Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
Specification
Pyrrolopyridazine derivatives
[Technical field]
This invention relates to pyrrolopyridazine derivatives or pharmaceutically
acceptable salts thereof; to pharmaceutical compositions comprising a
pyrrolopyridazine derivative (preferably compositions for the preventive agent
or
treatment of ulcerative disease) as an active ingredient; to the use of a
pyrrolopyridazine derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in
the
preparation of a pharmaceutical composition (preferably a composition for the
preventive agent or treatment of ulcerative disease); or to a method for the
prevention
or treatment of disease (preferably ulcerative disease), which method
comprises
administering a pharmaceutically effective amount of a pyrrolopyridazine
derivative
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof to a warm-blooded animal
(preferably a
human).
[Background of the invention]
It has been considered that an inbalance between aggressive factors and
protective
factors against the gastric mucous membrane induces peptic ulcers. Gastric
acid
secretion is an aggressive factor and suppression of gastric acid secretion is
useful in
the prevention and treatment of the disease. Anticholinergic agents, histamine
H2
receptor antagonists such as cimetidine and the like and proton pump
inhibitors such
as omeprazole and the like have been clinically used as a gastric acid
secretion
inhibitor. Although these agents are excellent therapeutic agents for
ulcerative
disease, the disease may recur after cessation of the therapy. It has been
recently
reported that Helicobacter pylori relates to recurrence of the ulcerative
disease.
Actually there have been some attempts to use a gastric acid secretion
inhibitor in
combination with an antibacterial agent for treatment of the disease.
Accordingly a compound that exhibits potent gastric acid secretory inhibition
activity, excellent gastric mucous membrane protection activity and potent
antibacterial activity against Helicobacter pylori would be expected to be an
excellent
medicament (preferably a prophylactic and therapeutic agent for ulcerative
disease).
S:(Chemical/SankyolFP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/tianslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
2
Some pyrrolopyridazine derivatives that have gastric acid secretory inhibition
activity and gastric mucous membrane protection activity have been known (for
example, WO 91/17164, WO 92/06979, WO 93/08190 and the like). The activity
against Helicobacter pvlori of some pyrrolopyridazine derivatives has also
been
known (for example, Japanese Patent Application Publication Hei 7-247285 and
the
like).
[Disclosure of the invention]
The inventors have continued an investigation on the pharmacological
activities of
pyrrolopyridazine derivatives in order to discover a medicament (preferably an
agent
for ulcerative disease) that exhibits potent gastric acid secretory inhibition
activity,
protects gastric mucous membranes and has excellent antibacterial activity
against
Helicobacterwlori for a long time. As a result, they found that some
pyrrolopyridazine derivatives substituted with specific substituents at the 3-
position
exhibit potent gastric acid secretory inhibition activity and gastric mucous
membrane
protection activity and exhibit excellent antibacterial activity against
Helicobacter
lori.
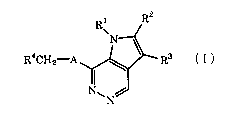
The pyrrolopyridazine derivative of the present invention has the following
formula:
R4CH2-A R3
N
(I)
wherein:
R1 represents a C2-C6 alkenyl group, a halogeno C2-C6 alkenyl group, a C3-C7
cycloalkyl group which may be optionally substituted with C1-C6 alkyl or a C3-
C7
cycloalkyl- C1-C6 alkyl group which may be optionally substituted with C1-C6
alkyl;
R2 represents a C1-C6 alkyl group;
S:/Chemical/SankyolFP200104IFP200104s.doc P83812IFP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
3
R3 represents a hydroxymethyl group, a C2-C6 aliphatic acyloxymethyl group, a
C6-
C1o arylcarbonyloxymethyl group which may be optionally substituted with
substituents selected from the group consisting of C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy
and
halogeno, a C1-C6 alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl group, a formyl group, a carboxyl
group,
a C1-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group or a C6-Clo aryloxycarbonyl group which may be
optionally substituted with substituents selected from the group consisting of
C1-C6
alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy and halogeno;
R4 represents a C6-Clo aryl group which may be optionally substituted with
substituents selected from the group consisting of C1-C6 alkyl, halogeno C1-C6
alkyl,
C1-C6 alkoxy, halogeno C1-C6 alkoxy and halogeno;
A represents an imino group, an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom;
In the formula (I) described above:
The C1-C6 alkyl group in the definition of R2 or the C1-C6 alkyl moiety
included in
the definition of R1, R3 or R4 is, for example, a methyl, ethyl, propyl,
isopropyl, butyl,
isobutyl, s-butyl t-butyl, pentyl or hexyl group; preferably a C1-C4 alkyl
group; more
preferably a methyl or ethyl group; and most preferably a methyl group.
The C2-C6 alkenyl group or C2-C6 alkenyl moiety of the halogeno C2-C6 alkenyl
group in the definition of Rl is, for example, a vinyl, 1-propenyl, 2-
propenyl,
isopropenyl, 1-butenyl, 2-butenyl, 1-methyl-1-propenyl, 1-methyl-2-propenyl, 2-
methyl-1-propenyl, 2-methyl-2-propenyl, 2-pentenyl or 2-hexenyl group;
preferably a
C2-C4 alkenyl group, more preferably a C3-C4 alkenyl group; still more
preferably a 2-
propenyl or 2-butenyl group; and most preferably a 2-butenyl group.
A typical example of a halogeno C2-C6 alkenyl group in the definition of Rl
is, for
example, a 2,2-difluorovinyl, 3-fluoro-2-propenyl, 3-chloro-2-propenyl, 3-
bromo-2-
propenyl, 3-iodo-2-propenyl, 3,3-difluoro-2-propenyl, 2,3-dichloro-2-propenyl,
3,3-
dichloro-2-propenyl, 2,3-dibromo-2-propenyl, 3,3-dibromo-2-propenyl, 4,4,4-
trifluoro-2-butenyl, 5-fluoro-2-pentenyl or 6-fluoro-2-hexenyl group;
preferably a 3-
chloro-2-propenyl, 3,3-difluoro-2-propenyl, 3,3-dichloro-2-propenyl or 4,4,4-
trifluoro-2-butenyl group; and more preferably a 3-chloro-2-propenyl, 3,3-
difluoro-2-
propenyl or 3,3-dichloro-2-propenyl group.
The C3-C7 cycloalkyl moiety of the C3-C7 cycloalkyl group which may be
optionally substituted with a C1-C6 alkyl group or of the C3-C7 cycloalkyl- C1-
C6 alkyl
group which may be optionally substituted with a C1-C6 alkyl group in the
definition
of R' is, for example, a cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl or
S:/Chemical/sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P838121FP-2001041tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
4
cycloheptyl group; preferably a C3-C6 cycloalkyl group; more preferably a
cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl group; and most preferably a
cyclopropyl
group.
A typical example of the C3-C7 cycloalkyl group which may be optionally
substituted with a C1-C6 alkyl group in the definition of Rl is, for example,
a
cyclopropyl, 2-methylcyclopropyl, 2-ethylcyclopropyl, 2-propylcyclopropyl, 2-
hexylcyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, 2-methylcyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, 2-
methylcyclopentyl,
2-ethylcyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, 2-methylcyclohexyl or cycloheptyl group;
preferably
a cyclopropyl, 2-methylcyclopropyl, 2-ethylcyclopropyl, cyclobutyl,
cyclopentyl, 2-
methylcyclopentyl, cyclohexyl or 2-methylcyclohexyl group; more preferably a
cyclopropyl, 2-methylcyclopropyl, cyclopentyl, 2-methylcyclopentyl, cyclohexyl
or
2-methylcyclohexyl group; and most preferably a cyclopropyl or 2-
methylcyclopropyl
group.
A typical example of the C3-C7 cycloalkyl- C1-C6 alkyl group which may be
optionally substituted with a C1-C6 alkyl group in the definition of R1 is,
for example,
a cyclopropylmethyl, 2-cyclopropylethyl, 2-methylcyclopropylmethyl, 2-(2-
methylcyclopropyl)ethyl, 3-(2-methylcyclopropyl)propyl, 6-(2-
methylcyclopropyl)hexyl, 2-ethylcyclopropylmethyl, 2-propylcyclopropylmethyl,
2-
hexylcyclopropylmethyl, cyclobutylmethyl, 2-methylcyclobutylmethyl,
cyclopentylmethyl, 2-cyclopentylethyl, 2-methylcyclopentylmethyl, 2-(2-
methylcyclopentyl)ethyl, 2-ethylcyclopentylmethyl, cyclohexylmethyl, 2-
cyclohexylethyl, 2-methylcyclohexylmethyl, 2-(2-methylcyclohexyl)ethyl or
cycloheptylmethyl group; preferably a cyclopropylmethyl, 2-cyclopropylethyl, 2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl, 2-(2-methylcyclopropyl)ethyl, 2-
ethylcyclopropylmethyl,
cyclobutylmethyl, 2-methylcyclobutylmethyl, cyclopentylmethyl, 2-
methylcyclopentylmethyl, cyclohexylmethyl or 2-methylcyclohexylmethyl group;
more preferably a cyclopropylmethyl, 2-methylcyclopropylmethyl, 2-
ethylcyclopropylmethyl, cyclobutylmethyl, 2-methylcyclobutylmethyl,
cyclopentylmethyl or 2-methylcyclohexylmethyl group; more preferably a
cyclopropylmethyl, 2-methylcyclopropylmethyl, cyclopentylmethyl or 2-
methylcyclohexylmethyl group; still more preferably a cyclopropylmethyl or 2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl group; and most preferably a 2-methylcyclopropylmethyl
group.
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/ua-ig/uanslation of
PCT specification/26.07.02
5
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
The C2-C6 aliphatic acyl moiety of the C2-C6 aliphatic acyloxymethyl group in
the
definition of R3 is, for example, an acetyl, propionyl, butyryl, isobutyryl,
valeryl,
isovaleryl or hexanoyl group; preferably a C2-C4 aliphatic acyl group; more
preferably
a C2-C3 aliphatic acyl group; and most preferably an acetyl group.
The C1-C6 alkoxy moiety of a substituent of the aryl group or a C1-C6 alkoxy
moiety of the halogeno C1-C6 alkoxy group of a substituent of the aryl group
in the
definition of R3 and R4 or the C1-C6 alkoxy moiety of the C1-C6
alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl group and the C1-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group in the
definition
of R3 is, for example, a methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy, isopropoxy, butoxy,
isobutoxy, s-
butoxy, t-butoxy, pentyloxy or hexyloxy group; preferably a C1-C4 alkoxy
group;
more preferably a methoxy or ethoxy group; and most preferably a methoxy
group.
The halogen atom included in the definition of Rl, R3 and R4 is, for example,
a
fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine atom; preferably a fluorine, chlorine or
bromine
atom; more preferably a fluorine or chlorine atom.
The C6-Clo aryl moiety of the optionally substituted C6-Clo aryl moiety in the
definition of R3 or of the optionally substituted C6-Clo aryl group in the
definition of
R4 is, for example, a phenyl or naphthyl group; preferably a phenyl group.
The number of the substitutents on the aryl group is, for example from 1 to 5;
preferably from 1 to 3; more preferably 1 or 2; and most preferably one.
The preferred C6-Clo aryl moiety which may be optionally substituted with
substituents selected from the group consisting of C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy
and
halogeno in the definition of R3 is, for example, a phenyl, methylphenyl,
dimethylphenyl, methoxyphenyl, dimethoxyphenyl, fluorophenyl, chlorophenyl,
bromophenyl, difluorophenyl, chlorofluorophenyl, dichlorophenyl, naphthyl,
methylnaphtyl, methoxynaphthyl, fluoronaphthyl, chloronaphthyl or
bromonaphthyl
group; more preferably a phenyl, methylphenyl, methoxyphenyl, fluorophenyl or
chlorophenyl group; most preferably a phenyl or methylphenyl group.
The preferred C6-Clo aryl group which may be optionally substituted with
substituents selected from the group consisting of CI-C6 alkyl, halogeno C1-C6
alkyl,
C1-C6 alkoxy, halogeno C1-C6 alkoxy, and halogeno in the definition of R4 is,
for
example, a phenyl, methylphenyl, trifluoromethylphenyl, methoxyphenyl,
trifluoromethoxyphenyl, difluoromethoxyphenyl, fluorophenyl, chlorophenyl,
bromophenyl, difluorophenyl, chlorofluorophenyl, dichlorophenyl,
trifluorophenyl,
trichlorophenyl, naphthyl, methylnaphtyl, methoxynaphthyl, fluoronaphthyl,
S:/ChemicaUSankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812IFP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
6
chloronaphthyl or bromonaphthyl group; more preferably a phenyl, 4-
methylphenyl,
4-trifluoromethylphenyl, 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl, 4-
difluoromethoxyphenyl, 2-, 3- or 4-fluorophenyl, 2-, 3- or 4-chlorophenyl, 4-
bromophenyl, 2,4- or 2,6-difluorophenyl, 4-chloro-2-fluorophenyl, 2-chloro-4-
fluorophenyl, 2,4- or 2,6-dichlorophenyl, 2,4,6-trifluorophenyl or 2,4,6-
trichlorophenyl group; still more preferably a 4-fluorophenyl, 4-chlorophenyl,
2,4-
difluorophenyl, 2,6-difluorophenyl, 4-chloro-2-fluorophenyl, 2-chloro-4-
fluorophenyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl or 2,6-dichlorophenyl group; and most
preferably a
4-fluorophenyl, 2,4-difluorophenyl or 4-chlorophenyl group.
The preferred group A is an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom; more preferably an
oxygen atom.
The compound of formula (I) in this invention can exist as an optical isomer
due to
an asymmetric carbon atoms) or as a geometrical isomer due to a double bonds)
or
to ring structure. The present invention encompasses a single isomer and
mixtures of
such isomers.
The pharmaceutically acceptable salts of compounds of formula (I) are acid
addition salts. Examples of such salt are, for example, a hydrohalogenic acid
salt such
as hydrofluoride, hydrochloride, hydrobromide, hydroiodide; a nitrate; a
perchlorate;
a sulfate; a phosphate; a carbonate; a C1-C6 alkylsulfonate which may be
optionally
substituted with fluorine atoms, such as methanesulfonate,
trifluoromethanesulfonate,
ethanesulfonate, pentafluoroethanesulfonate, propanesulfonate,
butanesulfonate,
pentanesulfonate, hexanesulfonate; a C6-Clo arylsulfonate such as
benzenesulfonate,
p-toluenesulfonate; a carboxylate such as acetate, propionate, lactate,
benzoate,
fumarate, maleate, succinate, citrate, tartrate, oxalate, malonate; or an
amino acid salt
such as glutamate or aspartate; preferably a hydrochloride, sulfate or
carboxylate and
most preferably a hydrochloride.
The compounds of formula (I) in this invention or salts thereof can exist as
hydrates. The present invention encompasses such hydrates.
Preferred compounds of formula (I) are:
(1) a compound wherein Rl is a C2-C4 alkenyl group, a C3-C4 alkenyl group
substituted with fluoro or chloro, a C3-C6 cycloalkyl group which may be
optionally
substituted with C1-CZ alkyl or a C3-C6 cycloalkyl- C1-C2 alkyl group which
may be
substituted with C1-C2 alkyl;
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP2001041FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
(2) a compound wherein R1 is a C3-C4 alkenyl group, a 3-chloro-2-propenyl
group, a
3,3-difluoro-2-propenyl group, a 3,3-dichloro-2-propenyl group, a cyclopropyl
group,
a 2-methylcyclpropyl group, a 2-ethylcyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, a
cyclopentyl group, a 2-methylcyclopentyl group, a cyclohexyl group, a 2-
methylcyclohexyl group, a cyclopropylmethyl group, a 2-methylcyclopropylmethyl
group, a 2-ethylcyclopropylinethyl group, a cyclobutylmethyl group, a 2-
methylcyclobutylmethyl group, a cyclopentylmethyl group or a 2-
methylcyclohexylmethyl group;
(3) a compound wherein Rl is a 2-propenyl group, a 2-butenyl group, a
cyclopropyl
group, a 2-methylcyclopropyl group, a cyclopentyl group, a 2-methylcyclopentyl
group, a cyclohexyl group, a 2-methylcyclohexyl group, a cyclopropylmethyl
group, a
2-methylcyclopropylmethyl group, a cyclopentylmethyl group or a 2-
methylcyclohexylmethyl group;
(4) a compound wherein Rl is a 2-propenyl group, a 2-butenyl group, a
cyclopropyl
group, a 2-methylcyclopropyl group, a cyclopropylmethyl group or a 2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl group;
(5) a compound wherein Rl is a 2-butenyl group, a cyclopropylmethyl group or a
2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl group;
(6) a compound wherein R2 is a C1-C4 alkyl group;
(7) a compound wherein R2 is a C1-C2 alkyl group;
(8) a compound wherein R2 is a methyl group;
(9) a compound wherein R3 is a hydroxymethyl group, a C2-C6 aliphatic
acyloxymethyl group, a benzoyloxymethyl group which may be optionally
substituted
with methyl, methoxy, fluoro or chloro, a C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl group,
a
formyl group, a carboxyl group, a C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl group or a
phenyloxycarbonyl group which may be optionally substituted with methyl,
methoxy,
fluoro or chloro;
(10) a compound wherein R3 is a hydroxymethyl group, a C2-C6 aliphatic
acyloxymethyl group, a benzoyloxymethyl group, a C1-C2 alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl
group, a formyl group, a carboxyl group, a C1-C2 alkoxycarbonyl group or a
phenyloxycarbonyl group;
( 11 ) a compound wherein R3 is a hydroxymethyl group, a C2-C4 aliphatic
acyloxymethyl group, a C1-C2 alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl group, a formyl group, a
carboxyl group or a C1-C2 alkoxycarbonyl group;
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104Jtsa-ig/translation
of PCT specificationl26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
8
(12) a compound wherein R3 is a hydroxymethyl group, a C2-C3 aliphatic
acyloxymethyl group, a formyl group or a carboxyl group;
(13) a compound wherein R3 is a hydroxymethyl group or an acetoxymethyl group;
(14) a compound wherein R4 is a phenyl group which is substituted with 1 to 3
substituents selected from the group consisting of C1-C4 alkyl, halogeno C,-C4
alkyl,
C1-C4 alkoxy, halogeno C1-C4 alkoxy, fluoro, chloro and bromo;
( 1 S) a compound wherein R4 is a phenyl group which is substituted with 1 to
3
substituents selected from the group consisting of methyl, trifluoromethyl,
methoxy,
trifluoromethoxy, difluoromethoxy, fluoro, chloro and bromo;
(16) a compound wherein R4 is a phenyl group which is substituted at the
positions)
selected from the group consisting of 2-, 4- and 6-position of the phenyl
group with 1
or 2 substituents selected from the group consisting of fluoro and chloro;
(17) a compound wherein R' is a phenyl group which is substituted at the 4-
position,
2,4-positions or 2,6-positions of the phenyl group with 1 or 2 substituents
selected
from the group consisting of fluoro and chloro;
(18) a compound wherein A is an oxygen atom or a sufur atom; and
(19) a compound wherein A is an oxygen atom.
In each group of claims (1)-(5), (6)-(8), (9)-(13), (14)-(17), or (18)-(19)
described
above, the larger the number of the claim is, the more preferable the compound
according to the claim is [similarly in the group of claims (20)-(24)
described below].
Compounds wherein Rl, R2, R3, R4 and A are optionally selected from groups of
claims (1)-(S), (6)-(8), (9)-(13), (14)-(17), and (18)-(19), respectively, are
also
preferable.
Such compounds are as follows for example:
(20) a compound wherein Rl is a C2-C4 alkenyl group, a C3-C4 alkenyl group
substituted with fluoro or chloro, a C3-C6 cycloalkyl group which may be
optionally
substituted with C1-C2 alkyl or a C3-C6 cycloalkyl- C1-C2 alkyl group which
may be
substituted with C1-C2 alkyl,
R2 is a C1-C4 alkyl group,
R3 is a hydroxymethyl group, a C2-C6 aliphatic acyloxymethyl group, a
benzoyloxymethyl group which may be optionally substituted with methyl,
methoxy,
fluoro or chloro, a C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl group, a formyl group, a
carboxyl
group, a C1-C4 alkoxycarbonyl group or a phenyloxycarbonyl group which may be
optionally substituted with methyl, methoxy, fluoro or chloro,
S:/Chemical/SankyoIFP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104Jtsa-ig/translation
of PCT specificationl26.07.02
9
R4 is a phenyl group which is substituted with 1 to 3 substituents selected
from the
group consisting of C~-C4 alkyl, halogeno CI-C4 alkyl, CI-Ca alkoxy, halogeno-
C~-C4
alkoxy, fluoro, chloro and bromo,
A is an oxygen atom or a sufur atom;
(21 ) a compound wherein R' is a C3-C4 alkenyl group, a 3-chloro-2-propenyl
group, a
3,3-difluoro-2-propenyl, a 3,3-dichloro-2-propenyl group, a cyclopropyl group,
a 2-
methylcyclpropyl group, a 2-ethylcyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, a
cyclopentyl group, a 2-methylcyclopentyl group, a cyclohexyl group, a 2-
methylcyclohexyl group, a cyclopropylmethyl group, a 2-methylcyclopropylmethyl
group, a 2-ethylcyclopropylmethyl group, a cyclobutylmethyl group, a 2-
methylcyclobutylmethyl group, a cyclopentylmethyl group or a 2-
methylcyclohexylmethyl group,
R2 is a C~-Ca alkyl group,
R3 is a hydroxymethyl group, a C2-C6 aliphatic acyloxymethyl group, a
benzoyloxymethyl group, a C,-C2 alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl group, a formyl group,
a
carboxyl group, a C1-C2 alkoxycarbonyl group or a phenyloxycarbonyl group,
R4 is a phenyl group which is substituted with 1 to 3 substituents selected
from the
group consisting of methyl, trifluoromethyl, methoxy, trifluoromethoxy,
difluoromethoxy, fluoro, chloro and bromo,
A is an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom;
(22) a compound wherein R' is a 2-propenyl group, a 2-butenyl group, a
cyclopropyl
group, a 2-methylcyclopropyl group, a cyclopentyl group, a 2-methylcyclopentyl
group, a cyclohexyl group, a 2-methylcyclohexyl group, a cyclopropylmethyl
group, a
2-methylcyclopropylmethyl group, a cyclopentylmethyl group or a 2-
methylcyclohexylmethyl group,
R2 is a C1-C2 alkyl group,
R3 is a hydroxymethyl group, a C2-C4 aliphatic acyloxymethyl group, a C~-C2
alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl group, a formyl group, a carboxyl group or a C~-C2
alkoxycarbonyl group,
R4 is a phenyl group which is substituted at the positions) selected from the
group
consisting of 2-, 4- and 6-position of the phenyl group with 1 or 2
substituents
selected from the group consisting of fluoro and chloro,
A is an oxygen atom;
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/ua-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
(23) a compound wherein R' is a 2-propenyl goup, a 2-butenyl goup, a
cyclopropyl
goup, a 2-methylcyclopropyl goup, a cyclopropylmethyl goup or a 2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl goup,
R2 is a C1-C2 alkyl goup,
R3 is a hydroxymethyl goup, a C2-C3 aliphatic acyloxymethyl goup, a formyl
goup
or a carboxyl group,
R4 is a phenyl goup which is substituted at the positions) selected from the
group
consisting of 2-, 4- and 6-position of the phenyl goup with 1 or 2
substituents
selected from the goup consisting of fluoro and chloro,
A is an oxygen atom; and
(24) a compound wherein R' is a 2-butenyl group, a cyclopropylmethyl goup or a
2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl goup
R2 is a methyl goup,
R3 is a hydroxymethyl goup or an acetoxymethyl goup,
R4 is a phenyl goup which is substituted at the 4-position, 2,4-positions or,
2,6-
positions of the phenyl goup with 1 or 2 substituents selected from the goup
consisting of fluoro and chloro,
A is an oxygen atom.
Preferred compounds of formula (I) can be exemplified in Table 1.
[Table 1
Rl R2
N
R4CH2-A R3
N~ N
(I)
S:/ChemicallSankyoIFP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
11
Exemp. R' R' R' A R" '
Comp.
No.
1 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O Ph
2 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O Ph
3 CH2C(CH3)=CH2 Me CH20H O Ph
4 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O Ph
CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20H O Ph
6 Pr' Me CH20H O Ph
7 2-MePr' Me CH20H O Ph
8 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O Ph
9 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O Ph
CH2Bu' Me CH20H O Ph
11 CH2Pn' Me CH20H O Ph
12 CH2Hx' Me CH20H O Ph
13 CH=CHCH2 Me CH20H O 2-FPh
14 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 2-FPh
CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 2-FPh
16 CH2Pr Me CH20H O 2-FPh
17 CH2(2-MePr) Me CH20H O 2-FPh
18 CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 4-FPh
19 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 4-FPh
CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 4-FPh
21 CH2C(CH3)=CH2 Me CH20H O 4-FPh
22 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 4-FPh
23 CH2CH=CHCH2CH3 Me CH20H O 4-FPh
24 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20H O 4-FPh
CH2CH=CHCI Me CH20H O 4-FPh
26 CH2CH=CC12 Me CH20H O 4-FPh
27 Pr' Me CH20H O 4-FPh
28 2-MePr' Me CH20H O 4-FPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104IFP200104s.doc P83812lFP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specificatiorJ26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
12
29 Bu' Me CH20H O 4-FPh
30 Pn' Me CH20H O 4-FPh
31 Hx' Me CH20H O 4-FPh
32 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 4-FPh
33 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 4-FPh
34 CH2CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 4-FPh
35 CH2Bu' Me CH20H O 4-FPh
36 CH2Pn' Me CH20H O 4-FPh
37 CH2(2-MePn') Me CH20H O 4-FPh
38 CH2Hx' Me CH20H O 4-FPh
39 CH2(2-MeHx') Me CH20H O 4-FPh
40 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
41 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
42 CH2C(CH3)=CH2 Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
43 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
44 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
45 Pr' Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
46 2-MePr' Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
47 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
48 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
49 CH2Bu' Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
50 CH2Pn' Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
51 CH2Hx' Me CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
52 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 2-CIPh
53 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 2-CIPh
54 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 2-CIPh
55 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 2-CIPh
56 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 2-CIPh
57 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 4-CIPh
58 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 4-CIPh
59 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 4-CIPh
60 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 4-CIPh
S:/ChemicallSankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-2001041tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specificationl26.07.U2
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
13
61 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 4-CIPh
62 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 2-F,4-CIPh
63 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 2-F,4-CIPh
64 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 2-F,4-CIPh
65 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 2-F,4-CIPh
66 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 2-C1,4-FPh
67 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 2-C1,4-FPh
68 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 2-C1,4-FPh
69 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 2-C1,4-FPh
70 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 2,4-diClPh
71 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 2,4-diClPh
72 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 2,4-diClPh
73 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 2,4-diClPh
74 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O Ph
75 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O Ph
76 CH2C(CH3)=CH2 Me CH20Ac O Ph
77 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O Ph
78 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20Ac O Ph
79 Pr' Me CH20Ac O Ph
80 2-MePr' Me CH20Ac O Ph
81 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O Ph
82 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O Ph
83 CH2Bu' Me CH20Ac O Ph
84 CH2Pn' Me CH20Ac O Ph
85 CH2Hx' Me CH20Ac O Ph
86 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2-FPh
87 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 2-FPh
88 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2-FPh
89 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 2-FPh
90 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 2-FPh
91 CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
92 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo1FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PC'T specificatiod26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
14
93 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
94 CH2C(CH3)=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
95 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
96 CH2CH=CHCH2CH3 Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
97 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
98 CH2CH=CHCI Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
99 CH2CH=CCI2 Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
100 Pr' Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
101 2-MePr' Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
102 Bu' Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
103 Pn' Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
104 Hx' Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
105 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
106 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
107 CH2CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
108 CH2Bu' Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
109 CH2Pn' Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
110 CH2(2-MePn') Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
111 CH2Hx' Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
112 CH2(2-MeHx') Me CH20Ac O 4-FPh
113 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
114 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
115 CH2C(CH3)=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
116 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
117 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
118 Pr' Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
119 2-MePr' Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
120 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
121 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
122 CH2Bu' Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
123 CH2Pn' Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
124 CH2Hx' Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
S:(Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104IFP200104s.doc P83812IFP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specificationl26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
125 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2-CIPh
126 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 2-CIPh
127 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2-CIPh
128 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 2-CIPh
129 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 2-CIPh
130 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 4-CIPh
131 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 4-CIPh
132 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 4-CIPh
133 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 4-CIPh
134 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 4-CIPh
135 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 2-F,4-CIPh
136 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2-F,4-CIPh
137 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 2-F,4-CIPh
138 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 2-F,4-CIPh
139 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 2-C1,4-FPh
140 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2-C1,4-FPh
141 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 2-C1,4-FPh
142 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 2-C1,4-FPh
143 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diClPh
144 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diClPh
145 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diClPh
146 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 2,4-diClPh
147 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O Ph
148 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp O Ph
149 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O Ph
150 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20Prp O Ph
151 Pr' Me CH20Prp O Ph
152 2-MePr' Me CH20Prp O Ph
153 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O Ph
154 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O Ph
155 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp O 2-FPh
156 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 2-FPh
S:/Chemi'al/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200t04/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
16
157 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O 2-FPh
158 CHZ(2-MePr') Me CHZOPrp O 2-FPh
159 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
160 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
161 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
162 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
163 CH2CH=CHCI Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
164 Pr' Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
165 2-MePr' Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
166 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
167 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
168 CH2Bu' Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
169 CH2Pn' Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
170 CH2Hx' Me CH20Prp O 4-FPh
171 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diFPh
172 CH2CH=CHZ Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diFPh
173 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diFPh
174 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diFPh
175 Pr' Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diFPh
176 2-MePr' Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diFPh
177 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diFPh
178 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diFPh
179 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 2-CIPh
180 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp O 2-CIPh
181 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 2-CIPh
182 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O 2-CIPh
183 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHzOPrp O 2-CIPh
184 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 4-CIPh
185 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp O 4-CIPh
186 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 4-CIPh
187 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O 4-CIPh
188 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 4-CIPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
17
189 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH24Prp O 2-F,4-CIPh
190 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHzOPrp O 2-F,4-CIPh
191 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O 2-F,4-CIPh
192 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 2-F,4-CIPh
193 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp O 2-C1,4-FPh
194 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 2-C1,4-FPh
195 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O 2-C1,4-FPh
196 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 2-C1,4-FPh
197 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diClPh
198 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diClPh
199 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diClPh
200 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 2,4-diClPh
201 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O Ph
202 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur O Ph
203 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur O Ph
204 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O Ph
205 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O 2-FPh
206 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur O 2-FPh
207 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur O 2-FPh
208 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 2-FPh
209 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur O 4-FPh
210 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O 4-FPh
211 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur O 4-FPh
212 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20Bur O 4-FPh
213 Pr' Me CH20Bur O 4-FPh
214 2-MePr' Me CH20Bur O 4-FPh
215 CH2Pr' Me CHZOBur O 4-FPh
216 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 4-FPh
217 CH2Bu' Me CH20Bur O 4-FPh
218 CH2Pn' Me CH20Bur O 4-FPh
219 CH2Hx' Me CH20Bur O 4-FPh
220 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O 2,4-diFPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
18
221 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur O 2,4-diFPh
222 Pr' Me CH20Bur O 2,4-diFPh
223 2-MePr' Me CH20Bur O 2,4-diFPh
224 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur O 2,4-diFPh
225 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 2,4-diFPh
226 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O 2-CIPh
227 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur O 2-CIPh
228 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur O 2-CIPh
229 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 2-CIPh
230 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O 4-CIPh
231 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur O 4-CIPh
232 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur O 4-CIPh
233 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 4-CIPh
234 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O 2-F,4-CIPh
235 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur O 2-F,4-CIPh
236 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur O 2-F,4-CIPh
237 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 2-F,4-CIPh
238 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O 2-C1,4-FPh
239 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur O 2-C1,4-FPh
240 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur O 2-C1,4-FPh
241 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 2-C1,4-FPh
242 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O 2,4-diClPh
243 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur O 2,4-diClPh
244 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur O 2,4-diClPh
245 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 2,4-diClPh
246 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20COPh O Ph
247 CH2Pr' Me CH20COPh O Ph
248 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh O Ph
249 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C0{4-Me)Ph O Ph
250 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20COPh O 2-FPh
251 CH2Pr' Me CH20COPh O 2-FPh
252 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh O 2-FPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-2001041tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
19
253 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C0(4-Me)Ph O 2-FPh
254 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
255 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
256 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C0(4-Me)Ph O 4-FPh
257 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
258 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
259 Pr' Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
260 2-MePr' Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
261 CH2Pr' Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
262 CH2Pr' Me CH20C0(4-Me)Ph O 4-FPh
263 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
264 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C0(4-Me)Ph O 4-FPh
265 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C0(4- O 4-FPh
Me0)Ph
266 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C0(4-F)Ph O 4-FPh
267 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C0(4-Cl)Ph O 4-FPh
268 CH2Bu' Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
269 CH2Pn' Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
270 CH2Hx' Me CH20COPh O 4-FPh
271 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20COPh O 2,4-diFPh
272 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C0(4-Me)Ph O 2,4-diFPh
273 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20COPh O 2,4-diFPh
274 Pr' Me CH20COPh O 2,4-diFPh
275 CH2Pr' Me CH20COPh O 2,4-diFPh
276 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh O 2,4-diFPh
277 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C0(4-Me)Ph O 2,4-diFPh
278 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20COPh O 2-CIPh
279 CH2Pr' Me CH20COPh O 2-CIPh
280 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh O 2-CIPh
281 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C0(4-Me)Ph O 2-CIPh
282 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20COPh O 4-CIPh
283 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20COPh O 4-CIPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812IF1'-2001041tsa-ig/danslation
of PCT specifi'ation/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
284 CHZPr' Me CH20COPh O 4-CiPh
285 CHZ(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh O 4-CIPh
286 CHZ(2-MePr') Me CHZOCO(4-Me)Ph O 4-CIPh
287 CHZCH=CHCH3 Me CHZOCOPh O 2-F,4-CIPh
288 CHZPr' Me CHZOCOPh O 2-F,4-CIPh
289 CHZ(2-MePr') Me CHzOCOPh O 2-F,4-CIPh
290 CHZ(2-MePr') Me CHZOCO(4-Me)Ph O 2-F,4-CIPh
291 CHZCH=CHCH3 Me CH20COPh O 2-C1,4-FPh
292 CHzPr' Me CHZOCOPh O 2-C1,4-FPh
293 CHZ(2-MePr') Me CHZOCOPh O 2-C1,4-FPh
294 CHZ(2-MePr') Me CHZOCO(4-Me)Ph O 2-C1,4-FPh
295 CHZCH=CHCH3 Me CHzOCOPh O 2,4-diClPh
296 CHZPr' Me CHzOCOPh O 2,4-diClPh
297 CHZ(2-MePr') Me CHZOCOPh O 2,4-diClPh
298 CHZ(2-MePr) Me CHZOCO(4-Me)Ph O 2,4-diClPh
299 CHZCH=CHCH3 Me CHZOCOZMe O Ph
300 CHZPr' Me CHzOCOzMe O Ph
301 CHz(2-MePr') Me CHzOCOzMe O Ph
302 CHZCH=CHCH3 Me CHzOCO2Me O 2-FPh
303 CHZPr' Me CH20COzMe O 2-FPh
304 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHzOCOzMe O 2-FPh
305 CH=CHCH3 Me CHZOCOZMe O 4-FPh
306 CHzCH=CHz Me CHZOCOZMe O 4-FPh
307 CHZCH=CHCH3 Me CHZOC02Me O 4-FPh
308 Pr' Me CH20COzMe O 4-FPh
309 2-MePr Me CHzOCOzMe O 4-FPh
310 CH2Pr' Me CHZOCOZMe O 4-FPh
311 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHZOCOZMe O 4-FPh
312 CHZBu' Me CHZOCOZMe O 4-FPh
313 CHZPn' Me CHZOCOZMe O 4-FPh
314 CHzHx' Me CHzOCOZMe O 4-FPh
315 CHzCH=CHCH3 Me CHZOCOZMe O 2,4-diFPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-2001041tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
21
316 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me O 2,4-diFPh
317 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 2,4-diFPh
318 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Me O 2-CIPh
319 CH2Pr' Me CH20COzMe O 2-CIPh
320 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 2-CIPh
321 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Me O 4-CIPh
322 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me O 4-CIPh
323 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 4-CIPh
324 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Me O 2-F,4-CIPh
325 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me O 2-F,4-CIPh
326 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 2-F,4-CIPh
327 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Me O 2-C1,4-FPh
328 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me O 2-C1,4-FPh
329 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 2-C1,4-FPh
330 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Me O 2,4-diClPh
331 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me O 2,4-diClPh
332 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 2,4-diClPh
333 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et O Ph
334 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O Ph
335 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O Ph
336 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et O 2-FPh
337 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 2-FPh
338 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 2-FPh
339 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et O 4-FPh
340 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Et O 4-FPh
341 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et O 4-FPh
342 Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 4-FPh
343 2-MePr' Me CH20C02Et O 4-FPh
344 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 4-FPh
345 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 4-FPh
346 CH2Bu' Me CH20C02Et O 4-FPh
347 CH2Pn' Me CH20C02Et O 4-FPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P838i2/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PC? specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
22
348 CH2Hx' Me CH20C02Et O 4-FPh
349 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et O 2,4-diFPh
350 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 2,4-diFPh
351 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 2,4-diFPh
352 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et O 2-CIPh
353 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 2-CIPh
354 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 2-CIPh
355 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et O 4-CIPh
356 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 4-CIPh
357 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 4-CIPh
358 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et O 2-F,4-CIPh
359 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 2-F,4-CIPh
360 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 2-F,4-CIPh
361 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et O 2-C1,4-FPh
362 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 2-C1,4-FPh
363 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 2-C1,4-FPh
364 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et O 2,4-diClPh
365 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 2,4-diCiPh
366 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 2,4-diClPh
367 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Pr O Ph
368 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O Ph
369 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Pr O 2-FPh
370 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O 2-FPh
371 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Pr O 4-FPh
372 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Pr O 4-FPh
373 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O 4-FPh
374 CH2Pn' Me CH20C02Pr O 4-FPh
375 CH2Hx' Me CH20C02Pr O 4-FPh
376 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Pr O 2,4-diFPh
377 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O 2,4-diFPh
378 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Pr O 2-CIPh
379 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O 2-CIPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104IFP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
23
380 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Pr O 4-CIPh
381 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O 4-CIPh
382 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Pr O 2-F,4-CIPh
383 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O 2-F,4-CIPh
384 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Pr O 2-C1,4-FPh
385 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O 2-C1,4-FPh
386 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Pr O 2,4-diClPh
387 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O 2,4-diClPh
388 CHZCH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Bu O Ph
389 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu O Ph
390 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Bu O 2-FPh
391 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu O 2-FPh
392 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Bu O 4-FPh
393 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Bu O 4-FPh
394 CH2(2-MePr) Me CH20C02Bu O 4-FPh
395 CH2Pn' Me CH20C02Bu O 4-FPh
396 CH2Hx Me CH20C02Bu O 4-FPh
397 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Bu O 2,4-diFPh
398 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu O 2,4-diFPh
399 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Bu O 2-CIPh
400 CHZ(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu O 2-CIPh
401 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Bu O 4-CIPh
402 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu O 4-CIPh
403 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Bu O 2-F,4-CIPh
404 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu O 2-F,4-CiPh
405 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Bu O 2-C1,4-FPh
406 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu O 2-C1,4-FPh
407 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Bu O 2,4-diClPh
408 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu O 2,4-diClPh
409 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O Ph
410 CH2Pr' Me CHO O Ph
411 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O Ph
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
24
412 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 2-FPh
413 CH2Pr' Me CHO O 2-FPh
414 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 2-FPh
415 CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 4-FPh
416 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO O 4-FPh
417 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 4-FPh
418 Pr' Me CHO O 4-FPh
419 2-MePr' Me CHO O 4-FPh
420 CH2Pr Me CHO O 4-FPh
421 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 4-FPh
422 CH2Bu' Me CHO O 4-FPh
423 CH2Pn' Me CHO O 4-FPh
424 CH2Hx' Me CHO O 4-FPh
425 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 2,4-diFPh
426 CH2Pr' Me CHO O 2,4-diFPh
427 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 2,4-diFPh
428 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 2-CIPh
429 CH2Pr' Me CHO O 2-CIPh
430 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 2-CIPh
431 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 4-CIPh
432 CH2Pr' Me CHO O 4-CIPh
433 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 4-CIPh
434 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 2-F,4-CIPh
435 CH2Pr Me CHO O 2-F,4-CIPh
436 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 2-F,4-CIPh
437 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 2-C1,4-FPh
438 CH2Pr' Me CHO O 2-C1,4-FPh
439 CH2(2-MePr) Me CHO O 2-C1,4-FPh
440 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 2,4-diClPh
441 CH2Pr' Me CHO O 2,4-diClPh
442 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 2,4-diClPh
443 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O Ph
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
444 CH2Pr' Me C02H O Ph
445 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O Ph
446 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02H O 2-FPh
447 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 2-FPh
448 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 2-FPh
449 CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O 4-FPh
450 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02H O 4-FPh
451 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O 4-FPh
452 Pr' Me C02H O 4-FPh
453 2-MePr' Me C02H O 4-FPh
454 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 4-FPh
455 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 4-FPh
456 CH2Bu' Me C02H O 4-FPh
457 CH2Pn' Me C02H O 4-FPh
458 CH2Hx' Me C02H O 4-FPh
459 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O 2,4-diFPh
460 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 2,4-diFPh
461 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 2,4-diFPh
462 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O 2-CIPh
463 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 2-CIPh
464 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 2-CIPh
465 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O 4-CIPh
466 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 4-CIPh
467 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 4-CIPh
468 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O 2-F,4-CIPh
469 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 2-F,4-CIPh
470 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 2-F,4-CIPh
471 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O 2-C1,4-FPh
472 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 2-C1,4-FPh
473 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 2-C1,4-FPh
474 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O 2,4-diClPh
475 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 2,4-diClPh
S:/Chemical/SankyoIFP200104IFP200104s.doc P838121FP-200104/tsa-ip./translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
26
476 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 2,4-diClPh
477 CHzCH=CHCH3 Me C02Me O Ph
478 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O Ph
479 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Me O 2-FPh
480 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O 2-FPh
481 CH=CHCH3 Me C02Me O 4-FPh
482 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Me O 4-FPh
483 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Me O 4-FPh
484 CH2Pr' Me C02Me O 4-FPh
485 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O 4-FPh
486 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Me O 2,4-diFPh
487 CH2Pr' Me C02Me O 2,4-diFPh
488 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O 2,4-diFPh
489 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Me O 2-CIPh
490 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O 2-CIPh
491 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Me O 4-CIPh
492 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O 4-CIPh
493 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Me O 2-F,4-CIPh
494 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O 2-F,4-CIPh
495 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Me O 2-C1,4-FPh
496 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O 2-C1,4-FPh
497 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Me O 2,4-diClPh
498 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O 2,4-diClPh
499 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Et O Ph
500 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O Ph
501 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Et O 2-FPh
502 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O 2-FPh
503 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Et O 4-FPh
504 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Et O 4-FPh
505 CH2Pr' Me C02Et O 4-FPh
506 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O 4-FPh
507 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Et O 2,4-diFPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specificationl26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
27
508 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O 2,4-diFPh
509 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Et O 2-CIPh
S 10 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O 2-CIPh
511 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Et O 4-CIPh
512 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O 4-CIPh
513 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Et O 2-F,4-CIPh
514 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O 2-F,4-CIPh
515 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Et O 2-C1,4-FPh
516 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O 2-C1,4-FPh
517 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Et O 2,4-diClPh
518 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O 2,4-diClPh
519 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Pr O Ph
520 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Bu O Ph
521 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Pr O 2-FPh
522 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Bu O 2-FPh
523 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Ph O 2-FPh
524 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Pr O 2-FPh
525 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Bu O 2-FPh
526 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Ph O 2-FPh
527 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02(4-Me)Ph O 2-FPh
528 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Pr O 4-FPh
529 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Bu O 4-FPh
530 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Ph O 4-FPh
531 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02(4-Me)Ph O 4-FPh
532 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Pr O 4-FPh
533 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Bu O 4-FPh
534 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Ph O 4-FPh
535 CH2Pr' Me C02Pr O 4-FPh
536 CH2Pr' Me C02Bu O 4-FPh
537 CH2Pr' Me C02Ph O 4-FPh
538 CH2Pr' Me C02(4-Me)Ph O 4-FPh
539 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Pr O 4-FPh
S:/Chemi'al/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
28
540 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Bu O 4-FPh
541 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Ph O 4-FPh
542 CHz(2-MePr') Me COz(4-Me)Ph O 4-FPh
543 CHz(2-MePr') Me COz(4-Me0)Ph O 4-FPh
544 CHz(2-MePr') Me COz(4-F)Ph O 4-FPh
545 CHz(2-MePr') Me COz(4-Cl)Ph O 4-FPh
546 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Pr O 2,4-diFPh
547 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me COzBu O 2,4-diFPh
548 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Pr O 2,4-diFPh
549 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Bu O 2,4-diFPh
550 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Ph O 2,4-diFPh
551 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Pr O 2-CIPh
552 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Bu O 2-CIPh
553 CHz(2-MePr') Me COzPr O 2-CIPh
554 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Bu O 2-CIPh
555 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Ph O 2-CIPh
556 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Pr O 4-CIPh
557 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Bu O 4-CIPh
558 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Pr O 4-CIPh
559 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Bu O 4-CIPh
560 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Ph O 4-CIPh
561 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02Pr O 2-F,4-CIPh
562 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Pr O 2-F,4-CIPh
563 CH2CH=CHz Me C02Pr O 2-C1,4-FPh
564 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Pr O 2-C1,4-FPh
565 CH2CH=CHz Me COzPr O 2,4-diClPh
566 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02Pr O 2,4-diClPh
567 CH2CH=CHz Et CH20H O Ph
568 CH2CH=CHz Pr CH20H O Ph
569 CH2Pr' Et CH20H O Ph
570 CH2Pr' Pr CH20H O Ph
571 CHz(2-MePr') Et CH20H O Ph
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-i8/translation
of PCT specificationl26.0?.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
29
572 CH2(2-MePr') Pr CH20H O Ph
573 CH=CHCH3 Et CH20H O 2-FPh
574 CH2CH=CH2 Et CH20H O 2-FPh
575 CH2CH=CH2 Pr CH20H O 2-FPh
576 CH2CH=CHCH3 Et CH20H O 2-FPh
577 CH2Pr' Et CH20H O 2-FPh
578 CH2Pr' Pr CH20H O 2-FPh
579 CH2(2-MePr') Et CH20H O 2-FPh
580 CH2(2-MePr') Pr CH20H O 2-FPh
581 CH2(2-MePr') Bu CH20H O 2-FPh
82 CH=CH2 Et CH20H O 4-FPh
583 CH=CHCH3 Et CH20H O 4-FPh
584 CH=CHCH3 Pr CH20H O 4-FPh
585 CH2CH=CH2 Et CH20H O 4-FPh
586 CH2CH=CH2 Pr CH20H O 4-FPh
587 CH2CH=CH2 Bu CH20H O 4-FPh
588 CH2C(CH3)=CH2 Et CH20H O 4-FPh
589 CH2CH=CHCH3 Et CH20H O 4-FPh
590 CH2CH=CHCH3 Pr CH20H O 4-FPh
591 CH2CH=CF2 Et CH20H O 4-FPh
592 CH2Pr' Et CH20H O 4-FPh
593 CH2Pr' Pr CH20H O 4-FPh
594 CH2(2-MePr') Et CH20H O 4-FPh
595 CH2(2-MePr') Pr CH20H O 4-FPh
596 CH2(2-MePr') Bu CH20H O 4-FPh
597 CH2Pn' Et CH20H O 4-FPh
598 CH2Hx' Et CH20H O 4-FPh
599 CH=CHCH3 Et CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
600 CH2CH=CH2 Et CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
601 CH2CH=CH2 Pr CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
602 CH2CH=CHCH3 Et CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
603 CH2CH=CF2 Et CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP2001041FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200t04/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
604 CH2Pr' Et CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
605 CH2Pr' Pr CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
606 CH2(2-MePr') Et CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
607 CH2(2-MePr') Pr CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
608 CH2(2-MePr') Bu CH20H O 2,4-diFPh
609 CH2CH=CH2 Et CH20Ac O Ph
610 CH2Pr' Et CH20Ac O Ph
611 CH2(2-MePr') Et CH20Ac O Ph
612 CH2(2-MePr') Pr CH20Ac O Ph
613 CH2CH=CH2 Et CH20Ac O 2-FPh
614 CH2Pr' Et CH20Ac O 2-FPh
615 CH2(2-MePr') Et CH20Ac O 2-FPh
616 CH2(2-MePr') Pr CH20Ac O 2-FPh
617 CH=CH2 Et CH20Ac O 4-FPh
618 CH=CHCH3 Et CH20Ac O 4-FPh
619 CH2CH=CH2 Et CH20Ac O 4-FPh
620 CH2CH=CH2 Pr CH20Ac O 4-FPh
621 CH2CH=CHCH3 Et CH20Ac O 4-FPh
622 CH2CH=CF2 Et CH20Ac O 4-FPh
623 CH2Pr' Et CH20Ac O 4-FPh
624 CH2Pr' Pr CH20Ac O 4-FPh
625 CH2(2-MePr') Et CH20Ac O 4-FPh
626 CH2(2-MePr') Pr CH20Ac O 4-FPh
627 CH2(2-MePr') Bu CH20Ac O 4-FPh
628 CH2CH=CH2 Et CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
629 CH2CH~HCH3 Et CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
630 CH2CH=CF2 Et CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
631 CH2Pr' Et CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
632 CH2Pr' Pr CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
633 CH2(2-MePr') Et CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
634 CH2(2-MePr') Pr CH20Ac O 2,4-diFPh
635 CH2CH=CH2 Et CHO O Ph
S:/Chemi'al/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812IFP-2001041tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
31
636 CHZCH=CHz Et C02H O Ph
637 CHZPr' Et CHO O Ph
638 CH2Pr' Et C02H O Ph
639 CH2(2-MePr') Et CHO O Ph
640 CH2(2-MePr') Et C02H O Ph
641 CHZCH=CH2 Et CHO O 2-FPh
642 CH2CH=CH2 Et C02H O 2-FPh
643 CH2Pr' Et CHO O 2-FPh
644 CH2Pr' Et C02H O 2-FPh
645 CH2(2-MePr') Et CHO O 2-FPh
646 CH2(2-MePr') Et C02H O 2-FPh
647 CH=CHCH3 Et CHO O 4-FPh
648 CH=CHCH3 Et C02H O 4-FPh
649 CH2CH=CH2 Et CHO O 4-FPh
650 CH2CH=CH2 Et C02H O 4-FPh
651 CH2CH=CH2 Et C02Me O 4-FPh
652 CH2CH=CH2 Et C02Et O 4-FPh
653 CH2CH=CHZ Pr CHO O 4-FPh
654 CH2CH=CH2 Pr C02H O 4-FPh
655 CH2CH=CHCH3 Et CHO O 4-FPh
656 CH2CH=CHCH3 Et C02H O 4-FPh
657 CH2CH=CF2 Et CHO O 4-FPh
658 CH2CH=CF2 Et C02H O 4-FPh
659 CH2Pr' Et CHO O 4-FPh
660 CH2Pr' Et C02H O 4-FPh
661 CH2Pr' Et C02Me O 4-FPh
662 CH2Pr' Et COZEt O 4-FPh
663 CH2Pr' Pr CHO O 4-FPh
664 CH2Pr' Pr C02H O 4-FPh
665 CH2(2-MePr') Et CHO O 4-FPh
666 CH2(2-MePr') Et C02H O 4-FPh
667 CH2(2-MePr') Et C02Me O 4-FPh
S:(Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200i04hsa-
ig/translationofPCTspecificationJ26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
32
668 CH2(2-MePr') Et C02Et O 4-FPh
669 CH2(2-MePr') Pr CHO O 4-FPh
670 CH2(2-MePr') Pr C02H O 4-FPh
671 CH2(2-MePr') Bu CHO O 4-FPh
672 CH2(2-MePr') Bu C02H O 4-FPh
673 CH2CH=CH2 Et CHO O 2,4-diFPh
674 CH2CH=CH2 Et C02H O 2,4-diFPh
675 CH2CH=CHCH3 Et CHO O 2,4-diFPh
676 CH2CH=CHCH3 Et C02H O 2,4-diFPh
677 CH2CH=CF2 Et CHO O 2,4-diFPh
678 CH2CH=CF2 Et C02H O 2,4-diFPh
679 CH2Pr' Et CHO O 2,4-diFPh
680 CH2Pr' Et C02H O 2,4-diFPh
681 CH2(2-MePr') Et CHO O 2,4-diFPh
682 CH2(2-MePr') Et C02H O 2,4-diFPh
683 CH2(2-MePr') Et C02Me O 2,4-diFPh
684 CH2(2-MePr') Et C02Et O 2,4-diFPh
685 CH2(2-MePr') Pr CHO O 2,4-diFPh
686 CH2(2-MePr') Pr C02H O 2,4-diFPh
687 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH24H O 4-MePh
688 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 4-CF3Ph
689 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH24H O 4-MeOPh
690 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 4-CHF20Ph
691 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 4-CF30Ph
692 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 4-BrPh
693 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 4-CF3Ph
694 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 4-CHF20Ph
695 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 4-CF30Ph
696 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 4-MePh
697 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 4-CF3Ph
698 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 4-MeOPh
699 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 4-CHF20Ph
S:/ChemicallSankyo/FP2001041FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
33
700 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 4-CF30Ph
701 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 4-BrPh
702 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 4-MePh
703 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 4-CF3Ph
704 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 4-MeOPh
705 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 4-CHF20Ph
706 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 4-CF30Ph
707 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 4-BrPh
708 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 4-MePh
709 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 4-CF3Ph
710 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 4-MeOPh
711 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 4-CHF20Ph
712 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 4-CF30Ph
713 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 4-BrPh
714 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 4-CF3Ph
715 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 4-CHF20Ph
716 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 4-CF30Ph
717 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 4-MePh
718 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 4-CF3Ph
719 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 4-MeOPh
720 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 4-CHF20Ph
721 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 4-CF30Ph
722 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 4-BrPh
723 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 4-MePh
724 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 4-CF3Ph
725 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 4-MeOPh
726 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 4-CHF20Ph
727 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 4-CF30Ph
728 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 4-BrPh
729 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp O 4-CF3Ph
730 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O 4-CF3Ph
731 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Me O 4-CF3Ph
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104IFP200104s.doc P83812IFP-2001041tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
34
732 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Et O 4-CF3Ph
733 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO O 4-CF3Ph
734 CH2CH=CH2 Me CO2H O 4-CF3Ph
735 CHZCH=CH2 Me COZMe O 4-CF3Ph
736 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Et O 4-CF3Ph
737 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp O 4-CF30Ph
738 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur O 4-CF30Ph
739 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Me O 4-CF30Ph
740 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Et O 4-CF30Ph
741 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO O 4-CF30Ph
742 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02H O 4-CF30Ph
743 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Me O 4-CF30Ph
744 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Et O 4-CF30Ph
745 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O 4-CF3Ph
746 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur O 4-CF3Ph
747 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me O 4-CF3Ph
748 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 4-CF3Ph
749 CH2Pr' Me CHO O 4-CF3Ph
750 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 4-CF3Ph
751 CH2Pr' Me C02Me O 4-CF3Ph
752 CH2Pr' Me C02Et O 4-CF3Ph
753 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp O 4-CF30Ph
754 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur O 4-CF30Ph
755 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me O 4-CF30Ph
756 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et O 4-CF30Ph
757 CH2Pr' Me CHO O 4-CF30Ph
758 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 4-CF30Ph
759 CH2Pr' Me C02Me O 4-CF30Ph
760 CH2Pr' Me C02Et O 4-CF30Ph
761 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 4-MePh
762 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 4-MePh
763 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 4-MePh
S:(Chemical/SankyoIFP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
764 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 4-MePh
765 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 4-MePh
766 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 4-MePh
767 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 4-CF3Ph
768 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 4-CF3Ph
769 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh O 4-CF3Ph
770 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 4-CF3Ph
771 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 4-CF3Ph
772 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O 4-CF3Ph
773 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 4-CF3Ph
774 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 4-CF3Ph
775 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O 4-CF3Ph
776 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O 4-CF3Ph
777 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Ph O 4-CF3Ph
778 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 4-MeOPh
779 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 4-MeOPh
780 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 4-MeOPh
781 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 4-MeOPh
782 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 4-MeOPh
783 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 4-MeOPh
784 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 4-CHF20Ph
785 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 4-CHF20Ph
786 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 4-CHF20Ph
787 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 4-CHF20Ph
788 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 4-CHF20Ph
789 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 4-CHF20Ph
790 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 4-CF30Ph
791 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 4-CF30Ph
792 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh O 4-CF30Ph
793 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 4-CF30Ph
794 CH2(2-MePr) Me CH20C02Et O 4-CF30Ph
795 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr O 4-CF30Ph
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
36
796 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 4-CF30Ph
797 CH2(2-MePr') Me COzH O 4-CF30Ph
798 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me O 4-CF30Ph
799 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et O 4-CF30Ph
800 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Ph O 4-CF30Ph
801 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp O 4-BrPh
802 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur O 4-BrPh
803 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me O 4-BrPh
804 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et O 4-BrPh
805 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO O 4-BrPh
806 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H O 4-BrPh
807 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H S Ph
808 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H NH Ph
809 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H S Ph
810 CH2Pr' Me CH20H S Ph
811 CH2Pr' Me CH20H NH Ph
812 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H S Ph
813 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H NH Ph
814 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H S 2-FPh
81 S CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H NH 2-FPh
816 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H S 2-FPh
817 CH2Pr' Me CH20H S 2-FPh
818 CH2Pr' Me CH20H NH 2-FPh
819 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H S 2-FPh
820 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H NH 2-FPh
821 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H S 4-FPh
822 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H S 4-FPh
823 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H NH 4-FPh
824 CH2C(CH3)=CH2 Me CH20H S 4-FPh
825 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H S 4-FPh
826 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H NH 4-FPh
827 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20H S 4-FPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/ua-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
37
828 CH2CH=CHC1 Me CH20H S 4-FPh
829 CH2CH=CCI2 Me CH20H S 4-FPh
830 Pr' Me CH20H S 4-FPh
831 2-MePr' Me CH20H S 4-FPh
832 CH2Pr' Me CH20H S 4-FPh
833 CH2Pr' Me CH20H NH 4-FPh
834 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H S 4-FPh
835 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H NH 4-FPh
836 CH2Bu' Me CH20H S 4-FPh
837 CH2Pn' Me CH20H S 4-FPh
838 CH2(2-MePn') Me CH20H S 4-FPh
839 CH2Hx' Me CH20H S 4-FPh
840 CH2(2-MeHx') Me CH20H S 4-FPh
841 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H S 2,4-diFPh
842 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H NH 2,4-diFPh
843 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H S 2,4-diFPh
844 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H NH 2,4-diFPh
845 CH2Pr' Me CH20H S 2,4-diFPh
846 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H S 2,4-diFPh
847 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H NH 2,4-diFPh
848 CH2Bu' Me CH20H S 2,4-diFPh
849 CH2Pn' Me CH20H S 2,4-diFPh
850 CH2Hx' Me CH20H S 2,4-diFPh
851 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H S 2-CIPh
852 CH2Pr' Me CH20H S 2-CIPh
853 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H S 2-CIPh
854 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H NH 2-CIPh
855 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H S 4-CIPh
856 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H S 4-CIPh
857 CH2Pr' Me CH20H S 4-CIPh
858 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H S 4-CIPh
859 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H NH 4-CIPh
S:/Chemi'al/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.do' P83812IFP-2001041tsa-ig/translation
of PCT spe'ification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
38
860 CH2CH=CHZ Me CHZOH S 2,4-diClPh
861 CHzPr' Me CHzOH S 2,4-diClPh
862 CHz(2-MePr') Me CHzOH S 2,4-diCIPh
863 CH2CH=CHZ Me CHZOAc S Ph
864 CHZCH=CHz Me CHZOAc NH Ph
865 CHZCH=CHCH3 Me CHZOAc S Ph
866 CH2Pr' Me CHzOAc S Ph
867 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHZOAc S Ph
868 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac NH Ph
869 CHZCH=CHZ Me CH20Ac S 2-FPh
870 CH2CH=CHZ Me CH20Ac NH 2-FPh
871 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHZOAc S 2-FPh
872 CHZPr' Me CHzOAc S 2-FPh
873 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHZOAc S 2-FPh
874 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHZOAc NH 2-FPh
875 CH=CHZ Me CHzOAc S 4-FPh
876 CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac S 4-FPh
877 CHZCH=CHZ Me CH20Ac S 4-FPh
878 CH2CH=CHz Me CHZOAc NH 4-FPh
879 CHzC(CH3)=CHz Me CHZOAc S 4-FPh
880 CHZCH=CHCH3 Me CHZOAc S 4-FPh
881 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHzOAc NH 4-FPh
882 CHZCH=CF2 Me CHZOAc S 4-FPh
883 CH2CH=CHCI Me CHZOAc S 4-FPh
884 CHZCH=CCIz Me CHzOAc S 4-FPh
885 Pr' Me CH20Ac S 4-FPh
886 2-MePr' Me CHzOAc S 4-FPh
887 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac S 4-FPh
888 CH2Pr' Me CHZOAc NH 4-FPh
889 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac S 4-FPh
890 CHZ(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac NH 4-FPh
891 CHZBu' Me CH20Ac S 4-FPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200t04/tsa-igJtranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
39
892 CH2Pn' Me CH20Ac S 4-FPh
893 CH2(2-MePn') Me CH20Ac S 4-FPh
894 CH2Hx' Me CH20Ac S 4-FPh
895 CH2(2-MeHx') Me CH20Ac S 4-FPh
896 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac S 2,4-diFPh
897 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac NH 2,4-diFPh
898 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac S 2,4-diFPh
899 CH2CH=CF2 Me CH20Ac S 2,4-diFPh
900 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac S 2,4-diFPh
901 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac S 2,4-diFPh
902 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac NH 2,4-diFPh
903 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac S 2-CIPh
904 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac NH 2-CIPh
905 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac S 2-CIPh
906 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac S 2-CIPh
907 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac S 2-CIPh
908 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac NH 2-CIPh
909 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac S 4-CIPh
910 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac NH 4-CIPh
911 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac S 4-CIPh
912 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac S 4-CIPh
913 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac S 4-CIPh
914 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac NH 4-CIPh
915 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac S 2,4-diClPh
916 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac S 2,4-diClPh
917 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac S 2,4-diCiPh
918 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp S Ph
919 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp S Ph
920 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp S Ph
921 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp NH Ph
922 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp S 2-FPh
923 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp S 2-FPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
924 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp S 2-FPh
925 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHZOPrp NH 2-FPh
926 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp S 4-FPh
927 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHZOPrp NH 4-FPh
928 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp S 4-FPh
929 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp S 4-FPh
930 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp S 4-FPh
931 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp NH 4-FPh
932 CH2Bu' Me CH20Prp S 4-FPh
933 CH2Pn' Me CH20Prp S 4-FPh
934 CH2Hx' Me CH20Prp S 4-FPh
935 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp S 2,4-diFPh
936 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp NH 2,4-diFPh
937 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Prp S 2,4-diFPh
938 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp S 2,4-diFPh
939 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp S 2,4-diFPh
940 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp NH 2,4-diFPh
941 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp S 2-CIPh
942 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp S 2-CIPh
943 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp S 2-CIPh
944 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp NH 2-CIPh
945 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp S 4-CIPh
946 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp S 4-CIPh
947 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp S 4-CIPh
948 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp NH 4-CIPh
949 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Prp S 2,4-diClPh
950 CH2Pr' Me CH20Prp S 2,4-diClPh
951 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Prp S 2,4-diClPh
952 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur S Ph
953 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur S 2-FPh
954 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur S 2-FPh
955 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur S 2-FPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specificationl26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
41
956 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur S 4-FPh
957 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur NH 4-FPh
958 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Bur S 4-FPh
959 Pr' Me CH20Bur S 4-FPh
960 2-MePr' Me CH20Bur S 4-FPh
961 CH2Pr' Me CH24Bur S 4-FPh
962 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur S 4-FPh
963 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur NH 4-FPh
964 CH2Bu' Me CH20Bur S 4-FPh
965 CH2Pn' Me CH20Bur S 4-FPh
966 CH2Hx' Me CH20Bur S 4-FPh
967 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur S 2,4-diFPh
968 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur NH 2,4-diFPh
969 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur S 2,4-diFPh
970 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur S 2,4-diFPh
971 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur NH 2,4-diFPh
972 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur S 2-CIPh
973 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur S 2-CIPh
974 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur S 2-CIPh
975 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur NH 2-CIPh
976 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur S 4-CIPh
977 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur S 4-CIPh
978 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur S 4-CIPh
979 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur NH 4-CIPh
980 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Bur S 2,4-diCIPh
981 CH2Pr' Me CH20Bur S 2,4-diClPh
982 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur S 2,4-diClPh
983 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Bur NH 2,4-diClPh
984 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh S Ph
985 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20COPh S 2-FPh
986 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh S 2-FPh
987 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20COPh S 4-FPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/ua-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
42
988 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHzOCOPh S 4-FPh
989 CH2Pr' Me CH20COPh S 4-FPh
990 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh S 4-FPh
991 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh NH 4-FPh
992 CH2CH=CHz Me CH20COPh S 2,4-diFPh
993 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20COPh S 2,4-diFPh
994 CH2Pr' Me CH20COPh S 2,4-diFPh
995 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh S 2,4-diFPh
996 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh NH 2,4-diFPh
997 CH2CH=CHz Me CH20COPh S 2-CIPh
998 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh S 2-CIPh
999 CH2CH=CHz Me CH20COPh S 4-CIPh
1000 CH2Pr' Me CH20COPh S 4-CIPh
1001 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh S 4-CIPh
1002 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh NH 4-CIPh
1003 CH2CH=CHz Me CH20COPh S 2,4-diClPh
1004 CH2Pr' Me CH20COPh S 2,4-diClPh
1005 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh S 2,4-diClPh
1006 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20COPh NH 2,4-diClPh
1007 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me S Ph
1008 CH2CH=CHz Me CH20C02Me S 2-FPh
1009 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me S 2-FPh
1010 CH2CH=CHz Me CH20C02Me S 4-FPh
1011 CH2CH=CHz Me CH20C02Me NH 4-FPh
1012 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Me S 4-FPh
1013 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me S 4-FPh
1014 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me S 4-FPh
1015 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me NH 4-FPh
1016 CH2CH=CHz Me CH20C02Me S 2,4-diFPh
1017 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me S 2,4-diFPh
1018 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me S 2,4-diFPh
1019 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me NH 2,4-diFPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-2001041tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
43
1020 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Me S 2-CIPh
1021 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me S 2-CIPh
1022 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Me S 4-CIPh
1023 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me S 4-CIPh
1024 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me S 4-CIPh
1025 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me NH 4-CIPh
1026 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Me S 2,4-diClPh
1027 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Me S 2,4-diClPh
1028 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me S 2,4-diClPh
1029 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Me NH 2,4-diClPh
1030 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et S Ph
1031 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Et S 2-FPh
1032 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et S 2-FPh
1033 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20CO2Et S 4-FPh
1034 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Et NH 4-FPh
1035 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20C02Et S 4-FPh
1036 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et S 4-FPh
1037 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et S 4-FPh
1038 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et NH 4-FPh
1039 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Et S 2,4-diFPh
1040 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et S 2,4-diFPh
1041 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et S 2,4-diFPh
1042 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et NH 2,4-diFPh
1043 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Et S 2-CIPh
1044 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et S 2-CiPh
1045 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Et S 4-CIPh
1046 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et S 4-CIPh
1047 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et S 4-CIPh
1048 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et NH 4-CIPh
1049 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Et S 2,4-diClPh
1050 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Et S 2,4-diClPh
1051 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et S 2,4-diClPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igJtranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
44
1052 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Et NH 2,4-diClPh
1053 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr S Ph
1054 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr S 2-FPh
1055 CHzCH=CH2 Me CH20C02Pr S 4-FPh
1056 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Pr S 4-FPh
1057 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr S 4-FPh
1058 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr NH 4-FPh
1059 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Pr S 2,4-diFPh
1060 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr S 2,4-diFPh
1061 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr NH 2,4-diFPh
1062 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr S 2-CIPh
1063 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Pr S 4-CIPh
1064 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr S 4-CIPh
1065 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Pr S 2,4-diClPh
1066 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr S 2,4-diClPh
1067 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Pr NH 2,4-diClPh
1068 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu S Ph
1069 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu S 2-FPh
1070 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Bu S 4-FPh
1071 CH2Pr' Me CH20C02Bu S 4-FPh
1072 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu S 4-FPh
1073 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu NH 4-FPh
1074 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Bu S 2,4-diFPh
1075 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu S 2,4-diFPh
1076 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu NH 2,4-diFPh
1077 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu S 2-CIPh
1078 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Bu S 4-CIPh
1079 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu S 4-CIPh
1080 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20C02Bu S 2,4-diClPh
1081 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu S 2,4-diClPh
1082 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20C02Bu NH 2,4-diClPh
1083 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO S Ph
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P838121FP-200104hsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
1084 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO S 2-FPh
1085 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO S 2-FPh
1086 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO S 4-FPh
1087 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO NH 4-FPh
1088 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO S 4-FPh
1089 CH2Pr' Me CHO S 4-FPh
1090 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO S 4-FPh
1091 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO NH 4-FPh
1092 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO S 2,4-diFPh
1093 CH2Pr' Me CHO S 2,4-diFPh
1094 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO S 2,4-diFPh
1095 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO NH 2,4-diFPh
1096 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO S 2-CIPh
1097 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO S 2-CIPh
1098 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO S 4-CIPh
1099 CH2Pr' Me CHO S 4-CIPh
1100 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO S 4-CIPh
1101 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO NH 4-CIPh
1102 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO S 2,4-diClPh
1103 CH2Pr' Me CHO S 2,4-diCIPh
1104 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO S 2,4-diClPh
1105 CH2(2-MePr') Me CHO NH 2,4-diClPh
1106 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H S Ph
1107 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02H S 2-FPh
1108 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H S 2-FPh
1109 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02H S 4-FPh
1110 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02H NH 4-FPh
1111 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H S 4-FPh
1112 CH2Pr' Me C02H S 4-FPh
1113 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H S 4-FPh
1114 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H NH 4-FPh
1115 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02H S 2,4-diFPh
S:IChemi'aVSankyo/FP200t04/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-
ig/translationofPCTspecifi'adon/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
46
1116 CH2Pr' Me C02H S 2,4-diFPh
1117 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H S 2,4-diFPh
1118 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H NH 2,4-diFPh
1119 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02H S 2-CIPh
1120 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H S 2-CIPh
1121 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02H S 4-CIPh
1122 CH2Pr' Me C02H S 4-CIPh
1123 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H S 4-CIPh
1124 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H NH 4-CIPh
1125 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02H S 2,4-diClPh
1126 CH2Pr' Me C02H S 2,4-diClPh
1127 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H S 2,4-diClPh
1128 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02H NH 2,4-diClPh
1129 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me S Ph
1130 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me S 2-FPh
1131 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Me S 4-FPh
1132 CH2Pr' Me C02Me S 4-FPh
1133 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me S 4-FPh
1134 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me NH 4-FPh
1135 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Me S 2,4-diFPh
1136 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me S 2,4-diFPh
1137 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me NH 2,4-diFPh
1138 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me S 2-CIPh
1139 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Me S 4-CIPh
1140 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me S 4-CIPh
1141 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Me S 2,4-diClPh
1142 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me S 2,4-diClPh
1143 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Me NH 2,4-diClPh
1144 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et S Ph
1145 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et S 2-FPh
1146 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Et S 4-FPh
1147 CH2Pr' Me C02Et S 4-FPh
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812IFP-2001041tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specificationl26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
47
1148 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et S 4-FPh
1149 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et NH 4-FPh
1150 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Et S 2,4-diFPh
11 S CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et S 2,4-diFPh
1
1152 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et NH 2,4-diFPh
1153 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et S 2-CIPh
1154 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Et S 4-CIPh
11 SS CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et S 4-CIPh
1156 CH2CH=CH2 Me C02Et S 2,4-diClPh
1157 CH2(2-MePr'} Me C02Et S 2,4-diCIPh
1158 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Et NH 2,4-diClPh
1159 CH2(2-MePr) Me C02Pr S 4-FPh
1160 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Bu S 4-FPh
1161 CH2(2-MePr') Me C02Ph S 4-FPh2
1162 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 2,6-diFPh
1163 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 2,6-diFPh
1164 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 2,6-diFPh
1165 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 2,6-diFPh
1166 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20H O 2,6-diClPh
1167 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20H O 2,6-diClPh
1168 CH2Pr' Me CH20H O 2,6-diClPh
1169 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H O 2,6-diCIPh
1170 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 2,6-diFPh
1171 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2,6-diFPh
1172 CH2Pre Me CH20Ac O 2,6-diFPh
1173 CH2(2-MePr) Me CH20Ac O 2,6-diFPh
1174 CH2CH=CH2 Me CH20Ac O 2,6-diClPh
1175 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CH20Ac O 2,6-diClPh
1176 CH2Pr' Me CH20Ac O 2,6-diClPh
1177 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20Ac O 2,6-diClPh
1178 CH2CH=CH2 Me CHO O 2,6-diFPh
1179 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 2,6-diFPh
S:/ChemicallSankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
48
1180 CH2Pr' Me CHO 0 2,6-diFPh
1181 CHz(2-MePr') Me CHO O 2,6-diFPh
1182 CH2CH=CHz Me CHO O 2,6-diClPh
1183 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me CHO O 2,6-diClPh
1184 CH2Pr' Me CHO O 2,6-diClPh
1185 CHz(2-MePr') Me CHO O 2,6-diClPh
1186 CH2CH=CHz Me C02H O 2,6-diFPh
1187 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O 2,6-diFPh
1188 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 2,6-diFPh
1189 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02H O 2,6-diFPh
1190 CH2CH=CHz Me C02H O 2,6-diClPh
1191 CH2CH=CHCH3 Me C02H O 2,6-diCiPh
1192 CH2Pr' Me C02H O 2,6-diCIPh
1193 CHz(2-MePr') Me C02H O 2,6-diClPh
1194 CH2CH=CHz Et CH20H O 2,6-diFPh
1195 CH2CH=CHCH3 Et CH20H O 2,6-diFPh
1196 CH2Pr' Et CH20H O 2,6-diFPh
1197 CHz(2-MePr') Et CH20H O 2,6-diFPh
1198 CH2CH=CHz Et CH20H O 2,6-diClPh
1199 CH2CH=CHCH3 Et CH20H O 2,6-diClPh
1200 CH2Pr' Et CH20H O 2,6-diClPh
1201 CH2(2-MePr') Et CH20H O 2,6-diClPh
1202 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20H S 2,6-diFPh
1203 CH2(2-MePr') Me CH20H NH 2,6-diFPh
1204 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20H S 2,6-diClPh
1205 CHz(2-MePr') Me CH20H NH 2,6-diCIPh
Throughout the table 1 the following abbreviations are used with the following
meanings.
Exemp. Comp. No. : Exemplification compound number,
Ac : acetyl, Bu : butyl, Bu' : cyclobutyl, Bur : butyryl,
Et : ethyl, Hx' : cyclohexyl, Me : methyl, Pn' : cyclopentyl
Ph : phenyl, Pr : propyl, Prp : propionyl, Pr' : cyclopropyl.
S:/Chemical/Sankyo1FP200104/FP200t04s.do' P83812/FP-200104/ua-ig/iranslation
of PCT specificationl26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
49
In Table 1, preferred compounds are the compounds of Exemplification
Compound numbers 2, 4, 8, 9, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30,
31, 32,
33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51,
56, 59, 61, 62,
63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 82, 90, 93, 95, 105, 106, 114,
116, 120, 121,
129, 132, 134, 138, 140, 142, 144, 146, 167, 178, 188, 192, 196, 200, 216,
225, 233,
237, 241, 245, 264, 277, 286, 290, 294, 298, 306, 307, 310, 311, 317, 323,
326, 329,
332, 345, 351, 357, 360, 363, 366, 373, 377, 381, 383, 385, 387, 394, 411,
414, 415,
416, 417, 418, 419, 420, 421, 422, 423, 424, 425, 426, 427, 430, 433, 436,
439, 442,
449, 450, 451, 452, 453, 454, 455, 456, 457, 458, 461, 467, 470, 473, 476,
478, 480,
481, 482, 483, 484, 485, 486, 487, 488, 492, 494, 496, 498, 503, 504, 505,
506, 507,
508, 512, 514, 516, 518, 539, 542, 548, 558, 562, 564, 566, 583, 585, 589,
592, 594,
595, 596, 597, 598, 600, 602, 604, 606, 607, 608, 625, 626, 627, 633, 634,
665, 666,
667, 668, 669, 670, 671, 672, 675, 676, 681, 682, 683, 684, 685, 686, 702,
703, 704,
705, 706, 707, 723, 724, 725, 726, 727, 728, 834, 846, 858, 862, 889, 901,
930, 939,
990, 1014, 1018, 1072, 1090, 1094, 1113, 1117, 1133, 1136, 1148, 1149, 1159,
1163,
1164, 1165, 1167, 1169, 1171, 1173, 1175, 1177, 1181, 1185, 1189 and 1193.
More preferred compounds are the compounds of Exemplification Compound
numbers 9, 19, 20, 22, 25, 32, 33, 40, 41, 43, 47, 48, 59, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65,
66, 67, 68,
69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 82, 93, 95, 105, 106, 114, 116, 120, 121, 134, 138, 142,
146, 167,
178, 311, 317, 416, 417, 420, 421, 427, 436, 439, 442, 450, 451, 454, 455,
461, 485,
506, 508, 589, 592, 594, 595, 596, 602, 606, 625, 633, 665, 666, 681, 682,
834, 846,
889, 1090, 1113, 1133, 1163, 1164, 1165, 1167, 1169, 1171, 1173, 1175 and
1177.
Futher more preferred compounds are the compounds of Exemplification
Compound numbers 9, 20, 22, 32, 33, 41, 43, 47, 48, 61, 63, 65, 69, 71, 73,
95, 106,
121, 421, 427, 455, 589, 594, 602, 606, 625, 1165 and 1169.
Still more preferred compounds are the compounds of Exemplification Compound
numbers 22, 33, 43, 48, 106, 121, 421, 455 and 594.
Most preferred compounds are the compounds of:
Exemplification compound number 22 : 1-(2-butenyl)-7-(4-fluorobenzyloxy)-3-
hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine,
Exemplification compound number 33 : 7-(4-fluorobenzyloxy)-3-hydroxymethyl-2-
methyl-1-(2-methylcyclopropylmethyl)pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyridazine,
Exemplification compound number 43 : 1-(2-butenyl)-7-(2,4-difluorobenzyloxy)-3-
hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine,
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification126.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
Exemplification compound number 48 : 7-(2,4-difluorobenzyloxy)-3-hydroxymethyl-
2-methyl-1-(2-methylcyclopropylmethyl)p yrrolo [2,3-d]pyridazine,
Exemplification compound number 106 : 3-acetoxymethyl-7-(4-fluorobenzyloxy)-2-
methyl-1-(2-methylcyclopropylmethyl)pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine, and
Exemplification compound number 121 : 3-acetoxymethyl-7-(2,4-
difluorobenzyloxy)-
2-methyl-1-(2-methylcyclopropylinethyl)pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine.
In addition, of the compounds described above, 1-[(1S,2S)-2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl] derivatives are preferred compounds.
The pyrrolopyridazine compounds of formula (I) can be prepared according to
the
following method.
ni Rz
m Rz
R4CH2-A Step 1
R CHz A
(II) (Ia)
Dl Rz
Step 2 R4CHz-A
Step 3 R4CHz-A CpzH
(Ic)
In the above reaction scheme Rl, R2, R4 and A have the same meanings as
described above.
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104IFP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PC'f specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
51
The step 1 is a process preparing a compound of formula (Ia) and is
accomplished
by reaction of a compound of formula (II) with an oxidizing agent in an inert
solvent.
The oxidizing agent employed is, for example, an oxidizing agent by which a
methyl group can be converted into a hydroxymethyl group, such as ammonium
cerium (N) nitrate, manganese (III) acetate or selenium dioxide; preferably
ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate. The amount of the oxidizing agent is from 1.5 to
10
(preferably 2 to 6) moles to one mole of the compound of formula (II).
The employed inert solvent is not particularly limited provided that it has no
adverse effect on the reaction and can dissolve the starting materials to a
certain
extent. Such a solvent is, for example, a halogeno-hydrocarbon such as
methylene
chloride, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, dichloroethane, chlorobenzene, or
dichlorobenzene; an ether such as diethyl ether, diisopropyl ether,
tetrahydrofuran,
dioxane, dimethoxyethane, or diethylene glycol dimethyl ether; a carboxylic
acid or a
carboxylic acid anhydride such as acetic acid, acetic anhydride, propionic
acid, or
benzoic acid; water; or mixtures thereof; and is preferably a carboxylic acid,
a
carboxylic acid anhydride, a carboxylic acid containing water or a mixture of
a
carboxylic acid and a carboxylic acid anhydride; and is more preferably acetic
acid,
acetic anhydride, acetic acid containing water or a mixture of acetic acid and
acetic
anhydride.
The reaction temperature is usually from 0°C to 150°C
(preferably from room
temperature to 100°C). The reaction time varies depending on the
reaction
temperature and other factors but it is from 30 minutes to 20 hours
(preferably from 1
hour to 10 hours).
When a carboxylic acid or a carboxylic acid anhydride is used as the inert
solvent
in the step 1, in certain cases a product esterified at the hydroxymethyl
group of
compound (Ia) by the carboxylic acid can be obtained. The esterified compound
is
hydrolyzed according to a conventional method to give the compound of formula
(Ia).
For example the esterified compound is treated with a base (for example an
alkali
metal hydroxide such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, or potassium
hydroxide; or an alkali metal carbonate such as sodium carbonate, potassium
carbonate; preferably an alkali metal hydroxide and most preferably lithium
hydroxide) at from 0°C to 100°C (preferably from 10°C to
50°C) for from 10 minutes
to 10 hours (preferably from 20 minutes to S hours) in an inert solvent
containing
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104hsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
52
water (for example, an alcohol containing water such as methanol containing
water or
ethanol containing water) to give a compound of formula (Ia).
A compound of formula (Id), which is a compound of formula (I) wherein R3 is a
C2-C6 aliphatic acyloxymethyl group, a C6-Clo arylcarbonyloxymethyl group
which
may be optionally substituted with substituents selected from the group
consisting of
C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy and halogeno, or a C1-C6 alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl
group,
can be prepared by acylation of a compound of formula (Ia).
m R2
R4CH2-A OR5
(Id)
In the formula of (Id), RS represents a C2-C6 aliphatic acyl group, a C6-Clo
arylcarbonyl group which may be optionally substituted with substituents
selected
from the group consisting of C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy and halogeno, or a C1-
C6
alkoxycarbonyl group, and Rl, R2, R4 and A have the same meanings as described
above.
The acylating reagent is, for example, a C2-C6 aliphatic acyl halide such as
acetyl
chloride, acetyl bromide, propionyl chloride, propionyl bromide, butyryl
chloride,
isobutyryl chloride, valeryl chloride, or hexanoyl chloride; a C2-C6 aliphatic
carboxylic acid anhydride such as acetic anhydride, propionic anhydride, or
hexanoic
anhydride; a C6-Clo arylcarbonyl halide which may be optionally substituted
with
substituents selected from the group consisting of C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy
and
halogeno, such as benzoyl chloride, benzoyl bromide, toluoyl chloride, toluoyl
bromide, methoxybenzoyl chloride, chlorobenzoyl chloride, fluorobenzoyl
chloride,
or naphthoyl chloride; or a C1-C6 alkoxycarbonyl halide such as
methoxycarbonyl
chloride, ethoxycarbonyl chloride, ethoxycarbonyl bromide, propoxycarbonyl
chloride, butoxycarbonyl chloride, pentyloxycarbonyl chloride, or
hexyloxycarbonyl
chloride; preferably a C2-C6 aliphatic acyl chloride, a C6-Clo arylcarbonyl
chloride
which may be optionally substituted with substituents selected from the group
S:(Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PC'T specification126.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
53
consisting of Cl-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy and halogeno or a Cl-C6 alkoxycarbonyl
chloride.
The employed base is, for example, an alkali metal amide such as lithium
amide,
sodium amide, or potassium amide; an alkali metal carbonate such as lithium
carbonate, sodium carbonate, or potassium carbonate; an alkali metal alkoxide
such as
lithium methoxide, sodium methoxide, sodium ethoxide, or potassium t-butoxide;
or
an organic amine such as triethylamine, tributylamine, diisopropylethylamine,
N-
ethylmorpholine, pyridine, picoline, 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)pyridine, quinoline,
N,N-
dimethylaniline, N,N-diethylaniline, 1,5-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene (DBN),
1,4-
diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (DABCO), or 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene
(DBLn;
preferably an organic amine and most preferably triethylamine or pyridine.
The employed inert solvent is not particularly limited provided that it has no
adverse effect on the reaction and can dissolve the starting materials to a
certain
extent. Such a solvent is, for example, an aromatic hydrocarbon such as
benzene,
toluene, or xylene; a halogeno-hydrocarbon such as methylene chloride,
chlorofonm,
carbon tetrachloride, dichloroethane, chlorobenzene, or dichlorobenzene; an
ether
such as diethyl ether, diisopropyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane,
dimethoxyethane, or
diethylene glycol dimethyl ether; or mixtures thereof; and is preferably a
halogeno-
hydrocarbon or an ether ; and is more preferably methylene chloride,
chloroform,
diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran.
The reaction temperature is usually from 0°C to 100°C
(preferably from 10°C to
50°C). The reaction time varies depending on the reaction temperature
and other
factors but it is from 10 minutes to 100 hours (preferably from 30 minutes to
5 hours).
The step 2 is a process for preparing a compound of formula (Ib) and is
accomplished by reaction of a compound of formula (Ia) with an oxidizing agent
in an
inert solvent.
The employed oxidizing agent is, for example, an oxidizing agent by which a
hydroxymethyl group can be converted into a formyl group, such as manganese
dioxide, pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), pyridinium dichromate (PDC), or a
mixture of dimethyl sulfoxide and an acid anhydride (for example an aliphatic
carboxylic acid anhydride which may be optionally substituted with halogeno,
such as
acetic anhydride, trifluoroacetic anhydride, or propionic anhydride;
preferably acetic
anhydride or trifluoroacetic anhydride); preferably manganese dioxide. The
amount
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812IFP-200104/ua-ig/translation
of PCT specification126.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
54
of the oxidizing agent is usually from 1 to 50 (preferably 2 to 30) moles to
one mole
of the compound of formula (Ia).
The employed inert solvent is not particularly limited provided that it has no
adverse effect on the reaction and can dissolve the starting materials to a
certain
extent. Such a solvent is, for example, an aromatic hydrocarbon such as
benzene,
toluene, or xylene; a halogeno-hydrocarbon such as methylene chloride,
chloroform,
carbon tetrachloride, dichloroethane, chlorobenzene, or dichlorobenzene; an
ether
such as diethyl ether, diisopropyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane,
dimethoxyethane, or
diethylene glycol dimethyl ether; or mixtures thereof; and is preferably a
halogeno-
hydrocarbon; and is most preferably methylene chloride.
The reaction temperature is usually from 0°C to 150°C
(preferably from room
temperature to 100°C). The reaction time varies depending on the
reaction
temperature and other factors but it is from 30 minutes to 40 hours
(preferably from 1
hour to 20 hours).
The step 3 is a process preparing a compound of formula (Ic) and is
accomplished
by reaction of a compound of formula (Ib) with an oxidizing agent in an inert
solvent.
The employed oxidizing agent is, for example, an oxidizing agent by which a
formyl group can be converted into a carboxyl group, such as silver oxide,
pyridinium
chlorochromate (PCC), or pyridinium dichromate (PDC); preferably silver oxide.
The
amount of the oxidizing agent is usually from 1 to 20 (preferably 2 to 10)
moles to
one mole of the compound of formula (Ib). When silver oxide is used as an
oxidizing
agent, silver oxide prepared by reaction of silver nitrate with an alkali
metal
hydroxide (preferably sodium hydroxide) is preferably used.
The employed inert solvent is not particularly limited provided that it has no
adverse effect on the reaction and can dissolve the starting materials to a
certain
extent. Such a solvent is, for example, a halogeno-hydrocarbon such as
methylene
chloride, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, dichloroethane, chlorobenzene, or
dichlorobenzene; an ether such as diethyl ether, diisopropyl ether,
tetrahydrofuran,
dioxane, dimethoxyethane, or diethylene glycol dimethyl ether; an alcohol such
as
methanol, or ethanol; a carboxylic acid such as acetic acid, propionic acid,
or benzoic
acid; water; or mixtures thereof; and is preferably an alcohol, an alchohol
containing
water, a carboxylic acid, a carboxylic acid containing water or water; and is
more
preferably an alcohol containing water; and is most preferably ethanol
containing
water.
S:/ChemicallSankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P838121FP-200104/ua-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
The reaction temperature is usually from 0°C to 150°C
(preferably from room
temperature to 100°C). The reaction time varies depending on the
reaction
temperature and other factors but it is from 1 hour to 72 hours (preferably
from 12
hours to 48 hours).
A compound of formula (Ie), which is a compound of formula (I) wherein R3 is a
C1-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group or a C6-C1o aryloxycarbonyl group which may be
optionally substituted with substituents selected from the group consisting of
C~-C6
alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy and halogeno, can be prepared by esterification of a
compound of
formula (Ic).
R1\ R2
N
R4CH2-A CO Rs
2
N~ N
(Ie)
In the formula (Ie), R6 represents a C1-C6 alkyl group, or a C6-Clo aryl group
which
may be optionally substituted with substituents selected from the group
consisting of
C1-C6 alkyl, C~-C6 alkoxy and halogeno and R', R2, R4 and A have the same
meanings
as described above.
The esterification is accomplished by reaction of a compound of formula (Ic)
with
a halogenating agent in an inert solvent to afford a carboxylic acid halide,
followed by
reaction of the carboxylic acid halide with an alcohol or a phenol derivative
in the
presence of a base in an inert solvent. The two step reactions can be carned
out in a
single reaction vessel, wherein the compound of formula (Ic) is reacted with a
halogenating agent and, if necessary, the solvent can be removed from the
reaction
mixture.
The halogenating agent employed is, for example, a thionyl halide such as
thionyl
chloride, thionyl bromide or a phosphorus halide such as phosphorus
trichloride,
phosphorus pentachloride, phosphorus oxychloride, or phosphorus oxybromide;
preferably thionyl chloride or phosphorus oxychloride.
The inert solvent employed in the reaction of the compound of formula (Ic)
with a
halogenating agent is not particularly limited provided that it has no adverse
effect on
S:(Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
56
the reaction and can dissolve the starting materials to a certain extent. Such
a solvent
is, for example, an aromatic hydrocarbon such as benzene, toluene, or xylene;
a
halogeno-hydrocarbon such as methylene chloride, chloroform, carbon
tetrachloride,
dichloroethane, chlorobenzene, or dichlorobenzene; an ether such as ether,
diisopropyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, dimethoxyethane, or diethylene
glycol
dimethyl ether; or mixtures thereof; and is preferably an ether; and is most
preferably
diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran.
The reaction temperature is usually from 0°C to 100°C
(preferably 10°C to 50°C).
The reaction time varies depending on the reaction temperature and other
factors but it
is from 10 minutes to 10 hours (preferably from 30 minutes to 5 hours).
The inert solvent employed in the reaction of the carboxylic acid halide with
an
alcohol or a phenol derivative is the same solovent as described in the
reaction of the
compound of formula (Ic) with a halogenating agent. The reaction temperature
and
the time required for the reaction are in the same range as described in the
reaction of
the compound of formula (Ic) with a halogenating agent.
In each step described above each desired compound may be isolated by
conventional procedures from the reaction mixture. For example, it may be
obtained
1) by filtration of the reaction mixture when insoluble material exists in the
reaction
mixture, followed by evaporation of the solvent of the filtrate; or by 1 )
concentration
of the reaction mixture, 2) addition of water to the residue followed by
partition
between water and an appropriate organic solvent immiscible with water, 3)
drying
the extract over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and the like, followed by 4)
concentration of the extract. The desired compound can be, if necessary, be
further
purified by conventional procedures such as recrystallization, column
chromatography
and the like.
A compound of formula (1) can be transformed into a pharmaceutically
acceptable
salt thereof by treatment of the compound of formula (I) with an acid
according to a
conventional technique. For example the desired salt can be obtained by
reaction of a
compound of formula (I) with an acid in an inert solvent (preferably an ether
such as
ether, tetrahydrofran, or dioxane; an alcohol such as methanol, ethanol, or
propanol;
or a halogeno-hydrocarbon such as methylene chloride, or chloroform) at room
temperature for from S minutes to 1 hour, followed by evaporation of the
solvent.
The starting compound of formula (II) is known or can easily be prepared by
the
reaction of a pyrrole compound of formula (III) with a compound of formula Rl-
X
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200t04/tsa-igltranslation
ofl'CT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
57
(IV) according to a known method (for example Japanese Patent Application
Publication Hei 7-247285);
H
R70zC N R2
OHC CH3
wherein R7 represents a Cl-C6 alkyl group, R2 has the same meanings as
described
above, X represents a halogen atom (preferably a chlorine or bromine atom),
and Rl
has the same meanings as described above.
The compounds of formula (III) and (IV) are also known or can easily be
obtained
by a known procedure (for example Japanese Patent Application Publication Hei
7-
247825; Monatschefte fur Chemie (1973), 104, 925; J. Chem. Soc.,
Perkin.Trans.II
(1979) 287 and the like).
In addition each desired optically active compound of formula (I) and (IV)
(for
example 1 S,2S-form) can be obtained by optical resolution of a racemic form
of the
corresponding compound (a mixture of 1 S,2S-form and 1 R,2R-form and the
like).
The optical resolution can be carried out by an appropriate selection from
conventional techniques such as chromatography on a column for optical
resolution,
preferential crystallization, and resolution of a mixture of diastereomeric
salts.
[Possibility of industrial use]
The compounds of formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof of
this
invention exhibit potent gastric acid secretion inhibition activity, gastric
mucous
membrane protection activity and potent antibacterial activity against
Helicobacter
pylori and they have excellent properties as a medicament. The compounds of
formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof are useful as a
prophylactic or
therapeutic medicament for ulcerative diseases such as peptic ulcer, acute or
chronic
gastric ulcer, gastrisis, reflux esophagitis, gastroesophageal reflux
disorder, dyspepsia,
gastric hyperacidity, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome etc. or a prophylactic or
therapeutic
medicament for bacterial infections arising from Helicobacter pylori.
When used as a prophylactic or therapeutic medicament for the diseases
described
above, a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof
(the
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
58
active ingredient) can be administered alone or can be presented as part of a
pharmaceutical formulation. The pharmaceutical formulation is prepared by
blending
the active ingredient with appropriate pharmaceutically acceptable excipients,
diluents
and the like, followed by formulation in the form of tablets, capsules,
granules,
powders or syrups and the like for oral administration or in the form of
injections and
the like for parenteral administration (preferably oral administration).
The production of such pharmaceutical formulations is carried out according to
general techniques known to those skilled in the art using additives such as
an
excipient, a binder, a disintegrant, a lubricant, a stabilizer, a corrigent, a
diluent and a
solvent for injections.
The excipient is, for example, a sugar derivative such as lactose, sucrose,
glucose,
mannitol, or sorbitol; a starch derivative such as corn starch, potato starch,
a-starch,
dextrin, or carboxymethyl starch; a cellulose derivative such as crystalline
cellulose,
low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose,
carboxymethyl cellulose, calcium carboxymethyl cellulose, or internally
bridged
sodium carboxymethyl cellulose; acacia; dextran; pullulan; a silicate
derivative such
as light silicic acid anhydride, synthetic aluminium silicate, or magnesium
aluminate
meta-silicate; a phosphonate derivative such as calcium phosphonate; a
carbonate
derivative such as calcium carbonate; a sulfate derivative such as calcium
sulfate; and
the like.
The binder is, for example, one of the excipients described above; gelatin;
polyvinylpyrrolidone; macrogol (trade mark) and the like.
The disintegrant is, for example, one of the excipients described above, a
chemically modified starch, cellulose derivative such as sodium
croscarmellose,
sodium carboxymethyl starch, bridged polyvinylpyrrolidone and the like.
The lubricant is, for example, talc; stearic acid; a metal salt of stearic
acid such as
calcium stearate, or magnesium stearate; colloidal silica; a wax such as bee
gum and
spermaceti; boric acid; glycol; a carboxylic acid such as fumaric acid, or
adipic acid; a
sodium carboxylate such as sodium benzoate; a sulfate such as sodium sulfate;
leucine; a laurylsulfate such as sodium laurylsulfate, or magnesium
laurylsulfate; a
silicic acid such as silicic acid anhydride, or a silicic acid hydrate; one of
the starch
derivatives described above in relation to the excipients; and the like.
The stabilizer is, for example, a p-oxybenzoate derivative such as
methylparaben,
or propylparaben; an alcohol such as chlorobutanol, benzyl alcohol, or
phenylethyl
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200t04s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
59
alcohol; benzalkonium chloride; a phenol derivative such as phenol, or cresol;
thimerosal; dehydroacetic acid; sorbic acid; and the like.
The corrigent is, for example, a sweetening, souring, or flavoring agent,
which are
conventionally used; and the like.
The solvent for injection is, for example, water, ethanol, glycerin and the
like.
Suitable dosage levels will depend on the condition of the disease, the age of
the
patient and the like, but typically suitable dosage levels for an active
ingredient of the
present invention are from 1 mg (preferably 5 mg) to 1000 mg (preferably S00
mg)
for oral administration and from 0.1 mg (preferably 1 mg) to 500 mg
(preferably 300
mg) for intravenous administration per unit dose, per day, for an adult human,
respectively. The dosages described above are preferably administered from one
time to six times throughout the day, depending on the condition of the
disease.
[The best mode for carrying out the invention]
The following Examples, Reference Examples, Test Examples and Formulation
Examples are intended to further illustrate the present invention and are not
intended
to limit the scope of the invention.
Example 1
3-Acetoxymethyl-7-(4-fluorobenzyloxy -2-meth~rl-1-[( 1 S,2S)-2-
methylc cly_ onropylmethvllpyrroloj2,3-dlpyridazine
To a solution of 7-(4-fluorobenzyloxy)-2,3-dimethyl-1-[(1S,2S)-2-
methylcyclopropylmethylJpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine (0.679 g, 2.00 mmol) in
acetic
acid (40 ml) was added ammonium cerium (N) nitrate (6.58 g, 12.0 mmol) at room
temperature. The mixture was stirred at 60°C for 3 hours, poured into
water and
extracted with ethyl acetate. The extract was washed with a saturated aqueous
sodium
chloride solution, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and concentrated in
vacuo.
The residue was chromatographed on a silica gel column using hexane/ethyl
acetate =
1/1 as the eluant to afford an oil which was crystallized in hexane to give
the title
compound (0.255 g, 28%) as pale yellow crystals.
Melting point : 122-123°C.
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 398 (M++1).
NMR spectrum (CDC13, 8 ppm) : 0.13-0.20 (m, 1H), 0.37-0.44 (m, 1H), 0.61-0.68
(m,
1H), 0.84-0.91 (m, 1H), 0.90 (d; J=5.9 Hz, 3H), 2.05 (s, 3H), 2.48 (s, 3H),
4.14 (dd;
S:/ChemicallSankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812IFP-200104Itsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
J=14.6 Hz, 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.31 (dd; J=14.6 Hz, 6.3 Hz, 1H), 5.27 (s, 2H), 5.65
(d;
J=12.0 Hz, 1H), 5.70 (d; J=12.0 Hz, 1H), 7.05-7.12 (m, 2H), 7.48-7.53 (m, 2H),
9.12
(s, 1H).
Example 2
7-(4-Fluorobenzyloxy)-3-hydroxymethyl-2-methyl-1-[(1 S,2Sl-2-
methylcyclopropylmethyllpyrrolo[2,3-d~pyridazine
To a solution of 7-(4-fluorobenzyloxy)-2,3-dimethyl-1-[(1S,2S)-2-
methylcyclopropylmethylJpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine (67.9 g, 200 mmol) in acetic
acid
(800 ml) was added ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate (329 g, 600 mmol) at room
temperature. The mixture was stirred at SS°C for 8 hours, poured into
water and
extracted with ethyl acetate. The extract was washed with a saturated aqueous
sodium
chloride solution, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and concentrated in
vacuo.
To the residue were added methanol (S00 ml) and a 2N aqueous lithium hydroxide
solution ( 160 ml) and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 40
minutes.
The reaction mixture was neutralized with 1N hydrochloric acid and the
methanol was
evaporated off in vacuo. The resulting mixture was extracted with chloroform.
The
extract was washed with a saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution, dried
over
anhydrous magnesium sulfate and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was
chromatographed on a silica gel column using ethyl acetate and ethyl
acetate/methanol = 9/1 as the eluant to afford crystals which were washed with
ethyl
acetate to give the title compound (24.6 g, 35%) as pale yellow crystals.
Melting point : 128-129°C.
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 356 (M++1 ).
NMR spectrum (CDCl3, 8 ppm) : 0.10-0.16 (m, 1H), 0.34-0.40 (m, 1H), 0.58-0.68
(m,
1H), 0.77-0.86 (m, 1H), 0.87 (d; J=5.9 Hz, 3H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 4.09 (dd; J=14.6
Hz, 7.3
Hz, 1H), 4.26 (dd; J=14.6 Hz, 6.3 Hz, 1H), 4.82 (s, 2H), 5.57 (d; J=11.7 Hz,
1H), 5.62
(d; J=11.7 Hz, 1 H), 7.04-7.09 (m, 2H), 7.47 (dd; J=8.8 Hz, 5.4 Hz, 2H), 9.07
(s, 1 H).
Optical rotation : [a]p2° _ +18.2° (C=1.00, MeOH).
S:/Chemical/Sanlryo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812IFP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
61
Example 3
7-1~4-Fluorobenzvloxy)-3-formyl-2-methyl-1-f ( 1 S,2Sl-2-
methvlcyclopropylmethyl]pyrrolo[2,3-dlpyridazine
To a solution of 7-(4-fluorobenzyloxy)-3-hydroxymethyl-2-methyl-1-[(1S,2S)-2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl]pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine (64.3 g, 181 mmol) in
methylene
chloride (900 ml) was added activated manganese dioxide (472 g, 5.43 mol) at
room
temperature. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 18 hours. The
reaction
mixture was filtered through celite (trade mark) and the filtrate was
concentrated in
vacuo. The crude crystals (45.7 g) were washed with ethyl acetate and hexane
to give
the title compound (44.3 g, 69%) as pale yellow crystals.
Melting point : 138.5-139.5°C.
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 354 (M++1).
NMR spectrum (CDC13, b ppm) : 0.19-0.26 (m, 1 H), 0.40-0.47 (m, 1 H), 0.71-
0.78 (m,
1H), 0.84-0.91 (m, 1H), 0.92 (d; J=5.9 Hz, 3H), 2.75 (s, 3H), 4.19 (dd; J=14.6
Hz, 7.1
Hz, 1 H), 4.3 S (dd; J=14.6 Hz, 6.6 Hz, 1 H), 5.67 (d; J=12.0 Hz, 1 H), 5.73
(d; J=12.0
Hz, 1H), 7.07-7.14 (m, 2H), 7.51 (dd; J=8.5 Hz, 5.4 Hz, 2H), 9.63 (s, 1H),
10.22 (s,
1 H).
Optical rotation : [a]D2o = +20.4° (C=1.00, MeOH).
Example 4
3-Carboxv-7 ~4-fluorobenzyloxy)-2-methyl-1-j(1 S,2S)-2-
methvlc~propylmeth~l]pyrrolo [2,3-dlp~idazine
To a solution of silver nitrate (0.85 g, 5 mmol) in water (2.5 ml) was added
an
aqueous 2N lithium hydroxide solution (3 ml), followed by a solution of 7-(4-
fluorobenzyloxy)-3-formyl-2-methyl-1-[( 1 S,2 S)-2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl]pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine (0.177 g, 0.5 mmol) in
ethanol (10
ml). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 48 hours. To the reaction
mixture was added 1N hydrochloric acid (3 ml) and the resulting mixture was
filtered
through celite (trade mark). The celite (trade mark) was washed with ethanol
(30 ml).
To the combined filtrates was added water and the resulting mixture was
extracted
with chloroform. The extract was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and
concentrated in vacuo. The residue was chromatographed on a silica gel column
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-iglhanslation
of PCT specificationl26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
62
using chloroform/isopropanol =19/1 as the eluant to give the title compound
(0.094 g,
51%) as pale yellow crystals.
Melting point : 170-225°C.
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 370 (M++1).
NMR spectrum (CDCl3, 8 ppm) : 0.20-0.25 (m, 1H), 0.40-0.46 (m, 1H), 0.63-0.69
(m,
1H), 0.86-0.92 (m, 1H), 0.91 (d; J=5.9 Hz, 3H), 2.86 (s, 3H), 3.60 (bs, 1H),
4.26 (dd;
J=14.7 Hz, 7.3 Hz, 1 H), 4.40 (dd; J=14.7 Hz, 6.8 Hz, 1 H), 5.67 (d; J=11.7
Hz, 1 H),
5.72 (d; J=11.7 Hz, 1H), 7.08-7.14 (m, 2H), 7.53 (dd; J=8.8 Hz, 5.4 Hz, 2H),
9.88 (bs,
1 H).
Optical rotation : [a]D2° _ +15.8° (C=1.00, MeOH),
Reference Example 1
7-(4-Fluorobenz~oxy)-2.3-dimethyl-1-L,1 S.2S2-2-
methylcyclo~ropylmeth~rllpyrroloj2,3-d]pyridazine
(a) Methyl 3-formyl-4,5-dimethyl-1-[(1S,2S1-2-methylcyclopropylmethyllpyrrole-
2-
carboxylate
Potassium tent-butoxide (3.49 g, 35.1 mmol) was added to a solution of methyl
3-
formyl-4,S-dimethylpyrrole-2-carboxylate (5.79 g, 31.9 mmol) and 18-crown-6
(0.41
g, 1.55 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (130 ml) and the mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 1 hour. After dropwise addition over 30 minutes of (1S,2S)-2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl bromide (5.71 g, 38.3 mmol) to the reaction mixture at
50°C, the mixture was heated under reflux for 3 hours. Potassium tent-
butoxide (0.36
g, 3.22 mmol) and (1S,2S)-2-methylcyclopropylmethyl bromide (0.48 g, 3.21
mmol)
were further added to the mixture and this mixture was heated for 1 hour. The
reaction mixture was poured into ice-water and extracted with ethyl acetate.
The
extract was washed with water and a saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution
and
then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solvent was removed in vacuo
to
afford the desired compound (8.26 g, 100%) as a pale brown oil.
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 250 (M++1)
NMR spectrum (CDC13, 8 ppm) : 0.25 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5 Hz, 1 H), 0.48 (dt; J=8 Hz,
5 Hz,
1H), 0.71-0.80 (m, 1H), 0.82-0.89 (m, 1H), 1.00 (d; J=6 Hz, 3H), 2.20 (s, 3H),
2.26 (s,
3H), 3.89 (s, 3H), 4.25 (d; J=7 Hz, 2H), 10.43 (s, 1H).
Optical rotation : [a]D2°=+17.6° (C=1.02, EtOH).
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP2001041FP200104s.doc P838121FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
63
ib~ 2,3-Dimethyl-1-f(1S.2S1-2-methylc~clopropMethyl]_6 7-dihydropyrrolof2,3-
~pyridazine-7-one
Hydrazine hydrate (1.92 g, 38.4 mmol) was added to a solution of methyl 3-
formyl-
4,5-dimethyl-1-[(1S,2S)-2-methylcyclopropylmethyl]pyrrole-2-carboxylate (7.96
g,
31.9 mmol) in acetic acid (38 ml) at room temperature and the mixture was
stirred at
90°C for 1 hour. After the reaction was completed, the reaction mixture
was cooled
to room temperature and poured into ice-water. The crude crystals were
collected by
filtration, washed with water and dissolved in a mixture of chloroform and
methanol
(9:1). The organic layer was separated, washed with a saturated aqueous sodium
chloride solution and then dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solvent
was
removed in vacuo and to the residue was added a mixture of toluene and hexane.
The
precipitate was collected by filtration to afford the desired compound (7.02
g, 95.0%)
as a pale yellowish white powder.
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 232 (M++1)
NMR spectrum (CDCl3, 8 ppm) : 0.22 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5 Hz, 1H), 0.64 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5
Hz,
1H), 0.86-0.95 (m, 2H), 0.98 (d; J=5 Hz, 3H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 2.35 (s, 3H), 4.44
(d; J=7
Hz, 2H), 8.05 (s, 1H), 9.97 (s, 1H).
Optical rotation : [a]D2° _ +11.2° (C=0.50, EtOH).
(c) 7-Chloro-2,3-dimethyl-1-j(1S.2S1-2-meth~cyclopropylmethyl]pyrroloj2,3-
~pyridazine
Phosphorus oxychloride (55 ml, 590 mmol) was added to 2,3-dimethyl-1-[(1S,2S)-
2-methylcyclopropylmethyl]-6,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine-7-one (6.95 g,
30.1
mmol) and the mixture was stirred at 90°C for 3.5 hours. After the
reaction was
completed, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and poured into
ice-
water. The aqueous solution was neutralized with a SN aqueous sodium hydroxide
solution and extracted with methylene chloride. The extract was washed with
water,
dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and then concentrated in vacuo. Hexane
was
added to the residue and the precipitate was collected by filtration to afford
the
desired compound (6.90 g, 92.0%) as a pale yellow powder.
Mass spectrum (CI, mlz) : 250 (M++1 )
NMR spectrum (CDC13, 8 ppm) : 0.29 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5 Hz, 1H), 0.54 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5
Hz,
1H), 0.73-1.02 (m, SH), 2.30 (s, 3H), 2.43 (s, 3H), 4.44 (d; J=6 Hz, 2H), 9.15
(s, 1H).
Optical rotation : [a]p °=+12.3° (C=1.01, EtOH).
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specificationl26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
64
(d) 7-(4-Fluorobenzyloxy)-2,3-dimethyl-1-f(1S,2S1-2-
methylcyclopropylmethyllpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyndazine
A solution of p-fluorobenzyl alcohol ( 1.45 g, 11.5 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran
(2 ml)
was added dropwise to a solution of sodium hydride (0.26 g, 10.8 mmol) in
tetrahydrofuran (6 ml) and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30
minutes. A solution of 7-chloro-2,3-dimethyl-1-[(1S,2S}-2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl]pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine (2.50 g, 10.0 mmol) in
tetrahydrofuran (13 ml) was added dropwise to the reaction mixture at room
temperature and the mixture was heated under reflux for 3 hours. After the
reaction
was completed, the reaction mixture was poured into ice-water and extracted
with
ethyl acetate. The extract was washed with a saturated aqueous sodium chloride
solution, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and then concentrated in
vacuo.
Hexane was added to the concentrated solution, and the precipitate was
collected by
filtration and then recrystallized from a mixture of ethyl acetate and hexane
to afford
the title compound (2.25 g, 66.4%) as pale brown crystals.
Mp : 114-115°C
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 340 (M++1)
1H-NMR spectrum (CDC13, 8 ppm) : 0.14 (dt; J= 8 Hz, 5 Hz, 1H), 0.39 (dt; J=8
Hz, 5
Hz, 1H), 0.59-0.65 (m, 1H), 0.76-0.85 (m, 1H), 0.89 (d; J=6 Hz, 3H), 2.26 (s,
3H),
2.36 (s, 3H), 4.13 (dd; J=15 Hz, 7 Hz, 1H), 4.27 (dd; J=15 Hz, 6 Hz, 1H), 5.63
(d;
J=12 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d; J=12 Hz, 1H), 7.05-7.12 (m, 2H), 7.47-7.52 (m, 2H),
8.96 (s,
1 H).
Optical rotation : [a]D2°=+17.9° (C=0.50, EtOH).
Reference Example 2
Methyl 3-formyl-4, 5-dimethyl-1-[~ 1 S,2 S~-2-methylcyclopropylmethyl]pyrrole-
2-
carboxylate
(a) Methy14,5-dimethyl-1-j(E)-2-meth~cycloproQylmethyllpyrrole-2-carboxylate
Potassium tert-butoxide (18.33 g, 164 mmol) was added to a solution of methyl
4,5-dimethylpyrrole-2-carboxylate (25.02 g, 163 mmol) and 18-crown-6 (3.19 g,
12.1
mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (150 ml) and the mixture was stirred at room
temperature
for 1 hour. To this mixture was added a solution of (E)-2-
methylcyclopropylmethyl
bromide (racemate, 12.70 g, 85.2 mmol) and the mixture was heated under reflux
for
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/ua-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
7 hours. After the reaction was completed, the reaction mixture was poured
into ice-
water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The extract was washed with water and
a
saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution, dried over anhydrous magnesium
sulfate
and then concentrated in vacuo. The residue was chromatographed on a column
using
toluene as the eluant to afford the desired compound (racemate, 13.50 g,
71.6%) as a
brown oil.
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 222 (M++1)
NMR spectrum (CDCl3, 8 ppm) : 0.20 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5 Hz, 1H), 0.48 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5
Hz,
1H), 0.67-0.93 (m, 2H), 0.98 (d; J=6 Hz, 3H), 2.01 (s, 3H), 2.18 (s, 3H), 3.76
(s, 3H),
4.21 (d; J=7 Hz, 2H), 6.76 (s, 1H).
(b) Methy14,5-dimethyl-1-f(1S,2S)-2-metl~lcyclo~roQylmethyllnyrrole-2-
carboxylate
Methyl 4,5-dimethyl-1-[(E)- 2-methylcyclopropylmethyl]pyrrole-2-carboxylate
( 10.00 g) was chromatographed by high pressure liquid chromatography to
afford the
title [(S,S) form] compound (3.33 g) and the [(R,R) form] compound (3.97 g),
which
is the antipode of the [(S,S) form] compound.
Separation conditions;
Column: CHIRALCEL OJ, SO~x500mm, Daicel Chemical Industries, Ltd.
Eluant: hexane/2-propanol = 1000/1
Flow rate: 25 ml per minute
The title [(S,S) form] compound:
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 222 (M++1)
NMR spectrum (CDCl3, 8 ppm) : 0.20 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5 Hz, 1 H), 0.48 (dt; J=8 Hz,
S Hz,
1H), 0.66-0.80 (m, 1H), 0.82-0.91 (m, 1H), 0.98 (d; J=6 Hz, 3H), 2.01 (s, 3H),
2.18 (s,
3H), 3.76 (s, 3H), 4.21 (d; J=7 Hz, 2H), 6.76 (s, 1H).
Optical rotation : [a]DZO=+17.6° (C=1.00, EtOH).
The antipode [(R,R) form] compound
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 222 (M++1)
NMR spectrum (CDC13, 8 ppm) : 0.20 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5 Hz, 1H), 0.48 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5
Hz,
1H), 0.66-0.80 (m, 1H), 0.82-0.91 (m, 1H), 0.98 (d; J=6 Hz, 3H), 2.01 (s, 3H),
2.18 (s,
3H), 3.77 (s, 3H), 4.21 (d; J=7 Hz, 2H), 6.76 (s, 1H).
Optical rotation : [a]D2°--17.0° (C=1.01, EtOH).
S:/Chemical/SankyoIFP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-2001041tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
66
(c) Methyl3-formyl-4,5-dimethyl-1-f(1S,2S)-2-methylcyclo~ropylmethyl~pyrrole-2-
carboxvlate
Phosphorus oxychloride (2.15 g, 14 mmol) was added to a solution of
dimethylformamide (1.10 g, 15 mmol) in toluene (2 ml) and the mixture was
stirred at
room temperature for 30 minutes. To this mixture was added a solution of
methyl 4,5-
dimethyl-1-[(1S,2S)-2-methylcyclopropylinethyl]pyrrole-2-carboxylate (2.21 g,
10
mmol) in toluene (6 ml) and the mixture was heated at 80°C for 10
hours. After the
reaction was completed, the reaction mixture was poured into water and
neutralized
with a saturated aqueous sodium hydrogencarbonate solution. The organic layer
was
separated, washed with a saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution, dried
over
anhydrous magnesium sulfate and then concentrated in vacuo. The residue was
chromatographed on a column using ethyl acetate/hexane = 10/1 as the eluant to
afford the title compound (1.95 g, 78.2%) as a pale yellow oil.
Reference Example 3
7-(4-Fluorobenzyloxy)-2,3-dimethyl-1-[( 1 S,2Sl-2-
methylcycloprop l~yl]p ry rolo(2,3-dlpyridazine
(a) 7-(4-Fluorobenzyloxy)-1-[(E)-2-methylcycloprop~rlmethyl]-2,3-
dimethylpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine (racematel
A reaction was carried out in a similar manner to that described in Reference
example 1 using (E}-2-methylcyclopropylmethyl bromide (racemate) instead of
(1S,2S)-2-methylcyclopropylmethyl bromide to afford the desired compound
(56%).
Mp : 120-122°C
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 340 (M++1 )
1H-NMR spectrum (CDCl3, 8 ppm) : 0.14 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5 Hz, 1H), 0.39 (dt; J=8
Hz, 5
Hz, 1H), 0.59-0.65 (m, 1H), 0.76-0.85 (m, 1H), 0.89 (d; J=6 Hz, 3H), 2.26 (s,
3H),
2.36 (s, 3H), 4.13 (dd; J=15 Hz, 7 Hz, 1H), 4.27 (dd; J=15 Hz, 6 Hz, 1H), 5.63
(d;
J=12 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d; J=12 Hz, 1H), 7.05-7.12 (m, 2H), 7.47-7.52 (m, 2H),
8.96 (s,
1 H).
(b) 7-(4-Fluorobenzyloxy)-2,3-dimethyl-1-f(1S 2S)-2-
methylcyclopropylmethLrllpyrrolo[2,3-dlpyridazine
7-(4-Fluorobenzyloxy)-1-[(E)-2-methylcyclopropylmethyl]- 2,3-
dimethylpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine (racemate, 25 g) was chromatographed by high
pressure liquid chromatography and recrystallized from ethyl acetate to afford
the title
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PC'f specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
67
[(S,S) form] compound (8.54 g) and the [(R,R) form] compound (7.60 g), which
is the
antipode of the [(S,S) form] compound.
Separation conditions;
Column: CHIRALCEL OJ, SO~x500mm, Daicel Chemical Industries, Ltd.
Eluant: hexane/ethanol = 90/10
Flow rate: 25 ml per minute
The title [(S,S) form] compound:
Mp : 114-115°C
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 340 (M++1 )
1H-NMR spectrum (CDC13, 8 ppm) : 0.14 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5 Hz, 1H), 0.39 (dt; J=8
Hz, 5
Hz, 1H), 0.59-0.65 (m, 1H), 0.76-0.85 (m, 1H), 0.89 (d; J=6 Hz, 3H), 2.26 (s,
3H),
2.36 (s, 3H), 4.13 (dd; J=15 Hz, 7 Hz, 1H), 4.27 (dd; J=15 Hz, 6Hz, 1H), 5.63
(d;
J=12 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d; J=12.2 Hz, 1H), 7.05-7.12 (m, 2H), 7.47-7.52 (m, 2H),
8.96 (s,
1 H).
Optical rotation : [a]D2°=+19.0° (C=0.99, MeOH).
The antipode [(R,R) form] compound:
Mp : 114-115°C
Mass spectrum (CI, m/z) : 340 (M++1 )
NMR spectrum (CDC13, b ppm) : 0.15 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5 Hz, 1H), 0.39 (dt; J=8 Hz, 5
Hz,
1H), 0.58-0.66 (m, 1H), 0.78-0.85 (m, 1H), 0.89 (d; J=6 Hz, 3H), 2.26 (s, 3H),
2.37 (s,
3H), 4.13 (dd; J=15 Hz, 7 Hz, 1H), 4.27 (dd; J=15 Hz, 6 Hz, 1H), 5.63 (d; J=12
Hz,
1H), 5.68 (d; J=12 Hz, 1H), 7.06-7.11 (m, 2H), 7.49-7.52 (m, 2H), 8.97 (s,
1H).
Optical rotations : [a]D2o=-18.8° (C=0.98, MeOH).
Test Example 1
Test on activity of protompotassium-adenosine triphosphatase (H+~K+-ATPase)
A microsomal fraction prepared in accordance with the method of Sachs, et al.
[J. Bio. Chem., 251, 7690(1976)] by homogenizing a fresh gastric mucosal layer
of
swine and then subjecting the homogenate to density gradient ultra
centrifugation was
employed as a proton potassium-adenosine triphosphatase preparation. A
solution
( 10 ~1) of a test compound dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide was added to 0.75
ml of a
70 mM tris hydrochloric acid buffer (5 mM magnesium chloride, 20 mM potassium
chloride, pH = 6.85) containing 30 to 80 pg/ml, in terms of the protein
concentration,
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104IFP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
68
of the enzyme preparation. The mixture was incubated with 200 times/min of
agitation at 37°C for 45 minutes. The enzymatic reaction was started by
adding 0.25
ml of an 8 mM solution of disodium adenosine triphosphate. After this
enzymatic
reaction was continued for 20 minutes, 1 ml of a 10% trichloroacetic acid -
activated
charcoal ( 100 mg) solution was added to terminate the reaction. The reaction
mixture
was centrifuged (at 4°C and 3000 rpm for 15 minutes). Inorganic
phosphoric acid
formed by the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate in the supernatant was
subjected
to colorimetry by the method of Yoda, et al. [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,
40,
880(1970)]. The amount of inorganic phosphoric acid in a reaction mixture free
from
potassium chloride was also measured. By subtracting this amount from the
amount
of inorganic phosphoric acid in the presence of potassium chloride,
protompotassium-
adenosine triphosphatase activity (H+'K+-ATPase) was determined. An inhibition
ratio (%) was determined from the active value of the control and the active
value of
the test compound at each concentration, whereby a 50% inhibitory
concentration
(ICSO ~.g/ml) against protompotassium-adenosine triphosphatase was determined.
As
a result, the compound of Example 2 had a 50% inhibitory concentration (ICSO)
of
0.015 ~g/ml, exhibiting excellent activity.
Test Example 2
Test for inhibition on gastric acid secretion in rats
After a group of rats was fasted overnight, they were subjected to midline
abdominal incision and their pylorus was ligated under anesthesia with ether.
The
stomach and duodenum were returned to their original positions in the body,
followed
by closing at the abdominal incision part. A test compound (0.3 to 10 mg/ml)
was
suspended in an aqueous solution containing 0.5% of sodium
carboxymethylcellulose
and 0.4% of Tween 80 (trade mark). The resulting suspension (1 ml/kg of body
weight) was orally administered to the rats through a stomach tube. Four hours
after
the ligation, the rats were sacrificed by inhalation of C02 gas. They were
subjected to
abdominal incision to remove their stomach. The content of the stomach was
collected in a glass-made graduated centrifuge tube. After centrifugation, the
amount
(ml) of the supernatant and the amount (ml) of the precipitate were measured.
The
precipitate of the amount exceeding 0.5 ml was regarded as feces and excluded
from
the data. The supernatant (100 p,1) was poured into a test tube. Distilled
water (4 ml)
S:/Chemical/Sankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/ua-igltranslation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
69
was added to the solution, and the solution was titrated to pH 7.0 with 0.01 N
sodium
hydroxide. A standard acid concentration solution obtained by adding 4 ml of
distilled water to 100 ~l of 0.1 N hydrochloric acid was titrated in a similar
manner.
Each parameter was calculated in accordance with the following equations:
(1) Acid concentration of gastric juice (mEq/1) = A/B x 100
A: amount (ml) of sodium hydroxide required for titration of 100 ~1 of
supernatant
B: amount (ml) of sodium hydroxide required for titration of 100 ~l of 0.1 N
hydrochloric acid
(2) Gastric acid output (AO, ~Eq/hr) = amount (ml) of supernatant of gastric
juice x acid concentration of gastric juice (mEq/1)/4
(3) Inhibition ratio (%) _ (C-D)/C x 100
C: AO (pEq/hr) of vehicle-administered group
D: AO (~Eq/hr) of test-compound-administered group
A SO% inhibitory dose (IDSo) was determined from a dose-inhibition ratio
curve on which an inhibition ratio at each dose versus logarithmic dose was
drawn in
accordance with the least squares. 95% confidence limit was determined
according to
Fieller's equation. As the results, the compound of Example 2 exhibited
excellent
activity, that is; an IDso less than 10 mg/kg.
Test example 3
Antibacterial action against Helicobacter pylori
The antibacterial activity of the compound of the invention was evaluated by
using Helicobacterwlori strains 9470, 9472 and 9474 and determining MIC
(Minimum Inhibitory Concentration) of the compound of the invention against
Helicobacterpylori.
Helicobacter pylori was cultured by plating for 4 days. A medium was
prepared by dissolving Brain Heart Infusion Agar (product of Difco
Laboratories) in a
prescribed amount of distilled water, sterilizing in an autoclave, adding
equine blood
(product of Nippon Seibutsu Zairyo) to give a concentration thereof of 7% and
then
solidifying the mixture.
Under microaerophilic conditions, Helicobacterwlori which had been
cultured at 37°C for 4 days was suspended in physiological saline to
give its viable
count of about 108 CFU/ml. The suspension was then diluted to 100 times and a
S:/ChemicallSankyo/FP200104/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
CA 02399380 2002-08-06
portion (about 10 p1) of the diluted suspension was inoculated in a medium for
measuring MIC. The medium employed for measuring MIC has the same
composition as the preculture medium. A compound of this invention was
dissolved
in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and two-fold serial dilutions were made with
sterilized
water. After mixing the solution and the medium in a ratio of 1:99, a
solidified
product in the Petri dish was employed as an MIC measuring medium. In a
similar
manner to that employed for the preculture, Helicobacter pylori was cultured
at 37°C
for 3 days under microaerophilic conditions. After completion of the
culturing,
growth of the bacteria in the inoculated portion was visually observed. The
minimum
concentration of a compound of this invention at which no bacterial growth was
observed was designated as MIC (pg/ml). The compound of Example 2 exhibited
excellent antibacterial activity, that is, an MIC less than 12.5 ~,g/ml.
Formulation Example 1
Tablets
The compound of Example 2 30.0 mg
Lactose 144.0 mg
Corn starch 25.0 mg
Magnesium stearate 1.0 m:;
200.0 mg
A tablet is prepared using the ingredients above. The components are blended
and
compressed by a tablet machine to form a tablet weighing 200 mg. The tablet
may be
coated if necessary, for example, to form a sugar-coated tablet.
[Effect of the invention]
The compounds of formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof of
this
invention exhibit potent gastric acid secretion inhibition activity, gastric
mucous
membrane protection activity and potent antibacterial activity against
Helicobacter
p_,ylori and they have excellent properties as medicaments. The compounds of
formula
(I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof are useful as a medicament,
especially
as a prophylactic or therapeutic medicament for ulcerative diseases such as
peptic
ulcer, acute or chronic gastric ulcer, gastrisis, reflux esophagitis,
gastroesophageal
reflux disorder, dyspepsia, gastric hyperacidity or Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
etc. or
prophylactic or therapeutic medicaments for bacterial infections arising from
Helicobacter pylori.
S:/ChemicallSankyo/FP200t 04/FP200104s.doc P83812/FP-200104/tsa-ig/translation
of PCT specification/26.07.02