Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~!-~~I ~~4~~;
CA 02410280 2002-10-29
TITLE OF INVENTION
SYSTEM OF LASER POSITIONING OF AN APERTURE
PROCESSING MACHINE
s BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of The Invention
The present invention relates to an aperture-processing machine, and in
particular, a system of laser positioning in an aperture-processing machine
used for
to locating the position of the aperture that is being processed on a work
piece
accurately.
Description of the Prior Art
15 At present, when aperture-processing machines such as the drilling machine
and lathe are used for aperture processing, in general, lines have to be drawn
on the
work piece to be processed beforehand. A centre bore is then made with a
piercing
mandrel before the aperture-processing machine is switched on for test
drilling. Based
on the result of test drill, the position of the work piece being processed is
adjusted.
2o This is repeated a number of times until the test drilled hole and the
position of the
centre bore are aligned before aperture processing is formally carried out. In
the
process, test drilling and adjustment of the position of the work piece being
processed
are usually repeated many times before an aperture with an acceptable position
can be
finalised. The adjustment is labour and time-consuming and easily leads to eye
fatigue
25 for the operating worker. Besides, it is difficult to guarantee the
precision of the
position of the aperture.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In order to overcome the existing technological shortcoming mentioned above,
3o the present invention provides a type of main bearing cutter centre of the
aperture-
processing machine that is capable of accurately marking on the work piece
being
processed. The work piece to be processed can be moved easily so that the
centre of
the aperture to be processed coincides with the cutter centre. Positioning is
~auue~iNfaic '.7dW~'
CA 02410280 2002-10-29
accomplished rapidly with a high precision and efficiency. Besides, it is a
laser
positioning in an aperture-processing machine that can effectively reduce eye
fatigue
of the operating worker.
To achieve the above-mentioned objective, the solution provided by the
present invention includes two laser-transmitting devices, each of which
transmits a
light beam. The two light beams become an angular set up. The point of their
intersection in space forms a common line of intersection. After both laser-
transmitting devices are fixed relative to the aperture-processing machine,
the
1 o common line of intersection formed at the point of intersection of the two
light beams
mentioned above coincides precisely with the axial line of the cutter centre
of the
aperture-processing machine, forming the reference for positioning.
In the present invention, the light beams transmitted by the laser
transmission
t5 devices mentioned above are planar. The relative vertical projection of the
said planar
beams is a fine, straight line. Therefore, the two planar beams should be very
thin
planes. When these two very thin planar beams intersect, the common line of
intersection will also be a very fine, straight line. When the surface of the
work piece
intersects the said straight line, the projection is a very small light dot.
As the said
2o common line of intersection coincides with the axial line of the cutter,
squaring
operation is achieved merely by aligning the position of the centre bore of
the work
piece with the said light dot. Therefore, by using the system of laser
positioning of the
present invention, it will not be necessary to repeat test drilling several
times when
carrying out aperture processing. The processing is done after direct
alignment.
A better way of applying the present invention is by fixing the two laser-
transmitting devices on the spindle box of the aperture-processing machine,
with its
transmission end facing the side of the main bearing cutter. T'he two planar
light
beams produced by them are found within the space where the main bearing
cutter is
situated.
The said spindle box can be fixed with a chassis relative to the main axial
symmetry. The laser transmitting devices are installed on the chassis.
2
:. '-."~"'"T'"~'~. a <~
CA 02410280 2002-10-29
There are holes on the fixed chassis. The laser transmission devices are
installed in the holes on the fixed chassis. There are female threads or male
threads at
their tail end. A regulatory screw with corresponding male threads or female
threads
and protruded shoulder is fixed in the female or male threads. The regulatory
screw
and the laser transmission devices are elarnped on the fixed chassis with the
help of
the screw threads.
The laser transmission devices mentioned in the present invention are pen-
shaped. Usually it is possible to use a conventional pen-shaped laser
transmitter.
to However, as the light beam generated by a conventional pen-shaped laser
transmitter
is usually a cylindrical beam, in the present invention, when the conventional
laser
transmitter that is capable of generating a cylindrical beam is used, a beam
expander
is installed at the transmission end of the laser transmitter. Through this
beam
expander, the cylindrical beam is expanded into a planar beam. This
constitutes the
is laser transmission device mentioned in the present invention.
For example, the pen-shaped laser transmission device mentioned in the
present invention may include a semiconductor-laser-diode type laser
transmitter.
Near the transmitting end of this semiconductor-laser-diode type laser
transmitter, a
2o beam expander is installed. This beam expander expands the cylindrical
laser beam
given out by the semiconductor-laser-diode type laser transmitter and the pen-
shaped
laser transmission device emits a planar beam from its transmission end.
The said beam expander is composed of a convex lens and a cylindrical lens.
25 The convex lens and the cylindrical lens are set up along the line of axis
of the
cylindrical laser beam mentioned. The beam expander may also be composed of a
convex lens and a corrugated lens. The convex lens and the corrugated lens are
set up
along the line of axis of the cylindrical laser beam mentioned or other forms
of beam
expander may be used to achieve the performance set by the present invention.
3o Besides, the laser transmitter of the present invention can be other forms
of laser
transmitters.
When installing the present invention, it is necessary to adjust the position
of
installation of the two laser transmission devices. Firstly, the two planar
beams
3
..~~.,>, ._ , z ......._.~.__
~,, -,.~--..
d?~,.".l~F~ '..',t '~'II
CA 02410280 2002-10-29
generated by them must be able to form an angular set up to guarantee the
production
of a common line of intersection when they intersect in the space. The angle
of the
laser transmission device is further adjusted to finally bring about precise
coincidence
of the common line of intersection of the two planar beams and the main
bearing
cutter centre of the aperture-processing machine. Therefore, the position of
the
aperture being processed can be accurately determined with high precision and
rapidity. The problem of several times of adjustment and testing is resolved.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, there are holes on the
to fixed chassis for installing the laser transmission device. The laser
transmission
device is pen-shaped, with female or male threads at its tail end. A
regulatory screw
with corresponding male threads or female threads and protruded shoulder is
fixed in
the female or male threads. The regulatory screw and the tail end of the laser
transmission devices are clamped on the fixed chassis with the help of the
screw
threads.
Adjusting the laser transmission device of the present invention can be
achieved as follows: When the regulatory screw is loosened, the laser
transmission
devices can be made to revolve on the fixed chassis together with the
regulatory screw
2o until the line of intersection produced by the intersecting fine, straight-
line light
beams from both the left and right laser transmission devices coincides
precisely with
the main bearing cutter centre of the aperture-processing machine. The laser
transmission devices are then fixed by hand until they stop moving. The
regulatory
screw is then turned tight. Upon completion of adjustment, the intersecting
line that is
in precise coincidence with the main bearing cutter centre is perpendicular to
the
operating platform. Regardless of the height of the work piece, the centre
marked on
the work piece will always be the cutter centre. Processing can be done
clearly and
precisely. Based on the theory of adjustment of the present invention, it is
also
possible to use other regulatory structures and not restricted to the use of a
regulatory
3o screw of the present invention.
The present invention has the advantages of rapidity, accuracy, low cost and
ease of use. It can
be used widely in processing machines such as drilling machines, lathes and
boring lathes.
4
7~.3::: ~~ i'~~:'.... ...
CA 02410280 2002-10-29
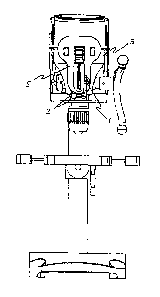
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is a schematic view showing the installation of the present
invention.
Figure 2 is the lateral view of Figure 1 in accordance with the present
invention.
s Figure 3 is a schematic view showing the principle of operation in
accordance
with the present invention.
Figure 4 is a schematic view showing the structure of the present invention.
Figure 5 is a schematic view showing the optical theory of the present
invention.
to Figure 6 is a schematic diagram showing the laser transmission device in
accordance with the present invention.
Figure 7 is a schematic view showing another preferred embodiment of a laser
transmission device in accordance with the present invention.
is DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
Preferred embodiment 1
The present invention is a type of system of laser positioning of an aperture-
processing machine. As shown in Figure 5, there are two laser transmission
devices
(2). Each laser transmission device (2) emits a light beam (13). The two light
beams
2o (13) form an angular set up. Their point of intersection in space forms a
common line
of intersection (8). After both laser transmitting devices (2) are fixed
relative to the
aperture-processing machine, the common line of intersection (8) formed at the
point
of intersection of the two light beams (13) mentioned above coincides exactly
with
the axial line of the cutter centre of the aperture-processing machine,
forming the
25 point of reference for positioning.
In the present invention, the light beams (13) transmitted by the laser
transmission devices (2) mentioned above are planar. The relative vertical
projection
of the said planar beam (13) is a fine, straight line (9). Therefore, the two
planar
3o beams (13) should be a very thin plane. When these two very thin planar
beams (13)
intersect, the common line of intersection (8) will also be a very fine,
straight line.
When the surface of the work piece intersects the said straight line, the
projection is a
very small light dot (14). As the said common line of intersection (8)
coincides with
,~~,- ,~,,.:~,~< ..., ..__.__...____
:~::1~~!~~~~, 9 ., xy
CA 02410280 2002-10-29
the axial line of the cutter, squaring operation is achieved merely by
aligning the
position of the centre bore of the work piece with the said light dot ( 14).
Therefore, by
using the system of laser positioning of the present invention, it will not be
necessary
to repeat test drilling several times when carrying out aperture processing.
The
processing is done after direct alignment. As the above-mentioned light point
(14) is
situated at an arbitrary height on the common line of intersection (8), the
present
invention is applicable to a work piece at an arbitrary height.
As shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, the present invention should be installed
to relative to the aperture-processing machine. In the present preferred
embodiment, the
aperture-processing machine is a type of drill machine. The system of
positioning in
the present invention can be fixed and linked to a spindle box (3). In the
present
preferred embodiment, two fixed chassises (1) can be installed on the spindle
box (3)
relative to the main axis symmetry. The laser transmission devices in the
present
invention are installed on the said fixed chassis (1). The transmitting end of
the said
laser transmission devices (2) face the side of the main bearing cutter. In
this way, the
light beams (13) emitted will fall within the space where the main bearing
cutter is.
When installing the present invention, it is necessary to adjust the position
of
2o installation of the two laser transmission devices (2). Firstly, the two
planar beams
(13) generated by them must be able to form an angular set up to guarantee the
production of a common line of intersection when they intersect in the space.
The
angle of the laser transmission device (2) is further adjusted to bring about
precise
coincidence of the common line of intersection (8) of the two planar beams
(13) and
the main bearing cutter centre of the aperture-processing machines. Therefore,
the
position of the aperture being processed can be accurately determined with
high
precision and rapidity. The problem of several times of adjustment and testing
is
resolved.
3o As shown in Figure 4, there are holes on the fixed chassis (I). Each laser
transmission device (2) is installed in the hole of the fixed chassis ( 1 ).
The tail end of
the device has female threads or male threads (7). A regulatory screw (6) with
corresponding male threads or female threads and a protruding shoulder is
installed in
the female or male threads (7). The regulatory screw (6) and the laser
transmission
6
--~-.....-__._. ._._........._"~....,....._....-~m..._
.~&l;v'~~:F~'~ " r'?.....
CA 02410280 2002-10-29
devices (2) are clamped on the chassises (1) with the help of the screw
threads. Figure
4 shows the dismounted front cover of the spindle box (3) of the aperture-
processing
machine. The tail end of the laser transmission device (2) and the regulatory
screw (6)
are clamped on the fixed chassis (1), tightened by the female and male threads
(7). By
loosening the regulatory screw (6), the angle of its axial plane can be
adjusted along
its axial line, thus adjusting the direction and position of the two planar
light beams.
The theory of the present invention is shown in Figure 3. The light planes
emitted by the laser transmission devices (2), that is, the position of
installation of the
t o axial plane along its axial line has an angle of intersection. The devices
are located
above the working platform of the aperture-processing machine. The two light
planes
intersect the operating platform, forming a fine, straight-line laser light
(9)
respectively. The two fine, straight-line laser light (9) have a light spot of
intersection
on the operating platform. The light spot is on the 0 spot on the central line
of the
t5 main bearing cutter. This is also the centre of the hole to be processed on
the work
piece.
As shown in Figure 6, in the present preferred embodiment, a type of laser
transmission equipment (10) made of a semiconductor laser diode tube is used.
It is
2o able to transmit an extremely fine, cylindrical beam of light (15). On the
same axis as
the cylindrical light beam (IS), a beam expander is installed. In the present
preferred
embodiment, the beam expander mentioned is composed of a convex lens (11) and
a
cylindrical lens (12). The convex (I 1) lens and cylindrical lens (12) are
installed along
the axial line of the cylindrical laser beam mentioned above. After
penetrating the set
25 of beam expander, the said cylindrical light beam ( 15) is expanded to
become a planar
light beam (13) for emission.
When using the present invention, the regulatory screw (6) is loosened. The
laser transmission devices can be made to revolve on the fixed chassis
together with
3o the regulatory screw (6) until the common line of intersection (8) of the
planar light
beams emitted by both the left and right laser transmission devices (13)
coincides
precisely with the central line of the main bearing cutter of the aperture-
processing
machine. The laser transmission devices are then fixed by hand until they stop
moving. The regulatory screw is then turned tight. Regardless of the height of
the
7
-~--_--w,-,~r x-~ ,~.~.....~.,..~., -
i.~ v.~x~ Wt 3' ' w9E
CA 02410280 2002-10-29
work piece, the centre of the aperture to be drilled marked on the work piece
will
always be on the central line of the cutter. It is obvious and accurate during
processing.
In the present preferred embodiment, it is also possible to achieve the
regulation of position of the plane of the light beams (13) by adjusting the
angle of the
cylindrical lens (12) and the cylindrical laser beam (15), thus adjusting the
common
line of intersection (8) of the light beam planes and the axial line of the
main bearing
cutter of the said aperture-processing machine so that they coincide exactly,
forming
the point of reference for positioning.
In the present preferred embodiment, the aperture-processing machine can also
be a boring lathe.
t5 In the course of application of the present invention, adjustment is easy,
positioning is rapid and observation is direct with high accuracy and low
cost. It can
be used widely in processing machines such as drilling machines, boring lathes
and
lathes.
2o Preferred embodiment 2
As shown in Figure 7, the difference between the present example and the
above-mentioned example lies in the fact that the said laser transmission
device (2)
can be composed of a semiconductor-laser-diode-type laser transmitter ( 10)
and beam
25 expander. The beam expander can be composed of a convex lens (11) and a
corrugated lens ( 16). The convex lens ( 11 ) and the corrugated lens ( 16)
are set up
along the axial line of the cylindrical laser beam mentioned. The
semiconductor-laser-
diode-type laser transmitter (10) can emit an extremely fine cylindrical beam
(15).
After penetrating through the said beam expander, this cylindrical beam (15)
is
3o expanded to become a planar light beam (13) and emitted.
In the present preferred embodiment, it is possible to adjust the position of
the
planar light beam (13) by the way described in the preferred embodiment I. The
adjustment of position of the plane of the light beam (13) can also be
achieved
8
~~s~r~w!'~"is?~ ' ~ ,' ~,r~?In yet
CA 02410280 2002-10-29
through the regulation of the angle of the corrugated lens ( 16) and the
cylindrical laser
light beam (15), thus adjusting the common line of intersection (8) of the
light beam
planes and the axial line of the main bearing cutter of the said aperture-
processing
machine so that they coincide exactly, forming the point of reference for
positioning.
The basic structure, principle and effects of the present preferred embodiment
are the same as those for application example 1 and will not be repeated here.
Having described the invention in detail, those skilled in the art will
appreciate
to that modifications may be made of this invention without departing from its
spirit.
Therefore, it is not intended to limit the present invention only to the
preferred
embodiments illustrated and described. Rather, the scope of the invention is
to be
determined by the appended claims and their equivalents.
9