Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02423022 2003-03-21
System and method for low si ature launch of rp---jectile
Background of the invention:
In many tactical situations, and in particular in urban Warfare, there is
great
importance in reducing the signatures associated with launching a projectile.
When
launching a projectile from a tube with a rocket motor, the exhaust gases
create a
high-pressure area and significant acoustical and optical signature is
observable.
These effects preclude firing from enclosures and makes the gunner easily
detectable.
In order to reduce such unwelcome effects, closed launched systems have been
designed, which confine the gaseous products of propellant combustion between
two
pistons moving in opposite directions in the launch tube. Schnabele et al. in
US Pat.
3.771,417 and Schnabele in US Patent 3,779,130 present a design of a launching
system for firing projectiles which has since been known as the double
"trapped
piston" design. One of the piston pushes and accelerates the projectile in the
launch
direction, while the other piston pushes a counter-mass until it is ejected in
the
backward direction. The pistons move until they run into mechanical stops at
the
forward and backward end of the launch tube. Even if the weights on both sides
of the
propelling charge are carefully matched, there might be some mismatch in the
timing
of the two pistons running into the stops, resulting in possible recoil
effects that might
adversely affect accuracy and gunner safety.
In addition, since at the end of the stroke momentum is transferred from the
pistons to the tube, the tube has to be stn~cturally designed to withstand the
impulsive
tensile forces, a requirement that undoubtedly contributes to the tube weight.
Alternatively, it might be necessary to incorporate into the design a
deforming
braking device such as taught in US Patent 4,148,244 by Schnabele at al. Such
a
device adds to the complexity of the design and to its weight.
The current invention presents solutions for containing the high-pressure
gaseous products of propellant combustion without axially loading the launch
tube
and without generating recoil forces.
Summary of the invention
According to the current invention, a projectile is launched from the tube
after
being pushed by a plate, which might serve as a piston, while another plate,
which
CA 02423022 2003-03-21
2
might serve as a piston, pushes a counter-mass until it is ejected in the
backward
direction. The counter-mass consists of a flowable medium of relatively high
density.
The two plates are interconnected and the structure connecting the two end-
plates
arrests them as soon as the distance between them reaches a pre-designed
value. In
one embodiment, the interconnecting structure is a sealed bellow that contains
the
gases between the two end-plates, without at all exposing the launch tube to
the high
pressure. In another embodiment, the interconnecting structure is a multitude
of ropes,
the gases being contained between the launch tube, serving as a pressure-
vessel and
the end-plates, serving as pistons.
Description of the Fi ures
Fig. I a shows a launching system according to a first embodiment of the
invention prior to launching the projectile.
Fig. 1b shows a launching system according to a first embodiment of the
invention after launching the projectile.
Fig. 2a shows a Launching system according to a second embodiment of the
invention prior to launching the projectile.
Fig. 2b shows a launching system according to a second embodiment of the
invention after launching the projectile.
Detailed description of preferred embodiments of the inyention.
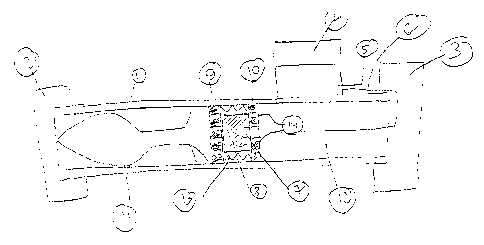
Figure 1 shows a first embodiment of the invention. The launching system
consists of a, preferably, throw-away launch tube 1 with removable covers 2,3
on both
ends. An optical sight 4 and a firing mechanism 5 are attached to launch tube
1. The
output of the firing mechanism (electric or pyrotechnic) is transferred
through an
electric conductor or a pyrotechnic cable (such as a Nonel-type pyrotechnic
cord) 6 to
the propellant ignition system 7. A propelling charge 8 is enclosed between
two
end-plates, 9,10, serving as pistons.
The projectile 11 is located ahead of the front end-plate 9 and the
counter-mass 12 which may, for example, be a flowable medium of relatively
high
density, is located behind the aft end-plate 10. The two end-plate 9,10 are
interconnected by an open connecting structure 13 consisting of several ropes
or
cables made of high-tensile strength material such as high-stxength steel or
CA 02423022 2003-03-21
3
high-strength fibers such as Kevlar or a combination thereof. If non-metallic,
the
ropes or cables might be coated with an insulating material such as rubber.
When the
gunner activates the firing mechanism 5, a signal is transferred through to
the
propellant ignition system 7. The propellant charge 8 is ignited and burns,
generating
high temperature, high pressure gases. The pressure generated within the
launch tube
1 and between the end-plates, serving as pistons 9, 10, impinges on the
pistons. The
projectile I 1 is pushed forward by end-plate 9 and subsequently ejected from
tube 1.
The counter-mass 12 is pushed backwards by end-plate 10 and is dispersed when
leaving tube 1.
The structure 13 connecting the two end-plates arrests them as soon as the
distance between them reaches a pre-designed value as determined by the
extended
length of the ropes. The ropes or cables might be of equal length or slightly
different
lengths and might vary in thickness as well. Accordingly, the arresting of the
pistons
can be spread over a certain time interval and not conducted abruptly.
In order to facilitate the dispersion of the counter-mass and in order to
gradually release the pressure between the end-plates once the projectile has
been
launched, several openings 14 such as holes or blow-out ports might be
provided in
the pistons.
Figure 2 shows a second embodiment of the invention. The elements which
are in common with the embodiment of Figure 1 are not shown, or numbered.
Reference is made herein to Figure 1 where appropriate. The launching system
consists of a, throw-away Launch tube 1 with removable covers 2,3 on both
ends. An
optical sight 4 and a firing mechanism 5 axe attached to the launch tube 1.
The output
of the firing mechanism (electric or pyrotechnic) is transferred through an
electric
conductor or a pyrotechnic cable (such as a Nonel-type pyrotechnic cord) 6 to
the
propellant ignition system 7.
A propelling charge 8 is enclosed between two end-plates 9,10 which are
connected by bellows 23. The two end-plates 9,10 together with the bellows 23
connecting them form a closed structure which serves as a pressure vessel. The
bellows are made, for example, of high-tensile strength material such as high-
strength
steel or fabric reinforced with high-strength fibers such as Kevlar or a
combination
thereof. If non-metallic, the bellows might be coated with an insulating
material such
as rubber. It should be noted that according to this second embodiment, the
launch
CA 02423022 2003-03-21
4
tube I is- not pressurized, a feature that enables a reduced-weight design.
The
end-plates 9,I0 do not serve in this case as pistons and no sealing is
required between
them and the launch tube I .
The projectile I1 is located ahead of the front end-plate 9 and the
counter-mass 12 which consists of a flowable medium of relatively high density
is
located behind the aft end-plate 10. When the gunner activates the firing
mechanism
5, a signal is transferred through to the propellant ignition system 7. The
propellant
charge 8 is ignited and burns generating high temperature, high pressure
gases. The
pressure generated within the bellows 23. and between the end-plates 9, 10
impinges
on the end-plates. The projectile II. is pushed forward by end-plate 9 and
subsequently ejected from the tube. The counter-mass 12 is pushed backwards by
end-plate 10 and is dispersed when leaving the tube.
The bellows 23 connecting the two end-plates arrests them as soon as the
distance between them reaches a pre-designed value as determined by the
extended
length of the bellows 23. It would be possible to connect the endplates with
some
high-strength ropes in addition to the bellows connection. Accordingly, the
arresting
of the end-plates can be spread over a certain time interval and not conducted
abruptly.
In order to facilitate the dispersion of the counter-mass and in order to
gradually release the pressure between the end-plates once the projectile has
been
launched, several openings 14 such as holes or blow-out ports might be
provided in
the pistons.