Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
ISOLATED HUMAN KINASE PROTEINS, NUCLEIC ACID MOLECULES
ENCODING HUMAN KINASE PROTEINS, AND USES THEREOF
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is in the field of kinase proteins that are related to
the
MAPlextracellular signal-regulated kinase subfamily, recombinant DNA
molecules, and protein
production. The present invention specifically provides novel peptides and
proteins that effect
protein phosphorylation and nucleic acid molecules encoding such peptide and
protein
molecules, all of which are useful in the development of human therapeutics
and diagnostic
compositions and methods.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Protein Kinases
Kinases regulate many different cell proliferation, differentiation, and
signaling processes
by adding phosphate groups to proteins. Uncontrolled signaling has been
implicated in a variety
of disease conditions including inflammation, cancer, arteriosclerosis, and
psoriasis. Reversible
protein phosphorylation is the main strategy for controlling activities of
eukaryotic cells. It is
estimated that more than 1000 of the 10,000 proteins active in a typical
mammalian cell are
phosphorylated. The high energy phosphate, which drives activation, is
generally transferred
from adenosine triphosphate molecules (ATP) to a particular protein by protein
kinases and
removed from that protein by protein phosphatases. Phosphorylation occurs in
response to
extracellular signals (hormones, neurotransmitters, growth and differentiation
factors, etc), cell
cycle checkpoints, and environmental or nutritional stresses and is roughly
analogous to turning
on a molecular switch. When the switch goes on, the appropriate protein kinase
activates a
metabolic enzyme, regulatory protein, receptor, cytoskeletal protein, ion
channel or pump, or
transcription factor.
The kinases comprise the largest known protein group, a superfamily of enzymes
with
widely varied functions and specificities. They are usually named after their
substrate, their
regulatory molecules, or some aspect of a mutant phenotype. With regard to
substrates, the
protein kinases may be roughly divided into two groups; those that
phosphorylate tyrosine
residues (protein tyrosine kinases, PTK) and those that phosphorylate serine
or threonine
residues (serine/threonine kinases, STK). A few protein kinases have dual
specificity and
1
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
phosphorylate threonine and tyrosine residues. Almost all kinases contain a
similar 2S0-300
amino acid catalytic domain. The N-terminal domain, which contains subdomains
I-IV,
generally folds into a two-lobed structure, which binds and orients the ATP
(or GTP) donor
molecule. The larger C terminal lobe, which contains subdomains VI A-XI, binds
the protein
substrate and carries out the transfer of the gamma phosphate from ATP to the
hydroxyl group of
a serine, threonine, or tyrosine residue. Subdomain V spans the two lobes.
The kinases may be categorized into families by the different amino acid
sequences
(generally between 5 and 100 residues) located on either side of, or inserted
into loops of, the
kinase domain. These added amino acid sequences allow the regulation of each
kinase as it
recognizes and interacts with its target protein. The primary structure of the
kinase domains is
conserved and can be further subdivided into 11 subdomains. Each of the 11
subdomains
contains specific residues and motifs or patterns of amino acids that are
characteristic of that
subdomain and axe highly conserved (Hardie, G. and Hanks, S. (1995) The
Protein Kinase Facts
Books, Vol I:7-20 Academic Press, San Diego, Calif.).
The second messenger dependent protein kinases primarily mediate the effects
of second
messengers such as cyclic AMP (cAMP), cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate,
phosphatidylinositol, 3,4,5-triphosphate, cyclic-ADPribose, arachidonic acid,
diacylglycerol and
calcium-calmodulin. The cyclic-AMP dependent protein kinases (PKA) are
important members
of the STK family. Cyclic-AMP is an intracellular mediator of hormone action
in all prokaryotic
and animal cells that have been studied. Such hormone-induced cellular
responses include
thyroid hormone secretion, cortisol secretion, progesterone secretion,
glycogen breakdown, bone
resorption, and regulation of heart rate and force of heart muscle
contraction. PKA is found in all
animal cells and is thought to account for the effects of cyclic-AMP in most
of these cells.
Altered PKA expression is implicated in a variety of disorders and diseases
including cancer,
thyroid disorders, diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease
(Isselbacher, K. J. et al.
(1994) Har~~ison's Principles of Ihte~nal Medicine, McGraw-Hill, New York,
N.Y., pp. 416-431,
1887). .
Calcium-calmodulin (CaM) dependent protein kinases are also members of STK
family.
Calmodulin is a calcium receptor that mediates many calcium regulated
processes by binding to
target proteins in response to the binding of calcium. The principle target
protein in these
processes is CaM dependent protein kinases. CaM-kinases are involved in
regulation of smooth
muscle contraction (MLC kinase), glycogen breakdown (phosphorylase kinase),
and
neurotransmission (CaM kinase I and CaM kinase II). CaM kinase I
phosphorylates a variety of
2
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
substrates including the neurotransmitter related proteins synapsin I and II,
the gene transcription
regulator, CREB, and the cystic fibrosis conductance regulator protein, CFTR
(Haribabu, B. et
al. (1995) EMBO Journal 14:3679-86). CaM II kinase also phosphorylates
synapsin at different
sites, and controls the synthesis of catecholamines in the brain through
phosphorylation and
activation of tyrosine hydroxylase. Many of the CaM kinases are activated by
phosphorylation in
addition to binding to CaM. The kinase may autophosphorylate itself, or be
phosphorylated by
another kinase as part of a "kinase cascade".
Another ligand-activated protein kinase is 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase
(AMPK)
(Gao, G. et al. (1996) J. Biol Chem. 15:8675-81). Mammalian AMPK is a
regulator of fatty acid
and sterol synthesis through phosphorylation of the enzymes acetyl-CoA
carboxylase and
hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase and mediates responses of these .pathways
to cellular
stresses such as heat shock and depletion of glucose and ATP. AMPK is a
heterotrimeric
complex comprised of a catalytic alpha subunit and two non-catalytic beta and
gamma subunits
that are believed to regulate the activity of the alpha subunit. Subunits of
AMPK have a much
wider distribution in non-lipogenic tissues such as brain, heart, spleen, and
lung than expected.
This distribution suggests that its role may extend beyond regulation of lipid
metabolism alone.
PRK (proliferation-related kinase) is a serum/cytokine inducible STK that is
involved in
regulation of the cell cycle and cell proliferation in human megakaroytic
cells (Li, B. et al.
(1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:19402-8). PRK is related to the polo (derived from
humans polo gene)
family of STKs implicated in cell division. PRK is downregulated in lung tumor
tissue and may
be a proto-oncogene whose deregulated expression in normal tissue leads to
oncogenic
transformation.
The cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs) are another group of STKs that
control the
progression of cells through the cell cycle. Cyclins are small regulatory
proteins that act by
binding to and activating CDKs that then trigger various phases of the cell
cycle by
phosphorylating and activating selected proteins involved in the mitotic
process. CDKs are
unique in that they require multiple inputs to become activated. In addition
to the binding of
cyclin, CDK activation requires the phosphorylation of a specific threonine
residue and the
dephosphorylation of a specific tyrosine residue.
Protein tyrosine kinases, PTKs, specifically phosphorylate tyrosine residues
on their
target proteins and may be divided into transmembrane, receptor PTKs and
nontransmembrane,
non-receptor PTKs. Transmembrane protein-tyrosine kinases are receptors for
most growth
factors. Binding of growth factor to the receptor activates the transfer of a
phosphate group from
3
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
ATP to selected tyrosine side chains of the receptor and other specific
proteins. Growth factors
(GF) associated with receptor PTKs include; epidermal GF, platelet-derived GF,
fibroblast GF,
hepatocyte GF, insulin and insulin-like GFs, nerve GF, vascular endothelial
GF, and macrophage
colony stimulating factor.
Non-receptor PTKs lack transmembrane regions and, instead, form complexes with
the
intracellular regions of cell surface receptors. Such receptors that function
through non-receptor
PTKs include those for cytokines, hormones (growth hormone and prolactin) and
antigen-
specific receptors on T and B lymphocytes.
Many of these PTKs were first identified as the products of mutant oncogenes
in cancer
cells where their activation was no longer subject to normal cellular
controls. In fact, about one
third of the known oncogenes encode PTKs, and it is well known that cellular
transformation
(oncogenesis) is often accompanied by increased tyrosine phosphorylation
activity (Carbonneau
H and Tonks NK (1992) Ahhu. Rev. Cell. Biol. 8:463-93). Regulation of PTK
activity may
therefore be an important strategy in controlling some types of cancer.
Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases (ERKs)/ Mito~en-Activated Protein (MAP)
Kinases
The protein provided by the present invention is a novel human mitogen-
activated protein
(MAP) kinase, also referred to as extracellular signal-regulated kinases
(ERKs). The MAP
kinases are members of the STK family. MAP kinases regulate numerous cellular
signaling
pathways and mediate signal transduction from the cell surface to the nucleus
via
phosphorylation cascades. Several subgroups have been identified, and each
manifests different
substrate specificities and responds to distinct extracellular stimuli (Egan,
S. E. and Weinberg, R.
A. (1993) Nature 365:71-7~3). MAP kinase signaling pathways are present in
mammalian cells
as well as in yeast. The extxacellular stimuli that activate mammalian
pathways include
epidermal growth factor (EGF), ultraviolet light, hyperosmolar medium, heat
shock, endotoxic
lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor
necrosis factor (TNF)
and interleukin-1 (IL-1). Altered MAP kinase expression is implicated in a
variety of disease
conditions including cancer, inflammation, immune disorders, and disorders
affecting growth
and development.
MAP kinases may be the central integration point for numerous biochemical
signals
because they are activated by a wide variety of extracellular signals, are
highly phosphorylated at
4
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
threonine and tyrosine residues, and are highly conserved between species
(Crews et al., Science
258: 478-480, 1992).
MEKl and MEK2 are also ERKs/MAP kinases. Constitutive activation of MEKl
causes
cellular transformation and therefore MEKl is an ideal drug target for
treating proliferative
diseases. Furthermore, inhibition of MEKl results in up to 80% reduction in
colon carcinoma
tumor growth, with no toxic side effects (Sebolt-Leopold et al., Nature Med.
5: 810-816, 1999).
Thus, inhibitors of MEK and other ERKs/MAP kinases are useful as safe,
effective treatments
for cancers such as colon cancer.
The ERK protein provided by the present invention shows a high degree of
structural
similarity to ERK7. ERK7 is constitutively active in serum-starved cells, and
this activity is
dependent on the presence of a C-terminal tail, which regulates the nuclear
localization and
growth inhibiting functions of ERK7. ERK7 therefore represents a novel type of
MAP kinase
characterized by the importance of interactions via its C-terminal tail,
rather than extracellular
signal-mediated activation cascades, in regulating its activity, localization,
and function (Abe et
al., Mol Cell Biol 1999 Feb;l9(2):1301-12)..
For a further review of ERKs/MAP kinases, see Crews et al., Science 258: 478-
480,
1992; Orth et al., Science 285: 1920-1923, 1999; Rampoldi et al., Cytogenet.
Cell Genet. 78:
301-303, 1997; Ryan et al., Nature 404: 892-897, 2000; Sebolt-Leopold et al.,
Nature Med. 5:
810-816, 1999; Seger et al., FASEB J. 9: 726-735, 1995; Seger et al., J. Biol.
Chem. 267: 25628-
25631, 1992; and Zheng et al., J. Biol. Chem. 268: 11435-11439, 1993.
Kinase proteins, particularly members of the MAP/extracellular signal-
regulated kinase
subfamily, are a major target for drug action and development. Accordingly, it
is valuable to the
field of pharmaceutical development to identify and characterize previously
unknown members of
this subfamily of kinase proteins. The present invention advances the state of
the art by providing
previously unidentified human kinase proteins that have homology to members of
the
MAP/extracellular signal-regulated kinase subfamily.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is based in part on the identification of amino acid
sequences of
human kinase peptides and proteins that are related to the MAP/extracellular
signal-regulated
kinase subfamily, as well as allelic variants and other mammalian orthologs
thereof. These
unique peptide sequences, and nucleic acid sequences that encode these
peptides, can be used as
5
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
models for the development of human therapeutic targets, aid in the
identification of therapeutic
proteins, and serve as targets for the development of human therapeutic agents
that modulate
kinase activity in cells and tissues that express the kinase. Experimental
data as provided in
Figure 1 indicates expression in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and
fetal), pancreas, fetal
heart, uterus, and prostate.
DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURE SHEETS
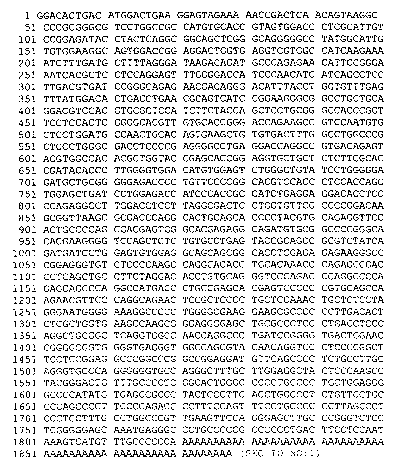
FIGURE 1 provides the nucleotide sequence of a cDNA molecule that encodes the
kinase
protein of the present invention. (SEQ ID NO:1 ) In addition, structure and
functional
information is provided, such as ATG start, stop and tissue distribution,
where available, that
allows one to readily determine specific uses of inventions based on this
molecular sequence.
Experimental data as provided in Figure 1 indicates expression in humans in
the larynx, kidney
(adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart, uterus, and prostate.
FIGURE 2 provides the predicted amino acid sequence, of the kinase of the
present
invention. (SEQ ID N0:2) In addition structure and functional information such
as protein
family, function, and modification sites is provided where available, allowing
one to readily
determine specific uses of inventions based on this molecular sequence.
FIGURE 3 provides genomic sequences that span the gene encoding the kinase
protein of
the present invention. (SEQ ID N0:3) In addition structure and functional
information, such as
intron/exon structure, promoter location, etc., is provided where available,
allowing one to
readily determine specific uses of inventions based on this molecular
sequence. As illustrated in
Figure 3, five SNPs were identified, including one SNP 5' of the ORF that may
affect
control/regulatory elements.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
General Description
The present invention is based on the sequencing of the human genome. During
the
sequencing and assembly of the human genome, analysis of the sequence
information revealed
previously unidentified fragments of the human genome that encode peptides
that share
structural andlor sequence homology to protein/peptide/domains identified and
characterized
within the art as being a kinase protein or part of a kinase protein and are
related to the
MAPlextracellular signal-regulated kinase subfamily. Utilizing these
sequences, additional
6
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
genomic sequences were assembled and transcript and/or cDNA sequences were
isolated and
characterized. Based on this analysis, the present invention provides amino
acid sequences of
human kinase peptides and proteins that are related to the MAP/extracellular
signal-regulated
kinase subfamily, nucleic acid sequences in the form of transcript sequences,
cDNA sequences
and/or genomic sequences that encode these kinase peptides and proteins,
nucleic acid variation
(allelic information), tissue distribution of expression, and information
about the closest art
known protein/peptide/domain that has structural or sequence homology to the
kinase of the
present invention.
In addition to being previously unknown, the peptides that are provided in the
present
invention are selected based on their ability to be used for the development
of commercially
important products and services. Specifically, the present peptides are
selected based on
homology and/or structural relatedness to known kinase proteins of the
MAP/extracellular
signal-regulated kinase subfamily and the expression pattern observed.
Experimental data as
provided in Figure 1 indicates expression in humans in the larynx, kidney
(adult and fetal),
pancreas, fetal heart, uterus, and prostate. The art has clearly established
the commercial
importance of members of this family of proteins and proteins that have
expression patterns
similar to that of the present gene. Some of the more specific features of the
peptides of the
present invention, and the uses thereof, are described herein, particularly in
the Background of
the Invention and in the annotation provided in the Figures, and/or are known
within the art for
each of the known MAP/extracellular signal-regulated kinase family or
subfamily of kinase
proteins.
Specific Embodiments
Peptide Molecules
The present invention provides nucleic acid sequences that encode protein
molecules that
have been identified as being members of the kinase family of proteins and are
related to the
MAP/extracellular signal-regulated kinase subfamily (protein sequences are
provided in Figure
2, transcript/cDNA sequences are provided in Figure l and genomic sequences
are provided in
Figure 3). The peptide sequences provided in Figure 2, as well as the obvious
variants described
herein, particularly allelic variants as identifed herein and using the
information in Figure 3, will
be referred herein as the kinase peptides of the present invention, kinase
peptides, or
peptideslproteins of the present invention.
7
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
The present invention provides isolated peptide and protein molecules that
consist of,
consist essentially of, or comprise the amino acid sequences of the kinase
peptides disclosed in
the Figure 2, (encoded by the nucleic acid molecule shown in Figure 1,
transcriptlcDNA or
Figure 3, genomic sequence), as well as all obvious variants of these peptides
that are within the
art to make and use. Some of these variants are described in detail below.
As used herein, a peptide is said to be "isolated" or "purified" when it is
substantially free
of cellular material or free of chemical precursors or other chemicals. The
peptides of the present
invention can be purified to homogeneity or other degrees of purity. The level
of purification will
be based on the intended use. The critical feature is that the preparation
allows for the desired
function of the peptide, even if in the presence of considerable amounts of
other components (the
features of an isolated nucleic acid molecule is discussed below).
In some uses, "substantially free of cellular material" includes preparations
of the peptide
having less than about 30% (by dry weight) other proteins (i.e., contaminating
protein), less than
about 20% other proteins, less than about 10% other proteins, or less than
about 5% other proteins.
When the peptide is recombinantly produced, it can also be substantially free
of culture medium,
i.e., culture medium represents less than about 20% of the volume of the
protein preparation.
The language "substantially free of chemical precursors or other chemicals"
includes
preparations of the peptide in which it is separated from chemical precursors
or other chemicals that
are involved in its synthesis. In one embodiment, the language "substantially
free of chemical
precursors or other chemicals" includes preparations of the kinase peptide
having less than about
30% (by dry weight) chemical precursors or other chemicals, less than about
20% chemical
precursors or other chemicals, less than about 10% chemical precursors or
other chemicals, or less
than about 5% chemical precursors or other chemicals.
The isolated kinase peptide can be purified from cells that naturally express
it, purified from
cells that have been altered to express it (recombinant), or synthesized using
known protein
synthesis methods. Experimental data as provided in Figure 1 indicates
expression in humans in the
larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart, uterus, and prostate.
For example, a nucleic
acid molecule encoding the kinase peptide is cloned into an expression vector,
the expression vector
introduced into a host cell and the protein expressed in the host cell. The
protein can then be
isolated from the cells by an appropriate purification scheme using standard
protein purification
techniques. Many of these techniques are described in detail below.
Accordingly, the present invention provides proteins that consist of the amino
acid
sequences provided in Figure 2 (SEQ ID N0:2), for example, proteins encoded by
the
8
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
transcript/cDNA nucleic acid sequences shown in Figure 1 (SEQ lD NO:1) and the
genomic
sequences provided in Figure 3 (SEQ ID N0:3). The amino acid sequence of such
a protein is
provided in Figure 2. A protein consists of an amino acid sequence when the
amino acid sequence
is the final amino acid sequence of the protein.
The present invention further provides proteins that consist essentially of
the amino acid
sequences provided in Figure 2 (SEQ lD N0:2), for example, proteins encoded by
the
transcripdcDNA nucleic acid sequences shown in Figure 1 (SEQ ID NO:1) and the
genomic
sequences provided in Figure 3 (SEQ ID N0:3). A protein consists essentially
of an amino acid
sequence when such an amino acid sequence is present with only a few
additional amino acid
residues, for example from about I to about 100 or so additional residues,
typically from 1 to about
additional residues in the final protein.
The present invention fiu~ther provides proteins that comprise the amino acid
sequences
provided in Figure 2 (SEQ ID N0:2), for example, proteins encoded by the
transcript/cDNA nucleic
acid sequences shown in Figure 1 (SEQ ID NO:1) and the genomic sequences
provided in Figure 3
15 (SEQ ID N0:3). A protein comprises an amino acid sequence when the amino
acid sequence is at
least part of the final amino acid sequence of the protein. In such a fashion,
the protein can be only
the peptide or have additional amino acid molecules, such as amino acid
residues (contiguous
encoded sequence) that are naturally associated with it or heterologous amino
acid residues/peptide
sequences. Such a protein can have a few additional amino acid residues or can
comprise several
20 hundred or more additional amino acids. The preferred classes of proteins
that are comprised of the
kinase peptides of the present invention are the naturally occurring mature
proteins. A brief
description of how various types of these proteins can be made/isolated is
provided below.
The kinase peptides of the present invention can be attached to heterologous
sequences to
form chimeric or fusion proteins. Such chimeric and fusion proteins comprise a
kinase peptide
operatively linked to a heterologous protein having an amino acid sequence not
substantially
homologous to the kinase peptide. "Operatively linked" indicates that the
kinase peptide and the
heterologous protein are fused in-frame. The heterologous protein can be fused
to the N-terminus
or C-terminus of the kinase peptide.
In some uses, the fusion protein does not affect the activity of the kinase
peptide per se. For
example, the fusion protein can include, but is not limited to, enzymatic
fusion proteins, for example
beta-galactosidase fusions, yeast two-hybrid GAL fusions, poly-His fusions,
MYC-tagged, HI
tagged and Ig fusions. Such fusion proteins, particularly poly-His fusions,
can facilitate the
9
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
purification of recombinant kinase peptide. In certain host cells (e.g.,
mammalian host cells),
expression and/or secretion of a protein can be increased by using a
heterologous signal sequence.
A chimeric or fusion protein can be produced by standard recombinant DNA
techniques.
For example, DNA fragments coding for the different protein sequences are
ligated together in
s frame in accordance with conventional techniques. In another embodiment, the
fusion gene can be
synthesized by conventional techniques including automated DNA synthesizers.
Alternatively, PCR
amplification of gene ~ fragments can be carried out using anchor primers
which give rise to
complementary overhangs between two consecutive gene fragments which can
subsequently be
annealed and re-amplified to generate a chimeric gene sequence (see Ausubel et
al., Current
Protocols ih Molecular Biolog~r, 1992). Moreover, many expression vectors are
commercially
available that already encode a fusion moiety (e.g., a GST protein). A kinase
peptide-encoding
nucleic acid can be cloned into such an expression vector such that the fusion
moiety is linked in-
frame to the kinase peptide.
As mentioned above, the present invention also provides and enables obvious
variants of the
1 S amino acid sequence of the proteins of the present invention, such as
naturally occurring mature
forms of the peptide, alleliclsequence variants of the peptides, non-naturally
occurring
recombinantly derived variants of the peptides, and orthologs and paralogs of
the peptides. Such
variants can readily be generated using art-known techniques in the fields of
recombinant nucleic
acid technology and protein biochemistry. It is understood, however, that
variants exclude any
amino acid sequences disclosed prior to the invention.
Such variants can readily be identified/made using molecular techniques and
the sequence
information disclosed herein. Further, such variants can readily be
distinguished from other
peptides based on sequence and/or structural homology to the kinase peptides
of the present
invention. The degree of homology/identity present will be based primarily on
whether the peptide
is a functional variant or non-functional variant, the amount of divergence
present in the paralog
family and the evolutionary distance between the orthologs.
To determine the percent identity of two amino acid sequences or two nucleic
acid
sequences, the sequences are aligned for optimal comparison purposes (e.g.,
gaps can be
introduced in one or both of a first and a second amino acid or nucleic acid
sequence for optimal
alignment and non-homologous sequences can be disregarded for comparison
purposes). In a
preferred embodiment, at least 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, or 90% or more of
the length
of a reference sequence is aligned for comparison purposes. The amino acid
residues or
nucleotides at corresponding amino acid positions or nucleotide positions are
then compared.
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
When a position in the first sequence is occupied by the same amino acid
residue or nucleotide
as the corresponding position in the second sequence, then the molecules are
identical at that
position (as used herein amino acid or nucleic acid "identity" is equivalent
to amino acid or
nucleic acid "homology"). The percent identity between the two sequences is a
function of the
number of identical positions shared by the sequences, taking into account the
number of gaps,
and the length of each gap, which need to be introduced for optimal alignment
of the two
sequences.
The comparison of sequences and determination of percent identity and
similarity
between two sequences can be accomplished using a mathematical algorithm.
(Computational
Molecular Biology, Lesk, A.M., ed., Oxford University Press, New York, 1988;
Biocomputing:
Informatics and Genome Projects, Smith, D.W., ed., Academic Press, New York,
1993; Computer
Analysis of Sequence Data, Part l, Griffin, A.M., and Griffin, H.G., eds.,
Humana Press, New
Jersey, 1994; Sequence Analysis in Molecular Biology, von Heinje, G., Academic
Press, 1987; and
Sequence Analysis Primer, Gribskov, M. and Devereux, J., eds., M Stockton
Press, New York,
1991). In a preferred embodiment, the percent identity between two amino acid
sequences is
determined using the Needleman and Wunsch (J. Mol. Biol. (48):444-453 (1970))
algorithm
which has been incorporated into the GAP program in the GCG software package
(available at
http://www.gcg.com), using either a Blossom 62 matrix or a PAM250 matrix, and
a gap weight
of 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, or 4 and a length weight of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6. In
yet another preferred
embodiment, the percent identity between two nucleotide sequences is
determined using the
GAP program in the GCG software package (Devereux, J., et al., Nucleic Acids
Res. 12(I):387
(1984)) (available at http://www.gcg.com), using a NWSgapdna.CMP matrix and a
gap weight of
40, 50, 60, 70, or 80 and a length weight of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6. In another
embodiment, the
percent identity between two amino acid or nucleotide sequences is determined
using the
algorithm of E. Myers and W. Miller (CABIOS, 4:11-17 (1989)) which has been
incorporated
into the ALIGN program (version 2.0), using a PAM120 weight residue table, a
gap length
penalty of 12 and a gap penalty of 4.
The nucleic acid and protein sequences of the present invention can further be
used as a
"query sequence" to perform a search against sequence databases to, for
example, identify other
family members or related sequences. Such seaxches can be performed using the
NBLAST and
XBLAST programs (version 2.0) of Altschul, et al. (J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-10
(1990)). BLAST
nucleotide searches can be performed with the NBLAST program, score = 100,
wordlength = 12
to obtain nucleotide sequences homologous to the nucleic acid molecules of the
invention.
11
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
BLAST protein searches can be performed with the XBLAST program, score = 50,
wordlength =
3 to obtain amino acid sequences homologous to the proteins of the invention.
To obtain gapped
alignments for comparison purposes, Gapped BLAST can be utilized as described
in Altschul et
al. (Nucleic Acids Res. 25(17):3389-3402 (1997)). When utilizing BLAST and
gapped BLAST
programs, the default parameters of the respective programs (e.g., XBLAST and
NBLAST) can
be used.
Full-length pre-processed forms, as well as mature processed forms, of
proteins that
comprise one of the peptides of the present invention can readily be
identified as having complete
sequence identity to one of the kinase peptides of the present invention as
well as being encoded by
the same genetic locus as the kinase peptide provided herein. The gene
provided by the present
invention is located on a genome component that has been mapped to human
chromosome 8 (as
indicated in Figure 3), which is supported by multiple lines of evidence, such
as STS and BAC map
data.
Allelic variants of a kinase peptide can readily be identified as being a
human protein having
a high degree (significant) of sequence homology/identity to at least a
portion of the kinase peptide
as well as being encoded by the same genetic locus as the kinase peptide
provided herein. Genetic
locus can readily be determined based on the genomic information provided in
Figure 3, such as the
genomic sequence mapped to the reference human. The gene provided by the
present invention is
located on a genome component that has been mapped to human chromosome 8 (as
indicated in
Figure 3), which is supported by multiple lines of evidence, such as STS and
BAC map data. As
used herein, two proteins (or a region of the proteins) have significant
homology when the amino
acid sequences are typically at least about 70-80%, 80-90%, and more typically
at least about 90-
95% or more homologous. A significantly homologous amino acid sequence,
according to the
present invention, will be encoded by a nucleic acid sequence that will
hybridize to a kinase
peptide encoding nucleic acid molecule under stringent conditions as more
fully described
below.
Figure 3 provides information on SNPs that have been found in the gene
encoding the
kinase protein of the present invention. The following variations were
identified: T1004G,
G1822T, A2023G, A2562G, and C6624A. SNPs such as these that are located in
introns and 5'
of the ORF may affect control/regulatory elements.
Paralogs of a kinase peptide can readily be identified as having some degree
of significant
sequence homology/identity to at least a portion of the kinase peptide, as
being encoded by a gene
from humans, and as having similar activity or function. Two proteins will
typically be considered
12
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
paralogs when the amino acid sequences are typically at least about 60% or
greater, and more
typically at least about 70% or greater homology through a given region or
domain. Such
paralogs will be encoded by a nucleic acid sequence that will hybridize to a
kinase peptide
encoding nucleic acid molecule under moderate to stringent conditions as more
fully described
below.
Orthologs of a kinase peptide can readily be identified as having some degree
of significant
sequence homology/identity to at least a portion of the kinase peptide as well
as being encoded by a
gene from another organism. Preferred orthologs will be isolated from mammals,
preferably
primates, for the development of human therapeutic targets and agents. Such
orthologs will be
encoded by a nucleic acid sequence that will hybridize to a kinase peptide
encoding nucleic acid
molecule under moderate to stringent conditions, as more fully described
below, depending on
the degree of relatedness of the two organisms yielding the proteins.
Non-naturally occurring variants of the kinase peptides of the present
invention can readily
be generated using recombinant techniques. Such variants include, but are not
limited to deletions,
additions and substitutions in the amino acid sequence of the kinase peptide.
For example, one class
of substitutions are conserved amino acid substitution. Such substitutions are
those that substitute a
given amino acid in a kinase peptide by another amino acid of like
characteristics. Typically seen
as conservative substitutions are the replacements, one for another, among the
aliphatic amino acids
Ala, Val, Leu, and Ile; interchange of the hydxoxyl residues Ser and Thr;
exchange of the acidic
residues Asp and Glu; substitution between the amide residues Asn and Gln;
exchange of the basic
residues Lys and Arg; and replacements among the aromatic residues Phe and
Tyr. Guidance
concerning which amino acid changes are likely to be phenotypically silent are
found in Bowie et
al., Science 247:1306-1310 (1990).
Variant kinase peptides can be fully functional or can lack function in one or
more activities,
e.g. ability to bind substrate, ability to phosphorylate substrate, ability to
mediate signaling, etc.
Fully functional variants typically contain only conservative variation or
variation in non-critical
residues or in non-critical regions. Figure 2 provides the result of protein
analysis and can be used
to identify critical domainslregions. Functional variants can also contain
substitution of similar
amino acids that result in no change or an insignificant change in function.
Alternatively, such
substitutions may positively or negatively affect function to some degree.
Non-functional variants typically contain one or more non-conservative amino
acid
substitutions, deletions, insertions, inversions, or truncation or a
substitution, insertion, inversion, or
deletion in a critical residue or critical region.
13
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
Amino acids that are essential for function can be identified by methods known
in the art,
such as site-directed mutagenesis or alanine-scanning mutagenesis (Cunningham
et al., Science
244:1081-1085 (1989)), particularly using the results provided in Figure 2.
The latter procedure
introduces single alanine mutations at every residue in the molecule. The
resulting mutant
molecules are then tested for biological activity such as kinase activity or
in assays such as an ih
vitro proliferative activity. Sites that are critical for binding
partner/substrate binding can also be
determined by structural analysis such as crystallization, nuclear magnetic
resonance or
photoaffinity labeling (Smith et al., J. Mol. Biol. 224:899-904 (1992); de Vos
et al. Science
255:306-312 (1992)).
The present invention further provides fragments of the kinase peptides, in
addition to
proteins and peptides that comprise and consist of such fragments,
particularly those comprising the
residues identified in Figure 2. The fragments to which the invention
pertains, however, are not to
be construed as encompassing fragments that may be disclosed publicly prior to
the present
invention.
As used herein, a fragment comprises at least 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, or more
contiguous amino
acid residues from a kinase peptide. Such fragments can be chosen based on the
ability to retain one
or more of the biological activities of the kinase peptide or could be chosen
for the ability to
perform a function, e.g. bind a substrate or act as an imrnunogen.
Particularly important fragments
are biologically active fragments, peptides that are, for example, about 8 or
more amino acids in
length. Such fragments will typically comprise a domain or motif of the kinase
peptide, e.g., active
site, a transmembrane domain or a substrate-binding domain. Further, possible
fragments include,
but are not limited to, domain or motif containing fragments, soluble peptide
fragments, and
fragments containing immunogenic structures. Predicted domains and functional
sites are readily
identifiable by computer programs well known and readily available to those of
skill in the art (e.g.,
PROSITE analysis). The results of one such analysis are provided in Figure 2.
Polypeptides often contain amino acids other than the 20 amino acids commonly
referred to
as the 20 naturally occurring amino acids. Further, many amino acids,
including the terminal amino
acids, may be modified by natural processes, such as processing and other post-
translational
modifications, or by chemical modification techniques well known in the art.
Common
modifications that occur naturally in kinase peptides are described in basic
texts, detailed
monographs, and the research literature, and they are well known to those of
skill in the art (some of
these features are identified in Figure 2).
14
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
Known modifications include, but are not limited to, acetylation, acylation,
ADP-
ribosylation, amidation, covalent attachment of flavin, covalent attachment of
a heme moiety,
covalent attachment of a nucleotide or nucleotide derivative, covalent
attachment of a lipid or lipid
derivative, covalent attachment of phosphotidylinositol, cross-linking,
cyclization, disulfide bond
formation, demethylation, formation of covalent crosslinlcs, formation of
cystine, formation of
pyroglutamate, formylation, gamma carboxylation, glycosylation, GPI anchor
formation,
hydroxylation, iodination, methylation, myristoylation, oxidation, proteolytic
processing,
phosphorylation, prenylation, racemization, selenoylation, sulfation, transfer-
RNA mediated
addition of amino acids to proteins such as arginylation, and ubiquitination.
Such modifications are well known to those of skill in the art and have been
described in
great detail in the scientific literature. Several particularly common
modifications, glycosylation,
lipid attachment, sulfation, gamma-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues,
hydroxylation and
ADP-ribosylation, for instance, are described in most basic texts, such as
Proteins - Structure ahd
Molecular Properties, 2nd Ed., T.E. Creighton, W. H. Freeman and Company, New
York (1993).
Many detailed reviews are available on this subject, such as by Wold, F.,
Posttrar~slational Covalent
Modification of Proteins, B.C. Johnson, Ed., Academic Press, New York 1-12
(1983); Seifter et al.
(Meth. Eraz~mol. 182: 626-646 (1990)) and Rattan et al. (Anh. N. Y. Acad. Sci.
663:48-62 (1992)).
Accordingly, the kinase peptides of the present invention also encompass
derivatives or
analogs in which a substituted amino acid residue is not one encoded by the
genetic code, in which
a substituent group is included, in which the mature kinase peptide is fixsed
with another compound,
such as a compound to increase the half life of the kinase peptide (for
example, polyethylene
glycol), or in which the additional amino acids are fused to the mature kinase
peptide, such as a
leader or secretory sequence or a sequence for purification of the mature
kinase peptide or a pro-
protein sequence.
Protein/Peptide Uses
The proteins of the present invention can be used in substantial and specific
assays
related to the functional information provided in the Figures; to raise
antibodies or to elicit
another immune response; as a reagent (including the labeled reagent) in
assays designed to
quantitatively determine levels of the protein (or its binding partner or
ligand) in biological
fluids; and as markers for tissues in which the corresponding protein is
preferentially expressed
(either constitutively or at a particular stage of tissue differentiation or
development or in a
disease state). Where the protein binds or potentially binds to another
protein or ligand (such as,
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
for example, in a kinase-efFector protein interaction or kinase-ligand
interaction), the protein can
be used to identify the binding partner/ligand so as to develop a system to
identify inhibitors of
the binding interaction. Any or all of these uses are capable of being
developed into reagent
grade or kit format for commercialization as commercial products.
Methods for performing the uses listed above are well known to those skilled
in the art.
References disclosing such methods include "Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory
Manual", 2d ed.,
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Sambrook, J., E. F. Fritsch and T.
Maniatis eds., 1989,
and "Methods in Enzymology: Guide to Molecular Cloning Techniques", Academic
Press,
Berger, S. L. and A. R. Kimmel eds., 1987.
The potential uses of the peptides of the present invention are based
primarily on the
source of the protein as well as the class/action of the protein. For example,
kinases isolated
from humans and their human/mammalian orthologs serve as targets for
identifying agents for
use in mammalian therapeutic applications, e.g. a human drug, particularly in
modulating a
biological or pathological response in a cell or tissue that expresses the
kinase. Experimental data
as provided in Figure 1 indicates that kinase proteins of the present
invention are expressed in
humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart, uterus,
and prostate.
Specifically, a virtual northern blot shows expression in the larynx, kidney,
and pancreas. In
addition, PCR-based tissue screening panels indicate expression in the fetal
heart, fetal kidney,
uterus, prostate, and pancreas. A large percentage of pharmaceutical agents
are being developed
that modulate the activity of kinase proteins, particularly members of the
MAP/extracellular
signal-regulated kinase subfamily (see Background of the Invention). The
structural and
functional information provided in the Background and Figures provide specific
and substantial
uses for the molecules of the present invention, particularly in combination
with the expression
information provided in Figure 1. Experimental data as provided in Figure 1
indicates expression
in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart,
uterus, and prostate. Such
uses can readily be determined using the information provided herein, that
which is known in the
art, and routine experimentation.
The proteins of the present invention (including variants and fragments that
may have been
disclosed prior to the present invention) are useful for biological assays
related to kinases that are
related to members of the MAP/extracellular signal-regulated kinase subfamily.
Such assays
involve any of the known kinase functions or activities or properties useful
for diagnosis and
treatment of kinase-related conditions that are specific for the subfamily of
kinases that the one of
the present invention belongs to, particularly in cells and tissues that
express the kinase.
16
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
Experimental data as provided in Figure 1 indicates that kinase proteins of
the present invention are
expressed in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal
heart, uterus, and
prostate. Specifically, a virtual northern blot shows expression in the
larynx, kidney, and pancreas.
In addition, PCR-based tissue screening panels indicate expression in the
fetal heart, fetal kidney,
uterus, prostate, and pancreas.
The proteins of the present invention are also useful in drug screening
assays, in cell-based
or cell-free systems. Cell-based systems can be native, i.e., cells that
normally express the kinase,
as a biopsy or expanded in cell culture. Experimental data as provided in
Figure 1 indicates
expression in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal
heart, uterus, and
prostate. In an alternate embodiment, cell-based assays involve recombinant
host cells expressing
the kinase protein.
The polypeptides can be used to identify compounds that modulate kinase
activity of the .
protein in its natural state or an altered form that causes a specific disease
or pathology associated
with the kinase. Both the kinases of the present invention and appropriate
variants and fragments
can be used in high-throughput screens to assay candidate compounds for the
ability to bind to the
kinase. These compounds can be fiu ther screened against a functional kinase
to determine the
effect of the compound on the kinase activity. Further, these compounds can be
tested in animal or
invertebrate systems to determine activity/effectiveness. Compounds can be
identified that activate
(agonist) or inactivate (antagonist) the kinase to a desired degree.
Further, the proteins of the present invention can be used to screen a
compound for the
ability to stimulate or inhibit interaction between the kinase protein and a
molecule that normally
interacts with the kinase protein, e.g. a substrate or a component of the
signal pathway that the
kinase protein normally interacts (for example, another kinase). Such assays
typically include the
steps of combining the kinase protein with a candidate compound under
conditions that allow the
kinase protein, or fragment, to interact with the target molecule, and to
detect the formation of a
complex between the protein and the target or to detect the biochemical
consequence of the
interaction with the kinase protein and the target, such as any of the
associated effects of signal
transduction such as protein phosphorylation, cAMP turnover, and adenylate
cyclase activation, etc.
Candidate compounds include, for example, 1) peptides such as soluble
peptides, including
Ig-tailed fusion peptides and members of random peptide libraries (see, e.g.,
Lam et al., Nature
354:82-84 (1991); Houghten et al., Nature 354:84-86 (1991)) and combinatorial
chemistry-derived
molecular libraries made of D- and/or L- configuration amino acids; 2)
phosphopeptides (e.g.,
members of random and partially degenerate, directed phosphopeptide libraries,
see, e.g., Songyang
17
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
et al., Cell 72:767-778 (1993)); 3) antibodies (e.g., polyclonal, monoclonal,
humanized, anti-
idiotypic, chimeric, and single chain antibodies as well as Fab, F(ab')2, Fab
expression library
fragments, and epitope-binding fragments of antibodies); and 4) small organic
and inorganic
molecules (e.g., molecules obtained from combinatorial and natural product
libraries).
One candidate compound is a soluble fragment of the receptor that competes for
substrate
binding. Other candidate compounds include mutant kinases or appropriate
fragments containing
mutations that affect kinase function and thus compete for substrate.
Accordingly, a fragment that
competes for substrate, for example with a higher affinity, or a fragment that
binds substrate but
does not allow release, is encompassed by the invention.
The invention further includes other end point assays to identify compounds
that modulate
(stimulate or inhibit) kinase activity. The assays typically involve an assay
of events in the signal
transduction pathway that indicate kinase activity. Thus, the phosphorylation
of a substrate,
activation of a protein, a change in the expression of genes that are up- or
down-regulated in
response to the kinase protein dependent signal cascade can be assayed.
Any of the biological or biochemical functions mediated by the kinase can be
used as an
endpoint assay. These include all of the biochemical or biochemical/biological
events described
herein, in the references cited herein, incorporated by reference for these
endpoint assay targets, and
other functions known to those of ordinary skill in the art or that can be
readily identified using the
information provided in the Figures, particularly Figure 2. Specifically, a
biological function of a
cell or tissues that expresses the kinase can be assayed. Experimental data as
provided in Figure 1
indicates that kinase proteins of the present invention are expressed in
humans in the larynx, kidney
(adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart, uterus, and prostate. Specifically,
a virtual northern blot
shows expression in the larynx, kidney, and pancreas. In addition, PCR-based
tissue screening
panels indicate expression in the fetal heart, fetal kidney, uterus, prostate,
and pancreas.
Binding and/or activating compounds can also be screened by using chimeric
kinase
proteins in which the amino terminal extracellular domain, or parts thereof,
the entire
transmembrane domain or subregions, such as any of the seven transmembrane
segments or any of
the intracellular or extracellular loops and the carboxy terminal
intracellular domain, or parts
thereof, can be replaced by heterologous domains or subregions. For example, a
substrate-binding
region can be used that interacts with a different substrate then that which
is recognized by the
native kinase. Accordingly, a different set of signal transduction components
is available as an end-
point assay for activation. This allows for assays to be performed in other
than the specific host cell
from which the kinase is derived.
18
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
The proteins of the present invention are also useful in competition binding
assays in
methods designed to discover compounds that interact with the kinase (e.g.
binding partners andlor
ligands). Thus, a compound is exposed to a kinase polypeptide under conditions
that allow the
compound to bind or to otherwise interact with the polypeptide. Soluble kinase
polypeptide is also
added to the mixture. If the test compound interacts with the soluble kinase
polypeptide, it
decreases the amount of complex formed or activity from the kinase target.
This type of assay is
particularly useful in cases in which compounds are sought that interact with
specific regions of the
kinase. Thus, the soluble polypeptide that competes with the target kinase
region is designed to
contain peptide sequences corresponding to the region of interest.
To perform cell free drug screening assays, it is sometimes desirable to
immobilize either
the kinase protein, or fragment, or its target molecule to facilitate
separation of complexes from
uncomplexed forms of one or both of the proteins, as well as to accommodate
automation of the
assay.
Techniques for immobilizing proteins on matrices can be used in the drug
screening assays.
In one embodiment, a fusion protein can be provided which adds a domain that
allows the protein to
be bound to a matrix. For example, glutathione-S-transferase fusion proteins
can be adsorbed onto
glutathione sepharose beads (Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, MO) or glutathione
derivatized microtitre
plates, which are then combined with the cell lysates (e.g., 35S-labeled) and
the candidate
compound, and the mixture incubated under conditions conducive to complex
formation (e.g., at
physiological conditions for salt and pIT). Following incubation, the beads
are washed to remove
any unbound label, and the matrix' immobilized and radiolabel determined
directly, or in the
supernatant after the complexes are dissociated. Alternatively, the complexes
can be dissociated
from the matrix, separated by SDS-PAGE, and the level of kinase-binding
protein found in the bead
fraction quantitated from the gel using standard electrophoretic techniques.
For example, either the
polypeptide or its target molecule can be immobilized utilizing conjugation of
biotin and
streptavidin using techniques well known in the art. Alternatively, antibodies
reactive with the
protein but which do not interfere with binding of the protein to its target
molecule can be
derivatized to the wells of the plate, and the protein trapped in the wells by
antibody conjugation.
Preparations of a kinase-binding protein and a candidate compound are
incubated in the kinase
protein-presenting wells and the amount of complex trapped in the well can be
quantitated.
Methods for detecting such complexes, in addition to those described above for
the GST-
immobilized complexes, include immunodetection of complexes using antibodies
reactive with the
kinase protein target molecule, or which are reactive with kinase protein and
compete with the
19
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
target molecule, as well as enzyme-linked assays which rely on detecting an
enzymatic activity
associated with the target molecule.
Agents that modulate one of the kinases of the present invention can be
identified using one
or more of the above assays, alone or in combination. It is generally
preferable to use a cell-based
or cell free system first and then confirm activity in an animal or other
model system. Such model
systems are well known in the art and can readily be employed in this context.
Modulators of kinase protein activity identified according to these drug
screening assays can
be used to treat a subject with a disorder mediated by the kinase pathway, by
treating cells or tissues
that express the kinase. Experimental data as provided in Figure 1 indicates
expression in humans in
the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart, uterus, and
prostate. These methods of
treatment include the steps of administering a modulator of kinase activity in
a pharmaceutical
composition to a subject in need of such treatment, the modulator being
identified as described
herein.
In yet another aspect of the invention, the kinase proteins can be used as
"bait proteins" in
a two-hybrid assay or three-hybrid assay (see, e.g., LT.S. Patent No.
5,283,317; Zervos et al.
(1993) Cell 72:223-232; Madura et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:12046-12054;
Bartel et al.
(1993) Biotech~ciques 14:920-924; Iwabuchi et al. (1993) Oncogehe 8:1693-1696;
and Brent
W094/10300), to identify other proteins, which bind to or interact with the
kinase and are
involved in kinase activity. Such kinase-binding proteins are also likely to
be involved in the
propagation of signals by the kinase proteins or kinase targets as, for
example, downstream
elements of a kinase-mediated signaling pathway. Alternatively, such kinase-
binding proteins
are likely to be kinase inhibitors.
The two-hybrid system is based on the modular nature of most transcription
factors,
which consist of separable DNA-binding and activation domains. Briefly, the
assay utilizes two
different DNA constructs. In one construct, the gene that codes for a kinase
protein is fused to a
gene encoding the DNA binding domain of a known transcription factor (e.g.,
GAL-4). In the
other construct, a DNA sequence, from a library of DNA sequences, that encodes
an unidentified
protein ("prey" or "sample") is fused to a gene that codes for the activation
domain of the known
transcription factor. If the "bait" and the "prey", proteins are able to
interact, in vivo, forming a
kinase-dependent complex, the DNA-binding and activation domains of the
transcription factor
are brought into close proximity. This proximity allows transcription of a
reporter gene (e.g.,
LacZ) which is operably linked to a transcriptional regulatory site responsive
to the transcription
factor. Expression of the reporter gene can be detected and cell colonies
containing the
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
functional transcription factor can be isolated and used to obtain the cloned
gene which encodes
the protein which interacts with the kinase protein.
This invention further pertains to novel agents identified by the above-
described
screening assays. Accordingly, it is within the scope of this invention to
further use an agent
identified as described herein in an appropriate animal model. For example, an
agent identified
as described herein (e.g., a kinase-modulating agent, an antisense kinase
nucleic acid molecule, a
kinase-specific antibody, or a kinase-binding partner) can be used in an
animal or other model to
determine the efficacy, toxicity, or side effects of treatment with such an
agent. Alternatively, an
agent identified as described herein can be used in an animal or other model
to determine the
mechanism of action of such an agent. Furthermore, this invention pertains to
uses of novel
agents identified by the above-described screening assays for treatments as
described herein.
The kinase proteins of the present invention are also useful to provide a
target for
diagnosing a disease or predisposition to disease mediated by the peptide.
Accordingly, the
invention provides methods for detecting the presence, or levels of, the
protein (or encoding
mRNA) in a cell, tissue, or organism. Experimental data as provided in Figure
1 indicates
expression in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal
heart, uterus, and
prostate. The method involves contacting a biological sample with a compound
capable of
interacting with the kinase protein such that the interaction can be detected.
Such an assay can be
provided in a single detection format or a mufti-detection format such as an
antibody chip array.
One agent for detecting a protein in a sample is an antibody capable of
selectively binding to
protein. A biological sample includes tissues, cells and biological fluids
isolated from a subject, as
well as tissues, cells and fluids present within a subject.
The peptides of the present invention also provide targets for diagnosing
active protein
activity, disease, or predisposition to disease, in a patient having a variant
peptide, particularly
activities and conditions that are known for other members of the family of
proteins to which the
present one belongs. Thus, the peptide can be isolated from a biological
sample and assayed for the
presence of a genetic mutation that results in aberrant peptide. This includes
amino acid
substitution, deletion, insertion, rearrangement, (as the result of aberrant
splicing events), and
inappropriate post-translational modification. Analytic methods include
altered electrophoretic
mobility, altered tryptic peptide digest, altered kinase activity in cell-
based or cell-free assay,
alteration in substrate or antibody-binding pattern, altered isoelectric
point, direct amino acid
sequencing, and any other of the known assay techniques useful for detecting
mutations in a protein.
21
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
Such an assay can be provided in a single detection format or a mufti-
detection format such as an
antibody chip array.
In vitro techniques for detection of peptide include enzyme linked
irnmunosorbent assays
(ELISAs), Western blots, immunoprecipitations and immunofluorescence using a
detection reagent,
such as an antibody or protein binding agent. Alternatively, the peptide can
be detected in vivo in a
subject by introducing into the subject a labeled anti-peptide antibody or
other types of detection
agent. For ~ example, the antibody can be labeled with a radioactive marker
whose presence and
location in a subject can be detected by standard imaging techniques.
Particularly useful are
methods that detect the allelic variant of a peptide expressed in a subject
and methods which detect
fragments of a peptide in a sample.
The peptides are also useful in pharmacogenomic analysis. Pharmacogenomics
deal with
clinically significant hereditary variations in the response to drugs due to
altered drug disposition
and abnormal action in affected persons. See, e.g., Eichelbaum, M. (Clip. Exp.
Pha~macol. Physiol.
23(10-11):983-985 (1996)), and Linder, M.W. (Clin. Chem. 43(2):254-266
(1997)). The clinical
outcomes of these variations result in severe toxicity of therapeutic drugs in
certain individuals or
therapeutic failure of drugs in certain individuals as a result of individual
variation in metabolism.
Thus, the genotype of tie individual can determine the way a therapeutic
compound acts on the
body or the way the body metabolizes the compound. Further, the activity of
drug metabolizing
enzymes effects both the intensity and duration of drug action. Thus, the
pharmacogenomics of the
individual permit the selection of effective compounds and effective dosages
of such compounds for
prophylactic or therapeutic treatment based on the individual's genotype. The
discovery of genetic
polymorphisms in some drug metabolizing enzymes has explained why some
patients do not obtain
the expected drug effects, show an exaggerated drug effect, or experience
serious toxicity from
standard drug dosages. Polymorphisms can be expressed in the phenotype of the
extensive
metabolizes and the phenotype of the poor metabolizes. Accordingly, genetic
polymorphism may
lead to allelic protein variants of the kinase protein in which one or more of
the kinase functions in
one population is different from those in another population. The peptides
thus allow a target to
ascertain a genetic predisposition that can affect treatment modality. Thus,
in a ligand-based
treatment, polymorphism may give rise to amino terminal extracellular domains
and/or other
substrate-binding regions that are more or less active in substrate binding,
and kinase activation.
Accordingly, substrate dosage would necessarily be modified to maximize the
therapeutic effect
within a given population containing a polymorphism. As an alternative to
genotyping, specific
polymorphic peptides could be identified.
22
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
The peptides are also useful for treating a disorder characterized by an
absence of,
inappropriate, or unwanted expression of the protein. Experimental data as
provided in Figure 1
indicates expression in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal),
pancreas, fetal heart, uterus,
and prostate. Accordingly, methods for treatment include the use of the kinase
protein or fragments.
Antibodies
The invention also provides antibodies that selectively bind to one of the
peptides of the
present invention, a protein comprising such a peptide, as well as variants
and fragments thereof.
As used herein, an antibody selectively binds a target peptide when it binds
the target peptide and
does not significantly bind to unrelated proteins. An antibody is still
considered to selectively bind
a peptide even if it also binds to other proteins that are not substantially
homologous with the target
peptide so long as such proteins share homology with a fragment or domain of
the peptide target of
the antibody. In this case, it would be understood that antibody binding to
the peptide is still
selective despite some degree of cross-reactivity.
As used herein, an antibody is defined in terms consistent with that
recognized within the
art: they are mufti-subunit proteins produced by a mammalian organism in
response to an antigen
challenge. The antibodies of the present invention include polyclonal
antibodies and monoclonal
antibodies, as well as fragments of such antibodies, including, but not
limited to, Fab or F(ab')a, and
Fv fragments.
Many methods are known for generating and/or identifying antibodies to a given
target
peptide. Several such methods are described by Harlow, Antibodies, Cold Spring
Harbor Press,
(1989).
In general, to generate antibodies, an isolated peptide is used as an
immunogen and is
administered to a mammalian organism, such as a rat, rabbit or mouse. The full-
length protein, an
antigenic peptide fragment or a fusion protein can be used. Particularly
important fragments axe
those covering functional domains, such as the domains identified in Figure 2,
and domain of
sequence homology or divergence amongst the family; such as those that can
readily be identified
using protein alignment methods and as presented in the Figures. '
Antibodies axe preferably prepared from regions or discrete fragments of the
kinase
proteins: Antibodies can be prepared from any region of the peptide as
described herein.
However, preferred regions will include those involved in functionlactivity
and/or kinase/binding
partner interaction. Figure 2 can be used to identify particularly important
regions while
sequence alignment can be used to identify conserved and unique sequence
fragments.
23
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
An antigenic fragment will typically comprise at least 8 contiguous amino acid
residues.
The antigenic peptide can comprise, however, at least 10, 12, 14, 16 or more
amino acid residues.
Such fragments can be selected on a physical property, such as fragments
correspond to regions that
are located bn the surface of the protein, e.g., hydrophilic regions or can be
selected based on
sequence uniqueness (see Figure 2).
Detection on an antibody of the present invention can be facilitated by
coupling (i.e.,
physically linking) the antibody to a detectable substance. Examples of
detectable substances
include various enzymes, prosthetic groups, fluorescent materials, luminescent
materials,
bioluminescent materials, and radioactive materials. Examples of suitable
enzymes include
horseradish peroxidase, allcaline phosphatase, (3-galactosidase, or
acetylcholinesterase; examples of
suitable prosthetic group complexes include streptavidin/biotin and
avidin/biotin; examples of
suitable fluorescent materials include umbelliferone, fluorescein, fluorescein
isothiocyanate,
rhodamine, dichlorotriazinylamine fluorescein, dansyl chloride or
phycoerythrin; an example of a
luminescent material includes luminol; examples of bioluminescent materials
include luciferase,
luciferin, and aequorin, and examples of suitable radioactive material include
lasI,131h 3sS or 3H.
Antibody Uses
The antibodies can be used to isolate one of the proteins of the present
invention by standard
techniques, such as affinity chromatography or immunoprecipitation. The
antibodies can facilitate
the purification of the natural protein from cells and recombinantly produced
protein expressed in
host cells. In addition, such antibodies are useful to detect the presence of
one of the proteins of the
present invention in cells or tissues to determine the pattern of expression
of the protein among
various tissues in an organism and over the course of normal development.
Experimental data as
provided in Figure 1 indicates that kinase proteins of the present invention
are expressed in humans
in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart, uterus, and
prostate. Specifically, a
virtual northern blot shows expression in the larynx, kidney, and pancreas. In
addition, PCR-based
tissue screening panels indicate expression in the fetal heart, fetal kidney,
uterus, prostate, and
pancreas. Further, such antibodies can be used to detect protein in situ, in
vitro, or in a cell lysate or
supernatant in order to evaluate the abundance and pattern of expression.
Also, such antibodies can
be used to assess abnormal tissue distribution or abnormal expression during
development or
progression of a biological condition. Antibody detection of circulating
fragments of the full length
protein can be used to identify turnover.
24
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
Further, the antibodies can be used to assess expression in disease states
such as in active
stages of the disease or in an individual with a predisposition toward disease
related to the protein's
function. When a disorder is caused by an inappropriate tissue distribution,
developmental
expression, level of expression of the protein, or expressed/processed form,
the antibody can be
prepared against the normal protein. Experimental data as provided in Figure 1
indicates expression
in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart,
uterus, and prostate. If a
disorder is characterized by a specific mutation in the protein, antibodies
specific for this mutant
protein can be used to assay for the presence of the specific mutant protein.
The antibodies can also be used to assess normal and aberrant subcellular
localization of
cells in the various tissues in an organism. Experimental data as provided in
Figure 1 indicates
expression in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal
heart, uterus, and
prostate. The diagnostic uses can be applied, not only in genetic testing, but
also in monitoring a
treatment modality. Accordingly, where treatment is ultimately aimed at
correcting expression level
or the presence of aberrant sequence and aberrant tissue distribution or
developmental expression,
antibodies directed against the protein or relevant fragments can be used to
monitor therapeutic
efficacy.
Additionally, antibodies are useful in pharmacogenomic analysis. Thus,
antibodies prepared
against polymorphic proteins can be used to identify individuals that require
modified treaixnent
modalities. The antibodies are also useful as diagnostic tools as an
immunological marker for
aberrant protein analyzed by electrophoretic mobility, isoelectric point,
tryptic peptide digest, and
other physical assays known to those in the art.
The antibodies are also useful for tissue typing. Experimental data as
provided in Figure 1
indicates expression in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal),
pancreas, fetal heart, uterus,
and prostate. Thus, where a specific protein has been correlated with
expression in a specific
tissue, antibodies that are specific for this protein can be used to identify
a tissue type.
The antibodies are also useful for inhibiting protein function, for example,
blocking the
binding of the kinase peptide to a binding partner such as a substrate. These
uses can also be
applied in a therapeutic context in which treatment involves inhibiting the
protein's function. An
antibody can be used, for example, to block binding, thus modulating
(agonizing or antagonizing)
the peptides activity. Antibodies can be prepared against specific fragments
containing sites
required for function or against intact protein that is associated with a cell
or cell membrane. See
Figure 2 for structural information relating to the proteins of the present
invention.
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
The invention also encompasses kits for using antibodies to detect the
presence of a protein
in a biological sample. The kit can comprise antibodies such as a labeled or
labelable antibody and
a compound or agent for detecting protein in a biological sample; means for
determining the amount
of protein in the sample; means for comparing the amount of protein in the
sample with a standard;
and instructions for use. Such a kit can be supplied to detect a single
protein or epitope or can be
configured to detect one of a multitude of epitopes, such as in an antibody
detection array. Arrays
are described in detail below for nuleic acid arrays and similar methods have
been developed for
antibody arrays.
Nucleic Acid Molecules
The present invention further provides isolated nucleic acid molecules that
encode a kinase
peptide or protein of the present invention (cDNA, transcript and genomic
sequence). Such nucleic
acid molecules will consist of, consist essentially of, or comprise a
nucleotide sequence that encodes
one of the kinase peptides of the present invention, an allelic variant
thereof, or an ortholog or
paralog thereof.
As used herein, an "isolated" nucleic acid molecule is one that is separated
from other
nucleic acid present in the natural source of the nucleic acid. Preferably, an
"isolated" nucleic acid
is free of sequences which naturally flank the nucleic acid (i.e., sequences
located at the 5' and 3'
ends of the nucleic acid) in the genomic DNA of the organism from which the
nucleic acid is
derived. However, there can be some flanking nucleotide sequences, for example
up to about SKB,
4KB, 3KB, 2I~B, or 1KB or less, particularly contiguous peptide encoding
sequences and peptide
encoding sequences within the same gene but separated by introns in the
genomic sequence. The
important point is that the nucleic acid is isolated from remote and
unimportant flanking sequences
such that it can be subjected to the specific manipulations described herein
such as recombinant
expression, preparation of probes and primers, and other uses specific to the
nucleic acid sequences.
Moreover, an "isolated" nucleic acid molecule, such as a transcript/cDNA
molecule, can be
substantially free of other cellular material, or culture medium when produced
by recombinant
techniques, or chemical precursors or other chemicals when chemically
synthesized. However, the
nucleic acid molecule can be fused to other coding or regulatory sequences and
still be considered
isolated.
For example, recombinant DNA molecules contained in a vector are considered
isolated.
Further examples of isolated DNA molecules include recombinant DNA molecules
maintained in
26
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
heterologous host cells or purified (partially or substantially) DNA molecules
in solution. Isolated
RNA molecules include in vivo or in vitro RNA transcripts of the isolated DNA
molecules of the
present invention. Isolated nucleic acid molecules according to the present
invention further include
such molecules produced synthetically.
Accordingly, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules that
consist of the
nucleotide sequence shown in Figure 1 or 3 (SEQ ID NO:l, transcript sequence
and SEQ ID N0:3,
genomic sequence), or any nucleic acid molecule that encodes the protein
provided in Figure 2,
SEQ ID N0:2. A nucleic acid molecule consists of a nucleotide sequence when
the nucleotide
sequence is the complete nucleotide sequence of the nucleic acid molecule.
The present invention further provides nucleic acid molecules that consist
essentially of the
nucleotide sequence shown in Figure 1 or 3 (SEQ ID NO:l, transcript sequence
and SEQ ID N0:3,
genomic sequence), or any nucleic acid molecule that encodes the protein
provided in Figure 2,
SEQ ID N0:2. A nucleic acid molecule consists essentially of a nucleotide
sequence when such a
nucleotide sequence is present with only a few additional nucleic acid
residues in the final nucleic
acid molecule.
The present invention further provides nucleic acid molecules that comprise
the nucleotide
sequences shown in Figure 1 or 3 (SEQ ID NO:1, transcript sequence and SEQ ID
N0:3; genomic
sequence), or any nucleic acid molecule that encodes the protein provided in
Figure 2, SEQ ID
N0:2. A nucleic acid molecule comprises a nucleotide sequence when the
nucleotide sequence is at
least part of the final nucleotide sequence of the nucleic acid molecule. In
such a fashion, the
nucleic acid molecule can be only the nucleotide sequence or have additional
nucleic acid residues,
such as nucleic acid residues that are naturally associated with it or
heterologous nucleotide
sequences. Such a nucleic acid molecule can have a few additional nucleotides
or can comprises
several hundred or more additional nucleotides. A brief description of how
various types of these
nucleic acid molecules can be readily made/isolated is provided below.
In Figures 1 and 3, both coding and non-coding sequences are provided. Because
of the
source of the present invention, humans genomic sequence (Figure 3) and
cDNA/transcript
sequences (Figure 1), the nucleic acid molecules in the Figures will contain
genomic intronic
sequences, 5' and 3' non-coding sequences, gene regulatory regions and non-
coding intergenic
sequences. In general such sequence features are either noted in Figures 1 and
3 or can readily
be identified using computational tools known in the art. As discussed below,
some of the non-
coding regions, particularly gene regulatory elements such as promoters, are
useful for a variety
of purposes, e.g. control of heterologous gene expression, target for
identifying gene activity
27
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
modulating compounds, and are particularly claimed as fragments of the genomic
sequence
provided herein.
The isolated nucleic acid molecules can encode the mature protein plus
additional amino or
carboxyl-terminal amino acids, or amino acids interior to the mature peptide
(when the mature form
has more than one peptide chain, for instance). Such sequences may play a role
in processing of a
protein from precursor to a mature form, facilitate protein trafficking,
prolong or shorten protein
half life or facilitate manipulation of a protein for assay or production,
among other things. As
generally is the case in situ, the additional amino acids may be processed
away from the mature
protein by cellular enzymes.
. As mentioned above, the isolated nucleic acid molecules include, but are not
limited to, the
sequence encoding the kinase peptide alone, the sequence encoding the mature
peptide and
additional coding sequences, such as a leader or secretory sequence (e.g., a
pre-pro or pro-protein
sequence), the sequence encoding the mature peptide, with or without the
additional coding
sequences, plus additional non-coding sequences, for example introns and non-
coding 5' and 3'
sequences such as transcribed but non-translated sequences that play a role in
transcription, mRNA
processing (including splicing and polyadenylation signals), ribosome binding
and stability of
mRNA. In addition, the nucleic acid molecule may be fused to a marker sequence
encoding, for
example, a peptide that facilitates purification.
Isolated nucleic acid molecules can be in the form of RNA, such as mRNA, or in
the form
?0 DNA, including cDNA and genomic DNA obtained by cloning or produced by
chemical synthetic
techniques or by a combination thereof. The nucleic acid, especially DNA, can
be double-stranded
or single-stranded. Single-stranded nucleic acid can be the coding strand
(sense strand) or the non
coding strand (anti-sense strand).
The invention further provides nucleic acid molecules that encode fragments of
the peptides
ZS of the present invention as well as nucleic acid molecules that encode
obvious variants of the kinase
proteins of the present invention that are described above. Such nucleic acid
molecules may be
naturally occurring, such as allelic variants (same locus), paralogs
(different locus), and orthologs
(different organism), or may be constructed by recombinant DNA methods or by
chemical
synthesis. Such non-naturally occurring variants may be made by mutagenesis
techniques,
30 including those applied to nucleic acid molecules, cells,, or organisms.
Accordingly, as discussed
above, the variants can contain nucleotide substitutions, deletions,
inversions and insertions.
Variation can occur in either or both the coding and non-coding regions. The
variations can
produce both conservative and non-conservative amino acid substitutions.
28
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
The present invention further provides non-coding fragments of the nucleic
acid molecules
provided ~in Figures 1 and 3. Preferred non-coding fragments include, but are
not limited to,
promoter sequences, enhancer sequences, gene modulating sequences and gene
tern>ination
sequences. Such fragments are useful in controlling heterologous gene
expression and in
developing screens to identify gene-modulating agents. A promoter can readily
be identified as
being 5' to the ATG start site in the genomic sequence provided in Figure 3.
A fragment comprises a contiguous nucleotide sequence greater than 12 or more
nucleotides. Further, a fragment could at least 30, 40, 50, 100, 250 or 500
nucleotides in length.
The length of the fragment will be based on its intended use. For example, the
fragment can encode
epitope bearing regions of the peptide, or can be useful as DNA probes and
primers. Such
fragments can be isolated using the known nucleotide sequence to synthesize an
oligonucleotide
probe. A labeled probe can then be used to screen a cDNA library, genomic DNA
library, or
mRNA to isolate nucleic acid corresponding to the coding region. Further,
primers can be used in
PCR reactions to clone specific regions of gene.
A probe/primer typically comprises substantially a purified oligonucleotide or
oligonucleotide pair. The oligonucleotide typically comprises a region of
nucleotide sequence that
hybridizes under stringent conditions to at least about 12, 20, 25, 40, 50 or
more consecutive
nucleotides.
Orthologs, homologs, and allelic variants can be identified using methods well
known in the
art. As described in the Peptide Section, these variants comprise a nucleotide
sequence encoding a
peptide that is typically 60-70%, 70-80%, 80-90%, and more typically at least
about. 90-95% or
more homologous to the nucleotide sequence shown in the Figure sheets or a
fragment of this
sequence. Such nucleic acid molecules can readily be identified as being able
to hybridize under
moderate to stringent conditions, to the nucleotide sequence shown in the
Figure sheets or a
fragment of the sequence. Allelic variants can readily be determined by
genetic locus of the
encoding gene. The gene provided by the present invention is located on a
genome component that
has been mapped to human chromosome 8 (as indicated in Figure 3), which is
supported by
multiple lines of evidence, such as STS and BAC map data.
Figure 3 provides information on SNPs that have been found in the gene
encoding the
kinase protein of the present invention. The following variations were
identified: T1004G, G1822T,
A2023G, A2562G, and C6624A. SNPs such as these that are located in introns and
5' of the ORF
may affect control/regulatory elements.
29
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
As used herein, the term "hybridizes under stringent conditions" is intended
to describe
conditions for hybridization and washing under which nucleotide sequences
encoding a peptide at
least 60-70% homologous to each other typically remain hybridized to each
other. The conditions
can be such that sequences at least about 60%, at least about 70%, or at least
about 80% or more
homologous to each other typically remain hybridized to each other. Such
stringent conditions are
known to those killed in the art and can be found in Current Protocols ih
Molecular Biology, John
Wiley & Sons, N.Y. (1989), 6.3.1-6.3.6. ' One example of stringent
hybridization conditions are
hybridization in 6X sodium chloride/sodium citrate (SSC) at about 45C,
followed by one or more
washes in 0.2 X SSC, 0.1% SDS at 50-65C. Examples of moderate to low
stringency hybridization
conditions are well known in the art.
Nucleic Acid Molecule Uses
The nucleic acid molecules of the present invention are useful for probes,
primers, chemical
. intermediates, and in biological assays. The nucleic acid molecules are
useful as a hybridization
1 S probe for messenger RNA, transcript/cDNA and genomic DNA to isolate full-
length cDNA and
genomic clones encoding the peptide described in Figure 2 and to isolate cDNA
and genomic
clones that correspond to variants (alleles, orthologs, etc.) producing the
same or related peptides
shown in Figure 2. As illustrated in Figure 3, five SNPs were identified,
including one SNP 5' of
the ORF that may affect control/regulatory elements.
The probe can correspond to any sequence along the entire length of the
nucleic acid
molecules provided in the Figures. Accordingly, it could be derived from 5'
noncoding regions, the
coding region, and 3' noncoding regions. However, as discussed, fragments are
not to be construed
as encompassing fragments disclosed prior to the present invention.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful as primers for PCR to amplify any
given region
of a nucleic acid molecule and are useful to synthesize antisense molecules of
desired length and
sequence.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful for constructing recombinant
vectors. Such
vectors include expression vectors that express a portion of, or all of, the
peptide sequences.
Vectors also include insertion vectors, used to integrate into another nucleic
acid molecule
sequence, such as into the cellular genome, to alter in situ expression of a
gene andlor gene product.
For example, an endogenous coding sequence can be replaced via homologous
recombination with
all or part of the coding region containing one or more specifically
introduced mutations.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful for expressing antigenic portions
of the proteins.
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful as probes for determining the
chromosomal
positions of the nucleic acid molecules by means of i~ situ hybridization
methods. The gene
provided by the present invention is located on a genome component that has
been mapped to
human chromosome 8 (as indicated in Figure 3), which is supported by multiple
lines of evidence,
such as STS and BAC map data.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful in making vectors containing the
gene regulatory
regions of the nucleic acid molecules of the present invention.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful for designing ribozymes
corresponding to all, or
a part, of the mRNA produced from the nucleic acid molecules described herein.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful for making vectors that express
part, or all, of the
peptides.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful for constructing host cells
expressing a part, or
all, of the nucleic acid molecules and peptides.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful for constructing transgenic animals
expressing
all, or a part, of the nucleic acid molecules and peptides.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful as hybridization probes for
determining the
presence, level, form and distribution of nucleic acid expression.
Experimental data as provided in
Figure 1 indicates that kinase proteins of the present invention are expressed
in humans in the
larynx, kidney (adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart, uterus, and prostate.
Specifically, a virtual
northern blot shows expression in the larynx, kidney, and pancreas. In
addition, PCR-based tissue
screening panels indicate expression in the fetal heart, fetal kidney, uterus,
prostate, and pancreas.
Accordingly, the probes can be used to detect the presence of, or to determine
levels of, a specific
nucleic acid molecule in cells, tissues, and in organisms. The nucleic acid
whose level is
determined can be DNA or RNA. Accordingly, probes corresponding to the
peptides described
herein can be used to assess expression and/or gene copy number in a given
cell, tissue, or
organism. These uses are relevant for diagnosis of disorders involving an
increase or decrease in
kinase protein expression relative to normal results.
Ih vitro techniques for detection of mRNA include Northern hybridizations and
in situ
hybridizations. In vitro techniques for detecting DNA includes Southern
hybridizations and in situ
hybridization.
Probes can be used as a part of a diagnostic test kit for identifying cells or
tissues that
express a kinase protein, such as by measuring a level of a kinase-encoding
nucleic acid in a sample
of cells from a subject e.g., mRNA or genomic DNA, or determining if a kinase
gene has been
31
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
mutated. Experimental data as provided in Figure 1 indicates that kinase
proteins of the present
invention are expressed in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and fetal),
pancreas, fetal heart,
uterus, and prostate. Specifically, a virtual northern blot shows expression
in the larynx, kidney,
and pancreas. In addition, PCR-based tissue screening panels indicate
expression in the fetal heart,
fetal kidney, uterus, prostate, and pancreas.
Nucleic acid expression assays are useful for drug screening to identify
compounds that
modulate kinase nucleic acid expression.
The invention thus provides a method for identifying a compound that can be
used to treat a
disorder associated with nucleic acid expression of the kinase gene,
particularly biological and
pathological processes that are mediated by the kinase in cells and tissues
that express it.
Experimental data as provided in Figure 1 indicates expression in humans in
the larynx, kidney
(adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart, uterus, and prostate. The method
typically includes assaying
the ability of the compound to modulate the expression of the kinase nucleic
acid and thus
identifying a compound that can be used to treat a disorder characterized by
undesired kinase
nucleic acid expression. The assays can be performed in cell-based and cell-
free systems. Cell-
based assays include cells naturally expressing the kinase nucleic acid or
recombinant cells
genetically engineered to express specific nucleic acid sequences.
The assay for kinase nucleic acid expression can involve direct assay of
nucleic acid levels,
such as mRNA levels, or on collateral compounds involved in the signal
pathway. Further, the
expression of genes that are up- or down-regulated in response to the kinase
protein signal pathway
can also be assayed. In this embodiment the regulatory regions of these genes
can be operably
linked to a reporter gene such as luciferase.
Thus, modulators of kinase gene expression can be identified in a method
wherein a cell is
contacted with a candidate compound and the expression of mRNA determined. The
level of
expression of kinase rnRNA in the presence of the candidate compound is
compared to the level of
expression of kinase mRNA in the absence of the candidate compound. The
candidate compound
can then be identified as a modulator of nucleic acid expression based on this
comparison and be
used, for example to treat a disorder characterized by aberrant nucleic acid
expression. When
expression of mRNA is statistically significantly greater in the presence of
the candidate compound
than in its absence, the candidate compound is identified as a stimulator of
nucleic acid expression.
When nucleic acid expression is statistically significantly less in the
presence of the candidate
compound than in its absence, the candidate compound is identified as an
inhibitor of nucleic acid
expression.
32
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
The invention further provides methods of treatment, with the nucleic acid as
a target, using
a compound identified through drug screening as a gene modulator to modulate
kinase nucleic acid
expression in cells and tissues that express the kinase. Experimental data as
provided in Figure 1
indicates that kinase proteins of the present invention are expressed in
humans in the larynx, kidney
(adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart, uterus, and prostate. Specifically,
a virtual northern blot
shows expression in the larynx, kidney, and pancreas. In addition, PCR-based
tissue screening
panels indicate expression in the fetal heart, fetal kidney, uterus, prostate,
and pancreas. Modulation
includes both up-regulation (i.e. activation or agonization) or down-
regulation (suppression or
antagonization) or nucleic acid expression.
Alternatively, a modulator for kinase nucleic acid expression can be a small
molecule or
drug identified using the screening assays described herein as long as the
drug or small molecule
inhibits the kinase nucleic acid expression in the cells and tissues that
express the protein.
Experimental data as provided in Figure 1 indicates expression in humans in
the larynx, kidney
(adult and fetal), pancreas, fetal heart, uterus, and prostate.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful for monitoring the effectiveness of
modulating
compounds on the expression or activity of the kinase gene in clinical trials
or in a treatment
regimen. Thus, the gene expression pattern can serve as a barometer for the
continuing
effectiveness of treatment with the compound, particularly with compounds to
which a patient can
develop resistance. The gene expression pattern can also serve as a marker
indicative of a
physiological response of the affected cells to the compound. Accordingly,
such monitoring would
allow either increased administration of the compound or the administration of
alternative
compounds to which the patient has not become resistant. Similarly, if the
level of nucleic acid
expression falls below a desirable level, administration of the compound could
be commensurately
decreased.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful in diagnostic assays for
qualitative changes in
kinase nucleic acid expression, and particularly in qualitative changes that
lead to pathology. The
nucleic acid molecules can be used to detect mutations in kinase genes and
gene expression
products such as mRNA. The nucleic acid molecules can be used as hybridization
probes to detect
naturally occurring genetic mutations in the kinase gene and thereby to
determine whether a subject
with the mutation is at risk for a disorder caused by the mutation. Mutations
include deletion,
addition, or substitution of one or more nucleotides in the gene, chromosomal
rearrangement, such
as inversion or transposition, modification of genomic DNA, such as aberrant
methylation patterns
or changes in gene copy number, such as amplification. Detection of a mutated
form of the kinase
33
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
gene associated with a dysfunction provides a diagnostic tool for an active
disease or susceptibility
to disease when the disease results from overexpression, underexpression, or
altered expression of a
kinase protein.
Individuals carrying mutations in the kinase gene can be detected at the
nucleic acid level by
a variety of techniques. Figure 3 provides information on SNPs that have been
found in the gene
encoding the kinase protein of the present invention. The following variations
were identified:
T1004G, G1822T, A2023G, A2562G, and C6624A. SNPs such as these that are
located in introns
and 5' of the ORF may affect control/regulatory elements. The gene provided by
the present
invention is located on a genome component that has been mapped to human
chromosome 8 (as
indicated in Figure 3), which is supported by multiple lines of evidence, such
as STS and BAC map
data. Genomic DNA can be analyzed directly or can be amplified by using PCR
prior to analysis.
RNA or cDNA can be used in the same way. In some uses, detection of the
mutation involves the
use of a probe/primer. in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (see, e.g. U.S.
Patent Nos. 4,683,195
and 4,683,202), such as anchor PCR or RACE PCR, or, alternatively, in a
ligation chain reaction
(LCR) (see, e.g., Landegran et al., Science 241:1077-1080 (1988); and Nakazawa
et al., PNAS
91:360-364 (1994)), the latter of which can be particularly useful for
detecting point mutations in
the gene (see Abravaya et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 23:675-682 (1995)). This
method can include the
steps of collecting a sample of cells- from a patient, isolating nucleic acid
(e.g., genomic, mRNA or
both) from the cells of the sample, contacting the nucleic acid sample with
one or more primers
which specifically hybridize to a gene under conditions such that
hybridization and amplification of
the gene (if present) occurs, and detecting the presence or absence of an
amplification product, or
detecting the size of the amplification product and comparing the length to a
control sample.
Deletions and insertions can be detected by a change in size of the amplified
product compared to
the normal genotype. Point mutations can be identified by hybridizing
amplified DNA to normal
RNA or antisense DNA sequences.
Alternatively, mutations in a kinase gene can be directly identified, for
example, by
alterations in restriction enzyme digestion patterns determined.by gel
electrophoresis.
Further, sequence-specific ribozymes (IJ.S. Patent No. 5,498,531) can be used
to score for
the presence of specific mutations by development or loss of a ribozyme
cleavage site. Perfectly
matched sequences can be distinguished from mismatched sequences by nuclease
cleavage
digestion assays or by differences in melting temperature.
Sequence changes at specific locations can also be assessed by nuclease
protection assays
such as RNase and S 1 protection or the chemical cleavage method. Furthermore,
sequence
34
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
differences between a mutant lcinase gene and a wild-type gene can be
determined by direct DNA
sequencing. A variety of automated sequencing procedures can be utilized when
performing the
diagnostic assays (Naeve, C.W., (1995) Biotechniques 19:448), including
sequencing by mass
spectrometry (see, e.g., PCT International Publication No. WO 94/16101; Cohen
et al., Adv.
Chromatogr. 36:127-162 (1996); and Griffin et al., Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol.
38:147-159 (1993)).
Other methods for detecting mutations in the gene include methods in which
protection
from cleavage agents is used to detect mismatched bases in RNA/RNA or RNA/DNA
duplexes
(Myers et al., Science 230:1242 (1985)); Cotton et al., PNAS 85:4397 (1988);
Saleeba et al., Meth.
Enzymol. 217:286-295 (1992)), electrophoretic mobility of mutant and wild type
nucleic acid is
compared (Orita et al., P1VAS 86:2766 (1989); Cotton et al., Mutat. Res.
285:125-144 (1993); and
Hayashi et al., Genet. Anal. Tech. Appl. 9:73-79 (1992)), and movement of
mutant or wild-type
fragments in polyacrylamide gels containing a gradient of denaturant is
assayed using denaturing
gradient gel electrophoresis (Myers et al., Nature 313:495 (1985)). Examples
of other techniques
for detecting point mutations include selective oligonucleotide hybridization,
selective
amplification, and selective primer extension.
The nucleic acid molecules are also useful for testing an individual for a
genotype that while
not necessarily causing the disease, nevertheless affects the treatment
modality. Thus, the nucleic
acid molecules can be used to study the relationship between an individual's
genotype and the
individual's response to a compound used for treatment (pharmacogenomic
relationship).
Accordingly, the nucleic acid molecules described herein can be used to assess
the mutation content
of the kinase gene in an individual in order to select an appropriate compound
or dosage regimen
for treatment. Figure 3 provides information on SNPs that have been found in
the gene encoding
the lcinase protein of the present invention. The following variations were
identified: T1004G,
G1822T, A2023G, A2562G, and C6624A. SNPs such as these that are located in
introns and 5' of
the ORF may affect control/regulatory elements.
Thus nucleic acid molecules displaying genetic variations that afFect
treatment provide a
diagnostic target that can be used to tailor treatment in an individual.
Accordingly, the production
of recombinant cells and animals containing these polymorphisms allow
effective clinical design of
treatment compounds and dosage regimens.
The nucleic acid molecules are thus useful as antisense constructs to control
kinase gene
expression in cells, tissues, and organisms. A DNA antisense nucleic acid
molecule is designed to
be complementary to a region of the gene involved in transcription, preventing
transcription and
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
hence production of kinase protein. An antisense RNA or DNA nucleic acid
molecule would
hybridize to the mRNA and thus block translation of mRNA into kinase protein.
Alternatively, a class of antisense molecules can be used to inactivate mRNA
in order to
decrease expression of kinase nucleic acid. Accordingly, these molecules can
treat a disorder
characterized by abnormal or undesired kinase nucleic acid expression. This
technique involves
cleavage by means of ribozymes containing nucleotide sequences complementary
to one or more
regions in the mRNA that attenuate the ability of the mRNA to be translated.
Possible regions
include coding regions and particularly coding regions corresponding to the
catalytic and other
functional activities of the kinase protein, such as substrate binding.
The nucleic acid molecules also provide vectors for gene therapy in patients
containing cells
that are aberrant in kinase gene expression. Thus, recombinant cells, which
include . the patient's
cells that have been engineered ex vivo and returned to the patient, are
introduced into an individual
where the cells produce the desired kinase protein to treat the individual.
The invention also encompasses kits for detecting the presence of a kinase
nucleic acid in a
biological sample. Experimental data as provided in Figure 1 indicates that
kinase proteins of the
present invention are expressed in humans in the larynx, kidney (adult and
fetal), pancreas, fetal
heart, uterus, and prostate. Specifically, a virtual northern blot shows
expression in the larynx,
kidney, and pancreas. In addition, PCR-based tissue screening panels indicate
expression in the
fetal heart, fetal kidney, uterus, prostate, and pancreas. For example, the
kit can comprise reagents
such as a labeled or labelable nucleic acid or agent capable of detecting
kinase nucleic acid in a
biological sample; means for determining, the amount of kinase nucleic acid in
the sample; and
means for comparing the amount of kinase nucleic acid in the sample with a
standard. The
compound or agent can be packaged in a suitable container. The kit can further
comprise
instructions for using the kit to detect kinase protein mRNA or DNA.
Nucleic Acid Arrays
The present invention further provides nucleic acid detection kits, such as
arrays or
microarrays of nucleic acid molecules that are based on the sequence
information provided in
Figures 1 and 3 (SEQ ID NOS:1 and 3).
As used herein "Arrays" or "Microarrays" refers to an array of distinct
polynucleotides or
oligonucleotides synthesized on a substrate, such as paper, nylon or other
type ,of membrane,
filter, chip, glass slide, or any other suitable solid support. In one
embodiment, the microarray is
prepared and used according to the methods described in US Patent 5,837,832,
Chee et al., PCT
36
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
application W095/11995 (Chee et al.), Lockhart, D. J. et al. (1996; Nat.
Biotech. 14: 1675-1680)
and Schena, M. et al. (1996; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 93: 10614-10619), all of
which are
incozporated herein in their entirety by reference. In other embodiments, such
arrays are
produced by the methods described by Brown et al., US Patent No. 5,807,522.
The microarray or detection kit is preferably composed of a large number of
unique,
single-stranded nucleic acid sequences, usually either synthetic antisense
oligonucleotides or
fragments of cDNAs, fixed to a solid support. The oligonucleotides are
preferably about 6-60
nucleotides in length, more preferably 15-30 nucleotides in length, and most
preferably about 20-
25 nucleotides in length. For a certain type of microarray or detection kit,
it may be preferable to
use oligonucleotides that are only 7-20 nucleotides in length. The microarray
or detection kit
may contain oligonucleotides that cover the known 5', or 3', sequence,
sequential
oligonucleotides which cover the full length sequence; or unique
oligonucleotides selected from
particular areas along the length of the sequence. Polynucleotides used in the
microarray or
detection kit may be oligonucleotides that are specific to a gene or genes of
interest.
In order to produce oligonucleotides to a known sequence for a microarray or
detection
kit, the genes) of interest (or an ORF identified from the contigs of the
present invention) is
typically examined using a computer algorithm which starts at the 5' or at the
3' end of the
nucleotide sequence. .Typical algorithms will then identify oligomers of
defined length that are
unique to the gene, have a GC content within a range suitable for
hybridization, and lack
predicted secondary structure that may interfere with hybridization. In
certain situations it may
be appropriate to use pairs of oligonucleotides on a microarray or detection
kit. The "pairs" will
be identical, except for one nucleotide that preferably is located in the
center of the sequence.
The second oligonucleotide in the pair (mismatched by one) serves as a
control. The number of
oligonucleotide pairs may range from two to one million. The oligomers are
synthesized at
designated areas on a substrate using a light-directed chemical process. The
substrate may be
paper, nylon or other type of membrane, filter, chip, glass slide or any other
suitable solid
support.
In another aspect, an oligonucleotide may be synthesized on the surface of the
substrate
by using a chemical coupling procedure and an ink jet application apparatus,
as described in PCT
application W095/251116 (Baldeschweiler et al.) which is incorporated herein
in its entirety by
reference. In another aspect, a "gridded" array analogous to a dot (or slot)
blot may be used to
arrange and link cDNA fragments or oligonucleotides to the surface of a
substrate using a
vacuum system, thermal, UV, mechanical or chemical bonding procedures. An
array, such as
37
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
those described above, may be produced by hand or by using available devices
(slot blot or dot
blot apparatus), materials (any suitable solid support), and machines
(including robotic
instruments), and may contain 8, 24, 96, 384, 1536, 6144 or more
oligonucleotides, or any other
number between two and one million which lends itself to the efficient use of
commercially
available instrumentation.
In order to conduct sample analysis using a microarray or detection kit, the
RNA or DNA
from a biological sample is made into hybridization probes. The mRNA is
isolated, and cDNA is
produced and used as a template to make antisense RNA (aRNA). The aRNA is
amplified in the
presence of fluorescent nucleotides, and labeled probes are incubated with the
microarray or
detection kit so that the probe sequences hybridize to complementary
oligonucleotides of the
microarray or detection kit. Incubation conditions are adjusted so that
hybridization occurs with
precise complementary matches or with various degrees of less complementarity.
After removal
of nonhybridized probes, a scanner is used to determine the levels and
patterns of fluorescence.
The scanned images are examined to determine degree of complementarity and the
relative
abundance of each oligonucleotide sequence on the microarray or detection kit.
The biological
samples may be obtained from any bodily fluids (such as blood, urine, saliva,
phlegm, gastric
juices, etc.), cultured cells, biopsies, or other tissue preparations. A
detection system may be
used to measure the absence, presence, and amount of hybridization for all of
the distinct
sequences simultaneously. This data may be used for large-scale correlation
studies on the
sequences, expression patterns, mutations, variants, or polymorphisms among
samples.
Using such arrays, the present invention provides methods to identify the
expression of
the kinase proteins/peptides of the present invention. In detail, such methods
comprise
incubating a test sample with one or more nucleic acid molecules and assaying
for binding of the
nucleic acid molecule with components within the test sample. Such assays will
typically
involve arrays comprising many genes, at least one of which is a gene of the
present invention
and or alleles of the kinase gene of the present invention. Figure 3 provides
information on SNPs
that have been found in the gene encoding the kinase protein of the present
invention. The
following variations were identified: T1004G, G1822T, A2023G, A2562G, and
C6624A. SNPs
such as these that are located in introns and 5' of the ORF may affect
control/regulatory
elements.
Conditions for incubating a nucleic acid molecule with a test sample vary.
Incubation
conditions depend on the format employed in the assay, the detection methods
employed, and the
type and nature of the nucleic acid molecule used in the assay. One skilled in
the art will
38
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
recognize that any one of the commonly available hybridization, amplification
or array assay
formats can readily be adapted to employ the novel fragments of the Human
genome disclosed
herein. Examples of such assays can be found in Chard, T, Ah Ihtroductio~c to
Radioimmuaoassay and Related Techniques, Elsevier Science Publishers,
Amsterdam, The
Netherlands (1986); Bullock, G. R. et al., Techniques in Immuhocytochemistry,
Academic
Press, Orlando, FL Vol. 1 (1 982), Vol. 2 (1983), Vol. 3 (1985); Tijssen, P.,
Practice avid
Theory of Enzyme Immunoassays: Laboratory Techniques in Biochemistry and
Molecular
Biology, Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, The Netherlands (1985).
The test samples of the present invention include cells, protein or membrane
extracts of
l0 cells. The test sample used in the above-described method will vary based
on the assay format,
nature of the detection method and the. tissues, cells or extracts used as the
sample to be assayed.
Methods for preparing' nucleic acid extracts or of cells are well known in the
art and can be
readily be adapted in order to obtain a sample that is compatible with the
system utilized.
In another embodiment of the present invention, kits are provided which
contain the
necessary reagents to carry out the assays of the present invention.
Specifically, the invention provides a compartmentalized kit to receive, in
close
confinement, one or more containers which comprises: (a) a first container
comprising one of the
nucleic acid molecules that can bind to a fragment of the Human genome
disclosed herein; and
(b) one or more other containers comprising one or more of the following: wash
reagents,
ZO reagents capable of detecting presence of a bound nucleic acid.
In detail, a cornpaxtmentalized kit includes any kit in which reagents are
contained in
separate containers. Such containers include small glass containers, plastic
containers, strips of
plastic, glass or paper, or arraying material such as silica. Such containers
allows one to
efficiently transfer reagents from one compartment to another compartment such
that the
?5 samples and reagents are not cross-contaminated, and the agents or
solutions of each container
can be added in a quantitative fashion from one compartment to another. Such
containers will
include a container which will accept the test sample, a container which
contains the nucleic acid
probe, containers which contain wash reagents (such as phosphate buffered
saline, Tris-buffers,
etc.), and containers which contain the reagents used to detect the bound
probe. One skilled in
30 the art will readily recognize that the previously unidentified kinase gene
of the present invention
can be routinely identified using the sequence information disclosed herein
can be readily
incorporated into one of the established kit formats which are well known in
the art, particularly
expression arrays.
39
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
Vectors/host cells
The invention also provides vectors containing the nucleic acid molecules
described herein.
The term "vector" refers to a vehicle, preferably a nucleic acid molecule,
which can transport the
nucleic acid molecules. When the vector is a nucleic acid molecule, the
nucleic acid molecules are
covalently linked to the vector nucleic acid. With this aspect of the
invention, the vector includes a
plasmid, single or double stranded phage, a single or double stranded RNA or
DNA viral vector, or
artificial chromosome, such as a BAC, PAC, YAC, OR MAC.
A vector can be maintained in the host cell as an extrachromosomal element
where it
replicates and produces additional copies of the nucleic acid molecules.
Alternatively, the vector
may integrate into the host cell genome and produce additional copies of the
nucleic acid molecules
when the host cell replicates.
The invention provides vectors for the maintenance (cloning vectors) or
vectors for
expression (expression vectors) of the nucleic acid molecules. The vectors can
function in
prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells or in both (shuttle vectors).
Expression vectors contain cis-acting regulatory regions that are operably
linked in the
vector to the nucleic acid molecules such that transcription of the nucleic
acid molecules is allowed
in a host cell. The nucleic acid molecules can be introduced into the host
cell with a separate
nucleic acid molecule capable of affecting transcription. Thus, the second
nucleic acid molecule
may provide a traps-acting factor interacting with the cis-regulatory control
region to allow
transcription of the nucleic acid molecules from the vector. Alternatively, a
traps-acting factor may
be supplied by the host cell. Finally, a traps-acting factor can be produced
from the vector itself. It
is understood, however, that in some embodiments, transcription and/or
translation of the nucleic
acid molecules can occur in a cell-free system.
The regulatory sequence to which the nucleic acid molecules described herein
can be
operably linked include promoters for directing mRNA transcription. These
include, but are not
limited to, the left promoter from bacteriophage ~,, the lac, TRP, and TAC
promoters from E. coli,
the early and Late promoters from SV40, the CMV immediate early promoter, the
adenovirus early
and late promoters, and retrovirus long-terminal repeats.
In addition to control regions that promote transcription, expression vectors
may also
include regions that modulate transcription, such as repressor binding sites
and enhancers.
Examples include the SV40 enhancer, the cytomegalovirus immediate early
enhancer, polyoma
enhancer, adenovirus enhancers, and retrovirus LTR enhancers.
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
In addition to containing sites for transcription initiation and control,
expression vectors can
also contain sequences necessary for transcription termination and, in the
transcribed region a
ribosome binding site for translation. Other regulatory control elements for
expression include
initiation and termination codons as well as polyadenylation signals. The
person of ordinary skill in
the art would be aware of the numerous regulatory sequences that are useful in
expression vectors.
Such regulatory sequences are described, for example, in Sambrook et al.,
Molecular Cloning: A
Laboratory Manual. 2nd. ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring
Harbor, NY,
(1989).
A variety of expression vectors can be used to express a nucleic acid
molecule. Such
vectors include chromosomal, episomal, and virus-derived vectors, for example
vectors derived
from bacterial plasmids, from bacteriophage, from yeast episomes, from yeast
chromosomal
elements, including yeast artificial chromosomes, from viruses such as
baculoviruses,
papovaviruses such as SV40, Vaccinia viruses, adenoviruses, poxviruses,
pseudorabies viruses, and
retroviruses. Vectors may also be derived from combinations of these sources
such as those derived
from plasmid and bacteriophage genetic elements, e.g. cosmids and phagemids.
Appropriate
cloning and expression vectors for prokaryotic and eukaryotic hosts are
described in Sambrook et
al., Molecular Clohihg: A Laboratory Manual. Z~cd. ed., Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory Press, Cold
Spring Harbor, NY, (1989).
The regulatory sequence may provide constitutive expression in one or more
host cells (i.e.
tissue specific) or may provide for inducible expression in one or more cell
types such as by
temperature, nutrient additive, or exogenous factor such as a hormone or other
ligand. A variety of
vectors providing for constitutive and inducible expression in prokaryotic and
eukaryotic hosts are
well known to those of ordinary skill in the art.
The nucleic acid molecules can be inserted into the vector nucleic acid by
well-known
methodology. Generally, the DNA sequence that will ultimately be expressed is
joined to an
expression vector by cleaving the DNA sequence and the expression vector with
one or more
restriction enzymes and then ligating the fragments together. Procedures for
restriction enzyme
digestion and ligation are well known to those of ordinary skill in the art.
The vector containing the appropriate nucleic acid molecule can be introduced
into an
appropriate host cell for propagation or expression using well-known
techniques. Bacterial cells
include, but are not limited to, E. coli, Streptomyces, and Salmonella
typhimurium. Eukaryotic cells
include, but are not limited to, yeast, insect cells such as Drosophila,
animal cells such as COS and
CHO cells, and plant cells.
41
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
As described herein, it may be desirable to express the peptide as a fusion
protein.
Accordingly, the invention provides fusion vectors that allow for the
production of the peptides.
Fusion vectors can increase the expression of a recombinant protein, increase
the solubility of the
recombinant protein, and aid in the purification of the protein by acting for
example as a ligand for
affinity purification. A proteolytic cleavage site may be introduced at the
junction of the fusion
moiety so that the desired peptide can ultimately be separated from the fusion
moiety. Proteolytic
enzymes include, but are not limited to, factor Xa, thrombin, and
enterokinase. Typical fusion
expression vectors include pGEX (Smith et al., Gene 67:31-40 (1988)), pMAL
(New England
Biolabs, Beverly, MA) and pRITS (Pharmacia, Piscataway, NJ) which fuse
glutathione S-
transferase (GST), maltose E binding protein, or protein A, respectively, to
the target recombinant
protein. Examples of suitable inducible non-fusion E. coli expression vectors
include pTrc (Amann
et al., Gene 69:301-315 (1988)) and pET 1 1d (Studier et al., Gene Expression
Technology: Methods
in Enzymology 1&5:60-89 (19900.
Recombinant protein expression can be maximized in host bacteria by providing
a genetic
background wherein the host cell has an impaired capacity to proteolytically
cleave the recombinant
protein. (Gottesman, S., Gene Expression Technology.' Methods in Enzymology
185,.Academic
Press, San Diego, California (1990) 119-128). Alternatively, the sequence of
the nucleic acid
molecule of interest can be altered to provide preferential codon usage for a
specific host cell, for
example E. coli. (Wada et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 20:2111-2118 (1992)).
The nucleic acid molecules can also be expressed by expression vectors that
are operative in
yeast. Examples of vectors for expression in yeast e.g., S cerevisiae include
pYepSecl (Baldari, et
al., EMBOJ. 6:229-234 (1987)), pMFa (I~urjan et al., Cell 30:933-943(1982)),
pJRY88 (Schultz et
al., Gene 54:113-123 (1987)), and pYES2 (Invitrogen Corporation, San Diego,
CA).
The nucleic acid molecules can also be expressed in insect cells using, for
example,
baculovirus expression vectors. Baculovirus vectors available for expression
of proteins in cultured
insect cells (e.g., Sf 9 cells) include the pAc series (Smith et al., Mol.
Cell Biol. 3:2156-2165
(1983)) and the pVL series (Lucklow et al., hirolo~ 170:31-39 (1989)).
In certain embodiments of the invention, the nucleic acid molecules described
herein are
expressed in mammalian cells using mammalian expression vectors. Examples of
mammalian
expression vectors include pCDM8 (Seed, B. Nature 329:840(1987)) and pMT2PC
(Kaufinan et al.,
EMBO J. 6:187-195 (1987)).
The expression vectors listed herein are provided by way of example only of
the well-
known vectors available to those of ordinary skill in the art that would be
useful to express the
42
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
nucleic acid molecules. The person of ordinary skill in the art would be aware
of other vectors
suitable for maintenance propagation or expression of the nucleic acid
molecules described herein.
These are found for example in Sambrook, J., Fritsh, E. F., and Maniatis, T.
Molecular Cloning: A
Laboratory Manual. 2nd, ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory
Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1989.
The invention also encompasses vectors in which the nucleic acid sequences
described
herein are cloned into the vector in reverse orientation, but operably linked
to a regulatory sequence
that permits transcription of antisense RNA. Thus, an antisense transcript can
be produced to all, or
to a portion, of the nucleic acid molecule sequences described herein,
including both coding and
non-coding regions. Expression of this antisense RNA is subject to each of the
parameters
described above in relation to expression of the sense RNA (regulatory
sequences, constitutive or
inducible expression, tissue-specific expression).
The invention also relates to recombinant host cells containing the vectors
described herein.
Host cells therefore include,prokaryotic cells, lower eukaryotic cells such as
yeast, other eukaryotic
cells such as insect cells, and higher eukaryotic cells such as mammalian
cells.
The recombinant host cells are prepared by introducing the vector constructs
described
herein into the cells by techniques readily available to the person of
ordinary skill in the art. These
include, but are not limited to, calcium phosphate transfection, DEAF-dextran-
mediated
transfection, cationic lipid-mediated transfection, electroporation,
transduction, infection,
lipofection, and other techniques such as those found in Sambrook, et al.
(Molecular Cloning: A
Laboratory Manual. 2nd, ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory
Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1989).
Host cells can contain more than one vector. Thus, different nucleotide
sequences can be
introduced on different vectors of the same cell. Similarly, the nucleic acid
molecules can be
introduced either alone or with other nucleic acid molecules that are not
related to the nucleic acid
molecules such as those providing trans-acting factors for expression vectors.
When more than one
vector is introduced into a cell, the vectors can be introduced independently,
co-introduced or joined
to the nucleic acid molecule vector.
In the case of bacteriophage and viral vectors, these can be introduced into
cells as packaged
or encapsulated virus by standard procedures for infection and transduction.
Viral vectors can be
replication-competent or replication-defective. In the case in which viral
replication is defective,
replication will occur in host cells providing functions that complement the
defects.
43
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
Vectors generally include selectable markers that enable the selection of the
subpopulation
of cells that contain the recombinant vector constructs. The marker can be
contained in the same
vector that contains the nucleic acid molecules described herein or may be on
a separate vector.
Markers include tetracycline or ampicillin-resistance genes for prokaryotic
host cells and
dihydrofolate reductase or neomycin resistance for eukaryotic host cells.
However, any marker that
provides selection for a phenotypic trait will be effective.
While the mature proteins can be produced in bacteria, yeast, mammalian cells,
and other
cells under the control of the appropriate regulatory sequences, cell- free
transcription and
translation systems can also be used to produce these proteins using RNA
derived from the DNA
constructs described herein.
Where secretion of the peptide is desired, which is difficult to achieve with
multi-
transmembrane domain containing proteins such as kinases, appropriate
secretion signals are
incorporated into the vector. The signal sequence can be endogenous to the
peptides .or
heterologous to these peptides.
Where the peptide is not secreted into the medium, which is typically the case
with kinases,
the protein can be isolated from the host cell by standard disruption
procedures, including freeze
thaw, sonication, mechanical disruption, use of lysing agents and the like.
The peptide can then be
recovered and purified by well-known purification methods including ammonium
sulfate
precipitation, acid extraction, anion or cationic exchange chromatography,
phosphocellulose
chromatography, hydrophobic-interaction chromatography, aff nity
chromatography,
hydroxylapatite chromatography, lectin chromatography, or high performance
liquid
chromatography.
It is also understood that depending upon the host cell in recombinant
production of the
peptides described herein, the peptides can have various glycosylation
patterns, depending upon the
cell, or maybe non-glycosylated as when produced in bacteria. In addition, the
peptides may
include an initial modified methionine in some cases as a result of a host-
mediated process.
Uses of vectors and host cells
The recombinant host cells expressing the peptides described herein have a
variety of uses.
First, the cells are useful for producing a kinase protein or peptide that can
be further purified to
produce desired amounts of kinase protein or fragments. Thus, host cells
containing expression
vectors are useful for peptide production.
44
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
Host cells are also useful for conducting cell-based assays involving the
kinase protein or
kinase protein fragments, such as those described above as well as other
formats known in the art.
Thus, a recombinant host cell expressing a native kinase protein is useful for
assaying compounds
that stimulate or inhibit kinase protein function.
Host cells are also useful for identifying kinase protein mutants in which
these functions are
affected. If the mutants naturally occur and give rise to a pathology, host
cells containing the
mutations are useful to assay compounds that have a desired effect on the
mutant kinase protein (for
example, stimulating or inhibiting function) which may not be indicated by
their effect on the native
kinase protein.
Genetically engineered host cells can be fiuther used to produce non-human
transgenic
animals. A transgenic animal is preferably a mammal, for example a rodent,
such as a rat or mouse,
in which one or more of the cells of the animal include a transgene. A
transgene is exogenous DNA
which is integrated into the genome of a cell from which a transgenic animal
develops and which
remains in the genome of the mature animal in one or more cell types or
tissues of the transgenic
animal. These animals are useful for studying the function of a kinase protein
and identifying and
evaluating modulators of kinase protein activity. Other examples of transgenic
animals include
non-human primates, sheep, dogs, cows, goats, chickens, and amphibians.
A transgenic animal can be produced by introducing nucleic acid into the male
pronuclei of
a fertilized oocyte, e.g., by microinjection, retroviral infection, and
allowing the oocyte to develop
in a pseudopregnant female foster animal. Any of the kinase protein nucleotide
sequences can be
introduced as a transgene into the genome of a non-human animal, such as a
mouse.
Any of the regulatory or other sequences useful in expression vectors can form
part of the
transgenic sequence. This includes intronic sequences and polyadenylation
signals, if not already
included. A tissue-specific regulatory sequences) can be operably linked to
the transgene to direct
~5 expression of the kinase protein to particular cells.
Methods for generating transgenic animals via embryo manipulation and
microinjection,
particularly animals such as mice, have become conventional in the art and are
described, for
example, in U.S. Patent Nos. 4,736,866 and 4,870,009, both by Leder et al.,
U.S. Patent No.
4,873,191 by Wagner et al. and in Hogan, B., Manipulating the Mouse Embryo,
(Cold Spring
Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y., 1986). Similar methods are
used for
production of other transgenic animals. A transgenic founder animal can be
identified based upon
the presence of the transgene in its genome and/or expression of transgenic
mRNA in tissues or
cells of the animals. A transgenic founder animal can then be used to breed
additional animals
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
carrying the transgene. Moreover, transgenic animals carrying a transgene can
further be bred to
other transgenic animals carrying other transgenes. A transgenic animal also
includes animals in
which the entire animal or tissues in the animal have been produced using the
homologously
recombinant host cells described herein.
In another embodiment, transgenic non-human animals can be produced which
contain
selected systems that allow for regulated expression of the transgene. One
example of such a
system is the crelloxP recombinase system of bacteriophage P 1. For a
description of the c~elloxP
recombinase system, see, e.g., Lalcso et al. PNAS 89:6232-6236 (1992). Another
example of a
recombinase system is the FLP recombinase system of S cerevisiae (O'Gorman et
al. Science
251:1351-1355 (1991). If a crelloxP recombinase system is used to regulate
expression of the
transgene, animals containing transgenes encoding both the Cre recombinase and
a selected protein
is required. Such animals can be provided through the construction of "double"
transgenic animals,
e.g., by mating two transgenic animals, one containing a transgene encoding a
selected protein and
the other containing a transgene encoding a recombinase.
Clones of the non-human transgenic animals described herein can also be
produced
according to the methods described in Wilinut, I. et al. Nature 385:810-813
(1997) and PCT
International Publication Nos. WO 97/07668 and WO 97/07669. In brief, a cell,
e.g., a somatic cell,
from the transgenic animal can be isolated and induced to exit the growth
cycle and enter Go phase.
The quiescent cell can then be fused, e.g., through the use of electrical
pulses, to an enucleated
oocyte from an animal of the same species from which the quiescent cell is
isolated. The
reconstructed oocyte is then cultured such that it develops to morula or
blastocyst and then
transferred to pseudopregnant female foster animal. The offspring born of this
female foster animal
will be a clone of the animal from which the cell, e.g., the somatic cell, is
isolated.
Transgenic animals containing recombinant cells that express the peptides
described herein
are useful to conduct the assays described herein in an in vivo context.
Accordingly, the vaxious
physiological factors that are present ih vivo and that could effect substrate
binding, kinase protein
activation, and signal transduction, may not be evident from in vitro cell-
free or cell-based assays.
Accordingly, it is useful to provide non-human transgenic animals to assay i~
vivo kinase protein
function, including substrate interaction, the effect of specific mutant
kinase proteins on kinase
protein function and substrate interaction, and the effect of chimeric kinase
proteins. It is also
possible to assess the effect of null mutations, that is, mutations that
substantially or completely
eliminate one or more kinase protein functions.
46
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
All publications and patents mentioned in the above specification are herein
incorporated
by reference. Various modifications and variations of the described method and
system of the
invention will be apparent to those skilled in the art without departing from
the scope and spirit
of the invention. Although the invention has been described in connection with
specific
preferred embodiments, it should be understood that the invention as claimed
should not be
unduly limited to such specific embodiments. Indeed, various modifications of
the above-
described modes for carrying out the invention which are obvious to those
skilled in the field of
molecular biology or related fields are intended to be within the scope of the
following claims.
47
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
SEQUENCE LISTING
<110> PE CORPORATION (NY)
<120> ISOLATED HUMAN KINASE PROTEINS, NUCLEIC
ACID MOLECULES ENCODING HUMAN KINASE PROTEINS, AND USES
THEREOF
<130> CL001011PCT
<140> TO BE ASSIGNED
<l41> 2001-12-06
<150> 09/732,025
<151> 2000-12-08
<150> 09/739,455
<151> 2000-12-19
<160> 4
<170> FastSEQ for Windows Version 4.0
<210> 1
<211> 1878
<212> DNA
<213> Homo Sapiens
<400> 1
ggacactgac atggactgaa ggagtagaaa aaccgactca acagtaaggc cccgcgggcg 60
tcctggccgc catgtgcacc gtagtggacc ctcgcattgt ccggagatac ctactcaggc 120
ggcagctcgg gcagggggcc tatggcattg tgtggaaggc agtggaccgg aggactggtg 180
aggtcgtggc catcaagaaa atctttgatg cttttaggga taagacagat gcccagagaa 240
cattccggga aatcacgctc ctccaggagt ttggggacca tcccaacatc atcagcctcc 300
ttgacgtgat ccgggcagag aacgacaggg acatttacct ggtgtttgag tttatggaca 360
ctgacctgaa cgcagtcatc cggaagggcg gcctgctgca ggacgtccac gtgcgctcca 420
tcttctacca gctcctgcgg gccacccggt tcctccactc ggggcacgtt gtgcaccggg 480
accagaagcc gtccaatgtg ctcctggatg ccaactgcac agtgaagctg tgtgactttg 540
gcctggcccg ctccctgggc gacctccccg aggggcctga ggaccaggcc gtgacagagt 600
acgtggccac acgctggtac cgagcaccgg aggtgctgct ctcttcgcac cgatacaccc 660
ttggggtgga catgtggagt ctgggctgta tcctggggga gatgctgcgg gggagacccc 720
tgttccccgg cacgtccacc ctccaccagc tggagctgat cctggagacc atcccaccgc 780
catctgagga ggacacctcc ccagaggcct tggacctcct taggcgactc ctggtgttcg 840
ccccggacaa gcggttaagc gcgacccagg cactgcagca cccctacgtg cagaggttcc 900
actgccccag cgacgagtgg gcacgagagg cagatgtgcg gccccgggca cacgaagggg 960
tccagctctc tgtgcctgag taccgcagcc gcgtctatca gatgatcctg gagtgtggag 1020
gcagcagcgg cacctcgaga gagaagggcc cggagggtgt ctccccaagc caggcacacc 1080
tgcacaaacc cagagccgac cctcagctgc cttctaggac acctgtgcag ggtcccagac 1140
ccaggcccca gagcagccca ggccatgacc ctgccgagca cgagtccccc cgtgcagcca 1200
agaacgttcc caggcagaac ccgctcccc tgctccaaac tgctctccta gggaatgggg 1260
aaaggccccc tggggcgaag gaagcgcccc ccttgacact ctcgctggtg aagccaagcg 1320
ggaggggagc tgcgccctcc ctgacctccc aggctgcggc tcaggtggcc aaccaggccc 1380
tgatccgggg tgactggaac cggggcggtg gggtgagggt ggccagcgta caacaggtcc 1440
ctccccggct tcctccggag gcccggcccg gccggaggat gttcagcccc tctgccttgc 1500
agggtgccca ggggggtgcc agggctttgc ttggaggcta ctcccaagcc tacgggactg 1560
tttgcccctc ggcactgggc cccctgcccc tgctggaggg gccccatatg tgagccgccc 1620
tactcccttc acctggccct ctgttcctgc cccagcccct tccccagacc cctttccagt 1680
ttcctgcccc ccttagccct ccctgctttg cctggcccgt tgaagttcca gggagcttgc 1740
ccgggtctcc tcgggggagc aaatgagggc cctgcccccg cccccctgac ttcctccaat 1800
aaagtcatgt ttgcccccca aaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaa 1860
aaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaa 1878
<210> 2
<211> 513
<212> PRT
<213> Homo Sapiens
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
<400> 2
Met Cys Thr Val Val Asp Pro Arg Ile Va1 Arg Arg Tyr Leu Leu Arg
1 5 10 15
Arg Gln Leu Gly Gln Gly Ala Tyr Gly Ile Val Trp Lys Ala Val Asp
20 25 30
Arg Arg Thr Gly Glu Val Val Ala Ile Lys Lys Ile Phe Asp Ala Phe
35 40 45
Arg Asp Lys Thr Asp Ala Gln Arg Thr Phe Arg Glu Ile Thr Leu Leu
50 55 60
Gln Glu Phe Gly Asp His Pro Asn Ile Ile Ser Leu Leu Asp Val Ile
65 70 75 80
Arg Ala Glu Asn Asp Arg Asp Ile Tyr Leu Val Phe Glu Phe Met Asp
85 90 95
Thr Asp Leu Asn Ala Val Ile Arg Lys Gly Gly Leu Leu Gln Asp Val
100 105 110
His Val Arg Ser Ile Phe Tyr Gln Leu Leu Arg Ala Thr Arg Phe Leu
115 120 125
His Ser Gly His Val Val His Arg Asp Gln Lys Pro Ser Asn Val Leu
130 135 140
Leu Asp Ala Asn Cys Thr Val Lys Leu Cys Asp Phe Gly Leu Ala Arg
145 150 155 160
Ser Leu Gly Asp Leu Pro Glu Gly Pro Glu Asp Gln Ala Val Thr Glu
165 170 175
Tyr Val Ala Thr Arg Trp Tyr Arg Ala Pro Glu Val Leu Leu Ser Ser
180 185 190
His Arg Tyr Thr Leu Gly Val Asp Met Trp Ser Leu Gly Cys I1e Leu
295 200 205
Gly Glu Met Leu Arg Gly Arg Pro Leu Phe Pro Gly Thr Ser Thr Leu
210 215 220
His Gln Leu Glu Leu I1e Leu Glu Thr Ile Pro Pro Pro Ser Glu Glu
225 230 ~ 235 240
Asp Thr Ser Pro Glu Ala Leu Asp Leu Leu Arg Arg Leu Leu Val Phe
245 250 255
Ala Pro Asp Lys Arg Leu Ser Ala Thr Gln Ala Leu Gln His Pro Tyr
260 265 270
Val Gln Arg Phe His Cys Pro Ser Asp Glu Trp Ala Arg Glu Ala Asp
275 280 285
Val Arg Pro Arg Ala His Glu Gly Val Gln Leu Ser Val Pro Glu Tyr
290 295 300
Arg Ser Arg Val Tyr Gln Met Ile Leu Glu Cys Gly Gly Ser Ser Gly
305 310 315 320
Thr Ser Arg Glu Lys Gly Pro Glu Gly Val Ser Pro Ser Gln Ala His
325 330 335
Leu His Lys Pro Arg Ala Asp Pro Gln Leu Pro Ser Arg Thr Pro Val
340 345 350
Gln Gly Pro Arg Pro Arg Pro Gln Ser Ser Pro Gly His Asp Pro Ala
355 360 365
Glu His Glu Ser Pro Arg Ala Ala Lys Asn Val Pro Arg Gln Asn Ser
370 375 380
Ala Pro Leu Leu Gln~Thr Ala Leu Leu Gly Asn Gly Glu Arg Pro Pro
385 390 395 400
Gly Ala Lys Glu Ala Pro Pro Leu Thr Leu Ser Leu Val Lys Pro Ser
405 410 415
Gly Arg Gly Ala Ala Pro Ser Leu Thr Ser Gln Ala Ala Ala Gln Val
420 425 430
Ala Asn Gln Ala Leu Ile Arg Gly Asp Trp Asn Arg Gly Gly Gly Val
435 440 445
Arg Val Ala Ser Val Gln Gln Val Pro Pro Arg Leu Pro Pro Glu Ala
450 455 460
Arg Pro Gly Arg Arg Met Phe Ser Pro Ser Ala Leu Gln Gly Ala Gln
465 470 475 480
Gly Gly Ala Arg Ala Leu Leu Gly Gly Tyr Ser Gln Ala Tyr Gly Thr
485 490 495
Val Cys Pro Ser Ala Leu Gly Pro Leu Pro Leu Leu Glu Gly Pro His
500 505 5l0
Met
2
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
<210> 3
<211> 8285
<212> DNA
<213> Homo sapiens
<220>
<222> misc_feature
<222> (1). .(8285)
<223> n = A,T,C or G
<400> 3
nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 60
nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 120
nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 180
nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 240
nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nttgttcctt ttccttcttt ttttgaattc 300
tttttgagca agtagtttgt gttgtggttg ttgtttgaga cagggtctgg ctctgtcacc 360
caggctggag tgcagtggcg caatccaggc tcactgcaac ctctgcctcc cggctcaagc 420
gatcctccta cctcagcctc ccaagtagct gggacaacag gctcatgtca ccacacccag 480
ctaattttcc tatttttttt ttttaataga aatgaggttt tatgttgccg aagctggtct 540
ccaattcctg agtcattagc cacgcccggc taatttttgt atttttagtg gagacggggt 600
ttcaccacgt tggccaggct ggtcttgaac ccttgacctc gggtgatcca cccgcctcgg 660
cctcccagag tgttgggatt acaggcgtga accaccgtgt cccgcccaaa taataatata 720
ctattaatac ttcacatgta acttaagaac cttacaatac atattctcat gttattttgt 780
aatagtataa atgtgtattt ccattatccc ccttcacttt ttgctattgg tgtcatgcat 840
tttacttcta caagttatag agtccacaac agatagttct tgtttctact ttagtcagct 900
gggctgggcg tggtcctgcg aggaggtggg cggggcgcac tgtggggcgg ggccggtggg 960
gacgtgggcg gggcgccatt gaggggaggg gcctgcgggg aggttgggtg ggcccactgt 1020
ggggcggagc cggggcctgc cgggggcggg gggtgttggg aggggcgccc cgaggggcgg 1080
ggccgggccg ccgtcggttc ccacggcaac cgactcaaca gtaaggcccc gcgggcgtcc 1140
tggccgccat gtgcaccgta gtggaccctc gcattgtccg gagataccta ctcaggcggc 1200
agctcgggca gggggtgagt gcctgggggt gcgtccgcgc gccgaggggc gcggcatatc 1260
tgcggataga ggacctgnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 1320
nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 1380
nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 1440
nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 1500
nnnnnnnncc cgggtcactg aaagaagggc ggaccccagg ctcaggtagc acaggggcga 1560
ggcccgagaa gggcctgagc ggttatgggg tgggcgcaga gtgaagggca gagccttgtg 1620
tatctgtgtg tgtgtgtgag catgtaagcc tgtgtgtgtg tgcgtgggtg tgtggggggg 1680
tgttcgaggg tgccatgggg gaggggagga agagccttcc aggcagtgca gacggtaagt 1740
gcgtaggccc agtgcagggt tgtgtatgtg caactggata ggagatggag agagacaggt 1800
gagtggtgag ggtccgatcg tgtgggagct ttggggaact tccaagactt tggtttttac 1860
tgttgctgag gctgggagct gtagcagctg ctggtgtcac tttacaaggc ccacccctgt 1920
gctgaggacc taccgtgggt gtgcacggga gcggcagacg gagatgagtt aaggggttag 1980
cgtagccacg cagcgagaga tgccagaggc tgggaccagg gtaggggcag aagagaccgt 2040
ggcaggggct agattctgga ggaatctgaa ggtagggcca atgggattgg gggtggatgg 2100
ggtgtgagag aaagggaggg agagtgcctg ggcagctgga aggatgatag ggcatccccg 2160
agcttcattt cctgcccaga cgctcccctc tgtggcctcc tttcctccag ggcctcgcca 2220
gctctcaccc tcccttccct ctacctcccc tcctctggaa gatgtcggag tctagggcag 2280
cctgcagttg cgggagccca cactcccatc ccctctcggg acccaggatg ggaaggagga 2340
gcctcatgtc tgtagggaca atctgggtgg gcaggggatg gggggaaggg gctggccctg 2400
tgtgacggca ctccttccca ggcctatggc attgtgtgga aggcagtgga ccggaggact 2460
ggtgaggtcg tggccatcaa gaaaatcttt gatgctttta gggataagac agatgcccag 2520
gtgagtgtgt ggggagaagc gtgggagagg atgggggcag gaaggggcag ccccttgccc 2580
tggtgcctgg aagctcaggt gggagctgga gcccagtcat agcagatgtt ctggcctgtc 2640
tcggaacact gcccccttgc cacgcctggt ctggtgggta ttgggtgaca gacatcagct 2700
cctttgggtc ctctcaggac atgggcttcc ttcttgctcc acccacccac acacctgtgt 2760
ttctgtctct tcagagaaca ttccgggaaa tcacgctcct ccaggtgagt ggcctgggcc 2820
ctccagtcca atccccttgc ccaggtacag atctctccag acaggagaga aactggcctt 2880
cttgggcccc agagcacagc ccctcctggc cttccagccg cctccgactc tctccccagg 2940
agtttgggga ccatcccaac atcatcagcc tccttgacgt gatccgggca gagaacgaca 3000
gggacattta cctggtgttt gagtttatgg gtgagtgagg ccccggccag cgccccagcc 3060
ccacctctgt tctgtcctga cgccgtctgc gggtccctct gcgtgtccct ctgcgtgtcc 3120
ctctgcagct ggcccacagt ggcttgctcc ctcaccatgt accctggact cagggacaga 3180
cagctgacta gtgtcagcct ccagagccag cagcgacccc tttcgtccca cctgccccag 3240
gctcctgctc tgaccacagt ttgcagttgc gttctccttt ttcttctcat tttatgaaac 3300
aaaggcaaca tgaaataaag tgttaaaact cctgcagacc tcaccgctgt gcccacaggc 3360
3
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
agtgcacagg atggaggagc ggggcggcca ggccgtgggc tggttcaaag tgggacagac 3420
ctgccaggtg cccctctccc actcccccca ggttgccccc ccagcccccc acccccgact 3480
gcagtgcgca ccctctctgc agacactgac ctgaacgcag tcatccggaa gggcggcctg 3540
ctgcaggacg tccacgtgcg ctccatcttc taccagctcc tgcgggccac ccggttcctc 3600
cactcggggc acgttgtgca ccgggaccag aaggtgcggt tcccccgccc ccgctatgcc 3660
acgtggcccg gctcccggcc ccacccagcc ccggggcctc agcctgcctc ctctctgcag 3720
ccgtccaatg tgctcctgga tgccaactgc acagtgaagc tgtgtgactt tggcctggcc 3780
cgctccctgg gcgacctccc tgaggggcct gaggaccagg ccgtgacaga gtacgtggcc 3840
acacgctggt accgagcacc ggaggtgctg ctctcttcgc accggtaata gcgagacatc 3900
cccaaccccc ctccacctcc ctgctgccct cctgcccagc cagggctccc aggcctcccg 3960
tactccgacc ctgccttggt ccacaagtgt tcccccattc accccccagc aaccccaccc 4020
ccacctctgc ctctgggtct ctccatgcct acaccgcttc ctgccccaga tacacccttg 4080
gggtggacat gtggagtctg ggctgtatcc tgggggagat gctgcggggg agacccctgt 4140
tccccggcac gtccaccctc caccagctgg agctgatcct ggagaccatc ccaccgccat 4200
ctgaggaggg tgagccaggc tgctggggct gggcaccagg aatgctgcag gtcagacagc 4260
acagctgtgg ggagacagca gctgacaggc taggactgtg ctgagaggag ggacggggac 4320
agggaggatc cagaggatgg ggcaggagcc ccaggaagac cgactggtga tgggggccca 4380
ggaggagctg ctgggggtgg gtgtgggcaa ggcagcacct ggcacagtca ccatgagagc 4440
caagcagtga ccgtgaaggg gccagcaggc tggacaaggt ccccaaggga ttcgggtagc 4500
aggggcaggg actgtcactg tgccgggagc tggggtgtgc agagacagct gggcaggaga 4560
gattcaggtg ctgagggaag aggtggagga aggcagtggt agaggggcca tgggggtcac 4620
tcttgagggt gggggcaaga gggagctgca ccgccaggca tagctgcttg tctgggtgga 4680
gcctcctggg ccgtggaggt gggcgccagc atccacttct gtgagcacac cccagggcca 4740
ggtgcccgag tgtggagcag gggtcatgtg cgggtgctcc cgtgcacagg ctgggtggca 4800
cgccctggtg atggggtgtt tgagccccgc cagacagcag aaaccctgta gagaggctgt 4860
gctccctggg gctggaagag atgactggcc ccagatgccc tgagccgccc cagccgacca 4920
ggcctgcctg ggtcacacca ccttctgctg ccccagacct cctggctctc ggctcaggct 4980
gccgtgcctc tgtgctgcac cagctggggt cccggtgagt gggggcactt cggtgagggt 5040
gacagggtgg cctatctcaa gggagcaggg ccaccttcct gcaagtttac tggggccagt 5100
ttgtaccagt tcagattctg cctgttttca agatggcagt cccaaaccca acaactgttg 5160
gccacactga aagcaggagc ccctctggtg ctcctagagg gtggcccaga ggagctgtgc 5220
cagggcgtgg agaggagggc accagggggc cgcaggggtc tctccaccct gcaggggccc 5280
agactgcctg caggtcaggc acaggggcat ctacctagac aggacagcag ggtggacccc 5340
agtttggaag ctgagccccc agccacgaac atggatctga ggaggggccc ttgggtcggg 5400
ccctggagac gacacacggc agcccacagg ccacgacaga cgctggatgc cctcctaccg 5460
ccagacacct ccccagaggc cttggacctc cttaggcgac tcctggtgtt cgccccggac 5520
aagcggttaa gcgcgaccca ggcactgcag cacccctacg tgcagaggtg ggggtgggag 558Q
agagtccccc aagtgcgggg ggacagaggt gggggcagga gagagccagc ccatgaggga 5640
cagcccccac agcagggacc ctgctgtgac ggcttgaggg gctcccttgg ccgcagcccg 5700
ggccccacct ccctggctcc ctgcaggttc cactgcccca gcgacgagtg ggcacgagag 5760
gcagatgtgc ggccccgggc acacgaaggg gtccagctct ctgtgcctga gtaccgcagc 5820
cgcgtctatc aggtgctccg gctctcgacc cctatcatcc cctgtctact gcaccctgga 5880
ggctgcctcc tatgtcagag acccccaaac gccccatgcc caggctgtga cctctgagca 5940
cccttcccct cccgcagatg atcctggagt gtggaggcag cagcggcacc tcgagagaga 6000
agggcccgga gggtgtctcc ccaagccagg cacacctgca caaacccaga gccgaccctc 6060
agctgccttc taggacacct gtgcagggtc ccagacccag gccccagagc agcccaggcc 6120
atgaccctgc cgagcacggt gtgtgatctt tgctggccgc ccacgcggag catggcccgg 6180
gccccttctg cctgtgctgc caactatgcg cagcattcgg ttcctgaccc tggggttgac 6240
ccactgaccc cggggttgac ccactgaccc cacagagtcc ccccgtgcag ccaagaacgt 6300
tcccaggcag aactccgctc ccctgctcca aactgctctc ctagggaatg gggaaaggcc 6360
ccctggggcg aaggaagcgc cccccttgac actctcgctg gtaagtcatg gtggggcggg 6420
cacaggaggg acccctcctc tgcacctttc agtgaccctg tgacatggcc cttcccaggt 6480
gaagccaagc gggaggggag ctgcgccctc cctgacctcc caggctgcgg ctcaggtggc 6540
caaccaggcc ctgatccggg gtgactggaa ccggggcggt ggggtgaggg tggccagcgt 6600
acaacaggta agcccggccc agtctgcccc cgtcccctca tcctcctttc ccctttcccc 6660
ttcccccctg cttttccctc ccttccccat gcttcccatt gcccctccaa tgtccagttc 6720
aaatctctcg aggacctcaa ggcctcccct ccactgcacc ccctctgatg gcccctttat 6780
gtgaccctca actgtacaca ggtccctccc cggcttcctc cggaggcccg gcccggccgg 6840
aggatgttca gcacctctgc cttgcagggt gcccaggggg gtgccagggc tttgcttgga 6900
ggctactccc aagcctacgg gactgtctgc cactcggcac tgggccacct gcccctgctg 6960
gaggggcacc atgtgtgagc cgccctactc ccttcacctg gccctctgtt cctgccccag 7020
ccccttcccc agacccctct ccagtctcct gcacccctta gccctccctg ctttgcctgg 7080
cccgttgaag ttccagggag cttgcccggg tctcctcggg ggagcagatg agggccctgc 7140
ccccgcccca ctgacttcct ccaataaagt catgtctgcc cccaacctaa gcagccatcg 7200
ttcctcccct cccctctgag gtcacagcat ccactagctg ggggccccgg cccctttcct 7260
gaagcctcca ctcctctgag gaccccaccc cacccccgtc ctgaaacctc caccccagag 7320
cccagtgccg ccccctagag gccctgccca ctgcacatcc agcactgggc ttttccctcc 7380
aggtttgcct ggggcagctt cttgttcttt gtccatcatt tccttacctg ctgtggcttc 7440
4
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
agggtccagg ctgcccccca gggtggtcct gtggggtagg gacgtagggt caccccctgg 7500
ccatgtttgt gactctgagc cagaggagag aaggggagag agaaggggga cacccctccc 7560
cctgctgtca gggactgcag cctgcgcccc ctagtatggc cactgcacct gatctgtctt 7620
caggtctccg taggtgaggg tgggagacag acatctcgcg aggtcagggt tacctcctct 7680
tgtcaccccc aggcaaggtc cctggtgtga gttcaggcca gggctgtgca gggctgcaaa 7740
gatcaaaggg gccctgtggg cacagacctg tgtcctaggg tgccaggtgt cctcagctgc 7800
acctgcccat gggttggggt tggaacacaa ggaggcagct ggaaagctca caggctggag 7860
gagctcacag tctaaagggc gcggcctgtg ctgtcggtgg cggagttggg ctgccaggct 7920
cacagtctgg gaagctcata ggccggagga gctcacagtt tgaagggtgc ggcctgtgct 7980
gtggtcggtg ttgggctgcc aggagagggg cgctgctggg ttgtggaagc cattgccacc 8040
atgggggagg gcggggaagg acaagatgtg ggtgggggag ctgagcagaa ggtgagagct 8100
ggcgctgccc tggtgctgga ccaggcacct gcaagagact cagaaaggga ggctgggttt 8160
gggagaaggt tggaggaggc ggaggaggga tcgggagggc ccgaggaagc ggtgagccag 8220
tcagagaccc agcccagggg ctgtttcctg agggggctgc cgagggaggt gcttgttgag 8280
cttca 8285
<210> 4
<211> 544
<212> PRT
<213> Rattus norvegicus
<400> 4
Met Cys Ala Ala Glu Va1 Asp Arg His Val Ser Gln Arg Tyr Leu Ile
1 5 10 15
Lys Arg Arg Leu Gly Lys Gly Ala Tyr Gly Ile Val Trp Lys Ala Met
20 25 30
Asp Arg Arg Thr Gly Glu Val Val Ala Ile Lys Lys Ile Phe Asp Ala
35 40 45
Phe Arg Asp Gln Thr Asp Ala Gln Arg Thr Phe Arg Glu Ile Met Leu
50 55 60
Leu Arg Glu Phe Gly Gly His Pro Asn Ile Tle Arg Leu Leu Asp Val
65 70 75 80
Ile Pro Ala Lys Asn Asp Arg Asp Ile Tyr Leu Val Phe Glu Ser Met
85 90 95
Asp Thr Asp Leu Asn Ala Val IIe GIn Lys Gly Arg Leu Leu Glu Asp
100 105 110
Ile His Lys Arg Cys Ile Phe Tyr Gln Leu Leu Arg Ala Thr Lys Phe
115 120 125
Ile His Ser Gly Arg Val Ile His Arg Asp Gln Lys Pro Ala Asn Val
130 135 140
Leu Leu Asp Ala Ala Cys Arg Val Lys Leu Cys Asp Phe Gly Leu Ala
145 150 155 160
Arg Ser Leu Ser Asp Phe Pro Glu Gly Leu Gly Gln Ala Leu Thr Glu
165 170 175
Tyr Val Ala Thr Arg Trp Tyr Arg Ala Pro Glu Val Leu Leu Ser Ser
180 185 190
Arg Trp Tyr Thr Pro Gly Val Asp Met Trp Ser Leu Gly Cys Ile Leu
195 200 205
Gly Glu Met Leu Arg Gly Gln Pro Leu Phe Pro Gly Thr Ser Thr Phe
210 215 220
His Gln Leu Glu Leu Ile Leu Glu Thr Ile Pro Leu Pro Ser Met Glu
225 230 235 240
Glu,Leu Gln Gly Leu Gly Ser Asp Tyr Ser Ala Leu Ile Leu Gln Asn
245 250 255
Leu Gly Ser Arg Pro Arg Gln Thr Leu Asp Ala Leu Leu Pro Pro Asp
260 265 270
Thr Pro Pro Glu Ala Leu Asp Leu Leu Lys Arg Leu Leu Ala Phe Ala
275 280 285
Pro Asp Lys Arg Leu Ser Ala Glu Gln Ala Leu Gln His Pro Tyr Val
290 295 300
Gln Arg Phe His Cys Pro Asp Arg Glu Trp Thr Arg Gly Ser Asp Val
305 310 315 320
Arg Leu Pro Val His Glu Gly Asp Gln Leu Ser Ala Pro Glu Tyr Arg
325 330 335
Asn Arg Leu Tyr Gln Met Ile Leu Glu Arg Arg Arg Asn Ser Arg 5er
340 345 350
Pro Arg Glu Glu Asp Leu Gly Val Val Ala Ser Arg Ala Glu Leu Arg
355 360 365
CA 02430624 2003-06-05
WO 02/46382 PCT/USO1/46172
Ala Ser Gln Arg Gln Ser Leu Lys Pro Gly Val Leu Pro Gln Val Leu
370 375 380
Ala Glu Thr Pro Ala Arg Lys Arg Gly Pro Lys Pro Gln Asn Gly His
385 390 395 400
Gly His Asp Pro Glu His Va1 Glu Val Arg Arg Gln Ser Ser Asp Pro
405 410 415
Leu Tyr Gln Leu Pro Pro Pro Gly Ser Gly Glu Arg Pro Pro Gly Ala
420 425 430
Thr Gly Glu Pro Pro Ser Ala Pro Ser Gly Val Lys Thr His Val Arg
435 440 445
Ala Val Ala Pro Ser Leu Thr Ser Gln Ala Ala Ala Gln Ala Ala Asn
450 455 460
Gln Pro Leu Ile Arg Ser Asp Pro Ala Arg Gly Gly Gly Pro Arg Ala
465 470 475 480
Val Gly Ala Arg Arg Val Pro Ser Arg Leu Pro Arg Glu Ala Pro Glu
485 490 495
Pro Arg Pro Gly Arg Arg Met Phe Gly Ile Ser Val Ser Gln Gly Ala
500 505 510
Gln Gly Ala Ala Arg Ala Ala Leu Gly Gly Tyr Ser Gln Ala Tyr Gly
515 520 525
Thr Val Cys Arg Ser Ala Leu Gly Arg Leu Pro Leu Leu Pro Gly Pro
530 535 ~ 540
6