Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
THIOUREA INHIBITORS OF HERPES VIRUSES
B_ackgroand of the Invention
Eight viruses have been identified which are members of the family
Herpesviridae (reviewed in Roizman, B. 1996. Herpesviridae, p. 2221-2230. In
B. N.
Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields Virology, 3rd ed.
Lippincott-
Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, PA). Each member of this family is
characterized by
an enveloped virus containing proteinaceous tegument and nucleocapsid, the
latter of
which houses the viruses' relatively large double-stranded DNA genome (i.e.
approximately 80-250 kilobases). Members of the human alphaherpesvirus
subfamily are neurotropic and include herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and
type
2 (HSV-2), and varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The human betaherpesviruses are
cytomegalovirus (HCMV), human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) and human herpesvirus 7
(HHV-7). The gammaherpesviruses are lymphotropic and include Epstein-Barr
virus
(EBV) and Kaposi's herpesvirus (HHV-8). Each of these herpesviruses is
causally-
related to human disease, including herpes labialis and herpes genitalis (HSV-
1 and
HSV-2 [Whitley, R.J. 1996. Herpes Simplex Viruses, p. 2297-2342. In B. N.
Fields,
D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields Virology, 3rd ed. Lippincott-Raven
Publishers, Philadelphia, PA]); chicken pox and shingles (VZV [Arvin, A. 1996.
Varicella-Zoster Virus, p. 2547-2585. In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P. M.
Howley (ed.), Fields Virology, 3rd ed. Lippincott-Raven Publishers,
Philadelphia,
PA]); infectious mononucleosis (EBV [Rickinson, A. B. and Kieff, E. 1996.
Epstein-
Barr Virus, p. 2397-2446. In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley
{ed.),
Fields Virology, 3rd ed. Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, PA]);
pneumonia and retinitis (HCMV [(Britt, W. J., and Afford, C. A. 1996.
Cytomegalovirus, p. 2493-2523. In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley
(ed.), Fields Virology, 3rd ed. Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia,
PA]);
exanthem subitum (HHV-6 [(Pellet, P. E, and Black, J. B. 1996. Human
Herpesvirus
6, p. 2587-2608. In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields
Virology, 3rd ed. Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, PA] and HHV-7
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-2-
[Frenkel, N., and Roffman, E. 1996. Human Herpesvirus 7, p. 2609-2622. In B.
N.
Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields Virology, 3rd ed.
Lippincott-
Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, PA]); and Kaposi's sarcoma (HHV-8 [Neipel, F.,
Albrecht, J.C., and Fleckenstein, B. 1997. Cell-homologous genes in the
Kaposi's
sarcoma-associated rhadinovirus human herpesvirus 8: determinants of its
pathogenicity? J. Virol. 71:4187-92, 19970. HCMV is considered in more detail
below. Following the primary infection, herpesviruses establish latency within
the
infected individual and remain there for the remainder of his/her life.
Periodic
reactivation of latent virus is clinically relevant. In the case of HSV,
reactivated
virus can be transmitted to infants during birth, causing either skin or eye
infection,
central nervous system infection, or disseminated infection (i.e. multiple
organs or
systems). Shingles is the clinical manifestation of VZV reactivation.
Treatment of
HSV and VZV is generally with antiviral drugs such as acyclovir (Glaxo
Wellcome),
ganciclovir (Roche) and foscarnet (Asta) which target viral encoded DNA
1 S polymerase.
HCMV is a ubiquitous opportunistic pathogen infecting 50-90% of the adult
population (Britt, W. J., and Afford, C. A. 1996. Cytomegalovirus, p. 2493-
2523. In
B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields Virology, 3rd ed.
Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, Pa.). Primary infection with HCMV
is
usually asymptomatic, although heterophile negative mononucleosis has been
observed. The virus is horizontally transmitted by sexual contact, breast
milk, and
saliva. Intrauterine transmission of HCMV from the pregnant mother to the
fetus
occurs and is often the cause of serious clinical consequences. HCMV remains
in a
latent state within the infected person for the remainder of his/her life.
Cell-mediated
immunity plays a central role in controlling reactivation from latency.
Impaired
cellular immunity leads to reactivation of latent HCMV in seropositive
persons.
HCMV disease is associated with deficient or immature cellular immunity.
There are 3 major categories of persons with HCMV disease (reviewed by Britt
and
Afford, 1996). (1) In immunocompromised (AIDS) patients, HCMV is one of the
two most common pathogens causing clinical disease (the other is
Preeumocystis).
The most common manifestation of HCMV in AIDS is retinitis, although infection
of
other organs including the adrenal glands, lungs, GI tract, and central
nervous system
are also reported frequently. 90% of AIDs patients have active HCMV infection;
25-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99128838
-3-
40% (-85,000 patients in the United States) have life- or sight-threatening
HCMV
disease. HCMV is the cause of death in 10% of persons with AIDS. (2) Due to
immune system suppression to reduce the risk of graft rejection, HCMV
reactivation
or reinfection is common amongst kidney, liver, heart, and allogeneic bone
marrow
transplant patients. Pneumonia is the most common HCMV disease in these
patients,
occurring in up to 70% of these transplant patients. (3) Congenital infection
due to
HCMV occurs in 1 % of all births, about 40K per year. Up to 25% of these
infants
are symptomatic for HCMV disease between ages 0-3 years. HCMV disease is
progressive, causing mental retardation and neurological abnormalities, in
children.
Recent studies suggest that treatment with anti-HCMV drugs may reduce
morbidity
in these children.
Several antiviral drugs are currently being marketed (Bron, D., R. Snoeck,
and L. Lagneaux. 1996. New insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of
cytomegalovirus. Exp. Opin. Invest. Drugs 5:337-344; Crumpacker, C. 1996.
Ganciclovir. New Eng. J. Med. 335:721-729; Sachs, S., and F. Alrabiah. 1996.
Novel
herpes treatments: a review. Exp. Opin. Invest. Drugs 5:169-183). These
include:
ganciclovir (Roche), a nucleoside analog with hemopoietic cell toxicity;
foscarnet
(Astray, a pyrophosphate analog with nephrotoxicity; and cidofovir, Gilead), a
nucleoside phosphonate with acute nephrotoxicity. Each of these drugs target
the
viral-encoded DNA polymerase, are typically administered intravenously due to
their
low bioavailability, and, as noted above, are the source of significant
toxicity.
Ganciclovir-resistant mutants which arise clinically are often cross-resistant
with
cidofovir. Hence, there is a need for safer (i.e. less toxic), orally
bioavailable anti-
viral drugs which are directed against novel viral targets.
Phenyl thioureas are disclosed for use in a variety of pharmaceutical
applications. Armistead, et al., WO 97/40028, teaches phenyl areas and
thioureas as
inhibitors of the inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) enzyme which is
taught to play a role in viral replication diseases such herpes.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-4-
X
f1(~ ~ ~~R~ )m
H H
Widdowson, et al., WO 96/25157, teaches phenyl urea and thiourea
compounds of the below formula for treating diseases mediated by the
chemokine,
interleukin-8.
Morin, Jr., et al., U.S. Patent No. 5,593,993 teaches certain phenyl thiourea
compounds for treatment of AIDs and the inhibition of the replication of HIV
and
related viruses.
Therefore, it is an object of this invention to provide compounds, and
pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, to inhibit and/or treat diseases
associated
with herpes viruses including human cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex viruses,
Epstein-Barr virus, varicella-zoster virus, human herpesviruses-6 and -7, and
Kaposi
herpesvirus.
Description of the Invention
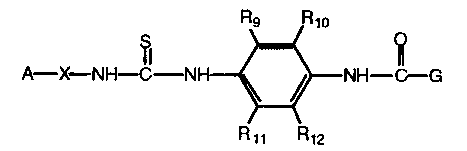
In accordance with the present invention are provided compounds having the
formula:
Rs Rio
S O
A-~.-NH~-NH ~ NH-~G
R»
I
wherein
A is heteroaryl;
Rq-R,Zare independently hydrogen, alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, perhaloalkyl
of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, halogen, alkoxy of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or
cyano, or R9 and R,o or R" and R,Z may be taken together to form aryl
of 5 to 7 carbon atoms;
W is O, NR6, or is absent;
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-5-
G is aryl or heteroaryl;
X is a bond, -NH, alkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, alkenyl of 1 to 6 carbon
atoms, aIkoxy of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, thioalkyl of 1 to 6 carbon
atoms, alkylamino of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, or (CH)J; and
J is alkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, cycloalkyl of 3 to 7 carbon atoms, phenyl
or
benzyl; and
n is an integer from 1 to 6;
or a pharmaceutical salt thereof.
In some preferred embodiments of the present invention A is a 5 or 10
membered mono or bicyclic heteroaryl having 1 or 2 heteroatoms. More
preferably,
A is pyridyl, furyl, imidazolyl, pyrrolyl, thienyl, or indanyl. Still more
preferably, A
is 3-pyridyl.
In some preferred embodiments of the present invention A is substituted with
one or more substitutents selected from alkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, alkenyl
of 2 to b
carbon atoms, alkynyl of 2 to 6 carbon atoms, perhaloalkyl of 1 to 6 carbon
atoms,
cycloalkyl of 3 to 10 carbon atoms, heterocycloalkyl of 3 to 10 carbon
members,
aryl, heteroaryl, halogen, -CN, -NO2, -COZR6, -CORE, -OR6, -SR6, -SORE, -
SOZR6,
-CONR,RB, -NR6N(R,RB), -N(R?Rg) or W-Y-(CHZ)n-Z wherein R6 and R, are
independently hydrogen, alkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, perhaloalkyl of 1 to 6
carbon
atoms, or aryl; RB is hydrogen, alkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, perhaloalkyl of
1 to 6
carbon atoms, cycloalkyl of 3 to 10 carbon atoms, heterocycloalkyl of 3 to 10
members, aryl or heteroaryl, or
R, and R8, taken together may form a 3 to 7 membered heterocycloalkyl;
W is O, NR6, or is absent;
Y is -(CO)- or -(C02)-, or is absent;
Z is alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, -CN, -COZR6, CORE, -CONR,RB, -OCOR6,
-NR6COR,, -OCONR6, -OR6, -SR6, -SORE, -S02R6, SR6N(R,RB), -N(R,RB) or phenyl;
and n is 1 to 6.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-6-
In still more preferred embodiments A is substituted with one or more
substitutents selected from halogen or alkyl of 1-6 carbon atoms.
In some embodiments of the present invention, at least 1 of R9-R,2 is not
S hydrogen. Preferably when one of R9 R~~ is not hydrogen, one or more of R9-
R,2 are
selected from halogen, methyl, methoxy, and cyano. More preferably each of R9-
R,z
is hydrogen.
G is preferably a 5 or 6 membered heteroaryl having 1 or 2 heteroatoms.
More preferably, G is furyl or thiadiazole and in still more preferred
embodiments, G
is 1,2,3 thiadiazolyl or 2-furyl. Alternatively, G may be alkyl of 1 to 6
carbon atoms
which optionally may be substituted, preferably by a halogen.
X is preferably a bond or straight chain lower alkyl group. When X is a lower
alkyl group it is preferred that X is methyl or ethyl.
Preferred compounds of the present invention are the following compounds
which include pharmaceutical salts thereof.
Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-2-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide;
Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-4-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide;
Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-3-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide;
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(6-chloro-pyridin-3-yl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide;
Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyrimidin-4-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide;
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-pyridin-3-yl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide;
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-bromo-pyridin-3-yl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide;
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1-tert-butyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide;
Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1-tert-butyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide;
[ 1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid { 4-[3-(5-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-3-yl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide;
Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-3-ylmethyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide;
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-3-ylmethyl-thioureido)-
phenyl]-
amide;
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-(3-indan-1-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-
amide;
Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-4-ylmethyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide;
[ 1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-4-ylmethyl-thioureido)-
phenyl]-
amide;
2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-pyridin-3-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide;
2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-pyridin-2-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide;
2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-pyridin-4-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide;
2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-pyridin-3-ylmethyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide;
2-Fluoro-N-{ 4-(3-( 1 H-indazol-5-yl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-benzamide;
N-{ 4-[3-( 1-tert-Butyl-1 H-imidazol-2-yl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-2-fluoro-
benzamide;
2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-pyridin-4-ylmethyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide;
2-Fluoro-N- { 4-[3-( 1-furan-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-benzamide;
2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-pyridin-4-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide;
2-Fluoro-N-(4- { 3-[ 1-( 1-methyl-1 H-pyrrol-2-yl)-ethyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-
benzamide; and
2-Fluoro-N-{ 4-[3-( 1-thiophen-3-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-benzamide.
Alkyl as used herein refers to straight or branched chain lower alkyl of 1 to
6
carbon atoms. Exemplary alkyl groups include methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl,
butyl, isobutyl, t-butyl, pentyl and hexyl.
Alkenyl as used herein refers to straight or branched chain lower alkyl of 2
to
6 carbon atoms containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenyl
includes
vinyl groups.
Alkynyl as used herein refers to straight or branched chain lower alkyl of 2
to
6 carbon atoms containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond.
Alkyl, alkenyl and alkynyl groups of the present invention may be substituted
or unsubstituted.
Cycloalkyl refers to a saturated mono or bicyclic ring system of 3 to 10
carbon atoms. Exemplary cycloalkyl groups include cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl and
cycloheptyl. Cycloalkyl groups of the present invention may be substituted or
unsubstituted.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99128838
_g_
Heterocycloalkyl refers to a saturated mono or bicyclic ring system of 3 to 10
members having 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, S and O, including, but not
limited to aziridinyl, azetidinyl, imidazolidinyl, morpholinyl,
thiomorpholinyl,
piperazinyl, pyrazolidinyl, piperidinyl, and pyrrolidinyl. HeterocycloalkyI
groups of
the present invention may be substituted or unsubstituted.
Aryl, as used herein refers to an aromatic mono or bicyclic ring of 5 to 10
carbon atoms. Exemplary aryl groups include phenyl, naphthyl, and biphenyl.
Aryl
groups of the present invention may be substituted or unsubstituted.
Heteroaryl as used herein refers to an aromatic mono or bicyclic ring of 5 to
10 members having 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, S or O including, but
not
limited to thiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, oxazolyl, furyl, indolyl, benzothiazolyl,
benzotriazolyl, benzodioxyl, indazolyl, and benzofuryl. Preferred heteroaryls
include
quinolyl, isoquinolyl, napthalenyl, benzofuranyl, benzothienyl, indolyl,
pyridyl,
pyrazinyl, thienyl, furyl, pyrrolyl, isoxazolyl, oxazolyl, isothiazolyl,
thiazolyl,
pyrazolyl, triazolyl, thiadiazolyl, and imidazolyl. Heteroaryl groups of the
present
invention may be substituted or unsubstituted.
Perhaloalkyl refers to an alkyl group of 1 to 6 carbon atoms in which three or
more hydrogens are substituted with halogen.
Phenyl as used herein refers to a 6 membered aromatic ring.
Halogen, as used herein refers to chlorine, bromine, iodine and fluorine.
Unless otherwise limited substitutents are unsubstituted and may include alkyl
of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, cycloalkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, heterocycloalkyl of
1 to 6
members, perhaloalkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, alkylamino, dialkylamino, aryl
or
heteroaryl.
Carbon number refers to the number of carbons in the carbon backbone and
does not include carbon atoms occurring in substituents such as an alkyl or
alkoxy
substituents.
Where terms are used in combination, the definition for each individual part
of
the combination applies unless defined otherwise. For instance,
alkylcycloalkyl is an
alkyl-cycloalkyl group in which alkyl and cycloalkyl are as previously
described.
Pharmaceutically acceptable salts are the acid addition salts which can be
formed from a compound of the above general formula and a pharmaceutically
acceptable acid such as phosphoric, sulfuric, hydrochloric, hydrobromic,
citric, malefic,
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-9-
succinic, fumaric, acetic, lactic, nitric, sulfonic, p-toluene sulfonic,
methane sulfonic
acid, and the like.
The compounds of this invention contain a chiral center, providing for various
seteroisomeric forms of the compounds such as racemic mixtures as well as the
individual optical isomers. In some preferred embodiments of the present
invention the
compounds of the present invention are substantially pure optical isomers. By
substantially pure is meant the composition contains greater than 75% of the
desired
isomer and may include no more than 25% of the undesired isomer. In more
preferred
embodiments the pure optical isomer is greater than 90% of the desired isomer.
In
some preferred emodiments, when the target is VZV, the (S) isomer is
preferred. The
individual isomers can be prepared directly or by asymmetric or stereospecific
synthesis or by conventional separation of optical isomers from the racemic
mixture.
Compounds of the present invention may be prepared by those skilled in the art
of organic synthesis employing methods described below which utilize readily
available reagents and starting materials unless otherwise described.
Compounds of the
present invention are thus prepared in accordance with the following schemes.
The novel compounds of the present invention are prepared according to the
following reaction schemes.
Referring to Methods 31 and 34, reacting appropriately substituted amines 2,
wherein the substitutents of A, and X are described as above, with
appropriately
substituted isothiocyanates 3, wherein the substituents Rg-R,2 and G are
described
above, either neat or in an appropriate solvent such as tetrahydrofuran,
acetonitrile,
ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, or N,N-dimethylformamide affords the desired
thioureas 1. Similarly, reaction of appropriately substituted isothiocyanates
4,
wherein the substitutents of A, and X are described as above with
appropriately
substituted anilines 5, wherein the substituents Itg-R,2 and G are described
above, in a
convenient solvent such as those listed above affords the desired thioureas 1.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 10-
Methods 31 and 34
R ~o
_ O
A~NH2 + S=C! ~ ~ ~ G
m ~n2
2 3
R ~o
A-~-H ~-H ~G
» R~2
1
Rs ~o
O
A-X-f~C~S + Fi
2
RW~2
4 5
Alternatively, appropriately substituted thioureas 1 can be prepared as
described by Methods 32 and 33 by reacting amines 2 and 5 in the presence of
either
one molar equivalent of 1,1'-thiocarbonyl diimidazole in an appropriate
solvent such
as dichloro-methane and tetrahydrofuran or mixtures thereof or one molar
equivalent
of 1,1'-thiocarbonyl-di-(1,2,4)-triazole in an appropriate solvent such as
dichloromethane and tetrahydrofuran or mixtures thereof at room temperature.
In certain instances, subsequent chemical modification of the final thioureas
1
was required. These methods, Methods 35-39, are summarized below.
Thioureas 1 wherein A comprises at least one substituent which is 1-
hydroxyethoxy or carboxy-methoxy, R9 R,2 and G are defined as above and X
equals
a bond, may be prepared from the corresponding alkyl esters by alkaline
hydrolysis
with aqueous sodium or potassium hydroxide in a suitable solvent such as
methanol,
tetrahydrofuran or mixtures thereof at room temperature in accordance with
Methods
35 and 36.
Thioureas 1 wherein A comprisese at least one substituent which is 1-
acyloxyethoxy or methansulfonoxyethoxy, R9-R,2 and G are defined as above and
X
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-11-
equals a bond, may be prepared from the corresponding 1-hydroxyethoxy
derivative
by acylation with appropriate acylating agents such as benzoic acid chloride
or
methanesulfonic acid chloride in the presence of a suitable tertiary amine
base such
as triethylamine or diisopropylethylamine in a suitable solvent such as
dichloromethane or the like at room temperature in accordance with Methods 37
and
38.
Thioureas 1 wherein A comprises at least one substituent which is 1-amino-
ethoxy, R9 R,Zand G are defined as above and X equals a bond, may be prepared
from the corresponding 1-methanesulfonoxy-ethoxy derivative by reaction with
an
appropriate secondary amine such as dimethylamine in a suitable solvent
mixture
such as tetrahydrofuran and water or the like at room temperature in
accordance with
Method 39.
Thioureas 1 wherein A comprises at least one substituent which is 1-amino-
alkyl, R9-R,2 and G are defined as above and X equals a bond, may be prepared
from
the corresponding 1-azidoalkyl derivative by reaction with stannous chloride
in a
suitable solvent such as methanol, ethanol or the like at room temperature in
accordance with Method 40.
The intermediate isothiocyanates 3 and 4 shown above in Methods 31 and 34
are prepared in accordance with Method 41 (below) essentially according to the
procedures of Staab, H.A. and Walther, G. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 657, 104
(1962)) by reacting appropriately substituted amines 5 or 2, respectively, X
is defined
above with one molar equivalent of 1,1'-thiocarbonyldiimidazole in an
appropriate
solvent such as dichloromethane and tetrahydrofuran or mixtures thereof.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 12-
Method 41
N
~N 2
H2N \ / -C-G -""~' S=C=N -C-G
\/
3
R4 5 R4 5
2
R3 \ ~ X-NH2 ~ Rs \ ~ X-N=C=S
v
R2 R~ R2 Ri
2 4
The intermediates 2 and 5 may be prepared according to the following
5 protocols:
According to Methods lA-1G, amines 2, wherein A is defined above and X is
defined above and amines 5, wherein R9-R,Z are defined above, may be prepared
by
reduction of the appropriately substituted nitrobenzenes and corresponding
heteroaryls according to a variety of procedures known to those skilled in the
art and
described in R. J. Lindsay, Comprehensive Organic Chemistry (ed. Sutherland),
Volume 2, Chapter 6.3.1, Aromatic Amines, 1979. Such procedures include the
reduction of nitrobenzenes to form anilines upon exposure to:
a) iron powder and a strong acid, such as hydrochloric acid {Methods lA)
either neat
or in alcohol solvent such as methanol or ethanol, at temperatures ranging
from
room temperature to the refluxing temperature of the solvent, or;
b) iron powder and glacial acetic acid (Method 1B), either neat or in alcohol
solvent
such as methanol or ethanol, at temperatures ranging from room temperature to
the
refluxing temperature of the solvent, or;
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-13-
c) iron powder and aqueous ammonium chloride (Method 1 C), either neat or in
alcohol solvent such as methanol or ethanol, at temperatures ranging from room
temperature to the refluxing temperature of the solvent, or;
d) tin and a strong mineral acid, such as hydrochloric acid (Method 1D),
either neat
or in alcohol solvent such as methanol or ethanol, at temperatures ranging
from
room temperature to the refluxing temperature of the solvent, or;
e) when substitutents of A and Rq-R,2 are selected from Cl, Br, I, -(OSOZ)-
CF,, or -
(OSOZ)-1-(4-methylphenyl), by catalytic reduction such as with hydrogen and
palladium on carbon (Method lE) in an appropriate solvent such as methanol,
ethanol, or ethyl acetate, under one or more atmospheres of pressure or;
f) when substituents of A and R9-R~2 are selected from Cl, Br, I, -(OSOZ)-CF3,
or
(OSOZ)-1-(4-methylphenyl), by catalytic reduction such as with cyclohexene and
palladium on carbon (Method 1F) in an appropriate solvent such as methanol or
ethanol, at temperatures ranging from room temperature to the refluxing
temperature of the solvent, or;
g) aqueous sodium hydrosulfite in alcohol solvent at temperatures ranging from
room
temperature to the refluxing temperature of the solvent (Method 1G).
Alternatively, according to Methods 3A-3C, amines 2, wherein A is defined
above and X is defined above and anilines 5, wherein R9-R,2 are defined above,
may
be prepared by the cleavage of the aniline nitrogen-carbon bond of amide and
carbamate derivatives of these anilines according to a variety of procedures
known to
those skilled in the art and described in Greene, Protective Groups in Or ag-
nic.
Synthesis volume 2, Chapter 7, 1991, and references therein. Such procedures
include:
a) the exposure of appropriately substituted arylamino-tert-butyl-carbamates
to a
strong acid such as trifluoroacetic acid (Method 3A)either neat or in an
appropriate
solvent such as dichloromethane at temperatures between 0°C and room
temperature, or;
b) the exposure of appropriately substituted arylamino-(2-trimethylsilylethyl)-
carbamates to a fluoride ion source such as tetrabutylammonium fluoride or
potassium fluoride (Method 3B) in aqueous acetonitrile or tetrahydrofuran or
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 14-
mixtures thereof at temperatures ranging from room temperature to the reflux
temperature of the solvent, or;
c) the exposure of appropriately substituted arylamino-trifluoroacetamides to
a strong
base such as sodium or potassium hydroxide or sodium or potassium carbonate in
an alcohol solvent such as methanol or ethanol (Method 3C) at temperatures
ranging from room temperature to the reflux temperature of the solvent.
Alternatively, according to Method 11, amines 2, wherein A is defined above,
and X equals a bond and at least one substituent of A is vinyl, may be
prepared by the
palladium catalyzed coupling of a vinyl trialkyltin reagent, such as
tributyIvinyltin,
with an appropriately substituted bromo- or iodo-aniline, for example 3-chloro-
4-
iodo-aniline, employing a palladium catalyst, such as
tris(dibenzylidineacetone)-
bipalladium, and a ligand, such as triphenylarsine, in a suitable solvent such
as
tetrahydrofuran or N-methylpyrrolidinone, at temperatures ranging from room
temperature to the reflux temperature of the solvent, essentially according to
the
procedures of V. Farina and G.P. Roth in Advances in Metal-Organic Chemistry,
Vol. S, 1-53, 1996 and references therein.
Alternatively, according to Method 42, amines 2, wherein A is defined above
and X is defined above and at least one substituent of A is defined as
dialkylamino,
may be prepared by the palladium catalyzed amination of an appropriately
substituted
3- or 5-bromo- or iodo-aniline, by secondary amines under conditions which
employ
a palladium catalyst, such as bis(dibenzylidineacetone)palladium, and a
ligand, such
as tri-o-tolylphosphine, and at least two molar equivalents of a strong base,
such as
lithium bis-(trimethyIsilyl)amide in a sealed tube, in a suitable solvent such
as
tetrahydrofuran or toluene, at temperatures ranging from room temperature to
100°C,
essentially according to the procedures of J.F. Hartwig and J. Louie
Tetrahedron
Letters 36 (21 ), 3609 ( 1995).
Alternatively, according to Method 43, amines 2, wherein A is defined above
and X is defined above and at least one substituent of A is defined as alkyl,
may be
prepared by the palladium catalyzed alkylation of an appropriately substituted
3- or
5-bromo-or iodo-aniline, by alkenes under condiditons which employ a palladium
catalyst such as [1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene]palladium(II) chloride-
dichloromethane complex and in the presence of 9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane and
a
suitable base such as aqueous sodium hydroxide in a suitable solvent such as
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PC'T/US99/28838
-15-
tetrahydrofuran or the like at temperatures ranging from room temperature to
the
reflux temperature of the solvent.
The acyl and carbamoyl amine derivatives utilized as starting materials in
Methods 3A-3C may be prepared by the derivatization of the corresponding
amines
S as described in Methods 2A-2G according to a variety of procedures known to
those
skilled in the art and described in Greene, Protective Groups in Organic
Synthesis
volume 2, Chapter 7, 1991, and references therein. Such procedures include:
a) the reaction of an appropriately substituted amine with di-tert-butyl-
dicarbonate
(Method 2A) in the presence or absence of one or more molar equivalents of a
tertiary amine such as triethylamine or N,N-diisopropylethylamine in a
suitable
solvent such as acetone, tetrahydrofuran, dimethylformamide, dichloromethane,
and the like, at temperatures ranging from room temperature to the reflux
temperature of the solvent to produce the corresponding arylamino-tert-butyl-
carbamate, or;
b) the reaction of an appropriately substituted aniline with 1-[2-
(trimethylsilyl)ethoxycarbonyl-oxy]benzotriazole (Method 2B} in the presence
of
a tertiary amine such as triethylamine or diisopropylethylamine in a suitable
solvent such as dimethylformamide at room temperature to produce the
corresponding heteroarylamino-(2-trimethylsilylethyl)-carbamate, or;
c} the reaction of an appropriately substituted aniline with a carboxylic acid
chloride or acid anhydride (Method 2C) either neat or in an appropriate
solvent
such as tetrahydrofuran, dimethylformamide, dichloromethane, pyridine and the
like, in the presence of one or more molar equivalents of a teriary amine base
such as triethylamine or N,N-diisopropylethyl-amine to produce the
corresponding arylaminoamide, or;
d) the reaction of an apptopriately substituted nitro aniline with a
carboxylic acid
chloride (Method 2D) in the absence of one or more molar equivalents of a
teriary amine base such as triethylamine or N,N-diisopropylethylamine either
neat
or in an appropriate solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-dioxane and the like
at
temperatures ranging from room temperature to the reflux temperature of the
solvent to produce the corresponding nitro arylaminoamide, or;
e) the reaction of an appropriately substituted aniline with a carboxylic acid
(Method
2E) in the presence of a coupling agent such as benzotriazole-1-yloxy-tris-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 16-
(dimethylamino)-phosphonium hexafluorophosphate, 2-(1H-benzotriazole-1-
yloxy)-1,1,3,3-tetra-methyluronium hexafluorophosphate, dicyclohexyl
carbodiimide and the like and in the presence of a tertiary amine such as
triethylamine or diisopropylethylamine in a suitable solvent such as
diichloromethane, dimethylformamide and the like, at room temperature to
produce the corresponding arylaminoamide, or;
f) the reaction of an appropriately protected aniline such as an
heteroarylamino-tert-
butyl-carbamate or the like in which at least one substituent of A and Rq-R,2
is
defined as -W-Y-(CHZ)~ Z wherein W, Y, and Z are defined as above, with a
carboxylic acid anhydride (Method 2F) in the presence of a suitable base such
as
pyridine in an appropriate such as dichloromethane, dimethylformamide or the
like at temperatures ranging from 0°C to room temperature to produce
the
corresponding carboxylic acid ester, or;
g) the reaction of an appropriately substituted aniline in which at least one
substituent of A is defined as hydroxyl with di-tert-butyl-dicarbonate (Method
2G) in the absence of one or more molar equivalents of a tertiary amine such
as
triethylamine or N,N-diisopropylethylamine in a suitable solvent such as
acetone,
tetrahydrofuran, dimethylformamide, dichloromethane, and the like, at
temperatures ranging from room temperature to the reflux temperature of the
solvent to produce the corresponding heteroarylamino-tert-butyl-carbamate.
Nitrobenzene intermediates that are ultimately converted to amines 2 and 5 by
methods shown above in Methods lA-1G may be prepared in accordance with
Methods 4A, 4C, 4E-4F.
Referring to Methods 4A, 4C, and 4E-4H, the nitrobenzene intermediates
which are ultimately converted into amines 2, where A comprises substituent
defined
as alkoxy, thioalkoxy, alkylsulfenyl, alkylsulfinyl, and dialkylamino may be
prepared
by the nucleophilic displacement of appropriately substituted 2-, 4-, and/or 6-
fluoro-,
chloro-, bromo-, iodo-, trifluoromethylsulfonyl-, or (4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl-
substituted nitrobenzenes or corresponding heteroaryls by methods which
include the
following:
a) reaction of alcohols with appropriately substituted 2- or 4- halo- or
sulfonate
esters of nitrobenzenes, benzonitriles or corresponding heteroaryls (Method
4A)
either neat or in an appropriate solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, dioxane,
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-17-
acetonitrile, N,N-dimethylformamide or dimethylsulfoxide in the presence or
absence of one or more molar equivalents of a base such as sodium carbonate,
potassium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, sodium hydride,
potassium hydride, or the like, at temperatures ranging from room temperature
to
the reflux temperature of the solvent;
b) reactions of preformed sodium, lithium, or potassium phenoxides with
appropriately substituted 2- or 4- halo- or sulfonate esters of nitrobenzenes,
benzonitriles or corresponding heteroaryls (Method 41-1) either neat or in an
appropriate solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, acetonitrile, N,N-
dimethylformamide or dimethylsulfoxide, at temperatures ranging from room
temperature to the reflux temperature of the solvent, or;
c) reaction of ammonia, primary or secondary amines with appropriately
substituted
2- or 4-halo- or sulfonate esters of nitrobenzenes, benzonitriles or
corresponding
heteroaryls (Methods 4C,F) either neat or in an appropriate solvent such as
tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, acetonitrile, N,N-dimethyl-formamide or
dimethylsulfoxide, at temperatures ranging from room temperature to the reflux
temperature of the solvent;
d) reaction of preformed sodium, lithium, or potassium salts of amines with
appropriately substituted 2- or 4- halo- or sulfonate esters of nitrobenzenes
or
benzonitriles (Method 4G) in an appropriate solvent such as tetrahydrofuran at
temperatures ranging from 0°C to the reflux temperature of the solvent,
or;
e) reaction of sodium sulfide with appropriately substituted 2- or 4- halo- or
sulfonate esters of nitrobenzenes or benzonitriles either neat or in an
appropriate
solvent such as tetrahydro-furan, dioxane, acetonitrile, N,N-dimethylformamide
or dimethylsulfoxide, at temperatures ranging from room temperature to the
reflux temperature of the solvent, followed by the addition of an alkyl halide
directly to the reaction mixture (Method 4E).
Alternatively, referring to Methods SC and 6, the nitrobenzene intermediates
and corresponding heteroaryls which are ultimately converted into amines 2,
wherein
at least one substitutent of A is defined as alkoxy may be prepared from the
corresponding substituted hydroxy-nitrobenzenes and corresponding heteroaryls
by
methods which include the following:
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 18-
a) reaction of the hydroxy-nitrobenzene with an alkyl halide or dialkyl
sulfonate ester
(Method SC) in the presence of a base, such as potassium carbonate, sodium
carbonate, potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydride, or sodium
hydride, in an appropriate solvent such as acetone, N,N-dimethylformamide,
tetrahydrofuran or dimethylsulfoxide at temperatures ranging from room
temperature to the reflux temperature of the solvent, or;
b) reaction of the hydroxy-nitrobenzene or corresponding heteroaryl with an
alkyl
alcohol, triphenylphosphine, and a dialkylazadicarboxylate reagent (Method 6),
such as diethylazodicarboxylate, in an anhydrous aprotic solvent such as
diethyl
ether or tetrahydrofuran at temperatures ranging from 0°C to the reflux
temperature of the solvent, essentially according to methods described in
Mitsunobu, O, Synthesis 1981, 1 and references therein.
In addition, referring to Method SA and SE, the carbamoyl amine derivatives
utilized as starting materials in Methods 3A-3C which are ultimately converted
into
amines 2, wherein at least one substituent of A is defined as alkoxy may be
prepared
the corresponding substituted hydroxy aryl- or heteroarylamino-tert-butyl-
carbamate
by reaction with alkyl halides, trifluormethane-sulfonates, 4-
methylbenzenesulfonates, dialkylsulfonate, ethylene carbonate and the like in
the
presence of a suitable base such as potassium carbonate in an appropriate
solvent
such as acetone, toluene, or N,N-dimethyl-formamide at temperatures ranging
from
room temperature to the reflux temperature of the solvent.
Alternatively, referring to Methods 7A-G, the nitrobenzene and corresponding
heteroaryls which are ultimately converted into amines 2, comprising at least
one
alkoxy at least one halogen, and X equals a bond, may be prepared by standard
halogenation reactions which include the following:
a) reaction of a 2- or 4- hydroxy-nitrobenzene or corresponding heteroaryl
with
aqueous sodium hypochlorite (Methods 7A and 7B), at room temperature or;
b) reaction of a 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy or 2,4-dimethoxynitrobenzene or
corresponding heteroaryl (Method 7C and 7D) with bromine in suitable solvent
such as chloroform, dichlormethane, glacial acetic acid or the like in the
presence
or the absence of silver trifluoroacetate at room temperature, or;
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/342b8 PCT/US99/28838
- 19-
c) reaction of a 2,4-dimethoxynitrobenzene or corresponding heteroaryl (Method
7E}
with benzyltrimethylammonium dichloroiodate in the presence of anhydrous zinc
chloride in a suitable solvent such as glacial acetic acid, at room
temperature or;
d) reaction of a 2-hydroxy-4-methoxynitrobenzene or corresponding heteroaryl
S (Method 7F} with benzyltrimethyl-ammonium dichloroiodate in the presence of
sodium bicarbonate in a suitable solvent mixture such as dichloromethane and
methanol, at room temperature or;
e) reaction of a 2,4-dimethoxynitrobenzene or corresponding heteroaryl (Method
7G)
with 3,5-dichloro-1-fluoropyridine triflate in a suitable solvent such as
tetrachloroethane, at a temperature ranging from room temperature to the
reflux
temperature of the solvent.
Referring to Method 8, the nitrobenzene intermediates or corresponding
heteroaryl which are ultimately converted into amines 2, wherein A is
substituted by
CF3 and X equals a bond may be prepared from the corresponding substituted 4-
iodo-
nitrobenzenes or corresponding heteroaryl by reaction with
trimethyl(trifluoromethyl)silane in the presence of cuprous iodide and
potassium
fluoride in a suitable solvent such as N,N-dimethyl-formamide or the like at a
temperature ranging from room temperature to the reflux temperature of the
solvent
in a sealed reaction vessel.
Referring to Methods 19A and 19B, the nitrobenzene intermediates which are
ultimately converted into amines 2, wherein A comprises a substituent defined
as -
HNCOCHZNR,R$ or -HNCOCHZSR6, and X equals a bond may be prepared from the
corresponding substituted 4-(N-chloroacetyl)-nitroaniline by reaction with
either a
suitable secondary amine such as dimethylamine, morpholine or the Like in a
suitable
solvent such as tetrahydrofuran and/or water mixtures at temperatures ranging
from
room temperature to the reflux temperature of the solvent or by reaction with
an
appropriate thiol in the presence of a suitable base such as sodium or
potassium
carbonate or the like in a suitable solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-
dioxane or the
like at temperatures ranging from room temperature to the reflux temperature
of the
solvent.
Referring to Method 25, the nitrobenzene intermediates or corresponding
heteroaryl which are ultimately converted into amines 2, wherein at least one
substituent of A is defined as triflate and X equals a bond may be prepared
from the
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-20-
corresponding phenol by reaction with trifluoromethane sulfonic anhydride in
the
presence of a tertiary amines such as triethylamine or diisopropyl-ethylamine
or the
like in a suitable solvent such as dichloromethane at temperatures ranging
from 0°C
to room temperature.
Referring to Methods 9, 9B, and 10, the carbamoyl amine derivatives utilized
as starting materials in Methods 3A-3C which are ultimately converted into
amines 2,
wherein at least one substituent A is defined as either alkylsulfenyl or
alkylsulfinyl,
may be prepared by reaction of the appropriate 4-alkylthio acylarylamino or
acylheteroarylamino or carbamoylarylamino or carbamoylheteroarylamino
derivative
with an appropriate oxidizing agent such as dimethyloxirane or sodium
periodate in a
suitable solvent mixture such as acetone and dichloromethane or water at room
temperature.
Referring to Method 12, the carbamoyl amine derivatives utilized as starting
materials in Methods 3A-3C which are ultimately converted into amines 2,
wherein a
substituent of A is defined as 1-hydroxyethyl and X equals a bond may be
prepared
by reacting the corresponding 4-vinyl carbamoyl aniline with sodium
borohydride in
the presence of mercuric acetate in a suitable solvent such as
tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-
dioxane or the like and water at room temperature.
Referring to Method 13, the carbamoyl amine derivatives utilized as starting
materials in Methods 3A-3C which are ultimately converted into amines 2,
wherein a
substituent of A is defined as 2-hydroxyethyl and X equals a bond, may be
prepared
by reacting the corresponding 4-vinyl carbamoyl aniline with sodium
borohydride in
the presence of glacial acetic acid in a suitable solvent such as
tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-
dioxane or the like at temperatures ranging from 0°C to room
temperature.
Referring to Method I4, the carbamoyl amine derivatives utilized as starting
materials in Methods 3A-3C which are ultimately converted into amines 2,
wherein a
substituent of A is defined as 1-azidoethyl and and X is defined above, may be
prepared by reacting the corresponding 4-(1-hydroxyethyl) carbamoyl aniline
with
hydrazoic acid in the presence of a dialkylazodicarboxylate such as
diethylazodicarboxylate and triphenylphosphine in a suitable solvent mixture
such as
tetrahydrofuran and dichloromethane at temperatures ranging from 0°C to
room
temperature.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-21-
Referring to Method 15, the carbamoyl amine derivatives utilized as starting
materials in Methods 3A-3C which are ultimately converted into amines 2,
wherein a
substituent of A is defined as 3-dimethylaminoprop-1-ynyl and X is defined
above,
may be prepared by reacting the corresponding 4-iodocarbamoyl aniline with 1-
dimethylamino-2-propyne in a suitable tertiary amine solvent such as
triethylamine or
diisopropylethylamine in the presence of bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium{II)
chloride and cuprous iodide at temperatures ranging from room temperature to
the
reflux temperature of the solvent.
Referring to Method 16, the carbamoyl amine derivatives utilized as starting
materials in Methods 3A-3C which are ultimately converted into amines 2,
wherein a
substituent of A is defined as 3-dimethylaminoacryloyl and X equals a bond,
may be
prepared by reacting the corresponding 4-(3-dimethylaminoprop-1-ynyl)carbamoyl
aniline with a suitable peracid such as 3-chloroperoxybenzoic acid in a
suitable
solvent mixture such as dichloromethane and methanol at temperatures ranging
from
0°C to room temperature.
Referring to Methods 17 and 18, the carbamoyl amine derivatives utilized as
starting materials in Methods 3A-3C which are ultimately converted into amines
2,
wherein a substituent of A is defined as either 4-isoxazol-S-yl or 4-(1H-
pyrazol-3-yl)
and X equals a bond, may be prepared by reacting the corresponding 4-(3-
dimethylamino-acryloyl)carbamoyl aniline with either hydroxylamine
hydrochloride
or hydrazine hydrate in a suitable solvent such as 1,4-dioxane or ethanol and
the like
at room temperature.
Referring to Method 20, the carbamoyl amine derivatives utilized as starting
materials in Methods 3A-3C which are ultimately converted into amines 2,
wherein a
substituent of A is defined as -HNCOZZ, Z is defined above and X equals a
bond,
may be prepared by reacting the corresponding 4-aminocarbamoyl aniline with
1,1-
carbonyl-di-(1,2,4)-triazole and an appropriately substituted alcohol in a
suitable
solvent mixture such as tetrahydrofuran and dichloromethane and the like at
temperatures ranging from room temperature to the reflux temperature of the
solvent.
Referring to Methods 26 and 30, the carbamoyl amine derivatives utilized as
starting materials in Methods 3A-3C which are ultimately converted into amines
2,
wherein at least one substituent of A is defined as dialkylamino and X is
defined
above may be prepared by reaction of appropriately substituted aldehydes in
the
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-22-
presence of either sodium cyanoboro-hydride or hydrogen gas and 10 % palladium
on
carbon in a suitable solvent such as water, methanol, tetrahydrofuran mixtures
or
toluene or the like at room temperature.
Referring to Methods 27 and 28, amines 2 wherein at least one substituent of
A is defined as hydroxy and X is defined above can be prepared by reaction of
the
corresponding ester such as acetate with an appropriate base such as sodium
bicarbonate or sodium hydroxide in a suitable solvent mixture such as methanol-
water mixtures at temperatures ranging from room temperature to the reflux
temperature of the solvent.
Referring to Method 29, amines 2 wherein at least one substituent of A is
defined as 2-hydroxybenzamido and X is defined above can be prepared by
reaction
of the corresponding N-(4-aminophenyl)phthalimide with lithium borohydride in
an
appropriate solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, diethyl ether, or the like at
room
temperature.
The intermediate amines 2 wherein X equals either -CHZ- or -(CHZ)2- can be
prepared by the following procedures:
a) reduction of an appropriately substituted benzo- phenyl- or corresponding
heteroarylacetonitrile with borane-dimethylsulfide complex in a suitable
solvent such as ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran or the like
a temperatures ranging from room temperature to the reflux temperature
of the solvent. (Method 44);
b) reduction under one or more atmospheres of hydrogen in the presence of a
suitable catalyst such as 5 % or 10 % palladium on carbon and an acid
such as 4-methyl-benzenesulfonic acid, hydrochloric acid or the like in a
suitable solvent such as ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, ethyl acetate,
ethanol or the like at room temperature. (Method 50);
c) reduction with lithium aluminum hydride in a suitable solvent such as
tetrahydrofuran or diethyl ether at temperatures ranging from 0°C to
room
temperature. (Method S 1 };
The unsaturated vitro precursors which are utilized as starting materials in
Method 51 and are ultimately converted to amines 2 wherein X equals -(CHZ)2-
can
be prepared by reaction of an appropriately substituted benzaldehyde or
corresponding heteroaryl with vitro-methane in the presence of ammonium
acetate in
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-23-
a suitable solvent such as acetic acid at temperatures ranging from room
temperature
to the reflux temperature of the solvent.(Method 53); The benzaldehydes or
corresponding heteroaryls, utilized as starting materials in Method 53, can be
prepared by diisobutylaluminum hydride reduction of an appropriately
substituted
benzonitrile or corresponding heteroaryl. (Method 52) The substituted
benzonitriles
or corresponding heteroaryls, utilized as starting materials in Method 52, can
be
prepared from the corresponding aryl or heteroaryl bromide by reaction with
copper
cyanide in a suitable solvent such as N,N-dimethylformamide at temperatures
ranging
from room temperatture to the reflux temperature of the solvent. (Method 59)
For amines 2, wherein X equals either -O(CHZ)zNH2 or -S(CH2)ZNH~, the
requisite nitrite precursors may be prepared by reaction of an appropriately
substituted phenol, thiophenol or corresponding heteroaryl with
bromoacetonitrile in
the presence of a suitable base such as potassium carbonate in an appropriate
solvent
such as acetone at room temperature according to Method 49.
Alternatively, for amines 2, wherein X equals -(CHZ),-, the nitrite precursors
can be prepared essentially according to the procedure of Wilk, B. Synthetic
Comm.
23, 2481 (1993), by reaction of an appropriately substituted phenethanol or
corresponding heteroaryl with acetone cyanohydrin and triphenylphosphine in
the
presence of a suitable azodicarboxylate such as diethyl azodicarboxylate in an
appropriate solvent such as diethyl ether or tetrahydro-furan or the like at
temperatures ranging from 0°C to room temperature. (Method 54)
Alternatively, intermediate amines 2 wherein X equals -(CH(CH3))- can be
prepared by acid or base catalyzed hydrolysis of the corresponding formamide
using
an appropriate acid catalyst such as 6N hydrochloric acid or a suitable base
catalyst
such as SN sodium or potassium hydroxide in an appropriate solvent mixture
such as
water and methanol or water and ethanol at temperatures ranging from room
temperature to the reflux temperature of the solvent. (Method 46)
The formamide precursors utilized as starting materials in Method 46 and
which are ultimately converted into amines 2, are prepared according to Method
45
by treatment of an appropriately substituted acetophenone with ammonium
formate,
formic acid and formamide at temperatures ranging from room temperature to the
reflux temperature of the solvent.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 24 -
Alternatively, amines 2 wherein X equals -(CH(CH3))- can be prepared by
reduction of an appropriately substituted O-methyl oxime in the presence of
sodium
borohydride and zirconium tetrachloride in a suitable solvent such as
tetrahydrofuran
or diethyl ether at room temperature Method 48 essentially according to the
procedure of Itsuno, S., Sakurai, Y., Ito, K. Synthesis 1988, 995. The
requisite O-
methyl oximes can be prepared from the corresponding acetophenone by reaction
with methoxylamine hydrochloride and pyridine in a suitable solvent such as
ethanol
or methanol at temperatures ranging from room temperature to the reflux
temperature
of the solvent. (Method 47)
Amines 2 for which X equals -CH(J)- where J is defined as above, can be
prepared by reduction of the appropriately substituted ketone by the methods
described above (Methods 45, 47, and 48). These requisite ketones, when not
commercially available, can be prepared by reaction of a suitably substituted
benzaldehyde with an appropriate organometallic reagent such as phenyllithium,
isopropylmagnesium bromide or ethylmagnesium bromide or the like in a suitable
solvent such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran at temperatures ranging from -
78 °C
to 0°C. (Method 57) The resulting alcohols can be oxidized to the
corresponding
ketone with an appropriate oxidizing agent such as chromium trioxide in
aqueous
sulfuric acid and acetone or pyridinium chlorochromate or pyridium dichromate
in an
appropriate solvent such as dichloromethane or the like at room temperature.
(Method 58)
The intermediate anilines 5 may be prepared as previously described Method
3A. Thus treating phenyl carbamic acid tent-butyl ester 6, wherein G is
described as
above, with neat trifluoroacetic acid at room temperature followed by
neutralization
with aqueous sodium hydroxide affords the desired anilines 5. The requisite
carbamic
acid esters 6, wherein Rg-R,2 and G are described as above, are prepared as
shown in
Method 2C by reaction of substituted acid chlorides, 8, where G is described
as
above, and 4-aminophenylcarbamic acid tert-butyl esters 7, wherein Rq-R,2 are
described above, in the presence of triethylamine in an appropriate solvent
such as
dichloromethane, dimethylsulfoxide, or dimethylformamide or mixturestthereof.
Carboxylic acid chlorides 8 are either commercially available or prepared from
the
corresponding carboxylic acid by reaction with oxalyl chloride in a suitable
solvent
such as dichloromethane at room temperature.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-25-
Method 2C, 3A
O ~ O
G-COOH ~O~ O O i. CF3C02H O
HN \ / NH2i HN ~ / N'C'G '_'i H2N ~ ~ N-C~_G
ii. NaOH
H
6
S
Alternatively, carbamic acid esters 6, wherein R9-R,2 and G are described as
above, are prepared as shown in Method 2E by reaction of substituted
carboxylic
acids 8a, wherein G is described as above, and an appropriately substituted 4-
aminophenyl carbamic acid tert-butyl esters 7 in the presence of a suitable
coupling
agent such as benzotriazole-1-yloxy-tris-(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluoro-
phosphate, 2-(1H-benzotriazole-1-yloxy)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluoro-
phosphage, dicyclo-hexyl carbodiimide or the like and in the presence of a
tertiary
amine base such as triethylamine or diisopropylethylamine in a suitable
solvent such
as dichloromethane, dimethylformamide and the like, at room temperature to
produce
the corresponding arylaminoamide.
Carboxylic acids 8a are either commercially available or are prepared
according to literature methods. For example, when G is a substituted
thiadiazole,
the acid is available from the corresponding carboxylic acid ester by reaction
with an
appropriate base such as sodium or potassium hydroxide in a suitable solvent
mixture
such as methanol or ethanol and water at room temperature.
Similarly, when G is either substituted or unsubstituted thiazole, substituted
or
unsubstituted oxazole, substituted or unsubstituted isothiazole or substituted
or
unsubstituted isoxazole, when not commercially available, the corresponding
carboxylic acid 8a is available from the corresponding ethyl or methyl ester
by
reaction with an appropriate base such as sodium or potassium hydroxide in a
suitable
solvent mixture such as methanol or ethanol and water at room temperature.
These
esters are either commercially available or can be prepared according to
literature
methods.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-26-
When the carboxylic acid ester precursors which are ultimately converted to
acids 8a are not commmercially available, they may be prepared by methods
known
in the literature. For example, 5-substituted-1,2,3-thiadiazole-4 carboxylic
acid esters
may be prepared essentially according to the procedure of Caron, M J. Org.
Chem.
51, 4075 (1986) and Taber, D. F., Ruckle, R. E. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 108, 7686
(1986). Thus, according to Method 21, treatment of a beta-keto carboxylic acid
ester
with 4-methylbenzenesulfonyl azide or methanesulfonyl azide or the like in the
presence of a tertiary amine base such triethylamine or diisopropylethylamine
in a
suitable solvent such as acetonitrile affords the corresponding diazo-beta-
keto
carboxylic acid ester. Treatment of this compound with 2,4-bis(4-
methoxyphenyl)-
1,3-dithia-2,4-diphosphetane-2,4-disulfide in a suitable solvent such as
benzene or
toluene or the like at temperatures ranging from room temperature to the
reflux
temperature of the solvent gives the desired 5-substituted-1,2,3-thiadiazole-4-
carboxylic acid ester.
Alternatively, 4-substituted-1,2,3-thiadiazole -5-carboxylic acid esters may
be
prepared essentially according to the procedure of Shafiee, A., Lalezari, L,
Yazdani,
S., Shahbazian, F. M., Partovi, T. J. Pharmaceutical Sci. 65, 304 (1976).
Thus,
according to Method 22 and 23, reaction of an appropriately substituted beta-
keto
carboxylic acid ester in a suitable alcoholic solvent such as methanol or
ethanol with
an aqueous solution semicarbazide hydrochloride at temperatures ranging from
room
temperature to the reflux temperature of the solvent in the presence of a
suitable base
such as pyridine gives corresponding semicarbazone derivative. Treatment of
this
compound with neat thionyl chloride at 0°C followed by treatment with
an excess
aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate affords the corresponding 4-substituted-
1,2,3-thiadiazole -5-carboxylic acid esters.
4-carboalkoxythiazoles are prepared essentially according to the procedure of
Schollkopf, U., Porsch, P., Lau, H. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1444 (1979). Thus,
according to Method 55 and 56, reaction of ethyl isocyanoacetate with N,N-
dimethylformamide dimethyl acetal in a suitable alcoholic solvent such as
ethanol at
room temperature gives the corresponding 3-dimethylamino-2-isocyano-acrylic
acid
ethyl ester. A solution of this compound in a suitable solvent such as
tetrahydrofuran
is treated with gaseous hydrogen sulfide in the presence of a suitable
tertiary amine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-27-
base such as triethylamine or diiso-propylethylamine or the like at room
temperature
to give the corresponding 4-carboethoxy-thiazole.
Additional appropriately substituted thiazoles may be prepared essentially
according to the procedure of Bredenkamp, M. W., Holzafel, C. W., van Zyl, W.
J.
Synthetic Comm. 20, 2235 (1990). Appropriate unsaturated oxazoles are prepared
essentially according to the procedure of Henneke, K. H., Schollkopf, U.,
Neudecker,
T. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1979 (1979). Substituted oxazoles may be prepared
essentially according to the procedures of Galeotti, N., Montagne, C., Poncet,
J.,
Jouin, P. Tetrahedron Lett. 33, 2807, ( 1992) and Shin, C., Okumura, K., Ito,
A.,
Nakamura, Y. Chemistry Lett. 1305, (1994).
The following specific examples are illustrative, but are not meant to be
limiting of the present invention.
EXAMPLE 1 (METHOD lA)
4-Methoxy-3-tritluoromethyl-phenylamine
A suspension of 4-methoxy-3-trifluoromethyl-nitrobenzene (2.2 g) and iron
powder
(1.68 g) in ethanol (35 mL) and water (15 mL) is treated with a solution of
concentrated hydrochloric acid (0.42 mL) in ethanol (6 mL} and water (3 mL)
and
the mixture is heated to reflux for approximately 1 hour. The mixture is then
cooled,
filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting oil is
dissolved in
ethyl acetate and extracted three times with 5% aqueous hydrochloric acid. The
pooled acidic extracts are then cooled in an ice bath and basified with solid
potassium
carbonate, then extracted with ethyl acetate. These organic extracts are
washed with
saturated aqueous sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate,
concentrated under reduced pressure, then passed through a short column of
silica gel
(ethyl acetate is used as the eluant) to provide the desired compound as an
amber oil.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00134268 PCT/US99/28838
-28-
2,6-Dichloro-benzene-I,4-diamine
3-Chloro-4-methylsulfanyl-phenylamine
2,6-Dibromo-benzene-1',4-diamine
3-Chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-phenylamine
3-Chloro-4-ethylsulfanyl-phenylamine
4-Methoxy-3-trifluoromethyl-phenylamine
3,5-Dichloro-4-methoxy-2-methyl-phenylamine
S-Chloro-2-ethoxy-4-methoxy-phenylamine
5-Chloro-4-ethoxy-2-methoxy-phenylamine
5-Iodo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenylamine
3,5-Diiodo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenylamine
3,5-Dibromo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenylamine
5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenylamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 ),N( 1 )-dimethyl-benzene- I ,4-diamine
3-Chloro-4-piperidin-1-yl-phenylamine
3-Chloro-4-pyrrolidin-1-yl-phenylamine
N( I )-Benzyl-2-chloro-benzene-1,4-diamine
3-Chloro-4-(4-methyl-piperazin- I -yl)-phenylamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-methyl-N( 1 )-( I -methyl-piperidin-4-yl)-benzene-1,4-diamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-methyl-N( 1 )-( 1-methyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-benzene-1,4-diamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-methyl-N( 1 )-phenyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
N( 1 )-( 1-Benzyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl}-2-chloro-N( 1 )-methyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-cyclopentyl-N( 1 )-methyl-benzene- I ,4-diamine
2-[(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-amino]-ethanol
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-hexyl-N( 1 )-methyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-isobutyl-N( 1 )-methyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
2-[(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-methyl-amino]-ethanol
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-N( 1 )-methyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-N( I }-methyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-benzene-1,4-diamine
N( I )-( I-Benzyl-piperidin-4-yl)-2-chloro-benzene-1,4-diamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-N( I )-methyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-29-
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzene-1,4-diamine
N( 1 )-( 1-Benzyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-2-chloro-benzene-1,4-diamine
3-Chloro-4-(1-methyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-phenylamine
3-Chloro-4-(2-dimethylamino-ethoxy)-phenylamine
3-Chloro-4-(3-dimethylamino-propoxy)-phenylamine
3-Chloro-4-(1-methyl-pyrrolidin-3-yloxy)-phenylamine
3-Chloro-4-cyclohexyloxy-phenylamine
EXAMPLE 2 (METHOD 1B)
4-Bromo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenylamine
A suspension of 4-bromo-2,4-dimethoxy-nitrobenzene (0.48 g) and iron powder
(0.42 g) in acetic acid (10 mL) and ethanol (10 mL) is heated to 120 °C
for
approximately 5 hours. The mixture is then cooled, filtered, and concentrated
under
reduced pressure. Water is added and the mixture is cooled in an ice bath and
neutralized with solid potassium carbonate and then extracted with
dichloromethane.
These organic extracts are washed with saturated aqueous sodium chloride,
dried over
anhydrous sodium sulfate, concentrated under reduced pressure, then
chromatographed over silica gel (20% ethyl acetate in hexanes is used as the
eluant)
to provide the desired compound as an amber oil.
EXAMPLE 3 (METHOD 1C)
(4-Amino-2,6~dichloro-phenoxy)-acetic acid tert-butyl ester
A soution of (4-nitro-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy)-acetic acid tert-butyl ester ( 1
g) in
ethanol (17 mL) and water (8.6 mL) is treated with iron powder (0.861 g) and
ammonium chloride (86 mg) and the mixture is heated to reflux for
approximately I
hour. The mixture is then filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure.
The
resulting oil is partitioned between water and ethyl acetate, and the organic
phase is
then washed with saturated aqueous sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous
sodium
sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure to provide the desired
compound as
a pale yellow solid.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 30 -
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
4-Chloro-benzene-1,2-diamine
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-acetamide
(4-Amino-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
(4-Amino-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy)-acetic acid tent-butyl ester
(2-Amino-4-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
(4-Amino-2-chloro-S-methoxy-phenoxy)-acetic acid methyl ester
(4-Amino-2-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy}-acetic acid tert-butyl ester
(2-Amino-4-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy)-acetic acid tert-butyl ester
N( 1 )-Benzyl-4-chloro-5-methoxy-benzene-1,2-diamine
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-amide
(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid ethyl ester
N-(4-Amino-5-chloro-2-methyl-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-5-chloro-2-methyl-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-5-chloro-2-methyl-phenyl)amide
N-(4-Amino-3-chloro-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-3-chloro-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-dimethylamino-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-piperidin-1-yl-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-morpholin-4-yl-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-methanesulfonamide
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-diethylamino-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-pyrrolidin-1-yl-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-azepan-1-yl-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-(2-methyl-piperidin-1-yl)-acetamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-31-
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-(3-methyl-piperidin-1-yl)-acetamide
3-Chloro-benzene-1,2-diamine
4-Chloro-N,N-dimethyl-benzene-1,2-diamine
EXAMPLE 4 (METHOD 1D)
3,5-Dichloro-4-phenoxy-phenylamine
To a slurry of 3,5-dichloro-4-phenoxy-nitrobenzene (6.1 g) and tin powder (12
g) is
added dropwise concentrated hydrochloric acid (60 mL). Ethanol (60mL) is added
and the mixture is heated to reflux for approximately 1 hour. The mixture is
then
cooled in an ice bath and basified by addition of solid sodium hydroxide. The
resulting suspension is filtered through a pad of diatomaceous earth and
extracted
three times with ethyl acetate. The combined organic extracts are then washed
with
saturated aqueous sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and
concentrated under reduced pressure to provide the desired product as a yellow
solid.
Recrystallization from ethyl acetate-hexanes provided the product as a pale
yellow
solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
1-Furan-2-yl-ethylamine
3-Chloro-4-isopropoxy-phenylamine
2-Butoxy-5-chloro-4-methoxy-phenylamine
3,5-Dichloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenylamine
2-Benzyloxy-5-chloro-4-methoxy-phenylamine
4-Benzyloxy-5-chloro-2-methoxy-phenylamine
5-Fluoro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenylamine
(4-Amino-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy)-acetic acid ethyl ester
3,5-Dichloro-4-phenoxy-phenylamine
2-(4-Amino-2-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy)-acetamide
(4-Amino-2-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-32-
2-(2-Amino-4-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy)-ethanol
2-(4-Amino-2-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy)-ethanol
4-(4-Amino-2-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy)-butyronitrile
4-Amino-2-chloro-5-methoxy-phenol
2-Amino-4-chloro-5-methoxy-phenol
5-Chloro-4-methoxy-2-morpholin-4-yl-phenylamine
4-Chloro-5-methoxy-N( 1 ),N( 1 )-dimethyl-benzene-1,2-diamine
5-Chloro-4-methoxy-2-piperidin-1-yl-phenylamine
5-Chloro-4-methoxy-2-pyrrolidin-1-yl-phenylamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-cyclohexyl-N( 1 )-methyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
N(2)-Benzyl-4-methoxy-benzene-1,2-diamine
2-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenoxy)-ethanol
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-cyclohexyl-N( 1 )-ethyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
4-Butoxy-3-chloro-phenylamine
(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
2-Chloro-N( 1 )-cyclohexyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
2-Chloro-N( 1 ),N( 1 )-dipropyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
3-Chloro-4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenylamine
3-Chloro-4-(octahydro-quinolin-1-yl)-phenylamine
N( 1 )-Allyl-2-chloro-N( 1 )-cyclohexyl-benzene-1,4-diamine
N-(4-Amino-2-methoxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-2-methoxy-5-methyl-phenyl)amide
N-(4-Amino-naphthalen-1-yI)-2-fluoro-benzamide
3-Chloro-N,N-dimethyl-benzene-1,2-diamine
3-Chloro-4-propoxy-phenylamine
3-Iodo-4-methoxy-phenylamine
3-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-aniline
3-Bromo-4-methoxy-phenylamine
3-Chloro-4-ethoxy-phenylamine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-33-
EXAMPLE 5 (Method lE)
(4-Amino-phenyl)-carbamic acid isobutyl ester
To a solution of N-(4-Nitro-phenyl)-isobutyrlamide (2.0 g) in 100 mL ethylene
glycol monomethyl ether (100 mL) is added 10% palladium on carbon (275 mg).
The mixture is hydrogenated for 2 hours at room temperature under 30 psi of
hydrogen on a Parr hydrogenation apparatus. The catalyst is then removed by
filtration through diatomaceous earth and the filtrate is evaporated to
dryness under
reduced pressure by azeotroping three times with heptane. Trituration of the
residue
with heptane provides the desired product as a white solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
2-Methyl-3H-benzoimidazol-5-ylamine
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-formamide
1 H-Benzoimidazol-5-ylamine
(4-Amino-phenyl)-carbamic acid isobutyl ester
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-isobutyramide
N-(5-Amino-pyridin-2-yl)-2-methyl-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (5-amino-pyridin-2-yl)-amide
N-(5-Amino-pyridin-2-yl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
[6-(2,2,2-Trifluoro-acetylamino)-pyridin-3-yl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
N-(S-Amino-pyridin-2-yI)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
(4-Amino-benzyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
2-(3,5-Bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
1-tert-Butyl-1H-imidazol-2-ylamine
3-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-5-trifluoromethyl-phenylamine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-34-
EXAMPLE 6 (METHOD 1F)
N-(4-Amino-2-methylphenyl)-2-tluorobenzamide
A mixture of 2-fluoro-N-(2-methyl-4-nitrophenyl)benzamide (4.55 g),
cyclohexene
(30 mL), ethanol (70 mL), water (30 mL) and 10% palladium on charcoal (3 g) is
heated at reflux for 30 minutes. The mixture is filtered through diatomaceous
earth
and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting oil is dissolved in 50
mL of
ethyl acetate and cooled at 4° C for 12 hours. Filtration provides the
product as a tan
solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
N-(4-Amino-2-methyl-phenyl}-acetamide
2-Methyl-benzooxazol-6-ylamine
N-(4-Amino-3-methoxy-phenyl)-acetamide
2-Acetylamino-5-amino-benzoic acid
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-acetamide
[4-(3-Amino-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Amino-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
N-(4-Amino-2-cyano-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-2,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-2-cyano-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-2-methoxy-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-2-methoxy-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-2-methoxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-benzoyl-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-benzoyl-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-2-benzoyl-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-3-methyl-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-3-methyl-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-35-
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-3-methyl-phenyl)-amide
5-Amino-2-[(2-fluorobenzoyl)amino]-N-phenylbenzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid' (4-amino-2-phenylcarbamoyl-phenyl)amide
N-(4-Amino-naphthalen-1-yl)-acetamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-naphthalen-1-yl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acetamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-2-cyano-phenyl)-amide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-2-methyl-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-2-methyl-phenyl)-amide
S-Amino-2-(2-fluoro-benzoylamino)-benzoic acid
S-Amino-2-[(furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-benzoic acid
N-(4-Amino-2-cyano-phenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-3-methyl-phenyl)-2,6-difluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-methoxy-phenyl}-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2-fluoro-N-(2-fluoro-benzoyl)-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
EXAMPLE 7 (METHOD 1G)
N-(4-Amino-2-chlorophenyl)-2-thiomorpholino-4-yl-acetamide
A solution of N-(2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl)-2-thiomorpholino-4-yl-acetamide (3.02
g}
in ethanol (200 mL) is added to a solution of sodium thiosulfate (12 g) in
water (60
mL). The mixture is heated at reflux for 12 hours, cooled and poured into
water.
The mixture is then extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate solution
is washed
twice with saturated aqueous sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous potassium
carbonate, filtered through a pad of diatomaceous earth and concentrated under
reduced pressure to give an oil. Toluene is added and the solution chilled to
give the
desired product as a light orange crystalline solid.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCTIUS99/28838
-36-
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-thiomorpholin-4-yl-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-2-dipropylamino-acetamide
EXAMPLE 8 (METHOD 2A)
(3-Chloro-4-iodo-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
To a solution of 3-chloro-4-iodo-aniline ( 10 g) in tetrahydrofuran (40 mL)
containing
diiso-propylethylamine (6.9 mL) is added di-tert-butyl-dicarbonate (8.6 g) and
the
lU mixture is heated to reflux. After approximately 15 hours additional
portions of
diisopropylethylamine (6.9 mL) and di-tert-butyl-dicarbonate (21 g) is added
and
heating is continued for approximately 24 hours. The solution is then cooled,
concentrated under reduced pressure, diluted with ethyl acetate, and washed
successively three times with 5% aqueous hydrochloric acid then once with
saturated
aqueous sodium chloride. The solution is dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate
then
concentrated under reduced pressure to provide the desired crude product as a
brown
oil. Crystallization is induced by addition of hexanes, and the collected
solid material
is recrystallized from hexanes to give the desired product as a white solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
N'-(4-Nitro-benzoyl)-hydrazinecarboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
(3-Chloro-4-iodo-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Bromo-3-chloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(3-Chloro-4-vinyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(3-Chloro-4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Amino-3-chloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Chloro-2-nitro-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(3-tert-Butoxycarbonylamino-5-chloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-37-
(4-Nitro-benzyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(3-Bromo-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(2-Amino-3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
EXAMPLE 9 (METHOD 2B)
(3-Ghloro-4-vinyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid2-trimethylsilanyl-ethyl ester
To a solution of 3-chloro-4-vinyl-phenylamine (3.4 g) in N,N-dimethylformamide
(44 mL) containing diisopropylethylamine (5.8 mL) is added 1-[2-
(trimethylsilyl)-
ethoxycarbonyl-oxy]benzotriazole (7.1 g) and the mixture is stirred at room
temperature under an atmosphere of argon for three days. The solution is then
diluted with water and extracted three times with diethyl ether. The combined
organic extracts are washed successively with water, saturated aqueous sodium
chloride, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under
reduced
pressure. The resulting residue is chromatographed over silica gel (10% ethyl
acetate
in hexanes is used as the eluant) to provide the desired product as a yellow
oil.
EXAMPLE 10 (METHOD 2C)
[4-(2-Fluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
To a solution of mono-N-(t-butoxycarbonyl)-1,4-phenylenediamine (1.58 g} and
triethylamine ( 1.50 mL) in 25 . mL of dichloromethane is added o-
fluorobenzoyl
chloride (1.20 g). A solid formed immediately forms and is filtered and washed
with
fresh solvent to yield a white solid, 1.90 g.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
N-(3-Methoxy-4-nitro-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-isobutyrlamide
2,2,2-Trifluoro-N-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-phenyl)-acetamide
[4-(2-Methyl-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-38-
Acetic acid 2-(4-tert-butoxycarbonylamino-phenylcarbamoyl)-phenyl ester
[4-(4-Fluoro-benzoylamino}-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(3-Fluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Fluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Methoxy-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(3-Methoxy-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(4-Methoxy-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2,2-Dimethyl-propionylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Bromo-acetylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2,2,2-Trifluoro-acetylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Benzoylamino-phenyl)-carbamic acid tent-butyl ester
(4-Methanesulfonylamino-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Phenylacetylamino-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Thiophene-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(3-Nitro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(3-Acetylamino-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(3-Methanesulfonylamino-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
Ethyl [3-[[[4-[[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]amino]phenyl]amino]carbonyl]-
phenyl] carbamate
[4-(2-Trifluoromethyl-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2,6-Difluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Chloro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Bromo-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Nitro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Benzo[b]thiophene-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
{4-[(Pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Naphthalene-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Naphthalene-1-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(3-Bromo-thiophene-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
{4-[(Biphenyl-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
N-(4-tert-Butoxycarbonylamino-phenyl)-phthalamic acid
[4-(2,3-Difluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-39-
[4-(2,5-Difluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2,4-Difluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Acetylamino-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tent-butyl ester
[4-(2-Methanesulfonylamino-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
[4-(2,3,4-Trifluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2,3,4,5,6-Pentafluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
N-(4-tert-Butoxycarbonylamino-phenyl)-isophthalamic acid methyl ester
2-Methylsulfanyl-N-[4-(2,2,2-trilluoro-acetylamino)-phenyl]-benzamide
[4-(3-Benzyloxy-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(3-Butoxy-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{ 4-[(5-Difluoromethyl-furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl }-carbamic acid tert-
butyl
ester
{4-[(Thiophene-3-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(5-Methyl-furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(S-Bromo-furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Hexanoylamino-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Thiophen-2-yl-acetylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{ 4-[(Pyridine-3-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl }-carbamic acid tort-butyl ester
{ 4-[(4-Bromo-furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl }-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Furan-3-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Phenoxycarbonylamino-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Benzo[1,3]dioxole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
[4-(3-Trifluoromethoxy-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
N-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
{4-[(Furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Phenoxy-acetylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(5-Nitro-furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{ 4-[(5-Chloro-furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl }-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
{4-[(3-Methyl-furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(2-Methoxy-acetylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(4-Furan-3-yl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid
tert-butyl ester
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-40-
{4-[(5-tert-Butyl-furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
N-[3-Cyano-4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-acetylamino)-phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid' [3-cyano-4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-acetylamino)-phenyl]amide
N-(4-Acetylamino-2-cyano-phenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
2,2,2-Trifluoro-N-(4-nitro-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-AcetyIamino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
2-Fluoro-N-[4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-acetylamino)-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl]benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-acetylamino)-3-trifluoramethyl-
phenyl]amide
2-Fluoro-N-(2-methyl-benzooxazol-6-yl)-benzamide
4-(2-Fluoro-benzoylamino)-2-hydroxy-benzoic acid phenyl ester
{4-[(Isoxazole-5-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
N-(4-Acetylamino-2-methoxy-phenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
2-Fluoro-N-[3-methoxy-4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-acetylamino)-phenyl]benzamide
2-Fluoro-N-(2-fluoro-benzoyl)-N-(4-nitro-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)benzamide
{4-[(1H-Pyrazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(1H-Imidazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(5-Methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-
butyl ester
{4-[(5-Furan-3-yl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carbonyl}-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid
tert-butyl ester
2,2,2-Trifluoro-N-(5-nitro-pyridin-2-yl)-acetamide
{4-[(1-Methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
4-(2-Fluoro-benzoylamino)-2-hydroxy-benzoic acid methyl ester
N-(S-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-oxalamic acid
Isoicazole-5-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
2-Fluoro-N-(4-nitro-benzyl)-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid 4-nitro-benzylamide
N-[3-Chloro-5-(2,2,2-trifluoro-acetylamino)-phenyl]-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
N-(3-Amino-5-chloro-phenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
[4-(2-Fluoro-benzoylamino)-benzyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-41-
[4-(2,6-Difluoro-benzoylamino)-benzyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
2,6-Difluoro-N-(4-vitro-benzyl)-benzamide
{4-[(Furan-2-carbonyl)=amino]-benzyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
N-(3-Amino-S-chloro-phenyl)-acetamide
[4-(3-Chloro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(4-Chloro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tent-butyl ester
(4-(4-Dimethylamino-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Benzenesulfonylamino-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[4-(3-Trifluoromethyl-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
2,2,2-Trifluoro-N-(5-vitro-pyrimidin-2-yl)-acetamide
EXAMPLE 11(METHOD 2D)
2-Chloro-N-(2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl)acetamide
A solution of 2-chloro-4-nitroaniline ( 19.0 g) and chloroacetyl chloride (30
mL) in
tetrahydrofuran (150 mL) is heated at reflux for 1 hour. The solution is
cooled and
concentrated under reduced pressure, giving a wet yellow solid. Ether (250 mL)
is
added and the yellow solid is collected.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materias the following
compounds were prepared:
N-(4-Nitro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acetamide
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-carbamic acid ethyl ester
2-Acetylamino-S-vitro-benzoic acid
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (5-chloro-2-hydroxy-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (2-methyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (2-methoxy-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
N-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-benzamide
2-Methoxy-N-(4-vitro-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-Nitro-phenyl)-acrylamide
N-(4-Nitro-phenyl)-isobutyrlamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT1US99/28838
-42-
[4-)acryloylamino)-phenyl]carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Nitro-phenyl)-carbamic acid isobutyl ester
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (5-vitro-pyridin-2-yl)-amide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (5-vitro-pyridin-2-yl)-amide
2-Fluoro-N-(5-vitro-pyridin-2-yl)-benzamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (2,5-dimethoxy-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
N-(2-Cyano-4-vitro-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzarnide
2-Fluoro-N-(2-methoxy-4-vitro-phenyl)-benzamide
2-Methyl-N-(5-vitro-pyridin-2-yl)-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (2-methoxy-5-methyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
2-Fluoro-N-(2-methoxy-S-methyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-benzamide
N-(2-Benzoyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(2-Benzoyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (2-benzoyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
N-(3-Methyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-acetamide
2-Fluoro-N-(3-methyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (3-methyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
2-Acetylamino-5-vitro-N-phenyl-benzamide
2-[(2-Fluorobenzoyl)amino]-5-vitro-N-phenylbenzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-vitro-2-phenylcarbamoyl-phenyl)-amide
2-Fluoro-N-(4-vitro-naphthalen-1-yl)-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-vitro-naphthalen-1-yl)-amide
N-(5-Chloro-2-hydroxy-4-vitro-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(5-Chloro-2-hydroxy-4-vitro-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (2-chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Nitro-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acetamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (2-cyano-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
2-Fluoro-N-(4-vitro-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-vitro-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amide
2-Fluoro-N-(2-methyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-benzamide
N-(5-Chloro-2-methyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-43-
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (5-chloro-2-methyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
2-(2-Fluoro-benzoylamino)-5-vitro-benzoic acid
2-[(Furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-5-vitro-benzoic acid
N-(3-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (3-chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-amide
2,6-Difluoro-N-(3-methyl-4-vitro-phenyl)-benzamide
2-Fluoro-N-(4-vitro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-vitro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amide
2-Chloro-N-(2-chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitrophenyl)methanesulfonamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid [3-methoxy-4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-acetylamino)-phenyl]-
amide
N-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
EXAMPLE 12
{4-[(4-Phenyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-
carbamic acid tert-butyl
A solution of 1-(N-tert-butoxycarbonyl)-1,4-phenylenediamine (0.8 g) and 4-
phenyl-
[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid (0.7 g) in dichloromethane (10 mL) is
treated
with triethylamine (1.3 mL) and benzotriazole-1-yloxy-tris(dimethylamino)-
phosphonium hexa-fluorophosphate ( 1.6 g). After stirring at room temperature,
the
reaction is diluted with water and extracted with dichloromethane. The organic
layer
is washed with 0.5 N hydrochloric acid, saturated sodium bicarbonate, and
water then
dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated under reduced
pressure to
give the desired product.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
{4-[(1H-Pyrrole-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Pyrazine-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(5-Methyl-thiophene-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tent-butyl
ester
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
{4-[(1-Methyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
{4-[(Quinoline-8-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Benzofuran-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Isoquinoline-1-carbonyl}-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tent-butyl ester
{ 4-[(Quinoline-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl }-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Pyridine-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Isoquinoline-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[{[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
{4-[(1H-[1,2,3]Triazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
[4-(2-Methylsulfanyl-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{4-[(Quinoline-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{ 4-[(4-Methyl-[ 1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl }-carbamic acid
tert-
butyl ester
{4-[(4-Phenyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-
butyl ester
{4-[(1H-Indole-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid 4-nitro-benzylamide
{4-[([1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-benzyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
Acetic acid 4-(4-tert-butoxycarbonylamino-phenylcarbarnoyl)-phenyl ester
{4-[(Quinoline-6-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
EXAMPLE 13 (METHOD 2F)
Acetic acid 2-(4-tert-butoxycarbonylamino-
2,6-dichloro-phenoxy)-ethyl ester
A solution of [3,5-dichloro-4-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-
butyl
ester (0.85 g) in pyridine ( 14 mL) is treated with acetic anhydride ( 1.24
mL) and the
mixture is stirred at room temperature for I S hours. The solvent is removed
under
reduced pressure and the residue dissolved in ethyl acetate. This solution is
then
washed twice with 5% aqueous hydrochloric acid, once with saturated aqueous
sodium bicarbonate, and then with saturated aqueous sodium chloride. The
solution
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-45-
is dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and the solvent is removed under
reduced
pressure to provide the desired product as a colorless oil.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
Phenylsulfanyl-acetonitrile
Acetic acid 2-(4-tert-butoxycarbonylamino-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy)-ethyl ester
EXAMPLE 14 (METHOD 2G)
(3,5-Dichloro-4-hydroxy-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
To a solution of 2,6-dichloro-4-amino phenol (9.5 g) in tetrahydrofuran (13U
mL) is
added di-tert-butyl-dicarbonate ( 11.7 g) and the mixture is heated to reflux
for
approximately 15 hours. The solution is then cooled, concentrated under
reduced
pressure, diluted with ethyl acetate, and washed successively three times with
S%
1 S aqueous hydrochloric acid then once with saturated aqueous sodium
chloride. The
solution is dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate then concentrated under
reduced
pressure to provide the desired crude product. This material is then
triturated with
cold dichloromethane to provide the product as a white solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compound was prepared:
(3-Amino-5-chloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
EXAMPLE 15 (METHOD 3A)
3,5-Dichloro-4-ethoxy-phenylamine
Trifluoroacetic acid (5 mL) is added to solid (3,5-dichloro-4-ethoxy-phenyl)-
carbamic acid tert-butyl ester (0.97 g) and the mixture is stirred for
approximately 45
minutes at room temperature. Water is then added, and the mixture is cooled in
an
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-46-
ice bath and basified with solid potassium carbonate. The solution is
extracted three
times with ethyl acetate and the combined organic phases are washed with
saturated
aqueous sodium chloride then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate.
Concentration
under reduced pressure and recrystallization from hexanes provides the desired
S product as a pale yellow crystalline solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
5-Bromo-pyridin-3-ylamine
3-Chloro-4-methanesulfonyl-phenylamine
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-methyl-benzamide
Acetic acid 2-(4-amino-phenylcarbamoyl)-phenyl ester
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-4-fluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-3-fluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-methoxy-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl}-3-methoxy-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-4-methoxy-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-phenyl-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-propionamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide
Thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
1H-Pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-3-nitro-benzamide
3-Acetylamino-N-(4-amino-phenyl)-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-3-dimethylamino-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-3-methanesulfonylamino-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-trifluoromethyl-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2,6-difluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-chloro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-bromo-benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-47-
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-nitro-benzamide
Pyrazine-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
S-Methyl-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
Quinoline-8-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
1-Methyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
Benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-isonicotinamide
Naphthalene-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
Naphthalene-1-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
Isoquinoline-1-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
Quinoline-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
3,5-Dichloro-4-ethoxy-phenylamine
4-Butoxy-3,5-dichloro-phenylamine
Isoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
1H-[1,2,3]Triazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
3-Bromo-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
4-Benzyloxy-3,5-dichloro-phenylamine
2-(4-Amino-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy)-acetamide
(4-Amino-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy)-acetic acid methyl ester
[3-(4-Amino-phenylcarbamoyl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid ethyl ester
2-Amino-N-(4-amino-phenyl)-benzamide
Biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2,3-difluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2,5-difluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2,4-difluoro-benzamide
2-Acetylamino-N-(4-amino-phenyl)-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-methanesulfonylamino-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2,3,4-trifluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2,3,4,5,6-pentafluoro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-methylsulfanyl-benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-48-
Acetic acid 2-(4-amino-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy)-ethyl ester
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-isophthalamic acid methyl ester
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-3-benzyloxy-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-3-butoxy-benzamide
(3-(4-Amino-phenylcarbamoyl)-phenoxy]-acetic acid ethyl ester
Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
Quinoline-4-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
5-Methyl-furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
5-Difluoromethyl-furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
1H-Indole-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
4-Methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
Thiophene-3-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
5-Chloro-furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
5-Nitro-furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl}-2-thiophen-2-yl-acetamide
3-Methyl-furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
5-Bromo-furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
4-Bromo-furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-nicotinamide
N-(4-Aminophenyl)-3-furancarboxamide
4-Phenyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
Acetic acid 3-(4-amino-phenylcarbamoyl)-phenyl ester
Benzo[1,3]dioxole-4-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-3-(2-dimethylamino-ethoxy)-benzamide
N-{4-Amino-phenyl)-3-trifluorornethoxy-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-3-(2-morpholin-4-yl-ethoxy)-benzamide
(4-Amino-phenyl)-carbamic acid hexyl ester
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
(4-Amino-phenyl)-carbamic acid phenyl ester
Hexanoic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-acrylamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-methoxy-acetamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-49-
4-Furan-3-yl-[I,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
5-tert-Butyl-furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
3-Chloro-4-methanesulfinyl-phenylamine
5-Methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
2-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-ethanol
(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid 2-piperidin-1-yl-ethyl ester
5-Chloro-N,N-dimethyl-benzene-1,3-diamine
3-(2-Methyl-butyl)-S-trifluoromethyl-phenylamine
3-Isobutyl-5-trifluoromethyl-phenylamine
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-aminomethyl-phenyl}-amide
N-(4-Aminomethyl-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-aminomethyl-phenyl}-amide
N-(4-Aminomethyl-phenyl)-2,6-difluoro-benzamide
Oxazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-3-chloro-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-4-chloro-benzamide
Acetic acid 4-(4-amino-phenylcarbamoyl)-phenyl ester
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-4-dimethylamino-benzamide
1-(4-Amino-phenyl}-3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thiourea
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-iodo-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-3-trifluoromethyl-benzamide
EXAMPLE 16 (METHOD 3B)
1-(4-Amino-2-chloro-phenyl)-ethanol
A 1M solution of tetrabutylarnmonium fluoride in tetrahydrofuran (5.7 mL) is
added
to [3-chloro-4-(1-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid 2-trimethylsilanyl-
ethyl ester
(0.5 g) and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for approximately 3.5
hours.
The solution is then concentrated under reduced pressure, dissolved in a 1:1
mixture
of ethyl acetate and hexanes, washed successively with water then saturated
aqueous
sodium chloride, and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Removal of the
solvent under reduced pressure followed by chromatography over silica gel (40%
ethyl acetate in hexanes is used as the eluant) provides the product as an
amber oil.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 50 -
EXAMPLE 17 (METHOD 3C)
N-(4-Amino-3-cyanophenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Potassium carbonate {5.0 g) is added to a solution of N-[3-cyano-4-(2,2,2-
trifluoroacetyl-amino)-phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide (2.5 g) in methanol (270 mL)
and
water (16 mL) and the mixture is retluxed overnight. After removing the
solvent
under reduced pressure, the residue is suspended in water and extracted with
dichlorornethane. The organic extracts are pooled, washed with water and then
saturated aqueous sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate,
filtered
and concentrated under reduced pressure to provide the desired compound as a
white
solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
N-(4-Amino-phenyl)-2-methanesulfinyl-benzamide
N-(4-Amino-3-cyano-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-3-cyano-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-3-cyano-phenyl)-acetamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-amino-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amide
N-(4-Amino-3-methoxy-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(4-Amino-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-amino-3-methoxy-phenyl)-amide
EXAMPLE 17 (METHOD 4A)
2-Chloro-1-cyctohexyloxy-4-nitro-benzene
Cylcohexanol (2.9 g) in dimethylsulfoxide (20 mL) is added slowly to a flask
containing potassium hydride (0.90 g, pre-washed three times with hexanes)
under an
atmosphere of argon and the solution is stirred for about 1 hour at room
temperature.
A solution of 3-chloro-4-fluoro-nitrobenzene ( 1 g) in dimethylsulfoxide ( 1 U
mL) is
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-51-
added and the resulting dark red colored solution is then heated for three
hours to
approximately 100 degrees. The reaction mixture is then cooled, diluted with
diethyl
ether (300 mL), and washed successively with saturated aqueous ammonium
chloride, three times with water, then with saturated aqueous sodium chloride.
The
S organic layer is then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, the solvent is
removed
under reduced pressure, and the resulting oil is chromatographed over silica
geI (5%
ethyl acetate in hexanes is used as the eluant) to provide the desired product
as an
orange solid.
EXAMPLE 18 (METHOD 4C)
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-methyl-( 1-methyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-amine
3-Chloro-4-fluoronitrobenzene ( 1.0 g) and N,N'-dimethyl-3-aminopyrrolidine (
1.72
g) are combined and stirred for approximately 24 hours. The mixture is then
diluted
with ethyl acetate, washed twice with water and once with saturated sodium
chloride,
and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. After removal of the solvent under
reduced
pressure the residue is chromatographed over silica gel (pure ethyl acetate
followed
by pure methanol is used as the eluants) to provide the desired product as a
yellow
oil.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-dipropyl-amine
I-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-piperidine
1-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-pyrrolidine
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-cyclohexyl-methyl-amine
Benzyl-(2-chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-amine
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-methyl-(1-methyl-piperidin-4-yl)-amine
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-cyclohexyl-ethyl-amine
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-cyclohexyl-amine
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-methyl-( 1-methyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-amine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-52-
(1-Benzyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-(2-chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-methyl-amine
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-cyclopentyl-methyl-amine
1-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-decahydro-quinoline
Allyl-(2-chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-cyclohexyl-amine
2-[(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-amino]-ethanol
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-isobutyl-methyl-amine
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-hexyl-methyl-amine
2-[(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-methyl-amino]-ethanol
N-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-N,N',N'-trimethyl-ethane-1,2-diamine
N-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-N,N',N'-trimethyl-propane-1,3-diamine
( 1-Benzyl-piperidin-4-yl)-(2-chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-amine
N-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-N',N'-dimethyl-ethane-1,2-diamine
N-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-N',N'-dimethyl-propane-1,3-diamine
(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-methyl-amine
( 1-Benzyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-(2-chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-amine
4-Piperidin-1-yl-3-trifluoromethyl-benzonitrile
4-Dimethylamino-3-trifluoromethyl-benzonitrile
4-(4-Methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-3-trifluoromethyl-benzonitrile
EXAMPLE 19 (METHOD 4E)
Butyl-(2-chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)thioether
A solution of 3-chloro-4-fluoro-nitrobenzene (5.0 g) and sodium sulfide (2.5
g) in
N,N-dimethylformamide (30 mL) is stirred at room temperature for 1 hour and
then
treated with 1-iodobutane (12.6 g). The solvent is then removed under reduced
pressure and the resulting residue is treated with ethyl acetate and hexanes
to
precipitate the inorganic salts. The solids are removed by filtration and the
filtrate is
reduced under reduced pressure. The resulting residue is then passed through
hydrous magnesium silicate using dichloromethane as the eluent to provide the
desired compound as a yellow solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-53-
I-Butylsulfanyl-2-chloro-4-vitro-benzene
2-Chloro-1-cyclohexylsulfanyl-4-vitro-benzene
2-Chloro-1-ethylsulfanyl-4-vitro-benzene
EXAMPLE 20 (METHOD 4F)
(4-Chloro-5-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl)-dimethyl-amine
To a solution of trifluoro-methanesulfonic acid 4-chloro-5-methoxy-2-vitro-
phenyl
ester (1.0 g) in tetrahydrofuran (2.0 mL) is added dimethylamine (4.0 mL of a
40%
aqueous solution) and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for
approximately
hours. The solution is then concentrated under reduced pressure and the
residue is
10 dissolved in ethyl acetate and then washed with water. The aqueous layer is
extracted
once with ethyl acetate and the combined organic layers are washed with
saturated
aqueous sodium chloride and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent
is
removed by evaporation under reduced pressure and the residue is triturated
with
hexanes to provide the desired product as a colorless solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
(4-Chloro-2-vitro-phenyl)-dimethyl-amine
4-(4-Chloro-S-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl)-morpholine
(4-Chloro-5-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl)-dimethyl-amine
1-(4-Chloro-5-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl)-piperidine
I-(4-Chloro-5-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl)-pyrrolidine
Benzyl-(4-chloro-5-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl)-amine
(2-Chloro-6-vitro-phenyl)-dimethyl-amine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 54 -
EXAMPLE 21 (METHOD 4G)
(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-methyl-phenyl-amine
n-Butyl lithium (12.3 mL of a 2.5 M solution in hexanes) is added dropwise to
a
solution of N-methyl aniline (3.0 g) in tetrahydrofuran (75 mL) at 0°C.
The mixture
is allowed to warm slowly to room temperature and is then re-cooled to
0°C and
added by cannula to a solution of 3-chloro-4-tluoronitrobenzene (4.9 g) in
tetrahydrofuran (35 mL) that is kept at -78 °C. Following the addition,
the reaction
mixture is permitted to warm to room temperature over the course of 1 hour,
and is
then concentrated under reduced pressure, quenched by addition of saturated
aqueous
ammonium chloride, and extracted three times with ethyl acetate. The pooled
organic layers are washed three times with 5% aqueous hydrochloric acid, once
with
water, once with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate, once with saturated
aqueous
sodium chloride, and then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Following
removal of the solvent under reduced pressure the residue is chromatographed
over
silica gel (5% diethyl ether in hexanes is used as the eluant) to provide the
desired
product as a clear colorless oil.
EXAMPLE 22 (METHOD 4H)
2,6-Dichloro-4-nitrophenol
3,4,5-Trichloronitrobenzene (14.86 g) is added to a solution of potassium
phenoxide
(8.66 g) in diethylene glycol (66 mL) and the mixture is heated to
160°C for
approximately 15 hours. The resulting dark brown solution is cooled to room
temperature, poured onto 100 mL cold water, and extracted twice with diethyl
ether.
The pooled organic extracts are washed with water, 10% aqueous sodium
hydroxide,
and then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Following removal of the
solvent
under reduced pressure the resulting oil is distilled in a Kugelrohr apparatus
to
provide a yellow oil that solidifies on standing. Recrystallization from
ethanol-water
provides the desired product as a pale yellow solid.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-55-
EXAMPLE 23 (METHOD SA)
(3,5-Dichloro-4-ethoxy-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
To a solution of (3,S-dichloro-4-hydroxy-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester ( 1.0
g) and potassium carbonate {1.0 g) in acetone (18 mL) is added ethyl iodide
(0.36
mL) and the mixture is stirred for approximately 15 hours at room temperature.
The
solution is then filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and
partitioned
between ethyl acetate and water. The separated aqueous layer is further
extracted
twice with ethyl acetate, and the pooled organic extracts are washed
successively with
10% aqueous sodium hydroxide, with water, and then dried over anhydrous sodium
sulfate. Evaporation of the solvent under reduced pressure gave the desired
product
as a tan solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
(3,5-Dichloro-4-ethoxy-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Butoxy-3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Benzyloxy-3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-Carbamoylmethoxy-3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[3,5-Dichloro-4-{2-nitrilo-ethoxy)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(4-tert-Butoxycarbonylamino-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy)-acetic acid methyl ester
3-Butoxy-benzoic acid methyl ester
3-tert-Butoxycarbonylmethoxy-benzoic acid methyl ester
3-Carbamoylmethoxy-benzoic acid methyl ester
[4-(3-Carbamoylmethoxy-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{ 4-[3-(2-Chloro-ethoxy)-benzoylamino]-phenyl }-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-56-
EXAMPLE 24 (METHOD 5C)
(2,6-Dichloro-4-nitro-phenoxy)-acetic acid tent-butyl ester
To a solution of 2,6-dichloro-4-nitrophenol (2.5 g) and potassium carbonate
(3.3 g) in
dimethyl-formamide (50 mL) is added tert-butyl-bromoacetate (10 mL) and the
mixture is stirred at room temperature for two days. The solution is then
poured into
500 mL water, extracted three times with hexanes, and the pooled organic
extracts
are washed with saturated aqueous ammonium chloride and then dried over
anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Evaporation of the solvent under reduced pressure
followed by trituration of the resulting oil with hexanes provides the desired
product
as a white solid.
Using the above procedure and starting materials the following compounds were
prepared:
3-Dimethylamino-1-(4-nitro-phenyl)-propenane
2-Chloro-1-isopropoxy-4-nitro-benzene
1,3-Dichloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-5-nitro-benzene
1-Chloro-4-ethoxy-2-methoxy-5-nitro-benzene
1-Butoxy-4-chloro-5-methoxy-2-nitro-benzene
1-Chloro-2-methoxy-5-nitro-4-(phenylmethoxy)benzene (CA name)
1-Chloro-4-methoxy-5-nitro-2-(phenylmethoxy)benzene (CA name)
(2,6-Dichloro-4-nitro-phenoxy)-acetic acid tert-butyl ester
(2,6-Dichloro-4-nitro-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
1-Chloro-4-methoxy-2-methyl-5-nitro-benzene
2-(4-Chloro-S-methoxy-2-nitro-phenoxy)-acetamide
2-(2-Chloro-S-methoxy-4-nitro-phenoxy)-acetamide
(4-Chloro-5-methoxy-2-nitro-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
(2-Chloro-5-methoxy-4-nitro-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
4-(2-Chloro-S-methoxy-4-nitro-phenoxy)-butyronitrile
2-(4-Chloro-5-methoxy-2-nitro-phenoxy)-ethanol
2-(2-Chloro-5-methoxy-4-nitro-phenoxy)-ethanol
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-57-
(2-Chloro-5-methoxy-4-nitro-phenoxy)-acetic acid tert-butyl ester
(2-Chloro-5-methoxy-4-nitro-phenoxy)-acetic acid methyl ester
(4-Chloro-5-methoxy-2-nitro-phenoxy)-acetic acid methyl ester
(4-Chloro-5-methoxy-2-nitro-phenoxy)-acetic acid tert-butyl ester
(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
1-Butoxy-2-chloro-4-nitro-benzene
2-Chloro-4-nitro-1-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-benzene
2-Chloro-4-nitro-1-propoxy-benzene
2-Chloro-1-ethoxy-4-nitro-benzene
1,3-Diiodo-2,4-dimethoxy-5-nitro-benzene
1,3-Dibromo-2,4-dimethoxy-5-nitro-benzene
3-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-nitrobenzene
EXAMPLE 25 (METHOD 5E)
[3,5-Dichloro-4-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-carbamic acid
tert-butyl ester
To a solution of (3,S-dichloro-4-hydroxy-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester ( 1.0
g) and potassium carbonate (0.55 g) in toluene (20 mL) is added ethylene
carbonate
(1.6 g) and the mixture is heated to reflux for 3 hours. To the cooled
reaction
mixture is added 2.5 M aqueous sodium hydroxide (50 mL), and the separated
organic layer is then washed successively with water, then saturated aqueous
sodium
chloride, and then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent is then
removed
by evaporation under reduced pressure and the resulting residue is
chromatographed
over silica gel (30% ethyl acetate in hexanes is used as the eluant) to
provide the
desired product as a white foam.
EXAMPLE 26 (METHOD 6)
3-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenoxy)-1-methyl-pyrrolidine
To a solution of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol (2.0 g} in tetrahydrofuran (60 mL) is
added
1-methyl-3-pyrrolidinol (2.3 g), triphenyl phosphine (6.0 g), and diethylazo-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-58-
dicarboxylate (3.6 mL) and the mixture is stirred at room temperature under an
atmosphere of argon for 1.5 hours. The solution is then concentrated under
reduced
pressure, diluted with ethyl acetate, washed successively with 10% aqueous
sodium
hydroxide, water, saturated aqueous sodium chloride, and dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate. The solvent is removed by evaporation under reduced
pressure
and the residue is chromatographed over silica gel (ethyl acetate then 10%
methanol
in dichloromethane is used as the eluant). Pooled product fractions are then
recrystallized from hexanes to provide the desired product as a yellow solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
4-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenoxy)-1-methyl-piperidine
3-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenoxy)-1-methyl-pyrrolidine
[2-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenoxy)-ethyl]-dimethyl-amine
[3-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenoxy)-propyl)-dimethyl-amine
EXAMPLE 27 (METHOD 7A)
2-Chloro-3-methoxy-6-vitro-phenol
and
2,4-Dichloro-3-methoxy-6-vitro-phenol
To a flask containing 3-methoxy-6-vitro-phenol (0.5 g) is added aqueous sodium
hypochlorite (5.25% aqueous solution, 21 mL) and the mixture is stirred at
room
temperature for approximately 24 hours. The mixture is then cooled in an ice-
bath,
acidified by addition of concentrated hydrochloric acid, then extracted twice
with
ethyl acetate. These organic extracts are dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate,
the solvent is removed by evaporation under reduced pressure, and the residue
is
chromatographed over silca gel (15% acetone in hexanes is used as the eluant)
to
provide both the mono- and di-chlorinated products as yellow solids.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 59 -
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
3-Chloro-2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-nitrobenzene
3,5-Dichloro-2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-nitrobenzene
EXAMPLE 28 (METHOD 7B)
2,4-Dichloro-3-methyl-6-vitro-phenol
To a solution of 3-methyl-4-vitro-phenol (5.0 g) in water ( 1 SO mL) is added
aqueous
sodium hypochlorite (5.25% aqueous solution, 230 mL) and the mixture is
stirred at
room temperature for approximately 15 hours. Additional aqueous sodium
hypochlorite (5.25% aqueous solution, 230 mL) is added and the mixture is
permitted
to stir at room temperature for 2.5 days. The mixture is then cooled in an ice-
bath,
acidified by addition of concentrated hydrochloric acid, then extracted twice
with
ethyl acetate. These organic extracts are dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate,
the solvent is removed by evaporation under reduced pressure, and the residue
is
chromatographed over silca gel (ethyl acetate is used as the eluant) to
provide the
desired product as a yellow solid. An analytically pure sample is obtained by
a single
recrystallization from chloroform.
EXAMPLE 29 (METHOD 7C)
1-Bromo-2,4-dimethoxy-5-vitro-benzene
To a solution of 2,4-dimethoxy-nitrobenzene (0.50 g) in chloroform (3 mL) is
added
dropwise a solution of bromine (0.23 g) in chloroform ( 1 mL) and the mixture
is
allowed to stir at room temperature for approximately 1 S hours. Additional
bromine
(0.15 g) in chloroform (1 mL) is added and the reaction is stirred for an
additional 4
hours. The mixture is then poured onto 5% aqueous sodium bisulfate and then
extracted with chloroform. Pooled organic extracts are then washed
successively
with 5% aqueous sodium bisulfate then saturated sodium chloride, and then
dried
over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Removal of the solvent under reduced pressure
and
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO bb/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-60-
recrystallization of the residue from toluene provides the desired product as
a yellow
solid.
EXAMPLE 30 (METHOD 7D)
2,4-Dibromo-3-methoxy-6-vitro-phenol
To a solution of 5-methoxy-2-vitro-phenol (0.25 g) and silver trifluoroacetate
(0.49
g) in glacial acetic acid (3 mL) is added dropwise a solution of bromine (1.42
g) in
glacial acetic acid (3 mL) and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for
approximately 24 hours. The solution is then partitioned between ethyl acetate
and
water, and the organic layer is washed successively three times with 5%
aqueous
sodium bisulfite, three times with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate, and
once
with saturated aqueous sodium chloride. The organic layer is then dried over
anhydrous magnesium sulfate and the solvent is removed under reduced pressure.
The residue is chromatographed over silica gel (20% ethyl acetate in hexanes
is used
as the eluant) then recrystallized from chloroform to provide the desired
dibrominated product as an orange solid.
EXAMPLE 31 (METHOD 7E)
1-Iodo-2,4-dimethoxy-5-vitro-benzene
To a solution of 2,4-dimethoxy-nitrobenzene ( 1.0 g) in glacial acetic acid
(30 mL) is
added benzyltrimethylammonium dichloroiodate (1.90 g) and anhydrous zinc
chloride (1.0 g) and the mixture is stirred at room temperature under an
atmosphere
of argon. Additional benzyltrimethylammonium dichloroiodate (0.4 g) is added
after
5 hours and again after 24 hours. Additional zinc chloride (0.5 g) and glacial
acetic
acid ( I S mL) is added after 24 hours. The mixture is permitted to stir at
room
temperature for 3 days and is then filtered, diluted with 5% aqueous sodium
bisulfite,
and extracted three times with ethyl acetate. These pooled organic extracts
are
washed successively with 5% aqueous sodium bisulfite, saturated aqueous sodium
chloride, then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. After removal of the
solvent
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-61 -
under reduced pressure the residue is triturated with hexanes to provide the
desired
product as a pale yellow solid.
EXAMPLE 32 (METHOD 7F)
2,4-Diiodo-3-methoxy-6-vitro-phenol
To a solution of S-methoxy-2-vitro-phenol (0.25 g) in dichloromethane (15 mL)
and
methanol (6 mL) is added benzyltrimethylammonium dichloroiodate (1.08 g) and
sodium bicarbonate (0.85 g) and the mixture is allowed to stir at room
temperature
for 24 hours. The solution is then filtered, the filtrate is concentrated
under reduced
pressure, the residue is dissolved in ethyl acetate and then washed
successively with
5% aqueous sodium bicarbonate, 5% aqueous sodium bisulfite, and saturated
aqueous
sodium chloride. After drying over anhydrous magnesium sulfate the solvent is
removed by evaporation under reduced pressure and the residue is
recrystallized from
toluene to provide the desired product as yellow needles.
EXAMPLE 33 (METHOD 7G)
1-Fluoro-2,4-dimethoxy-5-vitro-benzene
To a solution of 2,4-dimethoxy-nitrobenzene ( 1.0 g) in tetrachloroethane ( 10
mL) is
added 3,S-dichloro-1-fluoro-pyridinium triflate (85%, 5.07 g) and the mixture
is
heated to 120 °C for 5 hours. Additional 3,5-dichloro-1-fluoro-
pyridinium triflate
(85%, 0.25 g) is added and heating is continued for 1 hour. The solution is
then
cooled to room temperature and passed over a column of silica gel (hexanes
followed
by 30% ethyl acetate in hexanes is used as the eluant). Product containing
fractions
are combined, evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue is
crystallized from
hexanes to provide the desired product as a tan solid.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-62-
EXAMPLE 34 (METHOD 8)
3-Chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-nitrobenzene
A solution of 3-chloro-4-iodo-nitrobenzene (2.26 g),
trimethyl(trifluoromethyl)silane
(5.68 g), copper(I) iodide (2.28 g), and potassium fluoride (0.56 g) in N,N-
dimethylformamide (8 mL) is heated in a sealed tube to 80 °C for 40
hours. The
solution is then cooled, diluted with diethyl ether, filtered through
diatomaceous
earth, and the filtrate is washed successively with water, saturated aqueous
sodium
chloride, and then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent is removed
under reduced pressure and the residue is chromatographed over silica gel ( 1
%
diethyl ether in hexanes followed by 10% ethyl acetate in hexanes is used as
the
eluant) to provided the desired product as a colorless oil.
I S EXAMPLE 35 (METHOD 9)
(3-Chloro-4-methanesulfinyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
To a solution of (3-chloro-4-thiomethyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(0.89
g) in dichloromethane ( 15 mL) at 0 °C is added a solution of
dimethyldioxirane
00.11 M in acetone, 34 mL) and the mixture is stirred at 0 °C for 1
hour. The
solvent is removed under reduced pressure and the residue is dissolved in
dichloromethane, washed with saturated aqueous sodium chloride, and then dried
over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Removal of the solvent under reduced
pressure
gave the desired product as an orange foam.
EXAMPLE 36 (METHOD 9B)
[4-(2-Methylsulfinyl-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid
tert-butyl ester
To a solution of 2-methylsulfanyl-N-[4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-acetylamino)-phenyl]-
benzamide (234 mg) is added a saturated solution of sodium periodate (5 mL)
and
the mixture is stirred for 12 hours. The purple mixture is poured into water,
extracted
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-63-
with ethyl acetate, dried over anhydrous potassium carbonate and evaporated to
yield
a red solid, 101 mg.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
S compounds were prepared:
(4-(2-Methanesulfinyl-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
2-Methanesulfinyl-N-[4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-acetylamino)-phenyl]-benzamide
EXAMPLE 37 (METHOD 10)
(3-Chtoro-4-methanesulfonyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
To a solution of (3-chloro-4-thiomethyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(0.90
g) in dichloromethane (30 mL) at 0 °C is added a solution of
dimethyldioxirane
00.11 M in acetone, 80 mL) and the mixture is stirred at 0 °C for 1
hour. The
solvent is removed under reduced pressure and the residue is dissolved in
IS dichloromethane, washed with saturated aqueous sodium chloride, and then
dried
over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Removal of the solvent under reduced
pressure
gives the desired product as an orange foam.
EXAMPLE 38 (METHOD 11)
3-Chloro-4-vinyl-phenylamine
To a deoxygenated solution of 3-chloro-4-iodo-aniline (6.95 g), triphenyl
arsine (0.67
g), and tris(dibenzylideneacetone)palladium(0) (0.50 g) in tetrahydrofuran
(120 mL)
at 50 °C is added tributylvinyltin ( 10 g) and the mixture is stirred
for approximately
15 hours at 50 °C under an atmosphere of argon. The reaction is then
cooled, filtered
through diatomaceous earth, and the filtrate is evaporated to dryness under
reduced
pressure. The residue is dissolved in hexanes and then extracted three times
with 5%
aqueous hydrochloric acid. These aqueous acidic extracts are then basified
with solid
potassium carbonate and extracted three times with ethyl acetate. These pooled
organic extracts are then washed with saturated aqueous sodium chloride, dried
over
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-64-
anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent is removed under reduced
pressure.
The resulting residue is chromatographed over silica gel (hexanes and then 10%
ethyl
acetate in hexanes is used as the eluant) to provide the desired product as an
amber
oil.
S
EXAMPLE 39 (METHOD 12)
[3-Chloro-4-(1-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid
2-trimethylsilanyl-ethyl ester
(3-Chloro-4-vinyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid 2-trimethylsilanyl-ethyl ester (2.6 g}
is
added to a solution of mercuric acetate (3.48 g) in water (7 mL) and
tetrahydrofuran
(5.25 mL) and the mixture is stirred for approximately 15 hours. 3N Aqueous
sodium hydroxide (8.7 mL) and a 0.5 M solution of sodium borohydride in 3N
aqueous sodium hydroxide (8.7 mL) are then added and stirring is continued for
6
hours. The solution is then saturated with sodium chloride and extracted with
ethyl
acetate. These organic extracts are then washed with saturated aqueous sodium
chloride and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Following removal of the
solvent
under reduced pressure the residue is chromatographed over silica gel (20%
ethyl
acetate in hexanes is used as the eluant) to provide the desired product as a
white
solid.
EXAMPLE 40 (METHOD 13)
[3-Chloro-4-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
To a stirring suspension of sodium borohydride (0.45 g) in tetrahydrofuran (
13 mL)
at 0 °C is added glacial acetic acid (0.75 mL) and the mixture is
stirred at 0°C for 1
hour. The solution is then warmed to room temperature and (3-chloro-4-vinyl-
phenyl)-carbamic acid 2-trimethylsilanyl-ethyl ester ( 1.0 g) is added. The
reaction is
stirred at room temperature for approximately 15 hours and then heated to
reflux for
approximately 20 hours. The mixture is then cooled and solutions of 5 N
aqueous
sodium hydroxide (0.80 mL) and 30% aqueous hydrogen peroxide (0.56 mL) are
added. After stirnng for an additional 15 hours the layers are separated, the
aqueous
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-65-
layer is extracted three times with diethyl ether, and these organic extracts
are dried
over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Following removal of the solvent under
reduced
pressure the residue is chromatographed over silica gel (40% ethyl acetate in
hexanes
is used as the eluant) to provide the desired product as an amber oil.
EXAMPLE 41 (METHOD 14)
[4-(1-Azido-ethyl)-3-chloro-phenyl]-carbamic acid 2-trimethylsilanyl-ethyl
ester
To a solution of [3-chloro-4-(1-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid 2-
trimethyl-
silanyl-ethyl ester (1.25 g) in tetrahydrofuran (20 mL) at 0 °C under
an atmosphere of
argon is added triphenyl-phosphine (2.6 g), hydrazoic acid (approximately 2.5
molar
equivalents in dichloromethane, prepared by the method of Fieser and Fieser,
Reagents for Organic Synthesis, Vol. 1, pg. 446; Wiley, New York) and diethyl
azodicarboxylate (1.72 g). After approximately 10 minutes the solvent is
removed
under reduced pressure and the residue is chromatographed over silica gel (5%
ethyl
acetate in hexanes is used as the eluant) to provide the desired product as a
colorless
oil.
EXAMPLE 42 (METHOD 15)
[3-Chloro-4-(3-dimethylamino-prop-1-ynyl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid
tert-butyl ester
To a deoxygenated solution of (3-chloro-4-iodo-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-
butyl
ester (10.0 g) in triethylamine (120 ml) is added 1-dimethylamino-2-propyne
(2.82
g), bis(triphenyl-phosphine)palladium(II) chloride (0.4 g), and cuprous iodide
(0.054
g). The mixture is stirred at room temperature under an atmosphere of argon
for
approximately 6 hours and is then heated briefly (ca. 10 minutes) to
60°C. The
reaction mixture is then cooled, filtered through diatomaceous earth, and the
solvent
is removed by evaporation under reduced pressure. The residue is dissolved in
ethyl
acetate, washed three times with water, once with saturated aqueous sodium
chloride,
and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solvent is removed by
evaporation
under reduced pressure, and the residue is chromatographed over silica gel
(80%
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-66-
ethyl acetate in hexanes is used as the eluant) to give the purified product
as an amber
oil that solidified on standing.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
[3-Chloro-4-(3-dimethylamino-prop-1-ynyl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
[3-(4-Methoxy-phenyl)-prop-2-ynyl]-dimethyl-amine
4-(3-Dimethylamino-prop-1-ynyl)-benzonitrile
Dimethyl-[3-(4-nitro-phenyl)-prop-2-ynyl]-amine
EXAMPLE 43 (METHOD 16)
[3-Chloro-4-(3-dimethylamino-acryloyl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
To an ice cold solution of [3-chloro-4-(3-dimethylamino-prop-1-ynyl)-phenyl]-
carbamic acid tert-butyl ester (4.0 g) in dichloromethane (30 ml) is added in
small
portions 3-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (2.34 g). After the reaction is stirred at
0°C for
minutes, the mixture is passed over twenty weight equivalents of basic alumina
15 (Broclcmann Grade I, 150 mesh) and the N-oxide is eluted using a solution
of 5%
methanol in dichloromethane. All fractions containing the desired amine N-
oxide
were combined and evaporated to near dryness under reduced pressure. The
residue
is treated successively three times with small portions of methanol (ca. 50
ml)
followed by evaporation to near dryness under reduced pressure, and the volume
of
20 the solution is adjusted to 250 mL by addition of methanol. The methanolic
solution
of the N-oxide is then heated to reflux for approximately 15 hours, then
cooled, and
the solvent is evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure. The residue is
purified
by chromatography over silica gel (80% ethyl acetate in hexanes is used as the
eluant) to give the desired product as a pale yellow solid.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-67-
EXAMPLE 44 (METHOD 17)
(3-Chloro-4-isoxazol-5-yl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
A solution of [3-chloro-4-(3-dimethylamino-acryloyl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid
tert-
butyl ester (270 mg) in dioxane (3 ml) is treated with hydroxylamine
hydrochloride
(122 mg) and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for 10 days. The
mixture is
diluted with ethyl acetate, washed successively with water, 5% aqueous sodium
bicarbonate, saturated aqueous sodium chloride, and then dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate. The solvent is removed by evaporation under reduced
pressure
and the resulting residue is chromatographed over silica gel (33% ethyl
acetate in
hexanes is used as the eluant) to provide the desired product as a colorless
solid.
EXAMPLE 45 (METHOD 18)
[3-Chloro-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
A solution of [3-chloro-4-(3-dimethylamino-acryloyl)-phenyl]-carbamic acid
tert-
butyl ester (250 mg) in ethanol (1.25 ml) is treated with hydrazine hydrate
(0.25 ml)
and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for 3 hours. The mixture is
then
diluted with 30 mL of diethyl ether, washed three times with water, once with
saturated aqueous sodium chloride, and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate.
The solvent is removed by evaporation under reduced pressure and the resulting
residue is chromatographed over silica gel (67% ethyl acetate in hexanes is
used as
the eluant) to provide the desired product as an oil.
EXAMPLE 46 (METHOD 19A)
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitrophenyl}-2-thiomorpholino-4-yl-acetamide
To a solution N-(chloroacetyl)-2-chloro-4-nitroaniline (3.80 g) in
tetrahydrofuran (SO
mL) is added thiomorpholine (10 mL) and the solution allowed to stand for 1
hour.
This reaction mixture is poured into water a pale yellow solid is collected
and then
recrystallized from hot 2-propanol to give a pale yellow crystalline solid.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-68-
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
(4-{2-[Bis-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-amino]-acetylamino}-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-
butyl
ester
[4-(2-Dimethylamino-acetylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
{ 4-[3-(2-Dimethylamino-ethoxy)-benzoylamino]-phenyl }-carbamic acid tert-
butyl
ester
{ 4-[3-(2-Morpholin-4-yl-ethoxy)-benzoylamino]-phenyl }-carbamic acid tert-
butyl
ester
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-dimethylamino-acetamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-piperidin-1-yl-acetamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-morpholin-4-yl-acetamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-dipropylamino-acetamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-thiomorpholin-4-yl-acetamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-diethylamino-acetamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-pyrrolidin-1-yl-acetamide
2-Azepan-1-yl-N-(2-chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-acetamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-(2-methyl-piperi din-1-yl)-acetamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-(3-methyl-piperidin-1-yl)-acetamide
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-(4-methyl-piperidin-1-yl)-acetamide
EXAMPLE 47 (METHOD 19B)
N-(2-Chloro-4-nitrophenyl)-2-(2-dimethylaminoethylsulfanyl)acetamide
To a solution of N-(chloroacetyl)-2-chloro-4-nitroaniline (3.01 g) in N,N-
dimethylformamide ( 100 mL) is added powdered sodium carbonate (6.0 g) and 2-
dimethylaminoethanethiol hydrochloride (6.0 g). The mixture is stirred for 1
hour at
25° C, poured into water and extracted into ethyl acetate. The ethyl
acetate solution
is dried over anhydrous potassium carbonate and concentrated under reduced
pressure
to give an oil. The oil is crystallized from toluene-hexanes (3:1 ) to yield a
pale
yellow crystalline solid.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-69-
EXAMPLE 48 (METHOD 20)
(4-tert-butoxycarbonylamino-2-chloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid 2
piperidin-1-yl-ethyl ester
To a suspension of 1,1-carbonyl-di-(1,2,4)-triazole (4.0 g) in dichloromethane
(40
mL) is added a solution of (4-amino-3-chloro-phenyl) carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
(5.0 g) in dichloromethane (45 mL) dropwise over 20 minutes. The reaction is
stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes at which point a precipitate forms.
To
this mixture is added piperidineethanol (6.6 mL) and tetra-hydrofuran (20 mL)
is
added to maintain homogeneity. After heating at reflux overnight the reaction
is
cooled and then poured into water, the organic layer separated and then washed
with
saturated aqueous sodium chloride. The solution is dried over anhydrous sodium
sulfate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to a crude oil that
is purified
by chromatography over silica gel (5% methanol in dichloromethane is used as
the
eluant) to give the desired product as a white foam.
EXAMPLE 49
5-Phenyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid methyl ester
A solution of ethyl benzoylacetate ( 1.1 g) in acetonitrile ( 10 mL) is
treated with 4-
methylbenzenesulfonyl azide (1.3 g) and triethylamine (1.6 g). After stirring
overnight at room temperature, the reaction is concentrated under reduced
pressure
and the resulting crude product is dissolved in ethyl acetate and washed with
1 N
sodium hydroxide. The organic layer is then dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to yield a yellow
oil. This
oil is taken into dichloromethane and filtered through a pad of hydrous
magnesium
silicate, eluting with dichloromethane to give the partially purified
diazoketone as a
colorless oil. A sample of the diazoketone from above ( 1.2 g) is dissolved in
toluene
(25 mL) and treated with 2,4-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-dithia-2,4-diphosphetane-
2,4-disulfide (2.8 g) and the reaction is heated to reflux. After 3 hours, the
reaction is
cooled to room temperature, loaded onto a pad of silica gel and eluted with
dichloromethane. After removing the solvent under reduced pressure, the
resulting
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-70-
oil is purified by chromatography over silica gel (30% diethyl ether in
petroleum
ether is used as the eluant) and then recrystallized from hexanes to give the
desired
product as pale yellow needles.
S Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compound was prepared:
5-Phenyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid ethyl ester
5-Methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid methyl ester
EXAMPLE 54
Ethyl benzoylacetate semicarbazide
Ethyl benzoylacetate (5.0 g) is dissolved in methanol ( 10 mL) and added
rapidly to a
hot solution of semicarbazide hydrochloride (29 g) in water ( 130 mL). To this
is
added pyridine (4.1 g) and after heating to reflux for 5 minutes, the reaction
mixture
is cooled to -20 °C overnight. The resulting solid semicarbazone is
collected by
filtration, washed with water and then diethyl ether to give the desired
product as
white crystals.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compound was prepared:
Ethyl (Z)-3-[(aminocarbonyl)hydrazono]-4,4,4-trifluorobutanoate
3-[(Z)-2-(Aminocarbonyl)hydrazono]-3-phenylpropanoic acid ethyl
ester
3-[(E)-2-(Aminocarbonyl)hydrazono]-3-(3-furyl)propanoic acid ethyl
ster
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-71-
EXAMPLE 51
5-Phenyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester
A solution of ethyl benzoylacetate semicarbazone (2.5 g) in neat thionyl
chloride (5
mL) is stirred at 0 °C for 1 hour. Dichloromethane is then added (25
mL), the excess
thionyl chloride is destroyed slowly with saturated aqueous sodium
bicarbonate. The
precipitate which forms on quenching is removed by filtration and the filtrate
is
extracted with dichloromethane. Pooled organic extracts are dried over
anhydrous
magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure.
Chromatography over silica gel (50% hexanes in dichloromethane is used as the
eluant) affords the desired product as a colorless oil.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
4-Methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
4-Phenyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester
4-Furan-3-yl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-S-carboxylic acid ethyl ester
EXAMPLE 52
4-Methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid
4-Methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester (1.7 g) is
dissolved in
methanol ( 15 mL) and treated with 1 N sodium hydroxide ( 16 mL). After
stirring at
room temperature for 1 hour, the reaction is treated with concentrated
hydrochloric
acid ( 1.5 mL) and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting turbid
aqueous
layer is extracted twice with diethyl ether and the pooled organic layers are
dried over
anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure
to
give the desired compound as a white powder.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-72-
3-Ethoxycarbonylmethoxy-benzoic acid
5-Furan-3-yl-(1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid
Thiazole-4-carboxylic acid
4-Methyl-[I,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid
S-Methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid
EXAMPLE 53 (METHOD 25)
Trifluoro-methanesulfonic acid 4-chloro-5-methoxy-2-nitro-phenyl ester
To a solution of 4-chloro-5-methoxy-2-nitro-phenol (6.5 g) in dichloromethane
(150
mL) at 0 °C under an atmosphere of argon is added triethylamine ( 10 g)
and then a
solution of trifIuoro-methanesulfonic anhydride (13.5 g) in dichloromethane
(30 mL).
The solution is stirred at 0 °C for 10 minutes, and is then
diluted with
dichloromethane and washed successively with saturated aqueous sodium
bicarbonate
and saturated aqueous sodium chloride. After drying over anhydrous sodium
sulfate
the solvent is removed by evaporation under reduced pressure and the residue
is
dissolved in a solution of 20% dichloromethane in hexanes and passed through a
short column of hydrous magnesium silicate (20% dichloromethane in hexanes is
used as the eluant). Product containing fractions are pooled and the solvents
removed
by evaporation under reduced pressure to give the desired product as a yellow
oil.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
Trifluoro-methanesulfonic acid 4-chloro-S-methoxy-2-vitro-phenyl ester
Trifluoro-methanesulfonic acid 4-chloro-2-vitro-phenyl ester
Trifluoro-methanesulfonic acid 2-chloro-6-vitro-phenyl ester
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-73-
EXAMPLE 54 (METHOD 26)
[4-(3-Dimethylamino-benzoylamino)-phenyl)-carbamic acid t-butyl ester
A solution of [4-(3-amino-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid t-butyl ester
(SOS
S mg), sodium cyanoborohydride (250 mg), acetic acid (3 drops) and 40 %
aqueous
formaldehyde (4 mL) in 1:2 tetrahydrofuran-methanol (IS mL) is stirred for 15
minutes, and then poured into saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate and
extracted
into ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate solution is dried over anhydrous
potassium
carbonate and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a solid which is
recrystallized from acetonitrile to provide a pale pink crystalline solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
[4-(3-Dimethylamino-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(3-Bromo-S-trifluoromethyl-phenyl}-dimethyl-amine
N-(3-Chloro-S-dimethylamino-phenyl}-acetamide
EXAMPLE 55 (METHOD 27)
N-(4-Aminophenyl)-2-hydroxybenzamide
To a solution of 2-(4-aminophenylcarbamoyl) phenyl acetate (580 mg) in
methanol
( I O mL) is added saturated sodium bicarbonate (2 mL) and water (3 mL). The
mixture is heated at 80° C for 30 minutes, then poured into half-
saturated aqueous
sodium chloride and extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate solution
is dried
over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure to give
an oil
which is then triturated with diethyl ether to provide the desired product as
a white
solid.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-74-
EXAMPLE 56 (METHOD 28)
[4-(3-(Hydroxybenzoylamino)phenyl}carbamic acid t-butyl ester
To a solution of of 3-(4-aminophenylcarbamoyl) phenyl acetate (4.34 g) in
methanol
(75 mL) is added 0.1 N aqueous sodium hydroxide (25 mL) and tetrahydrofuran
(25
mL). This solution is heated at 40° C for 30 minutes, then cooled,
poured into 1 M
hydrochloric acid and extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate solution
is dried
over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure to give
a
white solid, which is further purified by trituration with diethyl ether.
EXAMPLE 57 (METHOD 29)
N-(4-Aminophenyl)-2-hydroxymethylbenzamide
To a solution of N-(4-aminophenyl)phthalimide (332 mg) in tetrahydrofuran (4
mL)
is added lithium borohydride (1.0 g) and the mixture is stirred for 1 hour at
25° C.
The mixture is poured into water and extracted into ethyl acetate. The ethyl
acetate
solution is dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced
pressure to give a white foam, which when triturated with diethyl ether
provides the
desired product as a white powder.
EXAMPLE 58 (METHOD 30)
(3-Chloro-5-dimethylamino-phenyl)-carbamic acid tent-butyl ester
To a solution of (3-amino-5-chloro-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(0.32 g) in
toluene (10 mL) is added aqueous formaldehyde (37%, 1.5 mL) then 10% palladium
on carbon (0.50 g) and the mixture is stirred under an atmosphere of hydrogen
for
approximately 15 hours. The solution is then filtered through diatomaceous
earth and
the filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue is
chromatographed
over silica gel (50% dichloromethane in hexanes is used as the eluant) to
provide the
desired product as a white solid.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-75-
EXAMPLE 59 (METHOD 35)
N-(4-{3-[3,5-Dichloro-4-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-thioureido}
phenyl)-acetamide
To a solution of acetic acid 2-{4-[3-(4-acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-
dichloro-
phenoxy }-ethyl ester (0.16 g) in a 1:1 mixture of tetrahydrofuran and
methanol (2.5
mL) is added 1 N aqueous sodium hydroxide ( 1 mL) and the mixture is stirred
for
approximately 2 hours at room temperature. The solution is then poured into 2
M
aqueous hydrochloric acid (3 mL), extracted into ethyl acetate, and the
extracts are
dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent is removed by evaporation
under
reduced pressure and the residue is triturated with diethyl ether to provide
the desired
product as a white solid.
EXAMPLE 60 (METHOD 36)
{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy}-acetic acid
To a solution of {4-[3-(4-acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro-
phenoxy}-
acetic acid ethyl ester (0.29 g) in a 1:1 mixture of tetrahydrofuran and
methanol (4
mL) is added 1 N aqueous sodium hydroxide (2 mL) and the mixture is stirred
for
approximately 2 hours at room temperature. The solution is then poured into 2
M
aqueous hydrochloric acid (5 mL), extracted into ethyl acetate, and the
extracts are
dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent is removed by evaporation
under
reduced pressure and the residue is triturated with diethyl ether to provide
the desired
product as a white solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
{ 4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy }-acetic acid
{ 2-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-4-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy }-acetic
acid
{ 4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy }-acetic
acid
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-76-
EXAMPLE 61 (METHOD 37)
Benzoic acid 2-{4-[3-(4-acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro
phenoxy}-ethyl ester
To an ice cooled solution of N-(4-{3-[3,5-dichloro-4-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-
phenyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-acetamide (0.20 g) in pyridine (2 mL) and tetrahydrofuran
(0.5
mL) is added benzoyl chloride (0.08 g) and the mixture is stirred at 0
°C for 1.5
hours. The mixture is then diluted with ethyl acetate, washed successively two
times
with 2% aqueous hydrochloric acid, once with saturated aqueous sodium
chloride,
then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. After removal of the solvent under
reduced pressure the residue is chromatographed over silica gel (5% methanol
in
dichloromethane is used as the eluant) and product containing fractions are
combined, evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue is recrystallized
from
acetone-hexanes to provide the desired product as a white powder.
EXAMPLE 62 (METHOD 38)
Methanesulfonic acid 2-{4-[3-(4-acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro
phenoxy}-ethyl ester
To an ice cooled solution of N-(4-{3-[3,S-dichloro-4-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-
phenyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-acetamide (0.20 g) in pyridine (2 mL) and tetrahydrofuran
(0.5
mL) is added methanesulfonyl chloride (0.11 g) and the solution is stirred at
0 °C for
45 minutes. The reaction mixture is then diluted with ethyl acetate, washed
successively twice with 2% aqueous hydrochloric acid, once with saturated
aqueous
sodium chloride, and then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. After
removing
the solvents by evaporation under reduced pressure the resulting residue is
recrystallized from acetone-hexanes to give the desired product as a white
powder.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-77-
EXAMPLE 63 (METHOD 39)
N-(4-{3-[3,5-Dichloro-4-(2-dimethylamino-ethoxy)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
acetamide
S To a solution of methanesulfonic acid 2-{4-[3-(4-acetylamino-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
2,6-dichlorophenoxy}-ethyl ester (0.33 g) in tetrahydrofuran (6 mL) is added
aqueous dimethyl-amine (8.8 M, 0.5 mL) and the mixture is stirred at room
temperature for 5 days. The reaction mixture is then diluted with ethyl
acetate, then
washed with saturated aqueous sodium chloride and dried over anhydrous
magnesium
sulfate. After removal of the solvent under reduced pressure the residue is
chromatographed over silica gel (pure methanol is used as the eluant). Pooled
product containing fractions are evaporated under reduced pressure and the
residue is
recrystallized from acetonitrile to provide the desired product as a white
powder.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
N-(4-{ 3-[3,5-Dichloro-4-(2-dimethylamino-ethoxy)-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-
acetamide
Benzoic acid 2-{4-[3-(4-acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy}-
ethyl
ester
EXAMPLE 64 (METHOD 40)
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[4-(1-amino-ethyl)-3-chloro-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
To a solution of tin(II) chloride dihydrate (0.25 g) in methanol (2.5 mL) is
added
furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[4-(1-azido-ethyl)-3-chloro-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide (0.22 g) and the solution is stirred for approximately I S hours
at room
temperature. The solution is then diluted with ethyl acetate, washed
successively
with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate then saturated aqueous sodium
chloride,
then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. After removal of the solvent by
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
_78_
evaporation under reduced pressure the residue is chromatographed over silica
gel
(8% methanol in dichloro-methane containing 1 % triethylamine is used as the
eluant)
to provide the desired product as a yellow solid.
EXAMPLE 65 (METHOD 41)
(1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-isothiocyanato-phenyl)-amide
To a ice cooled solution of 1,1'-thiocarbonyldiimidazole (7.28 g) in
tetrahydrofuran
(50 mL) is added [1,2,3]-thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl) amide
(9.0
g) in tetrahydrofuran (100 mL). After approximately one hour the solvent is
removed by evaporation and the residue is dissolved in ethyl acetate. Diethyl
ether is
added to precipitate the crude product, which is then collected by filtration,
dissolved
in dichloromethane, and passed through a plug of hydrous magnesium silicate.
After
removal of solvents, the residue is recrystallized from ethyl acetate-hexanes
to
provide the desired product as a slightly yellow solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
2-Fluoro-N-(4-isothiocyanato-phenyl)-benzamide
Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-isothiocyanato-phenyl)-amide
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-isothiocyanato-phenyl)-amide
Thiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-isothiocyanato-phenyl)-amide
EXAMPLE 66 (METHOD 42)
N,N-Dimethyl-5-trifluoromethyl-benzene-1,3-diamine
To a solution of 3-amino-5-bromo-benzotrifluoride (1.0 g) in degassed (argon)
tetrahydrofuran (2 mL) is added bis-(tri-o-tolylphosphino)palladium (0.15 g),
a
solution of dimethylamine in tetra-hydrofuran (2M, 4.2 mL), and a solution of
lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide in tetrahydrofuran (1M, 10.4 mL). The
reaction
mixture is heated in a sealed vessel to 100°C for approximately 2.5
hours to complete
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-79-
10
the reaction. The mixture is then cooled to room temperature, quenched by
addition
of water, and diluted with ethyl acetate. The product is extracted three times
into S%
aqueous hydrochloric acid, and pooled acidic extracts are then basified with
cooling
by addition of SN aqueous sodium hydroxide. This basic solution is then
extracted
with ethyl acetate, and these pooled organic extracts are washed with
saturated
aqueous sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and
evaporated to
dryness under reduced pressure. The resulting residue is chromatographed over
silica
gel (20-30% ethyl acetate in hexanes is used as the eluant) to provide the
desired
product as a slightly tinted solid.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
3-(4-Methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-5-trifluoromethyl-phenylamine
3-Morpholin-4-yl-S-trifluoromethyl-phenylamine
3-Piperidin-1-yl-5-trifluoromethyl-phenylamine
3-Pyrrolidin-1-yl-S-trifluoromethyl-phenylamine
N,N-Dimethyl-5-trifluoromethyl-benzene-1,3-diamine
N-Isobutyl-N-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-benzene-1,3-diamine
N-Butyl-N-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-benzene-1,3-diamine
EXAMPLE 67 (METHOD 43)
(3-Isobutyl-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
To a sealed tube containing tetrahydrofuran (5 mL) that is capped with a
rubber
septum and cooled in a dry ice-acetone bath is bubbled isobutylene for about 5
minutes. A solution of 9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane in tetrahydrofuran (0.5 M,
11
mL) is added, the vessel is sealed with a teflon cap, slowly warmed to room
temperature and kept at room temperature for approximately 2.5 hours. The
mixture
is then re-cooled in a dry ice-acetone bath, the teflon cap is replaced by a
rubber
septum, and argon is bubbled through the mixture with venting to removed the
excess
isobutylene. A solution of (3-bromo-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid
tert-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 80 -
butyl ester (1.7 g) in tetrahydrofuran (12 mL) is added, followed by [1,1'-
bis(diphenylphosphino)-ferrocene]palladium(II) chloride-dichlormethane complex
(0.12 g), and then 3N aqueous sodium hydroxide. The vessel is again sealed
with the
teflon cap and is then heated to 65°C for approximately 15 hours. The
mixture is
then cooled to room temperature, diluted with hexanes, washed with water,
saturated
aqueous sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and
evaporated
under reduced pressure. The resulting oil is chromatographed over silica gel
(5°h
ethyl acetate in hexanes is used as the eluant) to provide the desired product
as a
white powder.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
(3-(2-Methyl-butyl)-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
(3-Isobutyl-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
I S EXAMPLE 68 (METHOD 44)
2-(3,5-Dichloro-phenylsulfanyl)-ethylamine
To a solution of (3,5-dichlorophenylthio)acetonitrile ( 1.2g) in 3.0 mL of
ethylene
glycol dimethyl ether is added 0.6I mL of lOM borane dimethyl sulfide complex
and
the mixture heated at reflux for 0.5 hours. The reaction is cooled in an ice
bath and
2.0 mL of water and 2.0 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid is added. This
mixture
is heated at reflux for 0.5 hr. The clear solution is then cooled and basified
with SN
sodium hydroxide and extracted with ether. The ether extract is dried over
potassium
carbonate, filtered and concentrated to give l.Og of a colorless oil.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
2-(3-Bromo-phenylsulfanyl)-ethylamine
2-(4-Bromo-phenoxy)-ethylamine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-81-
2-(4-Iodo-phenoxy)-ethylarnine
2-(3,4-Dichloro-phenoxy)-ethylamine
2-{3-Chloro-phenylsulfanyl)-ethylamine
2-(3,4-Dichloro-phenylsulfanyl)-ethylamine
3-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-propylamine
2-(2-Fluoro-phenoxy)-ethylamine
2-(2-Chloro-phenoxy)-ethylamine
2-(3-Bromo-phenoxy)-ethylamine
2-(3-Fluoro-phenoxy)-ethylamine
2-(3-Iodo-phenoxy)-ethylamine
2-(3,5-Dichloro-phenylsulfanyl)-ethylamine
2-Phenylsulfanyl-ethylamine
1-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-ethylamine
EXAMPLE 69 (METHOD 45)
N-(1-Naphthalen-2-yl-ethyl)-formamide
A mixture of 2-acetylnaphthylene (3.0 g), ammonium formate (11.0 g), formic
acid
(3.3 mL}, and formamide (3.5 mL) is heated at 190°C for 3 hours. The
mixture is
cooled, poured into water and extracted with ether. The ether extract is dried
with
anhydrous potassium carbonate, filtered and concentrated to give a yellow oil,
which
is crystallized from toluene-hexanes to give a white solid, 1.97 g.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
N-[ 1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-2-methyl-propyl)-formamide
N-( 1-Naphthalen-2-yl-ethyl)-formamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-82-
EXAMPLE 70 (METHOD 46)
1-(2-Naphthyl)ethylamine
A mixture of N-(I-naphthalen-2-yl-ethyl)-formamide (1.12 g), ethanol (10 mL)
and 5
N sodium hydroxide (10 mL) is heated at reflux for 1 hour. The solution is
cooled,
poured into water and extracted with ether. The ether solution is dried with
anhydrous potassium carbonate, filtered and concentrated to give the product
(0.95 g)
as a pale yellow oil.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
I-(3-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-2-methyl-propylamine
[3-( 1-Amino-ethyl)-phenyl]-dimethyl-amine
3-(1-Amino-ethyl)-benzonitrile
EXAMPLE 71 (METHOD 47)
I S 1-(3-Trifiuoromethyl-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
Methoxylamine hydrochloride (2.33 g) is added to a solution of 3'-
(trifluoromethyl)-
acetophenone (1.5 g) in ethanol {20 mL) and pyridine (2 mL). The solution is
heated
at reflux for 45 minutes. The reaction mixture is then cooled, concentrated
under
reduced pressure and partitioned between water and ethyl acetate. The aqueous
layer
is extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers are washed with
saturated aqueous sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and
concentrated under reduced pressure to give the desired product as a colorless
oil
(1.61 g).
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-83-
3,S-Bis-trifluoromethyl-benzaldehyde oxime
1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-propan-I-one O-methyl-oxime
1-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-(3-Bromo-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-(3-Chloro-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-p-Tolyl-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
I -(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-pentan- I -one O-methyl-oxime
1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-2-phenyl-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
I-o-Tolyl-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-m-Tolyl-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-(2-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
3-( 1-Methoxyimino-ethyl)-benzonitrile
4-( I -Methoxyimino-ethyl)-benzonitrile
1-(4-Methoxy-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-(2-Methoxy-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-(4-Dimethylamino-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
I-(2-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
I-(3-Methoxy-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-(3-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-(4-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-Furan-2-yl-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-Pyridin-4-yl-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-(1-Methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-Thiophen-3-yl-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-phenyl-methanone O-methyl-oxime
1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
4-( 1-Methoxyimino-ethyl)-benzenesulfonamide
4-( 1-Methoxyimino-ethyl)-N,N-dimethyl-benzenesulf onamide
I-[4-(Piperidine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
4-( 1-Methoxyimino-ethyl)-N,N-dipropyl-benzenesulfonamide
2-Fluoro-N-[4-( 1-methoxyimino-ethyl)-phenyl]-benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-84-
1-(3,5-Bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime
1-[4-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-I-ethanone, O-methyloxime
1-[4-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-I-ethanone, O-methyloxime
1-[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-yl-1-ethanone, O-methyloxime
1-(4-Methylphenyl)-1-ethanone, O-methyloxime
1-[4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-benzyloxime
1-[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
1-[3-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
I-[2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
1-[2-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
I-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
I-[2,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
I-(3-bromophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
I-(3-methylphenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
1-[4-(4-morpholinyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(2-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(3,4-difluorophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
1-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
1-[3-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
I-[4-fluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(4-chloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(2,5-difluorophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(2-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
I-(3,4-dibromophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
1-(2-bromophenyl)ethanone O-methyloxime
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-85-
EXAMPLE 72 (METHOD 48)
1-(2-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
Sodium borohydride (1.17 g) is added slowly to a flask containing zirconium
S tetrachloride (1.8 g) in tetrahydrofuran (27 mL). A solution of 1-(2-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime (1.34 g) in tetrahydrofuran (7.7 mL) is added
and
the resulting solution is stirred at 25 °C for 12 hours. The reaction
mixture is then
cooled to 0 °C and water (16 mL) is slowly added. Excess ammonium
hydroxide is
added and the solution is extracted twice with ethyl acetate. The organic
portion is
washed twice with 1N hydrochloric acid. The aqueous (acid) layer is basified
with
sodium hydroxide and extracted twice with ethyl acetate. The organic layer is
then
washed with saturated aqueous sodium chloride and dried over anhydrous
magnesium
sulfate. The solvent is removed under reduced pressure to provide the desired
product as a yellow oil (0.20 g).
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
1-(3-Methoxy-phenyl)-ethylamine
1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-propylamine
1-Naphthalen-2-yl-ethylamine
4-( 1-Amino-ethyl)-benzonitrile
1-(4-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
1-(4-Methoxy-phenyl)-ethylamine
1-Prop-2-ynyl-pyrrolidine
1-(2-Methoxy-phenyl)-ethylamine
1-m-Tolyl-ethylamine
1-(2-Bromo-phenyl)-ethylamine
1-o-Tolyl-ethylamine
C-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-C-phenyl-methylamine
1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-pentylamine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCTNS99/28838
- 86 -
1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-2-phenyl-ethylamine
1-(2-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
I-(3-Bromo-phenyl)-ethylamine
I-(3-Chloro-phenyl}-ethylamine
[4-( I -Amino-ethyl)-phenyl]-dimethyl-amine
1-( 1-Methyl- I H-pyrrol-2-yl)-ethylamine
1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]propylamine
1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-I-butanamine or I-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)-
phenyl]butylamine
1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1-pentanamine
1-(4-methylphenyl)ethanamine
1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethylamine
1-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethylamine
1-(3-methylphenyl)ethanamine
1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethanamine
I-(2-Bromo-phenyl)-ethylamine
I-(2-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
1-(3-Bromo-phenyl)-ethylamine
1-{3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-ethylamine
4-( 1-Amino-ethyl)-N,N-dimethyl-benzenesulfonamide
1-[4-(Piperidine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-ethylamine
1-Quinolin-6-yl-ethylamine
1-(3,S-Bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
4-[( 1 S)-I-aminoethyl]benzonitrile
(S)-alpha-Methyl-3,S-bis(trifluoromethyl)-benzenemethanamine(S)-alpha-Methyl-
3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)-benzenemethanamine
I-Biphenyl-4-yl-ethylamine
1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethylamine
1-[4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanamine
1-[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanamine
N- { 4-[( 1 R)-1-aminoethyl]phenyl }-1,2,3-thiadiazole-4-carboxamide
N- { 4-[( 1 S)-1-aminoethyl]phenyl }-1,2,3-thiadiazole-4-carboxamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-87-
1-[3-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethylamine
I-[2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethylamine
1-[2-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethylamine
1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethylamine
1-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)ethylamine
I-[2,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethylamine
1-(2-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethylamine
I-(3,4-difluorophenyl)ethylamine
1-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)ethylamine
1-(3-fluorophenyl)ethylamine
I-(2,4-difluorophenyl)ethylamine
1-[3-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethylamine
I-[4-fluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethylamine
1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethylamine
I-(4-chloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethylamine
1-(3,4-dibromophenyl)ethylamine
1-(2-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)ethanamine 1-(2-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)ethylamine
EXAMPLE 73 (METHOD 49)
(2-Fluoro-5-trifluoromethyl-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
A solution of 2-fluoro-5-trifluoromethylphenol (25 g) in reagent grade acetone
(0.55
L) is treated with solid potassium carbonate (7.7 g) followed by the rapid
addition of
neat bromoacetonitrile ( 10 mL). The heterogenous mixture is stirred
vigorously for
approximately 20 hours whereupon it is poured into water and extracted into
diethyl
ether. The combined ether extracts are washed with saturated sodium chloride
and
dried over anhydrous potassium carbonate. Filtration and concen-tration under
reduced pressure gives a pale orange solid which is then chromatographed on
silica
g$1, eluting with dichloromethane, to give the desired product as white solid
(28.3 g).
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
1 S compounds were prepared:
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
_g8_
(3-Bromo-phenylsulfanyl)-acetonitrile
(3-Chloro-phenylsulfanyl)-acetonitrile
(4-Iodo-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
(3-Trifluoromethyl-phenylsulfanyl)-acetonitrile
(3,5-Dichloro-phenylsulfanyl)-acetonitrile
(3,4-Dichloro-phenylsulfanyl}-acetonitrile
(3,4-Dichloro-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
(2-Fluoro-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
(3-Fluoro-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
(2-Chloro-phenoxy}-acetonitrile
(3-Bromo-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
(2-Fluoro-5-trifluoromethyl-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
(3-Iodo-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
(4-Bromo-phenoxy)-acetonitrile
EXAMPLE 74 (METHOD 50)
3-Fluoro-5-tritluoromethylphenethylamine tosylate
A solution of 2.5 g of 3-fluoro-5-trifluoromethylphenylacetonitrile and 2.34 g
( 12.3
mmol) of p-toluenesulfonic acid in 75 ml of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether
is
hydrogenated for 3 hours at room temperature at 40 psi, using 200 mg 10%
palladium on carbon catalyst. The catalyst is filtered off and the solvent
evaporated to
half the volume. Upon standing, the p-toluenesulfonic acid salt of the desired
3-
fluoro-5-trifluoromethylphenethylamine crystallizes. The white crystals, 4.268
(91 %)
are collected by filtration.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
2-(3,5-Difluoro-phenyl)-ethylamine
2-(4-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
2-(3,4-Difluoro-phenyl)-ethylamine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
_ 89 _
2-(2-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethylamine
2-(3-Fluoro-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
2-(2-Fluoro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
2-(2,4-Bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
2-(4-Fluoro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethylamine
EXAMPLE 75 (METHOD 51)
(4-Aminomethyl-2-triouoromethyl-phenyl}-dimethyl-amine
A solution of 4-dimethylamino-3-trifluoromethylbenzonitrile (0.35 g) in
tetrahydrofuran (2 mL) is slowly added to a suspension of lithium aluminum
hydride
(0.1 g) in tetrahydrofuran (2 mL) at 0 °C and stirred under an
atmosphere of argon
for 2 hours. While at 0 °C water (0.1 mL) is slowly added followed by
5% sodium
hydroxide (0.1 mL) and water (0.3 mL). The resulting gray solid is filtered
and
washed with tetrahydrofuran. The filtrates are collected and concentrated
under
reduced pressure and the resulting oil is chromatographed over silica gel
(15%o
methanol in methylene chloride is used as the eluant) to provide the desired
product
as a pale orange oil (0.164 g}.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
4-Piperidin-1-yl-3-trifluoromethyl-benzylamine
(4-Aminomethyl-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-dimethyl-amine
4-(4-Methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-3-trifluoromethyl-benzylamine
(3-Aminomethyl-S-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-dimethyl-amine
[3-(2-Amino-ethyl)-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl]-dimethyl-amine
[4-(2-Amino-ethyl)-2-methyl-phenyl]-dimethyl-amine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-90-
EXAMPLE 76 (METHOD 52)
3-Dimethylamino-5-tritluoromethyl-benzaldehyde
Diisobutylaluminum hydride (10 mL of a IM solution in methylene chloride) is
added dropwise to a solution of 3-dimethylamino-S-trifluoromethylbenzonitrile
(1.06
g) in methylene chloride (25 mL) at 0 °C and the mixture stirred for 2
hours. While
still at 0 °C a saturated aqueous solution of sodium potassium tartrate
(8 mL) is
slowly added and the solution is stirred for 1.5 hours. The reaction mixture
is then
extracted with ethyl acetate, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and
concentrated under reduced pressure to provide the desired product as a yellow
solid
(0.97 g).
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
3-Dimethylamino-5-trifluoromethyl-benzaldehyde
4-Dimethylamino-3-methyl-benzaldehyde
EXAMPLE 77 (METHOD 53)
Dimethyl-[3-(2-vitro-vinyl)-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amine
Nitromethane (0.473 g) is added to a solution of 3-dimethylamino-S-
trifluoromethyl-
benzaldehyde (0.885 g) and ammonium acetate (0.339 g) in acetic acid (3.4 mL)
and
the solution is heated at 110 °C for 6 hours. The reaction mixture is
cooled to 0 °C
and a solid forms which is filtered and washed with 1:1 water-acetic acid.
This solid
is recrystallized from ethanol to provide the desired product as a red solid
(0.39 g).
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
Dimethyl-(3-(2-vitro-vinyl)-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amine
Dimethyl-[2-methyl-4-(2-vitro-vinyl)-phenyl]-amine
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-91 -
EXAMPLE 78 (METHOD 54)
3-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-propionitrile
Diethylazodicarboxylate (5.2 g) is added dropwise to a solution of 4-bromo-
phenethylalcohol (2.01 g), and triphenylphosphine (7.9 g) in diethyl ether (16
mL) at
0 °C. The reaction mixture is stirred for 10 minutes and a solution of
acetone
cyanohydrin (2.6 g) in diethyl ether ( 10 mL) is added. The clear orange
solution is
stirred for 5 minutes at 0 °C and then at 25 °C for 12 hours.
The reaction mixture is
then filtered, and washed with diethyl ether. The filtrate is concentrated
under
reduced pressure and chromatographed over silica gel ( 10% ethyl acetate-
hexanes is
used as the eluant) to provide the desired product as a pale yellow oil (2.04
g).
EXAMPLE 79 (METHOD 55)
1 S 3-Dimethylamino-2-isocyano-acrylic acid ethyl ester
To a solution of ethyl isocyanoacetate (5.0 g) in ethanol ( 100 mL) is added
N,N-
dimethyl-formamide dimethyl acetal (6.5 g) dropwise with stirring over 10
minutes.
The reaction is stirred for 24 hours and the ethanol is evaporated. The
resulting oil is
passed through magnesium silicate using 50% ethyl acetate-hexanes as the
eluant.
The solvents are removed and the resulting oil is crystallized from ethyl
acetate-
hexanes to yield light yellow needles, 3.U g.
EXAMPLE 80 (METHOD 56)
4-Carboethoxythiazole
A solution of 3-dimethylamino-2-isocyano-acrylic acid ethyl ester (1.0 g) and
triethylamine (3.0 g) in tetrahydrofuran (30 mL) is treated with gaseous
hydrogen
sulfide until all starting material is consumed. The mixture is concentrated
to an oil
and purified by column chromatography using silica and 25% ethyl acetate-
hexanes
as the eluant. The purified material (0.61 g) is isolated as an oil.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-92-
EXAMPLE 81 (METHOD 34)
N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-ureido]-phenyl}-
2-fluoro-benzamide
S A suspension of N-(4-amino-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide (0.43 g) in
acetonitrile (4
mL) is treated with 5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxyphenylisocyanate (0.40 g). The
mixture
becomes a solution and is allowed to stand for 12 hours. A white solid forms
and is
collected by filtration (0.79 g). [M+H] 444.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
Ex M+H COMPOUND NAME
NO.
$j 44$ N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-ureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
82 441 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-ureido]-phenyl
}-2-methyl-benzamide
83 435 (1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
ureido]-phenyl }-amide
84 443 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
ureido]-phenyl} amide
85 453 N-{4-[3-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
86 4U9 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-
ureido]-
phenyl}-amide
87 486 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ureido]-phenyl}-2-tluoro-
benzamide
88 458 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
89 476 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
ureido]-phenyl }-amide
90 423 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-benzyl)-
ureido]-
phenyl}-amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-93-
EXAMPLE 9I (METHOD 31)
N-(5-{[({(15)-1-[3,5-his(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethyl}amino)carbothioyl]
amino}-2-pyridinyl)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide
A mixture of N-(5-isothiocyanato-2-pyridinyl)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide (0.36
g)
and (S)-alpha-methyl-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)-benzenemethanamine (0.36 g) is
heated with acetonitrile (10 mL) until all solids are dissolved. The solution
is allowed
to stand for 12 hours. A white solid forms and is collected by filtration
(0.40 g).
[M+H] 520.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
EX. M+H COMPOUND NAME
NO.
92 506 [3-Chloro-5-(3-{4-[([1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-carbamic acid, tert-butyl
ester
93 409 1-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(4-morpholin-4-yl-phenyl)-
thiourea
94 370 1-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-
thiourea
95 338 1-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-p-tolyl-thiourea
96 414 {4-[3-(S-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenylsulfanyl}-
acetic
acid
97 384 1-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-[4-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-
thiourea
98 340 1-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-thiourea
99 395 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-N-
methyl-
acetamide
100 381 N-{3-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
101 411 {4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-carbamic
acid
ethyl ester
102 319 1-(2,4-Dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-thiourea
103 346 N-{4-[3-(2,4-Dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
104 316 N-{4-[3-(4-Methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
105 316 N-{4-[3-(2-Methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-94-
106 351 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
107 351 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
108 371 N-{4-[3-(3,S-Dichloro-4-hydroxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
109 385 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
110 381 N-{4-[3-(4-Chloro-2,S-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
111 389 N-{4-[3-(2-Chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl
}-acetamide
lI2 389 N-{4-[3-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
113 422 Benzoic acid 4-[3-(4-acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-hydroxy-
phenylester
114 457 N-{4-(3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
methyl-
benzamide
115 501 Acetic acid 2-{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl-
carbamoyl}-phenyl ester
116 461 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-4-
tluoro-
benzamide
117 461 N-{4-[3-(S-Chloro-2,4-dirnethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-
fluoro-
benzamide
118 461 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
119 473 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
methoxy-
benzamide
120 473 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-
methoxy-
benzamide
121 473 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-4-
methoxy-
benzamide
122 443 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
123 417 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
methanesulfonamide
I24 331 N-{4-[3-(3-Nitro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
125 339 1-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-3-(3-nitro-phenyl)-thiourea
126 337 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
127 439 {4-(3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-carbamic
acid
tert-butyl ester
128 351 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-hydroxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
129 385 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-hydroxy-2-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
acetamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-95-
130 318 N-{4-[3-(2,4-Dihydroxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
131 414 N-{4-[3-(2,4-Dimethoxy-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
acetamide
132 332 N-{4-[3-(2-Hydroxy-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
133 465 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-4-
fluoro-
benzamide
134 500 3-Acetylamino-N-{4-[3-(5-chloro-2.4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-benzamide
135 488 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-nitro-
benzamide
136 486 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-
dimethylamino-benzamide
137 536 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-
methane-
sulfony-amino-benzamide
138 S11 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
trifluoro-
methyl-benzamide
139 459 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
hydroxy-
benzamide
140 479 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,6-
difluoro-
benzamide
141 477 2-Chloro-N-{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
benzamide
142 522 2-Bromo-N-{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
143 488 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-nitro-
benzamide
144 445 1'yrazine-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
145 463 5-Methyl-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
146 494 Quinoline-8-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
147 446 1-Methyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
148 369 1-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(2-nitro-phenyl)-thiourea
149 369 1-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(4-nitro-phenyl)-thiourea
150 425 N-{4-[3-(5-Bromo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-96-
151 376 N-{4-[3-(3,4,5-Trimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
152 399 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
153 499 Benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
154 483 Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
155 444 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
isonicotinamide
156 493 Naphthalene-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
157 493 Naphthalene-1-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]- phenyl}-amide
I58 494 lsoquinoline-1-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
,
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
159 494 Quinoline-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
160 444 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
nicotinamide
161 478 5-Nitro-furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-amidecarbarnic acid phenyl
ester
162 459 {4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
163 467 5-Chloro-furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-amide
164 439 {4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-carbamic
acid
isobutyl ester
165 397 {4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-carbamic
acid
methyl ester
166 433 Furan-3-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
167 447 3-Methyl-furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
168 512 5-Bromo-furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
169 512 4-Bromo-furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
170 433 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido)-
phenyl }-amide
171 467 {4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-carbamic
acid
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-97-
hexyl ester
172 494 Isoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido)-phenyl }-amide
173 4S 1 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
174 434 1H-(1,2,3]Triazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
17S S28 3-Bromo-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyI)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
176 399 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-ethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
177 427 N-{4-[3-(4-Butoxy-3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
178 461 N-{4-[3-(4-Benzyloxy-3,S-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
I79 381 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
180 S30 (3-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenylcarbamoyl}-
phenyl)-carbamic acid ethyl ester
181 4S8 2-Amino-N-{4-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
182 S19 Biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
183 469 1-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-[4-(1,3-dioxo-1,3-dihydro-
isoindol-
2-yl)-phenyl]-thiourea
184 487 N-{4-[3-(S-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
phthalamic acid
18S 473 N-{4-[3-(S-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
hydroxy-
methyl-benzamide
186 479 N-{4-[3-(S-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,3-
difluoro-benzamide
187 479 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,5-
difluoro-benzamide
188 479 N-{4-[3-(S-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,4-
difluoro-benzamide
189 S00 2-Acetylamino-N-{4-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-benzamide
190 441 1-(S-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-phenanthridin-
2-yl)-thiourea
191 S36 N-{4-[3-(S-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
methane-
sulfonylamino-benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-98-
192 497 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,3,4-
trifluoro-benzamide
193 533 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
2,3,4,5,6-
pentafluoro-benzamide
194 489 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
methyl-
sulfanyl-benzamide
195 431 5-Methyl-furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimelhoxy-
phenyl)-
ureido]-phenyl}-amide
196 467 5-Difluoromethyl-furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-
dimethoxy-
phenyl)-ureido]-phenyl }-amide
197 472 N-{4-[3-(5-Iodo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
198 364 N-{4-[3-(5-Fluoro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
199 365 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
200 459 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
201 455 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-4-methoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
202 392 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-diethylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
203 432 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(cyclohexyl-methyl-amino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
204 506 1-Hydroxy-naphthalene-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-acetylamino-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl }-amide
205 406 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-morpholin-4-yl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
206 443 1-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(3-chloro-4-morpholin-4-yl-
phenyl)-
thiourea
207 372 1-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(5-chloro-2-methyl-phenyl)-
thiourea
208 501 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
isophthalamic acid methyl ester
209 487 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
isophthalamic acid
210 549 3-Benzyloxy-N-{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureidoJ-
phenyl}-
benzamide
211 434 N-(4-{3-[5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-(4-nitrilo-butoxy)-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
212 406 N-(4-{3-[5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-(2-nitrilo-ethoxy)-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-99-
213 406 N-(4-{3-[5-Chloro-4-methoxy-2-(2-nitrilo-ethoxy)-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
214 411 N-(4-{3-[5-Chloro-2-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-4-methoxy-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
215 411 N-(4-{3-[5-Chloro-4-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-2-methoxy-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
216 481 {4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-S-methoxy-
phenoxy}-
acetic acid tent-butyl ester
217 439 (4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-5-methoxy-
phenoxy}-
acetic acid methyl ester
218 481 {2-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-4-chloro-5-methoxy-
phenoxy}-
acetic acid tert-butyl ester
219 515 3-Butoxy-N-{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
benzamide
220 505 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
methane-
sulfinyl-benzamide
221 545 (3-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenylcarbamoyl}-
phenoxy)-acetic acid ethyl ester
222 517 (3-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenylcarbamoyl}-
phenoxy)-acetic acid
223 367 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
224 444 Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
225 494 Quinoline-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
226 436 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-4-methoxy-2-morpholin-4-yl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-acetamide
227 394 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-dimethylamino-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-acetamide
228 420 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-4-methoxy-2-pyrrolidin-1-yl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
acetamide
229 434 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-4-methoxy-2-piperidin-1-yl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
acetamide
230 405 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-methyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
231 415 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 100 -
232 427 N-{4-(3-(3-Chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-methoxy-
benzamide
233 387 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
234 411 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-methyl-
benzamide
235 433 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,6-difluoro-
benzamide
236 398 Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-
d~ioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
237 502 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(cyclohexyl-
methyl-
amino)-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
238 512 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(cyclohexyl-methyl-amino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
239 404 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-piperidin-1-yl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
240 364 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
241 426 N-{4-[3-(4-Benzylamino-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
242 390 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-pyrrolidin-1-yl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
243 419 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
acetamide
244 469 N-{4-[3-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
Iluoro-
benzamide
245 422 N-{4-(3-(2-Benzylamino-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
246 484 ~ Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(cyclohexyl-methyl-
amino)-
phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
247 508 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(cyclohexyl-methyl-amino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-methyl-benzamide
248 530 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4.-(cyclohexyl-methyl-amino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-2,6-difluoro-benzamide
249 495 Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(cyclohexyl-methyl-
amino)-
phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)- amide
250 524 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(cyclohexyl-methyl-amino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-3-methoxy-benzamide
251 376 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-nitrilo-ethoxy)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
acetamide
252 393 N-{4-[3-(4-sec-Butoxy-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
253 501 Acetic acid 3-{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-101-
carbamoyl}-phenyl ester
254 459 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-
hydroxy-
benzamide
255 487 Benzo[1,3]dioxole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
256 527 N-{4-(3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureidoJ-phenyl}-3-
trifluoro-
methoxy-benzamide
257 530 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-(2-
dimethylamino-ethoxy)-benzamide
258 572 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-(2-
morpholin-4-yl-ethoxy)-benzamide
259 406 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-cyano-phenyl}-
acetamide
260 521 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,5-dimethoxy-
phenyl }-2-fluoro-benzamide
261 441 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido)-2,5-dimethoxy-
phenyl }-acetamide
262 527 2-{4-(3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenoxy}-5-
chloro-
benzenesulfonic acid
263 562 2-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenoxy}-4,5-
dichloro-
benzenesulfonic acid
264 527 4-Phenyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-
dimethoxy-
phenyl)-thioureidoJ-phenyl }-amide
265 381 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
acetamide
266 393 N-{4-[3-(4-Butoxy-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
267 446 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(cyclohexyl-ethyl-amino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
acetamide
268 365 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-ethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
269 427 N-{4-[3-(4-Benzyloxy-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
270 317 {4-[(3-Methyl-furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-carbamic
acidtert-butyl
ester
271 456 N-{4-[3-(2-Benzylamino-5-chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
acetamide
272 420 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-dipropylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
273 458 N-(4-{3-[4-(Allyl-cyclohexyl-amino)-3-chloro-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
acetamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 102 -
274 411 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methoxy-phenyl}-
acetamide
275 415 N-{2-Chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
276 493 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
2,5-dimethoxy-phenyl }-amide
277 486 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-cyano-phenyl}-2-
tluoro-benzamide
278 495 N-{2-Chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
279 465 5-Methyl-[1,2,3)thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-
dimethoxy-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
280 517 5-Furan-3-yl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4
dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]- phenyl}amide
281 527 5-Phenyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-
dimethoxy-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
282 458 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(octahydro-quinolin-1-yl)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
acetamide
283 458 N-[5-C[[(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)amino)thioxomethyl]amino]-2-
pyridinyl]-2-methylbenzamide
284 434 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {5-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
pyridin-2-yl }-amide
285 425 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methoxy-5-methyl-
phenyl}-acetamide
286 505 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methoxy-5-methyl-
phenyl }-2-fluoro-benzamide
287 477 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
2-methoxy-5-methyl-phenyl }-amide
288 517 4-Furan-3-yl-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid{4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4
dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
289 462 N-{5-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-pyridin-2-yl}-2-
tluoro-benzamide
290 384 N-{4-[3-(4-Methoxy-3-tritluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
291 394 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-methyl-amino]-phenyl}-
thioureido)-
phenyl]-acetamide
292 485 N-{2-Benzoyl-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 103 -
293 565 N-{2-Benzoyl-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
294 537 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {2-benzoyl-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-amide
295 475 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-methyl-
phenyl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
296 447 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
3-methyl-phenyl }-amide
297 395 N-{4-(3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-methyl-
phenyl}-
acetamide
298 435 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-methyl-amino]-phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-acetamide
299 418 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-cyclohexylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
300 421 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-methyl-amino]-phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-acetamide
301 580 5-[[[(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)amino]thioxomethyl]amino]-2-[(2-
fluorobenzoyl)amino]-N-phenyl-benzamide
302 552 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
2-phenylcarbamoyl-phenyl }-amide
303 491 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methoxy-
phenyl}-
2-fluoro-benzamide
304 463 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
2-methoxy-phenyl }-amide
305 449 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl }-acetamide
306 458 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
2-cyano-phenyl}-amide
307 467 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {2-chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2;4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
308 501 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
2-trifluoromet6yl-phenyl}-amide
309 395 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methyl-
phenyl}-
acetamide
310 475 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methyl-
phenyl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
311 447 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
2-methyl-phenyl }-amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 104 -
312 378 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl}-acetamide
313 408 (4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl}-carbamic
acid
ethyl ester
314 382 N-{5-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-pyridin-2-yl}-
acetamide
315 509 N-(4-{3-[4-(1-Benzyl-piperidin-4-ylamino)-3-chloro-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
316 407 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-{2-dimethylamino-elhylamino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
317 408 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[(2-methoxy-ethyl)-methyl-amino]-phenyl}-
thiaureido)-
phenyl]-acetamide
318 421 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(3-dimethylamino-propylamino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
319 495 N-(4-{3-[4-(I-Benzyl-pyrrolidin-3-ylamino)-3-chloro-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
320 483 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {5-chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-2-hydroxy-phenyl }-amide
321 431 N-{5-Chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-hydroxy-
phenyl }-acetamide
322 511 (SH,IIH-Benzo[e]pyrrolo[1,2-a][1,4]diazepin-10-yl)-(2-chloro-4-
imidazol-I-
yl-phenyl)-methanone
323 451 [1,2,3)Thiadiazole-5-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
324 483 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
naphthalen-1-yl }-amide
325 511 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-naphthalen-I-yl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
326 429 N-{5-Chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methyl-
phenyl }-acetamide
327 509 N-{5-Chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methyl-
phenyl }-2-fluoro-benzamide
328 481 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {5-chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-2-methyl-phenyl }-amide
329 431 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-naphthalen-I-yl}-
acetamide
330 416 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
331 561 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-{4-[(I-benzyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-methyl-
amino]-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 105 -
3-chloro-phenyl}-thioureido)- phenyl]-amide
332 513 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[methyl-(1-methyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-amino]-
phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
333 463 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
2,6-
difluoro-benzamide
334 420 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(1-methyl-pyrrolidin-3-yloxy)-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
335 434 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(1-methyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
336 422 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(3-dimethylamino-propoxy)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
337 425 2-Acetylamino-5-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
benzoic acid
338 505 5-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-(2-fluoro-
benzoylamino)-benzoic acid
339 477 5-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-[(furan-2-
carbonyl)-
amino]-benzoic acid
340 545 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[methyl-(1-methyl-piperidin-4-yl)-amino]-
phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-2,6-difluoro-benzamide
341 503 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid[4-(3-{3-chloro-4-[methyl-(1-
methyl-
pyrrolidin-3-yl)-amino]-phenyl }-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
342 44.3 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
methyl-
benzamide
343 408 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-dimethylamino-ethoxy)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
344 499 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-{3-chloro-4-[methyl-(1-methyl-
piperidin-4-yl)-
amino]-phenyl }-thioureido)- phenyl]-amide
345 419 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-cyclohexyloxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
346 4-40 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
methyl-
benzamide
347 493 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-methyl-
phenyl}-2,6-
difluoro-benzamide
348 462 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-2,6-
difluoro-benzamide
349 531 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[methyl-(1-methyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-amino]-
phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-2,6-difluoro-benzamide
350 427 Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 106 -
351 430 Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
352 428 dine-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
353 417 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
354 496 Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-{3-chloro-4-[methyl-(1-methyl-
pymolidin-3-
yl)-amino]-phenyl }-thioureido)- phenyl]-amide
355 495 N-{3-Chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
356 467 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {3-chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
357 515 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-cyclohexylsulfanyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
358 449 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl}-acetamide
359 529 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl }-2-fluoro-benzamide
360 421 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido)-2-chloro-phenyl}-2-dimethyl-
amino-acetamide
361 473 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(2-dimethylamino-
acetylamino)-
phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
362 501 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-dimethylamino-acetylamino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
363 461 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl}-2-
piperidin-
1-yl-acetamide
364 541 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-piperidin-1-yl-acetylamino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
365 513 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(2-piperidin-1-yl-
acetylamino)-
phen~l]-thioureido}-phenyl)- amide
366 463 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl}-2-
morpholin-
4-yl-acetamide
367 543 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-morpholin-4-yl-acetylamino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
368 515 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(2-morpholin-4-yl-
acetylamino)-
phenyl)-thioureido}-phenyl)- amide
369 414 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methanesulfonylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 107 -
370 494 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methanesulfonylamino-phenyl)-thioureido)-
phenyl}-
2-Iluoro-benzamide
371 466 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-methanesulfonylamino-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
372 481 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl}-2-(2-
dimethy-
lamino-ethylsulfanyl)- acetamide
373 561 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[2-(2-dimethylamino-ethylsulfanyl)-
acetylamino]-
phenyl }-thioureido)-phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
374 585 N-[4-(3-{4-[(1-Benzyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-methyl-aminoj-3-chloro-
phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-2-methyl-benzamide
375 523 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[methyl-(1-methyl-piperidin-4-yl)-amino]-
phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-2-methyl-benzamide
376 510 Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-{3-chloro-4-[methyl-(1-methyl-
piperidin-4-
yl)-amino]-phenyl}-thioureido)- phenyl]-amide
377 347 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-vinyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
378 441 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
379 452 Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
380 487 N-{4-[3-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureidoj-phenyl}-
2,6-
difluoro-benzamide
381 486 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-cyano-
phenyl}-
2-fluoro-benzamide
382 458 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
3-cyano-phenyl}-amide
383 406 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-cyano-
phenyl}-
acetamide
384 395 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-2-methyl-isothioureido]-
phenyl}-
acetamide
385 396 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-2-methyl-isothioureido]-
phenyl}-
acetamide
386 461 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
387 489 N-{4-[3-(4-Butylsulfanyl-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
388 411 N-{4-[3-(S-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-methoxy-phenyl}-
acetamide
389 491 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-methoxy-phenyl}-
2-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 108 -
fluoro-benzamide
390 463 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
3-methoxy-phenyl }-amide
391 531 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(2-piperidin-1-
yl
acetyl-amino)-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
392 481 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methanesulfinyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,6-
difluoro-benzamide
393 497 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methanesulfonyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,6-
difluoro-benzamide
394 459 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methyl-
phenyl }-2-fluoro-benzamide
395 429 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methyl-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
396 533 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-{ 3-chloro-4-[2-(2-dimethyIamino-
ethylsulfanyl)-acetylamino]-phenyl }-thioureido)-phenyl ]-amide
397 458 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
398 460 [2-Chloro-4-(3-{4-[(furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-thioureido)-
phenyl]-
carbamic acid ethyl ester
399 488 (2-Chloro-4-{3-(4-(2-fluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
carbamic acid ethyl ester
400 440 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl}-benzamide
401 520 N-{4-[({[4-(Benzoylamino)-3-chloro-phenyl]-amino}-thioxomethyl)-amino]-
phenyl }-2-fluoro-benzamide
402 529 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl }-2-fluoro-benzamide
403 492 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-benzoylamino-3-chloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
404 416 N-{4-[3-(4-Amino-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
405 479 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl}-2-
thiomorpholin-4-yl-acetamide
406 531 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(2-thiomorpholin-4-yl-
acetylamino)-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
407 559 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-thiomorpholin-4-yl-acetylamino)-phenyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
408 461 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-methyl-
phenyl}-
2-fluoro-benzamide
409 430 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-(3-(4-acetylamino-3-chloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 109 -
phenyl}-amide
410 477 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl}-2-
dipropylamino-acetamide
411 529 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(2-dipropylamino-
acetylamino)-
phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)- amide
412 449 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl}-2-
diethyl-
amino-acetamide
413 501 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(2-diethylamino-
acetylamino)-
phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)- amide
414 529 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-diethylamino-acetylamino)-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
415 447 N-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-phenyl}-2-
pyrrolidin-
1-yl-acetamide
416 499 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-yl-
acetylamino)-
phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
417 527 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-yl-acetylamino)-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
418 475 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-methoxy-
phenyl }-2-fluoro-benzamide
419 445 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-methoxy-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
420 477 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-met6ylsulfanyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-3-methoxy-
phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
421 388 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-amino-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
422 527 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[4-(2-azepan-1-yl-acetylamino)-3-chloro-
phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
423 555 N-(4-{3-[4-(2-Azepan-1-yl-acetylamino)-3-chloro-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
424 527 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-{3-chloro-4-[2-(2-methyl-piperidin-1-yl)-
acetyl-amino]-phenyl }-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
425 555 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[2-(2-methyl-piperidin-1-yl)-acetylamino]-phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
426 339 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-2-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
427 339 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-4-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
428 367 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-pyridin-3-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide
429 339 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-3-yl-thioureido)-phenyl)-amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 110 -
430 353 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-amino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
431 406 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
432 380 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-m-tolyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide
433 434 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
434 381 N-{4-[3-(3-Amino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
435 388 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-amino-5-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
436 352 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-m-tolyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
437 416 N-{4-[3-(2-Amino-5-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl
}-2-fluoro-benzamide
438 571 (2-Chloro-4-{3-[4-(2-fluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
carbamic acid 2-piperidin-1-yl-ethyl ester
439 543 [2-Chloro-4-(3-{4-[(furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-thioureido)-
phenyl]-
carbamic acid 2-piperidin-1-yl-ethyl ester
440 388 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-amino-5-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
441 363 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-cyano-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
442 416 N-{4-[3-(3-Amino-5-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
443 367 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-pyridin-2-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide
444 367 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-pyridin-4-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide
445 374 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(6-chloro-pyridin-3-yl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
446 388 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-amino-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
447 396 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-hydrazinocarbonyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
448 410 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[3-(1-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
449 414 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-hydrazinocarbonyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-amide
450 399 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-isopropyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
451 380 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-isopropyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
452 409 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-isopropyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-111-
453 381 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-cyano-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
454 410 N-{4-[3-(3-Dimethylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
455 381 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-dimethylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
456 370 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-m-tolyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-
amide
457 424 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
458 479 N-{3-Chloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
459 449 N-{3-Chloro-4-(3-(3-chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
460 481 N-{3-Chloro-4-[3-(3-chloro-4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
461 391 N-{4-[3-(3-Cyano-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
462 395 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
463 424 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-hydrazinocarbonyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
464 400 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-(1-hydroxy-ethyl)-
phenyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
465 434 N-{4-[3-(2-Amino-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,6-difluoro-
benzamide
466 406 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-amino-5-chloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
467 398 Fnran-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
468 416 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
469 454 5-(3-{4-[(Furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-thioureido)-isophthalic
acid
dimethyl ester
470 434 Isoxazole-5-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
471 392 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(6-chloro-pyridin-3-yI)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
472 382 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-(1-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 112 -
473 368 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
474 354 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-hydroxy-phenyl)-thioureido)-
phenyl}-
amide
475 382 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-hydroxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
476 396 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-hydroxymethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
477 423 N-{4-[3-(3-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
478 413 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-acetylamino-phenyl)-
thioureido)-phenyl }-amide
479 400 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-dimethylamino-
phenyl)-
thioureido)-phenyl }-amide
480 340 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyrimidin-4-yl-thioureido)-phenyl)-
amide
481 378 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1H-indazol-5-yl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-amide
482 395 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-benzothiazol-5-yl-thioureido)-
phenyl]-amide
483 406 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1H-indazol-5-yl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
484 424 N-[4-(3-Benzothiazol-S-yl-thioureido)-phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
485 473 5-(3-{4-(([1,2,3)Thiadiazole-4-carbonyl)-amino)-phenyl}-
thioureido)-
isophthalic acid dimethyl ester
486 442 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[4-(1-azido-ethyl)-3-chloro-phenyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
487 396 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
488 368 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-hydroxymethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
489 416 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(S-chloro-2-dimethylamino-phenyl)-
thioureido)-phenyl }-amide
490 444 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-dimethylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
491 506 [3-Chloro-5-(3-{4-[([1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl
ester
492 470 N-(4-{3-[4-(1-Azido-ethyl)-3-chloro-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
493 337 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(1H-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-
ylideneamino)-
phenyl]-amide
494 378 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-(3-(1H-benzoimidazol-5-yl)-thioureido)-
phenyl}-
amide
495 392 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-methyl-1H-benzoimidazol-5-yl)-
thioureido)-phenyl }-amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 113 -
496 406 N-{4-[3-(1H-Benzoimidazol-5-yl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
497 420 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(2-methyl-1H-benzoimidazol-S-yl)-thioureido]-phenyl}
benzamide
498 452 [1,2,3)Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {5-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido)-pyridin-2-yl }-amide
499 445 Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid {5-[3-(S-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-pyridin-2-yl }-amide
500 434 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2-dimethylamino-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
501 484 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[4-(2-amino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-
3-
chloro-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
502 494 N-(4-{3-[4-(2-Amino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-3-chloro-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
2-fluoro-benzamide
503 434 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-2-dimethylamino-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
504 462 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-2-dimethylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,6-
difluoro-benzamide
505 416 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-2-dimethylamino-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
506 445 Pyridine-2-carboxylic acid {6-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureidoj-pyridin-3-yl }-amide
507 462 N-{6-[3-(5-Chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-pyridin-3-yl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
508 482 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-iodo-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
509 413 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-tert-butyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
510 387 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
511 415 N-{4-(3-(3-Chloro-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
512 434 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {6-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
pyridin-3-yl }-amide
513 435 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-bromo-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
514 452 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {6-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-pyridin-3-yl }-amide
515 426 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {5-[3-(3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-pyridin-2-yl }-amide
516 474 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 114 -
phenyl}-amide
517 502 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
51$ 450 N-{4-[3-(4-Amino-3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
519 539 N-{4-[3-(4-Amino-3,5-dibromo-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
520 392 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-pyridin-3-yl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
521 529 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-amino-3,5-dibromo-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
522 434 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-5-
dimethylamino-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
523 444 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-5-dimethylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
tluoro-
benzamide
524 416 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-5-dimethylamino-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
525 436 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-bromo-pyridin-3-yl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
526 379 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1H-benzotriazol-5-yl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
527 425 N-{4-[3-(1H-Benzotriazol-5-yI)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,6-difluoro-
benzamide
528 388 N-[4-({[2-(3-Chloro-phenyl)-hydrazino]-thioxomethyl}-amino)-phenyl]-
furan-2-carboxamide
529 416 N-[4-({[2-(3-Chloro-phenyl)-hydrazino)-thioxomethyl}-amino)-phenyl]-
2-
fluoro-benzamide
530 456 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-amino-3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
531 513 N-{4-[3-(3-Bromo-5-uifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
532 503 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-bromo-5-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-amide
533 374 {4-[(Furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-thiocarbamic
acid O-(3-chloro-
phenyl) ester
534 474 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-amino-3-chloro-5-
trifluoro-
methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
535 508 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-piperidin-1-yl-5-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 115 -
536 380 N-[4-(3-Benzyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
537 439 (1,2,3JThiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
538 449 N-{4-[3-(3,4-Dichloro-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
539 370 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-benzyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-
amide
540 424 N-[4-(3-Benzo[1,3]dioxol-5-ylmerhyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-2-fluoro-
benzamide
541 414 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-benzo[1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethyl-
thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
542 506 (1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-
benzyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
543 516 N-{4-(3-(3,5-Bis-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
544 352 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-benzyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
545 421 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-benzyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
546 396 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-benzo[1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethyl-thioureido)-
phenyl]-amide
547 488 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-
thioureidoJ-
phenyl }-amide
548 503 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-(3-(4-bromo-3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl }-amide
549 529 N-{4-[3-(3-Bromo-4-trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
550 519 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-bromo-4-trifluoromethoxy-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
551 473 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-trifluoromethylsulfanyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
552 412 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[2-(3-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
553 412 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[2-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
554 402 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
555 402 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
556 495 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-(2-methyl-butyl)-5-
trifluoro-
methyl-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
557 481 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-isobutyl-5-
trifluoromethyl-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- l lb
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
558 523 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-
yl)-5-
trifluoro-methyl-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
559 510 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-morpholin-4-yl-5-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl
}-amide
560 494 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-pyrrolidin-1-yl-5-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl
}-amide
561 384 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
562 419 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-chloro-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
563 429 N-(4-{3-[2-(3-Chloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
564 401 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-chloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
565 402 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
566 504 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-pyrrolidin-1-yl-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl}-benzamide
567 477 N-{4-[3-(3-Dimethylamino-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
568 520 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-morpholin-4-yl-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl}-benzamide
569 533 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[3-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-5-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-benzamide
570 518 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-piperidin-1-yl-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl}-benzamide
571 468 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-dimethylamino-5-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl
}-amide
572 405 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
573 384 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-(2-(3-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
574 366 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-phenethyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
575 384 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-phenethyl-thioureido)-
phenyl]-
amide
576 394 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-phenethyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide
577 505 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[3-(2-methyl-butyl)-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/Z8838
- 117 -
phenyl)-benzamide
578 491 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-isobutyl-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
benzamide
579 388 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-difluoro-benzyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
580 416 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Difluoro-benzyi)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
581 406 (1,2,3JThiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-difluoro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
5$2 421 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-benzyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
583 449 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
584 439 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
585 438 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-fluoro-5-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
586 466 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-lluoro-S-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
benzamide
587 456 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-fluoro-5-
trifluoromethyl-
benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
588 384 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1-phenyl-ethyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
589 394 2-Fluoro-N-{4-(3-(1-phenyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
590 366 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(I-phenyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
591 412 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
592 384 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[I-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
593 413 N-{4-[3-(1-tent-Butyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
594 510 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-(isobutyl-methyl-
amino)-5-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
595 510 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-(3-hydroxy-pyrrolidin-
I-yl)-5-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
596 520 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[3-(isobutyl-methyl-amino)-5-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-benzamide
597 510 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-(butyl-methyl-amino)-
5-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
598 520 N-(4-{3-[3-(Butyl-methyl-amino)-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 118 -
phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
599 520 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
600 442 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-fluoro-3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
601 522 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-piperidin-1-yl-3-
trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
602 482 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-dimethylamino-3-
trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
603 381 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-amino-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
604 445 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
605 380 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-p-tolyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
606 463 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
607 396 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-methoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
608 403 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1-ten-butyl-1H-imidazol-2-
yl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
609 384 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1-ten-butyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
610 492 N-{4-[3-(4-Dimethylamino-3-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
2-
fluoro-benzamide
611 427 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
612 380 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-phenyl-propyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
613 399 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-phenyl-propyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
614 502 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
615 550 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-iodo-3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
616 532 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(4-piperidin-1-yl-3-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-benzamide
6I7 537 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[4-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-
yl)-3-
trifluoromethyl-benzyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
618 482 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-dimethylamino-5-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 119 -
trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }amide
619 488 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,S-bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido-
methyl]-phenyl }-amide
620 421 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,S-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureidomethyl]-
phenyl}-amide
621 421 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureidomethyl]-
phenyl }-amide
622 45S Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido-methyl]-phenyl }-amide
623 466 2-Fluoro-N-{4-(3-(4-fluoro-3-trilluoromethyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
benzamide
624 456 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-fluoro-3-trifluoromethyl-
benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
62S 410 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(2-phenoxy-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
626 382 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-phenoxy-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
627 400 (1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-phenoxy-ethyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
628 409 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-phenyl-propyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
629 42S [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(S-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-
3-yl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-amide
630 439 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido-
methyl]-phenyl }-amide
631 473 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-thioureidomethyl]-phenyl }-amide
632 381 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-pyridin-3-ylmethyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide
633 3S3 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-3-ylmethyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-
amide
634 371 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-3-ylmethyl-
thioureido)-
phenyl]-amide
63S 439 (1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,S-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido-
methyl]-phenyl }-amide
636 492 N-{4-[3-(3-Dimethylamino-S-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
2-fluoro-benzamide
637 415 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-methoxy-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
638 399 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-p-tolyl-ethyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
639 44S [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 120 -
ethyl]-t6ioureido }-phenyl)-amide
640 506 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-tritluaromethyl-
phenyl)-
thioureidomethyl]-phenyl}-amide
641 516 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureidomethyl]-phenyl}-
2-
fluoro-benzamide
642 449 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-phenyl)-thioureidomethyl]-phenyl
}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
643 449 N-{4-[3-(3,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-thioureidomethyl]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
644 448 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-acetylamino-5-chloro-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
645 453 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
646 413 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1-methyl-3-phenyl-
propyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
647 463 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-bromo-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
648 413 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-phenyl-butyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
649 397 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-indan-1-yl-thioureido)-
phenyl]-
amide
650 400 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-methoxy-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
651 415 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
652 415 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
653 506 N-(4-{3-[2-(3-Dimethylamino-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethyl)-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
654 S 10 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-(3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-5-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
655 417 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-phenylsulfanyl-ethyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
656 427 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(2-phenylsulfanyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
657 399 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-phenylsulfanyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl
}-
amide
658 381 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-pyridin-4-ylmethyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide
659 353 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-4-ylmethyl-thioureido)-
phenyl]-amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/11S99/28838
-121-
660 371 [1,2,3)Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-pyridin-4-ylmethyl-
thioureido)-
phenyl]-amide
661 506 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-iodo-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
662 478 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-iodo-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
663 496 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-iodo-benzyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
664 479 N-(4-{3-[2-(3,5-Dichloro-phenoxy)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
665 451 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,5-dichloro-phenoxy)-ethyl)-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
666 445 N-(4-{3-[2-(3-Chloro-phenoxy)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
667 417 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-chloro-phenoxy)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
668 435 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-chloro-phenoxy)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
669 466 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(2-fluoro-5-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
benzamide
670 438 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-fluoro-5-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
671 456 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-fluoro-5-trifluoromethyl-
benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
672 416 N-{4-[3-(3,4-Difluoro-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
673 452 N-(4-{3-[2-(4-Dimethylamino-3-methyl-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
2-fluoro-benzamide
674 496 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-dimethylamino-5-
trifluoro-
methyl-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
675 388 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-difluoro-benzyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
676 406 [1,2,3)Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-difluoro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
677 433 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-fluoro-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
678 495 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-bromo-phenylsulfanyl)-
ethyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
679 477 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{ 3-[2-(3-bromo-phenylsulfanyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
680 505 N-(4-{3-[2-(3-Bromo-phenylsulfanyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 122 -
681 493 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-bromo-4-methoxy-
phenyl)-
ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)- amide
682 493 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(5-bromo-2-methoxy-
phenyl)-
ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)- amide
683 419 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2-chloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
684 402 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
685 419 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-chloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
686 475 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,3-diphenyl-propyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
687 547 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[4-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-3-trifluoromethyl-
benzyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-benzamide
688 469 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,5-dichloro-phenoxy)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
689 423 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
690 427 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-tert-butyl-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
691 399 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dimethyl-benzyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-amide
692 442 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-dimethylamino-3-
methyl-
phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
693 479 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-(2-(4-bromo-phenoxy)-ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
694 526 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-iodo-phenoxy)-ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
695 489 N-(4-{3-[2-(4-Bromo-phenoxy)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
696 536 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[2-(4-iodo-phenoxy)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
697 461 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-bromo-phenoxy)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
698 508 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-iodo-phenoxy)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
699 408 Oxazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
700 424 Thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 123 -
amide
701 491 Thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
702 408 Oxazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
703 469 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,4-dichloro-phenoxy)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
704 424 Thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureidoj-
phenyl}-
amide
705 458 Thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
706 400 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-phenylamino-ethyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
707 453 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2,4-dichloro-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
708 452 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
ethyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
709 453 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2,6-dichloro-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
710 485 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,4-dichloro-
phenylsulfanyl)-
ethyl]-thioureido)-phenyl)-amide
711 503 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2-fluoro-5-
trifluoromethyl-
phenylsulfanyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
712 668 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-5-(3-{4-[([1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-
phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxamide
713 413 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-ethyl-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
714 442 Oxazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-amide
715 475 Oxazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
716 420 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,4-difluoro-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
717 452 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
ethyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
718 435 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
719 463 N-(4-{3-[2-(3,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCTlUS99/28838
- 124 -
benzamide
720 420 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3,5-difluoro-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
721 412 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[2-(2-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
722 429 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-vitro-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
723 399 (1,2,3)Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1-methyl-2-phenyl-
ethyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
724 437 N-{4-[3-(4-ten-Butyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
725 409 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dimethyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-phenyl
}-2-fluoro-benzamide
726 400 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-hydroxy-1-phenyl-
ethyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
727 409 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-methyl-1-phenyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
728 399 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1-methyl-1-phenyl-
ethyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
729 405 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-chloro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
730 388 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-fluoro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
731 438 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-trifluoromethyl-
benzyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
732 388 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-fluoro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
733 435 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2-chloro-phenoxy)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
734 479 [1,2,3]ThiadiazoIe-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-bromo-phenoxy)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
735 418 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2-fluoro-phenoxy)-
ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
736 418 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
737 486 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2-fluoro-5-
trifluoromethyl-
phenoxy)-ethyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
738 384 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
739 435 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-bromo-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 125 -
740 374 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl}-amide
741 388 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-fluoro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
742 405 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
743 449 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-bromo-benzyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
744 332 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-acetamide
745 438 Thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-benzyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
746 455 Thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-fluoro-5-trifluoromethyl-
benzyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
747 426 Thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-tert-butyl-benzyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
748 374 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-fluoro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
749 374 [1,2,3JThiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
750 526 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-iodo-phenoxy)-
ethyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
751 409 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-phenyl-
acetamide
752 425 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-methoxy-
benzamide
753 425 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-3-methoxy-
benzamide
754 425 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-4-methoxy-
benzamide
755 429 2-Chloro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
756 429 4-Chloro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
757 453 Acetic acid 4-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenylcarbamoyl)-phenyl ester
758 394 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-benzamide
759 395 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
isonicotinamide
760 410 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-4-hydroxy-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 126 -
benzamide
761 429 3-Chloro-N-(4-{3-[I-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
762 470 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-fluoro-5-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
763 520 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2,4-bis-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
764 470 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-fluoro-3-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
765 438 4-Dimethylamino-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
benzamide
766 470 [1,2,3]ThiadiazoIe-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2-fluoro-3-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
767 470 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(2-fluoro-5-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
768 510 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-iodo-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
769 470 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(4-fluoro-2-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
770 463 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[2-(3-bromo-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
771 427 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-propyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
772 475 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[(4-fluoro-phenyl)-phenyl-methyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
benzamide
773 455 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-pentyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
774 489 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-2-phenyl-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
benzamide
775 409 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-o-tolyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
776 409 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-m-tolyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
777 425 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
778 412 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(2-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
779 429 N-(4-{3-[1-(3-Chloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
780 473 N-(4-{3-[1-(3-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00!34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 127 -
benzamide
781 429 N-(4-{3-[I-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
782 409 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-p-tolyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
783 473 N-(4-{3-[1-(2-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro
benzamide
784 429 N-(4-{3-[1-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
785 462 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
benzamide
786 462 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
benaamide
787 462 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[I-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
benzamide
788 425 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[I-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
789 425 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[I-(3-methoxy-phenyl)-ethyl)-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
790 441 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[I-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-2-methyl-propyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-benzamide
791 419 N-(4-{3-[I-(3-Cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
792 419 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
793 438 N-(4-{3-[I-(4-Dimethylamino-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
794 438 N-(4-{3-[I-(3-Dimethylamino-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
795 473 2-Bromo-N-(4-{3-[I-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
796 446 Quinoline-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl)-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
797 410 2-~uoro-N-{4-[3-(2-hydroxy-1-phenyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
798 332 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-isopropyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide
799 445 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-naphthalen-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
800 412 3-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[I-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
801 412 4-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[I-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
802 384 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-furan-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 128 -
803 395 2-~uoro-N-{4-[3-(1-pyridin-4-yl-ethyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-
benzamide
804 397 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(1-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
benzamide
805 401 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-thiophen-3-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
806 44S N-[4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-ethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl
}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
807 459 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-propoxy-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
808 459 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-isopropoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
809 473 N-{4-[3-(4-Butoxy-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
810 522 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-iodo-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
811 475 N-{4-[3-(3-Bromo-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
812 520 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl)-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-iodo-
benzamide
813 346 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
propionamide
814 286 N-[4-(3-Phenyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-acetamide
EXAMPLE 815 (METHOD 32)
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-(3-(2,5-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]
phenyl }-amide
To a solution of 2,5-dichloroaniline (0.16 g) in tetrahydrofuran (20 mL) is
added
freshly prepared 1,1'-thiocarbonyldiimidazole (0.20 g) and the mixture is
stirred for
approximately 30 minutes at room temperature. [1,2,3]-Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic
acid
(4-amino-phenyl) amide (0.22 g) is added to the reaction flask and the mixture
is
stirred for approximately 6 hours. The solvent is then removed by evaporation
under
reduced pressure and warm acetonitrile (3 mL) is added. After 15 hours the
mixture
is filtered and the collected precipitate is washed with acetonitrile then
diethyl ether,
and air dried to provide the desired product as a white powder.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 129 -
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
EX. M+H COMPOUND NAME
NO.
816 321 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
817 413 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
818 443 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-methoxy-
benzamide
819 443 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-methoxy-
benzamide
820 443 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-4-methoxy-
benzamide
821 431 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-4-methoxy-
benzamide
822 431 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-fluoro-
benzamide
823 431 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-4-fluoro-
benzamide
824 437 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl}-amide
825 511 {4-[3-(5-Bromo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-carbamic acid
hexyl ester
826 481 Hexanoic acid {4-[3-(5-bromo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
827 505 N-{4-[3-(5-Bromo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-tluoro-
benzamide
828 477 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-bromo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
829 SO 1 N-{4-[3-(5-Bromo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-2-methyl-
benzamide
830 517 N-{4-[3-(5-Bromo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-4-methoxy-
benzamide
831 395 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-ethoxy-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
832 395 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-4-ethoxy-2-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
833 423 N-{4-[3-(2-Butoxy-5-chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
834 423 N-{4-[3-(4-Butoxy-5-chloro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
835 457 N-{4-[3-(2-Benzyloxy-5-chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
836 457 N-{4-[3-(4-Benzyloxy-5-chloro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-lhioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
837 421 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 130 -
thioureido]-phenyl}-amide
838 424 2-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-5-methoxy-phenoxy}-
acetamide
839 367 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
840 367 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
841 447 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-(methyl-(1-methyl-piperidin-4-yl)-amino]-phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-acetamide
842 426 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(methyl-phenyl-amino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
acetamide
843 509 N-[4-(3-{4-[(1-Benzyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-methyl-amino]-3-chloro-phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-acetamide
844 418 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(cyclopentyl-methyl-amino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
acetamide
845 433 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[methyl-(1-methyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-amino]-phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl)-acetamide
846 419 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
847 447 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
848 465 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methylsulfanyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2,6-
difluoro-
benzamide
849 445 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
850 441 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
methyl-
benzamide
851 434 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-dimethylamino-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
852 444 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
853 517 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-{3-chloro-4-[methyl-(1-
methyl
piperidin-4-yl)-amino]-phenyl }-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
854 579 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-{4-[(1-benzyl-pyrrolidin-3-
yl)
methyl-amino]-3-chloro-phenyl }-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
855 527 N-[4-(3-{3-Chloro-4-[methyl-(1-methyl-piperidin-4-yl)-amino]-phenyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
856 435 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2-methoxy-4-
methyl-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
857 589 N-[4-(3-{4-[(1-Benzyl-pyrrolidin-3-yl)-methyl-amino]-3-chloro-phenyl}-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 131 -
thioureido)-phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
858 501 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl }-amide
859 366 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-phenyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-benzamide
860 338 Furan-2-carboxylic acid [4-(3-phenyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-amide
861 356 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid [4-(3-phenyl-thioureido)-phenyl]-
amide
862 365 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(1-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
acetamide
863 435 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(1-hydroxy-
ethyl)-phenyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
864 365 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
acetamide
865 445 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(1-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
866 417 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(1-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
867 37I [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-amino-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
868 SOI Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-bromo-4-trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
869 423 N-{4-[3-(3-tert-Butyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
870 440 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3,5-dichloro-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
974 485 N-{4-[3-(1-Benzofuran-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
trifluoromethyl-
benzamide
975 412 N-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
benzamide
976 446 Isoquinoline-1-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}
phenyl)-amide
977 468 Isoquinoline-1-carboxylic acid {4- [3-(1-benzofuran-2-yl-ethyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
978 506 Isoquinoline-1-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
979 453 Isoquinoline-1-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
980 435 Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
981 457 Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(1-benzofuran-2-yl-ethyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
982 495 Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 132 -
phenyl)-amide
983 442 Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
984 446 Isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
98S 468 Isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(I-benzofuran-2-yl-ethyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
986 4S3 Isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[I-(4-cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
987 S06 Isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-amide
988 446 Quinoline-3-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-
amide
989 446 Quinoline-4-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-
amide
990 446 Quinoline-6-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[I-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-
amide
991 446 Quinoline-8-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[L-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-
amide
992 462 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethylJ-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
trifluoromethyl-
benzamide
993 419 2-Cyano-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
994 473 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-isobutoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
99S 414 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-fluoro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
996 47S N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
997 398 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-fluoro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
998 464 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(4-methoxy-3-trifiuoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
benzamide
999 449 N-{4-[3-(2-Amino-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1000 4S9 N-(4-{3-(1-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1001 417 N-{4-[3-(S-Chloro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
1002 43S N-{4-[3-(1-Benzofuran-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
1003 448 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(4-methyl-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 133 -
1004 473 (S)-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
1005 473 N-(4-{3-[(1R)-1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
1006 494 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[2-methoxy-4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl)-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-benzamide
1007 399 N-{4-[3-(2-Amino-5-fluoro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
1008 502 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Dimethylsulfamoyl-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1009 542 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-{1-[4-(piperidine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-ethyl}-
thioureido)-phenyl]-
benzamide
1010 562 N-(4-{3-[2,4-Bis-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
2-fluoro-
benzamide
1011 409 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-((1S)-1-p-tolyl-ethyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-benzamide
1012 409 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-((IR)-1-p-tolyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
1013 394 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-((1S)-1-phenyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
1014 429 N-(4-{3-[(1R)-1-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
1015 429 N-(4-{3-[(1S)-1-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-fluoro-
benzamide
1016 394 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-((1R)-1-phenyl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
1017 432 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Cyano-phenyl)-ethyl)-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-methoxy-
benzamide
1018 447 N-{4-[3-(1-Benzofuran-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-methoxy-
benzamide
1019 485 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-methoxy-
benzamide
1020 419 3-Cyano-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
1021 462 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl)-thioureido}-phenyl)-4-
tritluoromethyl-
benzamide
1022 419 4-Cyano-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-
benzamide
1023 469 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2,3,5,6-
tetramethyl
phenyl)-benzamide
1024 480 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-
2-fluoro-
benzamide
1025 473 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2,5-
dimethoxy-phenyl)-
benzamide
1026 530 N-{3,5-Dichloro-4-[3-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-2-
fluoro-benzamide
1027 447 N-(3-Chloro-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1028 480 2,3,4,5-Tetrafluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-3-
methyl-
phenyl)-benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 134 -
1029 462 2,4,5-Trifluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-3-
methyl-phenyl)-
benzamide
1030 427 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-3-methyl-
phenyl)-
benzamide
1031 457 2-~uoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-methoxy-5-
methyl-
phenyl)-benzamide
1032 443 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl)-thioureido}-3-methoxy-
phenyl)-
benzamide
1033 570 N-(2,6-Dibromo-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1034 480 2-~uoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-
trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-benzamide
1035 541 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-2-
fluoro-benzamide
1036 487 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-2-
fluoro-benzamide
1037 503 N-{4-[3-(1-Benzofuran-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-2-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
1038 447 N-(2-Chloro-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1039 454 N-(2-Chloro-4-{3-[1-(4-cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1040 437 N-(2-Cyano-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1041 498 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-cyano-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1042 445 N-(2-Cyano-4.-{3-[1-(4-cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1043 460 N-{4-[3-(1-Benzofuran-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-2-cyano-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1044 517 N-(2-Benzoyl-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1045 427 2-~uoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-methyl-
phenyl)-
benzamide
1046 487 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-methyl-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1047 434 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-methyl-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 135 -
1048 449 N-{4-[3-(1-Benzofuran-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-2-methyl-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1049 456 N-(2-Dimethylamino-4-{3-[i-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-
fluoro-benzamide
1050 526 N-(2-Benzyloxy-4-{3-[I-(4-cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1051 519 N-(2-Benzyloxy-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl)-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1052 603 N-[4-{3-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-(2-morpholin-4-yl-
ethoxy)-
phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
1053 603 N-[4-{3-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-(2-morpholin-4-yl-
ethoxy)-
phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
1054 542 2-Fluoro-N-[4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-(2-
morpholin-4-yl-
ethoxy)-phenyl]-benzamide
1055 485 N-(2-Butoxy-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1056 492 N-(2-Butoxy-4-{3-[1-(4-cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1057 589 N-[4-{3-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-(2-diethylamino-
ethoxy)-
phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
1058 528 N-(2-(2-Diethylamino-ethoxy)-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-2-fluoro-benzamide
1059 589 N-[4-{3-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-ethyl)-thioureido}-2-(2-diethylamino-
ethoxy)-
phenyl]-2-fluoro-benzamide
1060 457 N-(2-Ethoxy-4-{3-(1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1061 464 N-(4-{3-[1-(4-Cyano-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-ethoxy-phenyl)-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
1062 468 2-Fluoro-N-[4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-(2-nitrilo-
ethoxy)-
phenyl]-benzamide
1063 475 N-[4-{3-[1-(4-Cyano-phenyl)-ethyl)-thioureido}-2-(2-nitrilo-ethoxy)-
phenyl]-2-
fluoro-benzamide
1064 443 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-2-methoxy-
phenyl)-
benzamide
1065 489 2-Fluoro-N-(5-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-thioureido}-biphenyl-2-
yl)-benzamide
1066 514 Isoquinoline-1-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-2-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amide
1067 503 Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl)-
thioureido}-2-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 136 -
trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amide
1068 514 Isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl)-
thioureido}-2-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amide
1069 471 Isoquinoline-1-carboxylic acid (2-cyano-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-
ethyl)-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
1070 460 Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid (2-cyano-4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
1071 471 Isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (2-cyano-4-{3-[I-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-
ethyl]-
thiourcido }-phenyl)-amide
1072 460 Isoquinoline-l-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-2-
methyl-phenyl)-amide
1073 449 Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-2-
methyl-phenyl)-amide
1074 460 Isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-2-
methyl-phenyl)-amide
1075 396 PYt'azine-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl)-
thioureido}-phenyl)-
amide
1076 401 Thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl]-
thioureido}-phenyl)-
amide
1077 401 Thiophene-3-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[1-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-ethyl)-
thioureido}-phenyl)-
amide
1078 500 2-Isopropyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-
trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
1079 466 2-Isopropyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
1080 466 2-Isopropyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
1081 534 2-Isopropyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
1082 480 2-Butyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
1083 514 2-Butyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
1084 480 2-Butyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
1085 548 2-Butyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
1086 438 2-Methyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 137 -
phenyl }-amide
1087 438 2-Methyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
1088 505 2-Methyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl}-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
1089 534 2-Phenyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
1090 500 2-Phenyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioareido]-
phenyl }-amide
1091 500 2-Phenyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
1092 568 2-Phenyl-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
1093 401 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-thiazol-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
1094 588 2-Fluoro-N-[4-(3-{1-[1-(toluene-4-sulfonyl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-ethyl}-
thioureido)-
phenyl]-benzamide
1095 446 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-quinolin-2-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
1096 446 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-quinolin-4-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
1097 446 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-isoquinolin-3-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
1098 446 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-isoquinolin-1-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
1099 446 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-quinolin-6-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
1100 446 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(1-quinolin-3-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
1101 413 2-Methoxy-N-{4-[3-(1-thiophen-3-yl-ethyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
EXAMPLE 871 (METHOD 33)
[1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]
phenyl }-amide
To a solution of 3,5-dichloroaniline (U.16 g) in tetrahydrofuran (20 mL) is
added
freshly prepared 1,1'-thiocarbonyl-di-(1,2,4)-triazole (0.20 g) and the
mixture is
stirred for approximately 30 minutes at room temperature. [1,2,3]-Thiadiazole-
4-
carboxylic acid (4-amino-phenyl) amide (0.22 g) is added to the reaction flask
and
the mixture is stirred for approximately 6 hours. The solvent is then removed
by
evaporation under reduced pressure and warm acetonitrile (3 mL) is added.
After 15
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 138 -
hours the mixture is filtered and the collected precipitate is washed with
acetonitrile
then diethyl ether, and air dried to provide the desired product as a white
powder.
[M+H] 424.
Using the above procedure and appropriate starting materials the following
compounds were prepared:
EX. M+H COMPOUND NAME
NO.
872 465 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-
fluoro-
benzamide
873 477 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
methoxy-
benzamide
874 465 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
875 477 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-3-
methoxy-
benzamide
876 399 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}
-acetamide
877 365 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methoxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
878 331 N-{4-[3-(2-Nitro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
879 331 N-{4-[3-(4-Nitro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
880 477 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-4-
methoxy-
benzamide
881 351 N-{4-[3-(2-Chloro-5-methoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
882 428 2-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy}-
acetamide
883 443 (4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy}-
acetic
acid
methyl ester
884 457 {4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy}-
acetic
acid
ethyl ester
$$$ 447 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-phenoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
886 410 N-(4-{3-[3,5-Dichloro-4-(2-nitrilo-ethoxy)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
acetamide
887 485 {4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro-phenoxy}-
acetic
acid
tert-butyl ester
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 139 -
888 469 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-2-methoxy-4-
methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
889 335 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
890 335 N-{4-[3-(5-Chloro-2-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
891 703 N-{4-[3-(4-{4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-
phenyldisulfanyl }-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl }-acetamide
892 369 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-acetamide
893 59$ N-{4-[3-(3,5-Diiodo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
894 504 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dibromo-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
895 317 N-{4-[3-(6-Methoxy-pyridin-3-yl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
896 347 N-{4-[3-(2,6-Dimethoxy-pyridin-3-yl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
897 457 Acetic acid 2-{4-[3-(4-acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2,6-dichloro-
phenoxy}-ethyl ester
898 365 4-[3-(4-Acetylamino-phenyl)-thioureido]-2-chloro-benzoic acid
899 346 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-cyano-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
900 512 N-(4-{3-[5-Chloro-2-(4-chloro-phenoxy)-4-pyrrol-1-yl-phenyl]-
thioureido}-
phenyl)-acetamide
901 355 N-{4-[3-(3,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
902 339 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-acetamide
903 447 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-iodo-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
904 400 N-{4-[3-(4-Bromo-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-acetamide
905 424 N-[4-(3-{4-[Bis-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-amino]-3-chloro-phenyl}-thioureido)-
phenyl]-acetamide
906 434 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(hexyl-methyl-amino)-phenyl)-thioureido}-phenyl)-
acetamide
907 406 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(isobutyl-methyl-amino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-
acetamide
908 389 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-
acetamide
909 441 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
910 459 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
911 469 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-
fluoro-
benzamide
912 435 N-{4-(3-(3,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 140 -
913 407 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
914 425 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl}-amide
915 480 N-{4-[3-(4-Bromo-3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
916 527 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-iodo-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
917 452 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-bromo-3-chloro-phenyl)-lhioureido)-
phenyl }-amide
918 499 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-iodo-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
919 391 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
920 470 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-bromo-3-chloro-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
921 517 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-iodo-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
922 419 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-tluoro-
benzamide
923 409 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid{4-[3-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-
phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
924 388 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-4-isoxazol-5-yl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
acetamide
925 387 N-(4-{3-[3-Chloro-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-phenyl)-thioureido}-phenyl)-
acetamide
926 355 N-{4-[3-(2,3-Dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-acetamide
927 435 N-{4-[3-(2,3-Dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
928 407 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-(3-(2,3-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
929 425 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2,3-dichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
930 355 N-{4-[3-(2,5-Dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
931 435 N-{4-[3-(2,5-Dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
932 407 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2,5-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
933 355 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
934 435 N-{4-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
935 407 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,5-dichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-
amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
-141-
936 390 N-{4-[3-(3,4,5-Trichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-acetamide
937 470 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3,4,5-trichloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
938 442 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3,4,5-trichloro-phenyl)-thioureidoj-
phenyl}-
amide
939 460 (1,2,3JThiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid{4-[3-(3,4,5-trichloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
940 458 [1,2,3)Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-4-isoxazol-5-yl-
phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl } -amide
941 457 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid(4-{3-[3-chloro-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-
yl)-
phenyl]-thioureido}-phenyl)-amide
942 391 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-phenyl)-
thioureido)-
phenyl }-amide
943 373 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
944 401 N-{4-[3-(3-Chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
945 373 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
946 401 N-{4-[3-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-tluoro-benzamide
947 391 [1,2,3)Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(4-chloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
948 401 N-{4-[3-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-thioureido)-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
949 396 3-(3-{4-[(Furan-2-carbonyl)-aminoj-phenyl}-thioureido)-benzoic acid
methyl
ester
950 424 3-{3-[4-(2-Fluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-benzoic acid
methyl
ester
951 414 3-(3-{4-[([1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-thioureido)-
benzoic
acid methyl ester
952 409 N-[4-([[[3-(Aminocarbonyl)phenyl]amino]thioxomethyl]amino]phenyl]-2-
fluoro-benzamide
953 373 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-chloro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
954 381 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-carbamoyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
955 399 [1,2,3]Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-carbamoyl-phenyl)-
thioureido]-phenyl }-amide
956 391 [1,2,3)Thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(2-chloro-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
957 356 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
958 383 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-(3-(3-nitro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00!34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 142 -
959 411 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-nitro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
960 422 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-triouoromethoxy-phenyl)-
thioureido]-
phenyl }-amide
961 450 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
benzamide
962 384 2-Fluoro-N-{4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-benzamide
963 410 3-{3-[4-(2-Fluoro-benzoylamino)-phenyl]-thioureido}-benzoic
acid
964 382 3-(3-{4-[(Furan-2-carbonyl)-amino]-phenyl}-thioureido)-benzoic
acid
965 408 N-{4-[3-(3-Acetyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-benzamide
966 502 N-{4-[3-(3-Butylsulfamoyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-2-fluoro-
benzamide
967 380 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-acetyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-phenyl}-
amide
968 447 Furan-2-carboxylic acid (4-{3-[3-(2-hydroxy-ethanesulfonyl)-phenyl]-
thioureido }-phenyl)-amide
969 475 2-Fluoro-N-(4-{3-[3-(2-hydroxy-ethanesulfonyl)-phenyl]-thioureido}-
phenyl)-benzamide
970 474 Furan-2-carboxylic acid {4-[3-(3-butylsulfamoyl-phenyl)-thioureido]-
phenyl}-amide
EXAMPLE 971 (METHOD 57)
1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-2-methyl-propan-1-of
To solution of 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (2.0 g) in diethyl ether (40 mL) at O
°C is
added dropwise isopropylmagesium bromide {2.0 M, 9.6 mL) with stirring. After
1.5
hours the reaction is quenched with aqueous ammonium chloride and extracted
with
diethyl ether. The diethyl ether extracts are washed with saturated sodium
chloride,
dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, flitered and evaporated to give an
oil. The
oil is purifed by silica gel chromatography eluting with 10% dichloromethane-
hexanes to give the product, a yellow oil {1.76 g).
EXAMPLE 972 (METHOD 58)
1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-2-methyl-propan-1-one
To a solution of 1-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-2-methyl-propan-1-of (1.6 g) in acetone
(10
mL) at O °C is added Jones reagent (20 mL) with stirring. After 10
minutes excess
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- I43 -
Jones reagent is destroyed by addition of isopropyl alcohol. Diethyl ether is
added
followed by anhydrous magnesium and the mixture is filtered and evaporated to
give
the product, a yellow oil ( 1.2 g).
EXAMPLE 973 (METHOD 59)
3-Dimethylamino-5-trifluoromethyl-benzonitrile
To a solution of 3-dimethylamino-5-trifluoromethylbromobenzene (7.3 g) in N,N-
dimethylformamide (20 mL) is added cuprous cyanide (2.7 g) and the reaction
heated
at reflux for 12 hours. The reaction is diluted with water (40 mL) and
dichloromethane is added. The dichloromethane fraction is washed with
concentrated
ammonium hydroxide, then water. The solution is dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate, filtered and concentrated to give a yellow solid which is
recrystallized from
hexanes to give a yellow solid, (4.7 g).
The foregoing compounds were tested for activity as herpes virus inhibitors
using the following assays.
HUMAN CYTOMEGALOVIRUS
Yield assay. Monolayer cultures of human foreskin fibroblasts are infected
with
HCMV wild-type, typically at a multiplicity of infection equal to 0.2, in the
presence
of inhibitor compound (varying concentrations). At three days post-infection,
total
virus produced in these cultures (i.e. virus yield) is assessed by harvesting
and titering
the virus in 12-well plates of cultured human foreskin fibroblasts (done in
the
absence of inhibitor). Plaques are quantified at 2 weeks post-infection. An
inhibitor
of HCMV is identified by the reduction in titer of virus yield in the
presence,
compared to the titer in the absence of compound. In this assay, the relative
anti-
HCMV activity of an inhibitor is typically determined by calculating the IC50
or
IC90 value, that is, the amount of compound required to reduce the virus yield
by
50% or 90%, respectively. Table I describes ICso data for compounds tested
against
HCMV.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- I44 -
Microtiter plate assay. Ninety-six well plate cultures of human foreskin
fibroblasts are infected in the presence of inhibitor compound with a HCMV
recombinant mutant virus whose genome contains the prokaryotic beta-
glucuronidase
gene (Jefferson, R. A., S. M. Burgess, and D. Hirsh. 1986. Beta-glucuronidase
from
Escherichia coli as a gene fusion marker. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:8447-
8451 )
whose expression is controlled by a viral promoter. An example of such a virus
is
RV 145 (Jones, T. R., V. P. Muzithras, and Y. Gluzman. 1991. Replacement
mutagenesis of the human cytomegalovirus genome: US 10 and US 11 gene products
are nonessential. J. Virol. 65:5860-5872). Since it is under the control of a
viral
promoter, beta-glucuronidase expression is an indirect indicator of growth and
replication of HCMV in this assay. At 96 hours post-infection, the infected
cell
lysates are prepared (using SOmM sodium phosphate [pH7.0] containing 0.1 %
Triton
X-100 and 0.1 % sarkosyl) and assayed for beta-glucuronidase activity using a
substrate for the enzyme which when cleaved yields either a product which can
be
measured colorimetrically in a spectrophotometer or fluorescently in a
microfluorimeter. Examples of such substrates are p-nitrophenyl-beta-D-
glucuronide
and methylumbelliferylglucuronide, respectively. The presence of an antiviral
compound is indicated by the reduced expression of the HCMV genome resident
beta-glucuronidase gene, compared to the absence of inhibitor. Thus, the
generation
of the chromophore or fluorophore product in this assay is correspondingly
reduced.
Data from this assay generated using varying amounts of inhibitor compound is
also
used to estimate the ICSp of an inhibitor compound.
HSV antiviral (ELISA) assay
Vero cells (ATCC #CCL-81 } are plated on 96-well tissue culture plates at 3.5x
10°
cells per 100p1 tissue culture DMEM (Dulbecco's modified Eagle media)
supplemented with 2% fetal bovine serum (FBS) in each well. After overnight
incubation @ 37°C {in 5% C02) and 30 minutes prior to infection with
HSV-1
(multiplicity of infection equal to 0.006), cells are either untreated, or
treated with
test compound (multiple concentrations} or reference standard drug control.
After
approximately 24 hours post-infection incubation @ 37°C (in 5% C02),
cells are
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 145 -
fixed for ELISA assay. The primary antibody is murine anti-HSV glycoprotein D
monoclonal primary antibody and the secondary antibody is goat anti-mouse IgG
linked to 13-galactosidase. Thus the extent of viral replication is determined
by
assessing !3-galactosidase activity by quantifying the generation of the 4-
methyl
umbelliferone fluorescent cleavage product after addition of the methyl
umbelliferyl-
f3-D-galactoside (Sigma #M1633) substrate on a microfluorimeter (365nm for
excitation and 450nm for emission). Antiviral activity (ICso) of the test
compound is
determined by comparing the flourescence obtained in absence of compound to
that
obtained in the presence of compound. Data is shown in Table I.
VZV antiviral (ELISA) assay
For the generation of stock VZV to be used in the assay, VZV strain Ellen
(ATCC
#VR-1367) is used to infect human foreskin fibroblast (HFF) cells at low
multiplicity
(less than 0.1) and incubated overnight at 37°C in 5% CO2. After the
overnight
incubation, the mixture of uninfected and VZV-infected HFF infected cells are
then
harvested and added to each well of 96-well plates (3.5x10° cells in
100 pl DMEM
supplemented with 2% FBS) which contain test compound or the reference
standard
drug control (in 100E.~1 DMEM supplemented with 2% FBS per well). These cells
are
incubated for three days at 37°C in 5% COZ, then fixed for ELISA assay.
The
primary antibody is murine anti-VZV glycoprotein II monoclonal antibody
(Applied
Biosystems, Inc. #13-145-100) and the secondary antibody is goat anti-mouse
IgG
linked to 13-galactosidase. Thus the extent of viral replication is determined
by
assessing B-galactosidase activity by quantifying the generation of the 4-
methyl
umbelliferone fluorescent cleavage product after addition of the methyl
umbelliferyl
13-D-galactoside (Sigma #M1633) substrate on a microfluorimeter (365nm for
excitation and 450nm for emission). Antiviral activity (ICso) of the test
compound is
determined by comparing the flourescence obtained in absence of compound to
that
obtained in the presence of compound. Data is shown in Table I.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 146 -
Table I describes ICso data for compounds tested against herpes viruses.
Example IC50 IC50 % inhibitionIC50
(ug/ml) (ug/ml) 10 ug/ml (ug/ml)
HCMV HSV VZV VZV
426 1.6 >10 2 1.8
427 0. 8 > 10 21 1. 2
428 >10 >10 0 >10
429 I >10 U >10
443 >10 >lU U >10
~'4 4 8 0 >lU
471 0.03 >10 27 >1U
480 7 >10 42 >IO
483 5 1.2 45 > 10
520 0.32 12 38 >10
525 0.018 2.5 39 > I
0
593 >0.5 I O > 10
608 >0.5 9 > 10
609 1.5 8 >10
629 0.5 >10 >10
632 >10 >10 >10
633 0.34 >10 >IU
634 0.12 >10 >10
649 0.02 > 10 0.5
658 >0.5 10
659 >0.5 > 10
660 >0.5 10
802 >10 >10 7.3
803 >10 >10 >7.5
804 >10 >10 5.7
805 8 > 10 1.6
1093 >10 >10 >10
1094 > 10 > 10 >7.
5
1095 2.4 > I 0 7.1
1096 5.7 > 10 6.7
1097 4 >10 5.50
1098 3.5 9 3.80
1099 5.6 > 10 >7.5
1100 4.6 >10 7.3
1101 >10 >10 1
Thus, in accordance with the present invention, compounds of the present
invention may be administered to a patient suffering from VZV, in an amount
effective to inhibit the virus. Compounds of the present invention are thus
useful to
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 147 -
ameliorate to eliminate the symptoms of VZV infections in mammals including,
but
not limited to humans.
Compounds of the invention may be administered to a patient either neat or
with a convention pharmaceutical carrier.
Applicable solid carriers can include one or more substances which may also
act
as flavoring agents, lubricants, solubilizers, suspending agents, fillers,
glidants,
compression aids, binders or tablet-disintegrating agents or an encapsulating
material.
In powders, the carrier is a finely divided solid which is in admixture with
the finely
divided active ingredient. In tablets, the active ingredient is mixed with a
carrier
having the necessary compression properties in suitable proportions and
compacted in
the shape and size desired. The powders and tablets preferably contain up to
99% of
the active ingredient. Suitable solid carriers include; for example, calcium
phosphate,
magnesium stearate, talc, sugars, lactose, dextrin, starch, gelatin,
cellulose, methyl
cellulose, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidine, low melting
waxes
I S and ion exchange resins.
Liquid Garners may be used in preparing solutions, suspensions, emulsions,
syrups and elixirs. The active ingredient of this invention can be dissolved
or
suspended in a pharmaceutically acceptable liquid carrier such as water, an
organic
solvent, a mixture of both or pharmaceutically acceptable oils or fat. The
liquid carrier
can contain other suitable pharmaceutical additives such as solubilizers,
emulsifiers,
buffers, preservatives, sweeteners, flavoring agents, suspending agents,
thickening
agents, colors, viscosity regulators, stabilizers or osmo-regulators. Suitable
examples
of liquid carriers for oral and parenteral administration include water
(particularly
containing additives as above e.g. cellulose derivatives, preferably sodium
carboxymethyl cellulose solution), alcohols (including monohydric alcohols and
polyhydric alcohols e.g. glycols) and their derivatives, and oils (e.g.
fractionated
coconut oil and arachis oil). For parenteral administration the carrier can
also be an
oily ester such as ethyl oleate and isopropyl myristate. Sterile liquid
carriers are used
in sterile liquid form compositions for parenteral administration.
Liquid pharmaceutical compositions which are sterile solutions or suspensions
can be utilized by, for example, intramuscular, intraperitoneal or
subcutaneous
inaection. Sterile solutions can also be administered intravenously. Oral
administration
may be either liquid or solid composition form.
CA 02350996 2001-05-16
WO 00/34268 PCT/US99/28838
- 148 -
Preferably the pharmaceutical composition is in unit dosage form, e.g. as
tablets
or capsules. In such form, the composition is sub-divided in unit dose
containing
appropriate quantities of the active ingredient; the unit dosage forms can be
packaged
compositions, for example packeted powders, vials, ampoules, prefilled
syringes or
sachets containing liquids. The unit dosage form can be, for example, a
capsule or
tablet itself, or it can be the appropriate number of any such compositions in
package
form.
The therapeutically effective dosage to be used in the treatment of CMV
infection must be subjectively determined by the attending physician. The
variables
involved include the the condition , age and weight of the patient. The novel
method
of the invention for treating CMV infection comprises administering toa
subject,
including humans, an effective amount of at least one compound of Formula 1 or
a
non-toxic, pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The compounds may be
administered orally, rectaliy, parenterally or topically to the skin and
mucosa. The
usual daily dose is depending on the specific compound, method of treatment
and
condition of the patient. The usual daily dose is 0.01 - 1000 mg/Kg for oral
application, preferably 0.5 - 500 mg/Kg, and 0.1 - 100 mg/Kg for parenteral
application, preferably 0.5 - 50 mg/Kg.