Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Stylus Computer
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to a data entry system and method based on
hand-writing-sound recognition system, through which, a naturally, easily
and quickly full text and functions input can be provided. It also relates to
a
computer mouse system for data entry and manipulation, for mobile and fix
1o electronic devices. It finally relates to a stylus-type computer device,
using
the above-mentioned data entry methods and means.
Background of the Invention
Miniaturization has been a key component to recent technological
advancement, enabling production of many devices that would otherwise
be impracticable for reasons of size alone. In fact, the very essence of, for
example, portable computers and cellular phones, is their size as a primary
2o feature.
Yet, primarily because of human constraints, there are many
obstacles to the growth of miniaturization in several areas. For example, it
1
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
may be desirable to have a portable computer that fits in one's wallet, but
such a computer would not be useable without a large input device that
enables human interaction with the computer. In other words, complex
miniature computers and devices such as cellular phones (now, also used
for the Internet, email, m-commerce, Short Massages Services, etc.),
notebooks, Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) devices, require keyboards,
numeric pads or other input facilities to allow the user to enter a phone
number, send e-mail or transcribe a letter, etc. Also a convenient LCD
display for viewing data entered or received is an important feature. Thus,
1o as advanced as miniaturization technology may get, there are other human
factors involved that prevent certain devices from realizing a truly
miniature state.
As is well known, the key feature of a successful technological
15 product, is its easily manipulations. For above-mentioned instruments and
similar devices, a quickly, easily and most importantly, naturally, full text
and fiinction entry system is vital. Also a display device of the width of a
standard text line is appreciable.
20 Proposals have been put forward to solve this fundamental man-
machine-interface problem of how to quickly and easily enter text and
functions using small communication devices.
2
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
The telephone-type keypad, is the most common input device for
small electronic and telecommunications instruments. It is integrated in
many electronic devices such as mobile and wired telephones, PDA,
notebooks, laptops, faxes, remote controllers of TVs or other electronic
devices, cameras, etc. This keypad has usually twelve keys, while the
number of characters and functions used for writing texts or massages are
at least seven times more. For example, a computer keyboard has more than
eighty keys, while some of those keys are used for two characters, symbols,
or functions.
Because of the telephone keypad limitations due to its insufficient
number of keys (e.g. mobile phone keypad), each key of a standard
telephone keypad contains a group of characters and usually one number.
Usage of the Internet or even entering a short message engages a lot of
complexity for the user.
One solution to solve this problem, is to provide multiple presses of
a single key for selecting a letter or symbol among those represented by a
key. This system is currently used for most mobile phone keypads. This is a
time consuming method and it frustrates the user.
To improve that system, word disambiguating software products are
developed. A dictionary database and language model are used to scan and
3
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
present possible words according to keys pressed. Later the user selects the
desired word among presented possibilities. Such approach engages a lot of
problems such as out of vocabulary words or obliging the user to
concentrate for selecting a word. In addition, entering numbers or single
characters are again time consuming procedures.
External miniaturized keyboards are also produced to overcome the
problem but they oblige the user to carry two different instruments,
interfering with the basic idea of small electronic products, which is their
to easy portability.
One recent technology that has attempted to overcome such
limitations is voice/speech- recognition technology. Voice recognition is
the process of recognizing one or more voice patterns from an individual's
15 voice as a corresponding computer input command, word, or function. For
example, rather than typing a letter on a keyboard a user speaks that letter,
wherein the recognition engine associates the voice pattern of that letter
with the corresponding computer input character of that letter. Thus,
individuals may operate devices in this manner without an input device
2o since the user's voice provides all of the input. Unfortunately,
considering
the many complex aspects of an individual's voice, there is yet a
recognition device that can accurately recognize voice patterns at a
suff cient level where input devices can be completely replaced.
4
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Additionally, several letters such as "B" and "P", or "D" and "T",
can easily be confused by a speech engine. This is not necessarily a
shortcoming of the engine as these letters can easily be confused by the
humans as well. Hereafter, a list of some of the problems and
disadvantages concerning voice/speech recognition systems;
- Only for one language, mostly English
- Recognizing only one person's voice
- Outside noise disturbance (specially, when using mobile
telecommunication instruments) reduces the recognition accuracy
- Not good for small displays because of correction inconvenience
(specially when using instruments with small LCDs, such as mobile
phones)
- Many mistakes may occur when speaking single words
(discontinuous speaking)
- Similar pronunciation for different words (e.g. two, to, too)
- Not predicting the user intention when writing numbers (e.g. twenty
four, 24)
- Not predicting the user intention when writing mixture of numbers
and symbols (e.g. six by four, 6 by 4, 6 x 4)
- Difficulty to distinguish between letters ( e.g. B, P)
5
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
- Usually many characters are pronounced with only one syllable,
making the recognition difficult (e.g. "write", "right").
Most importantly, due to the privacy issue, this system may not be
appropriate of being used in, for example, public places. Speaking letters,
words, or commands is not a discrete input system.
Another method of data input is the hand writing recognition
systems. Different directions for this method can be considered:
l0
a) Documents may be written by hand and later been read (e.g. delayed
procedure) and digitized by means such as optical readers. Recognition
of a person's hand-writing through this system is a very complicated
task because it only relies on written graphs which are completely
different for each person. There is not yet an appropriate recognition
system based on this method.
b) Real time hand-written detection means such as PDA devices, optical
readers, etc., that instantly process multiple input parameters such as
2o hand-written graphics, pen directions by which the graphics are written,
angles in graphics, time at which each point of graph was written etc.
6
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Because letters and characters are often simple graphs and in many
cases they loolc alike, misinterpreting errors may occur by the recognition
engine. Therefor some character writing restrictions are imposed to users.
The most known instruments using this system are palm-type PDA
devices. The device has a digitizing system and a sensitive writing surface.
A corresponding pen is provided for writing graphics on said surface. It has
also a small screen to print the data entered after being digitized. Usually
the procedure of writing a symbol must be accomplished without removing
1o the pen from the writing surface. A text must be written character-by-
character, separately. Hereafter some disadvantages of this system:
- Need of canying a sensitive writing surface.
- Writing is slow because the writing surface of a PDA is small and
user must survey to not exit it.
- User must carry both PDA and corresponding pen and more
importantly, using his both hands whole writing which is not
convenient in mobile environment.
- Display is of a small size
2o - The PDA itself is bulky and may not permanently been carried, for
example, in a user's pocket.
7
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Notwithstanding the miniaturization issue, portable and other
electronic devices have many security and efficiency problems. For
example, an individual who misplaces or loses a cellular phone must rush
to disconnect his or her communications service before a thief or other
person uses the phone to generate unauthorized charges. One known
method for preventing such unauthorized use is to lock the cellular phone
or other device with a code system. Although, effective in many cases, this
system is painstaking and inefficient for the true owner, who must activate
the phone via a lengthy process before dialing. Similarly, there is no simple
1o method for preventing unauthorized use of many electronic devices without
first locking the device with a code system or, other time consuming and
inefficient process.
The security issue becomes more vital, when the instrument is used
15 for purposes such as E-commerce or banking operations, which require, for
example, the credit card number or bank account information of the user.
Therefore, what is needed is a technology that resolves the human
constraint dilemma mentioned above, so that miniaturization can continue
20 to realize its true potential. Furthermore, such a technology should also
provide means for a more secure and efficient mechanism that can prevent
unauthorized use of devices and information among other things, as
compared with the prior art.
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
It is an object of this invention to provide the electronic instruments
with data entry needs (specially, mobile communication instruments), with
a familiar, quick, and easy data input systems. It is also another object of
this invention to provide the user with a familiar, easy to carry stylus-type
computer or PDA device, having discrete, quick, and easy data entry and
manipulation capabilities, and a large display to enable the user to, for
example, work on a display of A3/A4 paper width. The systems, devices,
and methods describe hereafter, may be used independently, or in
1o conjunction with other conununication devices and systems.
Brief Description of the Drawings
In the drawings in which like reference characters denote similar
elements throughout the several views:
FIG. 1 a shows a pen and a writing surface;
FIG. 1b demonstrates a sample of the pen directions while writing;
2o FIG. 2a shows a pen, writing a two-direction line;
FIG. 2b shows an imaginary waveform demonstration of the sounds
produced by the pen and the writing surface contact when writing the
above-mentioned line;
9
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIG. 3a shows a desired writing instrument tip to produce different
sounds for different directions when writing on a writing surface;
FIG. 3b shows a writing instrument tip surface structure for
producing above- mentioned different sound productions.;
FIG. 3c shows two different sound waveforms produced by a
structured tip of a pointing device, while drawing two similar lines in
opposite directions.
FIG. 3d shows a written symbol produced by a pen tip such as the
l0 one shown in FIG. 3b, and the waveform of the sounds produced by said
pen tip while writing that symbol on a writing surface.
FIG. 4a shows examples of different shapes of writing tips,
enhancing the production of different sounds while stroking in different
directions on the writing surface;
FIG. 4b shows an example of different texture of writing tips,
enhancing the production of different sounds while stroking in different
directions on the writing surface;
FIG. 4c shows an example of combination of different shapes and
2o different textures of writing tips, enhancing the production of different
sounds while stroking in different directions on the writing surface;
FIG. 4d shows a writing instrument angle relating to a writing
surface, while a user is writing.
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIG. 4e shows the contacted area of a conical (e.g. convex) pen tip
and a writing surface while writing;
FIG. 4f shows a front view of two different contacted areas of a pen
tip on a writing surface, at two different rotating to pen axis positions.
FIG. 4g shows side and front view of another pointing device
structured tip shape.
FIG. 5a shows a hand-written letter graph produced by a pen;
FIG. 5b shows the imaginary graph of the sounds produced by said
1o pen and writing surface contact during writing that letter;
FIG. 5c shows an imaginary speaking voice graph of that character;
FIG. 6 shows a standard computer keyboard containing keys
representing English characters and symbols.
FIG. 6a shows similar hand written characters.
FIG. 6b shows printed and hand written English uppercase and
lower case characters and resembling symbols.
FIG. 6c shows how three resembling hand written characters may
be written, to be distinguished by a recognizing system.
2o FIG. 6d shows still four resembling hand written characters, and a
proposal of how to write them to make distinguishing possible.
FIG. 6e shows a resembling, number and character;
11
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIGS. 6f 6j shows printing and hand written characters by
categories, and a proposal of directions to be respected while writing them,
to permit the recognition system to recognize them easier.
FIG. 6k shows all keyboard printed characters and and a proposal of
directions to be respected while writing them, to permit the recognition
system to recognize them easier.
FIG. 7 shows a diagram of hand writing recognition processing,
according to one embodiment of the invention;
to FIG. 7a shows a stylus-type computer using hand writing sound
recognition system as input system;
FIG. 7b shows a front view of pen-type tip, for said stylus-type
computer being equipped with additional features;
FIG. 7c shows a stylus-type computer according to one embodiment
of the invention;
FIG. 7d shows a the front view of a writing tip of a stylus-type
computer according to one embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 7e shows a stylus-type computer having an exponential means
to amplify sounds of contacts of the pointing tip on a writing surface while
writing.
FIG. 7f shows a stylus-type computer having a resonating chamber
to amplify sounds of contacts of the pointing tip on a writing surface while
writing.
12
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIGS. 8a-8d show said stylus-type computer and an example of a
writing tip in closed, open, and writing position according to one
embodiment of the invention;
FIGS. 9a-9c show the erasing feature and erasing procedure of said
computer according to one embodiment of this invention;
FIGS. l0a-lOb show anther erasing procedure of said computer
l0 according to one embodiment of this invention;
FIG. 11 shows a stylus-type computer according to one embodiment
of the invention having a flat or concave LCD display.
FIG. 11 a shows a stylus-type computer according to one
embodiment of the invention having a curved or cylindrical (e.g. convex)
LCD display.
FIG. l 1b-1 lc illustrate the average size of said curved/cylindrical
display.
FIG. 12 show a stylus-type computer having a button type mouse,
for manipulating and eventually entering data, according to one
embodiment of the invention.
13
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIG. 12a shows some of pen axis movements and positions of said
mouse, according to one embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 12b shows clicking pen axis movements/positions of said
mouse, according to one embodiment of the invention
FIG. 12c shows relatively to stylus axis rotating movements of said
mouse, at each position, according to one embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 12d shows the side view of another kind of movements of said
mouse caused by perpendicularly to stylus axis pushed by a user on mouse,
according to one embodiment of the invention;
to FIG. 12e shows the front view of the mouse and some pushing
directions.
FIG. 12f shows a side and front view of the mouse having a bull to
manipulate a pointer/selector mean on a display of the stylus type
computer.
FIGs. 13a-13c show how a menu list may be selected by the mouse
according to one embodiment of this invention;
FIGS. 14a-14f show how a menu may be selected by the mouse
2o manipulation according to one embodiment of this invention;
FIGS. 15a-15h show how a menu bar and a function may be selected
by using the mouse, according to one embodiment of this invention
14
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIGS. 16a-16d show how to advance or backward a text on a display
LCD, by using the mouse, according to one embodiment of this invention
FIGS. 17a-17f show how to advance or backward a cursor, character
by character, in a text by using the mouse, according to one embodiment of
this invention
FIGS. 18a-18d show, how to move a text selecting indicator on a
document displayed on the screen, when mouse in a predetermined
position, according to one embodiment of this invention
FIGS. 19a-19e show the procedure of selecting a portion of a text by
the mouse according to one embodiment of this invention;
- .
FIGS. 19a-19d show a copy procedure by using the mouse,
according to one embodiment of this invention
FIGS. 21 a-21 a show a paste procedure by using the mouse,
according to one embodiment of this invention
FIGs. 22a-22b show how a selected text may be deleted by using
the eraser, according to one embodiment of this invention
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIGS. 22c shows how a selected text may be deleted by using the
eraser, according to one embodiment of this invention
FIGs. 23a-23e show, a menu bar and a function selecting procedure,
by the computer "Normal Select" indicator using the mouse, when mouse is
in another predetermined position, according to one embodiment of this
invention;
FIGS. 24a-224h show, how to move a text selecting indicator on a
l0 document displayed on the screen and, a menu bar and a function selecting
procedure, by the computer "Normal Select" indicator, using the mouse in a
same predetermined position, according to one embodiment of this
invention;
FIGs. 24i-224n show how a cursor may be manipulated in a text by
perpendicularly to stylus axes pushes on the mouse, according to one
embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 25 shows different positions of the mouse and the clicl~ing
direction at each position.
2o FIG 25a shows the mouse in one predetermined position, wherein
text manipulating procedures and steps are assigned to the movements of
the mouse in that position.
16
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIG 25b shows the mouse in another predetermined position,
wherein menu and function manipulating procedures and steps are assigned
to the movements of the mouse in that position.
FIGS. 26a-26c show the mouse system and device described for the
stylus-type computer, to be used in other type of computers at different
locations on them according to one embodiment of this invention
FIG. 26d shows a computer equipped with a writing surface and the
input system of the invention, replacing the traditional keyboard;
FIG. 27a shows pressure buttons for the stylus-type computer
according to another embodiment of this invention;
FIGs. 27b-27f show an additional mufti directional button and their
function in the stylus-type computer, according to one embodiment of this
invention;
FIG. 27g-27j show a mufti position clip button for the stylus-type
computer according to another embodiment of this invention;
FTG. 27k shows a clip button of Figs. 27b-27f located closed to the
writing tip of the stylus computer according to one embodiment of the
invention;
FIG. 27L shows a mufti sectioned/directional clip in open position,
used as directional microphone andlor an antenna and/or a clip button for
the stylus computer according to one embodiment of the invention;
17
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIGS. 27m-27n show the multi-sectioned clip of FIG. 27L, in
variety of open positions;
FIG. 28a-28e show an additional input system by using the display
s and the mouse, according to one embodiment of the invention.
Figs. 29-29d show a cover for the stylus-type computer protecting
the LCD display when not in use and the steps of covering the computer,
according to one embodiment of the invention.
1o Figs. 29e-29g show the stylus type computer while it is used as a
telephone and tele-communicating instrument.
FIG. 30a shows a stylus-type computer according to one
embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 31 shows a stylus-type computer, having different navigation
buttons, according to one embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 31 a shows a cursor navigating button according to one
embodiment of the invention.
FIGS. 31b-31f show a cursor navigating on the screen by
manipulating said button according to one embodiment of the invention.
18
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIGs. 32a-32f show a menu navigating button and its manipulation
according to one embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 33a shows a mobile telephone having a writing-surface and a
microphone for inputting the sounds produced by a pen while writing on it
according to one embodiment of the invention. .
FIGS. 33b-33c show a wrist-mounted device such as a watch
combined with an electronic device such as telephone or PDA, having a
display, a writing surface and a microphone for inputting the sounds
to produced by a pen while writing on it, according to one embodiment of the
invention.
FIG. 33d show a wrist-mounted device such as a watch combined
with an electronic device such as telephone or PDA, having a display and a
microphone for inputting the sounds produced by a pen while writing on it,
15 according to one embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 33e shows a number of electronic devices, having at least a
display and eventually a microphone for inputting the sounds produced by a
pen while writing, according to one embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 33f 33g show an enhanced keypad to be combined with the
2o hand writing sound recognition system of the invention, permitting full
text
and function input;
19
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
FIG. 34a shows a stylus-type computer having means to determine
its pen tip position from a beacon, according to one embodiment of the
invention.
FIG. 34b shows the cover of the stylus-type computer of fig. 29a,
used as the beacon, according to one embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 35 shows a notepad having a horizontal beacon to permit a
stylus-type computer to determine its pin position on that notepad,
1o according to one embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 36 shows a notepad having horizontal and vertical barcodes
indicating a locations on that pad.
FIG. 37 shows a writing surface having indicating number, or sins,
or colors, to indicate locations on it.
FIG. 3~ shows a writing surface and a projector to project location
indicating signs on that surface.
Detailed Description of the Inyention
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
In the following description, a method of data entry is described, in
which a pointing device such as a pen, stylus, or even a user's finger is used
in conjunction with a writing surface to facilitate hand written data entry.
The input is based on the sounds produced by the contact of the pointing
device or ianger, and the writing surface during writing.
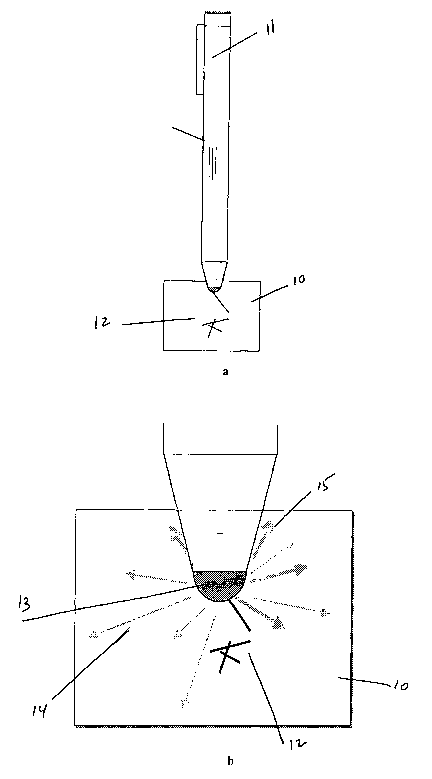
With initial reference to Fig.la, a pen (11) and a writing surface
(10) are shown wherein, two symbols (12), are written by the pen.
With reference to Fig.lb, a zoomed portion of a pen tip (13) is
shown. It demonstrates as example, some pen tip possible writing
movements and directions on the writing surface (10). The pen may move
in different directions (14). In this figure some of those directions (15) are
used to write the symbols (12) on the writing surface (10).
The contacts between the pen and the writing surface during
writing procedure, produce different sounds and noises. Those sounds may
vary depending on parameters such as pen tip surface structure, starting
point manner, symbol ending manner, pen directions, change in directions,
2o duration of each direction, speed in each direction, variation in pressure
force of the pen on the writing surface, etc.
21
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Fig. 2a shows a writing surface (20) and a pen (21). By using the
pen, a user has drawn a symbol (25) on the writing surface. The symbol
consists of two straight lines (22,23), drawn continuously wherein second
line direction is different from the first line. Each drawing has its own
characteristics. In this example, some of the characteristics are, information
such as starting point (24) manner, first and second line directions
(211,212) and duration, changing point manner (e.g. curved, straight,
accentuated), etc. Usually contacts of the tip of a pointing instrument on a
writing surface, while writing a symbol by a user, cause the production of
to different sounds and a sound waveform characterizing that symbol. Each
time that symbol is written by the same pointing device tip, the same user,
and in a same manner, same sound and waveform will be produced.
Fig Zb represents an imaginary waveform (26) of the sounds
15 produced during the writing of symbol (25) of fig. 2a, showing changes in
amplitude (y axis) over time (x axis). First part (26) of waveform relates to
the sound produced by pen tip shock on the drawing surface at the starting
point (24). Second part (27) of waveform relates to the sound produced
during the first line (22) drawing. Because the changing direction point (29)
2o is not accentuated, no sound may be produced. Third and last part (28) of
the waveform is produced by drawing the second line (23).
22
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
The sounds produced by a shock of the pen tip on a writing surface
may be different for each symbol. For example starting shock sound
waveform of letter "c", is stronger than starting point of letter "b". This is
also true for ending points. Ending point sound of letter "c" weakens slower
than ending point of letter "b". This is another additional parameter that
may be considered by a hand writing sound and/or sensor recognition
system (hereafter HWSRS) which will be explained in detail later.
Variation of sounds or sound waveforms produced by strokes of a
pointing device in different directions on a writing surface may not be
easily distinguished if the pointing device tip surface is smooth. On the
other hand those variations may easily be recognized if the pointing device
is equipped with a structured coarse tip surface, in a manner to produce a
different sound for a different direction. Fig. 3a illustrates the front view
of
a pointing device tip, and imaginary different waveforms (31) produced by
shifting that structured pointing device tip (30), in different directions
(32)
on a writing surface.
In order to produce such different sounds, one solution is to create a
pointing tip (35) as shown in Fig. 3b. Pointing tip (35) may be divided to
different portions (36), wherein each portion may be made of different
materials (33,34) to produce different sounds (37,38). This system will also
permit to have, for example, two different sounds (38,39), for two opposite
23
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
directions (331,332). Also, for better accuracy, neighboring portions rnay
be structured in a manner to produce distinctively significant different
sounds.
FIG. 3c, shows two parallel lines (341,342), drawn by a pointing
device having a structured tip such as a tip (35) described before. First line
(341) is drawn from right to left direction (345) producing a sound shown
by its sound waveform (343). Second line (342) was drawn parallel to the
first line. It was drawn by the same pointing device being in the same
1o position in the user's hand as for the drawing of the first line, but it
was
drawn in the opposite relationship, from left to right (346), producing a
different sound which is shown by its sound waveform (344). Because the
left side pen tip surface was different from the right side, two different
sounds were produced for two apparently similar lines. This is an
15 advantageous feature because it permits to have two different symbols for
apparently two similar symbols. For example the number "0", may be
written in clockwise direction, and the letter "O" may be written in counter
clockwise direction. By using this system, they will produce two different
sounds and therefor two different sound waveforms. They will easily be
20 recognized by a HWSRS.
FIG. 3d shows a written symbol (351), and its sound waveform
(352). The symbol is written by the pointing tip of FIG. 3b. To write this
24
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
symbol, the pointing tip has used five directions (353). Waveform (352) is
produced by five consecutive sounds (354) produced by five pointing tip
directions (353) during the drawing of the symbol.
It is understood that the pointing tip shown in FIG. 3b is only an
example. Many other forms or types of pointing tips maybe considered. For
example, a pointing tip maybe divided in less or more portions. As shown
in FIG. 4a, pointing tips can have different shapes and forms. Their surface
may be of different shapes and made from different materials, as shown in
to FIG. 4b. To enhance different sound production and to accentuate their
differences, as shown in FIG. 4c, the pointing tip surface may be divided
into different portions wherein each portion can be made from different
materials (410,411). In addition the divided portions of the pen tip can have
different forms.
As shown in FIG. 4b, a pointing tip may contain, for example,
different pins distributed on different locations on the tip surface. The pins
may be positioned on the tip surface in a manner to touch differently the
writing surface in each direction and to produce different sounds for each
2o direction. For this purpose, the pins may also have different shapes. They,
for example, may be longish (412), short (413), inclined to left or right, and
installed in different orientations on the pointing tip (415, 416). This will
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
permit to produce different sounds by the same portion of the tip but in
different shifting directions.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the tip surface may
have sensors (414), to produce different signals to indicate information
such as directions, duration of directions, etc., according to pressure force
applied on its different sensors by drawing movements of the pointing tip
while writing symbols or commands. Then accordingly, the device may
produce different sounds, different waveforms and other information
1o needed for HWSRS engine to recognize the written symbol.
Also the pointing device maybe equipped with a direction
recognition system being capable of recognizing the pointing device tip
directions on a writing surface or in space. Then accordingly, the device
may produce different sounds, different waveforms and other information
needed for HWSRS engine to recognize the written symbol.
To produce the same sound for the same direction, the pen tip
surface portion in touch with the writing surface, must always have the
2o same similarities (e.g. structure, texture, material, position). The above-
described pointing tip surface structures oblige the user to hold the pointing
device in a predetermined position in hand. To avoid that restriction, pen
26
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
tip (and its surface) must be structured in a way so that when it touches the
writing surface, the portion in touch will always be similar.
As shown in Fig. 4d, while writing a symbol, a user usually keeps
the stylus or pen (420) in the same position in his hand and the same angle
(424) in relationship with the writing surface (421). He usually does not
radically change the pen position (425) in his hand. Fig. 4e shows the side
view of a hemispherical form (e.g. convex) pointing device tip (430). While
writing with a pointing device tip having a curved form (convex surface)
to (435), on a flat writing surface (431), only a small portion (432) of the
pointing device tip surface, closed to contact point (433), between the
pointing device and the writing surface, may also get in contact with the
writing surface. If the tip has a harmonious form such as hemispherical
form, and by the fact that a user keeps always the pen in the same angle
15 relationship with the writing surface, the contact area will always have,
approximately, the same geometric form. If the tip surface is structured in a
way that the same contacted portion has the same structure, then the user
can take the pen, in any rotating position according to the stylus axis, in
his
hand and write on a writing surface. Fig. 4f shows the front view of a
20 hemispherical or conical (e.g. convex) pen tip (441). The pen tip is
structured in a way that every time the pen touches the writing surface with
a same predetermined angle but in different rotating positions (according to
pen axis), portions of the tip in contact with the writing surface (442, 443),
27
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
have the same form, structure, material, etc, (444, 445). It is understood
that the structure must be made in a way that when writing on a writing
surface, the pen tip produces different sounds for different directions.
Different structuring materials such as the pins described before, may be
used. Fig. 4g shows the side view cut (451) and the front view (452) of
another suggested pen tip form. It should be noted that the pen tip forms
and structures described in hereinabove, are only examples. Variety of
other pen tip forms and structures, made from variety of materials, may be
created by people skill in the art. For better and faster recognition,
plurality
l0 of hand written character sets and symbols sound waveforms and patterns,
may be produced by a user pen tip, in different writing angles relating to a
writing surface and introduced to the HWSRS .
Preferably also the writing surface may be structured in a way to
15 enhance the sounds produces by the pen tip.
It must be noted that while writing a symbol necessitating different
directions, consecutive different sounds produced accordingly by structured
pointing tip strokes on the writing surface, produce a waveform which
2o characterizes that symbol and only that symbol. For example, while writing
the letter "O", the pointing tip uses a variety of different short directions
that produce a characteristic waveform for. letter "O".
28
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Sounds, waveforms, and other characteristic information produced
by the pointing tip for each symbol or function may be patterned and
recorded, and later be processed by the HWSRS to recognize text or
drawings written by users. For example, waveforms of a user's hand-
s written sound character set, hereafter HWSCS, may be patterned as his
personal character set and "taught" to the HWSRS. For better accuracy, for
each writing surface a different Hand Writing Sound Character Set can be
provided.
1o FIG. 5a shows a stylus (511) having a structured tip (512). The
letter "e" (513) has been written by that stylus. FIG. 5b, is an imaginary
waveform of the sounds produced by said stylus while writing the letter
"e". Finally FIG. 5c, demonstrates an imaginary waveform of the letter "e"
pronounced by a user.
is
A comparison of these graphs demonstrate the advantages of the
present invention. First graph (513), the written letter "e", is a very short
graph. Depending on how, or by who this letter was written, it can easily be
misinterpreted by a traditional handwriting recognition engine, with for
20 example, the letter "c" or the letter '1". Contrary to it, the graph
(waveform)
of FIG. 5b, which was produced by sounds of pen tip movements on the
writing surface is a long graph with plurality of variations and
29
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
characteristics thanks to different sounds produced by different pen
directions while writing it. It will be easily recognized.
Finally the graph of FIG. 5c, is again a short graph with almost few
variations. It can be easily misinterpreted by the voice recognition engine
by letters such as b, d, p, or even an outside noise, etc. Waveform of sounds
produced by the pen tip contacts with the writing surface during a character
handwriting is much longer and varied, therefore the recognition by a voice
engine will be much easier.
l0
Hand writing input has many advantages comparing to voice input;
- it is discrete (privacy issue is solved)
- user intention is not considered ("24" is different than
"twenty four", 6X4 is different from, six by four, etc.)
- voice recognition engine shortcomings do not exist (p, is
different than b)
- words with similar pronunciation (e.g. two, to, too), are
written differently.
- discontinuous speaking issue is solved.
- Corrections are immediate
- It is good for all languages.
- outside noise is not a problem
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Traditional handwriting recognition systems are on character by
character basis. It is much easier to recognize a written character graph than
a written word graph. Two continuously written similar words never look
alike, even if they are written by the same person. On the other hand it will
be very difficult for a recognition system to distinguish the continuous
characters by which the written word is formed. But the traditional
handwriting recognition systems based on written graphs and character by
character basis, have a major problem that sometimes makes the
recognition difficult even by humans: Characters and symbol graphs are
to often too short and therefor in many cases they look alike. If they are not
written clearly, they may be misinterpreted and sometimes even not
recognized at all.
Also voice waveforms of a pronounced character and/or word may
be similar (e.g. "T", "Tee", "Tea". Therefore voice or speech recognition
systems are usually based on sentences. It is easier for a speech recognition
engine to recognize a sentence rather than a single word or letter. Speech
recognition system analyses the suggested received words and according to
a predicted sentence, decides for example, if a received word is "right", or
"write". This system is not good because in many cases, only single words,
letters or symbols, are inputted.
31
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
HWSRS brings the answer to all above-mentioned problems. It has
all advantages of handwriting system and solves its shortcomings. This
system may work, preferably, on character by character recognition basis,
but the recognition is based on recognizing waveforms, patterns and other
information of sounds produced by a pointing device tip on a writing
surface while writing those characters. Those waveforms, as explained
before, are much longer and more varied than written character graphs or
spoken sound waveforms, and contain more characteristic parameters such
as;
to - Start/end sound of a symbol, or a portion of a symbol if it is written
discontinuously;
- Number of syllables produced by writing a symbol wherein a
syllable refer to a portion of the symbol having a substantially
constant shape. The number depends on different angles in the hand
written graph and if the symbol is written continuously or
discontinuously. The number of syllables for each discontinuous
portion of a symbol is N+1, wherein, N, is the number of angles.
- Speed of writing in each direction causing changes in sound
accordingly;
2o - Differences in pressures on the writing surface while writing a
symbol, according to the shape of its written graph, causing changes
in sounds accordingly;
- Duration of writing time of each direction;
32
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Different users, or even a same user at a different writing period,
may use a different character set size (e.g. writing with smaller or
larger characters), causing shorter or longer sound for each
direction. Different portions of written characters may keep unique
relationship and proportion, even if they are written in different font
sizes. This resembles to "Octaves", in the music domain.
And other additional parameters deriving from this system;
Therefor recognizing becomes much easier.
Information such as length of a line, size of a character, etc., may
become available by using these parameters. According to these principles
and parameters, a sophisticated HWSRS, may even recognize symbols
according to hand written sound patterns of symbols written by a regular
pointing device tip such as a pen, or even a finger or nail of a user, on a
writing surface. In this case a structured tip may not be necessary.
The outside noise shortcoming may be easily overcome by
installing, for example, a microphone in the electronic device equipped
with the HWSRS or even in the pointing device itself. The sensors may be
connected to the pen tip by, for example, wires, so that only the sounds
produced inside the stylus as a result of the writing procedure are captured
and transmitted to the recognition engine.
33
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
In addition, for better accuracy, other systems such as hand written
graph recognition systems, pen/hand movements recognition systems,
voice/speech recognition, lip recognition, and/or other recognition systems,
separately or combined together, may be used in conjunction with the
HWSRS. For example, a user may write a symbol such as a character, a
word or a sentence, and speak it simultaneously. The combinations of
HWSRS and a voice recognition system may provide a better accuracy rate
for inputted characters. For a natural and user friendly inputting method,
while writing, a user may speak only the letters, words, sentences and other
to symbols which may naturally be spoken by people while writing a text.
Other symbols such as at least part of punctuations marks, etc., may only be
written without being speaking them.
The system may include one or more databases of letters, words and
15 symbols in different languages. A predictive word recognition system may
also be combined with the system to make the selection of a word possible
before entering it entirely. This system may allow an automatic selection of
the desired word by the system mostly before ending to enter it entirely and
sometimes even without the need of the user interference. This is possible,
2o because by writing, individually and sequentially, characters or symbols
(e.g. character by character basis) of a word, and the very small numbers of
corresponding words, in many cases, before finishing to enter the word
34
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
entirely, the word predictive system can either determine the desired word,
or may show a few possible words, and the user selects one of them.
Even if the user enters a wrong letter while writing a word, or the
HWSRS fails to identify a given letter, since in most cases other letters of
the word are entered correctly, the predictive word recognition system can
automatically correct the wrong letter.
It is understood that instead of being on character by character
1o basis, the system may be based on the recognition of an entire word or even
an entire sentence. In this case, sound waveform or sound pattern databases
for entire written words, symbols, or even sentences, may be provided to
the HWSRS.
15 For better accuracy and easier recognition, a user can "teach" (e.g.
train) the HWSRS, his/her hand writing. In this case the recognition
procedure will become easier and faster.
In addition, a user can create his own commands based on his hand
2o writing characteristics. For example his electronic device may be turned on
or turned off, only by his hand written instructions based on his hand
writing sound patterns and/or sound waveforms. He can also personalize
his instrument. In this case, the device can be manipulated by only his hand
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
writing input. A user can also cerate his own customized characters,
symbols, macros, functions, commands etc. A created symbol may refer to
plurality of other symbols or commands. Contrary to regular keyboards,
this system permits unlimited variety of symbols or commands to be
created and used by the user.
The user can also teach his signature to the HWSRS. In this case
his signature can never be imitated. For example, when opening a bank
account, the user can introduce the sound waveform of his signature, based
on his personal structured pointing tip and a selected writing surface, to his
bank references. The combination of the signature, personal structured
pointing tip and the selected writing surface will produce a unique sound
waveform and pattern, making the imitation impossible. Thanks to this
procedure, tele-banking transactions, e-commerce operations and the like
will become secured.
E-mails, short massaging services (SMS), etc., will become confidential.
First the user equips, for example, his friend's or his bank HWSRS, with
his hand written sound patterns or waveforms based on his personal
equipment (e.g. pointing tip structure, writing surface). Then all operations
2o or massages will be made or sent by his hand written sound patterns. They
will be compared with hand written sound patterns recorded in other party's
directory. After being matched the operation will be done and/or the
massage could be read.
36
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
For security reasons, a user can also create his own codes based on
his hand writing sound patterns. For above-described reasons, his codes are
strongly confidential permitting him to transmit coded documents which
maybe decoded by the other party, only if that party's recognition system
has a copy of coded patterns.
Numbers, digits, characters, symbols, commands, etc, may be
encoded by, for example, a user's customized additional meaningless (for
to non-concerned parties) written graphs, while writing a text, so that the
sound waveforms of symbols will have additional meaningless syllables.
These additional meaningless graphs may be written at any moment and
location (e.g. combined with the symbol or separately) while writing. They
will be filtered by the receiving party's HWSRS, familiar with customized
15 meaningless graphs of the user, resulting decoded information. This system
can help to send confidential information such as the credit card number of
a user in an E-Commerce operation.
It is understood that all voice or speech recognition systems and
2o other recognition systems such as traditional hand writing recognition
systems and technologies may be used to enhance the HWSRS.
37
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
The recognizing procedure may also, effectuate at a delayed time. It
means that all parameters, such as writing sounds, timings, writing speed,
etc., may be recorded while writing, and be processed later by a HWSRS,
to recognize the hand written symbols.
Almost every electronic device, and specially, mobile instrument,
may be equipped with input devices based on this method. Electronic
devices may be equipped with this HWSRS and a microphone connected to
eventually a writing surface. A user having a preferably a pointing device
to with a structured surface can input data by writing on that surface. FIGs.
33a-33e show some of those devices. For example, FIG. 33a shows a
mobile phone having a writing surface (3301), at least one microphone, and
a HWSRS. A user, having a pointing device with a structured surface
(3302), can input hand written data by using the pointing device on the
15 writing surface. Sounds produced by the strokes of the pointing device on
the writing surface while writing data, will be transmitted to a processor
and the HWSRS digitizes the data entered. This system can even be used in
very small devices such as the ones shown in FIGS. 33b-33d (e.g.
watchphone, wrist PDA device). FIG. 33b shows a wrist watchphone/PDA
2o device. FIG. 33c shows a LCD display unit (3311) and a writing surface
(3312) which are preferably located in the opposite side of the watch unit
(3313). A pointing device (3314) having preferably a structured tip surface
of the invention, is provided to input data by writing on the writing surface.
38
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
It is understood that an electronic device, itself, may be equipped with a
writing tip of the invention provided whithih a desired location of said
device.
By using a well-structured pointing tip, a good microphone, and a
sophisticated recognition engine, any surface on the device may be used for
writing on said surface. For example, as shown in FIG. 33d, the user can
input data on any surface of, for example, a watchphone metallic bracelet
(3315).
to
Depending on an electronic device design and/or concept, at least
on of, the microphone and/or the recognition system, may be integrated
within the pointing device (e.g. a pen) or within the electronic device
itself.
Of course, in case of the stylus computer those components may be
integrated within the stylus computer.
One advantage of using the HWSRS, is that it can be incorporated
in every electronic device without, eventually, the need of deforming those
devices.
Fig. 6 shows a traditional computer keyboard (600) containing
letters, numbers, punctuation marlcs, and other symbols for writing an
appropriate text or data. As is shown in Fig. 6a, when writing the keyboards
39
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
characters by hand, some of those characters, such as "1", "1", "~", "I" (602-
605), or "9", "g" (606-607), etc., may look almost alike. Distinguishing
between those characters will be impossible by a traditional hand writing
recognition system or even by the humans. This problem can be solved by
s using a structured pen tip and the HWSRS. Hereafter, some of most
important cases are described.
Fig. 6b shows a table (620) containing roman uppercase letters
arranged in a column (628) of the table, and the lowercase letters arranged
to in another column (629). Some of the characters and numbers, similar to
those letters, are written in next columns (630, 631). Proposed hand -
written symbols for those who are similar, are shown beside each of them
in white columns (641-644). Even the user himself, at his convenience, can
create his own hand written fonts, symbols, and written commands.
As shown, for some characters such as the letter "g" (632), there are some
apparently other similar characters such as the letter "q" (633), or the
number "9" (634). To permit the HWSRS to easily distinguish between
them, and because the HWSRS works on the sound waveforms and
2o patterns, of written symbols, as shown in Fig. 6c, the user may write those
letters, by using different directions ((635-637) for each. This will cause
different sound waveforms and patterns for each character, which then,
may easily be distinguished.
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
They will be patterned and memorized, according to the sound produced
while writing each of them. At each moment a user can create a new
symbols, or delete an old one. While writing symbols, the HWSRS,
compares them with the already patterned and memorized symbols. If the
system finds a pattern which matches with the inputted symbol, it selects
that pattern as the one entered.
As mentioned before, one objective of this system is to provide
to users, with a familiar input system and device. This is a very important
issue because people reject electronic devices with complicated input
systems. The traditional handwriting characters and standards should be
respected. Nevertheless for better accuracy some of advantages and
characteristics of this system may be used. For example, letter "O"
15 (uppercase), may be written in opposite clockwise direction (651), while
the number "0", maybe written in clockwise direction (652). They create
two different sounds and therefor two different sound waveforms. The
lowercase letter "o, may be written, as most people usually write (653).
2o There are some more specially difficult-to-distinguish characters.
For example, as shown in fig. 6d, if they are not differently hand written,
the lowercase letter "1" (660), the uppercase letter "I" (661), the number
"1" (662), or the character "~" (663), may never be distinguished by a
41
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
traditional hand writing system. To distinguish them from each other, they
can be written as in different common forms (664-667) respectively.
In addition, as shown in Fig. 6e, discontinuously written letters,
signs and numbers, such as upper case letters, "B" (669), or the number
"13" (66S), etc., may also be confused by a traditional hand writing
recognition system.
Fig. 6f shows a group of characters (670) that whole or part of them
to consists of a straight vertical line that may naturally be written
separately
from the rest of the same character (671). Because the handwriting
recognition system does not know the location (on a surface) where those
parts are written, for example, it can not know if a written symbol (672),
relates to the letter "T" (673), or to two separate characters, "~ -" or (I -
),
15 etc.
By using the HWSRS, the above mentioned problems may be
solved without deforming those characters. The third column from left
(674), shows the hand written characters corresponding to the printed
2o characters of the first column from left (6701). As it is shown, non of
those
written characters has been deformed. The only rules a user must follow, is
the (naturally common) directions by which the pen tip must stroke on the
writing surface. First column from right (675) shows proposal for directions
42
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
for each written character. It is understood that other directions may be
considered as well; even by the users. As mentioned before and shown
here, lowercase letter "1" (6712), and the number "1" (6711), can be written
differently. Character "~" (676), may be written by a straight line in upward
direction (677). Upward direction is not a common direction to write a
character. The reason to use it for this character, is that this character is
not
often used.
Now we can use a downwardly written straight line to write a lot of
l0 other characters and permit to distinguish them from each other and avoid
confusion. A straight line written in downward direction may always be
considered by the system, as a commencing part of a discontinuously
written symbol. When this line is written the system expects to receive
more written graphs) (e.g. strokes) to be followed after that line. By this
method uppercase letters such as "I, B, D, H, K, P, R, T" (678) and the
character "$" (683), may be written normally and been recognized by the
system. To not confuse the system, it must be noted that, as it is known by
hand writing principals, two different size of horizontal lines should be
used for writing characters, a short one and a long one. For example, the
2o horizontal line (679) used to write the letter "T", must be importantly
longer than horizontal lines (680) used for letter "I". This will permit to
avoid confusing situations while writing, for example, the letter "I", or two
consecutively written characters, "T-"
43
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Concerning the uppercase letter "F", to not confuse the uppercase
letter "F" with, for example, the uppercase letter "I", first an upside down
"L" form continuous line (6801) should be written, followed by one small
size horizontal line (680). Also, to not confuse the uppercase letter "E"
with, for example, the uppercase letter "I" continued by the character "-",
first an upside down "L" form continuous line (6811) should be written,
followed by two small size horizontal lines (681). Uppercase letters,
"L,M,N", may be written by a continuous line (682), as shown.
to
To make the system simple, we can consider that all non-text-
related characters having a straight line shape or starting with a straight
line, may be started in opposite direction relationship with text related
characters having the same characteristics.
With reference to Fig. 6g, three more characters (684), having
common characteristics are shown. They all are straight diagonal lines. By
writing the characters "/, \", in upward direction (68401-68402), we avoid
the possible confusion with the uppercase letter "X" (68405), because the
letter "X" is normally written by two downwardly written diagonal lines "\
/" (68406).
44
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Fig. 6h shows another group of symbols, which have a common
characteristic. They all have at least a horizontal line, written separately.
This group of characters may also be divided to text related group (685),
and non-text character group (686). The text related characters, "-" and " "
(6871), have two different lengths, respectively, short and long. They can
be written as commonly, from left to right direction (687). Other symbols
related to non text character group, preferably, may start with a short right-
to-left horizontal line (6882). After writing this line, the system expects
additional written information to complete the desired symbol. For
to example, by receiving an additional short right-to-left horizontal line
(688),
the system understands that the character "--" (6881), has just entered.
Other proposal directions (689), for other symbols (6883), are also shown.
It is important to follow the order of entering each discontinuous part of a
symbol. They are illustrated according to the habits of most users.
With reference to Fig. 6i another important part of hand writing
direction method is illustrated. The character "." (690), is shown. Some
other discontinuous characters such as ":" and ";" (69301), also contain the
sign ".", plus other signs. Again to avoid the confusion by the recognition
2o system, the character ".", may be written as a very small circle (691), in
opposite clockwise direction (692). Other characters containing the "." sign
(693), may start (694) with this sign but in clockwise direction (695). The
system understands that this is not the character ".", and it expect the rest
of
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
the symbol to be entered. Column 4 (4941), shows the parts of symbols to
be entered in order and as directions illustrated.
Fig. 6j shows additional printed symbols (696) available on a
standard keyboard, the hand writing form based on common writing habits
(697), and the direction to be taken for writing each symbol (698).
In addition, a special symbol or function sound waveform, produced
by an action such as a knocking action (e.g. a single tap) by, for example,
1o the pen tip on the writing surface, may indicate a space character or, "."
(e.g. dot character) to the HWSRS. This is specially important, because in
many cases, the end of a word, a character, a symbol, etc., is signaled by a
space character or a dot character. Each additional knocking action,
represent an additional space. Also the end of a discontinuous symbol may
15 be signaled to the system by an action, such as a contact of the pen tip on
the writing surface (e.g. to produce a waveform) or a voice signal, etc..
Fig. 6k shows all printed symbols and characters of a standard
keyboard and a proposal of a eventual direction to be respected while
20 writing each symbol, based on principles described. As it is shown, non of
the symbols has been deformed and the restrictions to be followed by the
user are minimal and logical, therefor they will easily be adopted by the
users. It is also understood that the principals and directions to write the
46
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
symbols, proposed above, are only some examples among a variety of
possibilities. Various omissions and substitutions and changes in the form
and details of the disclosed invention may be made by those skilled in the
art without departing from the spirit. of the invention. For example, the
lowercase characters may be written in importantly larger sizes in a text to
inform the HWSRS to consider them as uppercase characters. This can
facilitate there cognition system because it uses less patterns. Is must be
noted that these methods and invention may also, and even specially, be
applied for other languages such as Arabic, or Chines.
1o
As mentioned, a user may "teach" his handwriting to a recognition
system of the invention. At the beginning of use of an electronic device
having for example, a structured writing tip and a hand writing recognition
system of the invention, he may write all the symbols that he intends to
15 write (e.g. a character set in a language, his customized symbols, etc.).
The
recognition system may produce patterns (e.g. key pattern) for each
symbol, creating a "patterned character set" and use them for comparison
purpose for recognition of written symbols (e.g. inputs) by the user in the
future. During writing (e.g. texts, drawings, etc.), a user may add new
2o symbols (e.g. new key patterns) to his "patterned character set". As
mentioned before, for better recognition accuracy of written symbols on a
different surface having different structure (e.g. made from different
materials such as a paper, a wooden table, etc.) a user may either create a
47
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
new "patterned character set" for said surface by repeating the same
procedure of "teaching" explained here-above on said surface, or he may
write a few basic symbols (e.g. straight lines in different directions,
circles
in clockwise and counter clockwise direction, etc.) on said surface. Then
the system may automatically create a new "patterned character set" for
said surface, based on characteristics of the original "patterned character
set" and the characteristics of said written basic symbols on said surface.
According to one embodiment of the invention a behavior of the
to user may signal to the system to repeat a symbol as much as desired. For
example, while, or before, or after writing a symbol a user may tap, with
his finger or with the eraser etc. on the writing surface to repeat a last
written symbol.
15 According to another embodiment of the invention, to repeat a
written symbol, a user may, for example, press a predefined button
provided on the stylus to repeat a last written symbol. He may also repeat
an already entered symbol displayed on the screen of the stylus and situated
before a cursor (cursors will be described later in this application). A
single
2o press on a predefined button may repeat said symbol once. Each additional
press (e.g. tap) will cause an additional repeating of said symbol. For
continuous repeating of said symbol, the user may keep the button pressed.
48
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Said symbol will be repeated continuously until the user stops pressing said
button.
A digitized waveform of a symbol may sometime not match to ant
lcey pattern of the key pattern character sets, and therefore said written
symbol may not be recognized by the hand writing recognition system of
the invention. According to one embodiment of the invention, if a symbol
is not recognized by the system the inforniation relating to said symbol
(e.g. its graffiti, its waveform, its location in a text, etc.) may be stored
in a
to memory of for example, said stylus computer, to permit to a user an access
to said information for an eventual manipulation. For example, said symbol
may be a drawing to be saved or printed.
Fig. 7 shows a diagram 700 concerning the steps of input data (e.g.
15 sounds while writing symbols by a stylus writing tip on a writing surface)
and data output according to one embodiment of the invention. As shown,
at the step 701 sounds produced (and maybe amplified) are perceived by a
microphone at step 702 to produce waveforms. Said waveforms are
transmitted to a digitizer as shown in step 703. Depending on processing
2o procedure such as a real time recognition processing, the digitizer may for
example, transmit said digitized waveforms to a RAM 704 of the stylus
computer wherein a HWSRS system 706 may be installed. For reasons
such as a delayed recognition processing, or simply to record said digitized
49
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
waveforms, said digitized waveforms may be transmitted to a memory 707
of said stylus computer 700. Said digitized memorized input 708 may be
used in further processing (e.g. a delayed HWSRS processing). Said
memory 707 may also contain the digitized key patterns of waveforms of a
variety of predefined symbols used by the HWSRS for recognition of the
digitized input. After transmitting (in real time or delayed) a digitized
input
to the RAM 704 of said stylus computer, by using a microprocessor 705,
the HWSRS of the stylus computer of said stylus computer compares said
digitized input with said key patterns and tries to match said input to said
1o key patterns. After selecting the key patterns having the highest
similarity
with a the digitized input, the system selects the digitized symbols
corresponding to said selected key patterns. According to needs, said
digitized symbols may either be stored in the memory 707, or be
transmitted as an output to devices such as a display 7011 of said stylus
15 computer, or an external device 7012, etc.
The embodiment described here-above, relates to a data entry
method using sounds produced by contacts of a pointing device writing tip
on a writing surface while writing symbols on said surface. According to
2o another embodiment of the invention, as described before, sensors may be
provided within a writing tip of a pointing device such as a stylus computer
structured writing tip. Examples of said sensors and their structures have
already been described in this application. As described, said sensors may
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
perceive information such as pressure level (according to for example,
vibrations, heat, etc.) exercised on different portions of the structured
writing tip surface while writing a symbol on a writing surface, and conduct
said information to a digitizer of the stylus computer for a recognition
processing such as the one described in fig. 7. It is understood that all
embodiments and examples, described before and hereafter, relating to a
hand writing sound recognition system may be applied for recognition
based on any waveform produced by said pointing device writing tip
sensors.
As mentioned before and shown in Fig. 7a, another objective of this
invention is to provide the users with a familiar, user-friendly, highly
portable small electronic device in form of a stylus (750). The stylus can
function as a simple organizer, mobile communication device, PDA device,
computer, etc. Preferably, it may also have a structured pen tip of the
invention to produce hand writing sounds as input, a display (752), and the
HWSRS. The stylus may have an indicating means (751) to permit the user
to hold the stylus in a predetermined position in hand, while writing. This is
because the structured pen tip should always generate the same sound
(already patterned and introduced to the HWSRS) for the same direction.
FIG. 7b shows an imaginary stylus computer writing tip front view (770).
The pen tip may also have the conventional writing means, such as ink
(771), to simultaneously or separately, produce conventional hand writing
51
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
documents when and if needed. Communicating means such as laser,
infrared, etc., and other features such as camera (772), optical reader (773)
or the like, may be provided within the pen tip or anywhere else in/on the
stylus.
According to one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Fig. 7c,
a stylus computer 710 of the invention may comprise at least one
microphone 711 to perceive the sounds produced by the stylus writing tip
782 while writing on a writing surface. Said microphone, may be a
1o directional microphone. For a better perception, said microphone may be
provided near the pointing tip 712 of the stylus computer.
According to one embodiment of the invention, at least one
microphone may be provided inside the stylus computer body in a manner
is to perceive the sounds produced by the contacts of the pointing device tip
and a writing surface while writing on said surface. Said sounds may be
conducted into the stylus computer body. Sill, with reference to
Fig. 7c, for example, a microphone 713 may be provided inside the stylus
computer 710. To permit the passage of the sounds produced by the contact
20 of the writing tip on the writing surface, towards inside the stylus
computer
body, holes 714 may been provided in the stylus computer surface body,
preferably near the writing tip 712. Said holes may be designed in a manner
to amplify said sounds passing into the stylus body. Also, the stylus writing
52
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
tip 712 may be structured in a manner to contain holes permitting the
passage of said sounds into the stylus computer body. Fig. 7d shows an
example of a writing tip 720 of a stylus computer. As shown, for example
said writing tip may be designed in a manner to have empty passages (e.g.
holes) 721 between the structured parts 731. Also, sensors on said writing
tip, may for example, conduct the vibrations produced by the writing tip on
the writing surface, into the stylus and produce sounds which will be
received by said microphone located inside the stylus.
to To amplify the sounds produced by the writing tip on a writing
surface, an amplifying means may be provided within the stylus computer.
Fig. 7e shows a stylus computer 780 having an amplifying means 783
having an exponential form (e.g. similar to the form of conventional
loudspeakers). Sounds of contacts of a pointing tip 782 with a writing
15 surface while writing with said pointing tip on said writing surface may be
conducted inside said amplifying means 783 and being perceived by a
microphone 781 located in an appropriate location (e.g. at other end of the
amplifying means):
20 Sounds of contacts of a pointing tip with a writing surface while
writing with said pointing tip on said writing surface may still been more
amplified. According to one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Fig.
7f, to amplify said sounds, an amplifying means such as resonating
53
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
chamber 794 maybe provided within a stylus computer 790. The sounds
produced by contacts of the stylus writing tip 791 on a writing surface may
be conducted in a said resonating chamber 794, wherein said sounds may
be amplified. A microphone 792 may be provided within said chamber to
perceive said amplified sounds. This amplifying procedure may be in
addition to another amplifying procedure such as, already described
exponential means 793. It is understood that any transmitting and
amplifying means, known by the people skilled in the art, may be used for
perception of a high quality sounds. For example, the amplifying chamber
to may have any form, structure, maid from any materials, etc., for the
amplifying purposes.
As shown in FIG. 8a, the stylus (850) may contain alI computer
features and additional means such as at least one battery (851), memory
15 (RAM) (852), hard disk, microprocessor (853), a transceiver (854), a
microphone (857), an optical reader (856), a position detection means
(858), a writing start/end detection means (855), a speaker (859), a timer
(not shown), LCD display (not shown), etc.
20 To avoid undesirable operations when the stylus is not in use, the
structured pen tip may be in hidden position inside the stylus (840). FIG.Bb
shows the structured pen tip in open position outside the stylus (842). It
also shows a writing start/end detection means (855) having a pin (841).
54
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
While the tip is in contact with the writing surface (830) as shown in FIG.
8c, the writing detection pin (841) is in inside position to indicate a
writing
status. When the user lifts up the pen tip (FIG. 8d), the detection pin (841)
will exit to indicate a non-writing status. It is understood that the
detection
means described is only an example. Other writing start/end indication
means and systems may also be used. For example one or more sensors
may be installed in the structured pen tip, to indicate the system a writing
or
a non-writing status. Also the sounds created by the contact of the pen tip
with the writing surface may indicate a writing status. Silence may indicate
a non writing status.
With continued reference to FIG. 8d, the stylus (850) may have one
or more LCD displays (860) to display the data (861). It also may have an
eraser (863) for corrections. The eraser surface may have a special texture
to function as a conventional pen eraser on a writing surface, and
simultaneously create special sound to indicate the HWSRS of an erasing
status. Similarly to structured pen tip, eraser surface can also be made from
a special texture to produce plurality of sounds according to directions of
its strokes on the writing surface. Of course, those sounds should be
2o different from the structured pen tip sounds. Commands or functions such
as, onloff, send/receive communication, etc., may be assigned to the sounds
produced by eraser, when writing corresponding words or symbols on a
writing surface. Of course same microphone or an additional microphone
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
(preferably directional) may be provided to clearly capture the sounds
generated by said eraser contacts with the writing surface.
Fig. 9a, illustrates a writing surface such as a paper notepad (900)
with three handwritten characters (910) written by a user using the stylus
(850). The characters are digitized (920) by the stylus computer and
displayed on the LCD display (902) of the stylus. A cursor (904) is locating
after the last character entered. If a user wishes to erase, for example an
erroneously entered character, he can use the structured eraser (901). As
shown in FIGS. 9b and 9c, by giving for example, a straight stroke, in for
example, left or right direction (911), on the writing surface, the sound
produced by the contact of eraser and the writing surface, inform the
HWSRS of an erasing action. The last character entered will be erased from
the display (912) and the memory of the stylus computer. To erase an
additional character, an additional stroke may be introduced, and so on. If a
user desires to erase a character other than the last one, he can place the
cursor next to that character and produce the erasing procedure as described
before. Because this stylus may also be capable to produce conventional
written documents, for the reasons of practicality, more than one stroke
may be needed to erase simultaneously, a character on a notepad. In this
case the computerized erasing system may be modified to permit other
erasing systems. For example, consecutive short interval strokes (as in
traditional hand writing erasing procedure with a pencil rubber) may inform
56
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
the HWSRS to erase one character. To erase the next character at least a
short pause may be applied. For better perception of the sounds produced
by said eraser strokes on a writing surface, at least one additional
microphone (preferably directional) may be provided within or near said
eraser. It is understood that other possible erasing procedures based on this
principle, may also be applied. Also users can create their own customized
procedures or symbols or actions for erasing.
According to yet another embodiment of the invention, erasing
to procedure described before may be done by the structured pen tip. As
shown in FIG. 10a, a text (1001) is written by the stylus (1000), on a
writing surface (1002). Those letter are digitized (1002) and displayed on
the LCD display (1003) of the stylus. A cursor bar (1004) is located after
the last character entered. As shown in FIG. 10a, if the user desires to erase
a character, as in traditional hand writing procedure, he can cross out
(1010) on a writing surface with the pen tip (1011) to erase the last letter
before the cursor from the memory of the computer. The sounds produced
by the strokes of the pen tip on the writing surface, may inform the
HWSRS of an erasing status. The letter before the cursor will be erased
2o from the memory and display (1012). For each additional character to be
erased, a same procedure is needed.
57
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Fig. 11 shows the stylus type computer (1111), described before,
having flat display ( 1110) according to one embodiment of the invention.
FIG. l la illustrates the stylus computer (1100) according to one
embodiment of the invention. This stylus may have some or all of the
features described before. It may also have a curved (e.g. convex) LCD
display unit (1101) covering at least a portion of stylus computer surface.
FIG. l 1b demonstrates that display in semi-unfolded position (1112). The
dimensions of the surrounding surface of an average conventional stylus is
1o about 17 centimeter long by 4 to 5 centimeter large. To overview the whole
display a user may rotate the stylus in his hand.
Seventeen centimeter, is almost the size of a standard text line
written on an A3/A4 paper sheet. As shown in FIG. 11 c, a LCD display
15 screen (1121), covering a standard stylus form computer with dimension of
17 X 5 centimeters (1122), is large enough to display a real size text and
permit real size manipulations of that text. It is also large enough to view
pictures or to permit browsing on real size web pages. Combination of a
user- friendly hand writing input systems, as described before, and a large
2o display as mentioned now, in a familiar apparatus in the form of a pen,
creates a highly portable powerful miniaturized instrument. It can be
manufactured in many versions such as simple digitizing pens used by
everyone (e.g. reminder of shopping list for housewives), or as more
58
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
sophisticated instruments such as mobile phones, PDA devices, or
computers. One great advantage of this instrument is that there may be no
need to carry a writing surface. The user can write the input on any surface
available such as a table surface. It must be noted that the display unit 1112
of the stylus computer may be detachably attached to the stylus computer
and be connected to said stylus computer either by wires, or wirelessly.
Said display may be flexible (e.g. made from plastic materials), so that, for
example, when said stylus computer is not in use said display may be
enrolled around said stylus, or enrolled and being attached to said stylus, or
1o being inside said stylus computer or its cover. Said display may be
detached and/or deployed (e.g. unfolded) for use. By using this concept,
even larger displays (e.g. enrolling several times the stylus computer) may
be considered for integration and/or use with the stylus computer. Also the
stylus computer may be connected to any external display by means of
15 wires, or wirelessly. If said display is wirelessly connected to said
stylus,
wireless telecommunication means (e.g. blue tooth, infrared etc.) may be
provided within said display andlor said stylus.
According to one embodiment of the invention, as shown in FIG.12,
2o the stylus-type computer (1200), may also be equipped with a button-type-
mouse (e.g. pointing and/or selecting device) (1201), preferably installed at
the opposite side to the pointing tip (1202). With reference to Figs. 12a
tol2e, some possible physical movements of the mouse are shown. Fig. 12a
59
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
shows the mouse side (1210) of the stylus, wherein a mouse (1201) is
installed. The mouse can have one, two, or more installation positions on
the stylus axis, such as inner position (1212), or outer position (1213). To
change installation positions, the mouse may be pulled out (1241) or
pushed in (1242), in stylus axis. An indication mean (1216), or indicating
marks (1227), may indicate the mouse positioning. As shown in FIG. 12b,
the mouse can also have different click systems, for example, one to the
inside direction (1217) of the stylus, and one to the outside direction (1215)
of the stylus.
l0
Yet, as shown in FIG. 12c, the mouse (1201) may also have a
rotating movement (1219) in opposite directions for each positioning or
clicking status.
15 Still additionally, as illustrated in FIG. 12d, the mouse (1201), in
every positioning status such as inside position (1261) or outside position
(1262), may be pushed in all directions (1251, 1252, 1253, etc.)
perpendicularly to stylus axis. FIG. 12e shows the side view (1223) of the
mouse, and some of pressure directions (1272, 1273, etc.) on that mouse. It
2o also shows the front view (1222) of the mouse and some pressure directions
(1224, 1225, etc.) on it. It is also understood that the movement explained
here, are some examples among a variety of possibilities. Various
omissions and substitutions and changes in the form and details of the
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
disclosed invention may be effectuate by those skilled in the art without
departing from the spirit of the invention. For example, as shown in Fig.
12f, the stylus type computer mouse may be equipped with a bull system,
similar to those used in lap top computers, and be manipulated in the same
way as in laptops.
The above explained mouse movements and/or combinations of
them may be assigned to variety of computer commands, functions, system
modes, etc. They permit a complete, easy and fast manipulation of data and
l0 functions of the stylus-type computer. Some different embodiments will be
described hereafter, to demonstrate this matter. It must be noted that the
examples that explained before, or explain hereafter show only a few
methods as samples. It is appreciated to those skilled in the art that many
variations of the combinations of assignments can be employed without
15 departing from the spirit of the present invention.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the stylus computer
display may be similar to any computer display. It can contain program
icons, menus, show different windows, etc. For example, as shown in Fig.
20 13a, when opening a word processing program, the display (1300) may
show at least two different sections. A menu section (1301) located, for
example, on the top of the screen and a text section (1302) located, for
example, under the menu section. The menu section may contain one or
61
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
more menu lines (1303), each line containing a list of menu bar titles
(1304) that may be opened when needed. In this example a display showing
one of the lines of a menu list is illustrated. It is understood that a
display
unit of the stylus computer may show more than one line of a menu list at a
time, according to needs andlor limits of the surface available, etc..
According to one embodiment of the invention a user can scroll the
menu lists by using the mouse (1309). For example, for finding a menu list
containing a desired menu bar, the user first positions the mouse in menu
mode which, for example, is the inside position (1307). Then, as shown in
Figs. 13b-13c, by rotating the mouse in any direction (1308), new menu
lists (1313, 1323, etc.) scroll on the display. When a menu list containing a
desired menu appears, the user stops rotating.
I5 According to one embodiment of the invention, a user can navigate
in menu lists by using the mouse. For this purpose, as explained before and
shown in FIG. 14a, the user first locates the mouse (1400) in menu mode
position (1401). At this moment the system is in menu list selecting mode.
Then as shown in FIG. 14b, by pushing the mouse in stylus axe inside
2o direction (1411), strong enough to cause a click, the system will enter the
menu (bar) selecting mode and a menu (bar) selecting indicator mean
(1412) may appear at a location on the menu list. At this moment the
indicator may not point to any menu. Then, as shown in FIG. 14c, by
62
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
rotating the mouse (1421), the menu bar selecting indicator will navigate on
the menu bar titles (1422). If the selecting indicator reaches the last menu
on list and the user continues to rotate the mouse, as shown in FIG. 14d the
next menu list (1432) will appear and the menu bar selecting indicator will
jump to the first location (1433) of the new menu. It will continue to
advance as shown in FIG. 14e, until the user stops rotating the mouse
because, for example, the indicator has reached the desired menu. To exit
from menu mode and go back to menu list selecting mode, as shown in Fig.
14f, the user may, for example, click the mouse in inside direction and
1o simultaneously, shortly rotate it (1451) in any direction.
Figs. 15a to 15h show an example of navigation in the menus and
functions by mouse manipulations. With reference to FIG. 15a, a stylus-
type computer (1500) is shown. As described before, the upper portion of
is the LCD display (1503) is assigned to menu lists. To select a function in a
menu bar, the user has to view the menu list wherein that menu bar is
situated. If, for example, the user wants to change a font, he has to go to
corresponding menu list. For this purpose, first the user must positions the
mouse (1501) at menu selecting mode, for example, in inside (stylus axial)
2o position (1502). If the desired menu bar is not in current menu list (1504)
and the system is in menu (bar) selecting mode, then, he rotates (1505) the
mouse to advance the selecting indicator (1506) forward or backward, as
needed, to reach the last menu bar title (1510), as shown in FIG. 15b. If the
63
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
user continues to rotate the mouse, then next menu list (1520) will be
displayed, as shown in FIG. 15c. The menu selecting indicator will jump to
the next location of new menu list. If, for example, still this menu list is
not
the one desired by the user, he will continue to rotate the mouse, advancing
the menu bar indicator (1521) until it reaches the last menu title and as
shown in FIG. 15d, a new menu list (1530) appears on the screen. Again
the menu bar indicator jumps to the next location of the new menu list and
continues to advance in menu titles until the user stops rotating the mouse,
stopping the indicator on a menu title (1531). If by mistake, the selecting
1o menu title indicator was advanced more than needed, as illustrated in FIG.
15e, the user can rotate the mouse (1501) in the opposite direction (1541)
bringing back the menu bar selecting indicator and stopping it on desired
menu title (1542). As shown in FIG. 15f, at this time the user pushes the
mouse to the inside direction (1551) to click it. The system enters in
15 function selecting mode and the menu bar (e.g. popup menu surrounding
the pen surface and shown in extended flat position for demonstrating
purpose) (1552) opens. A function selecting indicator (1553) is located on
the current choice. As shown in FIG. 15g, to bring it to a desired choice, the
user will rotate (1562) the mouse (1401) in the needed direction until the
2o indicator reaches the desired function (1563). This popup menu may use
principals similar to popup menus of computers. As shown in FIG. 15h,
then the user again pushes the mouse to inside direction (1571) to click it.
The function is selected and displayed on the menu bar title (1572),
64
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
replacing the previous choice. Also the mouse exits the function selecting
mode and returns to menu (bar) selecting mode.
According to one embodiment of the invention, a text editing mode
can be assigned to one of the mouse positions on stylus axis and by using
the mouse rotating movements, while mouse is in text editing position, a
user may scroll text document lines or pages. FIG 16a shows a stylus-type
computer (1600) having, for example all of the features and systems
explained before. In this example, a text editing window (1601) is shown.
to The display unit is divided into two sections. The upper section (1602) is
assigned to menu lists and the lower section (1603) to the text. In this
example a display showing two lines of a text is illustrated. It is understood
that a display unit of the stylus computer may show less or more than two
lines according to needs and/or limits of the surface available, etc.. The
15 mouse button (1604) is in menu mode, for example, in inside position. As
shown in Fig. 16b, the user, for example, pulls the mouse out (1610) and
locates it in outside position and to enter the system in text editing mode.
Then, as shown in FIG. 16c, he can scroll forward the text lines and pages
(1608) by rotating the mouse in, for example, clockwise direction (1605),
20 or scroll backward the text lines and pages (1609), as shown in FIG.l6d, by
rotating the mouse in the opposite clockwise direction (1606).
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
According to yet, another embodiment of the invention, also a
cursor can be manipulated by rotating movements of a mouse. This matter
is illustrated in Figs. 17a-17f. As shown in Fig. 17a, first a user must
position the mouse in a position relating to text editing mode, for example,
in outside position (1701). If the text navigating mode is in line scrolling
mode, then as shown in FIG. 17b, the user clicks the mouse in outside
direction (1702), to bring the system in cursor (character) navigating mode.
If the cursor is in current page, it remains at the same position in the text.
If
the cursor is not in current page, then it may stay at its original location
in
to the text or will be brought, automatically, to current page and will be
located, for example, at the first position (1703) or last position, on the
last
line (1704) or any other predefined line or position in a line. Then, as
shown in Figs. 17c-17d, by rotating the mouse in, for example, clockwise
direction (1710), the cursor advances between the characters until it reaches
15 the last position on a line (1721). If a next line is available on the
screen,
the cursor jumps to the beginning of the next line and continues to advance
as long as the user rotates the mouse. If the current line is the last line on
the screen and the cursor reaches the last position on a line, then as shown
in FIG. 17e, if the user continues to rotate the mouse, then the next line
(1732) appears and the cursor advances in the next line (1733), and so on,
until the user stops rotating. If the user desires to move the cursor in
opposite direction (1741), he rotates the mouse oppositely (1742). To go
back to line scrolling mode the user, according to one embodiment of the
66
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
invention, pulls the mouse out to click it and simultaneously shortly rotates
it.
According to one embodiment of the invention, as shown in FIG.
18a, a text- select indicator (1801), for example, similar to those used in
computers, may be provided in the stylus-type computer device text editing
mode. As shown in FIG. 18b, the mouse ( 1 ~ 10) maybe used for moving
(1812) the indicator on the screen. For this purpose the mouse may be in a
position such as text editing mode, in this example, the outside position
to (1815). As shown in FIG. 18c, for example, to select a location (I821) in a
text, first, the user, by perpendicularly to stylus axis pushes on the mouse,
bring the indicator (1822) to that point. Then, as shown in FIG. 18d, by
clicking the mouse in outside direction (1831), the user selects that point
and a cursor (1832), installs there. To avoid confusion with other functions
15 (e.g. passage from line scrolling mode to cursor manipulating mode), while
clicking, the user should keep the mouse pushed for a longer time (e.g. one
second). Instead of clicking the mouse, the user may either press a
predefined button such as the one 2701, shown in fig. 27g (e.g. a clip-type
button which will be described later in this application) available on the
2o stylus computer, or proceed another action known by the people skilled in
the art.
67
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
According to yet another embodiment of the invention, by using
mouse movements, all, or a portion of a document or text may be selected.
FIG. 19a, shows a display (1901) of the stylus type computer (1900)
wherein a cursor (1902) is positioned on a specific location in a text (1903)
and the mouse (1907) is positioned on the text mode, for example, in
outside position (1908). If the system is in character/cursor manipulating
mode, as shown in FIG. 19b, to enter the text selecting mode, the user pulls
the mouse outward (1911), strong enough, to click it. He releases the button
to permit it to, preferably go back to its initial outside position. To do
select
1o a portion of a text, the user now rotates the mouse in either clockwise
direction or opposite clockwise direction. As shown in FIG. 19c, by
rotating the mouse in clockwise direction (1921), the system starts to select
progressively, for example, the text situated after the cursor position
(1922), according to rotation degree until the user stops rotating. If the
user
15 rotates the mouse oppositely (1931), then, as shown in FIG. 19d, starting
from cursor position, the system starts o select progressively, for example,
the text situated before the cursor position (1932), according to rotating
degree, until the user stops rotating. If the user wants to proceed to
operations such as, copy, clear, changing font, etc., on the text selected, he
2o may change the mouse position to menu selecting mode position (e.g.
inside position). The system will proceed to next procedures, described
hereafter.
68
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
As shown in FIG. 19e, if the user wants to exit the text selecting step, he
pulls the mouse towards outside direction until it clicks (1941) and releases
it. The system goes back to character (cursor) manipulating mode.
As shown in FIG. 20a, a text (2001) is selected by, for example, the
procedure described before. To apply, for example, an editing procedure
such as copying, on this selected text, the user, as described previously,
brings the mouse to menu selecting mode (2002) and looks for edit menu
(2003), selects it, and then as shown in FIG. 20b, by clicking the mouse to
to inside direction (2010), opens the menu (2021). Then, as described before
and shown in FIG. 20c, by rotating the mouse (2031), the user locates the
function selecting mode on the "copy" function (2032). Then as shown in
FIG. 20d, by pushing the mouse again in inside direction (2033), strong
enough to make the button clicking once, the system copies the text and
exits from function mode.
To make an operation such as, pasting the copied text elsewhere, as
known in computer domain, the user first must indicate the pasting location
to the system, by means of a cursor. For this purpose, as shown in FIG. 21a,
2o the user first brings the system to text editing mode by for example,
pulling
the mouse and positioning it in outside position (2100). Then, as described
before and shown in FIG. 21b, by pushing the mouse perpendicularly to the
stylus axis (2110) in directions needed, he moves the cursor (2111) to a
69
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
location, in where the text will be pasted. Then, as described for copying
procedure, the user bring back the system to menu selecting mode, by for
example, positioning the mouse in inside position, and looks for "edit"
menu (2112), by rotating the mouse (2113). After locating the menu
selecting indicator on the menu bar name (e.g. "Edit"), as shown in
FIG.21 c, he clicks the mouse in inside direction (2120), opening the menu
bar (2121). Then as described before and shown in FIG. 21d, by rotating
the mouse (2130), the user brings the function indicator on the desired
function (213I) which is the "Paste" function in this example. Then as
to shown in FIG. 21e, by clicking the mouse in inside direction (2140), the
paste function is selected and the copied text (2142) will be pasted into the
document in location that was pointed by the cursor (2141).
Also as shown in FIG. 22a, if a text (2201) is selected to be erased,
15 it can also be erased either by using the "Clear" function in "Edit" menu
bar, similar to procedure described for "paste" function, or; as shown in
FIG. 22b and described earlier, it can be cleared by using the erasing tool
(2211) and producing a predefined movement causing a sound waveform
known by the HWSRS as an indication for erasing. A single erasing
2o movement by the eraser on the writing surface, erases whole selected text.
Additional erasing movements will cause additional characters or symbols
of the text located before the cursor, to be erased. Instead of erasing tool,
as
also described earlier, the user can write a predefined cross out symbol
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
(2311) by the pen tip to cause production of an already patterned sound
waveform informing the HWSRS of an erasing command. Again, as
mentioned hereinbove, a single erasing movement by the pent tip on the
writing surface, erases whole selected text. Additional erasing movements
will cause additional characters or symbols of the text located before the
cursor, to be erased.
According to one embodiment of the invention, also a Normal
Select (pointer) indicator may point to a menu in a menu list and select a
1o function in that menu. As shown in Figs. 23a-23e, first the user positions
the mouse in menu mode, for example, in inside position. Then by
perpendicularly to stylus axis pushes (2340) on the mouse (2300), the user
moves the normal select indicator (2341) towards a desired menu in a menu
list (2342). When the indicator is brought on the desired menu title (2353),
15 as shown in FIG. 23c, to open the menu bar, the user can click the mouse
in, for example, inside direction (2360). The menu bar (2361) opens. To
select a function among those existing in the menu bar, the user can move
the indicator to the desired function (2371) by perpendicularly to stylus axis
pushes (2370) on the mouse (2300), and then to select that function he
2o clicks the mouse in inside direction (2373). To avoid confusion with mode
selecting, while clicking, the user may keep the mouse pushed for longer
time (e.g. one second). Instead of clicking the mouse, the user may either
press a predefined button such as the one 2701, shown in fig. 27g (e.g. a
71
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
clip-type button which will be described later in this application) available
on the stylus computer, or proceed another action known by the people
skilled in the art.
According to one embodiment of the invention, instead of assigning
the text select indicator and normal select indicator, to two different mouse
modes (e.g. inside and outside position), both indicators may be assigned to
only one mouse mode (e.g. inside position). As shown in FIG. 24a, the text
select indicator (2401) similar to those used in computers, may be provided
to in the stylus-type computer device. As shown in FIG. 24b, the mouse
(2410) maybe used fox moving the indicator (2412) on the screen. For this
purpose the mouse may be in a position such as menu selection mode, in
this example, inside position (2415). As shown in FIG. 24c, for example, to
select a location (2421) in text, first, the user, by perpendicularly to
stylus
15 axis pushes on the mouse, bring the indicator (2422) to that point. Then,
as
shown in FIG. 24d, by clicking the mouse in inside direction (2431), the
user selects that point and a cursor (2432) installs there. To avoid confusion
with other modes, while clicking, the user should keep the mouse pushed
for a longer time (e.g. one second). Instead of clicking the mouse, the user
2o may either press a predefined button such as the one 2701, shown in fig.
27g (e.g. a clip-type button which will be described later in this
application)
available on the stylus computer, or proceed another action known by the
people skilled in the art.
72
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
The indicator may also point to a menu in a menu list. As shown in
Figs. 24e-24f, by perpendicularly to stylus axis pushes (2440) on the
mouse, the user moves the indicator (2441) towards that menu list (2442).
As for computers, when the indicator reaches the menu list, it changes the
appearance from a bar shape (2441) to an arrow shape (2452). When the
indicator is brought on the desired menu title (2453), as shown in Fig. 24g,
to open the menu bar, the user can click the mouse in inside direction
(2460). The menu bar opens (2461). Also, as shown in Fig. 24h, to select a
to function among those existing in the menu bar, the user can move the
indicator to the desired function (2471) by perpendicularly to stylus axis
pushes on the mouse. then he selects that function by clicking the mouse in
inside direction (2473). To avoid confusion with other modes, while
clicking the user should push the mouse pushed for longer time (e.g. one
second). Instead of clicking the mouse, the user may either press a
predefined button such as the one 2701, shown in fig. 27g (e.g. a clip-type
button which will be described later in this application) available on the
stylus computer, or proceed another action known by the people skilled in
the art.
To the perpendicularly-to-stylus-axis pushes on, the mouse in other
position (e.g. outside position), which was freed by above mentioned
73
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
pointer assignment, for example, a cursor manipulating procedure in a text
may be assigned. Figs. 24i-24n, illustrate the procedure.
According to one embodiment of the invention, a cursor can also be
manipulated by, for example, perpendicularly pushes to stylus axis on a
mouse. As shown in FIG. 24i, first the user positions the mouse at text
editing mode (2481), for example, in outside position. If the text mode is in
line scrolling mode, then as shown in FIG. 24j, the user clicks the mouse in
outside direction (2482), to bring the system in character/cursor navigating
l0 mode. As described before, for example, if the cursor is in current page,
it
remains at the same position in the text. If the cursor is not in current
page,
then, for example, it will be brought to the current page and will be located,
for example, at the last (2483) or first position, of for example, the last
Iine
(2484) of the document. Then, as shown in Figs. 24k-24n, the cursor may
15 be navigated on the text in up (2490), left (2491), down (2492), or right
(2493) directions, by perpendicularly to stylus axis pushes in different
direction on mouse (2495-2498), accordingly.
As described before, the mouse may have one, two, or more
20 positions on the stylus computer, wherein for better and easier
functionality, each position may be assigned to a number of functions, for
example, in a same domain. Although, the mouse may have unlimited
numbers of positions on the stylus computer axis, for easier usage of the
74
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
mouse and to not frustrate the user, it is preferable to have a mouse with not
more than two positions on the stylus computer. For more functionality, in
addition, at each position side (e.g. inside, outside), an additional clicking
system may be provided for the mouse. it must be noted that instead of a
clicking system provided in the mouse, one or more predefined buttons
provided on the stylus computer may be used with the mouse as mouse
buttons. For example, while manipulating a mouse, the user may press a
predefined button such as the one 2701, shown in fig. 27g (e.g. a clip-type
button which will be described later in this application) available on the
to stylus computer. The mouse including its clicking system and/or the mouse
combined with its predefined corresponding buttons may function similar
to a computer mouse and may have at least all the functionality of a
computer mouse. It must be noted that the examples that explained before,
or explain hereafter show only a few methods as samples. It is appreciated
15 to those skilled in the art that many variations of the combinations of
assignments can be employed without departing from the spirit of the
present invention.
Fig. 25, according to one embodiment of the invention, shows a
2o mouse (2500), having two positions (2501, 2502) on the stylus axis
direction, on the stylus. Here also, for more functionality, in addition, at
each position side (e.g. inside, outside), a clicking system (2507, 2508) is
provided for the mouse.
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
According to one embodiment of the invention one of the mouse
positions, for example outside position, may be assigned to text editing
(manipulating) functions. Fig. 25a shows an example diagram of how the
mouse functions. At the first step (2510), the mouse is in linelpage scrolling
mode. By rotating (2511) the mouse in perpendicularly to the stylus axis, in
clockwise direction or oppositely, as shown in examples before, the user
can advance or move back a text document lines on the LCD display. If at
any time, the user pulls out the mouse strong enough to click it (2512), the
to system changes the mode and enters to cursorlcharacter mode (2520). Now
if the user rotates the mouse (2521), a cursor will advance or move back in
the text, character by character. To go back to line mode (2510), the user
may for example, pull out the mouse to for clicking (2519) and
simultaneously rotate the mouse shortly (2518).
On the other hand, if the user wants to select a portion of a text,
while the system is in cursor/character selecting step (mode) (2520), first he
must position the cursor before or after the text to be selected. Then he
pulls the mouse out to click it (2522) and the system enters into text
2o selecting step (mode) (2530). Now, by rotating the mouse in either
direction (2531), the text before or after the cursor will be selected
accordingly. The length of the text to be selected depends on rotating
quantity (degree). After selecting the text, the user can manipulate (e.g.
76
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
copy, bold, delete, etc.) the selected text portion. To go back to cursor
mode (2520), the user again pulls the mouse out and cliclcs it (2529).
The user may exit (2541-2543) the text mode at any step, by, for
example, positioning the mouse in another position (e.g. inside position,
menu selecting mode). The current text page, current cursor position, and
current selecting step may be kept as default. When the user enters the text
mode again, he will enter the text mode in the same position and step
(2545-2547), as he left.
It must be noted that the step of scrolling the text lines/pages (e.g.
line/page scrolling mode) may be omitted. In this case the user may scroll
the lines by being in cursor/character mode and rotating the mouse to
forward (or backward) the cursor. When the cursor reaches to the last (or
the first) position in a text and the user still continues to rotate, then the
next line/page may appear. It is understood that a text may comprise several
lines which one or more than one of said lines may been displayed at a
same time on the screen display unit of the stylus computer.
2o According to one embodiment of the invention, one of the mouse
positions, for example inside position, may be assigned to menu and
functions manipulation. Fig. 25b shows an example diagram of how in this
case, the mouse functions. At the first step (2550), the mouse is in menu list
77
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
selecting mode. By rotating (2551) the mouse in perpendicularly to the pen
axis, in clockwise or opposite clockwise direction, as shown in examples
before, the user can scroll forward or scroll back, the menu lists on the
LCD display. If at any time, the user pushes the mouse inside, strong
enough to click it (2552), the system selects the current menu list, changes
the mode (step) and enters to menu selecting mode (step) (2560). A menu
selecting indicator appears at a predefined location on the menu list. Now if
the user rotates the mouse (2561), the menu selecting indicator advances or
moves back (according to rotating direction by the user) on the menus of
the selected menu list, menu by menu. If the menu selecting indicator
reaches the last menu in the list and the user continues to rotate, then
according to rotating direction, the next or the precedent menu list appears.
The menu indicator jumps to first or last menu (according to rotating
direction) and continues to run on the menu titles until the user stops
rotating. To go back to menu list selecting mode (2560), the user may for
example, push the mouse in, for clicking (2559) and simultaneously rotate
the mouse shortly (2550.
In the other hand, if the user wants to select a function included in a
2o menu, while the system is in menu selecting mode (2560), first he must
position the menu selecting indicator on the menu to be selected. Then he
pushes the mouse in, to click it (2562) and the system enters in function
selecting mode (step) (2570). If there is only one function in that menu,
78
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
then that function is automatically selected. If there are two possibilities
and one of them is already in use (e.g. bold, normal), then the other
possibility is selected automatically. If there are two or more functions
excluding the current function in use, the a menu bar corresponding to the
menu opens. Now, by rotating the mouse in either direction (2571), as
needed, a function selecting indicator will be appeared and runs on the
function titles until the user stops the indicator on one of them as desired.
To select that function, the user again pushes the mouse in and clicks it
(2569). The function is finally selected and the system goes back to menu
1o selecting mode (step) (2560).
The user may exit the menu mode (2581-2583) by, for example,
pulling the mouse and positioning it in outside position (e.g. text selecting
mode). The current menu list may be kept as default. When the system
15 enters the menu mode again (2584), the default menu list will be displayed
on the screen.
It must be noted that the step of scrolling menu list (e.g. menu list
mode) may be omitted. In this case the user may scroll the lines by being in
2o menu selecting mode and rotating the mouse to forward (or backward) the
menu selecting indicator. When the indicator reaches to the last (or the
first) position in a menu list and the user still continues to rotate, then
the
next menu list (e.g. line) may appear. It is understood that a menu list may
79
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
comprise several lines which one or more than one of said lines may been
displayed at a same time on the screen display unit of the stylus computer.
It must be noted that the normal selecting indicator described
before, separately or in conjunction with mouse rotating movements, may
also be used to select functions.
According to one embodiment of the invention, written commands
may be provided for at least a part of commands assigned to mouse or other
1o buttons. For example, after selecting a portion of a text by the mouse
manipulations, the user can write on a writing surface, the word "copy".
The system at this moment copies the selected portion of the document. If
the user wants to paste that portion in another place, he can first bring the
cursor to that position and then write the word "paste". The system will
paste that copied portion in that location. To inform the system that the
words written, are not part of the text, but commands, various indicating
systems may be used such as:
- Special existing or customized, command reserved words or
2o symbols may be used for each command or a plu~lity of commands
(e.g. copy, cp) (e.g. a user may draw a predefined customized
symbol such as " " to inform the system to proceed to next page
in a text)
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Command words may be preceded by reserved existing or
customized words) such as, for example, "cm" (e.g. cmcopy,
cmopen, etc.),
Or any other possibilities based on this idea. For example to
advance five lines in a text the user may write "a105" (advance line
05 lines, wherein al is a reserved word)
According to one embodiment of the invention, the commands may
be written by a separate pen tip, provided on the stylus type computer. They
1o can also be inputted by the mouse structured surface, as described before.
For better perception of the sounds generated by said mouse surface
contacts with the writing surface, at least one additional microphone
(preferably directional) may be provided, inside (e.g. as described before
for the microphone of the writing tip), or outside the stylus computer body,
15 near said mouse. Also a button such as a clip button may be used to inform
the system of starting a written command input by the pen tip. In these
cases, no reserved or restricted words may be needed.
Also a pointing device tip may be structured in a manner that a
2o portion of it may be assigned to written commands. As shown in Fig. 4e, a
pointing device tip (415), may be structured in a manner that a structured
portion (418) of it may be assigned to text, and another differently
structured portion (419) of it, maybe assigned to hand written commands.
81
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
By writing a command with the command assigned part (419) of the
pointing device tip, on a writing surface, according to sounds produced and
after comparing them with patterned memorized waveforms, the HWSRS
interprets the written data or symbol as command.
According to one embodiment of the invention, as for regular
computers, the display may show different icons. The normal select pointer
may be used to, for example, select an icon, open files, use vertical and
horizontal elevators, run programs, and/or at least all other manipulations
l0 done with regular computer normal select pointers.
According to one embodiment of the invention, first the normal
select pointer may be positioned on the desired icon or object, by for
example, mouse perpendicularly or rotating movements. Then by clicking
the mouse, for example once, that object may be selected. A longer time
pushing and clicking procedure may select the object and keep it to, for
example, shift it somewhere else. To release that object, another long click
may be produced. Also, as for traditional computer mice, some functions or
commands me be assigned to double clicking of the stylus type computer.
2o All other manipulations by a traditional computer mouse may be possible
by the stylus type computer mouse of the invention. Those mouse
manipulations are known by computer users.
82
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
The mouse, having command and selecting systems and movements
as described, may be installed in all electronic devices such as computers,
laptops, PDA devices, mobile phones, wired phones, etc., which alI need a
simple navigating / selecting means. Some of those devices are shown in
Figs. 33a to 33e. Fig. 26a shows a laptop computer equipped with the
mouse of the invention (2601) on the side. As shown in FIG. 26b, the
mouse may be installed in another location (2602) on the computer, such as
in the center. Also as shown in FIG. 26c, it is understood that additional
complementary-to-mouse buttons or mice (2604) may be provided on the
1o computer. Figs. 33a-33e show a variety of electronic instrument equipped
with the mouse (3326), and the selecting system by the mouse, as
described.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the hand writing
15 sound recognition system of the invention and/or the mouse system of the
invention, may also be provided in computers and other electronic devices
equipped with keyboard, keypads or other input systems such as
voice/speech recognition, etc., replacing their input systems or combined
with them. As shown in Fig. 26d, a writing surface (2603), a microphone'
20 (not shown), the HWSRS of the invention, and all other materials needed
(not shown), are installed in a computer to permit a pen having preferably,
a pen tip of the invention, to produce sounds according to symbols written
by that pen tip on that surface. Preferably also the writing surface may be
83
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
structured in a way to enhance the sounds produces by the pen tip. The
microphone receives the sounds and transmits them to the computer that in
combination with HWSRS, digitizes the hand written data input. This
system may also be used for all other electronic instruments such as those
shown in Figs 33a-33e.
Also computers and other electronic instruments, equipped with
HWSRS and microphone, may not have a writing surface. In this case, by
writing on any place such as the cover of a computer, the corresponding
to sounds produced may be interpreted by the HWSRS. This system may also
be used for all other electronic instruments such as those shown in Figs
33a-33e.
One important advantage of this system is that, the HWSRS of the
15 invention may replace the bulky keyboards and frustrating keypads of
electronic devices and computers. By having a simple pointing device such
as a pen, preferably, having a structured tip of the invention, a user can
input an unlimited variety of data into electronic devices. Of course the
electronic instruments must be equipped with at least a HWSRS of the
20 invention and a microphone. They also, must have all other necessary
features such as processor, memory, etc. Preferably a structured writing
surface to enhance the sounds produced by the contact of pointing device
84
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
tip on the writing surface while writing, may also be provided within the
electronic instrument.
According to one embodiment of the invention, as shown in FIG.
27a, additional buttons (2701) used for some functions, specially those used
frequently, such as "Enter", "Next Line", "Tab", or "Caps Lock", may be
provided on the stylus computer.
In still another embodiment of the invention, instead of, or in
1o addition to, those buttons, a rotating and/or clicking system may be
provided on the pointing side of stylus-type computer. For example, as
shown in FIG. 27b, three frequently used functions, Enter, Tab and Caps
Lock (2711) are indicated on the stylus type pen head (2710), and a
selecting indicator (2712) is positioned on the body edge of the computer.
15 As shown in FIG. 27c-27d, by rotating (2719) the stylus head or body, and
bringing the indicating mark (2712) in front of indicated functions
(2714,2715), the function relating to that indicated function will be selected
and executed. The head may automatically move back to its original
location. For example, in FIG. 27c and FIG. 27d, functions Caps Lock, and
2o Enter (Next Line), are selected respectively. According to example shown
in Figs. 27e-27f, the Tab function (2720) will be executed by pushing the
head in inside direction (2721) and clicking it. Each additional click causes
an additional advance of the tab.
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
According yet to one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Fig.
27g, the stylus type computer (2700) may have a clip type button (2701).
By pushing on several locations on the clip, different functions or
commands may be executed. For example, as shown in Fig. 27h, by
pushing the clip button in the center (2710), for example, on/off commands
may be executed. Pushing the clip button on the sides may also execute
commands. For example, by pushing the left side (2720) of the clip button
(2721), "Enter" or "next line" function (2722) may be executed. Also, for
1o example, by pushing the right side (2730) of the clip button (2731), "Tab"
function (2731) may be executed. Each single press on the right side will
cause the cursor to jump to next tab location on the screen. Symbols such as
a space character may also be assigned to a press on a location on a clip
button. Also, for example, if a user presses a on a predefined location of the
15 clip button (e.g. a key of said clip button) and keeps it pressing, a
symbol or
a function assigned to said location pressed rnay be repeated until the user
stops pressing said key. Also double clicks on different locations of the clip
button may be assigned to different functions. For example, a double click
on the left side of the clip button may be assigned to "Caps Lock" function,
2o etc. also, for example, when the device is in telephone mode the clip
button
may be used for functions such as "Send"/ "End" (communication), etc..
86
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
An interaction such as a press or a double click on a location (e.g. a
lcey 2710, 2720, 2730, etc.) of a clip button 2701 may be used in
conjunction with the pointing and selecting device (e.g. a mouse) of the
stylus computer. The clip button keys may function as said mouse keys.
Said combined interaction with the mouse and clip button keys may either
replace the mouse clicking functions which have been described before, or
may add additional functionality to the already described mouse functions
of the stylus computer. For example, a user may manipulate a mouse with,
for example, his right hand to position a pointing indicator arrow on a file
l0 icon, and press or double click a key of the clip button with his left hand
to
select or open said file. Also during a text editing the user may use said
clip
button keys to, for example, select a menu, select a function, or change a
mode (e.g. change the mode from menu list to menu selecting and vise
versa, or from line selecting/scrolling mode in a text to cursor manipulating
15 mode and vise versa) etc.. For example, when the system is in menu
selecting mode, after locating a menu selecting indicator on a menu, a user
may press a predefined key of the clip button to open said menu bar. Also
when desiring to exit a mode such as exiting from menu selecting mode and
to enter menu list mode, instead of, clicking and simultaneously rotating,
2o the mouse, a predefined key of the button clip key (or any other type of
predefined keys) of the stylus may be used. In other words, the mouse with
its integrated clicking modes and/or the mouse with other keys assigned to
it may comprise at least all the functionality of a PC mouse.
87
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
The clip button may be located at a different location on the stylus
computer. For example, as shown in Fig. 27k, the stylus computer 2740 of
the invention may comprise a multi-function clip button 2741 of the
invention located closed to the writing tip 2742 of said stylus. It is
understood that for the reasons such as the convenience of use, said clip
button may be located at any location on the stylus, such as, closed to the
mouse, or closed to the writing point tip, or in the middle of the stylus,
etc..
In addition, said clip button may be designed in a manner to attach the
1o stylus computer to, for example, a user's pocket (e.g. similar to
attachment
of a regular pen to a user's pocket). Also, if needed, more than one clip
button may be provided on the stylus computer.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the stylus computer
15 2740 may contain at least one additional microphone 2743. Said
microphone may be provided in a manner to receive a user's voice. For this
reason, said microphone, preferably, may be located in a location 2744 on
the stylus closed to the user's mouth (e.g. at the opposite end of the stylus
relating to the other stylus end wherein the pointing tip is installed).
Yet, according to one embodiment of the invention, as shown in fig.
27L, a stylus computer 2750 may contain a muti-sectioned/directional
microphone 2751 to, for example, perceive a user's voice. Said microphone
88
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
2751 may be extended towards said user's mouth in a manner to clearly
perceive said user's voice. The mufti-sectioned structure 2752 of the
microphone may be used as an antenna of the stylus computer. Said
antenna may be a diversity antenna. In closed position said muti-sectioned
microphone and/or antenna, may have the appearance and/or the
functionality of the above-mentioned clip button of the stylus computer.
Figs. 27m-27n show different positions of the mufti-sectioned
microphonelantenna described here-above. With reference to fig. 27m, a
to clip button 2761 of the stylus computer 2760 having a mufti-sectioned
structure 2762 is shown. In this example, the clip button 2761 itself, may be
pivoted and/or rotated to help the adjustment of the stylus in a desired
position. Said clip button may have telescopic sections 2763 to be extended
from said clip button. If the clip button system contains keys 2764 under
15 said clip button (e.g. operated by presses on said clip button), while
rotating
said clip button for, for example, extending the microphone towards a
position, said buttons are uncovered and may be directly manipulated by a
user's forger. It is understood that the structure of the clip button may ,
comprise any extending technologies known by the people skilled in the
2o art. For example, as shown in fig. 27n, the clip button 2781 of the stylus
2780 may have a first fixed structure 2782, and additional pivoting 2883
structures 2784.
~9
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
By using a microphone closed to stylus writing tip and a multi-
sectioned microphone of the invention closed to a user's mouth, two clear
inputs may be perceived by the system for a same data (e.g. symbol)
inputted. A user, for example, may write a text while speaking said text.
For better recognition, the system may use both inputs (e.g. handwriting
sounds of the stokes and spoken input of the user), simultaneously. This
matter will be disclosed with more detail later in this application. While
writing, said microphone may function in a manner to automatically
permanently stay near the user's mouth. For this purpose, for example, a
to biasing means such as a wire may be provided to attach the microphone to,
for example, a user's part of the body or his dress. It is understood that
instead of having a multi-sectioned structure, the microphone may be
extended by a wire towards a user's mouth.
15 In yet another embodiment of the invention, as shown in FIG. 28a,
as a separate system or a complementary system to the hand written sound
input system of the invention, a menu list containing alphanumerical
characters and symbols (2801) may be provided with the stylus type
computer. A character or symbol may be chosen and inputted by any of the
2o menu selection methods described before. For example, after the
alphanumerical menu list is selected, the mouse (2800) may be rotated until
the menu selecting indicator (2802) is on a desired symbol (2803). Then as
shown in FIG. 28b, by clicking the mouse in inside direction (2805), the
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
character is selected/inputted and printed (2806) on the LCD screen. As
shown in Figs. 28c-28d, this procedure may be repeated for selecting
additional characters or symbols (2807). In addition as shown in Fig. 28e,
shortcut functions (e.g. bolding, font, size, etc.) may be applied on each
character by creating a menu bar (2831) for them. It is understood that if a
function (2832) contains sub functions (2833), by pressing the mouse after
the indicator (2834) is on that function, the sub function menu (2833)
opens. To select a function among those in the sub functions menu again
the user must rotate until he selects the desired function by clicking the
mouse in, for example, inside direction. As far as, the functions contain sub
functions, this procedure may be repeated until a function without a sub
function is selected.
According to one embodiment of the invention. The above-
described procedure may be applied to any menu bar having functions
containing sub functions, and so on.
According to one embodiment of the invention, a cover for said
stylus type computer may be provided to protect the display and all other
2o features of the device. In addition it may protect the pen-tip preventing
accidental erroneous inputs. Figs 29a to 29d illustrate the stylus type
computer (2900), the cover (2901), to cover the stylus computer. The cover
may have a special structure (2902) to permit the computer clip button
91
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
(2903) to be available (2999) and function even the cover the computer is
covered. (2904). This is because the stylus type computer may also have
telephony and telecommunication capabilities. When the device is used as a
mobile phone and the user receives a call, he may answer to that call while
the device is covered. The cover may also protect the device from water.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the stylus-type
computer can also function as a tele-communicating device, such as
wireless telephone or PDA device. As shown in Fig. 29e-29g, the stylus
to (2905) may be equipped with part or all equipment and systems of the
invention and additional not mentioned necessary features. It may be
equipped with a transceiver (not shown) and all other necessary features to
communicate with other electronic devices. For example, the device may
comprise at least a speaker (2907), a microphone (2906), a camera, etc. The
15 input systems and functions of the invention permit to dial numbers (2908)
by writing them on a writing surface, write and send massages (2911), send
files, pictures, receive, memorize and manipulate data, etc. Telephone
functions and menus may be organized similarly to other computer
functions and menus. For example, one or more menu lists and menu bars,
20 containing one or more functions, may be organized, even by the user for
telephone operations such as telephone directories, receivedlsent calls , etc.
In addition the stylus type computer device maybe equipped with voice
recognition systems to alternatively permit to input data and functions,
92
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
commands, etc., by voice or speech of a user. It may also dial numbers by
speech orders.
As shown in Fig. 29g, for better portability, the device may also
have a cover to protect it from shocks end eventually from water. To not
open the cover while, for example, receiving a call, means such as wholes
(2921,2922) on the cover, at the locations of the features such as, speaker,
microphone, camera, etc., may be provided. When the device is in
telephone mode the clip button (2923) may be used for some telephone
to functions. For example, functions such as "Send", "End", may be assigned
to pressing the left side of the button. Also, for example, functions "on",
"off', may be assigned to the center (2925) of the clip button, and function
"Voice (e.g. Mail) Box", may be assigned to the right side (2926) of the
clip button, etc. Of course at least a portion of a display of the stylus
telecommunication device may also be available for use while said device
is covered.
According to one embodiment of the invention, instead of, or in
addition to, the stylus computer display described before, a display unit
2o may be provided within the cover of the stylus
computer/telecommunication device of the invention, to permit the use of
said device for telephone manipulations such as seeing an incoming call
number, without being obliged to remove the cover of the device. The
93
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
connection between said display and said devivice may be established
either wirelessly, or by electrical connections. For example, electrical
contacts may be provided within said telecommunication device and within
said cover so that when said cover covers said electronic device said
contacts touch each other to permit electrical connections between said
telecommunication device and said display provided within said cover.
Also instead of a speaker, the received sounds or massages may be
transformed to corresponding vibrations and be transmitted to user's ear
l0 while the user keeps the stylus closed to his ear.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the stylus type
computer of the invention may also have telecommunications means, such
as infrared, laser, etc., to communicate with other electronic instruments
is such as other computers, PDA devices, TVs, etc. This will permit, for
example, to send and receive documents and data (e.g. tolfrom a computer,
to a printer, etc.).
Other types of buttons and mouse may also be considered for the
2o stylus-type-computer. For example, as shown in Fig. 30a, plurality of
buttons (3001, 3002) can replace some of the functions previously assigned
to the mouse. In this example, the mouse (3000), may for example, be used
for line/page up and down. Four buttons (3002) may move the cursor to
94
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
left, right, up, down, and other buttons (3001) may be assigned to other
functions.
In yet another embodiment of the invention, as shown in FIG. 31, a
stylus type computer (3000) may contain at least one mouse (3000 for a
group of function (e.g. page up/down), at least one multi-directional button
(3001) for functions such as cursor manipulations, and at least one multi-
function button (3002) for, for example, menu/function selecting
operations. Other additional single/multi function buttons (3003) may also
l0 provided.
FIG. 31a show's a muli-directional button (3101) that may be used
for cursor manipulation. By pressing the button at different edges (3102),
cursor will move to different direction (3103) accordingly. Figs. 31b to 31f
15 demonstrate a cursor (3111) which is directed to different locations on the
LCD display by different manipulations (3112) of the button (3102).
Figs. 32a-32f demonstrate how according to one embodiment of the
invention, another type of function selecting button (3201) may operate. As
2o shown in Figs. 32a-32b, by rotating this button to right (3202) or left
(3203), the menu selecting indicator (3204) is moved to left or right.
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
For selecting a menu, first the user brings the indicator on the menu
to be selected (3206). Then as shown in FIG. 32c, he may push the menu
selecting button (3221) to inside stylus direction. The menu bar (3222)
opens and the system is in function selecting mode and the key comes baclc
to its original position (e.g. click button). As shown in FIG. 32d, the user
then rotates the button (3223) to bring the function indicator (3224) on to-
be-selected function. Then as shown in FIG. 32e, The user again clicks the
selecting button (3221) to select the function. Finally, as shown in FIG. 32f,
the function (3225) is selected and the system exits the function selecting
to mode and goes back to menu selecting mode.
According to one embodiment of the invention, other hand written
input and recognition systems based, for example, on written graphs and
drawings of symbols or commands (e.g. delayed hand wiitten recognition
15 system), or based on the real time movements of, for example, a stylus tip
on a writing surface, may be used by the stylus type computer of the
invention. Also printed materials such as characters, images, etc., may be
scanned as data input by the stylus computer. For this purpose, the stylus
may be equipped with means such as optical reader, laser equipment,
2o camera, etc., and recognition systems such as OCR, and other technologies
such as those available today, or in the future.
96
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Also, other input and technologies and systems, such as voice,
speech, keyboard, keypad, digitizer, etc., may be used by the stylus type
computer.
Also, as mentioned before, the system may include one or more
databases of letters, words and symbols in different languages. A predictive
word recognition system may also be combined with the system to make
the selection of a word possible before entering it entirely. This system may
allow an automatic selection of the desired word by the system mostly
to before ending to enter it entirely and sometimes even without the need of
the user interference. This is possible, because by writing, individually and
sequentially, characters or symbols (e.g. character by character basis) of a
word, and the very small numbers of corresponding words, in many cases,
before finishing to enter the word entirely, the word predictive system can
15 either determine the desired word, or may show a few possible words, and
the user selects one of them. The selected possible words may be listed in a
bar list similar to menulfunction bar, and a user may select a desired word
among them by using the mouse movements and procedure, similarly to
selecting a function in a menu bar.
According to one embodiment of the invention, HWSRS may be
combined with other recognition systems to ease the recognition of
symbols to be entered. For example, while writing symbols (e.g. a letter, a
97
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
punctuation, a command, a word or a sentence, etc.) a user may
simultaneously pronounce said symbols. Then the HWSRS combined with
a voice recognition system will easier recognize said symbols.
According to one embodiment, as mentioned before, a user may
write a text word by writing it character by character separately (e.g. to
signal the end of each character, the user lifts the pen tip from the writing
surface after writing each character). Said user may also, simultaneously
speak said word while writing said word's letters. The HWSRS of the
to invention interprets each character of said word. After interpreting said
characters, the system compares said characters with the spoken word and
vise versa. Then after matching those two words (e.g. written word and
spoken word) with a dictionary database of written words and
corresponding key patterned spoken words, the system selects a candidate
15 word having the highest probability with the intended word which was
inputted by the user. This will permit a very natural manner of writing by a
user, while enabling the system to have a more accurate recognition
capability. Providing a directional microphone near the stylus writing tip,
and an extendable directional microphone closed to the user's mouth will
2o facilitate a better quality handwriting (based on sounds of the writing tip
on
a writing surface) and voice entry. Of course, the data entry methods (e.g.
using HWSRS and/or voice recognition) as described before, may be used
separately or combined with other data entry systems. For example, for a
98
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
still better accuracy of input recognition, in addition to, and simultaneously
with, said data entry methods, an optical handwriting recognition system
based on recognition of symbols based on the graffiti of written characters
may also be combined with other recognition means such as the ones
described before.
For a faster data entry the sound patterns concerning the symbols of
a shorthand writing system may also be memorized by a user and later
compared to shorthand written texts of said user during a data entry using
1o the HWSRS of this invention.
Also, commands such as "Caps Lock", may be inputted by voice.
For example, a user may say "Cap" and write "a". Then the system will
input an "A". Also, different speeds of writing while writing a symbol may
15 be assigned to different symbols. For example, writing fast a lower case
letter may correspond to a lower case version of said letter, and writing
slowly a same lower case character may correspond to its uppercase
version.
20 Also; as shown in Fig. 33f, characters and functions available on a
standard keyboard, may be assigned (3351) to different keys of a keypad
(3350) with limited number of keys (e.g. telephone keypad). The keypad
keys maybe the keys such as regular clicking keys, sensitive keys (e.g.
99
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
digitizer, touch sensitive, pressure keys, etc.), or other type of keys. By
writing a character (3352) among those (3353) assigned to a lcey (3354), (or
by writing a predefined symbol such as a straight line drawn in a predefined
direction causing a sound, assigned to a symbol or to a location on a key
corresponding to a symbol, on said key), on the same key, and if necessary,
simultaneously, pressing on the key, the key recognition system selects that
lcey, and the HWSRS understands that the character written on the key
selected, is one of those assigned to that key. This makes the recognition
much easier, because the HWSRS has to compare the character entered,
with only the patterns of the characters available on the selected key. It is
understood that the writing instrument (e.g. pen, stylus), may preferably
have a structured tip of the invention.
For enhancing the written input system, additional technologies and
means maybe used. For example, to locate the stylus tip position or its path
on the writing surface, the stylus may have means to send and receive back
signals (e.g. radar). Different technologies, such as laser, light, microwave,
infrared, etc., may be used for sending and receiving back the signals. As
shown in Fig. 34a, a reflecting beacon (3401) or the like, may be
2o positioned, on, for example, a writing surface (3404), 'to reflect the
stylus
pen tip sending signals (3403) frequently. The stylus may be equipped with
measuring systems to locate its pen tip position distance from the reflector,
based on the time a signal was sent and received back. The pen tip position
loo
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
(3402) will be calculated based on its distance from, for example, two
predetermined points (3405, 3409) on the beacon. It is understood that the
beacon relationship angle (3406) must be different from 90 degrees. It is
understood that by using the technologies described before, the system may
know at any moment, if the pen tip is in touch with the writing surface or
not. The positioning system has plurality of advantages such as indicating
the end of a word, sentence, etc. to the recognition system.
Also, a hand writing recognition system according to movements of
to the pointing device in the space may be provided. For example, a
reflecting/detecting means to scan/provide three dimensional parameters
relating to the locations of a pointing device tip in the space during the
writing procedure of a symbol may be used. A position of said pointing tip
in the space, at a precise time, may be determined by signals sentlreceived
15 by said pointing device tip, and detected and/or reflected to said signals
to
said pointing device tip and received by it
Also according to another embodiment of the invention, the
pointing device and its tip may structured and designed in a manner to
2o detect (e.g. by means of sensors), for example, the air pressure level
applied
on different portions of said pointing device and/or is tip.
lol
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
Also according to another embodiment of the invention, the
pointing device and/or its tip may be structured and designed in a manner to
detect, for example, the heat level of on different portions of said pointing
device and is tip in contact with the air while writing symbols. For example
the sensors may be heated permanently by a system and according to the
contact with the air of said pointing device while writing, the degree of heat
on each said portion may change accordingly. They may be detected, and
been analyzed by a recognition system.
to According yet to another embodiment of the invention, as shown in
Fig. 34b, the stylus cover (3410), may be used as the reflecting beacon.
It is understood that instead of using a reflecting beacon system, the
stylus pen tip may send to be detected signals to a detecting means. For this
15 purpose a detecting unit such as the beacon described before, may be
provided to detect those signals and if needed to process them. Then the
detecting mean may transmit the information (e.g. positions of the stylus tip
on precise times) to the stylus type computer. It is understood that said
reflecting beacon mat be constructed in a manner to provide a three
2o dimensional detecting/reflecting means.
102
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
The above mentioned positioning information at a precise time, may
be used by a real time hand writing recognition system procedure to
interpret the symbols written.
According to one embodiment of the invention, and by using the
technologies described before, the reflecting or detecting beacon may
horizontally be fixed on a writing surface. As shown in Fig. 35, note pads,
note books, and other writing surfaces may be manufactured having a
reflecting means incorporated.
to
According yet to another embodiment of the invention, the stylus
type computer may be equipped with a barcode reading/recognizing
systems. Said barcode reader may be installed in an appropriate place
within, or outside the stylus computer of the invention.
According to one embodiment of the invention, a stylus computer of
the invention may have a barcode reader installed near its writing tip to
scan the information concerning the position of said writing tip at different
fractions of time while writing a symbol.
According to yet another embodiment of the invention, a barcode
reader of the stylus type computer may be located on a rotating clip button
of the stylus computer in a manner to scan the information concerning the
103
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
position of said stylus computer writing tip at different fractions of time
during writing a symbol on a writing surface. For a good view of the
writing tip on a writing surface while writing symbols by a user, said clip
button may be rotated and fixed by said user, in an appropriate position.
It is understood that because of a variety of different movements of
the stylus computer while writing a text, for a better scan, more than one
barcode reader positioned at different of locations on the stylus and/or in
other locations, may be provided.
Fig. 36 shows a writing surface (3601). The horizontal locations on
the writing surface may be numerated by vertical barcodes (3602) and the
vertical locations on the writing surface may be numerated by horizontal
barcodes (3603). The intersections of those barcodes on the writing surface
(3604) indicate precise positions on the writing surface. For this purpose,
each point of interaction between two bars must have a unique information
property. For example, a predefined number of neighboring bars (e.g.
vertical and horizontal bars) around a crossing point of two bars (e.g. a
vertical bar and a horizontal bar) of said barcodes may always have a
2o different characteristics (e.g. different configuration of bars, bars
having
different colors, etc.) from the same predefined number of neighboring
barcodes around another crossing point of two bars of said barcodes on the
same writing surface. By reading said predefined neighboring number of
104
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
barcodes by a barcode reader installed, for example, on a stylus computer
of the invention, during the writing procedure, information such as a shape
of a graffiti of a written symbol, or drawings, or a location in a text or on
a
writing surface during writing a text, or end of a symbol, space between
two symbols, etc., may be provided and been processed either in real time,
and/or been stored for a delayed processing. It is understood that the bars of
the barcodes may have different characteristics such as having different
width, different colors, etc.. It must be noted that the horizontal and
vertical
barcodes shown, is only a sample. Variety of other directions for said bars
l0 of the barcodes may be considered. For example, a first group of bars may
be horizontal and a second crossing group of bars on the same surface may
be diagonal. Also more than two groups of bars wherein each of said group
of bars having a different direction, may be provided on a writing surface.
15 By equipping the stylus type computer tip with barcode readers and
systems, while writing, the position of the pen tip on the writing surface at
each moment, may be known by the system.
According to another embodiment of the invention, as shown in Fig.
20 37, each location on the writing pad may be,marked by means such as
different numbers, different colors, etc. for this purpose the stylus type
computer may be equipped with optical and/or color readers and
recognition systems.
105
CA 02433151 2003-06-26
WO 02/052372 PCT/USO1/49450
As shown in Fig. 38, barcodes, numbers, colors, and/or other
position indicating information, maybe projected on a writing surface, by
means of projectors (3801).
Thus, while there have been shown and described and pointed out
fundamental novel features ~of the invention as applied to alternative
embodiments thereof, it will be understood that various omissions and
substitutions
and changes in the form and details of the disclosed invention may be made by
those
skilled in the art without departing from the spirit of the invention. It is
the intention,
therefore, to be limited only as indicated by the scope of the claims appended
hereto. It is
to be understood that the drawings are not necessarily drawn to scale, but
that they are
merely conceptual in nature.
106