Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02357205 2001-09-13
CALL PROCESSING SYSTEM WITH INTERACTIVE VOICE RESPONSE
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a call processing system and, more
particularly, to a call processing system that provides interactive voice
response.
DESCRIPTION OF THE RELATED ART
Interactive voice response (IVR) systems are commonly used to automate the
process of obtaining and providing information to users. Usually an IVR system
interacts with the user via the dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) keypad on the
user's
telephone for input and the telephone speaker for output. Often, the IVR
system is
part of a larger system that provides other services, such as outdialing, text-
to-speech
conversion, speech recognition, etc. However, all known combined systems have
an
architecture that treats the IVR system like all of the other systems.
A typical combined system is disclosed in U.S. Patent 5,884,032 to Bateman et
al. which is connected to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) via a
digital
switch that is also connected to a data network to which all of the various
types of
systems, including the IVR system are connected. Often, the digital switch is
controlled by an automated call distribution (ACD) system that attempts to
route the
call to the appropriate subsystem based on routing information, such as the
number
that was called to reach the system, provided by, e.g., dialed number
identification
service (DNIS), or the number from which the call was initiated, e.g.,
automatic
number identification (ANI). However, often this is insufficient information
to make
a final determination of how the caller will be serviced by the call
processing system.
Therefore, calls end up being re-routed from subsystem to subsystem while
being
connected to the switch.
Furthermore, a typical call processing system is not easily scalable or able
to
overcome failure of key components. Part of the problem is that such systems
are
typically centered on the digital telecommunications switch. Another part of
the
problem is that the architecture of such systems generally does not have high
level
redundancy. There may be redundant components within the system but there is
now
known call processing system with an IVR that has wide area redundant
capabilities.
-1-
CA 02357205 2001-09-13
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
An object of the present junction is to initially provide interactive voice
response to incoming calls for rerouting calls when necessary.
Yet another object of the present invention is to provide a call processing
system with high redundancy that is able to continue to process incoming calls
despite
failure of major components.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
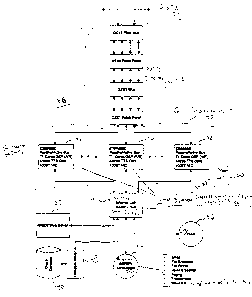
Fig. 1 is a block diagram of a prior art call processing system.
Fig. 2 is a block diagram of a local call processing system according to the
present invention.
Fig. 3 is a block diagram of power supply for a local call processing system
according to the present invention.
Fig. 4 is a distributed call processing system according to the present
invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
A simplified example of a conventional call processing system is illustrated
in
Fig. 1. A private branch exchange (PBX) 20 is connected to the PSTN 22 via
numerous connection 24, such as one or more T1 lines or analog telephone lines
(POTS). PBX 20 includes a conventional automatic call distributor (ACD) 26 for
distributing calls internally to human operators represented by desktop
computer
systems 28 and IVR system 30. Information systems and databases 32 are
accessible
by PBX 20 and the desktop systems 28 for information to distribute calls by
ACD 26
and provide or store information related to callers by the human operators.
There are numerous draw backs to conventional systems. First, conventional
call processing systems of the type illustrated in Fig. 1 typically use
propriety
hardware and software that is quite expensive compared to the component cost.
As a
result, maintenance and upgrades are expensive. Conventional systems were
designed
for a single site and thus, multi-site configurations require an additional
layer of
hardware and software that was not part of the original design, making multi-
site
expansion expensive and difficult. Not only were mufti-site configurations
designed
later, but many other services, such as speech recognition, were not part of
the original
-2-
CA 02357205 2001-09-13
design of a conventional PBX 20 and inclusion of such capability reduces the
number
of lines available for IVR system 30 as well as adding further complexities to
the
system architecture.
Illustrated in Fig. 2 is a block diagram of a first embodiment of a call
processing system 38 according to the present invention. Instead of using a
PBX to
provide services that were not contemplated during the design of the PBX, the
present
invention utilizes call processing unit 40 designed for flexibility,
efficiency, and
scalability. Call processing unit 40 is connected to PSTN 22 via a PSTN
interface 42
and to an internal communication interface 44. In the preferred embodiment,
call
processing unit 40 includes a plurality of digital signal processor (DSP)
cards 46, that
provide at least IVR and thus may be referred to as IVR servers. Each DSP card
46 is
capable of handling, e.g., 24 telephone calls simultaneously, i.e., a
telephone
connection provided by a T1 line, such as a Dialogic D480 SC-2T1 card
available
from Dialogic Corporation of Parsippany, New Jersey. A typical system may have
up
1 S to 20 such processor cards 46. Internal communication interface 44 may be
an
Ethernet LAN switch/hub, having sufficient capacity to communicate with DSP
cards
46 via e.g., a 100 Mbps connection.
Preferably, internal communication interface 44 is connected to computers that
act as servers for other functions. For example, database server 48, such as a
Compaq
Proliant 1600 running SCO Unixware 2.x, accesses database 50, such as Oracle
7.3,
for information required by processing cards 46 to provide programs and data
used in
the interactive voice response process and information used by human operators
in
communicating with callers. In addition, webserver 52 may be provided for
update of
the information in database 50, by one or more information providers, or to
provide
access to that information by users as an alternative to calling on the
telephone.
Each processor card 46 typically has 24 ports (for 24 calls) with a DSP
connected to each port. Each DSP is programmed to begin the IVR process with
the
caller when a call is received and is capable of outdialing operations, such
as for
predictive dialing. As the call progresses, additional data or functional
capabilities are
requested by the DSP via internal communication interface 44 from database
server 48
or other resource servers 54. In addition to IVR, the DSPs in processor cards
46 may
be programmed to provide text to speech. Alternatively, separate text-to-
speech cards,
such as Antares 2000/50, from Dialogic Corporation with software from Lernout
&
-3-
CA 02357205 2001-09-13
Hauspie of Burlington, Massachusetts, may be used and coupled to the caller
via
LAN/WAN 56 and the processor cards 46.
If the program executed by the DSP, receives a response from the caller that
requires assistance of resources that are not available at call processing
system 38, the
DSP requests that a human operator be called, or the caller be switched to
another call
processing unit 40 at a different location, as discussed below in more detail.
The
DSPs in processor cards 46 are programmed to route callers to another call
processing
unit 40 via network call routing by identifying a called number at which an
human
operator or another call processing unit can be connected to assist the caller
using a
second port to outdial to the called number and bridging the caller on the
first part to
the second part.
Web server 52 provides access to database 50 to update the database and may
also be used as an alternative to telephone calls by users. Call processing
unit 40 also
has access to resource servers 54 to obtain e-mail messages, transcription
(speech-to-
text) of messages left by callers via call processing unit 40, unified
messaging,
conference calling, or communicating by other means. In addition, processor
cards 46
are capable of outdialing operations and may be accessed by resource servers
54 for
sending facsimile forms or digital auto files requested callers, either to a
facsimile
number provided by the user, the same number the user called from, a number
obtained from database 50, or, particularly in the case of audio files,
directly to the
user while still connected. In addition, outdialing capabilities of call
processing unit
40 may be used by resource servers 54 for broadcasting voice messaging,
paging,
broadcasting facsimile etc. In addition to accessing local database SO via
database
server 48, requests can be made via LAN/WAN 56 to other databases.
The service provided to callers is preferably monitored by call processing
unit
40 with statistics sent to database 50, or a monitoring and reporting server
included in
resource servers 54. The information monitored may include information such as
length of time that the caller interacts with the IVR, length of time between
receipt of
a callers response and the beginning of output in response thereto, total time
of
connection, the length of time that network call routing is performed (i.e.,
that a caller
is bridged to a called party) and the type of interactive voice response
performed. One
of the advantages of bridging callers to human operators (or other call
processing
systems) at a remote terminal is that the caller can be returned to call
processing unit
-4-
CA 02357205 2001-09-13
40 for further IVR processing or other services after the remote connection is
broken
by the remote terminal.
Preferably call processing unit 40, internal communication interface 44 and
servers 48, 52, 54 are all constructed using conventional redundant capability
for
maximum reliability. For example, call processing unit 40 preferably includes
the
ability to "hot swap" processor cards 46, when a single card has a fault. To
ensure that
no DSP(s) are servicing callers when a card is swapped out, call processing
unit 40
further includes resource management unit 60 for allocating resources,
including the
ability to restrict subsequent calls from being routed to a particular
processor card 46,
by taking all DSPs on a processor card 46 out of service and reporting to a
system
operator when the processor card 46 is not handling any calls.
To ensure maximum reliability, power is preferably supplied to the
components illustrated in Fig. 2 using a power architecture as illustrated in
Fig. 3. In
addition to obtaining power from a commercial utility 70, an on-site
supplemental
generator 72 is coupled via transfer panel 74 through an uninterruptible power
supply
76 to alternating current (AC) powered equipment 78. UPS 76 maintains power in
a
conventional manner for sufficient time for resource management unit 60 or
another
component connected to the network to start operation of generator 72. In
addition, a
system operator may be informed of the power interruption, e.g., via an
outdialing
operation. In a typical embodiment, there is direct current (DC) powered
equipment
80, such as multiplexers, patch panels and routers, as well as AC powered
equipment
78. Therefore, transfer panel 74 is also connected to AC/DC Rectifier 82 and
battery
84 to ensure that there is no power interruption to DC powered equipment 80.
In addition to managing local resources, resource management unit 60
provides the capability of easily configuring a call processing system over a
widely
dispersed geographic area. Thus, database 50 preferably is capable of being
part of a
distributed database schematically illustrated in Fig. 4. Communication
between
database servers 48 is preferably provided by LAN/WAN 56. By dispersing the
locations of call processing systems throughout a region served, there is
greater
security from natural disasters and manmade disruptions to service. It is also
possible
to provide economy of telephone service by locating call processing systems in
areas
of highest use. Distribution of data can be accomplished using conventional
-5-
CA 02357205 2001-09-13
distributed database techniques to ensure redundant, up-to-date copies of the
database
at each location.
To provide flexibility of call processing functions, a hierarchical
organization
of call processing systems 38 is used. Preferably, multiple communication
trunks are
available for communication between the resource management units 60. The wide
area network represented by LAN/WAN 56 may be provided by one or more leased
lines. In addition, data communication between resource management units 60
may
be accomplished using the PSTN 22 which preferably includes a plurality of
long
distance carriers having separate physical connections to PSTN interface 42.
When, for example, a processing card 46 is replaced as described above,
resource management unit 60 detects the presence of the new processing card 46
and
registers the additional resources as available in database 50, or elsewhere.
In
addition, the updated resource capabilities are reported to a higher level
call
processing system. Addresses) for contacting the higher level call processing
system
are retrieved (or input) at start up of a call processing system 38. For
example, call
processing system 38A in Fig. 4 may be a primary call processing system which
receives reports from call processing systems 38B and 38C regarding total
resources
and resources in use. There may be separate call processing systems 38 at a
single
geographical location, in which case resource status is first reported via a
hierarchy of
co-located call processing systems 38 and then to a higher level call
processing system
at a remote location. Between any particular level, there may be only a single
lower
level and single higher level call processing system and there may be any
number of
levels. Preferably, the top level is redundant, or at least the address and
hierarchical
structure is stored in the redundant distributed database, so that if no
response is
received from an immediately higher level call processing center, that call
processing
can be leap-frogged by lower levels to a higher level, or if the highest level
is non-
responsive, a second level call processing system takes over, until a response
is
received.
The communication between resource management units 60 is not limited to
providing redundancy. Callers may be shifted from one call processing system
38 to
another based on schedule or capacity. Examples of schedules include expected
volume for time of day, local holidays, etc. Examples of shifting callers
based on
capacity include high resource use, or lack of a required resource at a
particular call
-6-
CA 02357205 2001-09-13
processing system. One way of implementing such shifts is to include in each
call
processing system a load balancer for balancing usage of the long distance
carriers by
outgoing calls, e.g., when bridging to a called party or contacting a remote
call
processing system, or performing an outdialing operation for any of the
services that
require outdialing.
The many features and advantages of the present invention are apparent from
the detailed specification and thus, it is intended by the appended claims to
cover all
such features and advantages of the system which fall within the true spirit
and scope
of the invention. Further, numerous modifications and changes will readily
occur to
those skilled in the art from the disclosure of this invention. It is not
desired to limit
the invention to the exact construction and operation illustrated and
described;
accordingly, suitable modification and equivalents may be resorted to, as
falling
within the scope and spirit of the invention.