Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/l~TZ00/00192
-1-
SAW APPARATUS AND FEED APPARATUS THEREFOR
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to a saw apparatus and a feed apparatus
therefor.
In particular the invention relates to a saw apparatus for cutting truss and
framing
members for buildings in predetermined lengths and at predetermined angles
using a
feed apparatus to accurately feed these to the saw apparatus in a controlled
manner.
However, it is to be understood that the invention is not to be limited as
such.
Moreover, because the invention may have many other applications, the prior
art and
possible applications of the invention discussed below are given by way of
example
only.
BACKGROUND ART
Conventional apparatus for cutting lengths of wood such as framing members
for buildings generally comprise a horizontal saw bench fitted with guides to
align the
wood, a saw blade which can be moved in the horizontal plane and turned
through
different angles, and which can be retracted beneath the saw bed, and a feed
device for
feeding the length of wood to the saw blade position. In cutting the
predetermined
lengths using a computer controlled apparatus, data related to the size and
length of the
wood is input to a program which computes the optimum lengths of framing
members
to be cut from the piece of wood, resulting in the minimum amount of scrap.
The wood
is then fed to the cutting position with the feed device and cut by moving the
blade
horizontally at a required angle to give the various lengths of wood with the
ends cut at
the required angles.
In the case of cutting very long inclined ends (small angles), the wood may be
positioned above the blade position with the blade retracted, after which the
blade is
raised to cut the wood. This operation inevitably requires an additional
device for
holding the wood down onto the saw bench, and also requires a large diameter
blade,
thus adding to the cost of the saw apparatus.
The cutting of very long inclined ends may also be achieved with a small blade
which is moved along the direction of the cut. In this case, due to the length
of the cut
the blade must be moved a considerable distance and hence the time for the
cutting
operation is longer.
Moreover, with conventional cutting methods, the removal of the sawdust from
the cut area can be a problem. In particular, in the case where the blade is
raised up
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-2-
through the wood, when the blade breaks through the top of the wood, the
sawdust is no
longer guided by the cut area and can spray haphazardly into the work area,
making
collection difficult.
In addition with conventional saw apparatus, since the saw bench is generally
horizontal, wood cut offs, and chips collecting on the surface must be
continuously
swept from the surface, thus hindering operation.
Furthermore, with conventional systems where the feed device is in the from of
a pushing member which may also be adapted for gripping the end of the length
of
wood, there is a disadvantage in that it takes time for the pushing member to
be
retracted back to the start position when a new length of wood is positioned
ready for
cutting. Moreover, there is a disadvantage in that in bringing the pushing
member up to
the new length of wood, the speed of the pushing member must be carefully
controlled
to avoid bumping the wood.
DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION
It is an object of the present invention to provide a saw apparatus which
addresses the above problems with conventional methods and apparatus for
cutting
wood, or which at least provides the public with a useful choice.
Moreover, it is an object of the present invention to provide a feed apparatus
for
accurately feeding and positioning lengths of material, such as in the case of
lengths of
timber to be cut by a saw apparatus.
Furthermore, it is an object of the present invention to provide a saw dust
removal device that addresses the aforementioned problems.
According to a first aspect of the present invention there is provided a saw
apparatus comprising:
a saw bench for supporting a length of material to be cut on a plane of the
saw
bench;
a feed device for feeding a length of material to be cut in a direction of
feed
relative to the saw bench, while being supported by the saw bench, and while
the
length of material is being cut, and
a circular saw blade assembly comprising:
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-3
a base member mounted relative to the saw bench so as to be movable in a
transverse direction across the direction of feed, and
a saw blade mounting device for rotatably mounting a circular saw blade on the
base member at a predetermined angle relative to the transverse movement
direction of
the base member in the plane of the saw bench, and having a device for
connection to a
drive source for rotating a circular saw blade when mounted thereon (or
comprising a
drive device).
With such a construction, a circular saw blade mounted on the circular saw
blade assembly can be inclined to the transverse movement direction of the
base
member and moved across the direction of feed at an incline to the direction
of feed.
Hence a length of material can be cut while being fed along the saw bench in a
direction
of feed relative to the saw bench. Long angle (small angle) cuts can thus be
made by
simply inclining the circular saw blade to the required angle, and moving the
circular
saw blade transverse to the direction of feed while feeding the length of
material in the
direction of feed.
Hence angle cuts can be made with a small diameter blade compared to the
conventional method of using a large diameter blade which is raised up through
the
wood. Moreover, the amount of transverse movement is much less than in the
conventional case where the blade is aligned with the direction of transverse
movement
and is moved along the cut while the length of material remains stationary.
Furthermore, since the cut is through the timber rather than from beneath, the
direction of sawdust is always on the outlet side of the cut, except perhaps
at the final
cut through the edge on completion of the cut.
The predetermined angle of the blade relative to the transverse movement
direction of the base member in the plane of the saw bench may be achieved by
providing an angle adjustment device for adjusting the angle of mounting the
saw blade
mounting device relative to the base member. Furthermore, there may be
provided a
blade depth adjusting device for adjusting the depth of the blade relative to
the base
member.
It is generally envisaged that in order to facilitate standard 90 degree cross
cuts,
the base member would be mounted so as to be movable transverse to the
direction of
feed, and the angle adjustment device would enable angle adjustment from zero
degrees
(for cross cuts) to a predetermined maximum angle which may be up to 360
degrees
(for cross cuts in the opposite direction). By enabling the full angular
adjustment
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-4-
through 360 degrees, the saw blade can be operated to cut all angles with the
material
being cut being moved in either direction.
The saw bench may be arranged horizontally so as to support the length of
material resting thereon, and be provided with a guide for guiding the length
of material
in the direction of feed. Alternatively the saw bench may be arranged at an
angle to the
horizontal, as required or desired.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a saw
apparatus substantially as described above, wherein the saw bench comprises
two
inclined support devices for supporting a length of material along a support
plane, the
support devices being inclined relative to each other, and being inclined to a
horizontal
plane. It is generally envisioned that the support devices would be inclined
at right
angles to each other, to thereby provide optimum support for rectangular
lengths of
material to be cut. However, other angles may be appropriate depending on
requirements.
With such an arrangement, a length of material to be cut can be positively
supported on the saw bench by its weight holding it against the inclined
surfaces.
Hence alignment of the length of material can be easily achieved by using the
weight of
the length of material to position the length of material. Moreover, by having
the saw
bench inclined to the horizontal, the various components of the circular saw
blade
assembly can be more easily accommodated in the overall structure, and more
easily
accessed. Furthermore, having the saw bench at an incline overcomes the
problem with
conventional horizontal saw benches with wood cut offs, and chips collecting
on the
surface.
The feed device may comprise a conventional feed device such as one where a
pushing member pushes against the end of the length of material to advance the
material to the cutting position. In this case, the material may be held in
position by
rollers along the feed path which are biased against the surface of the
material.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a saw
apparatus substantially as described above, wherein the feed device comprises:
a conveyer belt suspended between belt support rollers which are rotatably
mounted on a base structure, at least one of the rollers being adapted for
connection to a
drive device for driving the conveyer belt, and
a clamping device mounted relative to the base structure for clamping a member
to be fed against an outer peripheral surface of the conveyer belt.
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-5
With such an arrangement, a length of material to be cut can be fed in the
direction of feed by positioning the material on the conveyer belt and holding
the
material against the conveyer belt with the clamping device while rotating the
conveyer
belt. By using a conveyor belt feed device, the disadvantage in operating time
with the
conventional feed device which uses a pushing member is overcome.
The conveyer belt may be any suitable conveyer belt which can sufficiently
grip
the material to be fed when this is held thereagainst by the clamping device.
For example this may comprise a toothed belt type conveyer belt comprising
metal hoop wires embedded in a synthetic resin material with teeth formed on
the inner
peripheral surface.
From tests done using such a conveyor belt type feed apparatus, it was found
that the material could not be accurately fed in proportion to the number of
revolutions
of the conveyor belt. For example, when feeding a length of 100mm x SOmm wood,
of
around 6 meters length, the feed length determined by measuring the number of
rotations of the conveyor drive roller was inconsistent, with errors of up to
O.Smm per
metre. Hence such a feed apparatus with a standard toothed conveyor belt could
not be
used for accurate cutting of members such as truss and framing members.
The present inventor considered this problem to be due to lengthwise expansion
and contraction of the conveyor belt with the loading applied by the clamping
device
clamping the length of material against the conveyor belt surface. To minimise
this
lengthwise expansion and contraction, the present inventor therefore formed a
plurality
of continuous grooves around an outer peripheral surface of the conveyor belt
so that
expansion and contraction of the belt with the applied loading could be
absorbed by
sideways deformation rather than lengthwise deformation. From tests made with
such a
grooved belt it was found that the previous lengthwise inconsistency in feed
measurement when feeding a length of 100mm x SOmm wood, of around 6 meters
length, could be reduced to around 0.005 mm per metre.
Therefore, according to another aspect of the present invention there is
provided
a saw apparatus substantially as described above, wherein the conveyer belt
comprises a
toothed belt with a plurality of continuous grooves formed around an outer
peripheral
surface.
By providing continuous grooves in the outer peripheral surface, more accurate
feed can be achieved, for the reasons described above.
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-6
While the above described feed device is particularly applicable to the saw
apparatus of the present invention, the feed device is not limited to this
application, and
may be suitable for a variety of applications requiring accurate feeding and
positioning
of lengths of various types of materials.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a feed
device comprising:
a conveyer belt suspended between belt support rollers which are rotatably
mounted on a base structure, at least one of the rollers being adapted for
connection to a
drive device for driving the conveyer belt, and
a clamping device mounted relative to the base structure for clamping a member
to be fed against an outer peripheral surface of the conveyer belt, wherein
the conveyer
belt is formed with a plurality of continuous grooves around a peripheral
surface
thereof.
By forming the continuous grooves around an inner or outer peripheral surface
of the conveyor belt, then as mentioned above, the expansion and contraction
of the belt
with the transverse compressive loading can be absorbed by sideways
deformation of
the belt rather than lengthwise deformation.
To enable accurate measurement for determining feed, the conveyor belt is
preferably a toothed conveyor belt, and the continuous grooves are formed
around the
outer peripheral surface of the conveyor belt.
Moreover, there is provided a method of reducing lengthwise deformation of a
conveyor belt when loaded with a transverse compressive load, the method
involving
forming continuous grooves around a peripheral surface of the conveyor belt.
The saw apparatus of the present invention also comprises a saw dust removal
device for removing saw dust as this is discharged from the cut.
The saw dust removal device may comprise an intake located relative to the saw
blade in the vicinity of the teeth exiting from the cut, and a suction duct
connected to
the intake for drawing air in through the intake, wherein the suction duct
constitutes a
hollow support member of the circular saw blade assembly.
While the above described saw dust removal device is particularly applicable
to
the saw apparatus of the present invention, the saw dust removal device is not
limited to
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
this application, and may be suitable for a variety of applications requiring
removal of
saw dust from a cutting region.
Therefore according to another aspect of the present invention there is
provided
a saw dust removal device for the circular saw blade assembly, comprising an
intake
located relative to a saw blade of the circular saw blade assembly in the
vicinity of the
teeth of the saw blade as they exit from a cut, and a suction duct connected
to the intake
for drawing air in through the intake, wherein the suction duct constitutes a
hollow
support member of the circular saw blade assembly.
The present invention may also broadly be said to consist in the parts,
elements
and features referred to or indicated in the specification of the application,
individually
or collectively, and any or all combinations of any two or more of the parts,
elements
or features, and where specific integers are mentioned herein which have known
equivalents in the art to which this invention relates, such known equivalents
are
deemed to be incorporated herein as if individually set forth.
I S BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Further aspects of the present invention will become apparent from the ensuing
description which is given by way of example only and with reference to the
accompanying drawing in which;
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram illustrating a method of the present invention
for
making angled cuts in elongate members;
FIG. 2 is a schematic elevation view of a saw apparatus according to an
embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing details of an outfeed device, (A)
showing a plan view illustrating a sideways operating mechanism, and (B)
showing
details of operation in stacking cut wood.
FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram showing details of a feed device, (A) showing a
view in the direction of arrow A of FIG. 2, and (B) showing a cross sectional
view on
B-B of (A) illustrating details of a conveyor belt;
FIG. 5 is a left end view of the saw apparatus of FIG. 2, illustrating
components
of a saw bench and clamping device;
FIG. 6 is a right end schematic view of the saw apparatus of FIG. 2,
illustrating
components of a circular saw blade assembly and saw dust removal device;
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
_g_
FIG. 7 is an enlarged schematic view of the saw blade assembly shown in FIG.
6.
FIG. 8 is a flow chart illustrating the steps in operation of the saw
apparatus of
the embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 9 is a flow chart illustrating the steps in a sub-routine of the flow
chart of
FIG. 8, for measuring a length of material to be cut.
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
An embodiment of the present invention will now be described with reference to
FIG. 1 which illustrates a method of the present invention for making angled
cuts in
elongate members using a circular saw bench (not shown) along a plane of which
(plane of the page in FIG. 1 ) an elongate member I can be fed in a direction
of feed Y.
The method involves mounting a circular saw blade 2 so as to be movable in a
direction
X transverse to the direction of feed Y in a plane parallel to the plane of
the saw bench.
This may involve a conventional mounting device such as used for cross cut
circular
I S saw apparatus. In FIG. I this transverse direction X is shown as
perpendicular to the
direction of feed Y, however the circular saw blade 2 may be mounted so as to
be
movable at some other suitable angle as required or desired. It is generally
envisioned
that the circular saw blade 2 would be mounted so as to be movable at an angle
close to
90 degrees to the direction of feed Y, since increasing the angle increases
the distance
to be moved by the circular saw blade 2, which defeats one object of the
invention
which is to reduce the distance to be moved by the circular saw blade 2 in the
case of
cutting long angles. In the figure, the long angle is shown as 8.
Moreover, the circular saw blade 2 is shown mounted perpendicular to the plane
of the saw bench (plane of the paper in FIG. I ). However depending on
requirements
the circular saw blade 2 may be mounted at an incline to the plane of the saw
bench.
The method further involves inclining the circular saw blade 2 at a
predetermined angle to the transverse direction X in a plane of the saw bench
(plane of
the paper in FIG. 1). This incline may be achieved by an adjustable mount
between a
saw blade rotational support device and a transverse movement device. Cutting
of the
angle on the end of the elongate member 1 is then achieved by feeding the
elongate
member 1 along the saw bench in the direction of feed Y while synchronously
moving
the circular saw blade 2 in the direction X transverse to the direction of
feed Y.
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-9-
FIG. 1 shows the various stages in cutting the angle on the end of the
elongate
member 1. At position "a", the blade 2 is clear of the member 1 ready to be
moved in
direction X while the member 1 is moved in the direction Y so as to start
cutting at a'.
At position "b", the blade 2 has started to cut an angled cut in the member 1,
the end of
the member 1 being at b'. At position "c", the blade 2 has cut through the
member 1
leaving the section c' to fall away. At position "d", the blade 2 is clear of
the member 1
allowing the member 1 to be fed along the saw bench into a new position for
cutting if
required. Since the blade 2 can be turned through 360 degrees, the end of the
member 1
can be cut at various angles while being moved forward or backward in the Y
direction,
with the blade 2 being moved forward or backward in the X direction.
With the method illustrated in FIG. 1, long angles 8 can be cut in elongate
members 1 with only minimal transverse movement of the blade 2. Hence cutting
time
can be reduced. Moreover, compared to apparatus using a large diameter blade
which
is raised from beneath the member being cut, the saw dust from the cut can be
better
I S controlled since the only uncontrolled period is when the blade 2 clears
the cut at
position d'.
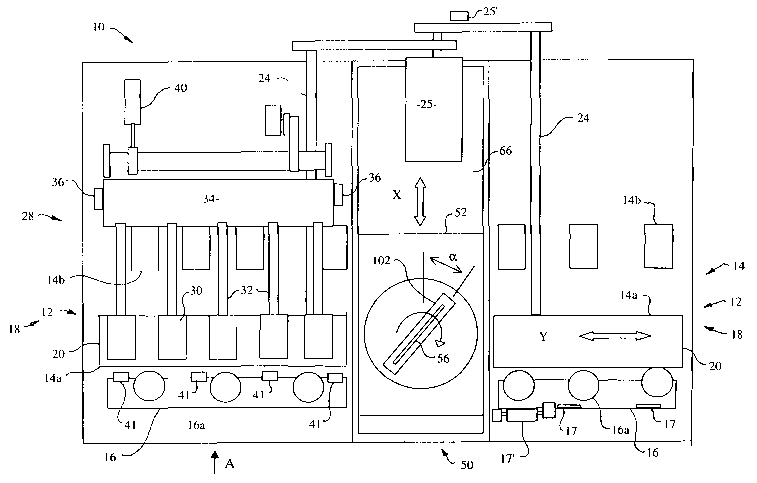
FIG. 2 through FIG. 7 illustrate a saw apparatus 10 according to an embodiment
of the present invention. The saw apparatus 10 of this embodiment is an
inclined
structure comprising two saw benches generally indicated by arrow 12, one at
each end
of the saw apparatus 10. Each saw bench 12 comprises two inclined support
devices,
one major support device 14 comprising two rows of rollers 14a and 14b for
supporting
a length of material to be cut on a plane inclined at approximately 20 degrees
to the
vertical, and a minor support device 16 comprising one row of rollers 16a with
a
support plane thereof inclined at right angles to the support plane of the
major support
device 14.
The minor support device 16 at the right hand end in FIG. 2 and as shown more
clearly in FIG. 3A, is mounted on the main frame by means of linear bearings
17 so as
to be movable sideways. Due to this arrangement, material being cut can be
easily
discharged to below the feed path Y if required by moving the minor support
device 16
away from the feed path Y. This is particularly useful in the case of cutting
short
members. The reason for having the linear bearings 17 arranged at an incline
to the
support device 16 as shown in FIG. 3 is to obviate the need for an anti skew
device
which would be required if they were aligned perpendicular to the support
device 16.
Sideways movement of the support device 16 for discharging material which has
been
cut is achieved by operation of a discharge pneumatic actuator 17'.
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-10-
Also as shown in FIG. 3, there is provided an outfeed device generally
indicated
by arrow 140. In FIG. 3, components the same as in FIG. 2 are denoted by the
same
reference symbols. The outfeed device 140 extends approximately 3 meters from
the
end of the right end major support device 14 (FIG. 2), for supporting and
stacking long
lengths of wood as they are discharged after being cut. The outfeed device 140
also
comprises an arrangement for discharging the material which has been cut to
below the
feed path Y which is operated similarly to the right end minor support device
16 as
described above. That is, there is provided a minor support device 160
comprising one
row of rollers 160a with a support plane thereof inclined at right angles to
the support
plane of the major support device 14. The minor support device 160 is mounted
on the
opposite side of the feed path Y to the support device 16, on a main frame
(not shown)
of the outfeed device 140 by means of linear bearings 170 so as to be movable
sideways. The sideways movement of the support device 160 for discharging
material
which has been cut is achieved by operation of a discharge pneumatic actuator
170'.
As shown in FIG. 3B, by moving the support device 160 sideways, in synchronous
with
the cutting operation of the wood, in the sequence indicated by the arrows in
FIG. 3B,
then the wood 1 as it is fed out from the saw apparatus 10 is first supported
on the
rollers 160a, while still being supported on the rollers 14a and 14b of the
major support
device 14 (top position in FIG. 3B). Then once the wood has been cut, the
support
device 160 is moved sideways (to the right in FIG. 3B) away from the feed path
Y so
that the cut wood can drop downwards from the feed path Y and onto a rack 180
(bottom position in FIG. 3B). The support device 160 is then moved sideways
towards
the feed path Y (to the left in FIG. 3B), so that the rollers 160a are again
brought into
position for supporting a new length of wood. At the same time a pusher member
162
of the support device 160 pushes the cut wood 1 which has just dropped onto
the rack
180, sideways to thus stack the cut wood on the rack 180.
Moreover with the present embodiment, each saw bench 12 is provided with a
feed device generally indicated by arrow 18 for feeding a length of material
supported
by the saw bench 12, in a direction of feed Y relative to the saw bench 12.
The feed devices 18 as more clearly shown in FIG. 4 each comprise: a toothed
belt type conveyer belt 20 suspended between belt support rollers 21 and 22
which are
rotatably mounted on bearings (not shown in the figures) mounted on a base
structure
of the saw bench 12. Idler rollers 23 are also provided for supporting the
conveyor belt
along its length. One of the belt support rollers 22 is connected to a drive
shaft 24
(FIG. 2) for driving the conveyer belt 20 by means of a feed drive motor 25.
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-11-
The feed drive motor 25 is connected by toothed belts to the respective drive
shafts 24 of the conveyor belts 20, such that the two drive shafts 24 are
rotated at the
same speed in the same direction. By monitoring the number of rotations of the
feed
drive motor 25 using a notch detector 25' for detecting the notches of the
drive pulley,
then the feed of the member 1 (FIG. 1 ) being fed can be accurately
controlled.
With the feed device 18 of the present embodiment, in order to reduce
lengthwise feed discrepancy which was found to occur when using a standard
toothed
belt conveyor belt, the conveyor belt 20 comprises metal hoop wires 26
embedded in a
synthetic resin material 26' and is formed with a plurality of continuous
grooves 27
formed around an outer peripheral surface of the conveyor belt 20 as shown in
FIG. 4B.
In FIG. 4 components the same as in FIG. 2 are denoted by the same reference
symbols.
Reference symbol 27' denotes the edge of a tooth of the toothed belt conveyor
belt 20.
Each feed device 18 further comprises a clamping device generally denoted by
arrow 28 (for clarity, only the clamping device 28 on the left side is shown
in FIG. 2)
mounted relative to the base structure of the saw bench 12, for clamping a
member to
being fed 1 against an outer peripheral surface of the conveyer belt 20 as
shown in FIG.
4B.
With the present embodiment, each clamping device 28 comprises five
clamping rollers 30 rotatably mounted on the end of finger supports 32 which
are in
turn secured to a clamping base 34. FIG. 5 illustrates the operation of the
clamping
device 28. The base 34 is mounted on the base structure of the saw apparatus
10 by
means of linear bearings 36 at each end. By operation of a crank linkage
generally
indicated by arrow 38, using a pneumatic clamping actuator 40, the clamping
base 34
can be moved along the linear bearings 36, thereby moving the clamping rollers
30
towards and away from the member being fed 1, and hence clamping this against
the
surface of the conveyor belt 20.
While not shown in the figures (only the monitor M shown in dotted outline in
FIG. 5), operation of the feed device 18 is performed by a computer programmed
with
suitable software. This effects the necessary control of the drive motor 25 to
give the
required feed in either direction by detecting the rotation of the drive motor
25 with the
notch detector 25' and sensing the location of the material being cut with
four position
sensors 41 arranged along the feed path Y. The computer also controls the
operation of
the clamping device 28 to correspond with the feed operation, and the
operation of the
discharge actuator 17'.
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-12-
Furthermore, the saw apparatus 10 comprises a circular saw blade assembly
generally indicated by arrow 50 comprising: a base member 52 mounted relative
to the
saw bench 12 so as to be movable in a transverse direction X across the
direction of
feed Y, and a saw blade mounting device in the form of a blade drive assembly
generally indicated by arrow 54 ( see FIG. 6 and FIG. 7) for rotatably
mounting a
circular saw blade 56 on the base member 52 at a predetermined angle oc
relative to the
transverse movement direction X of the base member 52 in the plane of the saw
bench
12.
The base member 52 is mounted on the main structure of the saw apparatus 10
by means of linear bearings (not shown) so as to be freely movable in the
transverse
direction X. As shown in FIG. 6, this transverse movement is provided by means
of a
toothed belt 58 which is clamped to the base member 52 with a clamp 60, and
which is
moved up and down by means of a transverse drive motor 62 connected by a
toothed
belt drive 64 to the toothed belt 58. The transverse movement of the base
member 52
can thus be accurately controlled by detecting the rotation of one of the
tooth wheels of
the toothed belt drive 64 using a notch detector 64', and outputting a
detection signal to
the computer. The computer uses this signal in co-ordinating and synchronising
the
transverse movement of the circular saw blade assembly 50 with the feed
operation by
the feed device 18.
Moreover, flexible plastics sheets 66 are stretched on either side of the base
member 52, and tensioned by cables 68 which pass around four pulleys 70
mounted on
the frame. These sheets 66 prevents material and saw dust from entering into
the rear
region of the saw apparatus 10.
The blade mounting device 54 includes a bearing and spindle 72 for mounting
the blade 56, and a blade drive electric motor 74 for driving the circular saw
blade 56
via a toothed belt and pulley drive 76.
The blade drive assembly 54 is mounted on the base member 52 by an angle
adjusting device generally indicated by arrow 78. The angle adjusting device
78
comprises blade end bearings 80 for rotatably supporting the peripheral edge
at the
blade end of the blade drive assembly 54 relative to the base member 52, and a
pedestal
bearing 82 (FIG. 7) for rotatably supporting the base end of the blade drive
assembly
54. The angle adjusting device 78 further includes a toothed belt drive 84
which is
driven by an angle setting motor 85. The angle a, of the blade 56 can thus be
accurately
controlled by detecting the rotation of one of the tooth wheels of the toothed
belt drive
84 with a notch detector 85' (FIG. 7) and outputting a detection signal to the
computer.
The computer uses this signal in co-ordinating the angle setting of the blade
56 with the
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-13-
transverse movement of the circular saw blade assembly 50 and the feed
operation by
the feed device 18.
By means of the angle adjusting device 78, the blade angle a can be adjusted
through a full 360 degrees by appropriate control of the angle setting motor
85.
Moreover, the saw blade mounting device 54 further comprises a blade depth
adjustment device generally indicated by arrow 86 (FIG. 7). The blade depth
adjustment device 86 comprises an adjustable mount in the form of two linear
bearings
88, between a base member 90 of the saw blade mounting device 54 and a moving
member 92 on which is mounted the bearing and spindle 72 and the blade drive
electric
motor 74. An actuator 94 is provided between the base member 90 and the moving
member 92 to move the moving member 92 and thus move the blade 56 to adjust
the
depth of cut. The blade depth can be controlled by means of a detent device
96, which
can be turned into or out of the path of movement of a lug 98 on the side of
the moving
member 92. Operation of the detent device 96 can also be controlled by the
computer
to suit requirements.
The saw apparatus 10 of the embodiment also comprises a saw dust removal
device generally indicated by arrow 100 (FIG. 6 and 7) for removing saw dust
as this is
discharged from the cut. The saw dust removal device 100 comprises an intake
102
(FIG. 2) which surrounds the saw blade 56 so as to be in the vicinity of the
teeth exiting
from the cut, and a suction duct 104 connected to the intake 102 for drawing
air in
through the intake 102 by means of a flexible suction pipe 106 which is
connected to a
standard suction type dust removal device (not shown). As shown in the
figures, the
suction duct 104 also constitutes a hollow support member of the circular saw
blade
assembly 50.
The operation of the saw apparatus 10 of the present embodiment will now be
described with reference to the flow chart of FIG. 8.
The case for making angled cuts in elongate members 1 such as the truss and
framing members for a house, as described beforehand with reference to FIG. 1,
will be
considered.
At first in step 1 (denoted by S 1 in FIG. 8 with subsequent steps similarly
denoted), the computer is programmed with details of the cutting requirements,
and the
dimensions of the wood (material to be cut).
Then in step 2, the components are set to the initial position. For example
the
height of the blade 56 is adjusted by operating the actuator 94 of the blade
depth
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-14-
adjusting device 86, the angle of the blade 56 is set by operating the angle
setting motor
85 to turn the blade 56 to the required angle oc, and the blade 56 is moved
away from
the feed path Y (position "a" in FIG. 1 ), by operating the transverse drive
motor 62.
Then in step 3, a first length of wood is fed to the feed device 18 by a
separate
feeder or by hand.
Next, in step 4 it is judged if there is a piece of wood on the conveyor belt
20,
by sensing for the presence of a piece of wood with the proximity sensors 41
arranged
along the feed path Y. If no wood is present, control returns to step 3 to
allow wood to
be fed.
When in step 4, the presence of a piece of wood is detected, control proceeds
to
step 5 to operate the clamping actuator 40 of the clamping device 28 to clamp
the wood
against the surface of the conveyor belt 20 with the clamping rollers 30. Here
the wood
is considered to be present when the wood is supported over at least 200mm of
the
conveyor belt 20 (as detected by the second sensor 41 when coming onto the
conveyor
or the third sensor 41 when going off the conveyor belt 20), to ensure
sufficient support
when operating the clamping device 28.
Once the clamping actuator 40 has been operated, control proceeds to step SA
to
determine if measurement of the wood is required. If measurement is not
required,
control proceeds to step 6 to operate the feed drive motor 25 to move the
conveyor belt
20 and feed the wood to the region of the saw blade 56.
Then in step 7 the saw blade 56 is rotated up to speed by the blade drive
motor
74, and the sawdust removal device 100 is started. This step may be at an
earlier stage
depending on requirements.
Control then proceeds to step 8 for synchronous control of the transverse
drive
motor 62 (step 9) and the feed drive motor 25 (step 10) to move the wood into
the
cutting region at a predetermined speed, and move the blade 56 (which has been
set at a
predetermined angle in step 2) into the feed path Y (from position "a" in FIG.
1 ) at a
predetermined speed. This synchronous operation is controlled accurately by
the
computer which co-ordinates the drive of the feed drive motor 25 and the
transverse
drive motor 62 so that the wood 1 is continuously fed in the Y direction while
the blade
56 is moved in the X direction from position "a" to position "d" in FIG. 1, to
thereby
cut the wood off at the required length and at the required angle.
Once the wood has been cut off, control then proceeds to step 11 where the
clamping actuator 40 of the right side clamping device 28 is released to
release the
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-15-
clamping rollers 30. Moreover, the discharge actuator 17' is operated to move
the
minor support device 16 away from the feed path Y to allow the cut off end of
the wood
to fall down to a short length rack (not shown). In the case of long lengths
of wood,
the discharge actuator 170' of the outfeed device 140 is also operated to move
the
minor support device 160 away from the feed path Y to the other side to allow
the cut
off wood to fall down to the rack 180.
Then in step 12, the blade drive motor 74 and the sawdust removal device 100
are switched off (depending on requirements) and the blade 56 is retracted
below (away
from) the plane of the saw bench 12 by operating the detent device 96 and the
actuator
94 of the blade depth adjusting device 86.
Control then returns to step 2 and the process is repeated.
If in step Sa, measurement of the wood is required, control proceeds to step
13
to perform a measurement routine as shown in FIG. 9. In step 14, the wood is
fed as in
step 6, with the distance fed being computed from the movement of the conveyor
20.
In step 15 it is judged if the end of the wood has been detected by one of
several infeed
position sensors (not shown) positioned along the infeed path. The infeed
sensors are
arranged at one meter intervals along a five meter infeed path prior to the
conveyor
section. Once any of the infeed sensors detect the end of the wood, then in
step 16, the
length of the wood is computed, based on the distance fed by the conveyor and
the
distance of the relevant infeed sensor from the second conveyor sensor 41.
Control
then returns to step 6 to continue the subsequent operations as described
above.
Other various cutting operations are also possible. For example the wood may
be cut while being moved in the opposite direction (from right to left), or
while the
blade is moving upwards. In the case of upward cutting however, it may be
necessary
to provide sideways support to keep the wood firmly supported on the minor
support
rollers 16a.
While the feed device 18 of the embodiment has been described as a feed device
for feeding material to the saw apparatus of the present invention, the feed
device 18 is
also applicable for feeding various types of material in other situations. For
example,
for feeding wood with a conventional horizontal saw bench type saw apparatus,
or for
feeding lengths of material in a nailing machine. The feed device of the
invention with
a plurality of continuous grooves around a peripheral surface of the conveyor
belt is
thus not limited to the feed device described in the embodiment, and covers
feed
devices for other applications. For example for feeding metals and plastics to
various
types of processing machines.
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-16-
Furthermore, while the circular saw blade assembly 50 of the embodiment has
been described in relation to the saw apparatus 10 of the present invention, a
circular
saw blade assembly of a similar construction comprising a base member able to
be
mounted relative to a saw bench so as to be movable in a transverse direction
across a
direction of feed, and a saw blade mounting device for rotatably mounting a
circular
saw blade on the base member at a predetermined angle relative to the
transverse
movement direction of the base member in the plane of the saw bench, and
having a
device for connection to a drive source for rotating a circular saw blade when
mounted
thereon (or comprising a drive device), is also applicable for use with other
types of
saw apparatus.
Moreover, while the saw dust removal device 100 of the embodiment has been
described in relation to the saw apparatus 10 of the present invention, a saw
dust
removal device of a similar construction where the suction duct constitutes a
hollow
support member of the circular saw blade assembly, is also applicable for
removing saw
dust in other situations with other types of saw apparatus.
Furthermore, the invention is not limited to the saw apparatus 10 of the
embodiment, where the saw bench 12 comprises two inclined support devices for
supporting a length of material to be cut on a plane inclined at approximately
20
degrees to the vertical, but also covers saw apparatus where the saw bench is
at other
angles. For example the invention is also applicable to saw apparatus with
conventional saw benches in a horizontal plane. Furthermore, the minor support
device
16 need not necessarily be inclined at right angles to the support plane of
the major
support device 14, and may be inclined at other angles as required or desired.
Moreover, while in the above the description has been for where notch
detectors
are used for monitoring the number of rotations of the various motors, other
methods
may be more suitable. For example use of an encoder and/or a resolver
incorporated
into the feed drive motor may give much greater accuracy.
Furthermore, the outfeed device as described above is not limited to use with
the
saw apparatus of the present invention and may be suitably modified for use
with other
types of equipment requiring the features thereof.
INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY
The invention offers the following advantages in industrial application,
however
it should be appreciated that all such advantages may not be realised on all
embodiments of the invention and the following list is given by way of example
only as
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-17-
being indicative of potential advantages of the present invention. Furthermore
it is not
intended that the advantages of the present invention be restricted to those
of the list
which follows:
By providing a feed device to enable cutting the material to be cut while
being
fed, angle cuts can be made with a small diameter blade compared to the
conventional
method of using a large diameter blade which is raised up through the material
being
cut. Moreover, the amount of transverse movement is much less than in the
conventional case where the blade is aligned with the direction of transverse
movement
and is moved along the cut while the material being cut remains stationary.
Furthermore, since the cut is through the timber rather than from beneath, the
direction
of sawdust is always on the outlet side of the cut, except perhaps at the
final cut
through the edge on completion of the cut.
2. By having the saw bench in the form of inclined support surfaces, a length
of
material to be cut can be positively supported on the saw bench by its weight
holding it
against the inclined surfaces. Hence alignment of the length of material can
be easily
achieved by using the weight of the length of material to position the length
of material.
Moreover, by having the saw bench inclined to the horizontal, the various
components
of the circular saw blade assembly can be more easily accommodated in the
overall
structure, and more easily accessed. Furthermore, having the saw bench at an
incline
overcomes the problem with conventional horizontal saw benches with wood cut
offs,
and chips collecting on the surface.
3. By using a conveyor belt feed device, the disadvantage in operating time
with
the conventional feed device which uses a pushing member is overcome.
4. By providing continuous grooves in the outer peripheral surface of the
conveyor belt of the conveyor belt feed device, expansion and contraction of
the belt
with the applied loading can be absorbed by sideways deformation rather than
lengthwise deformation, thus enabling accurate feed to be achieved.
5. By controlling the conveyor belt feed device described above, using a
computer
program, material being cut such as truss and framing members can be
accurately fed
to the saw apparatus in a controlled manner.
6. By providing a saw dust removal device where the suction duct constitutes a
hollow support member of the circular saw blade assembly, the design can be
made
compact and the use of materials and components can be optimised.
CA 02386394 2002-03-27
WO 01/23153 PCT/NZ00/00192
-18-
Aspects of the present invention have been described by way of example only
and it
should be appreciated that modifications and additions may be made thereto
without
departing from the scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims.