Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02356839 2001-06-22
WO 00/40053 PC'd'/US99I30569
-1-
CONFIGURABLE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
HAVING IP-BASED CAIPABILITIES
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
S Technical Field of the Invention
The present invention relates generally to communication systems, and, more
particularly, to a system and method for configuring the method of
communication in a
wireless communication system having Internet Protocol (IP) based
capabilities.
Background and Objects of the Invention
Mobile wireless communication is becoming; increasingly important for
providing
safety, convenience, improved productivity, and simple conversational
pleasure. One
prominent mobile wireless communication option is cellular communication.
Cellular
phones, for instance, can be found in cars, briefcases, purses and even
pockets.
In a mobile cellular telecommunications system, a mobile station normally
communicates with the base station correspondin~; to the cell area in which
the mobile
station is located. There are circumstances, however, under which
communication with the
mobile station changes from one cell within the telecommunications network to
another. A
first situation is a handover operation in which the a mobile station roams
into another cell
while in a telephone call or other transaction. In order to choose a best cell
fox use by the
roaming mobile station, signal strength measurements of cell signal
transmissions are
performed by the roaming mobile station. During the handover operation,
various nodes
in the network negotiate a cell change with the mobile station depending upon
the nature of
the handover.
A second situation in which communication with a mobile station or terminal
changes
from one cell to another is a part ofthe Idle Mode procedures ofthe
terminal/mobile station.
This process, by which a terminal chooses which cell to utilize, is referred
to as "camping
on" a cell. The process includes location updating so that the serving mobile
switching
CA 02356839 2001-06-22
WO 00/40053 PCT/US99130569
-2-
center (MSC) and corresponding visitor location register (VLR) maintain the
approximate
location ofthe terminal. The "camping on" process may, for example, occurwhen
aterminal
is powered up. The camping process may also occur when a terminal is not
engaged in a
telephone call but is moving around and monitoring the transmission quality
ofthe different
cells. In the event the terminal changes location are~us while monitoring the
quality ofthe cell
transmissions, the terminal will perform a location update.
For celluiax phone system providers to oiFfer cellular phone users new
services,
cellular wireless networks must be upgraded. To this end, there exist and/or
are planned
wireless telecommunication networks which are capable ofproviding both
standard GSM
services and IP based services andlor applications. One advantage provided by
such
networks is that they are backwards compatible. In other words, the network
provides
both GSM services and IP applications, such as V'oIP, to terminals which are
capable of
accessing IP based applications while at the same; time maintaining
conventional GSM
wireless communication services for terminals which cannot utilize IP
applications, such as
due to limitations of the terminal itself.
One IP based application which is accessilble by cellulax telephone users is
voice
over IP (VoIP). The VoIP application provides quality voice communications
over the
packetized Internet. VoIP, overthe current Internet, for example, canprovide
acceptable
voice communications at a greatly reduced cost to i;he user, when compared to
traditional
mobile telephone tolls.
Although capable of providing telecommunication services to many subscribers,
the
above-described wireless network is not without its shortcomings. For
instance, if a caller
wishes to make a call in a wireless network having a VoIP application, a
circuit switched
call is transmitted from the corresponding Base Station System to the Mobile
Switching
Center (MSC), which is then sent along a trunk from the MSC to a gateway
connected to
an Internet Service Provider (ISP). The gateway converts the call from a
circuit switched
voice call to a packet switched call for transmission on the Internet.
Although this method
ofutilizing the Internet realizes reduced call tariffs, the'VoiP call
nonetheless utilizes circuit
switchtransmission resources in handling the call. Accordingly, there is aneed
forplacing
~4'~ i'~]~~~ CA 02356839 2001-06-22
-3-
the point at which access is made to the Internet closer to the terminal
and/or mobile
station within the mobile communications network.
One approach is to place an interface for accessing the Internet within the
Base
Station Controllers (BSC) so that the switching circuitry of the network is
substantially bypassed when an IP based application is provided to a mobile
station
user. In a communications network utilizing this approach, some of the cells
in the
network may be capable of providing iP based applications and/or
communications,
such as VoIP, in addition to conventional GSM based communication. A. call
placed
by a terminal and/or mobile station served by these cells, for example, is
capable of
I 0 being transported over/through the Internet so as 1:o incur a relatively
inexpensive toll.
Because not every BSC in the mobile network will typically possess the
capability to
provide IP based services andlor applications to mobile stations served
thereby, there
exists a need for ensuring that terminals requesting an IP based service are
satisfactorily and cost effectively served.
One existing approach is described in PC'r Publication WO 96/28947, which
shows a mobile communications system combining several mobile communication
networks. The parameters on the basis of which a mobile terminal decides on a
handover operation include connection quality and at least one of price,
capacity,
transmission speed and availability.
2fl Another existing approach is described i:n PCT Publication WO 97/ 1 S 1
S7,
which shows a method and device for supporting a plurality of mobile station
operation modes in a wireless system by user control. Protocols from various
technologies are combined to form end user equipment which operates in
multiple
user-invoked modes of operation.
It is an object of the present invention to provide a communications system
in which the cell assignment to a terminal is dependent upon user preference.
It is another obj ect of the present invention to provide such a communication
system having enhanced communication of both network and terminal information
between the network and a terminal therein.
3Q
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02356839 2001-06-22 U~ ~~~Q3C5E9
-3a-
SUlHIMA.RY OF TIC INVENTION
The present invention overcomes shortcomings in existing communication
systems and satisfies a significant need for a comrnunication system having
improved
methods for accessing the system's IP based capabilities.
According to the present invention, there is provided a mobile communications
network, such as, for example, a Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN), divided
into
a number of cells which communicate with at Ie~ast one MSC via a number of
base
stations. At least one base station is capable of accessing an IP based
application,
such as VoIP by including a transcoder to convert a voice call transmitted by
a
terminal into a packet switched call for transport over the Internet. The
cells
associated with each base station
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02356839 2001-06-22
WO 00/40053 PC'~'/US99/30569
-4_
transmit their service capabilities, including its IP-based capabilities, so
that a terminal
receiving the transmission is aware of the service capabilities of its present
cell and
neighboring cells. Conversely, each terminal in the mobile communications
network
transmits its own capabilities, such as being IP capable, to the network. In
this way, both
the network and each terminal can be apprised of each other's capabilities so
that decisions
pertaining to providing service-related activities, such as transporting a
telephone call, are
effectively carried out.
The present invention further includes each terminal possessing an interface
and
necessary circuitry to facilitate the user in selecting a cell preference from
among cells which
I O only support GSM-related services and cells which support both GSM-related
services and
IP based applications: For example, the interface may allow the user to prefer
cells which
support VoIP for transporting telephone calls placed by the user's mobile
station overthe
Internet. The system selects a cell for providing a service to the terminal,
such as
transporting a telephone call placed thereby, based in part upon the service-
related
15 capabilities of cells in the immediate area of the terminal and upon the
selected cell
preference. As a result, the present communications system suitably matches
its available
services to the user's service preferences.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWIN('sS
20 A more complete understanding ofthe present invention may be had by
reference
to the following detailed description when taken in conjunction with the
accompanying
drawings wherein:
Figure 1 is a block diagram of a telecommunications system according to the
present invention;
25 Figure 2 is a block diagram of a terminal according to the present
invention;
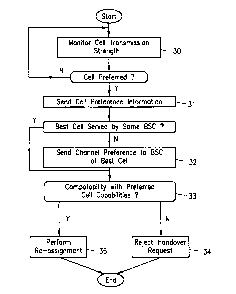
Figure 3 is a flow chart illustrating a handover operation in association with
the
present invention;
Figure 4 is a flow chart illustrating a cell reassignment operation in
association with
the present invention; and
CA 02356839 2001-06-22
WO 00/40053 PCT/US99/30569
-S_
Figure 5 is a flow chart illustrating a location update operation in
association with
the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EXEMPLARY
EMBODIMENTS
The present invention will now be described more fully hereinafter with
reference
to the accompanying drawings in which a preferred embodiment ofthe invention
is shown.
This invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should
not be
construed as being limited to the embodiment set forth herein. Rather, the
embodiment is
provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully
convey the
scope of the invention to those skilled in the art.
Refernng to Figures 1 and 2, there is shown a communications system I
including
mobile communications network 2 and Internet and/or IP network 3. Mobile
communications network 2 may preferably include a plurality ofinterconnected
MSCs 4,
each ofwhich communicates with one or more base station controllers (BSC) 5.
Each B SC
5 communicates with at least one base transceiver station (BTS) 6. A single
BTS 6 serves
one or more cells in mobile communications network 2. The operation of mobile
communications network 2 and in particular the interrelationship between MSCs
4, BSCs
5 and BTSs 6 in providing mobile cellular services are known in the art and
will not be
described herein for reasons of simplicity.
One or more BSCs 5 of mobile communi~;,ations network 2 may be capable of
accessing IP network 3 in order to provide one or more 1P applications to
subscribers of
the mobile communications network 2. ABSC 5 may, for example, have access to
IP
network 3 using one or more Internet Service Providers (ISP) 7.
One IP application which a BSC 5 preferably accesses and is capable
ofproviding
to subscribers ofmobile communications network 2 is VoIP, which provides
acceptable
voice communications at a greatly reduced subscriber cost, as explained above.
Accordingly, the BSCs 5 which are capable of providing VoIP to subscribers
ofthe mobile
communications network 2 include a transcoder unit 8 or other device which
converts a
CA 02356839 2001-06-22
WO 00/40053 PC'r/US99/30569
-6-
circuit switched (GS1V1) voice call to a packet switched call fortransport
over the Internet.
By including transcoder unit 8 within a B S C 5, a V'oIP telephone call placed
by a terminal
9, such as a mobile station, bypasses the switching circuitry (MSCs 4) of
mobile
communications network 2.
It is understood that a cell may be capable of accessing a number of IP based
applications in addition to VoIP through its corresponding B SC 5 . For
instance, a cell in
mobile communications network 2 may be capable ofaccessing anH.323 based
multimedia
application.
The present invention allows subscribers ofmobile communications network 2 to
mare effectively access communication services provided by mobile
communications
network 2 and IP network 3. It is understood th;~t not every BSC 5 may be
capable of
accessing IP network 3. It is also understood that a BSC 5 which may be
capable of
accessing IP network 3 may typically be capable of accessing a limited number
of IP
applications. Fox instance, an IP capable BSC 5 may utilize a specific ISP 7
in accessing
IP network 3 . Due to the fact that B SCs of mobile communications network 2
and thus the
cells corresponding thereto provide different IP applications and/or possess
different IP
based capabilities, the present invention allows a subscriber of mobile
communications
network 2 to select prefezxed capabilities for a cell to possess in order to
communicate
therewith.
Specifically; the present invention allows a subscriber to identify a
preference for
a cell/B SC which supports particular IP based applications withwhichthe
subscriber may
communicate. The mobile communications network 2 utilizes the identified cell
preference
in selecting a cell to communicate with the subscriber's terminal 9, such as
when mobile
communications network 2 performs cell handover procedures or while camping-on
a cell.
To facilitate the process of selecting a cell preference and assigning a cell
to
communicate with a terminal 9, information regarding network 2 is preferably
transmitted
to terminal 9. The information transmitted by mobile communications network 2
to a
terminal 9 preferably informs terminals 9 ofthe capabilities ofeach cell. In
otherwords, for
each cell, mobile communications network 2 provides a list of services and/or
applications,
CA 02356839 2001-06-22
WO 00/40053 ' PCT/US99/30569
including IP based applications, which are accessible thereby. In a preferred
embodiment
ofthe present invention, the Broadcast Control Channel (BCCI~ is modified to
include this
cell capability information. In this way; a terminal 9, upon receiving the
cell capability
broadcast, is capable ofdetermining the cell capabilities ofthe cell presently
serving terminal
9 and its neighboring cells.
As stated above, the present invention allows for the selection of a cell
preference
for use in assigning a terminal 9 to a cell within mobile communications
network 2. Referring
to Figure 2, terminal 9 preferably includes an interface 20 which is coupled
to transceiver
21 to receive the BCCH information pertaining to cell capabilities and to
generate the
necessary signals for presenting the cell capabilities to the subscriber on
display 22. Display
22 preferablyfurther~iisplaysthepresently assigned cell;-its capabilities,
andlorthe service
being provided to the subscriber.
Further, terminal 9 allows forthe selection or identification of a cell
preference for
use in assigningtenninal 9 to a cell, such as during a handover procedure
orwhile camping-
on a cell. The cell preference may be entered into terminal 9 by the
subscriber using keypad
23 . Alternatively, the cell preference may be stored, either permanently or
otherwise, on
a SIM card 24 which is operatively connectible to terminal 9. By possessing a
number of
SllVI cards having stored thereon different cell capability preferences,
terminal 9 may be
configured with different cell capability preferences simply by inserting
different SIM cards
24 therein.
The present invention allows mobile communications network 2 (Figure 1) to
determine the capabilities of terminals 9 located therein. In particular, a
terminal 9
preferably communicates to mobile communications network 2 its IP based
capabilities.
For example, the information may indicate whether terminal 9 complies with a
certain suite
of specifications, such as H.323 or SIP. Terminal capability information may
be utilized by
mobile communications network 2 in reaching cell assignment decisions, such as
during cell
handover or camping on a cell, by giving greater preference to assigning an IP
capable cell
to a terminal 9 which prefers communication with an IP capable cell and which
itselfis IP
capable. Specific channel types or target cells could be selected for
assignment to a
CA 02356839 2001-06-22
wU 00/40053 PCTlUS99/30569
_g_
terminal 9 based upon the terminal capability information. In a preferred
embodiment ofthe
present invention, the IP based capabilities of a terminal 9 are added to the
GSM classmark
corresponding to terminal 9 for communication to mobile communications network
2:
In addition, the subscriber profile, stored :in a Home Location Register
(HI,R) 10,
may preferably indicate whether IP support for a terminal 9 is preferred ar
forbidden. This
profile information may be downloaded and used together with the terminal
capability
information in the classmark in assigning a cell ito serve terminal 9.
The operation ofthe present invention will now be described with reference to
Figures 3-5. In performing acell handover operation in which cell selection is
based in part
upon the user's communication preferences, termin~~l 9 monitors the signal
strength of cells
in the area thereof at step 3 0. In the event one or more cells whose-
trailsinissions terminal
9 measured is a preferred cell or otherwise possesses preferred communication
capabilities,
terminal 9 sends preferred cell capability informationto mobile communications
network 2
at step 31. For example, terminal 9 may send. a cell preference listing to
mobile
communications network 2. Next, if mobile communications network 2 determines
that,
based upon the preferred cell information sent by terminal 9, the new cell for
communicating
with terminal 9 is associated with a different l3SC 5, then the channel
preference
corresponding to the cell capability preferences is sent to the BSC 5
corresponding to the
new cell at step 32. In this way, BSC 5 is aware of the preferred channel type
and
equipment which is needed to support it.
It is noted that the serving MSC 4 may not know the preferred channel type
corresponding to the preferred cell capability preference ofterminal 9.
Consequently, MSC
verifies that the preferred cell capability for the best cell is possible at
step 33. If the
preferred cell capability preference is not possible and/or compatible, then
the handover
operation to the selected cell is rejected at step 34. Alternatively, ifit is
determined that the
preferred cell capability preference is possible for the best cell, then
terminal 9 is handed
over thereto at step 35.
Figure 4 illustrates the process for selecting a cell for terminal 9 while
"camping on"
a cell. Initially, each basetransceiver station (BTS) ti broadcasts the IP
capabilities, ifany,
~~i-'G I'217~J 1 ~ 02356839 2001-06-22
-9-
for the cells corresponding thereto for reception by terminal 9 at step 41.
Next,
interface 20 interprets the cell IP capability information and displays the
information
on display 21 at step 42. At this point, a cell capability preference may be
identified
at step 43. This identification may be undertaken'by the subscriber manually
entering
the cell capability preference using terminal keypad 23 or by terminal 9
reading the
cell preference from SIM card 24 connected thereto.
In the event terminal 9 has indicated to molbile communications network 2 that
terminal 9 is to be camped onto a cell selected ox' preferred thereby, then
terminal 9
is camped onto the selected cell at step 44. If the cell camped onto during
step 44 is
in a new location area, then a location update is performed at step 45.
The steps for perfarming a location uI>date in the serving MSC 4 and
corresponding VLR is illustrated in Figure s.Upon a reception location update
request from terminal 9 at step s 1, MSC 4 receives and stores the classmark
therefor
at step 52. The classmark may include cell capability preference information
for
terminal 9. If it is determined that terminal 9 is n.ot registered with MSC 4,
MSC 4
notifies the I3LR 10 corresponding to terminal !a. HLR 10 thereupon sends data
pertaining to terminal 9 and including its cell capability preferences to MSC
4 at step
s3: Thereafter, the subscriber profile for terminal '9 is stored within 1VISC
4 and/or its
corresponding VLR at step s4.
Although the prefezred embodiments of the present invention have been
illustrated in the drawings and described in the foregoing detailed
description, it is
understood that the invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments, but
is
capable of numerous rearrangements, modifications and substitutions.
2s
AMENDED SHEET