ophthalmologic disorders.
There are also a number of patents on non
immunosuppressive compounds disclosing methods of use for
permitting or promoting wound healing (whether from injury
or surgery); controlling intraocular pressure (often
resulting from glaucoma); controlling neurodegenerative eye
disorders, including damage or injury to retinal neurons,
damage or injury to retinal ganglion cells, and macular
degeneration; stimulating neurite outgrowth; preventing or
reducing oxidative damage caused by free radicals; and
treating impaired oxygen and nutrient supply, as well as
impaired waste product removal, resulting from low blood
flow. These non-immunosuppressive substances fall into one
of two general categories: naturally occurring molecules,
such as proteins, glycoproteins, peptides, hormones, and
growth factors; and synthetic molecules.
Within the group of naturally occurring non
immunosuppressive molecules, several hormones, growth
factors, and signaling molecules have been patented for use
as supplements to naturally occurring quantities of such
molecules, as well as for targeting of specific cells where
the particular molecule does not naturally occur in a
mature individual. These patents generally claim methods
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 23 -
of use for reducing or preventing the symptoms of ocular
disease, or arresting or reversing vision loss.
Specifically, Louis et al., U.S. Patent Nos. 5,736,516
and 5,641,749, disclose the use of a glial cell line
derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) to stop or reverse the
degeneration of retinal neurons (i.e. photoreceptors) and
retinal ganglion cells caused by glaucoma, or other
degenerative or traumatic retinal diseases or injuries.
0'Brien, et al., U.S. Patent Nos. 5,714,459 and 5,700,909,
disclose the use of a glycoprotein, Saposin, and its
derivatives for stimulating neurite outgrowth and
increasing myelination. To stop or reverse degeneration of
retinal neurons, LaVail et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,667,968,
discloses the use of a variety of neurotrophic proteins,
including brain-derived neurotrophic factor, ciliary
neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3 or neurotrophin-4,
acidic or basic fibroblast growth factors, interleukin,
tumor necrosis factor-a, insulin-like growth factor-2 and
other growth factors. Wong et al., U.S. Patent No.
5,632,984, discloses the use of interferons, especially
interferon a-2a, for treating the symptoms of macular
degeneration by reducing hemorrhage and limiting
neovascularization. Finally, Wallace et al., U.S. Patent
No. 5,441,937, discloses the use of a lung-derived
neurotrophic factor (NTF) to maintain the functionality of
ciliary ganglion and parasympathetic neuron cells.
A key characteristic of factors derived from specific
cell lines is their localization to specific cell lines or
tissues; systemic treatment with these molecules would run
a substantial risk of unintended, and potentially
dangerous, effects in cell lines where the genes encoding
these molecules are inactive. Similarly, hormones and
growth factors often activate a large number of genes in
many cell lines; again, non-localized application of these
molecules would run a substantial risk of provoking an
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 24 -
inappropriate, and potentially dangerous, response.
Within the category of synthetic molecules, most of
the patented compounds are immunosuppressive and disclose
uses in treating inflammatory, autoimmune, and allergic
responses, as discussed above. A few others are non-
immunosuppressive and claim the ability to treat cellular
degeneration, and in some cases promote cellular
regeneration, most often in the context of their
antioxidant properties.
Specifically, Tso et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,527,533,
discloses the use of astaxanthin, a carotenoid antioxidant,
for preventing or reducing photoreceptor damage resulting
from the presence of free radicals. Similarly, Babcock et
al., U.S. Patent No. 5,252,319, discloses the use of
antioxidant aminosteroids for treating eye disease and
injury, by increasing resistance to oxidative damage.
Freeman, U.S. Patent No. 5,468,752, discloses the use of
the antiviral phosphonylmethoxyalkylcytosines to reduce
abnormally increased intraocular pressure.
Hamilton and Steiner disclose in U.S. Patent No.
5,614,547 novel pyrrolidine carboxylate compounds which
bind to the immunophilin FKBP12 and stimulate nerve growth,
but which lack immunosuppressive effects. Unexpectedly, it
has been discovered that these non-immunosuppressant
compounds promote improvements in vision and resolve
ophthalmologic disorders. Yet their novel small molecule
structure and non-immunosuppressive properties
differentiate them from FK506 and related immunosuppressive
compounds found in the prior art.
Further, these compounds may be differentiated from
the non-immunosuppressive compounds used to treat vision
disorders by their novel small molecule structure and their
lack of general, systemic effects. Naturally occurring
hormones, growth factors, cytokines, and signaling
molecules are generally multifunctional and activate many
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US9$/25577
- 25 -
genes in diverse cell lines. The present compounds do not,
thus avoiding the unexpected, and potentially dangerous,
side effects of systemic use. Similarly, the present
compounds also avoid the potential unexpected side effects
of introducing cell line-specific molecules into other cell
lines were they do not naturally occur.
Regardless of the cause, there exists a need to
prevent or treat neurological disorders, including
physically damaged nerves and neurodegenerative diseases;
for treat alopecia and promote hair growth; treat vision
disorders and/or improve vision; and treat memory
impairment and/or enhance memory performance. The present
invention provides such methods.
BRIEF SU~RY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is based on the discovery that
bridged heterocyclic derivative compounds may be useful for
treating neurodegenerative disorders, for treating alopecia
and related hair loss disorders, for treating vision
disorders and/or improving vision, and for treating memory
impairment and/or enhancing memory performance.
Accordingly, a novel class of heterocyclic derivative
compounds, containing one or more bridged moieties in the
central structure and/or its substituents, is provided.
These compounds stimulate neuranal regeneration and
outgrowth and as such are useful for treating neurological
disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. These compounds
also promote hair growth and as such are useful for
treating hair loss disorders. These compounds also are
useful for treating vision disorders, improving vision,
treating memory impairment, or enhancing memory
performance. A preferred feature of the compounds of the
present invention is that they do not exert any significant
immunosuppressive activity and/or are non-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 26 -
immunosuppressive.
In particular, the present invention provides methods
for treating neurodegenerative disorders comprising
administering to a patient in need thereof a
therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the
invention. By way of example, the disorder to be treated
may be associated with injury or cellular degeneration.
Thus, a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of
the invention may be administered to promote the
protection, survival, or regeneration of certain nerve,
hair, eye, or brain cells.
The present invention further relates to a
pharmaceutical composition which comprises:
(i) an effective amount of a bridged heterocyclic
derivative compound, containing one or more bridged
moieties in the central structure or its substituents, for
treating neurodegenerative disorders, for treating alopecia
and related hair loss disorders, for treating vision
disorders and/or improving vision, or for treating memory
impairment and/or enhancing memory performance in an
animal; and
(ii) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
It is further contemplated that a compound of the
invention may be administered separately, sequentially, or
simultaneously in combination or conjunction with an
effective amount of a second therapeutic agent or any other
agent useful for the treatment of the disorders enumerated
herein.
The invention also provides for the use of compound ( s )
of the invention in the manufacture of a medicament or
pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of the
disorders enumerated herein. Such pharmaceutical
compositions include, as appropriate to the specific
disorder, topical, systemic, oral or injectable
formulations. It is further contemplated that the
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/2557~
- 27 -
compounds) of the invention may be administered with an
effective amount of a second therapeutic agent for the
treatment of the enumerated disorders. A variety of
pharmaceutical formulations and different delivery
techniques are described in further detail below.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG. 1 is a photograph of mice treated with a vehicle
after six weeks. FIG. 1 shows that less than 3% of the
shaved area is covered with new hair growth when the
vehicle (control) is administered.
FIG. 2 is a photograph of mice treated with 10 uM of
a related compound, GPI 1046, after six weeks. FIG. 2
shows the remarkable effects of N-heterocyclic derivative
non-immunosuppressive neuroimmunophilin FKBP ligands
wherein 900 of the shaved area is covered with new hair
growth.
FIG. 3 is a photograph of mice treated with 30 uM of
GPI 1046 after six weeks. FIG. 3 shows the remarkable
ability of N-heterocyclic derivative non-immunosuppressive
neuroimmunophilin FKBP ligands to achieve, essentially,
complete hair regrowth in the shaved area.
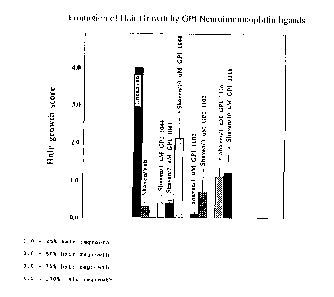
FIG. 4 is a bar graph depicting the relative hair
growth indices of mice treated with a vehicle, FK506, and
various related N-heterocyclic derivative non
immunosuppressive neuroimmunophilin FKBP ligands 14 days
after treatment with each identified compound. FIG. 4
demonstrates the remarkable early hair growth promoted by
N-heterocyclic derivative non-immunosuppressive
neuroimmunophilin FKBP ligands.
FIGS. 5A, 5B, and SC show that GPI 1046 protects
retinal ganglion cells against degeneration following
retinal ischemia.
FIG. 6 shows that GPI 1046 prevents degeneration of
optic nerve axons and myelin following retinal ischemia.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 28 -
FIG. 7 shows that GPI 1046 provides moderate
protection against retinal ganglion cell death after optic
nerve transection.
FIG. 8 shows that GPI 1046 treatment duration
significantly affects the process of optic nerve axonal
degeneration after transection.
FIG. 9 shows that GPI 1046 treatment produces a
greater effect on optic nerve axons than ganglion cell
bodies.
FIG. 10 shows that GPI 1046 treatment for 28 days
after optic nerve transection prevents myelin degeneration
in the proximal stump.
FIG. 11 shows that FKBP-12 immunohistochemistry labels
oligodendroglia (large dark cells with fibrous processes),
the cells which produce myelin, located between the
fascicles of optic nerve fibers, and also some optic nerve
axons.
FIG. 12 shows GPI 1046 treatment for 28 days after
optic nerve transection prevents myelin degeneration in the
distal stump.
FIG. 13 shows that 28 day treatment with GPI 1046
treatment beginning 8 weeks after onset of streptozotocin
induced diabetes decreases the extent of neovascularization
in the inner and outer retina and protects neurons in the
inner nuclear layer (INL) and ganglion cell layer (GCL)
from degeneration.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Definitions
~~Alkenyl" means a branched or unbranched unsaturated
hydrocarbon chain comprising a designated number of carbon
atoms. For example, C2-C6 straight or branched alkenyl
hydrocarbon chain contains 2 to 6 carbon atoms having at
least one double bond, and includes but is not limited to
substituents such as ethenyl, propenyl, iso-propenyl,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 29 -
butenyl, iso-butenyl, tert-butenyl, n-pentenyl, n-hexenyl,
and the like. It is also contemplated as within the scope
of the present invention that "alkenyl" may also refer to
an unsaturated hydrocarbon chain wherein any of the carbon
atoms of said alkenyl are optionally replaced with 0, NH,
S, or 502. For example, carbon 2 of 4-pentene can be
replaced with O to form (2-propene)oxymethyl.
"Alkoxy" means the group -OR wherein R is alkyl as
herein defined. Preferably, R is a branched or unbranched
saturated hydrocarbon chain containing 1 to 6 carbon atoms .
"Alkyl" means a branched or unbranched saturated
hydrocarbon chain comprising a designated number of carbon
atoms. For example, C1-C6 straight or branched alkyl
hydrocarbon chain contains 1 to 6 carbon atoms, and
includes but is not limited to substituents such as methyl,
ethyl, propyl, iso-propyl, butyl, iso-butyl, tert-butyl, n-
pentyl, n-hexyl, and the like. It is also contemplated as
within the scope of the present invention that "alkyl" may
also refer to a hydrocarbon chain wherein any of the carbon
atoms of said alkyl are optionally replaced with O, NH, S,
or S02. For example, carbon 2 of n-pentyl can be replaced
with O to form propyloxymethyl.
It should be kept in mind that, throughout this
application, "R" or "R~", where n is a number, is used to
designate various alkyl (and other) substituents. As
indicated throughout, these R groups are independently
selected. Thus, for example, the fact that R1 may be a
branched alkyl in one context does not require that R1 be
the same branched alkyl, and does not. prohibit that R1 be,
for example, a straight chain alkenyl, in another context
in the same molecule . It is intended that all "R~" are
selected independently of all other "R~", whether or not
the term "independently selected" is used or is
inadvertently omitted.
"Alopecia" refers to deficient hair growth and partial
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 30 -
or complete loss of hair, including without limitation
androgenic alopecia (male pattern baldness), toxic
alopecia, alopecia senilis, alopecia areata, alopecia
pelada and trichotillomania. Alopecia results when the
pilar cycle is disturbed. The most frequent phenomenon is
a shortening of the hair growth or anagen phase due to
cessation of cell proliferation. This results in an early
onset of the catagen phase, and consequently a large number
of hairs in the telogen phase during which the follicles
are detached from the dermal papillae, and the hairs fall
out. Alopecia has a number of etiologies, including
genetic factors, aging, local and systemic diseases,
febrile conditions, mental stresses, hormonal problems, and
secondary effects of drugs.
"Aralkyl" refers to alkyl or alkylene (alkenyl) chain
which is substituted with aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle or
heterocycle, or alternatively one or more aryl, heteroaryl,
carbocycle, or heterocycle(s) which is/are substituted with
alkyl or alkenyl, i.e. 'Alkyl/alkylene which is substituted
with Ar' or 'Ar which is substituted with alkyl/alkylene'.
"Aryl" or "aromatic" refers to an aromatic carbocyclic
or heterocyclic group having a single ring, for example a
phenyl ring; multiple rings, for example biphenyl; or
multiple condensed rings in which at least one ring is
aromatic, for example naphthyl, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl,
anthryl, or phenanthryl, which can be unsubstituted or
substituted with one or more other substituents as defined
above. The substituents attached to a phenyl ring portion
of an aryl moiety in the compounds of the invention may be
configured in the ortho-, meta-, or para- orientations
orientations, with the para- orientation being preferred.
Examples of typical aryl moieties included in the
scope of the present invention may include, but are not
limited to, the following:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 31 -
/ ~ / ~ / ~ \
\ \ \ /
/ ~ / ~ \ \
\ \ / /
/ \ /
/ \ / \
It should be kept in mind that, throughout this
application, "Ar" or "Ar"", where n is a number, is used to
designate various cyclic (and other) substituents. As
indicated throughout, these Ar groups are independently
selected. Thus, for example, the fact that Ar2 may be
phenyl in one context does not require that Ar2 be phenyl,
nor prohibit that Ar2 be, for example, pyridyl, in another
context in the same molecule. It i.s intended that all
"Arn" are selected independently of all other "Ar~", whether
or not the term "independently selected" is used or is
inadvertently omitted.
"Bridged ring" or "bridged ring moiety" refers to a
carbocyclic or heterocyclic moiety where two or more atoms
are shared between two or more ring structures, where any
such shared atom is C, N, S, or other heteroatom arranged
in a chemically reasonable substitution pattern.
Alternatively, a "bridged" compound also refers to a
carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring structure where one atom
at any position of a primary ring is bonded to a second
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 32 -
atom on the primary ring through either a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond which do not comprise a part of
the primary ring structure. The first and second atom may
or may not be adjacent to one another in the primary ring.
Illustrated below are specific nonlimiting examples of
bridged ring structures contemplated by the present
invention:
N~ _~," N -~," N~ _w,, N
N
N~ ~ N~ ~
N N N
N , N
~/~~III,,,,~~__''~~,, N"'M N"'M N
N
The present invention also contemplates other carbocyclic
or heterocyclic bridged ring structures, including bridged
rings wherein the bridging atoms are C or heteroatom(s)
arranged in chemically reasonable substitution patterns,
which are not described herein.
"Carbocycle" or "carbocyclic" refers to an organic
cyclic moiety in which the cyclic skeleton is comprised of
only carbon atoms, whereas the term "heterocycle" or
"heterocyclic" refers to an organic cyclic moiety in which
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 33 -
the cyclic skeleton contains one or more heteroatoms
selected from nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur, and which may or
may not include carbon atoms. The term "carbocycle" refers
to a carbocyclic moiety containing the indicated number of
carbon atoms. The term "C3-Cg cycloalkyl", therefore,
refers to an organic cyclic substituent in which three to
eight carbon atoms form a three, four, five, six, seven, or
eight-membered ring, including, for example, a cyclopropyl,
cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl, or
cyclooctyl ring.
"Carbocyclic" or "heterocyclic" each includes within
its scope a single ring system, multiple fused rings (for
example, bicyclic, tricyclic, or other similar bridged ring
systems or substituents, e.g. adamantyl) or multiple
condensed ring systems. One skilled in the art, therefore,
will appreciate that in the context of the present
invention, a cyclic structure formed by A and B (or J and
K) as described herein may comprise bi-, or tri-, or
multiple condensed and/or bridged ring systems.
Examples of preferred carbocyclic and heterocyclic
moieties include, without limitation, phenyl, benzyl,
naphthyl, indenyl, azulenyl, fluorenyl, anthracenyl,
indolyl, isoindolyl, indolinyl, benzofuranyl,
benzothiophenyl, indazolyl, benzimidazolyl, benzthiazolyl,
tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyridyl, pyrrolyl,
pyrrolidinyl, pyridinyl, pyrimidinyl, purinyl, quinolinyl,
isoquinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl, quinalizinyl, furyl,
thiophenyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl, benzoxazolyl, thiazolyl,
isoxazolyl, isotriazolyl, oxadiazolyl, triazolyl,
thiadiazolyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazinyl,
triazinyl, trithianyl, indolizinyl, pyrazolyl, pyrazolinyl,
pyrazolidinyl, thienyl, tetrahydroisoquinolinyl,
cinnolinyl, phthalazinyl, quinazolinyl, quinoxalinyl,
naphthyridinyl, pteridinyl, carbazolyl, acridinyl,
phenazinyl, phenothiazinyl, phenoxazinyl, and adamantyl.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 34 -
"Enhancing memory performance" refers to improving or
increasing the mental faculty by which to register, retain
or recall past experiences, knowledge, ideas, sensations,
thoughts or impressions.
"Eye" refers to the anatomical structure responsible
for vision in humans and other animals, and encompasses the
following anatomical structures, without limitation: lens,
vitreous body, ciliary body, posterior chamber, anterior
chamber, pupil, cornea, iris, canal of Schlemm, zonules of
Zinn, limbus, conjunctiva, choroid, retina, central vessels
of the retina, optic nerve, fovea centralis, macula lutea,
and sclera.
"GPI 1046" refers to the related N-heterocyclic
derivative neuroimmunophilin FKBP ligand 3-(3-pyridyl)-1-
propyl (2s)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-
pyrrolidinecarboxylate of formula
N
~O /
I ~II(N
GPI1046
"Halo" means at least one fluoro, chloro, bromo, or
iodo moiety.
"Heterocycle" or "heterocyclic", as used herein,
refers to a saturated, unsaturated or aromatic carbocyclic
group having a single ring, multiple fused rings(for
example, bicyclic, tricyclic, or other similar bridged ring
systems or substituents), or multiple condensed rings, and
having at least one hetero atom such as nitrogen, oxygen or
sulfur within at least one of the rings. This term also
includes "Heteroaryl" which refers to a heterocycle in
which at least one ring is aromatic. Any heterocyclic or
heteroaryl group can be unsubstituted or optionally
substituted with one or more groups, as defined above.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 35 -
Further, bi- or tricyclic heteroaryl moieties may comprise
at least one ring which is either completely or partially
saturated.
In the context of the invention, useful carbo- and
heterocyclic rings include, for example and without
limitation, phenyl, benzyl, naphthyl., indenyl, azulenyl,
fluorenyl, anthracenyl, indolyl, isoindolyl, indolinyl,
benzofuranyl, benzothiophenyl, indazolyl, benzimidazolyl,
benzthiazolyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydropyranyl,
pyridyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyridinyl, pyrimidinyl,
purinyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl,
quinolizinyl, furyl, thiophenyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl,
benzoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isoxazolyl, isotriazolyl,
oxadiazolyl, triazolyl, thiadiazolyl, pyridazinyl,
pyrimidinyl, pyrazinyl, triazinyl, trithianyl, indolizinyl,
pyrazolyl, pyrazolinyl, pyrazolidinyl, thienyl,
tetrahydroisoquinolinyl, cinnolinyl, phthalazinyl,
quinazolinyl, quinoxalinyl, naphthyridinyl, pteridinyl,
carbazolyl, acridinyl, phenazinyl, phenothiazinyl, and
phenoxazinyl.
As one skilled in the art will appreciate, such
heterocyclic moieties may exist in several isomeric forms,
all of which are encompassed by the present invention . For
example, a 1,3,5-triazine moiety is isomeric to a 1,2,4-
triazine group. Such positional isomers are to be
considered within the scope of the present invention.
Likewise, the heterocyclic or heteroaryl groups can be
bonded to other moieties in the compounds of the present
invention. The points) of attachment to these other
moieties is not to be construed as limiting on the scope of
the invention. Thus, by way of example, a pyridyl moiety
may be bound to other groups through the 2-, 3-, or 4
position of the pyridyl group. All such configurations are
to be construed as within the scope of the present
invention.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 36 -
Examples of heterocyclic or heteroaryl moieties
included in the scope of the present invention may include,
but are not limited to, the following:
C> C> U L=
C~C~C~C~rJ'
0700
,o ~~~c»?o
C~ r.~. C~ C~ C~ C
~5 I ~ ~ I
~~ N oc ~
N
,)
N ~ S ~O
H
20 I ~ ~ I
~N
O N O
a? ~'~
"Isomers" are different compounds that have the same
molecular formula and includes cyclic isomers such as
(iso}indole and other isomeric forms of cyclic moieties.
"Stereoisomers" are isomers that differ only in the way the
atoms are arranged in space. "Enantiomers" are a pair of
stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of
each other. "Diastereoisomers" are stereoisomers which are
not mirror images of each other. "Racemic mixture" means
a mixture containing equal parts of individual enantiomers.
"Non-racemic mixture" is a mixture containing unequal parts
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 37 -
of individual enantiomers or stereoisomers.
"Isosteres" are different compounds that have
different molecular formulae but exhibit the same or
similar properties. For example, tetrazole is an isostere
of carboxylic acid because it mimics the properties of
carboxylic acid even though they both have very different
molecular formulae. Tetrazole is one of many possible
isosteric replacements for carboxylic acid. Other
carboxylic acid isosteres contemplated by the present
invention include -COOH, -S03H, -S02HNR3, -P02 (R3) 2, -CN, -
P03 ( R3 ) 2, -OR3, -SR3, -NHCOR3, -N ( R3 ) 2, -CON ( R3 ) 2, -CONH ( O ) R3,
-CONHNHS02R3, -COHNS02R3, and -CONR3CN, wherein R3 is
hydrogen, hydroxy, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, Cl-
C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, C1-C6-alkylaryloxy, aryloxy, aryl-
C1-C6-alkyloxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino,
amino- C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio- C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-
alkylthio, sulfonyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl,
C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, carbocycle, heterocycle, and C02R9 where R9 is
hydrogen or C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl or
alkenyl. In addition, carboxylic acid isosteres can
include 5-7 membered carbocycles or heterocycles containing
any combination of CH2, O, S, or N in any chemically stable
oxidation state, where any of the atoms of said ring
structure are optionally substituted in one or more
positions. The following structures are non-limiting
examples of preferred carbocyclic and heterocyclic
isosteres contemplated by this invention:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 38 -
N ~ /N N
/ ~~N ~N OH
N
HN
HN~~ HOOC H N-N
H ~ O OH O
~N ~ \
N \NH ~ N NH
NON S ~~ HN
0
\ O /N ~ N
N / O
NH HN
O O ~ S
~N \N
s
0
OH
N N N
O O I ~ ( /N
O ~ HS H F H
OH
0
O
S
OH
2 5 ~- NH
.J
O ~OH
O
and -COOH, -S03H, -S02HNR3, -P02 (R3) 2, -CN, -P03 (R3) 2, -OR3, -
30 SR3, -NHCOR3, -N (R3) 2, -CON (R3) 2, -CONH (0) R3, -CONHNHS02R3, -
COHNS02R3, and -CONR3CN, wherein R3 is hydrogen, hydroxy,
halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-
alkenoxy, C1-C6-alkylaryloxy, aryloxy, aryl- C1-C6-alkyloxy,
cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino, amino- C1-C6-alkyl,
35 sulfhydryl, thio- C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-alkylthio, sulfonyl, C1-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 39 -
C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, aryl, heteroaryl,
carbocycle, heterocycle, and C02R4 where R4 is hydrogen or
C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl or alkenyl and where
the atoms of said ring structure may be optionally
substituted at one or more positions with R1, as defined
herein. The present invention contemplates that when
chemical substituents are added to a carboxylic isostere
then the inventive compound retains the properties of a
carboxylic isostere.
The present invention contemplates that when a
carboxylic isostere is optionally substituted with one or
more moieties selected from R3, as defined herein, then the
substitution cannot eliminate the carboxylic acid isosteric
properties of the inventive compound. The present
invention contemplates that the placement of one or more R3
substituents upon a carbocyclic or heterocyclic carboxylic
acid isostere shall not be permitted at one or more atom ( s )
which maintains) or is/are integral to the carboxylic acid
isosteric properties of the inventive compound, if such
substituent(s) would destroy the carboxylic acid isosteric
properties of the inventive compound.
Other carboxylic acid isosteres not specifically
exemplified or described in this specification are also
contemplated by the present invention.
"Memory impairment" refers to a diminished mental
registration, retention or recall of past experiences,
knowledge, ideas, sensations, thoughts or impressions.
Memory impairment may affect short and long-term
information retention, facility with spatial relationships,
memory (rehearsal) strategies, and verbal retrieval and
production. Common causes of memory impairment are age,
severe head trauma, brain anoxia or ischemia, alcoholic-
nutritional diseases, and drug intoxications. Examples of
memory impairment include, without limitation, benign
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 40 -
forgetfulness, amnesia and any disorder in which memory
deficiency is present, such as Korsakoff's amnesic
psychosis, dementia and learning disorders.
"Neopsic factors" or "neopsics" refers to compounds
useful in treating vision loss, preventing vision
degeneration, or promoting vision regeneration.
"Neopsis" refers to the process of treating vision
loss, preventing vision degeneration, or promoting vision
regeneration.
"Neurotrophic" as used herein includes without
limitation the ability to stimulate neuronal regeneration
or growth, and/or the ability to prevent or treat
neurodegeneration.
"Non-immunosuppressive" as used herein refers to the
inability of the compounds of the present invention to
trigger an immune response when compared to a control such
as FK506 or cyclosporin A. Assays for determining
immunosuppression are well known to those of ordinary skill
in the art. Specific, non-limiting examples of well known
assays include PMA and OKT3 wherein mitogens are used to
stimulate proliferation of human peripheral blood
lymphocytes (PBC) and the compounds are evaluated on their
ability to inhibit such proliferation.
30
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 41 -
"Ophthalmological" refers to anything about or
concerning the eye, without limitation, and is used
interchangeably with "ocular," "ophthalmic,"
"ophthalmologic," and other such terms, without limitation.
"Pharmaceutically acceptable carrier" as used herein
refers to any carrier, diluent, excipient, suspending
agent, lubricating agent, adjuvant, vehicle, delivery
system, emulsifier, disintegrant, absorbant, preservative,
surfactant, colorant, flavorant, or sweetener. For these
purposes, the compounds of the present invention may be
administered orally, parenterally, by inhalation spray,
topically, rectally, nasally, buccally, vaginally or via an
implanted reservoir in dosage formulations containing
conventional non-toxic pharmaceutically-acceptable
carriers, adjuvants and vehicles. The term parenteral as
used herein includes subcutaneous, intravenous,
intramuscular, intraperitoneally, intrathecally,
intraventricularly, intrasternal and intracranial injection
or infusion techniques.
"Pharmaceutically acceptable salt", as used herein,
refers to an organic or inorganic salt which is useful in
the treatment of a warm-blooded animal in need thereof.
Such salts can be acid or basic addition salts, depending
on the nature of the inventive compound to be used.
In the case of an acidic moiety in an inventive
compound, a salt may be formed by treatment of the
inventive compound with a basic compound, particularly an
inorganic base. Preferred inorganic salts are those formed
with alkali and alkaline earth metals such as lithium,
sodium, potassium, barium and calcium. Preferred organic
base salts include, for example, ammonium,
dibenzylammonium, benzylammonium, 2-hydroxyethylammonium,
bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonium, phenylethylbenzylamine,
dibenzyl-ethylenediamine, and the like salts. Other salts
of acidic moieties may include, for example, those salts
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 42 -
formed with procaine, quinine and N-methylglucosamine, plus
salts formed with basic amino acids such as glycine,
ornithine, histidine, phenylglycine, lysine and arginine.
Other suitable base salts, esters, or solvates include
magnesium salts; salts with organic bases, such as
dicyclohexylamine salts; and N-methyl-D-glucamine. An
especially preferred salt is a sodium or potassium salt of
an inventive compound.
With respect to basic moieties, a salt is formed by
the treatment of the desired inventive compound with an
acidic compound, particularly an inorganic acid. Preferred
inorganic salts of this type may include, for example, the
hydrochloric, hydrobromic, hydroiodic, sulfuric, phosphoric
or the like salts. Preferred organic salts of this type,
may include, for example, salts formed with formic, acetic,
succinic, citric, lactic, malefic, fumaric, palmitic,
cholic, pamoic, mucic, d-glutamic, d-camphoric, glutaric,
glycolic, phthalic, tartaric, lauric, stearic, salicyclic,
methanesulfonic, benzenesulfonic, para-toluenesulfonic,
sorbic, puric, benzoic, cinnamic and the like organic
acids. Other suitable acids are adipate, alginate,
aspartate, benzenesulfonate, bisulfate, butyrate,
camphorsulfonate, cyclopentanepropionate, digluconate,
dodecylsulfate, ethanesulfonate, glucoheptanoate, glycero-
phosphate, hemisulfate, heptanoate, hexanoate, 2-
hydroxyethanesulfonate, methanesulfonate, naphthylate, 2-
naphthalenesulfonate, nicotinate, oxalate, thiocyanate,
tosylate and undecanoate. An especially preferred salt of
this type is a hydrochloride or sulfate salt of the desired
inventive compound. Also, the basic nitrogen-containing
groups can be quarternized with such agents as: 1) lower
alkyl halides, such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, and butyl
chloride, bromides and iodides; 2) dialkyl sulfates like
dimethyl, diethyl, dibutyl and diamyl sulfates; 3) long
chain alkyls such as decyl, lauryl, myristyl and stearyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 43 -
substituted with one or more halide such as chloride,
bromide and iodide; and 4) aralkyl halides like benzyl and
phenethyl bromide and others.
Also encompassed in the scope of the present invention
are pharmaceutically acceptable esters of a carboxylic acid
or hydroxyl containing group, including a metabolically
labile ester or a prodrug form of an inventive compound.
A metabolically labile ester is one which may produce, for
example, an increase in blood levels and prolong the
efficacy of the corresponding non-esterified form of the
compound. A prodrug form is one which is not in an active
form of the molecule as administered but which becomes
therapeutically active after some in vivo activity or
biotransformation, such as metabolism, for example,
enzymatic or hydrolytic cleavage. Esters of an inventive
compound may include, for example, the methyl, ethyl,
propyl, and butyl esters, as well as other suitable esters
formed between an acidic moiety and a hydroxyl containing
moiety. Metabolically labile esters, may include, for
example, methoxymethyl, ethoxymethyl, iso-propoxymethyl, a-
methoxyethyl, groups such as a-((C1-C9)alkyloxy)ethyl; for
example, methoxyethyl, ethoxyethyl, propoxyethyl, iso-
propoxyethyl, etc.; 2-oxo-1,3-dioxolen-4-ylmethyl groups,
such as 5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3,dioxolen-4-ylmethyl, etc.; C1-C3
alkylthiomethyl groups, for example, methylthio-methyl,
ethylthiomethyl, isopropylthio-methyl, etc.; acyloxymethyl
groups, for example, pivaloyloxy-methyl, a-acetoxymethyl,
etc.; ethoxycarbonyl-1-methyl; or a-acyloxy-a-substituted
methyl groups, for example a-acetoxyethyl.
Further, the compounds of the invention may exist as
crystalline solids which can be crystallized from common
solvents such as ethanol, N,N-dimethyl-formamide, water, or
the like. Thus, crystalline forms of the compounds of the
invention may exist as solvates and/or hydrates of the
parent compounds or their pharmaceutically acceptable
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 44 -
salts. All of such forms likewise are to be construed as
falling within the scope of the invention.
"Pilar cycle" refers to the life cycle of hair
follicles, and includes three phases:
(1) the anagen phase, the period of active hair
growth which, insofar as scalp hair is
concerned, lasts about three to five years;
(2) the catagen phase, the period when growth stops
and the follicle atrophies which, insofar as
scalp hair is concerned, lasts about one to two
weeks; and
(3) the telogen phase, the rest period when hair
progressively separates and finally falls out
which, insofar as scalp hair is concerned, lasts
about three to four months.
Normally 80 to 90 percent of the follicles are in the
anagen phase, less than 1 percent being in the catagen
phase, and the rest being in the telogen phase . In the
telogen phase, hair is uniform in diameter with a slightly
bulbous, non-pigmented root. By contrast, in the anagen
phase, hair has a large colored bulb at its root.
"Preventing neurodegeneration" as used herein includes
the ability to inhibit or prevent neurodegeneration in
patients newly diagnosed as having a neurodegenerative
disease, or at risk of developing a new degenerative
disease and for inhibiting or preventing further
neurodegeneration in patients who are already suffering
from or have symptoms of a neurodegenerative disease when
the compounds are given concurrently.
"Preventing vision degeneration" as used herein
includes the ability to prevent degeneration of vision in
patients newly diagnosed as having a degenerative disease
affecting vision, or at risk of developing a new
degenerative disease affecting vision, and for preventing
further degeneration of vision in patients who are already
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 45 -
suffering from or have symptoms of a degenerative disease
affecting vision.
"Primary ring structure" refers to a 5-, 6-, or 7
membered ring structure which is depicted in the formula
drawings herein, or otherwise referred to by a designation
such as "...A and B (or J and K), taken together with the
atoms to which they are attached...". Such definition
shall apply to only one ring structure in any molecule
described in this application, regardless of the number or
confirmation of any substituent cyclic structures.
"Promoting hair growth" refers to maintaining,
inducing, stimulating, accelerating, or revitalizing the
germination of hair.
"Promoting vision regeneration" refers to maintaining,
improving, stimulating or accelerating recovery of, or
revitalizing one or more components of the visual system in
a manner which improves or enhances vision, either in the
presence or absence of any ophthalmologic disorder,
disease, or injury.
"Treating" or "treatment" as used herein covers any
treatment of a disease and/or condition in an animal,
particularly a human, and includes:
(i) preventing a disease and/or condition from
occurring in a subject which may be predisposed to the
disease and/or condition but has not yet been diagnosed as
having it;
(ii) inhibiting the disease and/or condition, i.e.,
arresting its development; or
(iii) relieving the disease and/or condition, i.e.,
causing regression of the disease and/or condition.
"Treating alopecia" refers to:
(i) preventing alopecia in an animal which may be
predisposed to alopecia; and/or
(ii) inhibiting, retarding or reducing alopecia;
and/or
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 46 -
(iii) promoting hair growth; and/or
(iv) prolonging the anagen phase of the hair cycle;
and/or
(v) converting vellus hair to growth as terminal hair.
Terminal hair is coarse, pigmented, long hair in which the
bulb of the hair follicle is seated deep in the dermis.
Vellus hair, on the other hand, is fine, thin, non
pigmented short hair in which the hair bulb is located
superficially in the dermis. As alopecia progresses, the
hairs change from the terminal to the vellus type.
"Vision", as used herein, refers to the ability of
humans and other animals to process images, and is used
interchangeably with "sight", "seeing", and other such
terms, without limitation.
"Vision disorder" refers to any disorder that.affects
or involves vision, including without limitation visual
impairment, orbital disorders, disorders of the lacrimal
apparatus, disorders of the eyelids, disorders of the
conjunctiva, disorders of the cornea, cataracts, disorders
of the uveal tract, disorders of the optic nerve or visual
pathways, free radical induced eye disorders and diseases,
immunologically-mediated eye disorders and diseases, eye
injuries, and symptoms and complications of eye disease,
eye disorder, or eye injury.
"Visual impairment" refers to any dysfunction in
vision including without limitation disturbances or
diminution in vision (e. g., binocular, central, peripheral,
scotopic), visual acuity for objects near and for, visual
field, ocular motility, color perception, adaptation to
light and dark, accommodation, refraction, and lacrimation.
See Physicians' Desk Reference (PDR) for Ophthalmology,
16th Edition, 6:47 (1988) .
"Warm-blooded animal" includes a mammal, including a
member of the human, equine, porcine, bovine, murine,
canine or feline species. In the case of a human, the term
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 47 -
"warm-blooded animal" may also be referred to as a
"patient". Further, as used herein, "a warm blooded animal
in need thereof" refers to a warm-blooded animal which is
susceptible to a disorder due to genetic or environmental
conditions or predispositions. This term also refers to a
warm blooded animal which has already suffered some degree
of injury or damage because of genetic or environmental
conditions to which the animal has been exposed or to which
it has been predisposed. Environmental conditions can
include treatment with a therapeutic compound, as well as
other types of injury or insult.
Further, as used throughout the teaching of the
invention, a designation of:
C_W or C'Y
wherein W or Y is H2, or similar designations, is meant to
denote that two hydrogen atoms are attached to the noted
carbon and that the bonds to each hydrogen are single
bonds.
Compounds of the Invention
The present invention relates to the surprising
discovery that the inventive compounds are neurotrophic,
are able to treat alopecia, and are able to treat vision
and memory disorders. Accordingly, a novel class of
bridged heterocyclic compounds are provided. A preferred
feature of the compounds of the present invention is that
they do not exert any significant immunosuppressive
activity.
Methods of the Present Invention
Treatinct Neurotrophic Disorders. The present
invention relates to the use of any of the compounds
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 48 -
described herein in the preparation of a medicament for the
treatment of a disease such as peripheral neuropathy caused
by physical injury or disease state, physical damage to the
brain, physical damage to the spinal cord, stroke
associated with brain damage, Alzheimer's Disease,
Parkinson's Disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
The present invention also relates to the use of carboxylic
acid and carboxylic acid isostere compounds for treating
the above-mentioned neuropathies, neurological disorders,
and neurological damage.
As neurotrophic agents, the compounds of this
invention can be periodically administered to a patient
undergoing treatment for neurological disorders or for
other reasons in which it is desirable to stimulate
neuronal regeneration and growth, such as in various
peripheral neuropathic and neurological disorders relating
to neurodegeneration. The compounds of this invention can
also be administered to mammals other than humans for
treatment of various mammalian neurological disorders.
The novel compounds of the present invention possess
an excellent degree of neurotrophic activity. This
activity is useful in the stimulation of damaged neurons,
the promotion of neuronal regeneration, the prevention of
neurodegeneration, and in the treatment of several
neurological disorders known to be associated with neuronal
degeneration and peripheral neuropath:ies. The neurological
disorders that may be treated include but are not limited
to: trigeminal neuralgia, glossopharyngeal neuralgia,
Bell's Palsy, myasthenia gravis, muscular dystrophy,
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, progressive muscular
atrophy, progressive bulbar inherited muscular atrophy,
herniated, ruptured or prolapsed invertebrate disk
syndromes, cervical spondylosis, plexus disorders, thoracic
outlet destruction syndromes, peripheral neuropathic such
as those caused by lead, dapsone, ticks, prophyria, or
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 49 -
Gullain-Barre syndrome, Alzheimer's disease, and
Parkinson's disease.
Treatincr Alopecia and Promoting Hair Growth. The
present invention also relates to a method for treating
alopecia or promoting hair growth in an animal, which
comprises administering to said animal an effective amount
of an inventive compound. The present invention also
relates to using the inventive compounds and compositions
in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of
alopecia or promoting hair growth in an animal.
The inventive method is particularly useful for
treating male pattern alopecia, alopecia senilis, alopecia
areata, alopecia resulting from skin lesions or tumors,
alopecia resulting from cancer therapy such as chemotherapy
and radiation, and alopecia resulting from systematic
disorders such as nutritional disorders and internal
secretion disorders.
Treating Vision and Memory Disorders. The present
invention provides a method for treating a vision disorder,
improving vision, treating memory impairment, or enhancing
memory performance in an animal by administering to a
patient a therapeutically effective amount of an inventive
compound.
The inventive methods are particularly useful for
treating various eye disorders including, but not limited
to visual disorders, diseases, injuries, and complications,
genetic disorders; disorders associated with aging or
degenerative vision diseases; vision disorders correlating
to physical injury to the eye, head, or other parts of the
body resulting from external forcesa disorders resulting
from environmental factors; disorders resulting from a
broad range of diseases; and combinations of any of the
above.
In particular, the compositions and methods of the
present invention are useful for improving vision, or
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 50 -
correcting, treating, or preventing visual (ocular)
impairment or dysfunction of the visual system, including
permanent and temporary visual impairment, without
limitation. The present invention is also useful in
preventing and treating ophthalmologic diseases and
disorders, treating damaged and injured eyes, and
preventing and treating diseases, disorders, and injuries
which result in vision deficiency, vision loss, or reduced
capacity to see or process images, and the symptoms and
complications resulting from same. The eye diseases and
disorders which may be treated or prevented by the
compositions and methods of the present invention are not
limited with regard to the cause of said diseases or
disorders. Accordingly, said compositions and methods are
applicable whether the disease or disorder is caused by
genetic or environmental factors, as well as any other
influences. The compositions and methods of the present
invention are particularly useful for eye problems or
vision loss or deficiency associated with all of the
following, without limitation: aging, cellular or
physiological degeneration, central nervous system or
neurological disorder, vascular defects, muscular defects,
and exposure to adverse environmental conditions or
substances.
The compositions and methods of the present invention
are particularly useful in correcting, treating, or
improving visual impairment, without limitation. Visual
impairment in varying degrees occurs in the presence of a
deviation from normal in one or more functions of the eye,
including (1) visual acuity for objects at distance and
near; (2) visual fields; and (3) ocular motility without
diplopia. See Physicians' Desk Reference (PDR) for
Ophthalmology, 16th Edition, 6:47 (1988). Vision is
imperfect without the coordinated function of all three.
Id.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 51 -
Said compositions and methods of use are also useful
in correcting, treating, or improving other ocular
functions including, without limitation, color perception,
adaptation to light and dark, accommodation,
metamorphopsia, and binocular vision. The compositions and
methods of use are particularly useful in treating,
correcting, or preventing ocular disturbances including,
without limitation, paresis of accommodation, iridoplegia,
entropion, ectropion, epiphora, lagophthalmos, scarring,
vitreous opacities, non-reactive pupil, light scattering
disturbances of the cornea or other media, and permanent
deformities of the orbit.
The compositions and methods of use of the present
invention are also highly useful in improving vision and
treating vision loss. Vision loss ranging from slight loss
to absolute loss may be treated or prevented using said
compositions and methods of use. Vision may be improved by
the treatment of eye disorders, diseases, and injuries
using the compositions and methods of the invention.
However, improvements in vision using the compositions and
methods of use are not so limited, and may occur in the
absence of any such disorder, disease, or injury.
The compositions and methods of the present invention
are also useful in the treatment or prevention of the
following non-limiting exemplary diseases and disorders,
and symptoms and complications resulting therefrom.
Vision disorders include but are not limited to the
following:
visual impairment, such as diminished visual acuity
for objects near and far, visual fields, and ocular
motility;
orbital disorders, such as orbital cellulitis,
periorbital cellulitis, cavernous sinus thrombosis, and
exophthalmos (proptosis);
disorders of the lacrimal apparatus, such as
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00116603 PCT/US98/25577
- 52 -
dacryostenosis, congenital dacryostenosis, and
dacryocystitis (acute or chronic);
disorders of the eyelids, such as lid edema,
blepharitis, ptosis, Bell's palsy, blepharospasm, hordeolum
(stye), external hordeolum, internal hordeolum (meibomian
stye), chalazion, entropion (inversion of the eyelid),
ectropion (eversion of the eyelid), tumors (benign and
malignant), xanthelasma, basil cell carcinoma, squamous
cell carcinoma, meibomian gland carcinoma, and melanoma;
disorders of the conjunctiva, such as pinguecula,
pterygium, and other neoplasms, acute conjunctivitis,
chronic conjunctivitis, adult gonococcal conjunctivitis,
neonatal conjunctivitis, trachoma (granular conjunctivitis
or Egyptian ophthalmia), inclusion conjunctivitis
(inclusion blenorrhea or swimming pool conjunctivitis),
neonatal inclusion conjunctivitis, adult inclusion
conjunctivitis, vernal keratoconjunctivitis,
keratoconjunctivitis sicca (keratitis sicca or dry eye
syndrome), episcleritis, scleritis, cicatricial pemphigoid
(ocular cicatricial pemphigoid or benign mucous membrane
pemphigoid), and subconjunctival hemorrhage;
disorders of the cornea, such as superficial punctate
keratitis, corneal ulcer, indolent ulcer, recurrent corneal
erosion, corneal epithelial basement membrane dystrophy,
corneal endothelial cell dystrophy, herpes simplex
keratitis (herpes simplex keratoconjunctivitis), dendritic
keratitis, disciform keratitis, ophthalmic herpes zoster,
phlyctenular keratoconjunctivitis (phlyctenular or
eczematous conjunctivitis), interstitial keratitis
(parenchymatous keratitis), peripheral ulcerative keratitis
(marginal keratolysis or peripheral rheumatoid ulceration),
keratomalacia (xerotic keratitis), xerophthalmia,
keratoconus, bullous keratopathy;
cataracts, including developmental or congenital
cataracts, juvenile or adult cataracts, nuclear cataract,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 53 -
posterior subcapsular cataracts;
disorders of the uveal tract, such as uveitis
(inflammation of the uveal tract or retina), anterior
uveitis, intermediate uveitis, posterior uveitis, iritis,
cyclitis, choroiditis, ankylosing spondylitis, Reiter's
syndrome, pars planitis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus
(CMV), acute retinal necrosis, toxocariasis, birdshot
choroidopathy, histoplasmosis (presumed ocular
histoplasmosis syndrome), Behcet's syndrome, sympathetic
ophthalmia, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome, sarcoidosis,
reticulum cell sarcoma, large cell lymphoma, syphilis,
tuberculosis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis,
endophthalmitis, and malignant melanoma of the choroid;
disorders of the retina, such as vascular
retinopathies (e.g., arteriosclerotic retinopathy and
hypertensive retinopathy), central and branch retinal
artery occlusion, central and branch retinal vein
occlusion, diabetic retinopathy (e. g., proliferative
retinopathy and non-proliferative retinopathy), macular
degeneration of the aged (age-related macular degeneration
or senile macular degeneration), neovascular macular
degeneration, retinal detachment, retinitis pigmentosa,
retinal photic injury, retinal ischemia-induced eye injury,
and glaucoma (e. g., primary glaucoma, chronic open-angle
glaucoma, acute or chronic angle-closure, congenital
(infantile) glaucoma, secondary glaucoma, and absolute
glaucoma);
disorders of the optic nerve or visual pathways, such
as papilledema (choked disk), papillitis (optic neuritis),
retrobulbar neuritis, ischemic optic neuropathy, toxic
amblyopia, optic atrophy, higher visual pathway lesions,
disorders of ocular motility (e. g., third cranial nerve
palsies, fourth cranial nerve palsies, sixth cranial nerve
palsies, internuclear ophthalmoplegia, and gaze palsies);
free radical induced eye disorders and diseases; and
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 54 -
immunologically-mediated diseases, such as Graves'
ophthalmopathy, conical cornea, dystrophia epithelialis
corneae, corneal leukoma, ocular pemphigus, Mooren's ulcer,
scleritis, and sarcoidosis. See The Merck Manual,
Sixteenth Edition, 217:2365-2397 (1992) and The Eye Book,
Cassel, Billig, and Randall, The Johns Hopkins University
Press (1998).
The compositions and methods of the present invention
are also useful in the treatment of the following non
limiting eye injuries, and symptoms and complications
resulting therefrom: conjunctival and corneal foreign body
injuries, corneal abrasion, intraocular foreign body
injuries, lacerations, lid lacerations, contusions, lid
contusions (black eye), trauma to the globe, laceration of
the iris, cataract, dislocated lens, glaucoma, vitreous
hemorrhage, orbital-floor fractures, retinal hemorrhage or
detachment, and rupture of the eyeball, anterior chamber
hemorrhage (traumatic hyphema), burns, eyelid burns,
chemical burns, chemical burns of the cornea and
conjunctiva, and ultraviolet light burns (sunburn). See
The Merck Manual, Sixteenth Edition, 217:2364-2365 (1992).
The compositions and methods of the present invention
are also useful in treating and/or preventing the following
non-limiting exemplary symptoms and complications of eye
disease, eye disorder or eye injury: subconjunctival
hemorrhages, vitreous hemorrhages, retinal hemorrhages,
floaters, retinal detachments, photophobia, ocular pain,
scotomas (negative and positive), errors of refraction,
emmetropia, ametropia, hyperopia (farsightedness), myopia
(nearsightedness), astigmatism, anisometropia, aniseikonia,
presbyopia, bleeding, recurrent bleeding, sympathetic
ophthalmia, inflammation, swelling, redness of the eye,
irritation of the eye, corneal ulceration and scarring,
iridocyclitis, perforation of the globe, lid deformities,
exophthalmos, impaired mobility of the eye, lid swelling,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 55 -
chemosis, loss of vision, including partial or total
blindness, optic neuritis, fever, malaise,
thrombophlebitis, cavernous sinus thrombosis,
panophthalmitis, infection of the meninges and brain,
papilledema, severe cerebral symptoms (headache, decreased
level of consciousness, and convulsions), cranial nerve
palsies, epiphora (chronic or persistent tearing), copious
reflux of mucus or pus, follicular subconjunctival
hyperplasia, corneal vascularization, cicatrization of the
conjunctiva, cornea, and lids, pannus, hypopyon,
lagophthalmos, phlyctenules, rubeosis iridis, bitemporal
hemianopia, and homonymous hemianopia. See The Merck
Manual, Sixteenth Edition, 217:2362-2363 (1992).
An inventive compound may be administered in
combination with an effective amount of one or more
factors) useful in treating vision disorder, improving
vision, treating memory impairment, or enhancing memory
performance.
In a preferred embodiment, the factors) to be
combined with an inventive compound is/are selected from
the group consisting of immunosuppressants for treating
autoimmune, inflammatory, and immunologically-mediated
disorders; wound healing agents for treating wounds
resulting from injury or surgery; antiglaucomatous
medications for treating abnormally elevated intraocular
pressure; neurotrophic factors and growth factors for
treating neurodegenerative disorders or stimulating neurite
outgrowth; compounds effective in limiting or preventing
hemorrhage or neovascularization for treating macular
degeneration; and antioxidants for treating oxidative
damage to eye tissues.
Pharmaceutical Compositions of the Present Invention
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical
composition comprising:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 56 -
(i) an effective amount of a bridged heterocyclic
compound; and
(ii) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
The general discussion above, relating to the utility
and administration of the compounds of the present
invention, also applies to the pharmaceutical compositions
of the present invention.
Pharmaceutical compositions typically include a
therapeutically effective amount of an inventive compound
described herein in admixture with one or more
pharmaceutically and physiologically acceptable formulation
materials. Suitable formulation materials include, but are
not limited to, antioxidants, preservatives, coloring,
flavoring and diluting agents, emulsifying agents,
suspending agents, solvents, fillers, bulking agents,
buffers, delivery vehicles, diluents, excipients and/or
pharmaceutical adjuvants. For example, a suitable vehicle
may be water for injection, physiological saline solution,
or artificial perilymph, possibly supplemented with other
materials common in compositions for parenteral
administration. Neutral buffered saline or saline mixed
with serum albumin are further exemplary vehicles.
The primary solvent in a vehicle may be either aqueous
or non-aqueous in nature. In addition, the vehicle may
contain other pharmaceutically-acceptable excipients for
modifying, modulating or maintaining the pH, osmolarity,
viscosity, clarity, color, sterility, stability, rate of
dissolution, or odor of the formulation. Similarly, the
vehicle may contain still other pharmaceutically-acceptable
excipients for modifying or maintaining the rate of release
of the therapeutic product(s), or for promoting the
absorption or penetration of the therapeutic products)
across the tympanic membrane. Such excipients are those
substances usually and customarily employed to formulate
dosages for administration in either unit dose or multi-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 57 -
dose form.
Once the therapeutic composition has been formulated,
it may be stored in sterile vials as a solution,
suspension, gel, emulsion, solid, or dehydrated or
lyophilized powder. Such formulations may be stored either
in a ready to use form or in a form, e.g., lyophilized,
requiring reconstitution prior to administration.
The optimal pharmaceutical formulations will be
determined by one skilled in the art depending upon
considerations such as the route of administration and
desired dosage. See, for example, "Remington's
Pharmaceutical Sciences", 18th ed. (1990, Mack Publishing
Co., Easton, PA 18042), pp. 1435-1712, the disclosure of
which is hereby incorporated by reference. Such
formulations may influence the physical state, stability,
rate of in vivo release, and rate of in vivo clearance of
the present therapeutic agents of the invention.
Other effective administration forms, such as ocular
slow-release formulations, inhalant mists, or orally active
formulations are also envisioned. For example, in a
sustained release formulation, an inventive compound may be
bound to or incorporated into particulate preparations of
polymeric compounds (such as polylactic acid, palyglycolic
acid, etc.) or liposomes. Hylauronic acid may also be
used, and this may have the effect of promoting sustained
duration in the circulation. Such therapeutic compositions
are typically in the form of a pyrogen-free, aqueous
solution comprising the inventive compound in a
pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle. One preferred vehicle
is sterile distilled water.
Certain formulations containing an inventive compound
may be administered orally. An inventive compound which is
administered in this fashion may be encapsulated and may be
formulated with or without those carriers customarily used
in the compounding of solid dosage forms. The capsule may
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 58 -
be designed to release the active portion of the
formulation at the point in the gastrointestinal tract when
bioavailability is maximized and pre-systemic degradation
is minimized. Additional excipients may be included to
facilitate absorption of the inventive compound. Diluents,
flavorings, low melting point waxes, vegetable oils,
lubricants, suspending agents, tablet disintegrating
agents, and binders may also be employed.
The formulation of topical preparations, including
solutions, suspensions, and ointments is well known to
those skilled in the art (see, for example, "Remington's
Pharmaceutical Sciences", 18th Edition, Chapter 86, pp.
1581-1592, Mack Publishing Company, 1990). Other modes of
administration are available, including injections.
Methods and means for producing preparations suitable for
such modes of administration are also well known.
In the treatment of ocular or neuronal disease or
injury it is also advantageous that a topically applied
formulation include an agent to promote the penetration or
transport of the therapeutic agent to the appropriate site.
Such agents are known in the art. Yet another preparation
may involve the formulation of an inventive compound with
an agent, such as injectable microspheres or liposomes,
that provides for the slow or sustained release of the
molecules which may then be delivered as a depot injection.
Other suitable means for the introduction of an inventive
compound include implantable drug delivery devices which
contain the inventive compound, or an implant including a
tunnel through which the inventive compound can be
continuously delivered.
The preparations of the present invention,
particularly topical preparations, may include other
components, for example acceptable preservatives, tonicity
agents, cosolvents, complexing agents, buffering agents or
other pH controlling agents, antimicrobials, antioxidants
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 59 -
and surfactants, as are well known in the art. Suitable
preservatives include, but are not limited to, benzalkonium
chloride, thimerosal, phenethyl alcohol, methylparaben,
propylparaben, chlorhexidine, sorbic acid and the like.
Hydrogen peroxide may also be used as preservative.
Suitable cosolvents include, but are not limited to,
glycerin, propylene glycol and polyethylene glycol.
Suitable complexing agents include caffeine, polyvinyl-
pyrrolidone, b-cyclodextrin or hydroxypropyl-b-
cyclodextrin. The buffers can be conventional buffers such
as borate, citrate, phosphate, bicarbonate, or tris-HC1.
Additional formulation components may include
materials which prolong the residence of the administered
therapeutic agent, particularly to maximize the topical
contact and promote absorption of the therapeutic agent.
Suitable materials may include polymers or gel forming
materials which increase the viscosity of the preparation.
The suitability of the formulations of the instant
invention for controlled release (era., sustained and
prolonged delivery) can be determined by various procedures
known in the art. Yet another preparation may involve an
effective quantity of an inventive compound in admixture
with non-toxic treatment acceptable excipients. For
example, the inventive compound may be prepared in tablet
form. By dissolving the tablets in sterile water, or other
appropriate vehicle, treatment solutions can be prepared in
unit dose form. Suitable excipients include, but are not
limited to, inert diluents, such as calcium carbonate,
sodium carbonate or bicarbonate, lactose, or calcium
phosphates or binding agents, such as starch, gelatin, or
acacia.
Neurotrophic Disorders. The present invention also
relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising:
(i) an effective amount of a bridged heterocyclic
compound for treating neurodegenerative
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00116603 PCT/US98/25577
- 60 -
diseases, neurological disorders, and nerve
damage, or promoting nerve growth in an animal;
and
(ii) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
As neurotrophic agents, the compounds can be
administered with other neurotrophic agents such as
neurotrophic growth factor, brain derived growth factor,
glial derived growth factor, cilial neurotrophic factor,
insulin growth factor and active truncated derivatives
thereof, acidic fibroblast growth factor, basic fibroblast
growth factor, platelet-derived growth factors,
neurotropin-3 and neurotropin 4/5. The dosage level of
other neurotrophic drugs will depend upon the factors
previously stated and the neurotrophic effectiveness of the
drug combination.
The neurotrophic compounds of this invention can be
periodically administered to a patient undergoing treatment
for neurological disorders or for other reasons in which it
is desirable to stimulate neuronal regeneration and growth,
such as in various peripheral neuropathic and neurological
disorders relating to neurodegeneration. The compounds of
this invention can also be administered to mammals other
than humans for treatment of various mammalian neurological
disorders.
Alopecia and Hair Growth. The present invention also
relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising:
(i) an effective amount of a bridged heterocyclic
compound for treating alopecia or promoting hair
growth in an animal; and
(ii) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
An inventive compound may be administered in
combination with an effective amount of one or more
factors) useful in treating alopecia or promoting hair
growth.
Vision and Memory Disorders. The present invention
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCTNS98/25577
- 61 -
also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising:
(i) an effective amount of a bridged heterocyclic
compound for treating a vision disorder,
improving vision, treating memory impairment, or
enhancing memory performance in an animal; and
(ii) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
An inventive compound may be administered in
combination with an effective amount of one or more
factors) useful in treating vision disorder, improving
vision, treating memory impairment, or enhancing memory
performance.
Routes of Administration
The compounds of the present invention may be
administered orally, parenterally, by inhalation spray,
topically, rectally, nasally, buccally, vaginally or via an
implanted reservoir in dosage formulations containing
conventional non-toxic pharmaceutically-acceptable
carriers, adjuvants and vehicles. The term parenteral as
used herein includes subcutaneous, intravenous,
intramuscular, intraperitoneal, intrathecal,
intraventricular, intrasternal, and intracranial injection
or infusion techniques.
For oral administration, the compounds of the present
invention may be provided in any suitable dosage form known
in the art. For example, the compositions may be
incorporated into tablets, powders, granules, beads,
chewable lozenges, capsules, liquids, aqueous suspensions
or solutions, or similar dosage forms, using conventional
equipment and techniques known in the art. Tablet dosage
forms are preferred. Tablets may contain carriers such as
lactose and corn starch, and/or lubricating agents such as
magnesium stearate. Capsules may contain diluents
including lactose and dried corn starch. Aqueous
suspensions may contain emulsifying and suspending agents
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 62 -
combined with the active ingredient.
When preparing dosage form incorporating the
compositions of the invention, the compounds may also be
blended with conventional excipients such as binders,
including gelatin, pregelatinized starch, and the like;
lubricants, such as hydrogenated vegetable oil, stearic
acid, and the like; diluents, such as lactose, mannose, and
sucrose; disintegrants, such as carboxymethylcellulose and
sodium starch glycolate; suspending agents, such as
povidone, polyvinyl alcohol, and the :Like; absorbants, such
as silicon dioxide; preservatives, such as methylparaben,
propylparaben, and sodium benzoate; surfactants, such as
sodium lauryl sulfate, polysorbatE 80, and the like;
colorants such as F.D.& C. dyes and lakes; flavorants; and
sweeteners.
The compounds of the present invention may be
administered in the form of sterile injectable
preparations, for example, as sterile injectable aqueous or
oleaginous suspensions. These suspensions may be
formulated according to techniques known in the art using
suitable dispersing or wetting agents and suspending
agents. The sterile injectable preparations may also be
sterile injectable solutions or suspensions in non-toxic
parenterally-acceptable diluents or solvents, for example,
as solutions in 1,3-butanediol. Among the acceptable
vehicles and solvents that may be employed are water,
Ringer's solution and isotonic sodium chloride solution.
In addition, sterile, fixed oils are conventionally
employed as solvents or suspending mediums. For this
purpose, any bland fixed oil may be employed including
synthetic mono- or di-glycerides. Fatty acids such as
oleic acid and its glyceride derivatives, including olive
oil and castor oil, especially in their polyoxyethylated
versions, are useful in the preparation of injectables.
These oil solutions or suspensions may also contain long-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 63 -
chain alcohol diluents or dispersants.
The compounds of this invention may also be
administered topically, especially when the conditions
addressed for treatment involve areas or organs readily
accessible by topical application, including neurological
disorders of the eye, the skin, or the lower intestinal
tract. Suitable topical formulations are readily prepared
for each of these areas.
For topical application to the eye, or ophthalmic use,
the compounds can be formulated as micronized suspensions
in isotonic, pH adjusted sterile saline, or, preferably, as
solutions in isotonic, pH adjusted sterile saline, either
with or without a preservative such as benzylalkonium
chloride. Alternatively for the ophthalmic uses the
compounds may be formulated in an ointment such as
petrolatum.
For topical application to the skin, the compounds can
be formulated in a suitable ointment containing the
compound suspended or dissolved in, for example, a mixture
with one or more of the following: mineral oil, liquid
petrolatum, white petrolatum, propylene glycol,
polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene compound, emulsifying wax
and water. Alternatively, the compounds can be formulated
in a suitable lotion or cream containing the active
compound suspended or dissolved in, for example, a mixture
of one or more of the following: mineral oil, sorbitan
monostearate, polysorbate 60, cetyl esters wax, cetearyl
alcohol, 2-octyldodecanol, benzyl alcohol and water.
Topical application for the lower intestinal tract an
be effected in a rectal suppository formulation (see below)
or in a suitable enema formulation.
The compounds of this invention may also be
administered rectally in the form of suppositories. These
compositions can be prepared by mixing the drug with a
suitable non-irritating excipient which is solid at room
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 64 -
temperature, but liquid at rectal temperature and,
therefore, will melt in the rectum to release the drug.
Such materials include cocoa butter, beeswax and
polyethylene glycols.
Compositions and methods of the invention also may
utilize controlled release technology. Thus, for example,
the inventive compounds may be incorporated into a
hydrophobic polymer matrix for controlled release over a
period of days. Such controlled release films are well
known to the art. Particularly preferred are transdermal
delivery systems. Other examples of polymers commonly
employed for this purpose that may be used in the present
invention include nondegradable ethylene-vinyl acetate
copolymer and degradable lactic acid-glycolic acid
copolymers which may be used externally or internally.
Certain hydrogels such as poly(hydroxyethylmethacrylate) or
poly(vinylalcohol) also may be useful, but for shorter
release cycles then the other polymer releases systems,
such as those mentioned above.
It is envisioned that the continuous administration or
sustained delivery of sensorineurotrophic compound may be
advantageous for a given condition. While continuous
administration may be accomplished via a mechanical means,
such as with an infusion pump, it is contemplated that
other modes of continuous or near continuous administration
may be practiced. For example, such administration may be
by subcutaneous or muscular injections as well as oral
pills and ear drops.
Techniques for formulating a variety of other
sustained- or controlled-delivery means, such as liposome
carriers, bio-erodible particles or beads and depot
injections, are also known to those skilled in the art.
To be effective therapeutically as central nervous
system targets, the compounds of the present invention
should readily penetrate the blood-brain barrier when
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 65 -
peripherally administered. Compounds which cannot
penetrate the blood-brain barrier can be effectively
administered by an intraventricular route or other
appropriate delivery system suitable for administration to
the brain.
To effectively treat alopecia or promote hair growth,
the compounds used in the inventive methods and
pharmaceutical compositions must readily affect the
targeted areas. For these purposes, the compounds are
preferably administered topically to the skin.
For topical application to the skin, the compounds can
be formulated into suitable ointments containing the
compounds suspended or dissolved in, for example, mixtures
with one or more of the following: mineral oil, liquid
petrolatum, white petrolatum, propylene glycol,
polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene compound, emulsifying wax
and water. Alternatively, the compounds can be formulated
into suitable lotions or creams containing the active
compound suspended or dissolved in, for example, a mixture
of one or more of the following: mineral oil, sorbitan
monostearate, polysorbate 60, cetyl ester wax, cetearyl
alcohol, 2-octyldodecanol, benzyl alcohol and water.
The compounds can be administered with other hair
revitalizing agents. Specific dose levels for the other
hair revitalizing agents will depend upon the factors
previously stated and the effectiveness of the drug
combination. Other routes of administration known in the
pharmaceutical art are also contemplated by this invention.
For the treatment of ocular conditions, the
sensorineurotrophic compound may be administered orally,
systemically, or directly into the eye, especially in those
situations where an invasive surgical procedure has already
taken place, or by topical application, inserts, injection
or implants. For example, slow-releasing implants
containing the molecules embedded in a biodegradable
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 66 -
polymer matrix can be used to deliver an inventive
compound. As noted, an inventive compound may be
administered in the eye, or it may be administered
topically in connection with one or more agents capable of
promoting penetration or transport of the inventive
compound across the membranes of the eye. The frequency of
dosing will depend on the pharmacokinetic parameters of the
inventive compound as formulated, and the route of
administration.
The final dosage regimen involved in a method for
treating the above-described conditions will be determined
by the attending physician, considering various factors
which modify the action of drugs, e.g., the age, condition,
body weight, sex and diet of the patient, the severity of
the condition, time of administration and other clinical
factors familiar to one skilled in the art.
Other routes of administration known in the
pharmaceutical art are also contemplated by this invention.
DosacL,e
dosage levels on the order of about 0.1 mg to about
10,000 mg of the active ingredient compound are useful in
the treatment of the above conditions, with preferred
levels of about 0.1 mg to about 1,000 mg. The specific
dose level for any particular patient will vary depending
upon a variety of factors, including the activity of the
specific compound employed; the age, body weight, general
health, sex and diet of the patient; the time of
administration; the rate of excretion; drug combination;
the severity of the particular disease or disorder being
treated; and the form of administration. Typically, in
vitro dosage-effect results provide useful guidance on the
proper doses for patient administration. Studies in animal
models are also helpful. The considerations for
determining the proper dose levels are well known in the
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 67 -
art .
The specific dose may be calculated according to
considerations of body weight, body surface area or organ
size. Further refinement of the calculations necessary to
determine the appropriate dosage for treatment involving
each of the above mentioned formulations is routinely made
by those of ordinary skill in the art and is within the
ambit of tasks routinely performed, especially in light of
the dosage information and assays disclosed herein.
Appropriate dosages may be determined using established
assays in conjunction with appropriate dose-response data.
One skilled in the art will appreciate that the dosage used
in localized formulations of the invention normally will be
smaller as compared to that used in a systemic injection or
oral administration.
The compounds can be administered with other agents)
for preventing and/or treating neurological disorders,
including physically damaged nerves and neurodegenerative
diseases; for treating alopecia and promoting hair growth;
for treating vision disorders and/or improving vision; and
for treating memory impairment and/or enhancing memory
performance. Specific dose levels for such other agents)
will depend upon the factors previously stated and the
effectiveness of the drug combination.
The compounds described in Formulas I-LXVII, below,
possess asymmetric centers and thus can be produced as
mixtures of stereoisomers or as individual R- and S-
stereoisomers. The individual stereoisomers may be
obtained by using an optically active starting material, by
resolving a racemic or non-racemic mixture of an
intermediate at some appropriate stage of the synthesis, or
by resolving the compounds of Formulas I-LXLVII. It is
understood that the compounds of Formulas I-LXVII encompass
individual stereoisomers as well as mixtures (racemic and
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 68 -
non-racemic) of stereoisomers. Preferably, S-stereoisomers
are used in the pharmaceutical compositions and methods of
the present invention.
The compounds useful in the invention comprise a
variety of structural families. As noted, the primary
consideration is that the compounds possess the desired
activity described herein. By way of description and not
limitation, therefore, the following structural formulae
are provided as exemplary of the compounds useful in
preventing and/or treating neurological disorders,
including physically damaged nerves and neurodegenerative
diseases; in treating alopecia and promoting hair growth;
in treating vision disorders and/or improving vision; and
in treating memory impairment and/or enhancing memory
performance:
The invention provides a compound of formula I''
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
A is hydrogen, C1 or C2 alkyl, or benzyl and B is C1-C4
straight or branched chain alkyl, benzyl, or
cyclohexylmethyl; or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a 5-7 membered saturated, unsaturated,
or aromatic heterocylic or carbocyclic ring which contains
one or more 0, C (R1) 2, S (0) P, N, NR1, or NR5 atoms; or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
V is CH, S, or N;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 69 -
X is O, CH2 or S;
m is 0 or 1;
G is
Y R\
w
W , O= i =O , or U ~''W .
R2 R~ R .
R1 is independently hydrogen, C1-C9 straight or
branched chain alkyl, or C2-C9 straight or branched chain
alkenyl or alkynyl, C3-C9 cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a
carboxylic acid or carboxylic acid isostere, N (R4) ~, Arl,
Ar4, a bridged ring moiety, or K-L, wherein said alkyl,
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, alkynyl, alkenyl, Arl, Ar4, or
bridged ring moiety, is optionally substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of:
2-furyl, 2-thienyl, pyridyl, phenyl, C3-C6
cycloalkyl wherein said furyl, thienyl, pyridyl,
phenyl or cycloalkyl group optionally is
substituted with C1-C9 alkoxy, (Arl) ", halo, halo-
C1-C6-alkyl, carbonyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6
thioester, cyano, imino, COOR6 in which R6 is
independently Ci-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl or alkenyl, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 alkoxy, C2-C4 alkenyloxy,
C1-C6 alkylaryloxy C1-C6 aryloxy, aryl- (C1-C6) -
alkyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, thio- (C1-C6) -alkyl,
C1-C6-alkylthio, sulfhydryl, sulfonyl, amino, (C1-
C6~-mono- or di-alkylamino, amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl,
aminocarboxy, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched
chain alkenyl optionally substituted with (Arl)",
C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl
substituted with C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-CB
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 70 -
cycloalkyl, and Ar2, and, wherein any carbon atom
of an alkyl or alkenyl group may optionally
replaced with O, NRS, or S (0) P;
Arl or Ar2, independently, is an alicyclic
or aromatic, mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or
heterocyclic ring, wherein the ring is
optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of halo, hydroxy, vitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl,
C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, C1-CQ alkoxy,
C2-C9 alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
wherein the individual ring contains 5-8
members; and wherein the heterocyclic ring
contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of 0, N, and
S, and, wherein any aromatic or tertiary
alkylamine is optionally oxidized to a
corresponding N-oxide;
or, R1 is independently a moiety of the formula:
i
x2
R3
wherein:
R3 is independently C1-C9 straight
or branched chain alkyl which is
optionally substituted with C3-C$
cycloalkyl or Arl;
X2 is 0 or NR6, wherein R6 is
independently selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 straight
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 71 -
or branched chain alkyl, and C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl;
R9 is independently selected from
the group consisting of phenyl,
benzyl, C1-CS straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-CS straight or
branched chain alkenyl, C1-C5 straight
or branched chain alkyl substituted
with phenyl, C2-CS straight or
branched chain alkenyl substituted
with phenyl, and a bridged ring
moiety,;
R2 is independently C1-C9 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched
chain alkenyl, C3-C8 cyc:Loalkyl, C5-C7
cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or Arl,
wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl, or bridged ring moiety, is
optionally substituted with one or more
substituents selected from the group consisting
of C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-CB
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, (Arl) ~ and
hydroxy; or,
R2 is independently either hydrogen or P;
Y is either oxygen or CH-P, provided that
if R2 is hydrogen, then Y is CH-P, or if Y is
oxygen then R2 is P;
P is hydrogen, 0- (C1-CQ straight
or branched chain alkyl) , O- (C2-C4
straight or branched chain alkenyl),
C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched
chain alkenyl, C5-C7 cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl substituted with C,-Cq
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 72 -
straight or branched chain alkyl or
C2-C9 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, (C1-C4 alkyl or C2-C4
al kenyl ) -Ars, or Ars;
U is either 0 or N, provided that:
when U is 0, then R' is a lone
pair of electrons and R " is selected
from the group consisting of Ar9, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, C1-C9 straight or branched
chain alkyl, and C2-C9 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, wherein said
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected
from the group consisting of Ar4 and
C3-CB cycloalkyl; and
when U is N, then R' and R"
are, independently, selected from the
group consisting of hydrogen, Ar4, C3-
Clo cycloalkyl, a C7-C12 bi- or tri-
cyclic carbocycle, C1-C9 straight or
branched chain alkyl, and C2-C9
straight or branched chain alkenyl,
wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of
Ar4 and C3-CB cycloalkyl; or R' and R"
are taken together to form a
heterocyclic 5- or 6-membered ring
selected from the group consisting of
pyrrolidine, imidazolidine,
pyrazolidine, piperidine, and
piperazine.
W and Y, independently, are 0, S, CH2 or H2;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 73 -
Z is C (Rl) 2, 0, S, a direct bond or NRl; or,
Z-R1 is independently
/C C.
J-K-L J K'---L! , or K"
''
D t
D'
wherein:
C and D are, independently, hydrogen, Ar9,
Arl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, or
C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; wherein
said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted
with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C3-CB
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl
oxygen, Arl and Ar4; wherein said alkyl, alkenyl,
cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl is optionally
substituted with C1-C6 alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl,
hydroxy, amino, halo, haloalkyl, thiocarbonyl,
C1-C6 ester, C1-C6 thioester, C1-C6 alkoxy, C1-C6
alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6 alkylamino,
amino- (C1-C6) alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio- (C1-C6) alkyl,
or sulfonyl; wherein any carbon atom of said
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted in
one or more positions) with oxygen to form a
carbonyl; or wherein any carbon atom of said
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0,
NRS, or ( SO ) P;
C' and D' are independently hydrogen, ArS,
C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein said
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted with
CS-C7 cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, or Ars,
wherein, one or two carbon atoms) of said alkyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 74 -
or alkenyl may be substituted with one or two
heteroatom(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of oxygen, sulfur, SO, and S02
in chemically reasonable substitution patterns,
or
T
Q
whe
rei
n
Q is hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl;
and
T is Ars or CS-C7 cycloalkyl
substituted at positions 3 and 4 with
substituents independently selected
from the group consisting of hydrogen,
hydroxy, 0- (C1-C9 alkyl} , O- (C2-C4
alkenyl), and carbonyl,
J is 0, NR1, S, or (CR1 } 2
K is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl; wherein said alkyl or
alkenyl is optionally substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from
the group consisting of C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched
chain alkenyl, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C,
cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, hydroxy,
carbonyl oxygen, and Ar3; wherein said alkyl,
alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl or Ar3, is
optionally substituted with C1-CQ alkyl, C2-C4
alkenyl, hydroxy, or carbonyl oxygen; wherein
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 75 -
any carbon atom of said alkyl, alkenyl,
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl or Ar3, is optionally
replaced with 0, NR" ', or S(0)p,
wherein R " ' is selected from
the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-
C4 straight or branched chain alkyl,
C3-C4 straight or branched chain
alkenyl or alkynyl, and C1-C9 bridging
alkyl wherein a bridge is formed
between the nitrogen and a carbon atom
of said alkyl or alkenyl chain
containing said heteroatom to form a
ring, wherein said ring is optionally
fused to an Ar3 group;
K' is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, wherein any carbon atom
of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with
amino, halo, haloalkyl, thiocarbonyl, ester,
thioester, alkoxy, alkenoxy, cyano, vitro,
imino, alkylamino, aminoalkyl, sulfhydryl,
thioalkyl, sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a
carbonyl, or wherein any carbon atom of said
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0,
NRS, S (0) p:
K" is C (Rl) 2, 0, S, a direct bond or NRl;
L is an aromatic amine or a tertiary amine
oxidized to a corresponding N-oxide; said
aromatic amine being selected from the group
consisting of pyridyl, pyrimidyl, quinolinyl,
and isoquinolinyl, said aromatic amine being
optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of halo, hydroxy, vitro,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 76 -
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl,
C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-C4 alkenyloxy, phenoxy,
benzyloxy, and amino; and wherein said tertiary
amine is NRXRYRZ, wherein RX, Ry, and RZ are
independently selected from the group consisting
of C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl and C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; wherein
said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted
with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight
or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar3;
wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl, or Ar3 is optionally substituted
with C1-C9 alkyl, C2-CQ alkenyl, hydroxy, or
carbonyl oxygen; wherein any carbon atom of said
alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar3
is optionally replaced with O, NR', S(0)p;
L' is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, wherein any carbon atom
of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with
amino, halo, haloalkyl, thiocarbonyl, ester,
thioester, alkoxy, alkenoxy, cyano, nitro,
imino, alkylamino, aminoalkyl, sulfhydryl,
thioalkyl, sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a
carbonyl, or wherein any carbon atom of said
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0,
NRS, S (O) p;
n is 1 or 2;
p is 0, 1, or 2;
t is 0, 1, 2, 3, or 9;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
_ 77 _
Ar3 is independently selected from the group
consisting of pyrrolidinyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl, pyrazyl,
pyridazyl, quinolinyl, and isoquinolinyl;
Ar4 is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of alkylamino, amido, amino, aminoalkyl, azo,
benzyloxy, C1-Cg straight or branched chain alkyl, C1-C9
alkoxy, C2-C9 alkenyloxy, C2-C9 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, carbonyl,
carboxy, cyano, diazo, ester, formanilido, halo, haloalkyl,
hydroxy, imino, isocyano, isonitrilo, nitrilo, nitro,
nitroso, phenoxy, sulfhydryl, sulfonylsulfoxy, thio,
thioalkyl, thiocarbonyl, thiocyano, thioester,
thioformamido, trifluoromethyl, and carboxylic and
heterocyclic moieties; wherein the individual alicyclic or
aromatic ring contains 5-8 members and wherein said
heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of 0, N, and S; and
wherein any aromatic or tertiary alkyl amine is optionally
oxidized to a corresponding N-oxide;
Ars is independently selected from the group
consisting of 1-napthyl, 2-napthyl, 2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2
thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl and
phenyl, monocyclic and bicyclic heterocyclic ring systems
with individual ring sizes being 5 or 6 which contain in
either or both rings a total of 1-4 heteroatom(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of oxygen,
nitrogen and sulfur; wherein Ars optionally contains 1-3
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl,
nitro, CF3, trifluoromethoxy, C1-C6 straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, O-
(C1-CQ straight or branched chain alkyl) , O- (C2-CQ straight
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
_ 78 _
or branched chain alkenyl), O-benzyl, O-phenyl, amino, 1,2-
methylenedioxy, carbonyl, and phenyl; and
RS is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, and C1-C4
bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is formed between the
nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl chain
containing said heteroatom to form a ring, wherein said
ring is optionally fused to an Ar4 or Arl group.
Additionally, the invention pravides methods for the
preventing and/or treating neurological disorders,
including physically damaged nerves and neurodegenerative
diseases; in treating alopecia and promoting hair growth;
in treating vision disorders and/or improving vision; and
in treating memory impairment and/or enhancing memory
performance by administering a compound of Formula I' to a
patient in need thereof.
Also provided are compounds of Formula I' for use in
the preparation of a medicament for preventing and/or
treating neurological disorders, including physically
damaged nerves and neurodegenerative diseases; in treating
alopecia and promoting hair growth; in treating vision
disorders and/or improving vision; and in treating memory
impairment and/or enhancing memory performance.
Additionally, there is provided a formulation adapted
for use in preventing and/or treating neurological
disorders, including physically damaged nerves and
neurodegenerative diseases; in treating alopecia and
promoting hair growth; in treating vision disorders and/or
improving vision; and in treating memory impairment and/or
enhancing memory performance, which comprises a compound of
Formula I' associated with a pharmaceutically acceptable
carrier, diluent or excipient therefor.
More specifically, the invention provides the
compounds described below, as well as methods, uses, and .
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
_ 79 _
formulations as described above.
I. HETEROCYCLIC THIOESTERS AND KETONES
FORMULA I
In particular, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula I
B
A Z
'R~
(~>
Y X
\W
R2
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
A and B, together with the nitrogen and carbon atoms
to which they are respectively attached, form a 5-7
membered saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring
containing one or more heteroatom(s) independently selected
from the group consisting of 0, S, S0, S02, N, NH, arid NR~;
or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
X is either 0 or S:
Z is either S, CH2, CHR1 or CR1R3;
W and Y are independently 0, S, CH2 or H2;
R, and R3 are independently C1-C6 straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, or a
bridged ring moiety, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of (Arl) ", C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl or CZ-C6 straight or branched chain
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 80 -
alkenyl substituted with (Arl) ~, C3-Cg cycloalkyl, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl or C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl substituted with C3-CB cycloalkyl, a
bridged ring moiety, and Ar2;
n is 1 or 2;
R2 is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-Ce
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl, wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl
is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-Cq
straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring moiety,
and hydroxy; and
Arl and Ar2 are independently an alicyclic or aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring,
wherein said ring is either unsubstituted or substituted
with one or more substituent(s) independently selected from
the group consisting of halo, hydroxyl, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C,-C9 alkoxy, C2-C4
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino; wherein the
individual ring size is 5-8 members; and wherein the
heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of 0, N, and S.
FORMULA II
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may also be a
compound of formula
8~.. I I
.~CH2)n
N Z
Q X
R2 (II)
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 81 -
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
n is 1 or 2~
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the pyrrolidine ring (when n=1) or
the piperidine ring (when n=2) are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
X is 0 or S;
Z is selected from the group consisting of S, CH2,
CHR1, and CR1R3;
R1 and R3 are independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-CS straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-CS
straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring moiety,
and Arl, wherein said alkyl, alkenyl or Arl is unsubstituted
or substituted with one or more substituent(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of halo,
nitro, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight
or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, hydroxy,
C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-CQ alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, amino,
and Arl;
R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C9 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, C3-CB cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl,
a bridged ring moiety, and Arl; and
Arl is independently phenyl, benzyl, pyridyl,
fluorenyl, thioindolyl or naphthyl, wherein said Arl is
unsubstituted or substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of halo, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, nitro, C1-C6
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 82 -
straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched
chain alkenyl, C1-CQ alkoxy, C2-Cq alkenyloxy, phenoxy,
benzyloxy, and amino.
Preferred compounds of formula II are presented in
TABLE I.
(CH2)n
N Z~~
i
O O X
R2 (II)
TABLE I
No n X Z R, RZ
1 1 O CHZ 3-Phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
2 1 O CHZ 3-(3-Pyridyl)propyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
3 1 O CHZ 3-Phenylpropyl tent-Butyl
4 1 O CHZ 3-(3-Pyridyl)propyl tert-Butyl
5 1 O CHZ 3-(3-Pyridyl)propyl Cyclohexyl
2 6 1 O CHZ 3-(3-Pyridyl)propyl Cyclopentyl
0
7 1 O CHZ 3-(3-Pyridyl)propyl Cycloheptyl
8 1 O CHZ 2-(9-Fluorenyl)ethyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
9 1 O S 2-Phenethyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
10 2 O S 2-Phenethyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
2 11 1 O S Methyl(2-thioindole) l , l-Dimethylpropyl
5
12 1 O S 2-Phenethyl Cyclohexyl
13 2 O S 2-Phenethyl tert-Butyl
14 2 O S 2-Phenethyl Phenyl
15 1 O CHZ 3-(4-Methoxyphenyl)propyl1,1-Dimethylpropyl
3 16 2 O CH2 4-(4-Methoxyphenyl)butyl1,1-Dimethylpropyl
0
17 2 O CH2 4-Phenylbutyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
18 2 O CHZ 4-Phenylbutyl Phenyl
19 2 O CHZ 4-Phenylbutyl Cyclohexyl
20 1 S CHz 3-Phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
3 21 1 S S 2-Phenethyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
5
22 2 S CHZ 3-Phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
23 2 S S 2-Phenethyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
24 2 O CHR, 3-Phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
25 2 O CHR, 3-Phenylpropyl Cyclohexyl
4 26 2 O CHR, 3-Phenylpropyl Phenyl
0
27 2 O CHR, 3-Phenylpropyl 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl
28 1 O S 2-Phenethyl Cyclopentyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 83 -
No n X Z R,
29 2 O S 3-Phenylpropyl tent-Butyl
30 1 O S 3-Phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
31 1 O S 3-(3-Pyridyl)propyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
32 1 O S , 3-Phenylpropyl Cyclohexyl
33 1 O S 4-Phenylbutyl Cyclohexyl
34 1 O S 4-Phenylbutyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
35 1 O S 3-(3-Pyridyl)propyl Cyclohexyl
36 1 O S 3,3-Diphenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
37 1 O S 3,3-Diphenylpropyl Cyclohexyl
38 1 O S 3-(4-MethoxyphenyI)propyl1,1-Dimethylpropyl
39 2 O S 4-Phenylbutyl ten-Butyl
40 2 O S 1,5-Diphenylpentyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
41 2 O S 1,5-Diphenylpentyl Phenyl
42 2 O S 3-(4-Methoxyphenyl)propyl1,1-Dimethylpropyl
43 2 O S 3-(4-Methoxyphenyl) propylPhenyl
44 2 O S 3-(1-Naphthyl)propyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
45 1 O S 3,3-Di(4-fluoro)phenyl-propyl1,1-Dimethylpropyl
46 1 O S, 4,4-Di(4-fluoro)phenylbutyl1,1-Dimethylpropyl
47 1 O S 3-(1-Naphthyl)propyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
2 48 1 O S 2, 2-Diphenylethyl 1, i-Dimethylpropyl
0
49 2 O S 2,2-Diphenylethyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
50 2 O S 3,3-Diphenylpropyl 1,I-Dimethylpropyl
51 1 O S 3-(4-{Trifluoromethyl}phenyl)propyl1,1-Dimethylpropyl
52 1 O S 3-(2-Naphthyl)propyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
2 53 2 O S 3-( 1-Naphthyl)propyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
5
54 1 O S 3-(3-Chloro)phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
55 1 O S 3-(3-{Trifluoromethyl}phenyl)propyl1,1-Dimethylpropyl
56 1 O S 3-(2-Biphenyl)propyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
57 1 O S 3-(2-Fluorophenyl)propyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
3 58 1 O S 3-(3-Fluorophenyl)propyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
0
59 2 O S 4-Phenylbutyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
60 2 O S 3-Phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
61 1 O S 3-(2-Chloro)phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
62 2 O S 3-(3-Chloro)phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
3 63 2 O S 3-(2-Fluoro)phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
5
64 2 O S 3-(3-Fluoro)phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
65 1 O S 3-(2,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)propyl1,1-Dimethylpropyl
66 1 O CH2 3-Phenylpropyl Cyclohexyl
67 1 O CHZ 3-Phenylethyl ten-Butyl
4 68 2 O CHz 4-Phenylbutyl Cyclohexyl
0
69 2 O CHR, 2-Phenylethyl tent-Butyl
70 1 O CHZ 3,3-Di(4-fluorophenyl)propyl1,1-Dimethylpropyl
71 2 O CHZ 3-Phenylpropyl 1,1-Dimethylpropyl
45 Preferred compounds of TABLE I are named as follows:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 84 -
1 (2S)-2-((1-Oxo-5-phenyl}-pentyl-1-(3,3-dimethyl-
1,2-dioxopentyl)pyrrolidine
2 3,3-Dimethyl-1-[(2S)-2-(5-(3-pyridyl)pentanoyl)-
1-pyrrolidine]-1,2-pentanedione
3 (2S)-2-({1-Oxo-4-phenyl}-butyl-1-(3,3-dimethyl-
1,2-dioxobutyl)pyrrolidine
9 2-Phenyl-1-ethyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
10 2-Phenyl-1-ethyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-piperidinecarbothioate
11 (3-Thioindolyl)methyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
12 2-Phenyl-1-ethyl (2S)-1-(2-cyclohexyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
14 2-Phenyl-1-ethyl 1-(2-phenyl-1,2-dioxoethyl)-2-
piperidinecarbothioate
//
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
_ 85 -
28 2-Phenyl-1-ethyl (2S)-1-(1-cyclopentyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
29 3-Phenyl-1-propyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxobutyl)-2-piperidinecarbothioate
30 3-Phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
31 3-(3-Pyridyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
32 3-Phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(2-cyclohexyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
33 4-Phenyl-1-butyl (2S)-1-(2-cyclohexyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
34 4-Phenyl-1-butyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
35 3-(3-Pyridyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(2-cyclohexyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
36 3,3-biphenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
37 3,3-biphenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(2-cyclohexyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
38 3- (para-Methoxyphenyl) -1-propyl (2S) -1- (3, 3-
dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidine-
carbothioate
39 4-Phenyl-1-butyl 1-(1,2-dioxo-3,3-dimethylbutyl)
-2-piperidinecarbothioate
1,5-biphenyl-3-pentyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-piperidinecarbothioate
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 86 -
41 1,5-biphenyl-3-mercaptopentyl 1-(3-phenyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)-2-piperidinecarbothioate
42 3-(para-Methoxyphenyl)-1-propyl 1-(1,2-dioxo-
3,3-dimethylpentyl)piperidine-2-carbothioate
43 3-(para-Methoxyphenyl)-1-propyl 1-(2-phenyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)piperidine-2-carbothioate
44 3-(1-Naphthyl)-1-propyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2
dioxopentyl)piperidine-2-carbothioate
45 3,3-Di(para-fluoro)phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3
dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidine
carbothioate
46 4,4-Di(para-fluorophenyl)butyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl
2-oxopentanoyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
47 3-(1-Naphthyl)propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
48 2,2-Diphenylethyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2
oxopentanoyl)tetrahydro-1H-2-pyrrolidine
carbothioate
49 2,2-Diphenylethyl (2S)-l-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarbothioate
50 3,3-Diphenylpropyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarbothioate
51 3- [4- (Trifluoromethyl) phenyl) propyl (2S) -1- (3, 3
dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-pyrrolidine
carbothioate
52 3-(2-Naphthyl)propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
53 3- ( 2-Naphthyl ) propyl ( 2R, S) -1- ( 3, 3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarbothioate
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 87 _
54 3-(3-Chlorophenyl)propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
55 3- [3- (Trifluoromethyl) phenyl] propyl (2S) -1- (3, 3-
dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-pyrrolidine-
carbothioate
56 3-(1-Biphenyl)propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
57 3-(2-Fluorophenyl)propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
58 3-(3-Fluorophenyl)propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
59 4-Phenylbutyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-
piperidinecarbothioate
60 3-Phenylpropyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-
2-piperidinecarbothioate
61 3-(2-Chlorophenyl)propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbothioate
62 3-(2-Chlorophenyl)propyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarbothioate
63 3-(2-Fluorophenyl)propyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarbothioate
64 3-(3-Fluorophenyl)propyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarbothioate
65 3-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-
d i m a t h y 1 - 2 - o x o p a n t a n o y 1 ) - 2 -
pyrrolidinecarbothioate
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
88 _
66 (2S)-2-((1-Oxo-4-phenyl}-butyl-1-(2-Cyclohexyl-
1,2-dioxoethyl)pyrrolidine
67 2-((1-Oxo-4-phenyl}-butyl-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxobutyl)pyrrolidine
68 2-({1-Oxo-6-phenyl}-hexyl-1-(2-Cyclohexyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)piperidine
69 2-((1-Oxo-[2-~2'-phenyl}ethyl]-4-phenyl}-butyl-
1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxobutyl)piperidine
70 1-( (2S) -2- [5, 5-di (4-Fluorophenyl) pentanoyl] -2
pyrrolidine}-3,3-dimethyl-1,2-pentanedione
71 3 , 3 - D i m a t h y 1 - 1 - [ 2 - ( 4 -
phenylpentanoyl)piperidino]-1,2-pentanedione
FORMULA III
Furthermore, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula III:
Rr
(III)
Rz
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
A, B, and C are independently CH2, 0, S, S0, 502, NH or
NR2;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more of A, B, and C are bonded to each other
through either
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 89 -
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
X is O or S;
Z is S, CH2, CHR1 or CR1R3;
Rl and R3 are independently C1-C6 straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, or a
bridged ring moiety, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of (Arl) ~, a bridged ring
moiety, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl or C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl substituted with (Arl)n,
C3-Ca cycloalkyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl or
C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl substituted with
C3-C8 cycloalkyl, and Ar2;
n is 1 or 2;
R2 is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-Ce
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl, wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl
is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-CQ straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-CQ
straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring moiety,
and hydroxyl; and
Arl and Ar2 are independently an alicyclic or aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring,
wherein said ring is either unsubstituted or substituted
with one or more substituent(s) independently selected from
the group consisting of halo, hydroxyl, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 90 -
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C~-C9 alkoxy, C2-C9
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino; wherein the
individual ring size is 5-8 members; and wherein the
heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of O, N, and S.
Preferred compounds of formula III are presented in
TABLE II:
Br,;,;~~C
A v. Z
N ~ \R~
O O X
R2
TABLE II
No. A B C X Z R, R2
72 CHZ S CHZ O S 2-phenethyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
73 CHZ S CHZ O CH2 3-phenylpropyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
,
74 CHZ CHz NH O S 2-phenethyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
75 CHZ S CHZ S S 2-phenethyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
FORMULA IV
Alternatively, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula IV:
Br;,,
C
,.>'...~
D
,,
2 5 A~ Z~
Ri
O O X
(IV)
R2
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
_ 91 _
A, B, C and D are independently CH2, 0, S, S0, 502, NH
or NR2;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more of A, B, C and D are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
X is O or S;
Z is S, CH2, CHR1 or CR1R3;
Rl and R3 are independently C1-C6 straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, or a
bridged ring moiety, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of (Arl) n, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl substituted with (Arl) ~, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl or C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl substituted with C3-Ce cycloalkyl, a
bridged ring moiety, and Ar2;
n is 1 or 2;
R2 is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, bridged ring moiety, or Arl,
wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl is
either unsubstituted or substituted with one or mr,rP
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C3-Ce cycloalkyl, C1-Cq straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-CQ straight or branched chain alkenyl,
bridged ring moiety, and hydroxyl; and
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 92 -
Arl and Ar2 are independently an alicyclic or aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring,
wherein said ring is either unsubstituted or substituted
with one or more substituent (s) independently selected from
the group consisting of halo, hydroxyl, nitro, trifluoro-
methyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkPr,«i r _r- ~, v...... ,.
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino; wherein the
individual ring size is 5-8 members; and wherein the
heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of 0, N, and S.
Preferred compounds of formula IV are presented in
TABLE III.
Br;,
C
Z
\R1
R2
TABLE III
No A B C D X Z R
76 CHZ CHZ O CHZ O CHZ 3-phenylpropyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
77 CHZ CHZ O CHZ O S 2-phenethyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
78 CHz CHZ S CHZ O CH2 3-phenylpropyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
2 5 79 CHZ CH2 S CH2 O S 2-phenethyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
FORMULA V
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may further be a
compound of formula V:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 93 -
~B
Z
I
Y
(V)
R2
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
V is CH, N, or S;
A and B, together with V and the carbon atom to which
they are respectively attached, form a 5-7 membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring one or more
heteroatom(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of 0, S, SO, 502, N, NH, and NR9; or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
R9 is independently either C1-C9 straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C9
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety,, or
Ar3, wherein RQ is either unsubstituted or substituted with
one or more substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, carbonyl,
carboxy, hydroxy, vitro, trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, C2-CQ alkenylaxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy,
thio-C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-alkylthio, sulfhydryl, amino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, aminocarboxyl, a bridged ring
moiety, and Ar9;
Ar3 and Ar4 are independently an alicyclic ar aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring;
wherein the individual ring size is 5-8 members; wherein
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 94 -
said heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of 0, N,
and S; and
R1, R2, W, X, Y, and Z are as defined in Formula I
above.
II. HETEROCYCLIC ESTERS AND AMIDES
FORMULA VI
Additionally, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula VI:
A Z
\N y
Y
,. W X
(VI)
R2
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
A and B, together with the nitrogen and carbon atoms
to which they are respectively attached, form a 5-7
membered saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring
containing one or more heteroatom(s) independently selected
from the group consisting of 0, S, SO, 502, N, NH, and NR1;
or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
X is O or S;
Z is 0, NH or NRI;
W and Y are independently O, S, CH2 or H2;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 95 -
Rl is independently C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, or a
bridged ring moiety, which is substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of (Arl)", C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl
or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl substituted with
(Arl)~, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl
substituted with C3-Cg cycloalkyl, a bridged ring moiety,
and Ar2;
n is 1 or 2;
R2 is independently either C1-C9 straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain or alkenyl,
C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety,
or Arl, wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or
cycloalkenyl is either unsubstituted or substituted with
one or more substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of C1-CQ straight or branched chain alkyl,
C2-C4 straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring
moiety, and hydroxyl; and
Arl and Ar2 are independently an alicyclic or aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring,
wherein the ring is either unsubstituted or substituted
with one or more substituent(s) independently selected from
the group consisting of halo, hydroxyl, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, C2-C4
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino; wherein the
individual ring size is 5-8 members; and wherein the
heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of 0, N, and S.
Suitable carbo- and heterocyclic rings include without
limitation naphthyl, indolyl, furyl, thiazolyl, thienyl,
pyridyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, fluorenyl and phenyl.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 96 -
FORMULA VII
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may also be a
compound of formula VII:
Br; _,,$-
,,,,~ _ .
O -Ri
O
\ O
~O
R2 (VII)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
A, B and C are independently CH2, 0, S, SO, S02, NH or
NR1;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more of A, B and C are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
R1 is C1-C5 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-CS
straight or branched chain alkenyl, or a bridged ring
moiety, which is substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of (Arl)n and C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl
substituted with (Arl)~%
n is 1 or 2;
R2 is independently either C1-C9 straight or branched
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 97 -
chain alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-CB
cycloalkyl, C5-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl; and
Arl is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi~- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of halo, hydroxyl, vitro, trifluoromethyl, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, Cz-C6 straight or branched
chain alkenyl, C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-C9 alkenyloxy, phenoxy,
benzyloxy, and amino; wherein the individual ring size is
5-8 members; and wherein the heterocyclic ring contains 1-6
heteroatom(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of 0, N, and S.
A preferred compound of formula VII is:
13r
In a particularly preferred embodiment of formula VII
compounds:
A is CH2;
B is CH2 or S;
C is CH2 or NH;
two or more of A, B, and C, taken together with the
atoms to which they are attached, form a saturated,
unsaturated, or aromatic heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged
ring moiety;
R1 is independently selected from the group consisting
of 3-phenylpropyl and 3-(3-pyridyl)propyl; and
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
_ 98 _
R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of l,l-dimethylpropyl, cyclohexyl, and tert-butyl.
Specific examples of this embodiment are presented in
TABLE IV:
Br._ ..
-R~
R2
IO
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 99 -
TABLE IV
No. A B C R~ Rz
80 CHz S CHz 3-phenylpropyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
81 CHz S CHz 3-(3-pyridyl)propyll , l-dimethylpropyl
82 CHz S CHz 3-phenylpropyl cyclohexyl
83 CHz S CHz 3-phenylpropyl tert-butyl
84 CHz CHz NH 3-phenylpropyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
85 CHz CHz NH 3-phenylpropyl cyclohexyl
86 CHz CHz NH 3-phenylpropyl tent-butyl
FORMULA VIII
In a further embodiment of this invention, the bridged
heterocyclic derivative may be a compound of formula VIII:
Br
~' C
B~, ;wD
O~R~
O
O
~O
R2
(VIII)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
A, B, C and D are independently CH2, 0, S, SO, 502, NH
or NR1;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more of A, B, C and D are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 100 -
Rl is independently C1-CS straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-CS straight or branched chain alkenyl, or a
bridged ring moiety, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of (Arl)n and C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl or C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl substituted with (Arl)~%
n is 1 or 2;
R2 is independently either C,-C~ straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-Ce
cycloalkyl, CS-C, cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl; and
Arl is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of halo, hydroxyl, nitro, trifluoromethyl, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched
chain alkenyl, C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-CA alkenyloxy, phenoxy,
benzyloxy, and amino; wherein the individual ring size is
5-8 members; and wherein the heterocyclic ring contains 1-6
heteroatom(s} independently selected from the group
consisting of 0, N, and S.
In a particularly preferred embodiment of formula VIII
compounds:
A is CH2;
B is CH2;
C is S, 0 or NH;
D is CH2;
Two or more of A, B, C, and D, taken together with the
atoms to which they are attached, form a saturated,
unsaturated, or aromatic heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCTNS98/25577
- 101 -
ring moiety;
R1 is independently selected from the group consisting
of 3-phenylpropyl and (3,4,5-trimethoxy)phenylpropyl; and
R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of 1,1-dimethylpropyl, cyclohexyl, tert-butyl, phenyl, and
3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl.
Specific examples of this embodiment are presented in
TABLE V.
Br,
,,, C
D
ANN i O~R~
O
TABLE V
No. A B C D R, Rz
87 CH2 CH2 S CH2 3-phenylpropyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
88 CH2 CHz O CHZ 3-phenylpropyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
89 CH2 CHz S CHZ 3-phenylpropylcyclohexyl
2 0 90 CHZ CHz O CHZ 3-phenylpropylcyclohexyl
91 CHZ CHZ S CHZ 3-phenylpropylphenyl
92 CHZ CHz O CH2 3-phenylpropylphenyl
93 CHZ CHZ NH CHZ 3-phenylpropyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
94 CHZ CH2 NH CHZ 3-phenylpropylphenyl
FORMULA IX
Additionally, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula IX:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 102 -
~B
Z\
Y
(IX)
R2
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
V is CH, N, or S;
A and B, together with V and the carbon atom to which
they are respectively attached, form a 5-7 membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring containing one
or more heteroatom(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of 0, S, S0, 502, N, NH, and NR; or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
R is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-Cg
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Ar3, wherein R is independently either unsubstituted or
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of halo, halo-C1-C6-
alkyl, carbonyl, carboxy, hydroxy, nitro, trifluoromethyl,
C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, C1-CQ alkoxy, C2-C4 alkenyloxy,
phenoxy, benzyloxy, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, CI-C6-alkylthio,
sulfhydryl, amino, C1-C6-alkylami no, amino-C1-C6-alkyl,
aminocarboxyl, a bridged ring moiety, and Ar4;
Ar3 and Ar4 are independently an alicyclic or aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring;
wherein the individual ring size is 5-8 members; wherein
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 103 -
said heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of 0, N,
and S; and
X is 0 or S;
Z is 0, NH or NRl;
W and Y are independently O, S, CH2 or H2;
R1 is independently C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, or a
bridged ring moiety, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of (Arl) n, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl substituted with (Arl) n, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl or C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl substituted with C3-Ca cycloalkyl,
and Ar2;
n is 1 or 2;
R2 is independently C1-Cg straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain or alkenyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl, wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl
is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C4 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C9
straight or branched chain alkenyl, and hydroxyl; and
Arl and Ar2 are independently an alicyclic or aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring,
wherein the ring is either unsubstituted or substituted
with one or more substituent(s) independently selected from
the group consisting of halo, hydroxyl, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C,-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-C9
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino; wherein the
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 104 -
individual ring size is 5-8 members; and wherein the
heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of 0, N, and S.
N-OXIDES OF HETEROCYCLIC ESTERS AMIDES
THIOESTERS AND KETONES
FORMULA X
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may further be a
compound of formula X:
g
X~Y/Z
I
O
(X)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
A and B, together with the nitrogen and carbon atoms
to which they are respectively attached, form a 5-7
membered saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring
containing one or more heteroatom(s) independently selected
from the group consisting of O, S, SO, 502, N, NH, and NR1;
or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
W is O, S, CH2, or H2;
R is independently C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C~
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl, which is optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 105 -
consisting of C,-Cq alkyl, C2-CQ alkenyl, hydroxy, C3-Ce
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, and
Ar2 ;
Arl and Ar2 are independently selected from the group
consisting of 1-napthyl, 2-napthyl, 1-indolyl, 2-indolyl,
2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-
pyridyl, 4-pyridyl and phenyl, having one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C2-C.A alkenyloxy,
phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
X is 0, NH, NR1, S, CH, CR1, or CR1R3;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; wherein
said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C$ cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar is
optionally substituted with C1-CQ alkyl, C~-Cq alkenyl,
hydroxy, or carbonyl oxygen; wherein any carbon atom of
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar is
optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR." S, SO, or S02;
R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-C9
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-C4 bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Z is an aromatic amine or a tertiary amine oxidized to
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 106 -
a corresponding N-oxide;
said aromatic amine is selected from the group
consisting of pyridyl, pyrimidyl, quinolinyl, or
isoquinolinyl, which is either unsubstituted or substituted
with one or more substituent(s) independently selected from
the group consisting of halo, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-C4
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
said tertiary amine is NR4RSR~, wherein R4, R5, and R6
are independently selected from the group consisting of a
bridged ring moiety, or C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl optionally
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
I5 selected from the group consisting of C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring
moiety, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein said
alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar is
optionally substituted with C1-Cq alkyl, C2-C9 alkenyl,
hydroxy, or carbonyl oxygen; wherein any carbon atom of
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar is
optionally replaced with O, NH, NR1, S, S0, or 502;
Ar is independently selected from the group consisting
of pyrrolidinyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl, pyrazyl, pyridazyl,
quinolinyl, and isoquinolinyl; and
R1 and R3 are independently hydrogen, C1-C9 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C3-CQ straight or branched chain
alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged ring moiety, or Y-Z.
FORMULA XI
Moreover, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may be
a compound of formula XI:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00116603 PCT/US98/25577
- 107 -
Bf, . ..~W
X~Y/Z
(XI)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
E, F, G and J are independently CH2, O, S, S0, S02, NH
or NRl;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more of E, F, G and J are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
W is 0, S, CH2, or H2;
R is independently C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-CB
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl, which is optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-Cq alkyl, C2-Cq alkenyl, hydroxy, C3-C~
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, and
Arl ;
Arl is independently selected from the group
consisting of 1-napthyl, 2-napthyl, 1-indolyl, 2-indolyl,
2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-
pyridyl, 4-pyridyl, and phenyl, having one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 108 -
consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, vitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C2-C9 alkenyloxy,
phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
X is O, NH, NR1, S, CH, CR1, or CR~R3;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; wherein
said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C?
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar is
optionally substituted with C1-CQ alkyl, C2-C4 alkenyl,
hydroxy, or carbonyl oxygen; wherein any carbon atom of
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar is
optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR2, S, S0, or 502;
R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C4 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-CQ
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-Ca bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Z is an aromatic amine or a tertiary amine oxidized to
a corresponding N-oxide;
said aromatic amine is pyridyl, pyrimidyl, quin-olinyl,
and isoquinolinyl, which is either unsubstituted or
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of halo, hydroxy, vitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, C2-C~
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 109 -
said tertiary amine is NR9RSR6, wherein R4, R5, and RE
are independently selected from the group consisting of C1-
C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, a bridged ring moiety,
and C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; wherein said
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C;,
cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, hydroxy, carbonyl
oxygen, and Ar; wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl, or Ar is optionally substituted with C1-C9
alkyl, C2-C4 alkenyl, hydroxy, or carbonyl oxygen; wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl, or Ar is optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR"
S, SO, or 502
Ar is independently selected from the group consisting
of pyrrolidinyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl, pyrazyl, pyridazyl,
quinolinyl, and isoquinolinyl; and
R1 and R3 are independently hydrogen, C1-C4 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C3-CQ straight or branched chain
alkenyl or alkynyl, or Y-Z.
FORMULA XII
Furthermore, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula XII:
Bf, .,, E-G
..
E\N X\Y/Z
O O
(XII)
R
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 110 -
E, F, and G are independently CH2, 0, S, S0, 502, NH or
NRl;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more of E, F, and G are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
W is O, S, CH2, or H2;
R is independently C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C$
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl, which is optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-CQ alkyl, C2-C4 alkenyl, hydroxy, C3-C$
cycloalkyl, C5-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, and
Arl ;
Arl is independently selected from the group
consisting of 1-napthyl, 2-napthyl, 1-indolyl, 2-indolyl,
2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-
pyridyl, 4-pyridyl and phenyl, having one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain al~:enyl, C2-C9 alkenyloxy,
phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
X is 0, NH, NR1, S, CH, CR1, or CR1R3;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; wherein
said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted with one or
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 111 -
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-CB cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar is
optionally substituted with C1-C9 alkyl, C2-C9 alkenyl,
hydroxy, or carbonyl oxygen; wherein any carbon atom of
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar is
optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR2, S, S0, or S02;
IO R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C4 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-CQ
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-CQ bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Z is an aromatic amine or a tertiary amine oxidized to
a corresponding N-oxide;
said aromatic amine is pyridyl, pyrimidyl, quinolinyl,
or isoquinolinyl, which is either unsubstituted or
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of halo, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-C9
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
said tertiary amine is NRQRSR6, wherein R9, R5, and R6
are independently selected from the group consisting of C1-
C6 straight or branched chain alkyl,a bridged ring moiety,
and C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; wherein said
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C,
cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, hydroxy, carbonyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 112 -
oxygen, and Ar; wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl, or Ar is optionally substituted with C1-CQ
alkyl, C2-C9 alkenyl, hydroxy, or carbonyl oxygen; wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl, or Ar is optionally replaced with O, NH, NR1,
S, S0, or S02;
Ar is independently selected from the group consisting
of pyrrolidinyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl, pyrazyl, pyridazyl,
quinolinyl, and isoquinolinyl; and
R1 and R3 are independently hydrogen, C,-Cq straight or
branched chain alkyl, C3-C9 straight or branched chain
alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged ring moiety, or Y-Z.
FORMULA XIII
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may also be a
compound of formula XIII:
Q.
X~Y/Z
(XIII)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
n is 1, 2, or 3, forming a 5-7 member heterocyclic
ring;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the primary ring (when n is 1, 2,
or 3) are bonded to each other thraugh either
a chemical bond or
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 113 -
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
W is 0, S, CH2, or H2;
R is independently C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-Ce
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl, which is optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C4 alkyl, C2-C9 alkenyl, hydroxy, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, and
Arl;
Arl is independently selected from the group
consisting of 1-napthyl, 2-napthyl, 1-indolyl, 2-indolyl,
2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-
pyridyl, 4-pyridyl and phenyl, having one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C2-CQ alkenyloxy,
phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
X is 0, NH, NR1, S, CH, CR1, or CR1R3;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; wherein
said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-CB cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar is
optionally substituted with C1-Cq alkyl, C2-C4 alkenyl,
hydroxy, or carbonyl oxygen; wherein any carbon atom of
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, or Ar is
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 114 -
optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR2, S, SO, or S02;
R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C4 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-C9
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-CQ bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Z is an aromatic amine or a tertiary amine oxidized to
a corresponding N-oxide;
said aromatic amine is pyridyl, pyrimidyl, quinolinyl,
or isoquinolinyl, which is either unsubstituted or
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of halo, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, C2-C9
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
said tertiary amine is NRQRSR~, wherein R4, R5, and R6
are independently selected from the group consisting of C1-
C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, a bridged ring moiety,
and C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; wherein said
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-CB cycloalkyl, C5-C7
cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, hydroxy, carbonyl
oxygen, and Ar; wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl, or Ar is optionally substituted with C1-C9
alkyl, C2-CQ alkenyl, hydroxy, or carbonyl oxygen; wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl, or Ar is optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR1,
S, S0, or S02;
Ar is independently selected from the group consisting
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 115 -
of pyrrolidinyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl, pyrazyl, pyridazyl,
quinolinyl, and isoquinolinyl; and
R1 and R3, independently, are hydrogen, C1-Cq straight
or branched chain alkyl, C3-C9 straight or branched chain
alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged ring moiety, or Y-Z.
Examples of the compounds of formula XIII when W is O are
presented in TABLE VI:
Br
. \N X\Y/Z
O~ ~ O
TABLE VI
No. n X Y Z R
95 1 O (CH~3 3-Pyridyl N-oxide1,1-dimethylpropyl
96 1 O (CH~3 2-Pyridyl N-oxide1,1-dimethylpropyl
97 1 O (CHz)3 4-Pyridyl N-oxide1,1-dimethylpropyl
98 1 O (CH,~3 2-Quinolyl N-oxide1,1-dimethylpropyl
99 1 O (CH~3 3-Quinolyl N-oxide1,1-dimethylpropyl
100 1 O (CH~3 4-Quinolyl N-oxide1,1-dimethylpropyl
Preferred compounds of formula XIII may be selected
from the group consisting of:
3-(2-Pyridyl)-1-propyl(2S)-1-(1,1-Dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate, N-oxide;
3-(3-Pyridyl)-1-propyl(2S)-1-(1,1-Dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate, N-oxide;
3-(9-Pyridyl)-1-propyl(2S)-1-(1,1-Dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate, N-oxide;
3-(2-Quinolyl)-1-propyl(2S)-1-(1,1-Dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate, N-oxide;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 116 -
3-(3-Quinolyl)-1-propyl(2S)-1-(1,1-Dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate, N-oxide;
3-(4-Quinolyl)-1-propyl(2S)-1-(1,1-Dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate, N-oxide;
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, and solvates
thereof.
FORMULA XIV
Additionally, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula XIV:
B
A
\V X~Y/Z
O O
(XIV)
R
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
V is CH, N, or S;
A and B, together with V and the carbon atom to which
they are respectively attached, form a 5-7 memberPC~
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring cantaining one
or more heteroatom(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of O, S, S0, S02, N, NH, and NR7; or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
R7 is independently either C1-C9 straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C9
cycloalkyl, CS-C, cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Ar3, wherein R7 is either unsubstituted or substituted with
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 117 -
one or more substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, carbonyl,
carboxy, hydroxy, nitro, trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, C1-C4 alkoxy, C2-CQ
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-
alkylthio, sulfhydryl, amino, C1-C6-alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-
alkyl, aminocarboxyl, and Ar4;
Ar3 and Ar4 are independently an alicyclic or aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring;
wherein the individual ring size is 5-8 members; wherein
said heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of O, N,
and S; and
R, W, X, Y, and Z are as defined in Formula X above.
IV. N-LINKED UREAS AND CARBAMATES OF HETEROCYCLIC
THIOESTERS
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may further be a
compound of formula XV:
B
A S-~Y-Z
\N 1 \D
X
R1 (xv)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
A and B, together with the nitrogen and carbon atoms
to which they are respectively attached, form a 5-7
membered saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 118 -
containing one or more heteroatom(s) independently selected
from the group consisting of O, S, SO, 502, N, NH, and NR3;
or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
X is either 0 or S;
Y is a direct bond., C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-CE,-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR3, S, SO, or S02;
R3 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-Cq bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Ar is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with.one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6-alkylamino, amido, amino, amino-C1-C6-
alkyl, azo, benzyloxy, C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C,-C9 alkoxy, C2-C9 alkenyloxy, C2-C9 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl,
carbonyl, carboxy, cyano, diazo, C,.-C6-ester, formanilido,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 119 -
halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, imino, isocyano,
isonitrilo, nitrilo, vitro, nitroso, phenoxy, sulfhydryl,
sulfonylsulfoxy, thio, thin-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl,
thiocyano, thio-C1-C6-ester, thioformamido, trifluoromethyl,
and carboxylic and heterocyclic moieties; wherein the
individual ring size is 5-8 members; wherein said
heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of O, N, and S; and
wherein any aromatic or tertiary alkyl amine is optionally
oxidized to a corresponding N-oxide;
Z is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, vitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR3, S, SO, or 502;
C and D are independently hydrogen, Ar, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl; wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C3-C8 cycloalkyl; CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl_ or cycloalkenyl is
optionally substituted with C1-Cf;-alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl,
hydroxy, amino, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-
ester, thio-C1-C6-ester, C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano,
vitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, or sulfonyl; wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with oxygen to form
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 120 -
a carbonyl; or wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or
alkenyl is optionally replaced with O, NH, NR3, S, S0, or
S02;
W is O or S; and
U is either 0 or N, provided that:
when U is O, then R1 is a lone pair of
electrons and R2 is selected from the group
consisting of Ar, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, a bridged
ring moiety, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of Ar and C3-Ce cycloalkyl; and
when U is N, then R1 and R2 are
independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, Ar, C3-Clo cycloalkyl, a bridged ring
moiety, C7-C12 bi- or tri-cyclic carbocycle, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, and C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein said
alkyl or alkenyl is substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of Ar, a bridged ring moiety,
and C3-C8 cycloalkyl; or R1 and R2 are taken
together to form a heterocyclic 5 or 6 membered
ring selected from the group consisting of
pyrrolidine, imidazolidine, pyrazolidine,
piperidine, and piperazine.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XV, Ar is
independently selected from the group consisting of phenyl,
benzyl, naphthyl, indolyl, pyridyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl,
pyridinyl, pyrimidinyl, purinyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl,
furyl, fluorenyl, thiophenyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 121 -
thiazolyl, pyrazolyl, and thienyl.
FORMULA XVI
Moreover, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may be
a compound of formula XVI:
Br ;;'F~G~ J
'~,
N ~ \
D
X
(XVI)
Ri
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
E, F, G and J are independently CH2, O, S, S0, 502, NH,
or NR3;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more of E, F, G and J are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
X is either 0 or S;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C~-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 122 -
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0, or 502;
R3 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C4 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-C4
straight or branched chain alkenyl. or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-CQ bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Ar is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6-alkylamino, amido, amino, amino-C1-C6-
alkyl, azo, benzyloxy, C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-C9 alkenyloxy, C2-C9 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, C3-CB cycloalkyl, CS-C, cycloalkenyl,
carbonyl, carboxy, cyano, diazo, C1-C6-ester, formanilido,
halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, imino, isocyano,
isonitrilo, nitrilo, nitro, nitroso, phenoxy, sulfhydryl,
sulfonylsulfoxy, thio, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl,
thiocyano, thio-C1-C6-ester, thioformamido, trifluoromethyl,
and carboxylic and heterocyclic moieties, including
alicyclic and aromatic structures; wherein the individual
ring size is 5-8 members; wherein said heterocyclic ring
contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of 0, N, and S; and wherein any aromatic
or tertiary alkyl .amine is optionally oxidized to a
corresponding N-oxide
Z is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 123 -
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-Cb-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0, or 502;
C and D are independently hydrogen, Ar, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl; wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl is
optionally substituted with C1-C6-alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl,
hydroxy, amino, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-
ester, thio-Cl-C6-ester, C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano,
nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkyl amino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, or sulfonyl; wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with oxygen to form
a carbonyl; or wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or
alkenyl is optionally replaced with O, NH, NR3, S, S0, or
S02;
4V is 0 or S; and
U is either 0 or N, provided that:
when U is O, then R1 is a lone pair of
electrons and R2 is selected from the group
consisting of Ar, C3-CB cycloalkyl, a bridged
ring moiety, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 124 -
group consisting of Ar and C3-CB cycloalkyl; and
when U is N, then R1 and R2 are,
independently, selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, Ar, a bridged ring
moiety, C3-Clo cycloalkyl, C7-C12 bi- or tri-cyclic
carbocycle, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of Ar and C3-CB cycloalkyl; or
R1 and R2 are taken together to form a
heterocyclic 5 or 6 membered ring selected from
the group consisting of pyrrolidine,
imidazolidine, pyrazolidine, piperidine, and
piperazine.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XVI, Ar is
independently selected from the group consisting of phenyl,
benzyl, naphthyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyridinyl,
pyrimidinyl, purinyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, furyl,
thiophenyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, pyrazolyl, and
thienyl.
FORMULA XVII
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may also be a
compound of formula XVII:
Br;;~~~ c
E '
\N S\Y~z~D
3 0 RZ \ /~
a w
(XVII)
R~
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 125 -
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
E, F, and G are independently CH2, O, S, S0, 502, NH,
and NR3;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more of E, F, and G are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
X is either 0 or S;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
Cl-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkyl amino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0, or S02;
R3 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C4 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-C4
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-C9 bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Ar is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 126 -
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6-alkyl amino, amido, amino, amino-C1-C6-
alkyl, azo, benzyloxy, C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-C9 alkenyloxy, C2-C9 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, C3-CB cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl,
carbonyl, carboxy, cyano, diazo, C1-C6-ester, formanilido,
halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, imino, isocyano,
isonitrilo, nitrilo, nitro, nitrosa, phenoxy, sulfhydryl,
sulfonylsulfoxy, thio, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl,
thiocyano, thio-C1-C6-ester, thioformamido, trifluoromethyl,
and carboxylic and heterocyclic moieties, including
alicyclic and aromatic structures; wherein the individual
ring size is 5-8 members; wherein said heterocyclic ring
contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of O, N, and S; and wherein any aromatic
or tertiary alkyl amine is optionally oxidized to a
corresponding N-oxide;
Z is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more position (s) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0, or 502;
C and D are independently hydrogen, Ar, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl; wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C3-CB cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 127 -
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl is
optionally substituted with C1-C6-alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl,
hydroxy, amino, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-
ester, thio-C1-C6-ester, C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano,
nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, or sulfonyl; wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with oxygen to form
a carbonyl; or wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or
alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0, or
S02
W is 0 or S; and
U is either 0 or N, provided that:
when U is O, then R1 is a lone pair of
electrons and R2 is selected from the group
consisting of Ar, a bridged ring moiety, C3-Cg
cycloalkyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of Ar and C3-C8 cycloalkyl; and
when U is N, then R1 and R2 are,
independently, selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, Ar, a bridged ring
moiety, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C7-C12 bi- or tri-cyclic
carbocycle, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of Ar and C3-CB cycloalkyl; or
R1 and R2 are taken together to form a
heterocyclic 5 or 6 membered ring selected from
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 128 -
the group consisting of pyrrolidine,
imidazolidine, pyrazolidine, piperidine, and
piperazine.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XVII, Ar is
independently selected from the group consisting of phenyl,
benzyl, naphthyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyridinyl,
pyrimidinyl, purinyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, furyl,
thiophenyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, pyrazolyl, and
thienyl.
FORMULA XVIII
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may further be a
compound of formula XVIII:
(CHy)n C
','N S\Y~Z~D
R2~ X
U W
(XVIII)
Ry
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
n is 1, 2 or 3;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the primary ring (when n is 1, 2
or 3) are bonded to each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 129 -
X is either O or S;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkeny.l is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0, or 502;
R3 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-Cq
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-CQ bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Ar is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or
more substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of C1-C6-alkylamino, amido, amino, amino-C1-C6-
alkyl, azo, benzyloxy, C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-C9 alkenyloxy, C2-C9 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl,
carbonyl, carboxy, cyano, diazo, C1-C6-ester, formanilido,
halo, halo-C~-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, imino, isocyano,
isonitrilo, nitrilo, nitro, nitroso, phenoxy, sulfhydryl,
sulfonylsulfoxy, thio, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl,
thiocyano, thio-C1-C6-ester, thioformamido, trifluoromethyl,
and carboxylic and heterocyclic moieties, including
alicyclic and aromatic structures; wherein the individual
ring size is 5-8 members; wherein said heterocyclic ring
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 130 -
contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of 0, N, and S; and wherein any aromatic
or tertiary alkyl amine is optionally oxidized to a
corresponding N-oxide;
Z is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more position (s) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0, or 502;
C and D are independently hydrogen, Ar, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl; wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl is
optionally substituted with C1-Cf;-alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl,
hydroxy, amino, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-
ester, thio-C1-C6-ester, alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano,
nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, or sulfonyl; wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with oxygen to form
a carbonyl; or wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or
alkenyl is optionally replaced with O, NH, NR3, S, S0, or
S02 ;
W is O or S: and
U is either 0 or N, provided that:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/Z5577
- 131 -
when U is O, then R1 is a lone pair of
electrons and R2 is selected from the group
consisting of Ar, a bridged ring moiety, C3-CB
cycloalkyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain or
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of Ar and C3-CB cycloalkyl; and
when U is N, then R1 and R2 are,
independently, selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, Ar, a bridged ring
moiety, C3-Clo cycloalkyl, C7-C12 bi- or tri-cyclic
carbocycle, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of Ar and C3-C8 cycloalkyl; or
R1 and R2 are taken together to form a
heterocyclic 5 or 6 membered ring selected from
the group consisting of pyrrolidine,
imidazolidine, pyrazolidine, piperidine, and
piperazine.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XVIII, Ar is
independently selected from the group consisting of phenyl,
benzyl, naphthyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyridinyl,
pyrimidinyl, purinyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, furyl,
thiophenyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, pyrazolyl, and
thienyl.
Exemplary compounds in which U is N and X is 0 of
formula XVIII are presented in TABLE VII.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00116603 PCT/US98/25577
- I32 -
Br
Rz\
c
\Y/Z\D
TABLE VII
No. n W Y Z C D R R
101 1 O (CHZ)2CH 3-Pyridyl H H 2-Methylbutyl
102 1 O (CH2)2CH 3-Pyridyl H H 1,1-dimethylpropyl
103 1 O (CHZ)2CH 4-MethoxyphenylH H 1,1-dimethylpropyl
104 1 O CHz CH Phenyl H H I ,1-dimethylpropyl
105 1 S (CHZ)zCH 4-MethoxyphenylH H Cyclohexyl
106 1 O (CHZ)ZCH 3-Pyridyl H H Cyclohexyl
107 I S (CHZ)ZCH 3-Pyridyl H H Cyclohexyl
108 1 S (CHZ)2CH 3-Pyridyl H H 1-Adamantyl
109 1 S (CH2)ZCH 3-Pyridyl H H 1,1-dimethylpropyl
110 1 O (CH2)2CH Phenyl Phenyl H 1,1-dimethyipropyl
111 2 O (CHZ)2CH Phenyl H H 1,1-dimethylpropyl
112 2 O (CH2)ZCH Phenyl H H Phenyl
2 0 113 2 O DirectCH 2-Phenylethyl2-PhenylethylH Phenyl
bond
114 2 O DirectCH 2-Phenylethyl2-PhenylethylH Cyclohexyl
bond
115 2 S DirectCH 2-Phenylethyl2-PhenylethylH Cyclohexyl
bond
116 2 O (CHZ)ZCH 4-MethoxyphenylH H Cyclohexyl
The most preferred compounds of formula XVIII are
selected from the group consisting of:
3-(3-Pyridyl)-1-propyl-2S-1-[(2-methylbutyl)
carbamoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate;
3-(3-Pyridyl)-1-propyl-2S-1-[(1',1'-
Dimethylpropyl) carbamoyl]pyrrolidine-2-
carboxylate;
3-(3-Pyridyl)-1-propyl-2S-1-[(cyclohexyl)
thiocarbamoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 133 -
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, and solvates
thereof.
FORMULA XIX
Additionally, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula XIX:
B C
,4 S i
\V ~Y/ \D
R2 ~ X
U W
(XIX)
R~
o r a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
V is CH, N, or S:
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkeny:l is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0, or 502;
R3 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C,-CQ bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/Z5577
- 134 -
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Ar is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or
more substituent(s); wherein the individual ring size is 5
8 members; wherein said heterocyclic ring contains 1-6
heteroatom(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of 0, N, and S; and wherein any aromatic or
tertiary alkyl amine is optionally oxidized to a
corresponding N-oxide;
Z is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0, or 502;
C and D are independently hydrogen, Ar, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl; wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl is
optionally substituted with C1-C6-alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl,
hydroxy, amino, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-
ester, thio-C1-C6-ester, C1-C6-alkoxy, Cz-C6-alkenoxy, cyano,
nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfhydryl, thio-CI-C6-alkyl, or sulfonyl; wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with oxygen to form
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 135 -
a carbonyl; or wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or
alkenyl is optionally replaced with O, NH, NR3, S, S0, or
502; and
A, B, Rl, R2, U, W, and X are as otherwise defined in
formula XV.
V. N-LINKED SULFONAMIDES OF HETEROCYCLIC THIOESTERS
FORMULA XX
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may further be a
compound of formula XX:
B C
\N \Y/ \D
I~O
R,
(XX)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
A and B, together with the nitrogen and carbon atoms
to which they are respectively attached, form a S-7
membered saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring
containing one or more heteroatom(s) independently selected
from the group consisting of O, S, SO, 502, N, NH, and NR2;
or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
X is either 0 or S;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 136 -
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
Ci-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced
with O, NH, NR3, S, S0, or 502;
R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-CQ straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-CQ
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-CQ bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Ar is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or
more substituent(s); wherein the individual ring size is 5-
8 members; wherein the heterocyclic ring contains 1-6
heteroatom(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of O, N, and S; wherein any aromatic or tertiary
alkyl amine is optionally oxidized to a corresponding N-
oxide;
Z is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions} with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any atom
of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH,
NR2, S, S0, Or 502
C and D are independently hydrogen, Ar, C1-C6 straight
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 137 -
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl; wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C3-Ce cycloalkyl, CS-C,
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl is
optionally substituted with C1-Cb-alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl,
hydroxy, amino, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-
ester, thio-C1-C6-ester, C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano,
nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkyl amino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, or sulfonyl; wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with oxygen to form
a carbonyl; or wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or
alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR2, S, S0, or
S02; and
Rl is independently selected from the group consisting
of Ar, a bridged ring moiety, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more substituent(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of Ar, a
bridged ring moiety, C3-CB cycloalkyl, amino, halo, halo-C1-
C6-alkyl, hydroxy, trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, carbonyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thin-C1-C6-
ester, C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-
C6-alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-
alkyl, and sulfonyl, wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0,
or 502.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XX, Ar is
independently selected from the group consisting of phenyl,
benzyl, naphthyl, indolyl, pyridyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 138 -
pyridinyl, pyrimidinyl, purinyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl,
furyl, fluorenyl, thiophenyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl,
thiazolyl, pyrazolyl, and thienyl.
In another preferred embodiment of formula XX, A and
B, together with the nitrogen and carbon atoms to which
they are respectfully attached, form a 6 membered saturated
or unsaturated heterocyclic ring or heterocyclic bridged
ring moiety: and R2 is CQ-C7 branched chain alkyl, C9-C7
cycloalkyl, phenyl, or 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl.
In another preferred embodiment of formula XX, the
compound is selected from the group consisting of:
3-(para-Methoxyphenyl)-1-propylmercaptyl(2S)-N-
(benzenesulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate;
3-(para-Methoxyphenyl)-1-propylmercaptyl(2S)-N-
(a-toluenesulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate;
3-(para-Methoxyphenyl)-1-propylmercaptyl(2S)-N-
(a-toluenesulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate;
1,5-biphenyl-3-pentylmercaptyl N-(para-
toluenesulfonyl)pipecolate;
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, and solvates
thereof.
FORMULA XXI
Moreover, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may be
a compound of formula XXI:
Br: ;,,F'~G\~ c
E S\Y/Z\D
ii
\o X (XXI )
Ri
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 139 -
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
E, F, G and J are independently CH2, 0, S, SO, 502, NH
or NR2;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more of E, F, G and J are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
X is either 0 or S;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced
with 0, NH, NR2, S, SO, or 502;
R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C4 straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-C9
straight or branched chain alkeny:L or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-CQ bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Z is a direct bond, C,-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 140 -
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thio-C1-C6-ester,
C1-CE-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C,-C6-
alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any atom
of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH,
NR2, S, S0, or 502;
Ar is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or
more substituent(s); wherein the individual ring size is 5-
8 members; wherein the heterocyclic ring contains 1-6
heteroatom(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of O, N, and S; wherein any aromatic or tertiary
alkyl amine is optionally oxidized to a corresponding N-
oxide;
C and D are independently hydrogen, Ar, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl; wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C3-Ce cycloalkyl, C,-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl is
optionally substituted with C1-C6-alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl,
hydroxy, amino, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-
ester, thio-C1-C6-ester, C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano,
nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino, amino-C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-alkyl, or sulfonyl; wherein any
carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with oxygen to form
a carbonyl; or wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or
alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR2, S, SO, or
S02; and
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 141 -
Rl is independently selected from the group consisting
of Ar, a bridged ring moiety, C3-CB cycloalkyl, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more substituent(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of Ar, a
bridged ring moiety, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, amino, halo, halo-C1-
C6-alkyl, hydroxy, trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, carbonyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-ester, thin-C1-C6-
ester, C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-
C6-alkylamino, amino-C,-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-C1-C6-
alkyl, and sulfonyl, wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR3, S, S0,
or 502.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XXI, Ar is
independently selected from the group consisting of phenyl,
benzyl, naphthyl, indolyl, pyridyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl,
pyridinyl, pyrimidinyl, purinyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl,
furyl, fluorenyl, thiophenyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl,
thiazolyl, pyrazolyl, and thienyl.
FORMULA XXII
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may also be a
compound of formula XXII:
Br; ., F- c c
,,,,
E~N S\Y/Z\D
p'
\o
R~ (XXII)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 142 -
E, F, and G are independently CH2, 0, S, S0, 502, NH or
NR2
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more of E, F, and G are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
X is either 0 or S;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more position (s) with amino, halo,
halo- (C1-C6) -alkyl, thiocarbonyl, (C1-C6) -ester, thio- (C1-C6) -
ester, (C1-C6) -alkoxy, (C2-C6) -alkenaxy, cyano, nitro, imino,
(C1-C6) -alkylamino, amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-
(C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or
wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally replaced with O, NH, NR2, S, S0, or 502;
R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-CQ straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-C9
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C1-C9 bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Ar is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or
more substituent(s); wherein the individual ring size is 5-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 143 -
8 members; wherein the heterocyclic ring contains 1-6
heteroatom(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of 0, N, and S; wherein any aromatic or tertiary
alkyl amine is optionally oxidized to a corresponding N
oxide;
Z is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo- (C1-C6) -alkyl, thiocarbonyl, (C1-C6) -ester, thio- (C1-C6) -
ester, (C1-C6) -alkoxy, (C2-C6) -alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino,
(C,-C6) -alkylamino, amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-
(C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or
wherein any atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
replaced with 0, NH, NR2, S, S0, o.r 502;
C and D are independently hydrogen, Ar, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C3-CB cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl is
optionally substituted with C1-CQ alkyl, C2-CQ alkenyl, or
hydroxy; wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl
is optionally substituted in one or more positions) with
oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any carbon atom of
said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH,
NR2, S, SO, or 502; and
R1 is independently selected from the group consisting
of Ar, a bridged ring moiety, C3-Cg cycloalkyl, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more substituent(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of Ar, a
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 144 -
bridged ring moiety, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, amino, halo, halo-
(C1-C6) -alkyl, hydroxy, trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, carbonyl, thiocarbonyl, (C1-C6) -ester, thio- (C1-C6) -
ester, (C1-C6) -alkoxy, (C2-C6) -alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino,
(C1-C6) -alkylamino, amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-
(C1-C6) -alkyl, and sulfonyl, wherein any carbon atom of said
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR3, S,
S0, or 502.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XXII, Ar is
independently selected from the group consisting of phenyl,
benzyl, naphthyl, indolyl, pyridyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl,
pyridinyl, pyrimidinyl, purinyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl,
furyl, fluorenyl, thiophenyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl,
thiazolyl, pyrazolyl, and thienyl.
FORMULA XXIII
Additionally, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula XXIII:
Br
c
Y~Z~D
(XXIII)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
n is 1, 2 or 3;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the primary ring (when n is 1, 2
or 3) are bonded to each other through either
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 145 -
a chemical bond or
atoms} other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
X is either 0 or S;
Y is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo- (C1-C6} -alkyl, thiocarbonyl, (C,-C6} -ester, thio- (C1-C6) -
ester, (C1-C6) -alkoxy, (C2-C6) -alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino,
(C1-C6) -alkylamino, amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-
(C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or
wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR2, S, SO, or 502;
Z is a direct bond, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein
any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted in one or more positions) with amino, halo,
halo- (C1-C6) -alkyl, thiocarbonyl, (C1-C6) -ester, thio- (C1-C6) -
ester, (C1-C6) -alkoxy, (C2-C6) -alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino,
(C1-C6) -alkylamino, amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-
(C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfonyl, or oxygen to form a carbonyl, or
wherein any atom of said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
replaced with 0, NH, NR2, S, S0, or 502;
R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-CQ straight or branched chain alkyl, C3-CQ
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, and C,-CQ bridging alkyl wherein a bridge is
formed between the nitrogen and a carbon atom of said alkyl
or alkenyl chain containing said heteroatom to form a ring,
wherein said ring is optionally fused to an Ar group;
Ar is independently an alicyclic or aromatic, mono-,
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 146 -
bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring, wherein the
ring is either unsubstituted or substituted with one or
more substituent(s); wherein the individual ring size is 5-
8 members; wherein the heterocyclic ring contains 1-6
heteroatom(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of 0, N, and S; wherein any aromatic or tertiary
alkyl amine is optionally oxidized to a corresponding N-
oxide;
C and D are independently hydrogen, Ar, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of C3-CB cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, carbonyl oxygen, and Ar; wherein
said alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl is
optionally substituted with C1-Cq alkyl, C2-C9 alkenyl, or
hydroxy; wherein any carbon atom of said alkyl or alkenyl
is optionally substituted in one or more positions) with
oxygen to form a carbonyl, or wherein any carbon atom of
said alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH,
NR2, S, S0, or S02; and
R1 is independently selected from the group consisting
of Ar, a bridged ring moiety, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is
optionally substituted with one or more substituent(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of Ar, a
bridged ring moiety, C3-Cg cycloalkyl, amino, halo,-halo-
(C1-C6) -alkyl, hydroxy, trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, CZ-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, carbonyl, thiocarbonyl, (C1-C6) -ester, thio- (C1-C6) -
ester, (C1-C6) -alkoxy, (C2-C6) -alkenoxy, cyano, nitro, imino,
(C1-C6) -alkylamino, amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio-
(C1-C6) -alkyl, and sulfonyl, wherein any carbon atom of said
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 147 -
alkyl or alkenyl is optionally replaced with 0, NH, NR3, S,
S0, or S02.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XXIII, Ar is
independently selected from the group consisting of phenyl,
benzyl, naphthyl, indolyl, pyridyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl,
pyridinyl, pyrimidinyl, purinyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl,
furyl, fluorenyl, thiophenyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl,
thiazolyl, pyrazolyl, and thienyl.
Exemplary compounds of formula XXIII are presented in
TABLE VIII:
Br
c
Y'~Z~D
TABLE VIII
No. n Y Z C D R,
117 1 CHZ CH Phenyl H Phenyl
118 1 CH2 CH Phenyl H a-Methylphenyl
2 0 119 1 CHZ CH Phenyl H 4-Methylphenyl
120 1 (CH~Z CH p-MethoxyphenylH Phenyl
121 1 (CH~2 CH p-MethoxyphenylH a-Methylphenyl
122 1 (CH~z CH p-MethoxyphenylH 4-Methylphenyl
123 1 (CH~Z CH Phenyl Phenyl Phenyl
124 1 (CH~2 CH Phenyl Phenyl a-Methylphenyl
125 1 (CH~2 CH Phenyl Phenyl 4-Methylphenyl
126 2 (CH~3 CH Phenyl H Phenyl
127 2 (CH2)3 CH Phenyl H a-Methylphenyl
128 2 (CH~3 CH Phenyl H 4-Methylphenyl
129 2 (CH~3 CH Phenyl H 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl
130 2 (CH~3 CH Phenyl H Cyclohexyl
131 2 Direct CH 3-Phenylpropyl3-PhenylpropylPhenyl
bond
132 2 Direct CH 3-Phenylpropyl3-Phenylpropyla-Methylphenyl
bond
133 2 Direct CH 3-Phenylpropyl3-Phenylpropyl4-Methylphenyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 148 -
bond
3 5 134 2 Direct CH 3-Phenylethyl 3-Phenylethyl 4-Methylphenyl
bond
135 2 Direct CH 3-(4-Methoxy 3-Phenylpropyl 4-Methylphenyl
bond phenyl)propyl
136 2 Direct CH 3-(2-Pyridyl) 3-Phenylpropyl 4-Methylphenyl
bond propyl
The most preferred compounds of formula XXIII are
40 selected from the group consisting of:
3-(para-Methoxyphenyl)-1-propylmercaptyl(2S)-N-
(benzenesulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate;
3-(para-Methoxyphenyl)-1-propylmercaptyl(2S)-N-
45 (a-toluenesulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate;
3-(para-Methoxyphenyl)-1-propylmercaptyl(2S)-N-
(a-toluenesulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate;
50 1,5-biphenyl-3-pentylmercaptyl N-(para-
toluenesulfonyl)pipecolate;
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, and solvates
thereof.
FORMULA XXIV
Moreover, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may be
a compound of formula XXIV:
C
A\V S\Y/Z\D
~S\ O X
(XXIV)
R~
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 149 -
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
V is CH, N, or S;
A, B, C, D, Rl, X, Y, and Z are as defined in formula
XX above.
PYRROLIDINE DERIVATIVES
FORMULA XXV
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may also be a
compound of formula XXV:
Q
Y
~~Z~n
(XXV)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the primary ring (when t is 1, 2
or 3) are bonded to each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
R1 is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 150 -
Arl, wherein said Rl is unsubstituted or substituted with
one or more substituents independently selected from the
group consisting of C1-C6 alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, a bridged ring
moiety, and Ar2;
Arl and Ar2 are independently selected from the group
consisting of 1-napthyl, 2-napthyl, 2-indolyl, 3-indolyl,
2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-
pyridyl, 4-pyridyl and phenyl, wherein said Arl is
unsubstituted or substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C1-C9 al.koxy, C2-C9
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
X is 0, S, CH2 or H2;
Y is O or NR2, wherein R2 is a direct bond to a Z,
hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl; and
each Z, independently, is C1-C6 straight or branched
chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl,
wherein said Z is substituted with nt'1P nr mnro
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of Arl, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, and C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl substituted with C3-Ce cycloalkyl; or Z is the
fragment
O
CH
X2 Ra
R3
wherein:
R3 is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl which is unsubstituted or substituted with C3-CB
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 151 -
cycloalkyl,a bridged ring moiety, or Arl;
X2 is 0 or NRS, wherein RS is independently selected
from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl;
R9 is independently selected from the group consisting
of phenyl, benzyl, C1-CS straight or branched chain alkyl,
C2-CS straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring
moiety, C1-CS straight or branched chain alkyl substituted
with phenyl, and C2-CS straight or branched chain alkenyl
substituted with phenyl;
n is 1 or 2, and;
t is 1, 2 or 3.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XXV, Z and R1 are
lipophilic.
In another preferred embodiment of formula XXV, the
compound is selected from the group consisting of:
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-phenyl-1-prop-2-(E)-enyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-
1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3
dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidine
carboxylate;
3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-1-prop-2-(E)-enyl
(2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2
pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-(4,5-dichlorophenyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-
d i m a t h y 1 - 1 , 2 - d i o x o p a n t y 1 ) - 2 -
pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3- (4, 5-dichlorophenyl) -1-prop-2- (E) -enyl (2S) -1-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 152 -
(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl}-2-pyrrolidine-
carboxylate;
3-(4,5-methylenedioxyphenyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1
(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidine
carboxylate;
3-(4,5-methylenedioxyphenyl)-1-prop-2-(E)-enyl
(2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2
pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-cyclohexyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-cyclohexyl-1-prop-2-(E}-enyl (2S)-1-(3,3-
d i m a t h y 1 - 1 , 2 - d i o x o p a n t y 1 ) - 2 -
pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
( 1R) -l, 3-diphenyl-1-propyl (2S) -1- ( 3, 3-dimethyl-
1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
(1R)-1,3-Biphenyl-1-prop-2-(E)~enyl (2S)-1-(3,3-
dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidine-
carboxylate;
(1R}-1-cyclohexyl-3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-
dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidine-
carboxylate;
(1R)-1-cyclohexyl-3-phenyl-1-prop-2-(E)-enyl
(2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-
pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
(1R)-1-(4,5-dichlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-1-propyl
( 2 S) -1- ( 3, 3-dimethyl-1, 2-dioxopentyl ) -2-
pyrrolidine-carboxylate;
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(1,2-dioxo-2-
cyclohexyl)ethyl-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(1,2-dioxo-4-
cyclohexyl)butyl-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 153 -
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(1,2-dioxo-2-[2-
furanyl])ethyl-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(1,2-dioxo-2-[2-
thienyl])ethyl-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(1,2-dioxo-2-[2-
thiazolyl])ethyl-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(1,2-dioxo-2-
phenyl)ethyl-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
1,7-diphenyl-4-heptyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxo-4-hydroxybutyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxamide;
1-[1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-L-proline]-
L-phenylalanine ethyl ester;
1-[1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-L-proline]-
L-leucine ethyl ester;
1-[1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-L-proline]-
L-phenylglycine ethyl ester;
1-[1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-L-proline]-
L-phenylalanine phenyl ester;
1-[1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-L-proline]-
L-phenylalanine benzyl ester;
1-[1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-L-proline]-
L-isoleucine ethyl ester;
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, and solvates
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 154 -
thereof.
FORMULA XXVI
Additionally, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula XXVI:
Rr
(XXVI)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the pyrrolidine ring are bonded to
each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure
R1 is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-CB
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety,. or
Arl, wherein said R1 is unsubstituted or substituted with
one or more substituents independently selected from the
group consisting of C1-C6 alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl, C3-CE
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, a bridged ring
moiety, and Ar2;
Ar, and Ar2 are independently selected fram the group
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98I25577
- 155 -
consisting of 1-napthyl, 2-napthyl, 2-indolyl, 3-indolyl,
2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-
pyridyl, 4-pyridyl and phenyl, wherein said Arl is
unsubstituted or substituted with one or more
substituent(s} independently selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-
C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C1-CQ alkoxy, C2-C9
alkenyloxy, phenoxy, benzyloxy, and amino;
Z is C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein said Z is
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of Arl, C3-Ce cycloalkyl,
and C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl or C2-C6 straight
or branched chain alkenyl substituted with C3-CB cycloalkyl;
or Z is the fragment
O
CH
R3
wherein:
R3 is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl which is unsubstituted or substituted with C3-C8
cycloalkyl, a bridged ring moiety, or Arl;
X2 is O or NRS, wherein RS is independently selected
from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl; and
RQ is independently selected from the group consisting
of phenyl, benzyl, C1-CS straight or branched chain alkyl,
C2-CS straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring
moiety, C1-CS straight or branched chain alkyl substituted
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98125577
- 156 -
with phenyl, and C2-CS straight or branched chain alkenyl
substituted with phenyl.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XXVI, R1 is
independently selected from the group consisting of C1-C9
straight or branched chain alkyl, 2-cyclohexyl, 4-
cyclohexyl, 2-furanyl, 2-thienyl, 2-thiazolyl, and 9-
hydroxybutyl.
In another preferred embodiment of formula XXVI, Z and
R1 are lipophilic.
FORMULA XXVII
Furthermore, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula XXVII:
Q r
(XXVII)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the pyrrolidine ring are bonded to
each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
Z' is the fragment
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 157 -
O
CH
X2 R4
R3
wherein:
R3 is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl or unsubstituted Arl, wherein said alkyl is
unsubstituted or substituted with C3-C8 cycloalkyl, a
bridged ring moiety, or Arl;
X2 is 0 or NRS, wherein RS is independently selected
from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl;
R9 is independently selected from the group consisting
of phenyl, benzyl, C1-CS straight or branched chain alkyl,
C2-CS straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring
moiety, C1-CS straight or branched chain alkyl substituted
with phenyl, and C2-CS straight or branched chain alkenyl
substituted with phenyl; and
Arl is as defined in formula XXVI.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XXVII, Z' is
lipophilic.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 158 -
FORMULA XXVIII
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may also be a
compound of formula XXVIII:
Q r
Y (Z)"
(XXVIII)
wherein:
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the pyrrolidine ring are bonded to
each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
R1 is independently C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C6
cycloalkyl, a bridged ring moiety, or Arl, wherein said
alkyl or alkenyl is unsubstituted or substituted with C3-C6
cycloalkyl or Ar2;
Arl and Ar2 are independently selected from the group
consisting of 2-furyl, 2-thienyl, and phenyl;
X is selected from the group consisting of oxygen and
sulfur;
Y is oxygen or NR2, wherein R2 is independently a
direct bond to a Z, hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl;
each Z, independently, is hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, or CZ-C6 straight or branched chain
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 159 -
alkenyl, wherein said Z is substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of 2-furyl, 2-thienyl, C3-C6 cycloalkyl, pyridyl,
and phenyl, each having one or more substituent(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen and C1-C9 alkoxy; and
n is 1 or 2.
In a preferred embodiment of formula XXVIII, Z and R1
are lipophilic.
In another preferred embodiment of formula XXVIII, the
compound is selected from the group consisting of:
3-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-
d i m a t h y 1 - 1 , 2 - d i o x o p a n t y 1 ) - 2 -
pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-prop-2-(E)-enyl (2S)-
1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-pyrralidine-
carboxylate;
2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl (2S)-1-(3,3-
d i m a t h y 1 - 1 , 2 - d i o x o p a n t y 1 ) - 2 -
pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-(3-pyridyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3- (2-pyridyl) -1-propyl (2S) -1- (3, 3-dimethyl-1, 2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-(4-pyridyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(2-tert-butyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-phenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(2-cyclohexylethyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 160 -
3-(3-pyridyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(2-
cyclohexylethyl-1,2-dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidine-
carboxylate;
3- (3-pyridyl) -1-propyl (2S) -1- (2-tert-butyl-l, 2
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3,3-Biphenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3- (3-pyridyl) -1-propyl (2S) -1- (2-cyclohexyl-1, 2-
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-(3-pyridyl)-1-propyl (2S)-N-([2-thienyl]
glyoxyl)pyrrolidinecarboxylat.e;
3,3-Biphenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1~,2-
dioxobutyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3,3-Biphenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-cyclohexylglyoxyl-
2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3,3-Biphenyl-1-propyl (2S)-1-{2-thienyl)glyoxyl-
2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, and solvates
thereof.
In another preferred embodiment of formula XXVIII, the
compound is selected from the group consisting of:
3-(3-pyridyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-1,2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3- (2-pyridyl ) -1-propyl (2S) -1-~ ( 3, 3-dimethyl-1, 2-
dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
3-(3-pyridyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(2-cyclohexyl-1,2-
dioxoethyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylate;
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, and solvates
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 161 -
thereof.
In another preferred embodiment of formula XXVIII, the
compound is 3-(3-pyridyl)-1-propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-
1,2-dioxopentyl)-2-pyrrolidine-carboxylate, and
pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, and solvates
thereof.
FORMULA XXIX
Additionally, the bridged heterocyclic derivative may
be a compound of formula XXIX:
Y (Z)n
(XXIX)
R~
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
V is CH, N, or S;
A and B, together with V and the carbon atom to which
they are respectively attached, form a 5-7 membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring containing one
or more heteroatom(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of 0, S, S0, S02, N, NH, and NR; or,
A and B, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
R is independently either C1-C9 straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C9
cycloalkyl, C5-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
3-(3-pyridyl)-1-p
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00116603 PCT/US98/25577
- 162 -
Arl, wherein R is independently either unsubstituted of
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of halo, halo- (C1-C6) -
alkyl, carbonyl, carboxy, hydroxy, nitro, trifluoromethyl,
C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, C1-C9 alkoxy, C2-C9 alkenyloxy,
phenoxy, benzyloxy, thio-(C1-C6)-alkyl, alkylthio,
sulfhydryl, amino, (C1-C6) -alkylamino, amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl,
aminocarboxyl, a bridged ring moiety, and Ar2;
R1 is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-Ce
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl, wherein said R1 is unsubstituted or substituted with
one or more substituents independently selected from the
group consisting of C1-C6 alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl, C3-Ce
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, hydroxy, a bridged ring
moiety, and Ar2;
Arl and Ar2 are independently an alicyclic or aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring,
wherein the ring is either unsubstituted or substituted
with one or more substituent(s); wherein the individual
ring size is 5-8 members; wherein said heterocyclic ring
contains 1-6 heteroatom(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of 0, N, and S;
X is 0, S, CH2 or H2;
Y is 0 or NR2, wherein R2 is a direct bond to a Z,
hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl; and
each Z, independently, is C1-C6 straight or branched
chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl,
wherein said Z is substituted with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of Arl, C3-Ce cycloalkyl, and C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 163 -
alkenyl substituted with C3-Ce cycloalkyl; or Z is the
fragment
O
CH
~ X2 R4
wherein: Rs
R3 is independently C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl which is unsubstituted or substituted with C3-CB
cycloalkyl, a bridged ring moiety, or Arl;
X2 is O or NRS, wherein RS is independently selected
from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, and C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl; and
R4 is independently selected from the group consisting
of phenyl, benzyl, C1-CS straight or branched chain alkyl,
C2-CS straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring
moiety, C1-CS straight or branched chain alkyl substituted
with phenyl, and C2-CS straight or branched chain alkenyl
substituted with phenyl; and,
n is 1 or 2.
Other compounds which are bridged heterocyclic
derivatives within the scope of the present invention are
those compounds which may possess immunosuppressive, non-
immunosuppressive, or other activities as long as they also
are useful in preventing and/or treating neurological
disorders, including physically damaged nerves and
neurodegenerative diseases; in treating alopecia and
promoting hair growth; in treating vision disorders and/or
improving vision; and in treating memory impairment and/or
enhancing memory performance. For example, such compounds
may include, but are not limited to those below:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 164 -
COMPOUND 16?
Ocain et al., Biochemical and Biophysical Research
Communications (1993) 3:192, incorporated herein by
reference, discloses an exemplary pipecolic acid derivative
represented by Formula XXX. This compound is prepared by
reacting 4-phenyl-1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione with
rapamycin.
FORMULA (XXX)
h
~'QMe
"WAY-124,466"
COMPOUND 168
Chakraborty et al., Chemistrv and Bioloav (1995)
2:157-161, incorporated herein by reference, discloses an
exemplary pipecolic acid derivative represented by Formula
XXXI.
FORMULA (XXXI)
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 165 -
RAP-Pa
COMPOUNDS 169-171
Ikeda et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. (1994) II6:4143-4144,
incorporated herein by reference, discloses exemplary
pipecolic acid derivatives represented by Formula XXXII and
Table XII.
FORMULA (XXXII)
TABLE XII
Compound Structure
169 n = 1
170 n = 2
171 n = 3
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 166 -
COMPOUNDS 172-175
Wang et al., Biooraanic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters
(1994) 4:1161-1166, 9, incorporated herein by reference,
discloses exemplary pipecolic acid derivatives represented
by Formula XXXIII and Table XIII.
FORMULA (XXXIII)
TABLE XIII
Compound Structure
172 X=H,H
173 X = CHZ
174 X = H, CH3
175 X=O
COMPOUND 176
Birkenshaw et al., Bioor anic & Medicinal Chemistry
Letters (1994) 4(21):2501-2506, incorporated herein by
reference, discloses an exemplary pipecolic acid derivative
represented by
Formula XXXIV:
OH
OMe OMe
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 167 -
FORMULA (XXXIV)
COMPOUNDS 177-187
Holt et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc.(1993) 115:9925-9938,
incorporated herein by reference, discloses exemplary
pipecolic acid derivatives represented by Formula XXXV and
Tables XIV and XV.
FORMULA (XXXV)
TABLE XV
Compound RZ
177
2 0 178
Me
179 / OMe
OMe
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00116603 PCT/US98/25577
- 168 -
180
181
5-
182
183
184
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- ls9 -
lgs
186
187
COMPOUNDS 188-196
Caffery et al., Bioorctanic & Medicinal Chemistry
Letters (1994) 4121):2507-2510, Incorporated herein by
reference, discloses exemplary pipecolic acid derivatives
represented by Formulas XXXVI-XXXVIII and Tables XVI-XVIII.
FORMULA XXXVI
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 170 -
TABLE XVI
Compound Structure
188 y = 1
189 y = 2
190 y = 3
FORMULA XXXVII
0
N
O
O
O O
TABLE XVII
Compound Structure
191 n = 1
192 n=2
193 n=3
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 171 -
FORMULA XXXVIII
0
N
O
O
H
O Oi
.._.
TABLE XVIII
Compound Structure
194 n = 1
195 n = 2
196 n=3
COMPOUND 197
Teague et al., Bioor a~ & Medicinal Chemistry
Letters (1993) 3110):1947-1950, incorporated herein by
reference, discloses an exemplary pipecolic acid derivative
represented by
Formula XXXIX. Ho.
FORMULA XXXIX
~a
~R
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98125577
- 172 -
COMPOUNDS 198-200
Yamashita et al., Bioorcranic & Medicinal Chemistry
Letters (1994) 4(2):325-328, incorporated herein by
reference, discloses exemplary pipecolic acid derivatives
represented by Formula XL and Table XIX.
FORMULA XL
~O R
' IIvIIN
0 O
~O
TABLE XIX
Compound Structure
198 R = phenyl
199 R = N(allyl)2
200
COMPOUNDS 201-221
Holt et al., Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry
Letters(1994) 4(2):315-320, incorporated herein by
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 173 -
reference, discloses exemplary pipecolic acid derivatives
represented by Formula XLI and Tables XX-XXII.
FORMULA XLI
R
TABLE XX
Compound No.
i
201
202
203
204
205
206
2 5 207
208
209
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 174 -
Compound No.
210
0
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
2I8
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 175 -
Table XXII
Compound No. Structure
219
220
221
COMPOUNDS 222-234
Holt et al., Bioorcranic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters
(1993) 3(10)_:1977-1980, incorporated herein by reference,
discloses exemplary pipecolic acid derivatives represented
by Formulas XLII and XLIII and Tables XXIII-XXV.
FORMULA XLII
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 176 -
TABLE XXIII
Compound Structure
222 X = OH
223 X = OMe
224 X = O-iso-Pr
225 X = OBn
226 X = OCH (Me)Ph
227 X = OCH~CHCHPh
228 X = OCHzCH2CH2(3,4-OMez)Ph
229 X = NHBn
230 X = NHCHzCHZCH2Ph
FORMULA XLIII
25
TABLE XXIV
Compound Structure
3 0 231 R = Me
232 R = Bn
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 177 -
TABLE XXV
Compound Structure
Ho. , ~
233
HO.
234
p ~ ~ OH
N
O
O MeO....
O O
OMe
1~
COMPOUNDS 235-249
Hauske et al., J. Med. Chem. (1992) 35:4284-4296,
incorporated herein by reference, discloses exemplary
pipecolic acid derivatives represented by Formulas XLIV
XLVII and Tables XXVI-XXIX.
FORMULA XLIV
O
N \R2
R~
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 178
TABLE XXVI
Compound Structure
235 ~=2
O OH
S
''~'Cfh
RZ=Phe-
O-tert-butyl
236 ~=2
OcH,
i
RZ= Phe-
O-tert-butyl
FORMULA XLV
R,
TABLE XXVII
Compound Structure
237 R, = m-OCH3Ph
R3 = Val-O-tert-butyl
238 R, = m-OCH3Ph
R3 = Leu-O-tert-butyl
2 0 239 R, = m-OCH3Ph
R3 = Ileu-O-tert-butyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 179 -
240 R, = m-OCH3Ph
R3 = hexahydro-Phe-O-tert-butyl
241 R, = m-OCH3Ph
2 5 R3 = allylalanine-O-tert-butyl
242 R, = b-naphthyl
R3 = Val-O-tert-butyl
30 FORMULA XLVI
TABLE XXVIII
Compound Structure
243 R, = CHZ(CO)-m-OCH3Ph
R, = CH2Ph
4 0 RS = OCH3
244 R, = CHZ(CO)-b-naphthyl
R4 = CHZPh
RS = OCH3
FORMULA XLVII
~R,
H
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 180 -
TABLE XXIX
Compound Structure
245 R, = m-OCH3Ph
X = traps-CH=CH-
R, = H
Y = OC(O)Ph
246 R,. = m-OCH3Ph
X = traps-CH=CH
~=H
Y = OC(O)CF3
247 R, = m-OCH3Ph
X = traps-CH=CH-
R4=_
y=_
248 R, = m-OCH3Ph
X = traps-CH=CH-
R, = H
Y = OCHzCH=CHZ
249 R, = m-OCH3Ph
X=C=O
R4=H
Y=Ph
COMPOUND 250
Teague et al., Biooraanic & Med. Chem. Letters (1994)
4(13):1581-1584, incorporated herein by reference,
discloses an exemplary pipecolic acid derivative
represented by Formula XLVIII.
FORMULA XLVII:I
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 181 -
OH
SLB506
COMPOUNDS 251-254
Stocks et al., Bioor anic & Med. Chem. Letters (1994)
4112):1457-1460, incorporated herein by reference,
discloses exemplary pipecolic acid derivatives represented
by Formula XLIX and Tables XXX and XXXI.
TABLE XXX
Compound No. Structure
2 51 Ho_
Me0
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 182 -
FORMULA XLIX
10 TABLE XXXI
Compound Structure
252 R, = H
RZ = OMe
R3 = CHZOme
253 R, = H
RZ=H
R3=1-I
254 R, = Me
Rz=H
R3=H
COMPOUNDS 255-276
Additional exemplary pipecolic acid derivatives are
represented by Formulas L-LIV and Tables XXXII-XXXVI.
FORMULA L
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 183 -
TABLE XXXII
Compound Structure
255 R = 3,4-dichloro
256 R = 3,4,5-trimethoxy
257 R=H
258 R = 3-(2,5-Dimethoxy)phenylpropyl
259 R = 3-(3,4-Methylenedioxy)phenylpropyl
FORMULA LI
15
TABLE XXXIII
Compound Structure
260 R = 4-(p-Methoxy)butyl
261 R = 3-Phenylpropyl
2 0 262 R = 3-(3-Pyridyl)propyl
FORMULA LII
TABLE XXXIV
Compound Structure
3 0 263 R = 3-(3-Pyridyl)propyl
264 R = 1,7-biphenyl-4-heptyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 184 -
265 R = 4-(4-Methoxy)butyl
266 R = 1-Phenyl-6-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-hexyl
267 R = 3-(2,5-Dimethoxy)phenylpropyl
268 R = 3-(3,4-Methylenedioxy)phenylpropyl
269 R = 1, 5-Diphenylpentyl
FORMULA LIII
TABLE XXXV
Compound Structure
270 R = 4-(4-Methoxy;)butyl
271 R = 3-Cyclohexylpropyl
272 R = 3-Phenylpropyl
FORMULA LIV
TABLE XXXV:I
Compound Structure
273 R = 3-Cyclohexylpropyl
274 R = 3-Phenylpropyl
3 0 275 R = 4-(4-Methoxy)butyl
276 R = 1,7-biphenyl-4-heptyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 185 -
The names of some of the compounds identified above
are provided below in Table XXXVII.
TABLE XXXVII
Compound Name of Species
172 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl (2S)-1-[2-(3,4,5-
trimethoxyphenyl)acetyl]hexahydro-2-
pyridinecarboxylate
173 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl (2S)-1-[2-(3,4,5-
trimethoxyphenyl)acryloyl]hexahydro-2-
pyridinecarboxylate
179 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl (2S)-1-[2-(3,4,5-
trimethoxyphenyl)propanoyl]hexahydro-2-
pyridinecarboxylate
175 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl (2S)-1-[2-oxo-2-(3,4,5-
trimethoxyphenyl)acetyl]hexahydro-2-
pyridinecarboxylate
177 3-cyclohexylpropyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)hexahydro-2-pyridinecarboxylate
178 3-phenylpropyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)hexahydro-2-pyridinecarboxylate
179 3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propyl (2S)-1-(3,3-
dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)hexahydro-2-
pyridinecarboxylate
180 (1R)-2,2-dimethyl-1-phenethyl-3-butenyl (2S)-1-
(3,3-dimethyl-2-oxopentan-oyl)hexahydro-2-
pyridinecarboxylate
181 (1R)-1,3-diphenylpropyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)hexahydro-2-pyridinecarboxylate
182 (1R)-1-cyclohexyl-3-phenylpropyl (2S)-1-(3,.3-
dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)hexahydro-2-
pyridinecarboxylate
183 (1S)-1,3-diphenylpropyl (2S)-1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)hexahydro-2-pyridinecarboxylate
184 (1S)-1-cyclohexyl-3-phenylpropyl (2S)-1-(3,3-
dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)hexahydro-2-
pyridinecarboxylate
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 186 -
Compound Name of Species
185 (22aS)-15,15-dimethylperhydropyrido[2,1-
c][1,9,4]dioxazacyclononadecine-1,12,16,17-
tetraone
186 (24aS)-17,17-dimethylperhydropyrido(2,1-
c][1,9,4]dioxazacyclohenicosine-1,14,18,19-
tetraone
201 ethyl 1-(2-oxo-3-phenylpropanoyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
202 ethyl 1-pyruvoyl-2-piperidinecarboxylate
203 ethyl 1-(2-oxobutanoyl)-2-piperidine-carboxylate
204 ethyl 1-(3-methyl-2-oxobutanoyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
205 ethyl 1-(4-methyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
206 ethyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-oxobutanoyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
207 ethyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
208 4-[2-(ethyloxycarbonyl)piperidino]-2,2-dimethyl-
3,4-dioxobutyl acetate
209 ethyl 1-[2-(2-hydroxytetrahydro-2H-2-pyranyl)-2-
oxoacetyl]-2-piperidinecarboxylate
210 ethyl 1-[2-(2-methoxytetrahydro-2H-2-pyranyl)-2-
oxoacetyl]-2-piperidinecarboxylate
211 ethyl 1-[2-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)-2-oxoacetyl]-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
212 ethyl 1-[2-(1-methoxycyclohexyl)-2-oxoacetyl]-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
213 ethyl 1-(2-cyclohexyl-2-oxoacetyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
214 ethyl 1-(2-oxo-2-piperidinoacetyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
215 ethyl 1-(2-(3,4-dihydro-2H-6-pyranyl)-2-
oxoacetyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 187 -
Compound Name of Species
216 ethyl 1-(2-oxo-2-phenylacetyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
217 ethyl 1-(4-methyl-2-oxo-1-thioxopentyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
218 3-phenylpropyl 1-(2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-
pentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
219 (1R)-1-phenyl-3-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)propyl
1-(3,3-dimethylbutanoyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
220 (1R)-1,3-diphenylpropyl 1-(benzylsulfonyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
221 3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)propyl 1-
(benzylsulfonyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
222 1-(2-[(2R,3R,6S)-6-[(2S,3E,5E,7E,9S,11R)-2,13-
dimethoxy-3,9,11-trimethyl-12-oxo-3,5,7-
tridecatrienyl]-2-hydroxy-3-methyltetrahydro-2H-
2-pyranyl)-2-oxoacetyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylic
acid
223 methyl 1-(2-[(2R,3R,6S)-6-[(2S,3E,5E,7E,9S,11R)-
2,13-dimethoxy-3,9,11-trimethyl-12-oxo-3,5,7-
tridecatrienyl]-2-hydroxy-3-methyl-tetrahydro-
2H-2-pyranyl)-2-oxoacetyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
224 isopropyl 1-(2-[(2R,3R,6S)-6-
[(2S,3E,5E,7E,9S,11R)-2,13-dimethoxy-3,9,11-
trimethyl-12-oxo-3,5,7-tridecatrienyl]-2-
hydroxy-3-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-2-pyranyl)-2-
oxoacetyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
225 benzyl 1-(2-[(2R,3R,6S)-6-[(2S,3E,5E,7E,9S,11R)-
2,13-dimethoxy-3,9,11-trimethyl-12-oxo-3,5,7-
tridecatrienyl]-2-hydroxy-3-methyl-tetrahydro-
2H-2-pyranyl)-2-oxoacetyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
226 1-phenylethyl 1-(2-[(2R,3R,6S)-6-
[(2S,3E,5E,7E,9S,11R)-2,13-dimethoxy-3,9,11-
trimethyl-12-oxo-3,5,7-tridecatrienyl]-2-
hydroxy-3-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-2-pyranyl)-2-
oxoacetyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 188 -
Compound Name of Species
227 (Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenyl 1-(2-[(2R,3R,6S)-6-
[(2S,3E,5E,7E,9S,11R)-2,13-dimethoxy-3,9,11-
trimethyl-12-oxo-3,5,7-tridecatrienyl]-2-
hydroxy-3-methyltetrahydro-2H-2-pyranyl)-2-
oxoacetyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
228 3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propyl 1-(2-[(2R,3R,6S)-
6-[(2S,3E,5E,7E,9S,11R)-2,13-dimethoxy-3,9,11-
trimethyl-12-oxo-3,5,7-tridecatrienyl)-2-
hydroxy-3-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-2-pyranyl)-2-
oxoacetyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
229 N2-benzyl-1-(2-[(2R,3R,6S)-6-
[(2S,3E,5E,7E,9S,11R)-2,'13-dimethoxy-3,9,11-
trimethyl-12-oxo-3,5,7-tridecatrienyl]-2-
hydroxy-3-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-2-pyranyl)-2-
oxoacetyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
230 N2-(3-phenylpropyl)-1-(2-[(2R,3R,6S)-6-
[(2S,3E,5E,7E,9S,11R)-2,:13-dimethoxy-3,9,11-
trimethyl-12-oxo-3,5,7-tridecatrienyl]-2-
hydroxy-3-methyltetrahydro-2H-2-pyranyl)-2-
oxoacetyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate.
231 (E)-3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-propenyl 1-(3,3-
dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidine-
carboxylate
232 (E)-3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-2-propenyl 1-
(3,3-dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidine-
carboxylate
233 (E)-3-phenyl-2-propenyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-oxo
pentanoyl}-2-piperidinecarboxylate
234 (E)-3-((3-(2,5-dimethoxy)-phenylpropyl)-phenyl)-
2-propenyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
235 (E)-3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-propenyl 1-(3,3-
dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidine-
carboxylate
236 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl 1-(2-oxo-2-
phenylacetyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
237 3-phenylpropyl 1-(2-oxo-~-phenylacetyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
238 3-(3-pyridyl)propyl 1-(2-oxo-2-phenylacetyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 189 -
Compound Name of Species
239 3-(3-pyridyl)propyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
240 4-phenyl-1-(3-phenylpropyl)butyl 1-(3,3-
dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidine-
carboxylate
241 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
242 1-(4-methoxyphenethyl)-4-phenylbutyl 1-(3,3-
dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidine-
carboxylate
243 3-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)propyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
244 3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)propyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-
2-oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidine-carboxylate
245 1-phenethyl-3-phenylpropyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxopentanoyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
246 9-(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl 1-(2-cyclohexyl-2-
oxoacetyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
247 3-cyclohexylpropyl 1-(2-cyclohexyl-2-oxoacetyl)-
2-piperidinecarboxylate
248 3-phenylpropyl 1-(2-cyclohexyl-2-oxoacetyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
249 3-cyclohexylpropyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxobutanoyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
250 3-phenylpropyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-oxobutanoyl)-2-
piperidinecarboxylate
251 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl 1-(3,3-dimethyl-2-
oxobutanoyl)-2-piperidinecarboxylate
252 4-phenyl-1-(3-phenylpropyl)butyl 1-(3,3-
dimethyl-2-oxobutanoyl)-2-piperidine-carboxylate
FORMULA LV
In yet a further embodiment, there is provided a
compound of formula LV:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 190 -
K
J
B
N A
M
O O m ~ (LV)
o r a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
m is 0-3;
A is CH2, 0, NH, or N-(C1-C9 alkyl) ;
B and D are independently hydrogen, Ar, C5-C7
cycloalkyl substituted C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, CS-C,
cycloalkenyl substituted C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, or Ar
substituted C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl or C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, wherein in each case,
one or two carbon atoms) of said alkyl or alkenyl may be
substituted with one or two heteroatom(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of oxygen, sulfur, S0,
and S02 in chemically reasonable substitution patterns, or
the fragment
T
wherein Q is hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; and
T is Ar or CS-C7 cycloalkyl substituted at
positions 3 and 4 with substituents
independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, hydroxy, O- (C1-C~ alkyl) , O- (C2-C9
alkenyl), and carbonyl;
Ar is independently selected from the group consisting
of 1-napthyl, 2-napthyl, 2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCTNS98/25577
- 191 -
thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl and phenyl,
monocyclic and bicyclic heterocyclic ring systems with
individual ring sizes being 5 or 6 which contain in either
or both rings a total of 1-4 heteroatom(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen and
sulfur; wherein Ar contains 1-3 substituent(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl, vitro, CF3,
trifluoromethoxy, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl,
C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, O- (C1-C9 straight
or branched chain alkyl), O-(C2-C9 straight or branched
chain alkenyl), 0-benzyl, O-phenyl, amino, 1,2-
methylenedioxy, carbonyl, and phenyl;
L is either hydrogen or U; M is either oxygen or CH-U,
provided that if L is hydrogen, then M is CH-U, or if M is
oxygen then L is U;
U is hydrogen, O-(C1-C4 straight or branched chain
alkyl), O-(C2-C4 straight or branched chain alkenyl), C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched
chain alkenyl, C5-C7 cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl
substituted with C1-CQ straight or branched chain alkyl or
C2-CQ straight or branched chain alkenyl, (C,-Cq alkyl or CZ-
CQ alkenyl)-Ar, or Ar;
J is hydrogen, C1 or C2 alkyl, or benzyl;
K is C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl, benzyl or
cyclohexylmethyl; or
J and K are taken together to form a 5-7 membered
heterocyclic ring which is substituted with oxygen, sulfur,
SO, or S02, or
J and K, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety.
Representative species of Formula LV are presented in
Table XXXVIII:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 192 -
s
m ~D
)n
O
N
hi O
O
~O
L
TABLE XXXVIII
Cpd. n m B D L
253 2 0 3-Phenylpropyl3-(3-Pyridyl)propylPhenyl
254 2 0 3-Phenylpropyl3-(2-Pyridyl)propylPhenyl
255 2 0 3-Phenylpropyl2-(4-Methozyphenyl)ethylPhenyl
1 5 256 2 0 3-Phenylpropyl3-Phenylpropyl Phenyl
257 2 0 3-Phenylpropyl3-Phenylpropyl 3,4,5-Trimethozyphenyl
258 2 0 3-Phenylpropyl2-(3-Pyridyl)propyl3,4,5-Trimethozyphenyl
259 2 0 3-Phenylpropyl3-(2-Pyridyl)propyl3,4,5-Trimethozyphenyl
260 2 0 3-Phenylpropyl3-(4-Methozyphenyl)propyl3,4,5-Trimethozyphenyl
2 0 261 2 0 3-Phenylpropyl3-(3-Pyridyl) propyl3-iso-propozyphenyl
FORMULA (LVI)
U.S. Patent No. 5,330,993, incorporated herein by
reference, discloses an exemplary pipecolic acid derivative
25 of formula LVI:
B
A
30 (LVI)
D
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
35 thereof, wherein:
A is 0, NH, or N- (C1-CQ alkyl) ;
B is hydrogen, CHL-Ar, C,-C6 straight or branched chain
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 193 -
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl, CS-C7
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, Ar substituted C1-C6 alkyl or
C2-C6 alkenyl, or
T
Q t
wherein L and Q are independently hydrogen, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl; and
T is Ar or CS-C, cyclohexyl substituted at positions 3
and 4 with substituents independently selected from the
group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, 0-(C1-CQ alkyl), 0-
(C2-C9 alkenyl) , and carbonyl;
Ar is independently selected from the group consisting
of 1-napthyl, 2-napthyl, 2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 2-
pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl and phenyl having 1-3
substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, nitro, CF3, C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched
chain alkenyl, 0-(C1-C4 straight or branched chain alkyl),
O-(C2-C4 straight or branched chain alkenyl), O-benzyl, 0-
phenyl, amino, and phenyl.
D is hydrogen or U; E is oxygen or CH-U, provided that
if D is hydrogen, then E is CH-U, or if E is oxygen, then
D is U;
U is hydrogen, O-(C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl) , 0- (C2-Cq straight or branched chain alkenyl) , C1-C6
straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched
chain alkenyl, CS-C7-cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl
substituted with C1-CQ straight or branched chain alkyl or
C2-Cq straight or branched chain alkenyl, 2-indolyl, 3-
indolyl, (C1-CQ alkyl or C2-CQ alkenyl ) -Ar, or Ar;
J is hydrogen, C1 or C2 alkyl, or benzyl;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 194 -
K is C1-CQ straight or branched chain alkyl, benzyl or
cyclohexylethyl; or
J and K are taken together to form a 5-7 membered
heterocyclic ring which is substituted with oxygen, sulfur,
S0, or 502; or
in the bridged heterocyclic derivative of the present
invention J and K, taken together with the atoms to which
they are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or
aromatic heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety.
FORMULA LVII
A preferred bridged heterocyclic derivative is a
compound of Formula LVII:
BI
(LVII)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
n is 2;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the piperidine ring (when n=2) are
bonded to each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
D is phenyl, methoxy, 2-furyl, or 3,4,5-
trimethoxyphenyl; and
B is benzyl, 3-phenylpropyl, 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl,
4-phenylbutyl, phenethyl, 3-cyclohexylpropyl, 4-
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 195 -
cyclohexylbutyl, 3-cyclopentylpropy:l, 4-cyclohexylbutyl, 3-
phenoxybenzyl, 3-(3-indolyl)propyl, or 4-(4-
methoxyphenyl)butyl;
provided that:
when D is phenyl, then B is benzyl, 3-phenylpropyl, 4-
(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl, 4-phenylbutyl, phenethyl, or 4-
cyclohexylbutyl;
when D is methoxy, B is benzyl, 4-cyclohexylbutyl, 3-
cyclohexylpropyl, or 3-cyclopentylpropyl;
when D is 2-furyl, then B is benzyl; and
when D is 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, then B is 4-
cyclohexylbutyl, 3-phenoxybenzyl, 4-phenylbutyl, 3-(3-
indolyl)propyl, or 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butyl.
Representative species of Formula LVII are presented
in Table XXXIX.
TABLE XXXIX
Cpd. B D n
262 Benzyl Phenyl 2
263 3-Phenylpropyl Phenyl 2
2 0 264 4-(4-Methoxyphenyl} Phenyl 2
butyl
265 4-Phenylbutyl Phenyl 2
266 Phenethyl Phenyl 2
267 4-Cyclohexylbutyl Phenyl 2
268 Benzyl Methoxy 2
2 5 269 4-Cyclohexylbutyl Methoxy 2
269 3-Cyclohexylpropyl Methoxy 2
270 3-Cyclopentylpropyl Methoxy 2
271 Benzyl 2-Furyl 2
272 4-Cyclohexylbutyl 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl 2
30 273 3-Phenoxybenzyl 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl 2
274 4-Phenylbutyl 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl 2
275 3-(3-Indolyl)propyl 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl 2
276 4-(4-Methoxyphenyl)butyl3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl 2
35 FORMULA LVIII
The bridged heterocyclic derivative may also be a
compound of formula LVIII:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 196 -
B
A
(LVIII)
m
D
o r a
pnarmaceutic
ally acceptable salt, ester, or solvate thereof, wherein:
V is CH, N, or S
J and K, taken together with V and the carbon atom to
which they are respectively attached, form a 5-7 membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring containing one
or more heteroatom(s) selected from the group consisting of
0, S, S0, 502, N, NH, and NR, or
J and K, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
R is independently either C1-C9 straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C9
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl, wherein R is independently either unsubstituted of
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of halo, halo(C,-C6)-
alkyl, carbonyl, carboxy, hydroxy, nitro, trifluoromethyl,
C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, C2-Cq alkenyloxy,
phenoxy, benzyloxy, thio- (C1-C6) -alkyl, (C1-C6) -alkylthio,
sulfhydryl, amino, (C1-C6) -alkylamino, amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl,
aminocarboxyl, a bridged ring moiety, and Ar2;
Arl and Ar2 are independently an alicyclic or aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring;
wherein the individual ring size is 5-8 members; wherein
said heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of 0, N,
and S;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 197 -
A, B, D, L, M, and m are as defined in Formula LV,
above.
VI. SMALL MOLECULE SULFONAMIDES
FORMULA LIX
In an additional embodiment of the invention, there is
provided a compound of formula LIX:
K B
A
\ n D
O
(LIX)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or solvate
thereof, wherein:
A is CH2, O, NH, or N-(C1-C9 alkyl);
B and D are independently Ar, hydrogen, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is unsubstituted or
substituted with CS-C7 cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl or Ar,
and wherein one or two carbon atoms) of said alkyl or
alkenyl may be substituted with one or two heteroatom(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of 0, S,
SO, and S02 in chemically reasonable substitution patterns,
or
T
Q
wherein Q is hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl; and
T is Ar or CS-C7 cycloalkyl substituted at
positions 3 and 4 with one or more
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 198 -
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, 0- (C1-C9
alkyl), 0-(C2-CQ alkenyl), and carbonyl;
provided that both B and D are not hydrogen;
Ar is independently selected from the group consisting
of phenyl, 1-napthyl, 2-naphthyl, 2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-
thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl,
monocyclic and bicyclic heterocyclic ring systems with
individual ring sizes being 5 or 6 which contain in either
or both rings a total of 1-4 heteroatoms independently
selected from the group consisting of O, N, and S; wherein
Ar contains 1-3 substituent(s) independently selected from
the group consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain
aikenyl, O- (C1-C4 straight or branched chain alkyl) , O- (C2-C9
straight or branched chain alkenyl), O-benzyl, O-phenyl,
1,2-methylenedioxy, amino, carboxyl, and phenyl;
E is C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, CS-C7 cycloalkyl, CS-C,
cycloalkenyl substituted with C1-C4 straight or branched
chain alkyl or C2-CQ straight or branched chain alkenyl,
(C2-C4 alkyl or C2-C4 alkenyl ) -Ar, or Ar;
J is hydrogen, C1 or CZ alkyl, or benzyl; K is C1-C4
straight or branched chain alkyl, benzyl, or
cyclohexylmethyl; or J and K are taken together to form a
5-7 membered heterocyclic ring which is substituted with O,
S, S0, or S02, or
J and K, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
n is 0 to 3; and
the stereochemistry at carbon positions 1 and 2 is R
or S.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 199 -
FORMULA LX
In a preferred embodiment of Formula LIX, J and K are
taken together and the bridged heterocyclic derivative is
a compound of Formula LX:
10
D
(LX)
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein:
n is 1 or 2;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the pyrrolidine ring (when n=1) or
the piperidine ring (when n=2) are bonded to each other
through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure; and
m is 0 or 1.
In a more preferred embodiment, B is selected from the
group consisting of hydrogen, benzyl, 2-phenylethyl, and 3
phenylpropyl;
D is selected from the group consisting of phenyl, 3-
phenylpropyl, 3-phenoxyphenyl, and 4-phenoxyphenyl; and
E is selected from the group consisting of phenyl, 9
methylphenyl, 9-methoxyphenyl, 2-thienyl, 2,4,6
triisopropylphenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 3-methoxyphenyl, 2
methoxyphenyl, 3,5-dimethoxyphenyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl,
methyl, 1-naphthyl, 8-quinolyl, 1-(5-N,N-dimethylamino)
naphthyl, 4-iodophenyl, 2,4,6-trimethylphenyl, benzyl, 4
nitrophenyl, 2-nitrophenyl, 4-chlorophenyl, and E-styrenyl.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 200 -
FORMULA LXI
Another exemplary bridged heterocyclic derivative is
a compound of formula LXI:
Br
E, _ ( LX I )
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or solvate
thereof, wherein:
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the primary piperidine ring are
bonded to each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
B and D are independently Ar, hydrogen, C1-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is unsubstituted or
substituted with CS-C7 cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl or Ar,
and wherein one or two carbon atoms) of said alkyl or
alkenyl may be substituted with one or two heteroatom(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of 0, S,
S0, and S02 in chemically reasonable substitution patterns,
or
T
Q
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 201 -
wherein Q is hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl; and
T is Ar or CS-C, cycloalkyl substituted at positions 3
and 4 with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, 0
(C1-C4 alkyl) , O- (C2-C4 alkenyl) , and carbonyl;
provided that both B and D are not hydrogen;
Ar is independently selected from the group consisting
of phenyl, 1-napthyl, 2-naphthyl, 2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2
thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl,
monocyclic and bicyclic heterocyclic ring systems with
individual ring sizes being 5 or 6 which contain in either
or both rings a total of 1-4 heteroatoms independently
selected from the group consisting of 0, N, and S; wherein
Ar contains 1-3 substituent(s) independently selected from
the group consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, nitro,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, 0- (C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl) , O- (C2-C4
straight or branched chain alkenyl), 0-benzyl, 0-phenyl,
1,2-methylenedioxy, amino, carboxyl, and phenyl;
E is C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, CS-C7 cyclaalkyl, CS-C,
cycloalkenyl substituted with C1-C4 straight or branched
chain alkyl or C2-C4 straight or branched chain alkenyl,
(C2-C9 alkyl or C2-Cq alkenyl)-Ar, or Ar; and
m is 0 to 3.
FORMULA LXII
A further exemplary bridged heterocyclic derivative is
a compound of Formula LXII:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00!16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 202 -
a
Br
m
(LXII)
t
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein:
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the primary pyrrolidine ring are
bonded to each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
B and D are independently Ar, hydrogen, C,-C6 straight
or branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, wherein said alkyl or alkenyl is unsubstituted or
substituted with CS-C7 cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, or Ar,
and wherein one or two carbon atoms) of said alkyl or
alkenyl may be substituted with one or two heteroatom(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of 0, S,
S0, and S02 in chemically reasonable substitution patterns,
or
T
wherein Q is hydrogen, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, or C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl; and
T is Ar or C5-C7 cycloalkyl substituted at
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 203 -
positions 3 and 4 with one or more
substituent(s) independently selected from the
group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, 0-(C1-C9
alkyl), 0-(C2-C9 alkenyl), and carbonyl;
provided that both B and D are not hydrogen;
Ar is independently selected from the group consisting
of phenyl, 1-napthyl, 2-naphthyl, 2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-
thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl,
monocyclic and bicyclic.heterocyclic ring systems with
individual ring sizes being 5 or 6 which contain in either
or both rings a total of 1-4 heteroatoms independently
selected from the group consisting of O, N, and S; wherein
Ar contains 1-3 substituent(s) independently selected from
the group consisting of hydrogen, halo, hydroxy, vitro,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, C1-C6 straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain
alkenyl, 0- (C1-CQ straight or branched chain alkyl) , O- (C2-C4
straight or branched chain alkenyl), O-benzyl, 0-phenyl,
1,2-methylenedioxy, amino, carboxyl, and phenyl;
E is C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl, CS-C7 cycloalkyl, CS-C7
cycloalkenyl substituted with C1-CQ straight or branched
chain alkyl or C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl,
(C2-C4 alkyl or C2-C4 alkenyl) -Ar, or Ar; and
m is 0 to 3.
FORMULA LXIII
A further exemplary bridged heterocyclic derivative is
a compound of LXIII:
K
J~ A
D
S02 O
(LXIII)
E
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 204 -
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof, wherein:
V is CH, N, or S;
J and K, taken together with V and the carbon atom to
which they are respectively attached, form a 5-7 membered
saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic ring containing one
or more heteroatom(s) selected from the group consisting of
0, S, S0, 502, N, NH, and NR, or
J and K, taken together with the atoms to which they
are attached, form a saturated, unsaturated, or aromatic
heterocylic or carbocyclic bridged ring moiety;
R is independently either C1-C9 straight or branched
chain alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, C3-C9
cycloalkyl, CS-C7 cycloalkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, or
Arl, wherein R is independently either unsubst~.tuted of
substituted with one or more substituent(s) independently
selected from the group consisting of halo, halo(C1-C6)-
alkyl, carbonyl, carboxy, hydroxy, nitro, trifluoromethyl,
C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl, C1-CQ alkoxy, C2-C4 alkenyloxy,
phenoxy, benzyloxy, thio- (C1-C6) -alkyl, (Cz-C6) -alkylthio,
sulfhydryl, amino, (C1-C6) -alkylamino, amino- (C,-C6) -alkyl,
aminocarboxyl, a bridged ring moiety, and Ar2;
Arl and Ar2 are independently an alicyclic or aromatic,
mono-, bi- or tricyclic, carbo- or heterocyclic ring;
wherein the individual ring size is 5-8 members; wherein
said heterocyclic ring contains 1-6 heteroatom(s)
independently selected from the group consisting of 0, N,
and S;
A, B, D, E, and n are as defined in Formula LIX above.
Representative species of Formulas LIX-LXIII are
presented in Table XL.
TABLE XL
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 205 -
Cpd. Structure and name
278
4-phenyl-
1-butyl-1-
(benzylsulfonyl)-(2R,S)-2-pipecolinate
279
1, 5-
diphenyl-
3-pentyl-N-(a-toluenesulfonyl)-pipecolate
280
1, 7-
diphenyl-
4-heptyl-N-(para-toluene-sulfonyl)pipecolate
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 206 -
Cpd. Structure and name
281
3- ( 3-
pyridyl)-
1-propyl-(2S)-N-(a-toluenesulfonyl)-pyrrolidine-
2-carboxylate
282
4-
phen
yl-1-butyl-N-(para-toluenesulfonyl)pipecolate
283
4-
pheny
1-1-butyl-N-(benzenesulfonyl)-pipecolate
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 207 -
Cpd. Structure and name
284
4-
phenyl-
1-butyl-N-(a-toluenesulfonyl)pipecolate
VII. CARBOXYLIC ACID ISOSTERES
Another preferred embodiment of the invention is a
compound of formula LXIV:
Q.
R2
(LXIV)
in which:
n is 1-3;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the primary ring (when n is 1-3)
are bonded to each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
X is either 0 or S;
R1 is independently selected from the group consisting
of C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl, CZ-C9 straight or
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 208 -
branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring moiety, aryl,
heteroaryl, carbocycle, or heterocycle;
D is a bond, or a C1-Clo straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-Clo alkenyl or C2-Clo alkynyl; and
R2is independently a carboxylic acid or a carboxylic
acid isostere;
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof.
Preferred embodiments of this invention are where R2
is independently a carbocycle or heterocycle containing any
combination of CH2, O, S, or N in any chemically stable
oxidation state, where any of the atoms of said ring
structure are optionally substituted in one or more
positions with R3.
Especially preferred embodiments of this invention are
where R2 is
"~ ~ " OH independently
H ~ ( N HN~ ~ ~ selected from
" HOOC H
the group
H ° °H ° below:
~"-
" NH I N NH
~N~ 6 ~~ HN
O O
O /N
NH ~~ HN
N ~ S N
6
O
OH
N / ~ ~~N ~ N
° °
O ~ HS H F H
OH
O
OH
NH ~ ~ ~ I
.J
3 5 '~°H
°
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 209 -
where the atoms of said ring structure may be optionally
substituted at one or more positions with R3.
Another preferred embodiment of this invention is
where R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of -COOH, -S03H, -S02HNR3, -P02 (R3) 2, -CN, -P03 (R3} 2, -OR3, -
SR3, -NHCOR3, -N ( R3 ) 2, -CON ( R3 ) 2, -CONH ( 0 } R3, -CONHNHS02R3, -
COHNS02R3, and -CONR3CN wherein R3 is hydrogen, hydroxy,
halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-
alkenoxy, C,-C6-alkylaryloxy, aryloxy, aryl- C1-C6-alkyloxy,
cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino, amino- C1-C6-alkyl,
sulfhydryl, thio- C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-alkylthio, sulfonyl, C1-
C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged ring moiety,
aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle, heterocycle, and COzR~ where
R4 is hydrogen or C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl or
alkenyl.
Preferred embodiments of this invention are: (2S)-1-
(Z,2-dioxo-3,3-dimethylpentyl)-2-hydroxymethyl pyrrolidine;
(2S)-1-(1,2-dioxo-3,3-dimethylpentyl)-2-
pyrrolidinetetrazole; (2S)-1-(1,2-dioxo-3,3-
dimethylpentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile; and (2S)-1-(1,2-
dioxo-3,3-dimethylpentyl)-2-aminocarbonyl piperidine.
A compound of the present invention, especially
formula LXIV, wherein n is 1, X is 0, D is a bond. R, is
l,l,dimethylpropyl, and R2 is -CN, is named (2S)-1-(1,2-
dioxo-3,3-dimethylpentyl)-2-pyrrolidine-carbonitrile.
Specific embodiments of the inventive compounds are
presented in Tables XLI, XLII, and XLIII. The present
invention contemplates employing the compounds of Tables
XLI, XLII and XLIII, below.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 210 -
~CH2)n
/ Rz
N D
X
Table XLI
when D is a bond and R2 is COOH,
No. X n _ R,
_
285 O 1 3,4,5-trimethylphenyl
286 O 2 3,4,5-trimethylphenyl
287 O 1 tent-butyl
287 O 3 tert-butyl
288 O 1 cyclopentyl
289 O 2 cyclopentyl
290 O 3 cyclopentyl
2 0 291 O 1 cyclohexyl
292 O 2 cyclohexyl
293 O 3 cyclohexyl
294 O 1 cycloheptyl
295 O 2 cycloheptyl
296 O 3 cycloheptyl
297 O 1 2-thienyl
298 O 2 2-thienyl
299 O 3 2-thienyl
300 O 1 2-furyl
301 O 2 2-furyl
302 O 3 2-furyl
303 O 3 phenyl
304 O 1 1,1-dimethylpentyl
305 O 2 l,l-dimethylhexyl
306 O 3 ethyl
307
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 211 -
~CH2)n
/ R2
N D
X
TABLE XLII
No. X n R, D RZ
308 S 1 1,1-dimethyl propyl CHz COOH
309 S 1 1, I-dimethyl propyl bond COOH
310 O 1 I, I-dimethyl propyl CHZ OH
311 O 1 1,1-dimethyl propyl bond S03H
312 O 1 1,1-dimethyl propyl CH2 CN
313 O 1 1,1-dimethyl propyl bond CN
314 O 1 1,1-dimethyl propyl bond tetrazolyl
315 S 1 phenyl (CH2)2 COON
316 S 1 phenyl (CHZ)3 COOH
2 317 S 2 phenyl CHZ COOH
0
318 O 1 1,1-dimethyl propyl bond CONHZ
319 O 2 1,1-dimethyl propyl bond CONHZ
320 S 2 2-furyl bond P03H2
321 O 2 propyl (CH2)2 COOH
2 322 O 1 propyl (CHZ)3 COOH
5
323 O 1 tert-butyl (CH )4 COON
z
324 O 1 methyl (CHAS COOH
325 O 2 phenyl (CH2)6 COON
326 O 2 3,4,5- trimethoxy- CHZ COON
phenyl
30 327 O 2 3,4,5- trimethoxy- CHz tetrazolyl
phenyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 212
TABLE XLIII
/ Rz
D
R~
No. n X D RZ R,
328 1 S bond COOH Phenyl
329 1 O bond COOH a-MethylBenzyl
330 2 O bond COOH 4-MethylBenzyl
331 1 O bond Tetrazole Benzyl
332 1 O bond S03H a-MethyIBenzyl
333 1 O CHZ COOH 4-MethylBenzyl
334 1 O bond S02HNMe Benzyl
335 1 O bond CN a-MethylBenzyl
336 1 O bond P03Hz 4-MethylBenzyl
337 2 O bond COOH Benzyl
338 2 O bond COOH a-MethylBenzyl
2 339 2 O bond COOH 4-MethylBenzyl
0
340 2 S bond COOH 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl
341 2 O bond COOH Cyclohexyl
342 2 O bond P02HEt i-propyl
343 2 O bond P03HPropyl ethyl
2 344 2 O bond P03(Et)2 Methyl
5
345 2 O bond OMe tert-butyl
346 I O bond OEt n-pentyl
347 2 O bond OPropyl n-hexyl
348 1 O bond OButyl Cyclohexyl
30 349 1 O bond OPentyl cyclopentyl
350 1 O bond OHexyl n-heptyl
351 1 O bond SMe n-octyl
352 1 O bond SEt n-nonyl
353 2 O bond SPropyl 2-indolyl
3 354 2 O bond SButyl 2-furyl
5
355 2 O bond NHCOMe 2-thiazolyl
356 2 O bond NHCOEt 2-thienyl
357 1 O CHZ N(Me)Z 2-pyridyl
358 1 O (CH~2 N(Me)Et 1,1-dimethylpropyl
40 359 1 O (CH~3 CON(Me)2 1,1-dimethylpropyl
360 1 O (CH~4 CONHMe 1,1-dimethylpropyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCTNS98/25577
- 213 -
361 1 O (CHAS CONHEt 1,1-dimethylpropyl
362 1 O (CH~6 CONHPropyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
363 1 O bond CONH(O)Me Benzyl
364 1 O bond CONH(O)Et a-Methylphenyl
365 1 . bond CONH(O)Propyl 4-Methylphenyl
O
366 1 O (CH2)2 COOH Benzyl
367 1 O bond COOH a-Methylphenyl
368 1 O bond COOH 4-Methylphenyl
369 1 O CH2 , COOH 1,1-dimethylpropyl
370 1 O (CH~Z COOH 1,1-dimethylbutyl
371 1 O (CH~3 COOH l, l-dimethylpentyl
372 1 O (CH~4 COOH 1,1-dimethylhexyl
373 1 O (CHs COOH 1,1-dimethylethyl
374 1 O (CH~6 COOH iso-propyl
375 1 O (CHI, COOH tert-butyl
376 1 O (CH~$ COOH 1,I-dimethylpropyl
377 1 O (CH~9 COOH benzyl
378 1 O (CH~,a COOH 1,1-dimethylpropyl
2 379 1 O C2H2 COOH cyclohexylmethyl
0
380 1 O 2-OH,Et COOH 1,1-dimethylpropyl
381 1 O 2-butylene COOH 1,1-dimethylpropyl
382 1 S i-Pro COOH 1,1-dimethylpropyl
383 2 S t-Bu COOH phenyl
2 384 2 O 2-NOZ-hexylCOOH 1,1-dimethylpropyl
5
385 1 O (CH~z CN 1,1-dimethylpropyl
386 1 O (CH~3 CN 1,1-dimethylpropyl
387 3 O bond CONHNHSOZMe Benzyl
388 3 O bond CONHNHSOzEt a-Methylphenyl
3 389 3 O bond CONHSOZMe 4-Methylphenyl
0
390 1 O bond CONHNHSOZEt Phenyl
391 2 O bond CON(Me)CN a-Methylphenyl
392 1 O bond CON(Et)CN 4-Methylphenyl
393 1 O (CH~2 COOH methyl
35 394 1 O (CH~3 COOH ethyl
395 1 O (CH~4 COON n-propyl
396 1 O (CHs COOH t-butyl
397 1 O (CH~6 COOH Pentyl
398 1 O (CHI, COOH Hexyl
4 399 1 O (CH~B COOH Heptyl
0
400 1 O (CH~9 COOH Octyl
401 1 O CZH2 COOH Cyclohexyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
214
No. n X D R, R~
402 2 O bond ~~~ 1,1-dimethylpropyl
N
HN~ ~~
N
403 1 O bond ~ N 1,1-dimethylpropyl
'N
HOOG~ 'N
404 1 O bond ~~N 1,1-dimethylpropyl
,_N
~//N
H~C~
~?
405 I O bond ~~p~«, 1,1-dimethylpropyl
H-N
406 1 O bond ~ ~" 1,1-dimethylpropyl
N
\
N\NI
407 1 O bond ~ ° I ,1-dimethylpropyl
NH
5
°
408 1 O bond s °" 1,1-dimethylpropyl
,N
/O
409 1 O bond ~ ° 1,1-dimethylpropyl
~NH
HN
\\\\O
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 215
-
No. n X D R R~
410 1 O bond ~ 1,1-dimethylpropyl
,
N
~
0
OH
411 I O bond ~ 1,1-dimethylpropyl
"
0
0
412 1 O bond ~ 1,1-dimethylpropyl
N
'\
N
H5
H
413 1 O bond ~ 1,1-dimethylpropyl
~~
N
F
H
414 1 O bond ~ 1,1-dimethylpropyl
~
\
_NH
_~/O
O
415 1 O bond ~~N 1,1-dimethylpropyl
~Et
~~N
416 1 O bond ~~N l , l-dimethylpropyl
HN'
~\'\\S
4I7 1 O bond ~ 1,1-dimethylpropyl
,.N
I~/
AY
B~N
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 216 -
No. n X D RZ R,
418 1 O bond f ° 1,1-dimethylpropyl
°
419 1 O bond ~ 1,1-dimethylpropyl
. ~ ~
i
420 1 O bond ° 1,1-dimethylpropyl
421 1 O bond COOH 1,1-dimethylpropyl
422 2 O bond COOH 1,1-dimethylpropyl
FORMULA LXV
Another preferred embodiment of this aspect of the
invention is a compound of the formula LXV:
Br
(LXV)
in which
X, Y, and Z are independently selected from the group
consisting of C, 0, S, or N, provided that X, Y, and Z are
not all C;
n is 1-3~
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 217 -
any two or more atoms of the primary ring (when n is 1-3)
are bonded to each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which dales) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
A is selected from the group consisting of L1, L2, L3.
or L4, in which
O
O \
L~ is ~O , L2 is ~s
R~ R~
E\
=O , and L4 is \N
L3 is ~ o
R' R~
and R1 and E, independently, are selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged
ring moiety, aryl, heteroaryl, carbacycle, and heterocycle;
R2is carboxylic acid or a carboxylic acid isostere;
wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, carbocycle, heterocycle, or carboxylic acid
isostere is optionally substituted with one or more
substituents selected from R3, where
R3 is hydrogen, hydroxy, halo, halo (C1-C6) -alkyl,
thiocarbonyl, (C1-C6) -alkoxy, (C2-C6) -alkenoxy,
(C1-C6) -alkylaryloxy, aryloxy, aryl- (C1-C6)
alkyloxy, cyano, nitro; imino, (C1-C6)
alkylamino, amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfhydryl,
thio- (C1-C6) -alkyl, (C1-C6) -alkylthio, sulfonyl,
C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 218 -
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a
bridged ring moiety, aryl, heteroaryl,
carbocycle, heterocycle, or C02R' where R' is
hydrogen or C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl or alkenyl;
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof.
Preferred embodiments of this embodiment of the
invention are those in which R2 is independently a
carbocycle or heterocycle containing any combination of CH2,
0, S, or N in any chemically stable oxidation state, where
any of the atoms of said ring structure are optionally
substituted in one or more positions with R3.
Especially preferred embodiments of this aspect of the
invention are the use of those compounds in which R2 is
independently selected from the group below:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 219 -
H
\ / N OH
N \N N
HN
HN\ N HOOC H N-N
H ~ O H O
N
N ~NH ~ I ~ N NH
S ~~ HN
° O
O
N
/ ~ ~ /N
N~ ~ O
NH ~ HN
° °\ ~ S\
N ~ N
S
°
OH
v
~O O ( ~N I ~N
N HS H F H
O H
2 0 °H
0
0
OH
NH ~ ~ ~
I .aJ
2 5 0 °" o
where the atoms of said ring structure may be optionally
substituted at one or more positions with R3.
Another preferred embodiment of this invention is
30 where R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of -COOH, -S03H, -S02HNR3, -P02 (R3) 2, -CN, -P03 (R3) 2, -OR3,
SR3, -NHCOR3, -N (R3) 2, -CON (R3) 2, -CONH (0) R3, -CONHNHS02R3,
-COHNS02R3, and -CONR3CN .
Preferred embodiments of this embodiment are the
35 compounds (2S)-1-(phenylmethyl)carbamoyl-2-hydroxymethyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 220 -
(4-thiazolidine), (2S)-1-(1,1-dimethyl propyl)carbamoyl-2-
(4-thiazolidine)tetrazole and (2S)-1-(phenylmethyl)
carbamoyl-2-(4-thiazolidine) carbonitrile.
The following structures are non-limiting examples of
preferred carbocyclic and heterocyclic isosteres
contemplated by this aspect of the invention:
H
/N\ ~ ~ ~ /N~ ~ N OH
N N
I
HN\N "OOI: H ~ N-N
SH ~ 0 OH O
~N-C ~ ~ ~ ~
N NH f il N NH
N\NI ~ \O HN
0 O
~\ ///O, ' /"~ ~ N
N \ H ~ O
N ~~ HN
0 \N \N~
S
0
2 0 off
N / ~~N ~~ ~ N
0 O ~ NI ~ N
0 ~ HS H F H
OH
0
S
2 5 °"
NH I ~ ~ I
.J
O ~OH
in which the atoms of said ring structure may be optionally
30 substituted at one or more positions with R3 wherein R3 is
hydrogen, hydroxy, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C,-
C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, C1-C6-alkylaryloxy, aryloxy, aryl-
C1-C6-alkyloxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C,-C6-alkylamino, amino-
C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio- C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-alkylthio,
35 sulfonyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 221 -
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle, heterocycle, and
C02R' where R' is hydrogen or C1-C9 straight or branched
chain alkyl or alkenyl. The present invention contemplates
that when chemical substituents are added to a carboxylic
isostere then the compound retains the properties of a
carboxylic isostere. Particularly, the present invention
contemplates that when a carboxylic isostere is optionally
substituted with one or more moieties selected from R3, then
the substitution cannot eliminate the carboxylic acid
isosteric properties of the compound. The present
invention contemplates that the placement of one or more R3
substituents upon a carbocyclic or heterocyclic carboxylic
acid isostere shall not be at an atoms) which maintains or
is integral to the carboxylic acid isosteric properties of
the inventive compound if such a substituent(s) would
destroy the carboxylic acid isosteric properties of the
inventive compound.
Other carboxylic acid isosteres not specifically
exemplified or described in this specification are also
contemplated by the present invention.
A compound for use in the present invention,
especially formula LXV, wherein n is 1, X is 0, D is a
bond, R1 is l,l,dimethylpropyl, and R2 is -CN, is named
(2S)-1-(1,2-dioxo-3,3-dimethylpentyl)-2-
pyrrolidinecarbonitrile.
Specific embodiments of the inventive compounds are
presented in Tables XLIV, XLV, and XLVI. The present
invention contemplates employing the compounds of Tables
XLIV, XLV, and XLVI, below, for use in compositions and
methods of the invention.
TABLE XLIV
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 222 -
Y~~CH2)n
~R2
N D
A
~N o
R~
No. n D R2 A y R~
423 1 bond COOH H S Benzyl
424 1 bond COOH H S a-MethylBenzyi
425 1 bond COON H S 4-MethylBenzyl
426 1 bond Tetrazole H S Benzyl
427 1 bond S03H H O a-MethylBenzyl
428 1 CHZ COOH H O 4-MethyIBenzyi
429 1 bond SOZHNMe H O Benryl
430 1 bond CN H N a-MethylBenzyl
431 1 bond P03HZ H N 4-MethylBenzyl
432 2 bond COOH H N Benzyl
433 2 bond COOH H S a-MethylBenzyl
2 434 2 bond COOH H S 4-MethyIBenzyl
0
435 2 bond COOH H S 3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl
436 2 bond COOH H S Cyclohexyi
437 2 bond POZHEt H O i-propyl
438 2 bond P03HPropyl H O ethyl
2 439 2 bond P03(Et)2 H N Methyl
5
440 2 bond OMe H S tert-butyl
441 2 bond OEt H S n-pentyl
442 2 bond OPropyi H S n-hexyl
443 1 bond OButyl H O Cyclohexyl
3 444 1 bond OPentyl H N cyciopentyl
0
445 1 bond OHexyl H S n-heptyl
446 1 bond SMe H S n-octyl
447 1 bond SEt H O n-nonyl
44.8 2 bond SPropyl H N 2-indolyl
35 449 2 bond SButyi H O 2-furyl
450 2 bond NHCOMe H S 2-thiazolyl
451 2 bond NHCOEt H S 2-thienyl
452 1 CHZ N(Me)Z H N 2-pyridyi
453 1 (CH~2 N(Me)Et H S 1,1-dimethylpropyl
4 454 I (CHZ)3 CON(Me)2 H O 1,1-dimethylpropyl
0
455 1 (CHZ)4 CONHMe H N 1,1-dimethylpropyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 223 -
No. n D R2 A y R'
456 1 (CHAS CONHEt H S 1,1-dimethylpropyl
457 1 (CH~6 CONHPropyl H S 1,1-dimethylpropyl
TABLE XLV
(CH2)n
/R2
N /D
/$02
R/~
No. n D R2 Y R,
458 bond CONH(O)Me S Benzyl
459 bond CONH(O)Et S a-Methylphenyl
460 1 bond CONH(O)Propyl S 4-MethylphenyI
461 2 bond COOH S Benzyl
462 2 bond COOH O a-Methylphenyl
463 2 bond COOH O 4-Methylphenyl
2 464 1 CHZ COOH N benzyl
0
465 1 (CH~2 COON N benzyl
466 1 (CH~3 COOH N benzyl
467 1 (CH~4 COOH S benzyl
468 1 (CHAS COOH S benzyl
2 469 1 (CH~6 COOH S benzyl
5
470 1 (CH~7 COON S benzyl
471 1 (CH~g COOH O benzyl
472 1 (CH~9 COOH O benzyl
473 1 (CH~,o COOH O benzyl
3 474 1 CZHz COOH N benzyl
0
475 1 2-OH,Et COOH N benzyl
476 1 2butyleneCOOH S benzyl
477 1 i-Pro COOH S benzyl
478 1 tert-Bu COOH S benzyl
3 479 1 2-nitro COOH S benzyl Hexyl
5
480 3 (CH~Z CN S benzyl
481 1 (CHZ)3 CN S benzyl
482 3 bond CONHNHSOZMe N Benzyl
483 3 bond CONHNHS02Et N a-Methylphenyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 224 -
484 3 bond CONHSOZMe N 4-Methylphenyl
485 2 bond CONHNHSOZEt N Phenyl
486 2 bond CON(Me)CN O a-Methylphenyl
487 2 bond CON(Et)CN O 4-Methylphenyl
488 1 (CH~2 COOH O methyl
489 1 (CHZ)3 COOH O ethyl
490 1 (CH~4 COOH N n-propyl
491 1 (CHs COOH N t-butyl
492 1 (CH~6 COOH N Pentyl
493 1 (CHI, COOH S Hexyl
494 1 (CH~B COOH S Heptyl
495 1 (CH~9 COOH S Octyl
496 1 (CH~,o COOH S Nonyl
497 1 CZHZ COOH S Cyclohexyl
TABLE XLVI
Y ~CH2)n
R2
No. n X D RZ Y R,
498 1 O bond ~ N off O 1,1-dimethylpropyl
N-N
2 5 499 1 O bond ~ ~ S 1,1-dimethylpropyl
N
N
N
500 1 O bond .~ S 1,1-dimethylpropyl
N
HN~
N
501 1 O bond ~~N ~N O 1,1-dimethylpropyl
--~~~N~
M ~ Me
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 225 -
No. n X D R2 Y R,
502 1 O bond ~ N I, I-dimethylpropyl
I 'N
HOOC H
503 1 O bond ~ ~N~ S I, I-dimethylpropyl
0
OH
504 I O bond ~ °" N 1,1-dimethylpropyl
i
0
0
505 1 O bond ~ N 1,1-dimethylpropyl
~~N
HS
506 1 O bond ~ S 1,1-dimethylpropyl
I ~N
b
507 1 O bond ~ ° O 1, I-dimethylpropyl
N'
NH
O
508 1 O bond ~ ° S l,l-dimethylpropyl
NH
S\ /
~\\O
509 1 O bond °" S 1,1-dimethylpropyl
~ ~ ~N
°
510 I O bond ~ ° O 1,1-dimethylpropyl
NH
HN
~\(\\'O
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 226 -
No. n X D R2 Y R~
51 i 1 O bond ° S l, i-dimethylpropyl
NH
O
512 1 O bond ~~ O 1,1-dimethylpropyl
°H
513 1 O bond ~ S 1,1-dimethylpropyl
0
514 1 O bond ~N\ /E~ N 1,1-dimethylpropyl
O- /~'N
S 15 1 O bond ~ ~ O 1,1-dimethylpropyl
,o
H ~\\(N
s
516 1 O bond ~ S l, i-dimethylpropyl
/j-'--Me
S ~~~
N
Compounds 517-610 are also exemplified for use in the
present invention, and are defined as where Y is located at
the 3-position of the heterocyclic ring for compounds 423-
516, and n, A, D, Y, X, R1, and R2 remain the same as
defined for compounds 423-516 in Tables XLIV, XLV, and
XLVI.
Exemplary compound 611 is defined where S is located
at the 3-position of the heterocyclic ring (3-
thiazolidine), n is 1, R1 is 1,1-dimethylpropyl, D is a
bond, R2 i s COON .
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 227 -
Exemplary compound 612 is defined where 0 is located
at the 2-position of the heterocyclic ring (2-
oxopentanoyl), n is 1, R1 is 1,1-dimethylpropyl, D is a
bond, R2 is COOH (i.e. 3-(3,3-dimethyl-2-oxopentanoyl)-1,3-
oxazolidine-4-carboxylic acid).
The present invention also contemplates other ring
locations for the heteroatoms 0, N, and S in heterocyclic
compounds. Also contemplated by the present invention are
heterocycles containing 3 or more heteroatoms chosen
independently from O, N, and S.
TABLE XLVII
(CH2)n
/R2
N D
L~
R~
No. n D R~ L R,
613 I CHZ OH 1,2-dioxoethylbenzyl
614 1 bond -CN 1,2-dioxoethylI,1-dimethylpropyl
615 1 bond tetrazole1,2-dioxoethyll,I-dimethylpropyl
616 2 band CONH2 1,2-dioxoethyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
617 I bond COOH 1,2-dioxoethyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
618 2 bond COOH 1,2-dioxoethyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
FORMULA LXVI
In another embodiment of the invention, there is
provided a compound of formula LXVI:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 228 -
BP., ~CH2~~
~ RZ
N D
A
N O
(LXVI)
R~
in which:
n is 1-3;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the primary ring (when n is 1-3)
are bonded to each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
R1 and A are independently selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, C1-C9 straight or branched chain
alkyl, CZ-C9 straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged
ring moiety, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle, and heterocycle;
D is a bond, or a C1-Clo straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-Clo alkenyl or C2-C1o alkynyl;
R2 is independently carboxylic acid or a carboxylic
acid isostere;
wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, carbocycle, heterocycle, or carboxylic acid
isostere is optionally substituted with one or more
substituents selected from R3, where
R3 is hydrogen, hydroxy, halo, halo (C1-C6) -alkyl,
thiocarbonyl, (C1-C6) -alkoxy, (C2-C6) -alkenoxy,
(C1-C6) -alkylaryloxy, aryloxy, aryl- (C1-C6) -
alkyloxy, cyano, nitro, imino, (C1-C6) -alkylamino,
amino- (C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio- (C1-C6) -
alkyl, (C1-C6) -alkylthio, sulfonyl, C1-C6 straight
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/2557?
- 229 -
or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or
branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle,
heterocycle, and C02R4 where R' is hydrogen or C1-
C9 straight or branched chain alkyl or alkenyl;
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or solvate
thereof.
A preferred compound for use in this embodiment of
this invention is (2S)-1-(cyclohexyl)carbamoyl-2
pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid.
Other preferred compounds for use in this embodiment
of this invention are those in which R2 is independently a
carbocycle or heterocycle containing any combination of CH2,
0, S, or N in any chemically stable oxidation state, where
any of the atoms of said ring structure are optionally
substituted in one or more positions with R3.
Especially preferred embodiments of this aspect of the
invention are those in which R2 is independently selected
from the group below:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 230 -
yi/ ~ ~N~ Y// N N OH
HN' ~ N ~ NI H
N HOOC _H N-N
H~ ° °
~N~
N ~ N NH
I
N\N ~ ~O
O O
O /
I NH ~~ HN
N S N
S
O
OH
/ N ~ ~~N
\° ~
'N
° ~l~ HS ~ F H
OH
O
OH
NH
2 0 ° °" °
where the atoms of said ring structure may be optionally
substituted at one or more positions with R3.
Another preferred embodiment of this invention is
where R2 is independently selected from the group consisting
of -COOH, -S03H, -S02HNR3, -P02 (R3) 2, -CN, -P03 (R3) 2, -OR3,
SR3, -NHCOR3, -N ( R3 ) 2, -CON ( R3 ) 2, -CONH ( 0 ) R3, -CONHNHS02R3, -
COHNS02R3, and -CONR3CN .
"Isosteres" are different compounds that have
different molecular formulae but exhibit the same or
34 similar properties. For example, tetrazole is an isostere
of carboxylic acid because it mimics the properties of
carboxylic acid even though they both have very different
molecular formulae. Tetrazole is one of many possible
isosteric replacements for carboxylic acid. Other
carboxylic acid isosteres contemplated by the present
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00116603 PCT/US98/25577
- 231 -
invention include -COOH, -S03H, -S02HNR3, -P02 (R3) 2, -CN, -
P03 ( R3 ) 2, -OR3, -SR3, -NHCOR3, -N ( R3 ) 2, -CON ( R3 ) 2, -CONH (O) R3.
-CONHNHS02R3, -COHNS02R3, and -CONR3CN wherein R3 is hydrogen,
hydroxy, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-C6-alkoxy,
C2-C6-alkenoxy, C1-C6-alkylaryloxy, aryloxy, aryl- C1-C6-
alkyloxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino, amino- C1-
C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio- C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-alkylthio,
sulfonyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle, heterocycle, and
C02R9 where RQ is hydrogen or C1-C9 straight or branched
chain alkyl or alkenyl.
In addition, carboxylic acid isosteres can include 5-7
membered carbocycles or heterocycles containing any
combination of CH2, O, S, or N in any chemically stable
oxidation state, where any of the atoms of said ring
structure are optionally substituted in one or more
positions. The following structures are non-limiting
examples of preferred carbocyclic and heterocyclic
isosteres contemplated by this aspect of the invention:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98I25577
- 232 -
H
~N~ ~ ~ ~ N OH
N N N
~~H~
HN\ ~ HOOC H ~ N-~N
sH ~ o off o
NH - 'N
N NH
N S ~~ HN
O O
S) O
IO ~~N~ N /N~O ~ 'N
~NH H
0 \ S\
N
S
O
OH
I5 ~ O O /N ~ /N
0 H HS H/ F /H
OH
O
0
S
OH
2 0 NH
O ~OH
0
where the atoms of said ring structure may be optionally
substituted at one or more positions with R3 wherein R3 is
25 hydrogen, hydroxy, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-
C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, C1-C6-alkylaryloxy, aryloxy, aryl-
C1-C6-alkyloxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino, amino-
C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio- C1-C6-alkyl; C1-C6-alkylthio,
sulfonyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C6
30 straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged
ring moiety, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle, heterocycle, and
C02R9 where R° is hydrogen or C1-C9 straight or branched
chain alkyl or alkenyl. The present invention contemplates
that when chemical substituents are added to a carboxylic
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCTNS98/25577
- 233 -
isostere then the inventive compound retains the properties
of a carboxylic isostere.
The present invention contemplates that when a
carboxylic isostere is optionally substituted with one or
more moieties selected from R3, then the substitution cannot
eliminate the carboxylic acid isosteric properties of the
inventive compound. The present invention contemplates
that the placement of one or more Rj substituents upon a
carbocyclic or heterocyclic carboxylic acid isostere shall
not be permitted at one or more atoms) which maintains)
or is/are integral to the carboxylic acid isosteric
properties of the inventive compound, if such
substituent(s) would destroy the carboxylic acid isosteric
properties of the inventive compound.
A compound of the present invention, especially
formula LXVI, wherein n is 1, X is 0, D is a bond, R1 is
l,l,dimethylpropyl, and R2 is -CN, is named (2S)-1-(1,2-
dioxo-3,3-dimethylpentyl)-2-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile.
Specific embodiments of the inventive compounds are
presented in Table XLVIII. The present invention
contemplates employing the compounds of Table XLVIII,
below, for use in compositions and methods of the
invention.
30
No. n D RZ A R~
619 1 bond COOH I-f cyclohexyl
620 I bond COOH H a-MethylBenzyl
3 5 621 1 bond COOH H 4-MethylBenzyl
TABLE XLVIII
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCTNS98/25577
- 234 -
No. n D R A
622 1 bond Tetrazole H Benzyl
623 1 bond S03H H a-MethylBenzyl
624 1 CH2 COOH H 4-MethylBenzyl
625 1 bond S02HNMe H Benzyl
626 1 bond CN H a-MethylBenzyl
627 1 bond P03H2 H 4-MethylBenzyl
628 2 bond COON H Benzyl
629 2 bond COOH H a-MethylBenzyl
630 2 bond COOH H 2-butyl
631 2 bond COON H 2-butyl
632 2 bond COOH H Cyclohexyl
633 2 bond POZHEt H i-propyl
634 2 bond P03HPropyl H ethyl
635 2 bond P03(Et)2 H Methyl
636 2 bond OMe H tert-butyl
637 2 bond OEt H n-pentyl
638 2 bond OPropyl H n-hexyl
639 1 bond OButyl H Cyclohexyl
639 1 bond OPentyl H cyclopentyl
2 640 1 bond OHexyl H heptyl
0
641 1 bond SMe H n-octyl
642 1 bond SEt H n-hexyl
643 2 bond SPropyl H n-hexyl
644 2 bond SButyl H n-hexyl
2 645 2 bond NHCOMe H n-hexyl
5
646 2 bond NHCOEt H 2-thienyl
647 1 CHz N(Me)2 H adamantyl
648 1 (CH~z N(Me)Et H adamantyl
649 1 (CH~3 CON(Me)Z H adamantyl
3 650 1 (CH~4 CONHMe H adamantyl
0
651 1 (CHAS CONHEt H adamantyl
652 1 (CH~6 CONHPropyl H adamantyl
653 1 bond CONH(O)Me H Benzyl
654 1 bond CONH(O)Et H a-methylphenyl.
3 655 1 bond CONH(O)Propyl H 4-Methylphenyl
5
657 2 bond COON H Benzyl
658 2 bond COOH H a-Methylphenyl
659 2 bond COOH H 4-Methylphenyl
660 1 CH2 COOH Me cyclohexyl
4 661 1 (CH~2 COOH Et cyclohexyl
0
662 1 (CH~3 COON Prop cyclohexyl
663 1 (CH~4 COOH But cyclohexyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 235 -
No. n D R2 A R,
664 1 (CHs COOH H cyclohexyl
665 1 (CH~6 COOH H cyclohexyl
666 1 (CH~7 COOH H cyclohexyl
667 1 (CH~B COOH H cyclohexyl
668 1 (CH~9 COON H cyclohexyl
669 1 (CH~,o COOH H cyclohexyl
670 1 CZHZ COON H cyclohexyl
671 1 2-OH,Et COOH H cyclohexyl
672 1 2-butylene- COOH H cyclohexyl
673 1 i-Pro CbOH H cyclohexyl
674 1 tert-Bu COOH H cyclohexyl
675 1 2-nitro Hexyl COOH H cyclohexyl
676 3 (CH~}2 CN H cyclohexyl
677 1 (CH~3 CN H cyclohexyl
I5 678 3 bond CONHNHSOZMe H Benzyl
679 3 bond CONHNHSOZEt H a-Methylphenyl
680 3 bond CONHSOZMe H 4-Methylphenyl
681 2 bond CONHNHS02Et H Phenyl
682 2 bond CON(Me)CN H a-Methylphenyl
2 0 683 2 bond CON(Et)CN H 4-Methylphenyl
684 1 (CH~2 COOH H methyl
685 1 (CH~3 COOH H ethyl
686 1 (CH~4 COOH H n-propyl
687 1 (CHAS COOH H t-butyl
2 5 688 1 (CHZ)6 COOH H Pentyl
689 1 (CHZ)7 COON H Hexyl
690 1 (CH~B COOH H Heptyl
691 1 (CH~9 COOH H Octyl
692 1 (CH~,o COOH H Nonyl
3 0 693 1 CZHZ COOH H Cyclohexyl
694 1 bond ,~ H cyclohexyl
N
HN~
N
695 1 bond \ H cyclohexyl
'N
HOOC /H
696 1 bond ~~" ~N H cyclohexyl
N
M ~ Me
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 236 -
No. n D R p R
697 1 bond ~ " °" H cyclohexyl
N-N
698 1 bond ~ " H cyclohexyl
N
~N
N
699 1 bond ° H cyclohexyl
~NH
S
~\('\'0
700 1 bond °" H cyclohexyl
~N
O
701 1 bond ° H cyclohexyl
NH
HN
~,('1'O
702 1 bond i ~ H cyclohexyl
0
OH
703 1 bond o" H cyclohexyl
0
NH
704 1 bond \ H cyclohexyl
-N
'N
HS H
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 237
-
No. n D
705 1 bond N H cyclohexyl
'
N
N
F H
706 1 bond H cyclohexyl
~NH
HN'
/
~(
\'O
707 1 bond ~ H cyclohexyl
\ /
N
Ifr'
/r--Et
O ~~~
N
708 1 bond ~ 'N H cyclohexyl
HN'
~\('\'S
709 1 bond .~~N~Me H cyclohexyl
-~\'S- ~N
710 1 bond ° H cyclohexyl
a
711 1 bond ~~ H cyclohexyl
s
OH
712 1 bond H cyclohexyl
OH
O
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 238 -
TABLE IL
(CHt)n
/Ri
N D
R~
No. n D R L R
713 1 CHZ OH I,2-dioxoethylbenzyl
714 1 bond -CN 1,2-dioxoethyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
715 1 bond tetrazole 1,2-dioxoethyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
716 2 bond CONH2 1,2-dioxoethylI,1-dimethylpropyl
717 1 bond COOH I,2-dioxoethyl1,1-dimethylpropyl
718 2 bond COOH 1,2-dioxoethylI,I-dimethylpropyl
FORMULA LXVII
Another preferred embodiment of the invention is a
compound of the formula LXVII:
Bf ~~; ,' (CHZ)n
~ ~Rz
N D
O ~~O
(LXVII)
in which:
n is 1-3;
the primary ring structure optionally includes Br,
wherein Br is a heterocylic bridged ring moiety, wherein
any two or more atoms of the primary ring (when n is f-3)
are bonded to each other through either
a chemical bond or
atoms) other than a bond
which doles) not comprise a part of the primary ring
structure;
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 239 -
R1 is independently selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl, C2-C9
straight or branched chain alkenyl, a bridged ring moiety,
aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle, or heterocycle;
D is a bond, or a C1-Clo straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-Clo alkenyl or C2-Clo alkynyl;
R2 is independently a carboxylic acid or a carboxylic
acid isostere;
wherein said alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, heteroaryl,
carbocycle, heterocycle, or carboxylic acid isostere is
optionally substituted with one or more substituents
selected from R3, where
R3 is independently hydrogen, hydroxy,
halo, , halo- (C1-C6) -alkoxy, thiocarbonyl, (C1
C6) -alkoxy, (C2-C6) -alkenyloxy, (C1-C6)
alkylaryloxy, aryloxy, aryl- (C1-C6) -alkyloxy,
cyano, nitro, imino, (C1-C6) -alkylamino, amino-
(C1-C6) -alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio- (C1-C6) alkyl, (C1-
C6) -alkylthio, sulfonyl, C1-Cf; straight or
branched chain alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched
chain alkenyl or alkynyl, a bridged ring moiety,
aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle, heterocycle, or
C02R9 where RQ is hydrogen or C1-C9 straight or
branched chain alkyl or alkenyl;
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or solvate
thereof.
A preferred embodiment of this invention is the use
of a compound in which R2 is independently a carbocycle or
heterocycle containing any combinatian of CHz, O, S, or N
in any chemically stable oxidation state, where any of the
atoms of said ring structure are optionally substituted in
one or more positions with R3.
Especially preferred embodiments of this aspect of
the invention are the use of those compounds in which R2 is
independently selected from the group below:
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 240 -
OH
N I ~N ~ N
HN~ ~ HN
N HOOC H N--N
~ H ~ H
N
N NH
N
N / S ~ /NH
N p HN\/
~\'O
O
IO p ~ N
~N~ / O
I NH ~ ~ HN
0\ S
N N
S
O
H
I5
0 O ( /N ,N
O H HS H/ F /H
OH
OH
NH I ~ ~ ~ I
O OH
0
in which the atoms of said ring structure may be optionally
substituted at one or more positions with R3.
Another preferred embodiment of this ;nvant;"n
where R2 is independently selected from the group
consisting of -COOH, -S03H, -S02HNR3, -P02.(R3) 2, -CN, -
P03 ( R3 ) 2, -OR3, -SR3, -NHCOR3, -N ( R3 ) 2, -CON ( R3 ) 2, -CONH ( 0 ) R3,
-CONHNHS02R3, -COHNS02R3, and -CONR3CN .
Preferred embodiments of this i n«Pnt; ~n ~,-o +-~,..
following compounds: (2S)-1-(phenylmethyl)sulfonyl-2-
hydroxymethyl pyrrolidine; (2S)-1-(phenylmethyl)-sulfonyl-
2-pyrrolidinetetrazole; (2S)-1-(phenyl-methyl)-sulfonyl-2-
pyrrolidine carbonitrile; and compounds 719-821.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCTIUS98/25577
- 241 -
"Isosteres" are different compounds that have
different molecular formulae but exhibit the same or
similar properties. For example, tetrazole is an isostere
of carboxylic acid because it mimics the properties of
carboxylic acid even though they both have very different
molecular formulae. Tetrazole is one of many possible
isosteric replacements for carboxylic acid. Other
carboxylic acid isosteres contemplated by the present
invention include -COOH, -S03H, -S02HNR3, -P02 (R3) 2, -CN, -
P03 (R3) 2, -OR3, -SR3, -NHCOR3, -N (R3) 2, -CON (R3) 2, -CONH (O) R3,
-CONHNHS02R3, -COHNS02R3, and -CONR3CN, wherein R3 is
hydrogen, hydroxy, halo, halo-C1-C6-alkyl, thiocarbonyl, C1-
C6-alkoxy, C2-C6-alkenoxy, C1-C6-alkylaryloxy, aryloxy, aryl-
C1-C6-alkyloxy, cyano, nitro, imino, C1-C6-alkylamino,
amino- C1-C6-alkyl, sulfhydryl, thio- C1-C6-alkyl, C1-C6-
alkylthio, sulfonyl, C1-C6 straight or branched chain
alkyl, C2-C6 straight or branched chain alkenyl or alkynyl,
a bridged ring moiety, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle,
heterocycle, and C02R4 where R' is hydrogen or C1-C9 straight
or branched chain alkyl or alkenyl.
In addition, carboxylic acid isosteres can include 5-
7 membered carbocycles or heterocycles containing any
combination of CH2, 0, S, or N in any chemically stable
oxidation state, where any of the atoms of said ring
structure are optionally substituted in one or more
positions. The following structures are non-limiting
examples of preferred carbocyclic and heterocyclic
isosteres contemplated by this aspect of the invention.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 242 -
N
N N N OH
HN~ ~ N~ HN
N HOOC H N-N
H ~ O H O
~N
N NH /N NH
N~ ~ S HN
N O
O
O
lO N
\N O ~"
O
NH
HN
N
S
O
off
O ( N I N
O
O ~ HS H F H
OH
0
OH
NH ~ ~ I
~J
O OH
O
where the atoms of said ring structure may be optionally
substituted at one or more positions with R3. The present
invention contemplates that when chemical substituents are
added to a carboxylic isostere then the inventive compound
retains the properties of a carboxylic isostere. The
present invention contemplates that when a carboxylic
isostere is optionally substituted with one or more
moieties selected from R3, then the substitution can not
eliminate the carboxylic acid isosteric properties of the
inventive compound. The present invention contemplates
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 243 -
that the placement of one or more R3 substituents upon a
carbocyclic or heterocyclic carboxylic acid isostere shall
not be at an atoms) which maintains or is integral to the
carboxylic acid isosteric properties of the inventive
compound if such a substituent(s) would destroy the
carboxylic acid isosteric properties of the inventive
compound.
Other carboxylic acid isosteres not specifically
exemplified or described in this specification are also
contemplated by the present invention.
A compound of the present invention, especially
formula LXVII, wherein n is 1, D is a bond, R1 is
phenylmethyl, and R2 is -CN, is named (2S)-1-(phenylmethyl)
sulfonyl-2-pyrrolidine carbonitrile.
Specific embodiments of the inventive compounds are
presented in Tables L and LI. The present invention
contemplates employing the compounds of Tables L and LI,
below, for use in compositions and methods of the
invention.
TABLE L
(CHZ)n
/ R2
N D
o '~o
R~
No. n D RZ R,
719 1 bond COOH Benzyl
3 0 720 1 bond COOH a-MethylBenzyl
721 1 bond COOH 4-MethyIBenzyl
722 1 bond Tetrazole Benzyl
723 1 bond S03H a-MethyLBenzyl
724 1 CHZ COOH 4-MethylBenzyl
3 5 725 1 bond SOZHNMe Benzyl
726 1 bond CN a-MethylBenzyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 244 -
No. n D R R,
727 1 bond P03Hz 4-MethylBenzyl
728 2 bond COOH Benzyl
729 2 bond COOH a-MethyIBenzyl
730 2 bond COOH 4-MethylBenzyl
731 2 bond COOH 3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl
732 2 bond COOH Cyclohexyl
733 2 bond POZHEt i-propyl
734 2 bond P03HPropyl ethyl
735 2 bond P03(Et)2 Methyl
736 2 bond OMe tert-butyl
737 2 bond OEt n-pentyl
738 2 bond OPropyl n-hexyl
739 1 bond OButyl Cyclohexyl
740 1 bond OPentyl cyclopentyl
741 1 bond OHexyl n-heptyl
742 1 bond SMe n-octyl
743 1 bond SEt n-nonyl
744 2 bond SPropyl 2-indolyl
745 2 bond SButyl 2-furyl
2 746 2 bond NHCOMe 2-thiazolyl
0
747 2 bond NHCOEt 2-thienyl
748 1 CHZ N(Me)Z 2-pyridyl
749 1 (CH~z N(Me)Et benzyl
750 1 (CH~3 CON(Me}2 benzyl
2 751 1 (CH~4 CONHMe benzyl
5
752 1 (CHAS CONHEt benzyl
753 1 (CH~6 CONHPropyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
754 1 bond CONH(O)Me Benzyl
755 1 bond CONH(O)Et a-Methylphenyl
3 756 1 bond CONH(O)Propyl 4-Methylphenyl
0
757 2 bond COON Benzyl
758 2 bond COOH a-Methylphenyl
759 2 bond COOH 4-Methylphenyl
760 1 CH2 COOH benzyl .
3 761 1 (CH~2 COOH benzyl
5
762 1 (CH~3 COON benzyl
763 1 (CH~4 COOH benzyl
764 1 (CHs COOH benzyl
765 1 (CH~6 COOH benzyl
4 766 1 (CH~7 COOH benzyl
0
767 1 (CHZ)$ COOH benzyl
768 1 (CHZ)9 COOH benzyl
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00116603 PCT/US98/25577
- 245 -
No. n D R2 R,
769 1 (CH~,o COOH benzyl
770 1 C2H2 COOH benzyl
771 1 2-hydroxyethylCOOH benzyl
772 1 2-butylene COOH benzyl
773 1 i-Propyl COOH benzyl
774 1 tert-Butyl COOH benzyl
775 1 2-nitrohexyl COOH benzyl
776 3 (CH~Z CN benzyl
777 1 (CH~3 CN benzyl
778 3 bond CONHNHSOZMe Benzyl
779 3 bond CONHNHSOZEt a-Methylphenyl
780 3 bond CONHSOZMe 4-Methylphenyl
781 2 bond CONHNHSOZEt Phenyl
782 2 bond CON(Me)CN a-Methylphenyl
783 2 bond CON(Et)CN 4-Methylphenyl
784 1 (CHZ)Z COOH methyl
785 1 (CH~3 COOH ethyl
786 1 (CH~4 COON n-propyl
787 1 (CHAS COOH t-butyl
2 788 1 (CH~6 COOH Pentyl
0
789 1 (CHI, COOH Hexyl
790 1 (CH~g COOH Heptyl
791 1 (CH~9 COOH Octyl
792 1 (CH~,o COOH Nonyl
2 793 1 C2H2 COOH Cyclohexyl
5
794 1 bond benzyl
\ 'N\
r'
//N
I
HN '/~
N
795 1 bond benzyl
~N\
,N
N /~
H3C~
CH3
796 1 bond benzyl
N
\\N
N
HOOC H
797 1 bond ~ " off benzyl
N-N
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 246 -
No. n D R R
3 0 798 1 bond ~ S" benzyl
N'
~N
N
N
799 1 bond ~ o l~~yl
NH
S
0
800 1 bond S aH benzyl
/N
O
801 1 bond ° benzyl
~NH
HN
O
802 1 bond ~ benzyl
'N\
\O
OH
3 5 803 1 bond benzyl
804 1 bond ~ benzyl
N
~~N
N
HS H
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
247
No. n D Rz R,
805 1 bond ~ benzyl
\
N
N
F H
806 1 bond ~ benzyl
\ N
I NH
O
O
807 1 bond ~ benzyl
N
~' /j--Et
O
N
4 0 808 1 bond ~ benzyl
\ / N'
\O
HN
S
809 1 bond ~ ~~yl
N
Ir' ir--Me
S ~~~
N
810 1 bond ~ ° benzyl
NH
O
811 1 bond ~~ benzyl
s
OH
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
WO 00/16603 PCT/US98/25577
- 248 -
No. n D R R
812 1 bond benzyl
813 1 bond CHZOH benzyl
814 1 bond CONHZ benzyl
815 1 bond CN benzyl
TABLE LI
~CH2)n
~Rz
~ D
L\
R~
No. n D R L R
816 1 CHZ OH 1,2-dioxoethyl ~~yl
817 1 bond -CN 1,2-dioxoethyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
818 1 bond tetrazole 1,2-dioxoethyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
819 2 bond CONH2 1,2-dioxoethyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
820 1 bond COOH 1,2-dioxoethyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
821 2 bond COON 1,2-dioxoethyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl
Svnthesis of Compounds of the Invention
The compounds for use in the methods and compositions
of the invention may be readily prepared by standard
techniques of organic chemistry, utilizing the general
synthetic pathways depicted below.
In the preparation of the compounds of the invention,
one skilled in the art will understand that one may need
to protect or block various reactive functionalities on the
starting compounds or intermediates while a desired
reaction is carried out on other portions of the molecule.
CA 02344376 2001-03-16
i
DEMANDES OU BREVETS VOLUMINEUX
LA PRESENTS PARTIE DE CETTE DEMANDS OU CE BREVET
COMPREND PLUS D'UN TOME.
CECI EST LE TOME '( DE
NOTE: ~ Pour les tomes additionels, veuillez contacter to Bureau canadien des
brevets
JUMBO APPLICAT10NS/PATENTS
THiS SECT10N OF THE APPL1CATION/PATENT CONTAINS MORE
THAN ONE VOLUME ,
THIS IS VOLUME ~ , OF
NOTE: For additional volumes please contact the Canadian Patent Office