Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
1
TITLE
STORAGE AND TRANSPORTATION DEVICE
This invention relates to an apparatus for storage and
transportation of elongate coilable members such as tubing, cables and
the like.
In particular, the invention is concerned with a demountable cable
reel.
Timber cable reels are well known but the majority of these are
expensive to construct in terms of labour content and due to their shape
l0 and size, there is a high cost of transportation to a cable manufacturer in
the first instance and subsequently when being returned for rewinding.
Moreover, empty reels are prone to damage during storage and
transportation.
To reduce shipping and storage costs of empty cable reels, it has
been proposed to provide a demountable reel where the generally
circular end flanges are removable from the spool, and in some cases the
spool itself is demountable to a more compact shape. Many of these
demountable cable reels rely upon elongate bolts extending via the
hollow interior of the spool between opposed flanges for their structural
2o integrity when wound with cable or the like.
Demountable cable reels which rely primarily for structural integrity
in an assembled state only on bolts extending between opposed flanges
are described in US Patent 2652992, US Patent 1767710, US Patent
1915825, US Patent 2266903. German Patent DE 2439488, European
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (R ULE 26) ROlfl U
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
2
Patent Application EP 1987000401297 (Publication No. EP 250295) and
US Patent 5588628.
French Patent Application 88 04881 describes a demountable
cable reel wherein structural integrity in an assembled state relies
partially upon bolts extending between opposed flanges and partially
upon interengagement between spool elements and the opposed flanges.
European Patent Application 91121835.2 (Publication No.
0491400 A1 ) describes a demountable cable reel having core elements
bolted at opposite ends to the opposed end flanges.
to Demountable cable reels having foldable core elements and/or
flange elements are described in US Patent 5409179, US Patent
5467939, European Patent Application 94401537.9 (Publication No. EP
0636567 A1 ) and British Patent 1170714.
US Patent 5464171 describes a demountable cable reel where
integrally formed flange/spool members interconnect intermediate the
ends of the spool.
International Patent Application No. PCT/US97/13809 (Publication
No. WO 98/06654) describes a spool comprised of a plurality of
interlocking elements.
In the interest of both cost and convenience, there is a requirement
for a simple demountable cable reel with integral locking or fastening
means to avoid the need for separate fasteners such as bolts or the like
which are easily lost in transit.
Australian Patent 442191 describes a cable reel comprising a pair
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (R ULE 26) ROlfl U
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
3
of circular end flanges, each with an array or radial slots spaced about a
central shaft aperture. Core elements comprising a disc like member with
radially extending arms which are insertable through the slots of a
respective flange for connection with corresponding arms of a core
element extending through an opposite flange. A cylindrical spool acts as
a spacer to keep the flanges apart.
Other demountable cable reels having circular end flanges and
non-demountable cylindrical spools are described in US Patents
5868348, 5743486, 5242129, 5660354 and 5727752.
Demountable cable reels having planar flanges and demountable
or collapsible spools but otherwise with integral connecting means are
described in Australian Patent 224780, British Patent GB 2269157,
Australian Patent 592112, US Patent 5806788 and Australian Patent
678296.
Although the last mentioned group of prior art cable reels has
some advantages over the previously mentioned prior art cable reels,
each suffers one or more practical shortcomings in use.
For example, the cable reels of British Patent 2269157, Australian
Patent 592112, Australian Patent 442191 and Australian Patent 224780
are not considered sufficiently robust for larger capacity cables.
While the cable reels of US Patent 5806788 and Australian Patent
678296 are better suited to more robust duty, each suffers the
disadvantage that in order to replace a flange damaged in handling or
transportation, the reel must first be emptied of cable which is time
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE26) ROlAU
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
4
consuming and inconvenient.
With a move by cable manufacturers towards moulded plastics
demountable cable reels of ever increasing capacity, it is not uncommon
for an end flange to be damaged due to rough handling or insecure
shipping.
In the event of damage to a flange on a fully wound cable reel,
there is a need to be able to replace that flange without the need to first
remove the cable and then to rewind the cable onto the repaired reel as
remote site reel repairs may be carried out without having to return the
l0 loaded reel to the cable manufacturer.
It is an aim of the present invention to overcome or ameliorate at
least some of the shortcomings associated with prior art cable reels and
otherwise to provide users with a convenient choice.
According to one aspect of the invention there is provided a
demountable reel for elongate coilable objects, said reel comprising:-
a pair of end flanges, said end flanges each including an inwardly
facing spool connecting boss:
a generally cylindrical spool comprising two or more spool
elements, each said spool connecting boss and said spool being
2o engagable by axial alignment of complementary engagement members
and releasably securable by axial misalignment between said
complementary engagement means, said reel being characterised in that
an end flange may be removably replaced by a substitute end flange with
an elongate object coiled in situ about said spool.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (R ULE 26) ROl~4 U
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
Suitably each said end flange includes reinforcement means
adjacent a perimetral rim member.
If required said spool connecting boss may be recessed below an
inner face of said flange.
5 Preferably said spool connecting boss projects outwardly from an
inner face of said flange.
Suitably said boss includes a central shaft aperture.
If required each said flange may include a plurality of radially
spaced apertures to locate, in use, tensionable members extending
l0 between opposed flanges.
Suitably said radially spaced apertures include reinforcing means.
If required said spool may comprise two or more separate elements
releasabiy connectable adjacent transverse edges to form a cylindrical
spool.
Alternatively said spool may comprise two or more spool elements
with an integrally formed hinge joint, said two or more spool elements
being movable between an extended storage and/or transportation
position and a contracted position forming a cylindrical spool.
If required said spool elements may include axially extending
reinforcing members. Additionally or alternatively said elements may
include radially extending reinforcing elements.
Preferably said reinforcing elements are integrally formed adjacent
an inner surface of said spools elements.
Said spool elements preferably comprise shouldered end portions.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26) ROl~1 U
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
6
Suitably, said complementary engagement members associated
with said flanges comprise a plurality of circumferentially spaced radially
oriented projections and/or recesses on said boss.
The complementary engagement means associated with said spool
elements comprise circumferentially spaced radially oriented projections
and/or recesses in said shouldered end portions.
The spool and respective flanges may be releasably secured by
engagement of projections on said boss behind projections on said spool
by at least partial relative rotation between said flanges and said spool.
to Suitably at least one cam member is provided to wedgingly engage
said spool with respective end flanges.
If required said cam member may be operative in a radial direction.
Suitably stop means is provided to limit relative rotation between
said spool and respective flanges.
Preferably, releasable locking means is provided to prevent
disengagement between said spool and a respective flange.
Suitably said locking means is adapted to prevent relative rotation
between said spool and a respective flange when said complementary
engagement means are engaged.
2o Most preferably, said locking means is actuable from an exterior
region of each said flange.
In order that the invention may be more fully understood and put
into practical effect, reference will now be made to preferred
embodiments illustrated in the accompanying drawings in which:-
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (R ULE 26) ROlfl U
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
7
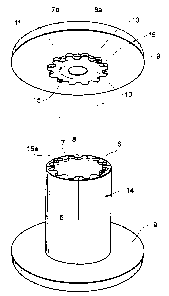
FIG. 1 shows elements of a cable reel spool according
to the
invention;
FIG. 2 shows one embodiment of a cable reel end flange;
FIG. 3 shows a second embodiment of a cable reel end
flange;
FIG. 4 shows schematically the alignment of engagement
members
of an end flange and a spool;
FIG. 5 shows an exploded reel assembly;
FIG. 6 shows a partial cross sectional engagement between
a
1o spool and the flange of FIG. 3;
FIG. 7 shows a partial cross sectional engagement between
a
spool and the flange of FIG. 2;
FIG. 8 shows a plan view of the engagement between a
spool and
a flange;
FIG. 9 shows one embodiment of the connection means
of a spool
element;
FIG. 10 shows an alternative embodiment of the connection
means
of a spool element;
FIG. 11 shows yet another embodiment of a connection
means of a
2 spool element;
o
FIG. 12 shows still another embodiment of a connection
means of a
spool element;
FIG. 13 shows a partial inner view of a spool element;
FIG. 14 shows a reinforcing insert for a flange;
FIG.15 shows a part cross sectional view of engagement
between a
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26) ROlfl U
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AiT00/00356
8
flange and a spool;
FIG. 16 shows one embodiment of a flange locking means;
FIG. 17 shows a flange; and
FIG.18 shows a part cross sectional view of a reinforced flange rim.
In FIG. 1 spool elements 1, 2 have a keyed rib 3 on one edge and
a complimentary keyhole slotted aperture 4 on an opposite edge to
enable a cylindrical spool to be assembled from four identical elements by
slidable engagement of a rib 3 of one element with the slotted aperture 4
of an adjacent element.
1o Each spool element has a smooth arcuate outer surface 5 and
arcuate end walls 6 comprising a series of alternately spaced teeth 7 and
apertures 8.
FIGS. 2 and 3 show alternative embodiments of an end flange 9
having a spool supporting boss 10 and a central shaft aperture 11.
In FIG. 2, the boss 10 is located in a recess 12a in inner flange
wall 12 whereas in FIG. 3, the boss 10 sits proud of inner flange wall 12.
In both cases, boss 10 comprises a cylindrical base 13 with a
spaced array of teeth 7a extending radially from the outer end of base 13
to form a recessed region between teeth 7 and flange wall 12.
2o FIG. 4 shows schematically the engagement of a cylindrical spool
14, formed from the elements shown in FIG. 1 and the boss 10 of the
flange 9 shown in either of FIG. 2 or FIG. 3.
As can be seen, when the teeth 7a of boss 10 are aligned with
apertures 8 of the end wall of spool 14 and similarly the apertures 8a of
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26) ROlAU
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
9
boss 10 are aligned with teeth 7 of the end wall of spool 14, the
complementary shapes of the respective teeth and apertures enables the
spool 14 to engage over boss 10.
Apertures 15 are optionally provided in teeth 7a, the purpose of
which apertures 15 will be described later.
FIG. 5 shows an exploded view of a cable reel assembly
comprising spool 14 assembled from the elements shown in FIG. 1 and
the flanges of FIG. 3.
After the respective teeth and apertures of the spool end walls and
to the flange are aligned and the teeth 7a of flange 9 are located within
apertures 8 of the spool end wall 6, the flange 9 is partially rotated
relative to spool 14 such that teeth 7a of flange 9 are located behind teeth
7 of spool 14, thereby removably securing the flange 9 to spool 14.
FIG. 6 is a part cross sectional view of the securement of flange 9
of FIG. 3 to spool 14.
FIG. 7 is a part cross sectional view of the securement of flange 9
of FIG. 2 to spool 14.
FIG. 8 is a plan view of the assembly shown in FIG 6 with the teeth
7 of spool 14 engaged behind teeth 7a of flange 9 with apertures 15 in
2o teeth 7a aligned with apertures 15a in teeth 7 aligned to receive an
elongate bolt (not shown) if required.
Apertures 15, 15a permit the use of tensionable bolts between
opposed flanges of a cable reel for additional reinforcement, particularly
on larger diameter/capacity reels.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (R ULE 26) ROlfl U
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
FIG. 9 shows an alternative form of connection for spool elements.
As shown, one edge 20 of spool element 21 is formed with a V-
shaped channel 27 having spaced apertures 22 therein.
The opposite edge 23 is formed with a complementary V-shaped
5 rib 24 having pins 25 with enlarged deformable heads 26 thereon.
As can be seen, when the respective adjacent edges of spool
elements 21 are brought together, the initial engagement between
channel 27 and rib 24 guides the headed pins 25 into alignment with
respective apertures 22. When fully engaged the rib 24 and channel 27
1o reinforce the connection between the edges 21 and 23 of adjacent spool
elements to prevent deformation when wound with a cable or the like.
FIG. 10 shows an alternative means of connecting spool elements.
In this embodiment, opposed edges of each spool element 28 are
formed with alignable abutments 29, 30, one abutment 29 having a
slotted recess 31 and the other having a barbed deformable pin 32 for
engagement therein.
FIG. 11 shows a modification to the embodiment of FIG. 1.
In this embodiment, short keyed ribs 35 on one edge of a spool
element 36 are adapted for insertion into corresponding keyhole slots 37
2 0 of an adjacent spool element. The short keyhole slots 37 permit resilient
deformation to receive the keyed ribs 35 when pushed together in a
generally tangential direction.
Located between keyed ribs 35 are one or more slotted apertures
38 to receive one or more tongues 39 which assist in alignment and
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26) ROlAU
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
11
reinforcement of the edges when assembled.
FIGS. 12, 12a and 12b shows yet another means of connecting
spool elements.
In this embodiment one edge 40 of a spool element 41 is provided
with spaced apertures 42 to receive deformable head pins 43 mounted on
an integrally hinged flap 44 of an adjacent spool element 41.
On the inner side of flap 44 are deformable barbed pins 45, which,
when the two spool elements are rotated together about hinged flap 44,
engage in apertures 46 in abutments formed on the underside of an
opposite edge of a spool element.
FIG. 12a shows a variation wherein the heads of pins 43 are
located in a recess 47 formed between inclined edge 48 of spool element
49 and the integrally hinged flap 50 having apertures 51 to receive pins
43.
FIG. 12 also shows optional reinforcing ribs 52 extending axially
along the inner wall 53 of spool element 41 and radially extending ribs 54
also or alternatively extending along inner wall 53.
FIG. 13 shows schematically a transversely extending reinforcing
rib 55 extending between opposed end walls 56 of a spool element 57.
FIG. 14 shows a steel reinforcing element 60 which may be
employed in the flanges of larger capacity cable reels according to the
invention.
The reenforcing element comprises a central shaft reinforcing tube
61, a plurality of radially spaced webs 62 and retaining plates 63 for
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (R ULE 26) ROlfl U
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
12
tensionable bolts not shown which extend between opposed reel flanges.
Retaining plates 63 have keyhole apertures 64 for ease of
inserting and connection of the tensionable bolts.
Suitably, the reinforcing element 60 is placed into an injection
moulding die for the reel flange and is encapsulated in the moulding
process.
FIG. 15 shows a port cross sectional view of a reel assembly
showing a flange 70, a spool 71 mounted on flange boss 72 and a
tensionable steel bolt 73 extending between opposed flanges.
to In this view, an alternative embodiment is illustrated in that a dual
diameter boss 72 comprises a larger diameter portion 72a and a smaller
diameter portion 72b to accommodate a smaller diameter spool if
required.
FIG. 16 shows a locking means to prevent disengagement between
the end flange and a spool of a cable reel.
In a radially directed reinforcing rib 80 of flange 81, there is formed
an integrally hinged tab 82 having a pin 83 extending from an underside
thereof.
In the locked position shown, tab 82 lies against the outer face 84
of flange 81 with pin 83 extending through an aperture 83 in face 84 and
thence into an aligned aperture (not shown) into an end wall portion of a
spool (not shown) to prevent relative rotation therebetween when the
flange and spool are secured.
FIG. 17 shows a variation in flange design incorporating reinforcing
ribs 90 extending radially between boss 91 and the inner wall 92 of a
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (R ULE 26) ROlA U
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
13
recess 93 in flange 94.
Buttressed ribs 95 reinforce the region oft he join between the floor
96 and side wall 92 of recess 93.
In this embodiment reference is made to the spool element 51 a of
FIG. 12.
For additional reinforcement of the connection between a spool
assembled from elements 41 a and flange 94 of FIG. 17, cavities 97 are
provided in the end walls of spool elements 41 a to accommodate ribs 90
yet allow sufficient relative rotation between the spool and flange for
securement.
Additionally tabs 98, upstanding from the outer surface of the spool
initially engage in aligned recesses 99 when the respective teeth and
apertures therebetween of the flange and spool when first engaged. As
the flange and spool are secured by relative rotation therebetween tabs
98 locate within slotted apertures 100 and, by resilient recovery, drop
below shouldered edges 101 to form a locking means to prevent
accidental disengagement between the spool and flange. The locking
tabs are accessible from the outer face of opposed flanges to release the
locking means.
2o FIG. 18 shows a means of reinforcing the outer rims of flanges on
larger capacity cable reels.
In this embodiment, rather than have right angle joints between a
flange wall 102 and the outer rim 103, (and any adjacent circumferential
reinforcing ribs) which are prone to damage arising from stress
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (R ULE 26) ROlfl U
CA 02405175 2002-10-07
WO 00/64797 PCT/AU00/00356
14
concentration at the right angle joint, the rim 103 as shown has oppositely
directed gently undulating ribs 104, 105 with radially disposed reinforcing
ribs therebetween.
It will be appreciated that many modifications and variations may
be made to the various embodiments of the invention without departing
from the spirit and scope thereof.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (R ULE 26) ROlA U