Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02392909 2005-06-14
24080-758
PUMP HOUSING
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to pumps such as
compressors and vacuum pumps, and in particular to a housing
for a pump.
Discussion of the Prior Art
Reciprocating piston or diaphragm pumps typically
have a metal housing, for example, a cast aluminum alloy, in
which bearings are mounted which journal the shaft which
drives the pump. A metal housing is needed, particularly
far larger pumps, to withstand the forces of driving she
piston or diaphragm and containing the pressure exerts~d in
the compression chamber of the pump.
A rotary electric motor is usually used to drive
these pumps and the motor requires cooling. In one such
pump, the motor is provided between two housings, each of
which is separate from the other and houses one compression
chamber. The shaft of the motor is a through shaft sc that
each end of the shaft mounts one of the pistons or
diaphragms that work to vary the volume of the compression
chamber in the housing at the corresponding end of the
shaft. Further out from where the piston or diaphragm is
mounted, a rotary fan blade is mounted to each end of 'the
shaft to draw a flow of cooling air into the housing a~~ that
end and blow it onto the rotor and stator coils of the
motor.
For cooling efficiency, it is desirable to make
the part of the housing in which the rotary fan blade is
mounted circular and just slightly larger than the diameter
1
CA 02392909 2005-06-14
24080-758
of the fan blade. The clearance between the tips of the fan
blades and the interior housing surface should be as small
as possible because, if not, the air drawn into the housing
by the fan blades will simply blow back out past the tips of
the blade, and not be directed over the coils of the motor.
For applications in which the pump is contained inside of a
separate enclosure, it may be permissible to leave the end
of the housing at which the fan blade is mounted open.
However, if the pump is going to be exposed or sold as a
stand-alone product, the end of the housing must be closed
with a cover which permits air to be drawn into the housing,
but prevents the insertion of larger objects or fingers.
This cover, typically called a fan guard, should not
deleteriously affect the operation of the fan nor add to the
lateral size or detract from the appearance of the fan.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The invention provides a pump housing having' a
generally cylindrical open end with an axial fan propeller
mounted on a shaft in said open end to draw air into said
open end from outside of said housing, said open end being
covered by a perforated fan guard which permits air drawn by
said fan propeller to pass by the perforated fan guard,
characterized in that said fan guard has peripheral
angularly spaced tabs which extend into the open end o:F the
housing in a direction parallel to the axis of the shaj_t,
each said tab having a crescent-shaped profile and an ear
protruding from an outer surface of said tab, and wherein
similarly shaped crescent-shaped recesses are formed in the
housing to receive the tabs with a curved inner surface of
3'0 the recess against a similarly curved outer surface of the
tab, and holes are formed in said housing which open into
said recesses, wherein the ear of each tab snaps into the
2
CA 02392909 2005-06-14
24080-758
hole in the corresponding recess to hold the fan guard in
place over the end of the housing,
The fan guard easily attaches to the housing,
without requiring any special machining of the housing, does
not increase the internal clearance for the fan and does not
add to the lateral size of the housing or detract from its
appearance.
2a
CA 02392909 2002-05-28
WO 01/38743 PCT/US00/32384
In a preferred form, the recesses and holes are cast-in features of the
housing. The
holes which are formed in the recesses preferably have a horizontal axis to
permit them
to be formed during the casting process, since inserts in the die move in this
direction,
which is perpendicular to the parting line of the casting. As a consequence,
the axes of
all the holes in the recesses are parallel to one another. Each ear also has
an axis, which
is the major direction it extends from the tab, and this axis of the ear
generally
corresponds to the axis of the hole, so that the ear axis is parallel to the
hole axis when
the ear is received in the hole. A ramped surface is preferably provided on
the distal end
of the ear, to flex the tab inwardly upon insertion of the fan guard in the
end of the
housing, and the proximate end of the ear is squared off so that the ear snaps
into the hole
and the near side of the hole is caught by the proximal end of the ear when
the snap-in
fan guard tabs are inserted into the end of the housing.
The crescent-shaped tabs, which are also referred to herein as D-shaped, are
preferably somewhat smaller than the similarly shaped recesses in the housing
so that the
inward surface of the tabs approximates a continuation of the inner surface of
the housing
so as not to interfere with the fan blades or require an excessive clearance
between the
tips of the fan blades and the interior of the housing. It is preferred that
the inner surface
of the tab be somewhat recessed within the crescent-shaped recess so that if
the ear is not
fully engaged in the hole, or if the fan guard is removed with the fan
turning, the tabs do
not flex so far inwardly as to interfere with the tips of the blade.
Any number of tabs and corresponding recesses around the periphery of the
crank
case portion of the housing may be provided. In a preferred form, four tabs
and
corresponding recesses are provided. The tabs and recesses are provided with
two on
each side of the housing and the two on each side spaced as far apart as
possible, with one
3
CA 02392909 2002-05-28
WO 01/38743 PCT/US00/32384
toward the top of the crank case portion and the other toward the bottom of
the crank case
portion on each side. Spacing the holes apart vertically helps provide a
secure fixation.
The fan guard will generally be round, but it is desirable to provide at least
one
feature which extends radially from the fan guard or otherwise serves to
position the fan
guard angularly in the proper location relative to the housing. This feature
may fit into
a similarly shaped opening in the compression chamber portion of the housing
without
adding to the width or height of the compressor.
It is also noted that if the ears and holes have their axes horizontal, and
the
housing recesses are arranged symmetrically on opposite sides of a vertical
axis, the holes
and ears on opposite sides of the housing at the top of the housing will be
along one
horizontal axis and at the bottom of the housing will be along a different
horizontal axis.
Thus, the tabs at the top press against the housing opposite to one another
and the tabs
at the bottom press against the housing opposite to one another to hold the
fan guard in
position.
The foregoing and other objects and advantages of the invention will appear in
the detailed description which follows. In the description, reference is made
to the
accompanying drawings which illustrate a preferred embodiment of the
invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is a perspective view of a pump incorporating the invention;
Fig. 2 is a view like Fig. 1, but with the fan guards exploded off of the pump
housings;
Fig. 3 is a sectional view with its plane radial to the shaft of the pump and
through
the ears on the tabs of the fan guard with the fan guard assembled to the
housing;
4
CA 02392909 2002-05-28
WO 01/38743 PCT/US00/32384
Fig. 4 is a detail view from the same plane as Fig. 3 of a single one of the
tabs and
recesses with the ear received in the hole; and
Fig. 5 is a longitudinal cross-sectional view of one of the tabs received in a
recess
with the ear engaged in the hole.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
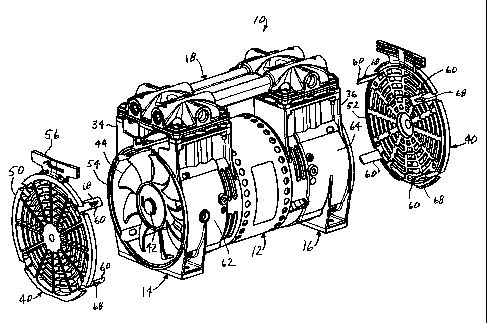
Fig. 1 illustrates a pump 10 of the invention having a motor 12 with a housing
14
at one end and a housing 16 at the other. The housings 14 and 16 are cast of
aluminum
alloy and are identical. A monolithic head 18, which includes head members 20
and 22
and connecting tubes 24 and 26 in a single casting, is bolted to the housings
14 and 16
above the respective compression chamber portions 34 and 36 of the respective
housings
14 and 16 to help hold the housings 14 and 16 together and maintain their
angular
position with respect to each other.
The pump 10 also includes fan guards 40, one at each end, which are identical
to
one another. Refernng to Fig. 2, the motor 12 has a shaft 42 which extends
through it
and into both housings 14 and 16, nearly to the end of each respective
housing. Each end
of the shaft 42 mounts a rotary fan blade 44 which is rotated by the shaft 42
in a direction
so as to draw air into each respective housing 14 and 16 and direct it over
the coils of the
motor 12. The housing of the motor 12 is provided with holes to provide for
the exhaust
of cooling air and additional ventilation slots adjacent to the motor may be
provided in
the housings 14 and 16. The housings 14 and 16 mount bearings (bearings not
shown)
which journal the shaft 42. The housings 14 and 16 also have openings in them
which
provide for the axial through-flow of air so that air moved by the fan blades
44 reaches
the coils of the motor 12.
S
CA 02392909 2002-05-28
WO 01/38743 PCT/US00/32384
Each fan guard 40 is perforated, having radial spokes with spaced circular
ribs
running between them to provide for the inlet of cooling air past the guard
40. Each
guard 40 has a rim SO which on its inner side defines a groove 52 in which a
lip 54 of
the adjacent housing 14, 16 is received to help locate the fan guard 40
radially relative
to the housing.
A projection 56 extends radially from the rim 50 and fits into opening 58
which
is formed in the compression chamber portion 34 or 36 of each housing 14 or
16. The
projection 56 helps locate the fan guard 40 angularly relative to the housing
14 or 16 to
which it is assembled, and also provides a nameplate. The fan guard 40 is made
of a
suitable resilient plastic resin, such as a polyester polymer.
Each guard 40 has four tabs 60, each in a different quadrant, which extend
parallel
to the shaft 42 into the end of the respective crank case portion 62 or 64 of
the
corresponding housing 14 or 16. As best shown in Fig. 4, each tab 60 is D- or
crescent-
shaped generally and fits into a similarly shaped, but slightly larger recess
66 which is
formed in the respective housing 14 or 16 at a corresponding angular location
and also
runs parallel to the shaft 42. Each tab 60 has an ear 68 which snaps into a
hole 70 formed
in the recess 66. The recess 66 and hole 70 are both features which can
readily be cast
in features by persons of ordinary skill in the art. When the tab 60 is
received in the
recess 66 and the ear 68 is engaged in the hole 70, the inner surface 72 of
the tab 60 is
slightly recessed from the circular surface 74 of the housing, which circular
surface 74
is only slightly spaced from the tips of the fan blade 44. The surface 72 is
so recessed
so that if the guard 40 is removed from the housing with the fan running, the
tab 60 will
not be moved so far inwardly as to interfere with the rotating fan blade. In
addition, since
6
CA 02392909 2002-05-28
WO 01/38743 PCT/US00/32384
the tab 60 is recessed from the surface 74, the tab 60 does not increase the
required
amount of clearance between the tips of the fan blade and housing.
As illustrated in Fig. 3, there are two tabs 60 and corresponding recesses 66
in the
upper portion of the crank case and two in the lower portion. The two in the
upper
portion are both aligned along a single horizontal line 80 and in the lower
portion are
aligned along horizontal line 82. Although the recesses 66 and arcuate
surfaces of the
tabs 60 are symmetrical about lines which are radial to the shaft 42 along
lines 84 and 86,
the ears 68 and holes 70 are not, being aligned along the horizontal lines 80
and 82,
which are perpendicular to the major parting line of the housing 14, 16
casting.
As best shown in Fig. 5, each tab 60 has a ramped lead-in, or distal, surface
90
which serves to flex the tab 60 inwardly when the guard is inserted in the
housing. Each
ear 68 also has a proximal surface 92 which is at a right angle or nearly
right angle to
outer side 94 of the ear 68 so as to provide for a snap-in connection of the
ear 68 in the
hole 70.
A preferred embodiment of the invention has been described in considerable
detail. Many modifications and variations to the embodiment described will be
apparent
to persons skilled in the art, so the invention should not be limited to the
embodiment
described.
7