Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02408866 2008-07-04
RAPID EXCHANGE STENT DELNERY
SYSTEM AND ASSOCIATED COAIPONENTS
Field of the Invention
The present invention generally relates to stent delivery catheters, such as
biliary stent delivery catheters. More specifically, the present invention
relates to
rapid exchange type stent delivery catheters for delivering a self-expanding
stent to a
bodily lumen, such as the biliary tract.
Background of the Invention
Endoscopic procedures for treating abnomial pathologies within the
alimentary canal system and biliary tree (including the biliary, hepatic, and
pancreatic
ducts) are increasing in nuniber. The endoscope provides access to the general
area of
a desired duct using direct visualization. However, the duct itself must be
navigated
using a catheter in conjunction with a guidewire under fluoroscopy. A wide
variety of
catheters are known for treatment of such targeted anatomical regions.
Examples of
biliary catheters are disclosed in U.S. Patent Number 5,921,971 to Argo et al.
and
PCT International Publication No. 00/69498 to De Toledo et al.
Argo et al. `971 discloses a catheter for use in biliary procedures, wherein
the
catheter includes a shaft having a proximal end and a distal end. A guidewire
lumen
extends through the shaft from a proximal guidewire port located proximal of
the
distal end of the shaft, to a distal guidewire port located at the distal end
of the shaft.
The shaft may also include a slot or channel extending from a proxinial end of
the
shaft to the proximal guidewire port. Catheters incorporating such a guidewire
opening and chaimel are often referred to as rapid exchange or single operator
exchange type biliary catheters.
De Toledo et al. `498 discloses single operator drainage catheter delivery
system including a guide member having a guidewire lumen extending through a
distal portion thereof, with a proximal guidewire port located distal of the
proximal
end. A placement catheter is disposed over the guide member has a catheter
lumen
extending through a distal portion thereof, with a proximal guidewire port
located
distal of the proximal end. Locating the proxinial guidewire ports as such
allows the
delivery system to be used by a single person with a shorter guidewire. A
drainage
catheter (a.k.a. a plastic stent) is disposed about the guide member distal of
the
-1-
CA 02408866 2002-11-12
WO 02/074378 PCT/US01/45625
placement catheter. The drainage catheter delivery system preferably includes
a
means for releasably connecting the placement catheter to the drainage
catheter,
wherein the releasable connecting means disconnects the drainage catheter upon
displacement of the guide member. However, De Toledo et al. `498 does not
disclose
a rapid exchange biliary catheter system for the delivery of a metallic self-
expanding
stent, which requires a retractable sheath.
U.S. Patent No. 5,484,444 to Braunschweiler et al., and U.S. Patent No.
5,709,703 to Lukic et al. disclose a stent delivery device which has an
elongated
sheath with a self-expandable stent placed in contracted condition within the
distal
area of the sheath. An elongated core is arranged in the sheath for
longitudinal
motion relative to the sheath to facilitate stent delivery. However,
Braunschweiler et
al. `444 and Lukic et al. `703 do not provide a rapid exchange feature as in
De Toledo
et al. `498.
U.S. Patent No. 5,743,874 to Fischell et al. discloses a catheter capable of
performing balloon angioplasty followed by delivery of a self-expanding stent.
The
catheter includes an outer sheath which may be pulled back to deploy the self-
expanding stent. In one embodiment, the catheter includes a guide wire entry
port
located just proximal of the stent to permit rapid exchange capability. To
provide the
guide wire entry port, Fischell et al. `874 provides a sloped plug disposed in
the inner
tube and an elongate side opening in the outer sheath. The elongate side
opening in
the outer sheath is necessary to permit retraction of the outer sheath for
stent
deployment. By providing such a long side opening, a major portion of the
inner
workings of the catheter are exposed to bodily fluids and interference from
other
devices, which may compromise performance of the stent delivery catheter. This
undesirable feature, in addition to others not specifically mentioned herein,
leaves a
need for an improved rapid exchange stent delivery catheter.
Summarv of the Invention
The present invention provides an improved rapid exchange catheter system
for the delivery of a self-expanding stent to a bodily lumen (e.g., biliary
tract, blood
vessel, etc.), such as a metallic biliary stent commercially available from
Boston
Scientific Corporation under the trade name WallstentTM. In an exemplary
embodiment, the rapid exchange stent delivery catheter includes an inner
tubular
member and an outer tubular member slidably disposed thereon. The inner
tubular
-2-
CA 02408866 2002-11-12
WO 02/074378 PCT/US01/45625
member has a guide wire lumen with a proximal rapid exchange type guide wire
opening. The outer tubular member also has a rapid exchange type guide wire
opening that is preferably shorter than the guide wire lumen of the inner
tubular
member in order to protect the inner workings of the catheter from bodily
fluids and
other devices.
The outer tubular member may include a guide wire access sleeve in which the
guide wire opening is disposed. The guide wire access sleeve has a guide wire
ramp
extending into the guide wire lumen of the inner tubular member. The guide
wire
sleeve may be a separate component from the remainder of the outer tubular
member
to facilitate efficient manufacture.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Figure 1 is a plan view of a rapid exchange stent delivery catheter system in
accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, shown in the
delivery state;
Figure 2 is a plan view of a distal portion of the rapid exchange stent
delivery
catheter system illustrated in Figure 1, shown in the deployment state;
Figure 3 is a plan view of a distal portion of the outer tubular member of the
rapid exchange catheter illustrated in Figure 1;
Figure 4 is a plan view of an inner tubular member of the rapid exchange
catheter illustrated in Figure 1;
Figures 5A and 5B are cross-sectional views taken along lines 5A-5A and 5B-
5B, respectively, in Figure 4;
Figure 6 is a plan view of a self-expanding metallic stent suitable for
delivery
by the rapid exchange catheter illustrated in Figure 1;
Figure 7A is an isometric view of a guide wire sleeve of the outer tubular
member illustrated in Figure 3; and
Figure 7B is a longitudinal sectional view of the guide wire sleeve
illustrated
in Figure 7A.
Detailed Descp~ption of the Invention
The following detailed description should be read with reference to the
drawings in which similar elements in different drawings are numbered the
same.
The drawings, which are not necessarily to scale, depict illustrative
embodiments and
are not intended to limit the scope of the invention. Those skilled in the art
will
-3-
CA 02408866 2002-11-12
WO 02/074378 PCT/US01/45625
recognize that the dimensions and materials discussed herein are merely
exemplary
and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
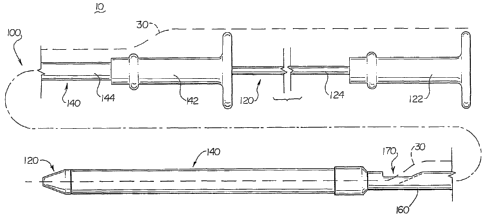
Refer now to Figures 1 and 2 which illustrate plan views of a rapid exchange
stent delivery catheter system 10 in accordance with an embodiment of the
present
invention. The rapid exchange stent delivery catheter system 10 includes a
rapid
exchange catheter 100 which is advanced over a guide wire 30 (shown in
phantom) to
deliver and deploy a self-expanding stent 20 in a bodily lumen.
The rapid exchange stent delivery catheter system 10 is suitable for biliary
applications and intravascular applications. In biliary applications, the
rapid exchange
lo stent delivery catheter system 10 is sized to fit within an endoscope (not
shown) and
to navigate to the desired site in the biliary tract. In vascular
applications, the rapid
exchange stent delivery catheter system 10 is sized to fit within an
introducer sheath
(not shown) and/or a guide catheter (not shown) to navigate to the desired
vascular
site.
The rapid exchange stent delivery catheter 100 includes an inner tubular
member 120 slidably disposed in an outer tubular member 140. The outer tubular
member 140 includes a lumen (not visible) extending therethrough to slidably
accommodate the inner tubular member 120. The inner tubular member 120
includes
a guide wire lumen 130 extending through a distal portion thereof to
accommodate
the guide wire 30.
To provide rapid exchange capability for the rapid exchange stent delivery
catheter 100, the guide wire 30 exits through a guide wire opening 170 in the
outer
tubular member 140 as will be discussed in greater detail with reference to
Figures 3,
7A and 7B. The guide wire 30 extends through a relatively short guide wire
lumen
and enters through a distal guide wire opening in the inner tubular member
129, as
will be discussed in greater detail with reference to Figures 4, 5A and 5B. In
practice,
the device 100 may be inserted over the guide wire 30 from the tip end first.
A proximal handle 122 is connected to a proximal portion 124 of the inner
tubular member 120. Similarly, a distal handle 142 is connected to a proximal
portion
144 of the outer tubular member 140. The distal handle 142 may be
longitudinally
displaced relative to the proximal handle 122 to selectively expose or cover
the self-
expanding stent 20, which is disposed about a distal portion of the inner
tubular
member 120. In Figure 1, the distal handle 142 has been longitudinally
displaced in
-4-
CA 02408866 2002-11-12
WO 02/074378 PCT/US01/45625
the distal direction relative to proximal handle 122 such that the outer
tubular member
140 covers the self-expanding stent 20. In Figure 2, the distal handle 142 has
been
longitudinally displaced in the proximal direction relative to proximal handle
122 to
retract the outer tubular member 140 relative to the inner tubular member 120
to
expose and deploy the self- expanding stent 20.
With additional reference to Figure 3, the outer tubular member 140 includes,
from the proximal end to the distal end, a proximal portion 144, a main outer
portion
(not visible) a guide wire sleeve 160 and a distal outer portion 146. The
proximal end
of the proximal outer portion 144 is connected to the distal handle 142. The
distal
handle 142 may be injection molded over the proximal outer portion 144. The
distal
end of the proximal outer portion 144 is connected to the proximal end of the
main
outer portion (not visible). The distal end of the main outer portion (not
visible) is
connected to the proximal end of the guide wire sleeve 160, and the distal end
of the
guide wire sleeve 160 is connected to the proximal end of the distal outer
portion 146.
The various portions of the outer tubular member 140 may be connected by
adhesive,
by thermal means or by any other suitable means known to those skilled in the
art.
The proximal outer portion 144 may be formed of PEBAX, having a length of
approximately 8.0 inches (20.3 cm), an outside profile of approximately 0.120
inches
(9F) (0.30 cm), and an inside diameter of approximately 0.083 inches (0.21
cm). The
guide wire sleeve 160 is discussed in greater detail with reference to Figures
7A and
7B. The main outer portion (not visible) may be formed of PEBAX/wire
braid/PTFE
composite, having a length of approximately 55.0 inches (0.140 cm), an outside
profile of approximately 6F (0.079 inches), and an inside diameter of
approximately
0.057 inches (0.145 cm). The distal outer portion 146 may be formed of
PEBAX/wire
braid/PTFE composite, having a length of approximately 10.6 inches (27 cm), an
outside profile of approximately 8F 0.105 inches, and an inside diameter of
approximately 0.090 inches (0.229 cm).
A radiopaque marker band 42 may be disposed adjacent the distal end of the
distal outer portion 146 to facilitate radiographic placement of the catheter
100 and to
radiographically indicate the position of the outer tubular member 140
relative to the
inner tubular member 120 to aid in deploying the self-expanding stent 20.
With additional reference to Figures 4, 5A and 5B, the inner tubular member
120 includes a distal inner portion 126 connected to the distal end of the
proximal
-5-
CA 02408866 2002-11-12
WO 02/074378 PCT/US01/45625
inner portion 124. The proximal inner portion 124 and the distal inner portion
126 are
essentially the same, except the proximal inner portion 124 is reinforced with
a SST
hypotube. The inner portions 124/126 may be formed of PEEK, having a length of
approximately 88.6 inches (225 cm), an outside profile of approximately 0.052
inches
(0.13 cm), and an inside diameter of approximately 0.037 inches (0.094 cm). A
jacket
formed of LDPE, having a length of approximately 5.9 inches (15 cm), an
outside
profile of approximately 0.80 inches (0.020 cm), and an inside diameter of
approximately 0.055 inches (0.14 cm) may be disposed about the inner member
120
to consume the clearance between the inner member 120 and the outer member 140
proximal of the stent 20 to prevent kinking. The various portions of the inner
tubular
member 120 may be connected by adhesive, by thermal means or by any other
suitable means known to those skilled in the art.
A distal head 132 is connected to the distal end of the distal inner portion
126
to limit distal displacement of the outer tubular member 140. A distal bond
region
134 is disposed immediately proximal of the distal head 132. A holding sleeve
136
and a stent cup 138 prevent slippage of the stent 20. Radiopaque marker bands
44/48
are disposed on the distal inner portion 126 and are separated by a distance
approximately equal to the length of the stent 20. The distal outer portion
146 of the
outer tubular member 140 contains the self-expanding stent 20 during delivery.
The distal inner portion 126 includes a proximal guide wire opening 128 and a
distal guide wire opening 129. A guide wire lumen 130 extends between the
proximal
guide wire opening 128 and the distal guide wire opening 129 to accommodate
the
guide wire 30 therein. The proximal guide wire opening 128 has a length which
is
greater than the length of the guide wire opening 170 of the guide wire sleeve
160.
The length of the proximal guide wire opening 128 is sufficient to allow
longitudinal
displacement of the outer tubular member 140 relative to the inner tubular
member
120 to permit full exposure and deployment of the self-expanding stent 20. The
length of the proximal guide wire opening 128 is preferably slightly longer
than the
length of the constrained portion of the stent 20 to avoid wedging the guide
wire 30
between the inner tubular member 120 and the outer tubular member 140 prior to
full
deployment of the stent 20.
The guide wire lumen 130 may be eccentrically positioned in the distal inner
portion 126 as seen in Figures 5A and 5B. For example, the upper wall may have
a
-6-
CA 02408866 2002-11-12
WO 02/074378 PCT/US01/45625
thickness of approximately 0.003 inches and the lower wall may have a
thickness of
approximately 0.011 inches. The upper thinner wall portion may be removed
(skived)
to define the proximal guide wire opening 128. By removing only the thin-
walled
portion of the distal inner portion 126, the column strength of the inner
tubular
member 120 is not significantly compromised.
A solid mandrel (not shown) may be inserted into the proximal lumen (not
visible) of the inner tubular member 120 proximal of the guide wire opening
128 for
improved column strength. The solid mandrel may be formed of stainless steel
having an outside diameter of approximately 0.030 inches with a tapered end. A
stainless steel hypotube (not shown) having an outside diameter of
approximately
0.079 inches may be disposed about the proximal inner portion 124 for added
column
strength and durability. The proximal handle 122 may be injection molded over
the
proximal end of the hypotube and the proximal end of the proximal inner
portion 124.
A distal radiopaque marker 44 is disposed on the distal inner portion 126 to
radiographically mark the distal end of the stent 20. A proximal radiopaque
marker
48 is disposed on the distal inner portion 126 to radiographically mark the
proximal
end of the stent 20. A mid radiopaque marker 46 is disposed on the distal
inner
portion 126 distal of the holding sleeve 138 to radiographically facilitate
deployment
of the stent 20.
With reference to Figure 6, the stent 20 may comprise any self-expanding
stent suitable for biliary or intravascular applications. For example, in
biliary
applications, the self-expanding stent 20 may comprise a metallic stent
commercially
available from Boston Scientific Corporation under the trade name Wallstent
TM.
With reference to Figures 7A and 7B, the guide wire sleeve 160 includes a
proximal portion 164, a distal portion 162 and a lumen 166 extending
therethrough.
The distal portion 162 is flared to fit over and be connected to the distal
outer portion
146. The proximal portion 164 is sized to fit within and be connected to the
main
outer portion.
A guide wire opening 170 extends through the exterior wall of the guide wire
sleeve 160. A ramp 172 extends from the exterior wall into the lumen 166. When
assembled, the ramp 172 extends through the proximal guide wire opening 128 of
the
inner tubular member 120 and into the guide wire lumen 130. The ramp 172 is
moveable within the proximal guide wire opening 128 to facilitate a smooth
transition
-7-
CA 02408866 2002-11-12
WO 02/074378 PCT/US01/45625
of the guide wire 30 from the guide wire lumen 130 to exterior of the catheter
100,
regardless of the positiori of the outer tubular member 140 relative to the
inner tubular
member 120.
The guide wire sleeve 160 may have a length of approximately 1.0 inch, a
distal outside diameter of approximately 0.122 inches, a proximal outside
diameter of
approximately 0.087 inches, a distal inside diameter of approximately 0.107
inches,
and a proximal inside diameter of approximately 0.070 inches. The ramp 172 may
be
an integral extension of the exterior wall of the guide wire sleeve 160 and
may have a
length of approximately 0.090 inches and a width of approximately 0.50 inches.
The
ramp 172 may extend into the lumen 166 at an angle of approximately 30 degrees
to a
point approximately 0.14 inches away from the opposite wall.
The guide wire sleeve 160 may be an intrigal part of the outer tubular member
140 but is preferably a separately manufactured component. For example, the
guide
wire sleeve 160 may be formed of injection molded nylon or polypropylene. If
the
guide wire sleeve 160 is injection molded, manufacturing artifacts such as
hole 168
may be filled or removed depending on the particular application. By
manufacturing
the guide wire sleeve 160 separately, more manufacturing flexibility and
efficiency
are achieved. For example, the guide wire sleeve 160 may be made of a material
that
is not melt sensitive or that is readily bonded to facilitate connection to
other catheter
components using adhesive or thermal means. In addition, the guide wire sleeve
160
may be inspected prior entering the production floor to eliminate non-
conforming
parts and increase efficiency. Further, the dimensions may be controlled
better to
provide greater consistency at bond sites. These and other advantages not
specifically
mentioned herein may be obtained by manufacturing the guide wire sleeve 160 as
a
separate component, but such is not essential to the present invention.
Those skilled in the art will recognize that the present invention may be
manifested in a variety of forms other than the specific embodiments described
and
contemplated herein. Accordingly, departures in form and detail may be made
without departing from the scope and spirit of the present invention as
described in
the appended claims.
-8-