Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02388275 2002-05-30
A-3508
Rotary printing machine
The invention relates to a rotary printing machine having at
least one integrated image-setting device for a printing form
which, during image setting, is fixed to a form cylinder that
can be driven in rotation in relation to the image-setting
device.
A printing machine of this type is described in DE 197 23 147
A1. This printing machine contains two different drive
systems. During printing operation, a main drive is used to
drive all the components which are needed for printing and
which are coupled to one another via a gear train. During the
image-setting operation, an auxiliary drive is used to drive
the form cylinder separately, the main drive being stopped and
the form cylinder being uncoupled from the gear train with the
aid of isolating clutches. It is necessary to stop the main
drive in order not to permit mechanical oscillations and
shocks which are produced during the operation of the main
drive acting on the image-setting system comprising the image-
setting device and form cylinder. These mechanical
oscillations and shocks would cause image-setting errors and
printing errors. During image-setting, the auxiliary drive, in
addition to the form cylinder, can also be used to drive
components which cause only slight mechanical oscillations.
After image-setting, the form cylinder must be coupled into
the main drive train in the correct phase, to which end
special precautions have to be taken. Linking the form
cylinder into the gear train again in the correct phase can be
monitored by measuring systems or can be carried out by
mechanical means, such as phase clutches.
-1-
~ " r. II~~.LEI~Ii1 '. :I'~
CA 02388275 2002-05-30
In order to avoid printing errors DE 94 03 673 A1 discloses
the art of compensating for mechanical oscillations in the
printing machine during image-setting by means of corrective
driving of the image-setting heads in the circumferential
direction.
It is an object of the invention to develop a rotary printing
machine which has a low outlay on material and cost when
driving a form cylinder during printing and image-setting
operation.
The object is achieved by a rotary printing machine which has
the features as claimed in claim 1.
Advantageous refinements emerge from the subclaims.
The use of a speed-change gear mechanism between the gears
driving the form cylinder during printing operation and the
form cylinder itself, has the advantage that during the
setting of an image on the printing form, the rotary printing
machine is driven in a noncritical oscillation range, while
the form cylinder is driven, in accordance with the
transmission ratio of the speed-change gear mechanism, is
driven at a multiple of the rotational speed of the remaining
components in the drive train of the rotary printing machine
for the purpose of setting an image. Depending on the natural
oscillation characteristics of the rotary printing machine,
the speed-change gear mechanism may be designed with different
transmission ratios. The remaining rotational oscillations in
the drive train and the effects thereof on the image-setting
process are low, because of the low rotational speed. As a
result, the image-setting quality can be increased. The drive
gear train does not need to be isolated for the image-setting
operation. A dedicated drive for the form cylinder during
-2-
r II~I~ill~ll 9' ~ ~ I
CA 02388275 2002-05-30
image setting is not required. The speed-change gear mechanism
can be engaged and disengaged automatically before and after
the setting of an image. The form cylinder can be coupled to a
rotary encoder, which supplies the current rotational speed
and the cylinder position to control electronics during the
setting of an image.
The invention is to be explained in more detail using an
exemplary embodiment; in the drawing:
fig. 1 shows a schematic diagram of a four-color rotary
printing machine,
fig. 2 shows a schematic drawing of the drive of a form
cylinder,
fig. 3 shows a detailed view of the epicyclic gear mechanism
of fig. 2 during printing operation, and
fig. 4 shows a detailed view of the epicyclic gear mechanism
of fig. 2 during image-setting operation.
A sheet-fed printing machine 1 shown in fig. 1 contains a
feeder 2, four printing units 3, 4, 5, 6 and a deliverer 7.
Each printing unit 3-6 contains a form cylinder 8, a transfer
cylinder 9, an impression cylinder 10, two transfer cylinders
11, 12, a large number of ink transfer rolls 13 and damping-
solution transfer rolls 14, and image-setting devices 15.
Transfer drums 16 are arranged between the printing units 3-6.
Further cylinders 17, 18 are used to supply sheets 19 to the
first printing unit 3. In the deliverer 7 there are
diffraction cylinders 20, 21, over which the chains 22 of a
chain gripper system are placed. The cylinders and rolls in
the printing units 3-6, and also all the rotationally driven
cylinders or drums in the feeder 2 and deliverer 7 are
connected to one another by a gear mechanism. A further gear
train 23-25 acts on the gear of the transfer cylinder 12/4 of
-3-
i~iii~ni~,f r~ I ~ i
CA 02388275 2002-05-30
the second printing unit 4. From the shaft of the gear 25
there is a belt pulley 26 belonging to a belt drive 27. The
second belt pulley 28 is seated on the shaft of a main drive
motor 29. The main drive motor 29 and the speed-change gear
mechanism 30 are connected to a control device 31 belonging to
the sheet-fed printing machine 1. In addition to further
actuators and sensors, the image-setting devices 15 are also
connected to the control device 31.
During printing operation, sheets 19 are conveyed from the
feeder 2 through the printing units 3-6 to the deliverer 7,
the main drive motor 29 driving all the components via said
gear mechanism. The speed-change gear mechanisms 30 are out of
action. During the driving of the sheet-fed printing machine
1, harmonic and nonharmonic oscillations are produced as a
result of eccentricities, imbalance and subassemblies which
are moved to and fro, such as oscillating grippers or gripper
mechanisms. The effects of the oscillations and shocks on the
printing quality are reduced during printing by the high
pressure between the transfer cylinders 9 and the respective
printing cylinders 10.
During image-setting operations, in order to avoid
circumferential and axial oscillations, the form cylinder 8 is
driven via the speed-change gear mechanism 30. During image-
setting operation, the transfer cylinders 9 are thrown off the
form cylinders 8 and the impression cylinders 10.
Using fig. 2 and fig. 3 the intention below is to use printing
unit 3 to describe how the drive of the form cylinder 8 is
carried out during printing operation and during image-setting
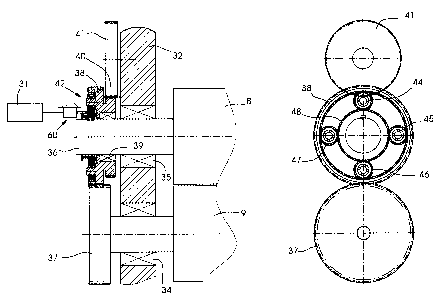
operation. Fig. 2 shows a sectional illustration of a side
wall 32 of the sheet-fed printing machine 1. The side wall 32
contains bearings 33, 34 to accommodate the shaft journals 35,
-4-
I I'.;
hh.~l~! ~h~ ~ '.
CA 02388275 2002-05-30
36 of the form cylinder 8 and of the transfer cylinder 9.
Fixed on the shaft journal 35 is a gear 37 belonging to the
gear train for driving the transfer cylinder 9 during
printing. On the shaft journal 36, a gear 38 is arranged such
that it can rotate in a bearing 39. The gear 38 is combined in
structural terms with a further gear 90 in order to drive the
inking and damping units. The gear 38 is continuously engaged
with the gear 37, and gear 40 is continuously engaged with a
further gear 41.
Also assigned to the gear 38 is an epicyclic gear mechanism
42. The epicyclic gear mechanism 42 comprises an internally
toothed gear 43, four uniformly distributed planet gears 44-47
and an internally located central gear 48. The gear 43 is
formed on the outer surface of a section turned out of the
gear 38. The planet gears 44-47 are connected to the gear 43
and the gear 48. The planet gears 44-47 run on bearings 49-52,
which are fixed to bolts 53-56, which are fixed to the turned-
out portion of the gear 38. The central gear 48 is connected
to the shaft journal 36 by a key 57 and can be displaced in
the axial direction on the shaft journal 36. The central gear
48 further has a lateral ring gear 58, with which a lateral
ring gear 59 on the gear 38 is associated. In order to
displace the gear 48 in the axial direction, a fixed-position
pulling magnet 60 is provided. On its pulling armature 61
there is a roller 62 which engages in a circumferential groove
63 which is machined in a connecting piece 64 on the gear 48.
During printing operation, the pulling magnet 61 with the
roller 62 is in the position shown in fig. 3. The ring gear 58
is engaged with the ring gear 59. If the gears 37 and 38 are
set rotating via the main drive motor 29 and the gear train,
then the torque is transmitted to the form cylinder 8 via the
ring gears 59, 58, the key 57 and the shaft journal 36.
-5-
r n~nlw<I~~ s~ ~ ~ '.
CA 02388275 2002-05-30
Because the ring gears 58, 59 are engaged, the epicyclic gear
mechanism 42 is blocked. The rotational speed of the form
cylinder 8 is given by the numbers of teeth and diameters of
the gears 37 and 38.
During image-setting operation, the pulling armature 61 with
the roller 62 is in the position shown in fig. 4. The ring
gears 58, 59 are disengaged. When the gear 38 is driven via
the gear 37, the planet gears 44-47 run around the central
gear 38. The rotational speed of the gear 48 and of the form
cylinder 8 is increased by a multiple of the input rotational
speed at the gear 43, in accordance with the radii of the
gears 43, 44-47, 48. Therefore, the gears arranged upstream of
the gears 38, 37 in the drive train can be operated with a low
rotational speed, so that no or very few mechanical
disturbances on the systems comprising image-setting devices
15 and form cylinders 8 are produced.
The invention is not restricted to the epicyclic gear
mechanism illustrated in the exemplary embodiment and having
fixed-point ring gears 58, 59. Any desired speed-change gear
mechanism can be used which has the effect that, during image-
setting operation, the drive train is operated in a rotational
speed range in which no disruptive oscillations or shocks
occur. In this case, the transmission ratio of the speed-
change gear mechanism can be matched to the natural
oscillation range of the rotary printing machine.
The control device 31 is used to control the main drive motor
29, the pulling magnet 60 or similar adjusting device, and to
control the image-setting devices 15. The control device 31
can contain a program which has the effect that the speed-
change gear mechanism 30 is automatically connected up with a
higher transmission ratio when the rotary printing machine 1
-6-
ayiiruii9 s;
CA 02388275 2002-05-30
is switched from printing operation to image-setting
operation.
p 9 ~ Y~ I,, ~ 1 ~I
CA 02388275 2002-05-30
List of designations
1 Sheet-fed printing machine
2 Feeder
3-6 Printing unit
7 Deliverer
8 Form cylinder
9 Transfer cylinder
Impression cylinder
11, 12 Transfer cylinder
13 Ink transfer roll
14 Damping-solution transfer roll
Image-setting device
16 Transfer drum
17, 18 Cylinder
19 Sheet
20, 21 Diffraction cylinder
22 Chain
23-25 Gear train
26 Belt pulley
27 Belt drive
28 Belt pulley
29 Main drive motor
30 Speed-change gear mechanism
31 Control device
32 Side wall
33,34 Bearing
35,36 Shaft journal
37,38 Gear
39 Bearing
40,41 Gear
92 Epicyclic gear mechanism
43 Gear
44-47 Planet gear
_g_
l~Irt~ll~~:~ ~ I
CA 02388275 2002-05-30
48 Central gear
49-52 Bearing
53-56 Bolt
57 Key
58, 59 Ring gear
60 Pulling magnet
61 Pulling armature
62 Roller
63 Groove
64 Connecting piece
-9-