Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
r
CA 02366169 2001-12-27
TRAINING SEARCH METHOD FOR MANNER OF MOVING BODY IN SPORT USING
MOBILE IMAGE COMMUNICATION
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a method of searching
training for a basic manner of moving a body in a sport performed
by moving a body.
Description of the Related Art
According to the present invention, as a training method
for training a basic manner of moving a body in a sport performed
by moving a body, a trainer has performed a typical action or
the like and then cause a trainee to perform an action or the
like, and the trainer has explained the difference between the
typical action and the action to the trainee with voice or body
action. In addition, a larger number of media described as
follows have been spread. That is, a trainer herself or himself
performs a typical action, and voice, a training book, or the
like is added to the typical action, so that self-training can
be achieved.
The following invention is disclosed as USP. No. 5,184, 295
(issued on February 2, 1993 ) . That is, a typical action or the
like is input as a video image, and the image and an action or
the like performed by a trainee are overlapped by an arithmetic
operation process, so that training is performed with a
three-dimensional image. However, according to this patent,
since the excellent typical action or the like is recorded as
1
CA 02366169 2001-12-27
a video image in advance, training which is fitted to the age
and the physical strength of the trainee and which is effective
for only the trainee or training which performs a gradual
training method in accordance with each trainee cannot be
achieved.
Therefore, an action or the like of a trainee is recorded
as a video image, one screen of this image is reproduced on a
display, and a range of an action to which attention must be
paid, a basic line or the like of a body constituting an optimum
pose, and the like are indicated on an action image of the trainee
on the screen with lines or the like. This application was filed
by the present inventor of this application prior to the above
invention. In Japan, the application was filed on August 3,
1994. The application is disclosed in Japanese Unexamined
Patent Publication No. 7-144038, and is patented on June 12,
1999 as Patent No. 5,857,855 in the United States of America.
On the other hand, with recent development of
communication devices; a novel digital TV transceiver system
for separating video data from data linked with the video data
and transmitting these data by the same channel has also been
able to be provided.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is an object of the present invention to provide a system
which can display a video image and data of a trainer which are
desired to be seen by a trainee with a mobile communication
device and which can displa~i'"~ video image and/or data of the
2
' CA 02366169 2001-12-27
trainee or a third party on the same screen without being
overlapped while being linked with each other.
An aspect of the present invention uses a multi-functional,
high-performance mobile image communication terminal such as
a portable telephone, a mobile network system such as a PDC
or/and a PHS, a gateway for performing protocol conversion or
the like, and the Internet, one camera or a plurality of cameras
for photographing a body action of a trainer such as a player
actor, and a system for encoding video information of the camera
to transfer the encoded information to a video server through
a cable or/and wireless network circuit, and a system which
receives various pieces of information of the body action and
transfers the data to a data server through a cable or/and
wireless network circuit.
Therefore, a trainee such as an auditory user searches a
data server by the mobile. image communication terminal to
automatically calculate the data and video data related to the
data, so that the data and the video data can be shown on the
same screen while being linked with each other.
According to another aspect of the present invention, the
data of the data server or/and the video server is data of a
trainer such as a coach or an instructor, and these data and
the data or/and the video image of the trainee are displayed
on the same screen without being overlapped and compared with
each other, so as to make it possible to perform training.
According to still another aspect of the present invention,
in means for causing a trainer to train a manner of moving a
3
CA 02366169 2001-12-27
body for a trainee, the trainer searches for two still images
through mobile image communication from the video server or/and
the data server on which the data of the trainee and displays
the still images, and these still images are simultaneously
displayed and compared and examined, so as to make the trainee
to understand the difference between bath the actions.
According to still another aspect of the present invention,
in means for causing a trainer to train a manner of moving a
body for a trainee, actions of a sport performed by the same
trainee are picked as images from substantially the same place,
the images are reproduced without being overlapped on the same
screen such as a mobile display, any one of the images is set
as a moving image, and the other image is set as a still image,
so as to make the trainee to understand the relation between
the images.
According to still another aspect of the present invention,
a sport, an action, a movement, or the like performed by a trainee
before the trainee is trained by a trainer is picked as an image,
thereafter, the trainee picks a sport action performed after
the trainee is trained by the trainer as an image from the same
place, these images are reproduced without being overlapped on
the same screen such as a mobile display, and the two images
are simultaneously compared with each other and examined, so
as to make the trainee to understand the degree of improvement .
According to still another aspect of the present invention,
when a moving image of a sport action of a trainer or a trainee
is reproduced_on a mobile,. ~c~~~3lay, a line or a grid-like line
4
' CA 02366169 2001-12-27
r
serving as a reference when the trainee sees the image is
displayed on the image, so as to make the trainee to understand
the degree of an act such as the sport, an action, or a movement.
According to still another aspect of the present invention,
a moving image of a sport action of a trainer or a trainee is
displayed on a mobile display as still images of respective
frames, a basic line of a body featuring the frame is drawn on
the corresponding image along the image, the image on the screen
is switched to the next frame while the basic line is left on
the screen, a basic line of the body featuring the frame is drawn
on the corresponding image along the image, the basic lines of
the body featuring the subsequent frames are drawn on the
corresponding images along the images, finally, the image of
the sport action is erased, and only a plurality of basic lines
are displayed on one screen in place of the moving image, so
as to make the trainee to understand the change of the basic
lines of the body.
According to still another aspect of the present invention,
a video still image of a sport action of a trainer or a trainee
is displayed on a mobile display, and letters or/and symbols
are described by the trainer on a part of the video still image,
so as to make the trainee to understand a training point.
According to still another aspect of the present invention,
sport actions at different places are simultaneously picked as
images , the images are reproduced without being overlapped on
the same screen of a mobile display, and the two images are
simultaneously compared with each other, so as to make a trainee
° CA 02366169 2001-12-27
to understand the difference between both the images.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF~THE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is a block diagram of a system used in the present
invention;
Fig. 2 is an illustrational diagram of Fig. 1;
Fig. 3 is a diagram showing an addressing form of golf in
training;
Fig. 4 is a diagram showing a tee back form of golf in
training;
Fig. 5 is a diagram obtained when a golf ball is hit in
training;
Fig. 6 is an addressing diagram showing one of two images
displayed on a screen as a still image and the other as: a moving
image to compare the two images with each other and to examine
the images;
Fig. 7 is a top swing diagram showing one of two images
displayed on a screen as a still image and the other as a moving
image to compare the two images with each other and to examine
the images;
Fig. 8 is a diagram showing a manner of moving a body in
golf swing;
Fig. 9 is a diagram in which top swings of a trainer and
a trainee in an actual golf course are compared with each other;
and
Fig. l0 is a diagram in which forms of a trainee before
training and after trainin.gat~ compared with each other to make
6
CA 02366169 2001-12-27
the trainee to understand the difference between both the forms.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
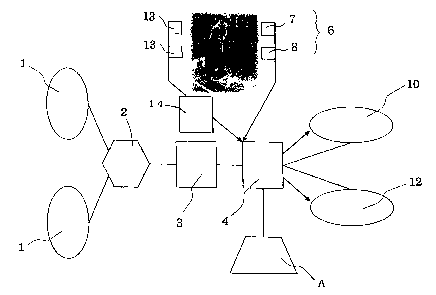
Fig. 1 shows a golf play as an example of the present
invention. In Fig. 1, reference numeral (1) denotes a
multi-functional, high-performance mobile communication
device (to be referred to as a portable telephone terminal
hereinafter ) such as a portable telephone; ( 2 ) denotes a mobile
communication network system such as a PDC/PHS; ( 3 ) denotes a
gateway for performing protocol conversion; (4) denotes the
Internet.
In Fig. 2, reference numeral ( 5 ) denotes a driving range;
( 6 ) denotes a plurality of cameras for a boom shot video image
( 7 ) or a zoom wide video image ( 8 ) . The plurality of cameras
(6) is connected to an encoder (9) including a digital disk
recorder, a still image file device, a frame synchronizer, and
the like and having a time compression function, a multiplexing
function, and a packet transmission function. Reference
numeral ( 1 ) denotes a video server connected to the cameras ( 6 )
through the Internet (4).
The camera (6) makes a boom shot video image to really
capture the actions and situations of a body when a player plays,
e.g., golf. In addition, the plurality of cameras (6) are
prepared at important points such as a grip to obtain the zoom
wide video image.
In Fig. 2, reference numeral ( 13 ) denotes a terminal to
which data of every move of a player. In this embodiment, two
7
' CA 02366169 2001-12-27
terminals (13) are prepared to cover a lack of input data and
to improve the reliability of the data.
In addition, reference numeral ( 12 ) denotes a data server.
The data server can store data transmitted from the data
terminal ( 13 ) through a data transfer device ( 14 ) and a network
circuit, and can also store profiles of players and additional
data (contents) if necessary.
Furthermore, the data server ( 12 ) has a data server program
having a master maintenance function, a terminal master
updating function, and a data searching function, and a data
transfer function of a search result and a data convert program
having an input data real time display data convert function,
an input data file transceiver function, a database updating
function, a database updating function, and a master updating
tile terminal transfer function.
With respect to the time compression function described
above, since a protocol, i.e., MPEG2 (Moving Picture Experts
Group 2 ) exists, time compression of information is performed
by using the characteristics of the protocol, and a link of time
and video images, a link of time and data, and the like are
combined to each other, so that the various data can be
incorporated.
More specifically, in the MPEG2, frames are not decoded
in the order of reception. As frames subjected to time
compression, I frame, P frame, and predicted B frame formed by
the I and P frames are known.
For example, frames ,why received in the order of IBBP
8
' CA 02366169 2001-12-27
are decoded in the order of IPPB, the P frame is calculated for
example, and the two B frames are calculated by using the I frame,
so that two B frames are formed by using a new I frame. More
specifically, by applying a process technique for the frames,
two basic data stream formats are processed by software, so that
packet multiplying transmission can be performed. In addition,
data is incorporated as a closed-caption-added text data by a
TS (Transform Stream) packet and transmitted to a trainee (user),
so that the trainee (user) can select data according to his/her
taste.
In Fig. 2, reference symbol (A) denotes a fixed terminal
such as a personal computer . As a matter of course, the f fixed
terminal (A) can also search for data through the Internet ( 4 ) .
However, according to the present invention, especially, a
mobile terminal (1) such as a portable telephone is used.
When the present invention is performed, as shown in the
driving ranges shown in Fig. 2, at the driving range or an actual
golf course, a trainee (B) picks images of a form of, e.g., a
driver with the camera (6), and stores the images in a video
image server ( 10 ) through the encoder ( 9 ) and the Internet ( 4 ) .
A trainer uses a known system or program software in the
fixed terminal (A) such as a personal computer to draw grid-like
lines or graphics on the graphic. More specifically, for
example, in golf, the trainer trains a trainee such that the
position of the head of the trainee must not be moved especially
when the trainee swings a golf club. This is performed for the
following reason. Although the trainee cannot sufficiently
9
CA 02366169 2001-12-27
understand that the position of the head must not be moved even
though the trainee watches a screen on which the trainee plays
golf, the trainee can easily understand that the position of
the head must not be moved by drawing a plurality of grid-like
lines on the screen.
For the sake of descriptive convenience, an operation will
be descried by only the parts of the configuration and the means .
For example, a trainee who makes a request for her/his form
in advance calls the video image server ( 10 ) by using the her/his
portable telephone terminal (1) through the mobile
communication net system ( 2 ) , the gateway ( 3 ) , and the Internet
( 4 ) to search for her/his driver form. As a result, as shown
in Figs. 3 to 7, video images on which a plurality of lines are
drawn can be displayed on the display of the mobile communication
device (1).
In Fig. 3, the left shoulder "excessively moves down" . As
shown in Fig. 3, if the left shoulder is not swung along the
upper side of the inverted triangle as shown in Fig. 3, a ball
may be "hooked" or sliced. In a take-back state shown in Fig.
4, when the left shoulder excessively moves up, immediately
after the ball shown in Fig. 5 is hit, i.e., in impact, the
trainee is good because shaking of her/his head, i. e. , so-called
"sway" does not occur. When training is performed by using the
method of the present invention, a correct form can be realized,
and a preferable training :result can be given to the trainee.
In addition, in Figs. 6 and 7, image of a form of the same
trainee are picked from diffnt positions, and the images are
CA 02366169 2001-12-27
displayed without being overlapped on the same screen. An
optimum range in which the body can be inclined and moved can
also be indicated by using a line or a circle in place of a
grid-like line. In this manner, training by the trainer can
be correctly performed to make it possible that the trainee
understands a good form.
More specifically, in golf swing by using a club, by using
a straight line connecting both the shoulders, a line connecting
both the ends of the straight line to the hands through the elbows,
and a line connecting the grip of the club to the club head,
it can be decided whether a correct shot can be performed or
not. When lines connecting both the shoulders and the hands
always constitute the same triangle, it is understood that a
shot can be performed with a correct form. However, as shown
in Fig. 8, the above lines are drawn on each screen, the image
is erased, and only the lines drawn as shown in Fig. 8 are
extracted on the screen, so that the trainer can understandably
explain to the trainee the correct form. In this manner, when
training is performed by using the system according to the
present invention, the trainee can understand a correct form
and obtains a preferable training result.
In the video image server ( 10 ) , a correct form including
the position of a club face when the club of the trainee is
addressed or set at the top, the position of the club in an impact
or finish state, and a manner of folding arms is photographed
and input in advance.
In this state, the trainee visually compares her/his form
11
CA 02366169 2001-12-27
with a form of a professional trainer whose figure is similar
to the trainee, so that the trainee wants to correct her/his
form. Therefore, the trainee searches the video image server
( 10 ) for the video image of her/his top position through the
mobile communication device ( 1 ) first, and, at the same time,
the trainee searches the video image server ( 10 ) for the video
image of a corresponding top position of the trainer. ~'~Both the
video images are displayed in parallel as shown in Fig. 9. As
a result, the difference between the form of the trainee (self )
and the form of the trainer is apparent at glance. Therefore,
points to be corrected can be easily understood.
In this case, one of the forms of the trainee and the trainer
is displayed as a still image, and the other is displayed as
a moving image, so as to make it possible that the trainee
understands the correct form.
In addition, when the trainer performs training while
watching the image of the trainee, the system is designed such
that letters or graphics for the training can be drawn on the
image of the trainee.
The above description has been made by using a form of a
golf play as an example. As a matter of course, the present
invention is not limited to golf, and the present invention is
effective to correct forms of all kinds of sports. When
training is performed by using the system, a trainee can
understand her/his weak points . For this reason, the form of
the trainee could be corrected into a correct form, and a
preferable training result'~'could be obtained.
12
CA 02366169 2001-12-27
More specifically, in Fig. 10, the present invention is
applied to training of baseball, the right and left side of a
screen show the same trainee (student). As the right image,
an image obtained before a trainer performs training is picked.
Thereafter, the training is performed, an image (left side)
obtained after the form is improved by the training is arranged
on the left side, and the left elbow is not sufficiently
stretched out. For this reason, the trainer points out the weak
point, and trainer shows to the trainee the right screen picked
thereafter. As a result, the trainer makes the trainee to
understand the degree of improvement and to recognize the
difference between the correct form and the wrong form, so that
a preferable training result can be obtained.
In general, according to the present invention, as has been
described above, by using a mobile communication terminal such
as a portable telephone, the images of plays or the like of
a trainer and a trainee are displayed on two divided monitor
displays such that the images are compared with each other. For
this reason, a very understandable training method can be easily
and simply provided.
13